Abstract
Environmental contamination by toxic heavy metals is a serious worldwide phenomenon. Thus, their removal is a crucial issue. In this study, we found an efficient adsorbent to remove Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution using two materials. Chemical modification was used to obtain palygorskite clay from diatomite. The adsorbents were characterized using X-ray florescence, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. The effects of contact time, initial concentration, temperature and pH on the adsorption process were investigated. Our results showed that the (%) of maximum adsorption capacity of diatomite was 78.44% for Cu2+ at pH 4 and 77.3% for Ni2+ at pH 7, while the (%) of the maximum adsorption on palygorskite reached 91% for Cu2+ and 87.05% for Ni2+, in the same condition. The results indicate that the pseudo-second-order model can describe the adsorption process. Furthermore, the adsorption isotherms could be adopted by the Langmuir and the Freundlich models with good correlation coefficient (R2). Thus, our results showed that palygorskite prepared from Tunisian diatomite is a good adsorbent for the removal of heavy metals from water.
1. Introduction
Heavy metal ions play a very important role in certain industries due to their technological importance. However, they pose serious dangerous effects because they are persisting in the environment. In addition, metal ions have a chronic toxicity, persistency and accumulation tendency in body tissues. For example, copper is known as the highest mammalian toxic specie; its inhalation is linked with an augmentation in lung cancer and its accumulation in the vital organs causes many diseases and disorders [1]. It is widely used in ornamental ponds and in water supply reservoirs. Nickel is recognized as the most recalcitrant pollutant. It is not biodegradable and can cause dermatitis, allergic sensitization, respiratory distress and dizziness. It is extensively used in electroplating, zinc base casting, battery industries and silver refineries. Thus, the removal of Cu2+and Ni2+is considered of high importance. Traditional methods were applied for heavy metals elimination such as ion exchange, chemical precipitation, membrane filtration, biological treatment and adsorption [2,3]. Among all these technologies, adsorption is the most useful method due to its efficiency and lower cost. For this purpose, many researchers used various kinds of low-cost and natural adsorbents, such as coconut coir pith, sludge ash, diatomite and different type of minerals clays, such as palygorskite, kaolin, sepiollite, montmorillonite and so forth.
Palygorskite, known also as attapulgite, is a kind of a mineral clay; it is crystalline hydrated magnesium silicate consisting of a type of 2:1 layer phyllosilicate (tetrahedral: octahedral) [4,5]. Palygorskite contains mainly Mg2+ and other cations such as Fe3+ and Al3+ with significant quantities [6]. Bradly reported the ideal structure of palygorskite {(Mg,Al)4Si8(O,OH,H2O)24·nH2O} for the first time in 1940 [7]. Furthermore, this kind of clay has numerous advantages: a high adsorption capacity, fibrous morphology, porous structure, high surface area, moderate cation exchange, excellent salt residence and charge in the lattice [8]. Due to its special properties, palygorskite has gained attention from the chemical industry. It can be used in ion exchange, catalysis and water softening. In addition, the literature provides various works for the removal of heavy metals using palygorskite in its natural and modified state. Due to these abundant uses, the consumption of palygorskite increases rapidly and calls for further work seeking cheaper and natural materials for their synthesis. Palygorskite may be obtained from other clays. Despite the various applications of palygorskite, very few reports have shown its preparation from other mineral clay, so there are no references indicating its formation or synthesis from natural rock, such as diatomaceous earth. Previous work reports the formation of other kinds of clay from palygorskite or diatomite, such as the formation of kaolinite from palygorskite and sepiolite [9]. In addition, A. Chaisena performed the synthesis of sodium zeolite from natural and modified diatomite [10].
Diatomaceous earth or diatomite (SiO2·nH2O) is a sedimentary rock with a porous structure, low conductivity coefficient and low density. It consists essentially of high quantities of silicon dioxide SiO2and low quantities of Al2O3 and Fe2O3 according to the clay impurities such as palygorskite and montmorillonite [11]. Additionally, the reactivity of diatomite is linked to the reactivity of the hydroxyl groups and the acid sites on the surface of the amorphous silica. Due to its specific characteristics, diatomite has attracted extensive research attention as an adsorbent for its natural and modified structure for the removal of heavy metals.
In order to meet the big demand of palygorskite, our study focuses on the synthesis of palygorskite clay from Tunisian diatomite as cheap raw materials. To confirm its efficiency, the prepared clay was used to remove Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution and compared its adsorption capacity with natural diatomite powder. All adsorbents were characterized via XRF, XRD and FTIR. Thereafter, the effect of certain factors (contact time, initial concentration, temperature and pH) on the adsorption process were evaluated. In addition, the use of pseudo-first- and pseudo-second-order models for analyzing the adsorption systems was investigated and the applicability of two known isotherm models (Langmuir and Freundlich) was studied. Lastly, the thermodynamics parameters were calculated at different temperatures for Cu2+ and Ni2+adsorption on diatomite and palygorskite.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The raw diatomite was obtained in Gafsa, Tunisia. Palygorskite was prepared from diatomite using hydrochloric acid HCl (Panreac, 37%), sodium hydroxide NaOH (Sigma Aldrich, USA ≥ 98%), iron (III) chloride 6-hydrate FeCl3.6H2O (Panreac, %) and magnesium chloride hexahydrate Cl2Mg.6H2O (Fluka, %). The chemicals tested were copper chloride CuCl2 (Merck, 98%) and ammonium nickel (II) sulfate hexahydrate (NH4)2Ni(SO4)2·6H2O (Sigma Aldrich, USA≥98).All the chemical components were used without any purification.
2.2. Preparation of Palygorskite
The raw diatomite was completely crushed with hammers to obtain a powder sample. Then, an acid solution was used (HCl 2M) to remove fine and other adhered impurities. Specifically, the crushed powder was mixed with HCl at a solid g/mL ratio of 10% at room temperature for 3 h. Finally, the resulting material was filtered and rinsed with HCl and distilled water several times and then dried into a vacuum oven at 100 °C for 24 h.
The preparation of palygorskite from treated diatomite was carried out using the procedure reported in literature [12,13,14,15]: 3 g of treated diatomaceous earth was mixed with 5 mL of 1 M of MgCl2 under ultrasonic vibration for 30 min. Then, 1 M of FeCl3 was added to the mixture. After 1 h, 50 mL of 2 M NaOH was added slowly under continuous agitation for 24 h. Lastly, the mixture was filtered and washed with distilled water several times to remove Cl−. The final sample was oven dried at 100 °C for 24 h.
2.3. Kinetics Batch Experiments
The experiments were conducted in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks containing 0.5 g of adsorbent and 50 mL of copper(II) ornickel(II) solutions, varying the concentrations from 40 to 100 mg/L. The flasks were agitated on a shaker at 300 rpm and room temperature. Samples were taken at predetermined time intervals (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 60, 90 and 180 min) to determine the residual metal ion concentrations in the solution. The pH solution was adjusted using NaOH (0.1 M) and HCl (0.1 M). The solution was filtered through a 0.22 μm membrane filter.The concentration of heavy metals ions remaining in each solution was determined by spectrophotometry using the following calorimetric method: 10% of ethylenediaminetetraaceticacid (EDTA) was added to the Cu2+ suspension to form a blue specific complex [16,17] and 1% of dimethylglyoxime (DMG) was added for the Ni2+ solution; this reagent forms a red complex [18,19]. The absorbance was measured after 30 min at 750 nm and 465 nm for Cu2+ and Ni2+, respectively. The adsorption of the two metallic ions was carried out on diatomite and palygorskite under the same conditions. The thermodynamic parameters were established by studying the adsorption of the two metallic ions, varying the temperature from 25 °C to 45 °C. The adsorption capacity at the equilibrium was calculated using Equation (1):
where
: the initial concentration (mg/g)
: the concentration at time t (mg/g)
m: the mass of adsorbent (mg)
V: the volume of solution (mL)
2.4. Analysis
The raw and purified diatomite was analyzed by powder XRD via a PANalytical CubiX3 diffractometer using CuKα (λCuKα-media = 1.5418Å, λCuKα1 = 1.54060Å, λCuKα2 = 1.54439Å) radiation (operating at 40 kV and 40 mA) over the angular range of 5–70° 2θ (step size = 0.04 and time per step = 353 s) at room temperature.
The chemical composition of the diatomite sample (before and after the treatment) was measured by XRF technique using PANalytical AXIOS (WDXRF) spectrometer (Almelo, the Netherlands).
Diatomite and palygorskite were characterized by attenuated total reflectance, FTIR spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR, PerkinElmer Spectrum, London, UK) in the range from 450 to 4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 8 cm−1. Diatomite and palygorskite were characterized by attenuated total reflectance, FTIR spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR, PerkinElmer Spectrum) in the range from 450 to 4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 8 cm−1.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of Adsorbents
3.1.1. XRF Studies
The chemical composition of the samples was obtained by X-ray florescence (XRF) technique (Almelo, the Netherlands). Table 1 shows that the raw material contains low quantities of SiO2 (29.60%) with small quantities of other minerals components. However, the amount of silica increased to 78.83% after using HCl solution. These results of XRF analysis are in agreement with those reported by Li and coauthors, although the diatomite was from different sources containing mainly SiO2 with percentage ranging from 62.8 to 90.1% [20].

Table 1.
Composition of natural diatomite (before and after treatment) and palygorskite.
In general, the quantities of SiO2 on palygorskite do not exceed 60% [21]. As shown in Table 1, after the modification, the amount of SiO2 decreased to 33.5% while the quantity of mineral compounds such as MgO increased to 9.71%. Similar results were found in a previous analysis of two natural Algerian palygorskites which contained 39.314 and 7.930% of SiO2 and MgO, respectively, for the first form of palygorskite and 40.317% (SiO2) and 8.876% (MgO) for the second form of clay [22].
3.1.2. XRD Studies
Figure 1 shows the diffractrogram of the 3 samples determined by X-ray diffraction. The analysis of the raw material confirmed that the latter containeds mall quantities of silica with different mineral components. Three mineral phases were identified: the calcite CaCO3, dolomite CaMg(CO3)2 and Ca5(PO3)4(OH,F,Cl) in the region 20–25°2θ. Thus, this sample corresponds to a diatomite that is not pure, however, it contains large amounts of other minerals according to the existence of different kinds of clay minerals (palygorskite, sepilite and smectites).

Figure 1.
Analyses of XRD for (a) raw and purified diatomite; (b) palygorskite.
As shown in Figure 1a, the characteristic peaks of treated diatomite were 21.76, 26.66 and 31.96. Thus three crystalline polymorphs of silica were identified as SiO2 (cristobalite, tridymite and quartz) and the sample contained significant amounts of amorphous (noncrystalline) material and kept the quantities of mineral clays after treatment (the small peaks at low values of 2θ). Then, the acid solution has eliminated carbonates, calcite and dolomite, as well as apatite; however, it did not remove clays such as palygorskite [23].
Figure 1b shows the new sample was a complex mixture of amorphous material with a set of minerals: The SiO2 still existed under its three allotropic forms. The typical diffraction peak in 2θ = 8.57 can confirm the presence of the palygorskite plane crystal face [24]. The peaks in 2θ = 2 1.93, 29.58 and 32.20 indicate a monoclinic symmetry with Ce/m space group [25]. The diffractrograms confirmed that the palygorskite type Mg5(Si,Al)8O20(OH)2·8H2O was formed successfully from the modified diatomite.
3.1.3. FTIR studies
FTIR (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy) was carried out between 450 and 4000 cm−1 to analyze the surface characteristics of diatomite (before and after treatment) and palygorskite (Figure 2). The peak at 876 and 1431cm−1 confirmed the presence of calcite in the raw diatomite. As shown in Figure 2, two absorption peaks at 3328 cm−1 and 1658 cm−1 were related to the O–H vibration of the physically absorbed H2O and structural hydroxyl groups were recorded [26]. The other two vibrations at around 1023 cm−1 and 465 cm−1 were related to the asymmetric stretching vibration mode of siloxane (Si–O–Si) [27]. The peak at 786 cm−1 was attributed to Al–O–Si stretching vibration according to the clay minerals in diatomite [28].

Figure 2.
FTIR spectra of raw and treated diatomite and palygorskite.
The most changes resulting after treatment was the disappearance of the two bands at 875 and 1431 cm−1.
The strong band around band at 3395 cm−1 was attributed to the hydroxide stretching of Mg/Fe–OH [29] of the surface of the sample. In addition, the appearance of two peaks at 1642 and 1480 cm−1 confirms the coordination with Mg. Furthermore, the band at 1029 cm−1 corresponds to the Si–O–Si stretching and the peak at 1329 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibration of Al–O–Si.
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.1. Effect of Contact Time and Initial Concentration of the Adsorption of Copper and Nickel by Treated Diatomite and Palygorskite
The contact time is an important factor affecting the adsorption process. The experiment was carried out in 50 mL of solution with 0.5 g of adsorbents at 25 °C. The effect of contact time on copper and nickel removal by the two samples is shown in Figure 3. It is clear that the removal efficiency of 100 mg/L of Cu2+ solution was a rapid process and reached 73% and 85.44% on diatomite and palygorskite, respectively, within the first 20 min. In addition, an increase of the contact time favored the increase of Cu2+ removal to 78.44% on diatomite and 91% on palygorskite when the adsorption process reached equilibrium after 90 min. The adsorption process of Ni2+occurredin two different phases: fast phase from 0 to 20 min and slow phase after 20 min. The removal capacity of diatomite was 67.96% before 20 min and increased to 77.3%; however, the (%) of adsorption capacity was, in the first phase, 79.58% on palygorskite and increased in the second phase to 89.97%. This fact is due to the decrease of the available sites due to the saturation of the adsorbent surface by the metal. Moreover, Figure 4 shows that the (%) of the removal of metallic ions was strongly dependent on the initial concentration of Cu2+ and Ni2+ ions. The effect of initial metal concentration on the (%) of the adsorption process was carried at room temperature and the initial pH chosen was 4 for Cu2+ and 7 for Ni2+. The results indicate that the adsorption capacity of diatomite and palygorskite increased positively with the initial concentration of the metal ion. Thus, this increase is due to the presence of the driving force of concentration allowing an increase of the residence between the adsorbent and solution [30]. As observed in a previous study, the adsorption of Cu2+ on three materials (chitin (CH), chitosan (CS) and chitosan-ethylenediaminetetra-acetic acid (CS-EDTA)) occurs in two steps: rapid step from 0 to 30 min and slow step after 30 min. The adsorption capacity of CS-EDTA was 110 mg/L, Cs 67 mg/L and CH 58 mg/L for the same concentration of Cu2+ (300 mg/L) [31]. In other work, the effect of contact time on of the removal of 20 mg/L of Mn2+, Fe2+, Ni2+ and Cu2+ on activated carbon obtained from cow bone was studied and the removal increased with time and reached a maximum after 20 min of agitation for the four heavy metals ions [32].

Figure 3.
Effect of contact time on the adsorption of Cu(II) and Ni(II) on diatomite and palygorskite at different concentration (madsorbent = 0.5 g, v = 300 rpm, T = 25 °C, pHCu2+ = 7, pHNi2+ = 4).

Figure 4.
Percentage of removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ by diatomite and palygorskie (madsorbent = 0.5 g, v = 300 rpm, T = 25 °C, pHCu2+ = 4., pHNi2+ = 7).
3.2.2. Comparative Experiment
To avoid the precipitation of the metal ions at pH 6 for Cu2+ and 8for Ni2+ and to compare the capacity adsorption of diatomite and clay, the initial solution pH was adjusted at 4 (Cu2+) and 7 (Ni2+). The maximum adsorption capacities of diatomite were 38.093 mg/g (Cu2+) and 28.65 mg/g (Ni2+) and increased, in the same condition, to 44.06 mg/g (Cu2+) and 34.23 mg/g for (Ni2+) forpalygorskite. The results indicate that palygorskite is the most efficient. The comparison between ourresults and adsorption capacities of materials reported in the literature is important despite the difficulties related to the differencein experimental conditions. For example, in previous work, it was demonstrated that zeolite and clay are moreefficient then diatomite for the removal of Cu2+ with adsorption capacities 0.128, 0.096 and 0.047 mmol/g at pH5 for zeolite,clay and diatomite, respectively [33]. In other work, the adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ was studied on two different adsorbents (palygorskite and vermiculite); the maximum adsorption on palygorskite was 12.53 mg/g (Cu2+ at pH 5.10) and 11.57 mg/g (Ni2+ at pH 4.85), however, the maximum adsorption increased using the vermiculite as adsorbent (32.68 mg/g for Cu2+ and 37.85 mg/g for Ni2+) [34].
3.2.3. Effect of pH
The pH value of the aqueous solution is a significant parameter in the adsorption process. Thus, the dependence of the adsorption process on pH is due to the consumption of the metallic ion as metal hydroxide ion pairs or precipitates and the competition between the hydrogen ions and the metal for the active sites on the surface. Moreover, the mechanism of adsorption at the surface of the adsorbent can reflect the nature of physicochemical interactions between the metal ions and the active sites of diatomite or palygorskite in the solution. In order to determine the effect of pH, the experiments were performed at different initial pHs ranging from 2 to 11. The analysis of the results, presented in Figure 5, shows that the adsorption capacity of the two materials reached a maximum at pH = 7 for Ni2+ and at pH = 5 for Cu2+. The experiments show that the optimum pH was 6 for Ni2+ and 4 for Cu2+, since the copper ions precipitate as hydroxide Cu (OH)2 at pH > 4 and the nickel ions precipitate as hydroxide Ni(OH)2 at pH > 7. Thus, the precipitation of copper hydroxide and nickel hydroxide caused a decrease of the adsorption capacity and their removal from solution at these pHs is not due to the adsorption process. Comparing to previous work of the adsorption of Ni2+ and Cu2+ by γ-alumina nanoparticles, the optimum pH was 6 for Ni2+ and 5 for Cu2+ and it was demonstrated that the adsorption capacity increased with the pH, which is not due to the adsorption process [35]. In other work about the adsorption of heavy metals on natural iron-oxide-coated sand, it was demonstrated that the optimum pH was 7 for Ni2+ and 5 for Cu2+; the effects of pH changes were explained by the type of the adsorbent, its behavior in the solution and the type of adsorbed ions [36].
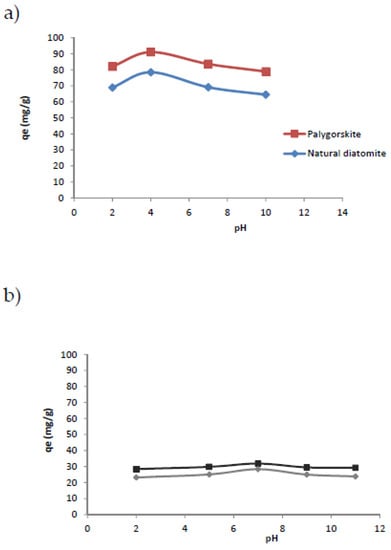
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on the adsorption of Cu2+ (a) and Ni2+ (b) on diatomite and palygorskite (madsorbent = 0.5 g, v = 300 rpm).
3.2.4. Effect of Temperature
Several previous studies have investigated the effect of temperature on heavy metal uptake. In this study, the removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ from aqueous solution using diatomite and palygorskite has been investigated at three different temperatures ranging from 25 to 45 °C.As noted, the Cu2+ and Ni2+ adsorption decreased as the temperature increased. This decrease with temperature can be due to the weakening of attractive forces between metal ions and adsorbent.
3.2.5. Stimulation Modeling of Adsorption Data
In the present study, the pseudo-first-order kinetic and pseudo-second-order kinetic were used for the interpretation of the kinetic batch experiment. The equation of the pseudo-first-order model proposed by Lagergren [37] can be written as follows:
where:
qt: the amount of solute adsorption at different time
k1: the constant of pseudo-first-order model
qe: the equilibrium adsorption capacity
The equation of the pseudo-second-order model equation as given by Ho and McKay [38] can be expressed as:
where:
qt: the amount of solute adsorption at different time
qe:the equilibrium adsorption capacity
k2 (g/mg min): the rate constant of pseudo-second-order adsorption
The results reported in Table 2 show that the coefficient of correlation (R2) of the pseudo-second-order model is close with 1 and the values of qe calculated agreed with the value of qe experimental. However, the results of the pseudo-first-order model are completely different with coefficient of correlation far then the unity and the two values of qe calculated and qe experimental are different. These values evidence that the pseudo-second-order model is valid to describe the kinetic adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ on diatomite and palygorskite [39].

Table 2.
Parameters for kinetics models for Cu2+ and Ni2+ adsorption onto treated diatomite.
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms
In our work, Langmuir and Freundlich models were checked to quantify the adsorption capacity of diatomite and palygorskite.
3.3.1. Langmuir Isotherm
The Langmuir model is an indication of a monolayer adsorption onto homogeneity of the surface of adsorbents with identical sites. It can be expressed by the equation as follows:
where
qe: quantity adsorbed at equilibrium
Ce: the concentration of metals adsorbed at equilibrium
qm: constant related to the area occupied by a monolayer of adsorbate reflecting the
adsorption capacity (mg/g)
Kl: Langmuir constant
3.3.2. Freundlich Isotherm
The Freundlich model is available for a multilayer gas adsorption onto heterogeneityof the surface of adsorbents without uniform distribution of adsorption energy and affinities.
The Freundlich equation model is given as follows:
where:
qe: quantity adsorbed at equilibrium
Ce: concentration at equilibrium
Kf: Freundlich constant
The values calculated from those two models arelisted in Table 3. The adsorption of copper and nickel was well represented by the Langmuir isotherm with a coefficient of correlation close to 1. As shown in Table 3, the value of maximum adsorption capacity on diatomite qm calculated was 111.10 mg/g and 90.91 mg/g for Cu2+ and Ni2+, respectively and on palygorskite, it was 333.33 mg/g for Cu2+ and 166.67 mg/g for Ni2+. Those values are higher than qm calculated in a previous study [40] where the maximum adsorption capacity of copper on acid-activated palygorskitewas 93.02 mg/g. Petra et al. found qm 295 mg/g for the adsorption of Cu2+ on activated saponite and 129 mg/g for Ni2+ on the same adsorbent [41]. In addition, Igherase and coworkers [42] demonstrated that the maximum adsorption capacity of Cu2+ on polyaniline-grafted chitosan was 83.30 mg/g. Senthil Kumar [43] reported a maximum adsorption capacity of cashew nutshell of 18.868 mg/g. Furthermore, the qm of the barley straw for the biosorption of nickel was 35.8 mg/g [44]. The biosorption of nickel using waste pomace from an olive oil factory was also low based on the value qm, which was 14.8 mg/g [45]. Compared with these adsorbents, it is clear that palygorskite prepared from diatomite has a good adsorption capacity. The high value of qm can be due to the homogeneous distribution of high-energy sites on the surface of the adsorbents. As given in Table 3, the value of KL(diatomite) was higher than KL of palygorskite, indicating the lower affinities of the surface of diatomite than the surface of palygorskite. The value of n, calculated from the Freundlich equation, is superior then 1 indicates that the adsorption is favorable and the high values of Kf indicate a very high adsorption capacity for copper and nickel adsorption in aqueous solution.

Table 3.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters for Cu2+ and Ni2+adsorption onto treated diatomite and palygorskite.
3.4. Thermodynamic Studies
The effect of temperature was investigated from 25 °C to 45 °C on the removal efficiency of the adsorbents using 100 mg/L of Cu2+ and 80 mg/L of Ni2+. The adsorption capacities of these two adsorbents decreased with increasing temperature. The decrease of uptake of copper and nickel ions at a higher temperature indicated the exothermic adsorption. The thermodynamic parameters, such as 𝚫G°, 𝚫H°and 𝚫S°,were determined to evaluate the effect of temperature, using the following equations:
where:
Kc: the equilibrium constant
Cads: the adsorbent phase concentration at equilibrium (mg/L)
Ce: the equilibrium concentration in solution (mg/L)
R: the universal gas constant (KJ/mol K)
T: the solution temperature (K)
The thermodynamic parameters are shown in Table 4. The values of ΔH° (KJ·mol−1) and ΔS° (KJ·mol−1) were obtained from the slope and intercept of a plot of lnKd versus 1/T. In general, the change of free energy for the physisorption is in the interval (−80–0) KJ·mol–1 and the chemisorption is in the interval (−400–80) KJ·mol–1. In our study, the values of ΔH°in the interval (−80–0) KJ·mol–1, indicating a physical adsorption process. It can be seen from Table 4 that 𝚫H° values are negative, thus the distribution coefficient values Kd increased with the increase of temperature, which shows the exothermic nature of the adsorption involving low “van der Waals” attraction forces type and confirms the decrease of the adsorption capacity of metal when the temperature increases [46]. In addition, the values of ΔS° were negative, corresponding to a decrease in the degree of freedom of adsorbed species and shows the decrease in the randomness at the solid-solution interface of Cu2+ and Ni2+ onto the palygorskite and diatomite surface, which would cause a decrease in entropy during the adsorption process. Furthermore, the values of ΔS° for the adsorption of Ni2+ onto palygorskite and diatomite for the two metals ions from 25 °C to 45 °C are negative, indicating a spontaneous and favorite adsorption process. However, the values of ΔG° are positive at 35 and 45 °C for the adsorption of Cu2+, indicating that the adsorption was not favorite and not spontaneous [47].

Table 4.
Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ onto treated diatomite and palygorskite.
4. Conclusions
In this study, diatomaceous earth was used to prepare palygorskite clay. The characterization of modified diatomite confirms that palygorskite was prepared successfully. These two mineral adsorbents were used for copper and nickel removal in aqueous solution and compared. The results and the parameters obtained indicated that palygorskite clay is able to remove Cu2+ and Ni2+ ions. Moreover, the removal of metal ions increases using palygorskite as anadsorbent. Palygorskite showed better results than natural diatomite. Furthermore, the results obtained from different initial concentrations of Cu(II) and Ni(II) show that Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms can be used to fit the data and estimate model parameter. The adsorption kinetics of metals ions onto diatomite and palygorskite can be described by the pseudo-second-order model. The values of thermodynamic parameters showed that the adsorption of Cu2+ and Ni2+ was spontaneous and exothermic. According to the results of the pH effect, the maximum adsorption was detected at pH 4 for Cu2+ (II) and pH 7 for Ni2+. The decrease of the adsorption capacity at higher values of pH is due to the precipitation of copper hydroxide Cu (OH)2 and nickel hydroxide Ni(OH)2. The results of the present work confirmed that palygorskite prepared from Tunisian diatomite hasa good and important potential to be used as an efficient adsorbent to remove heavy metals from effluents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and H.N.; Methodology, M.A. and S.A.; Investigation, H.N.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, H.N.; Writing-Review & Editing, J.L. and S.A.; Funding Acquisition, J.L.
Funding
This research was funded by Department of Education of the Basque Government grant number [IT1008-16]” and “The APC was funded by Department of Education of the Basque Government.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Department of Education of Basque Government (IT1008-16).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barros, F.C.; Sousa, F.W.; Cavalcante, R.M.; Carvalho, T.V.; Dias, F.S.; Queiroz, D.C.; Nascimento, R.F. Removal of Copper, Nickel and Zinc Ions from Aqueous Solution by Chitosan-8-Hydroxyquinoline Beads. CLEAN–Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, M.; Ahmed Basha, C.; Velan, M. Removal of copper (II) ions from synthetic electroplating rinse water using polyethyleneimine modified ion-exchange resin. Desalin. Water. Treat. 2016, 57, 20350–20367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M.; Ismaeili, J.; Najafzadeh, S. Design and evaluation of chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite nanofiber membrane for the removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. 2014, 45, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Xu, B.; Xie, J. Kinetics and thermodynamics of Eu (III) and U (VI) adsorption onto palygorskite. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 219, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, S.; Borisover, M.; Lapides, I. Few introducing comments on the thermal analysis of organoclays. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 105, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gionis, V.; Kacandes, G.H.; Kastritis, I.D.; Chryssikos, G.D. Combined near-infrared and X-ray diffraction investigation of the octahedral sheet composition of palygorskite. Clays Clay Miner. 2007, 55, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, E.; Gamba, A.; Tilocca, A. On the unusual stability of Maya blue paint: molecular dynamics simulations. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 57, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, A. A comparative study about adsorption of natural palygorskite for methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, H.; Arocena, J.M. Kaolinite formation from palygorskite and sepiolite in rhizosphere soils. Clays Clay Miner. 2008, 56, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaisena, A.; Rangsriwatananon, K. Synthesis of sodium zeolites from natural and modified diatomite. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.T.; Lai, C.W.; Hsien, K.J. Characterization and adsorption properties of diatomaceous earth modified by hydrofluoric acid etching. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoja, M.L.; Jones, H.; Garelick, H.; Mohamedbakr, H.G.; Burkitbayev, M. The removal of arsenate from water using iron-modified diatomite (D-Fe): isotherm and column experiments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Song, J.; Zhao, J. Synthesis and Characterization of MgO Modified Diatomite for Phosphorus Recovery in Eutrophic Water. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2016, 62, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yang, Q.; Fu, L.; Yang, H. Synthesis and magnetic property of SiO2 coated Fe3O4/palygorskite. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2015, 8, 56–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Yue, L.; Zhao, X.; Gao, L. Preparation of silica powder with high whiteness from palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 50, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, I.; Rumińska, M. UV spectrophotometric studies of Cu (II) ions separation by ultrafiltration enhanced with poly (sodium acrylate). Desalin. Water 2016, 57, 1436–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo-Barrera, A.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Martinez, F.B. Simultaneous determination of copper and cobalt with EDTA using derivative spectrophotometry. Analyst 1985, 110, 1313–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Adsorption and desorption of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solution by a lignocellulose/montmorillonite nanocomposite. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Meng, C. Synthesis of zeolite Y from diatomite and its modification by dimethylglyoxime for the removal of Ni (II) from aqueous solution. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.Q.; Shi, L.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Sun, L.B. Direct Synthesis of Zeolites from a Natural Clay, Attapulgite. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 6124–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, K.M.; Novo, B.L.; Felix, A.A.; Afonso, J.C.; Bertolino, L.C.; Silva, F.A. Ore Dressing and Technological Characterization of Palygorskite from Piauí/Brazil for Application as Adsorbent of Heavy Metals:In Characterization of Minerals, Metals and Materials. In Characterization of Minerals, Metals and Materials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Belaroui, L.S.; Dali Youcef, L.; Ouali, A.F.F.A.F.; Bengueddach, A.B.D.E.L.K.A.D.E.R.; Lopez Galindo, A. Mineralogical and chemical characterization of palygorskite from East-Algeria. Rev. Soc. Esp. Miner. Macla 2014, 19. Available online: http://www.ehu.eus/sem/macla_pdf/macla19/Belaroui.et.al_SEM2014.WEB.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2018).
- Cai, Y.; Xue, J.; Polya, D.A. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic study of Mg-rich, Mg-poor and acid leached palygorskites. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2007, 66, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Dong, Y.; Wang, X. Adsorption of Pb (II) on diatomite as affected via aqueous solution chemistry and temperature. Coll. Surf. A 2009, 339, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.L.D.G.; Fortes, A.C.; Oliveira, M.E.R.; de Freitas, R.M.; da Silva Filho, E.C.; Soares, M.F.D.L.R.; da Silva Leite, C.M. Palygorskite organophilic for dermopharmaceutical application. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 115, 2287–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourmoradi, H.; Nikaeen, M.; Khiadani, H.H. Removal of benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and xylene (BTEX) from aqueous solutions by montmorillonite modified with nonionic surfactant: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic study. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 191, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, J.; Nasri, N.S.; Ahmad Zaini, M.A.; Hamza, U.D.; Ani, F.N. Adsorption of benzene and toluene onto KOH activated coconut shell based carbon treated with NH3. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshdeh, R.K.; Abbasizadeh, S.; Nikou, M.R.K.; Badii, K.; Sharafi, M.S. Liquid Phase adsorption kinetics and equilibrium of toluene by novel modified-diatomite. J. Environ. Heal. Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusmin, R.; Sarkar, B.; Biswas, B.; Churchman, J.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R. Structural, electrokinetic and surface properties of activated palygorskite for environmental application. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 134, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.W.; Kan, C.C.; Rogel, B.D.; Dalida, M.L.P. Adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solution on chitosan-coated sand. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labidi, A.; Salaberria, A.M.; Fernandes, S.C.; Labidi, J.; Abderrabba, M. Adsorption of copper on chitin-based materials: Kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. 2016, 65, 10–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.C.; Gómez, R.; Giraldo, L. Removal of Mn, Fe, Ni and Cu ions from wastewater using cow bone charcoal. Materials 2010, 3, 452–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šljivić, M.; Smičiklas, I.; Pejanović, S.; Plećaš, I. Comparative study of Cu2+ adsorption on a zeolite, a clay and a diatomite from Serbia. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourliva, A.; Sikalidis, A.K.; Papadopoulou, L.; Betsiou, M. Removal of Cu2+ and Ni2+ ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto natural palygorskite and vermiculite. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladgar, M.; Beheshti, M.; Sabzyan, H. Single and binary adsorption of nickel and copper from aqueous solutions by γ-alumina nanoparticles: equilibrium and kinetic modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 211, 1060–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujelben, N.; Bouzid, J.; Elouear, Z. Adsorption of nickel and copper onto natural iron oxide-coated sand from aqueous solutions: study in single and binary systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labidi, A.; Saad, A.; Abderrabba, M. Copper adsorption onto starch as biopolymer: Isothermal equilibrium and kinetic studies. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 1274–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. Zurtheorie der sogenannten adsorption gelosterstoffe, KungligaSvenskaVetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, K.S.; Ardejani, F.D.; Badii, K.; Olya, M.E. Preparation and characterization of novel nano-mineral for the removal of several heavy metals from aqueous solution: Batch and continuous systems. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3108–S3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, A. Removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto acid-activated palygorskite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 149, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petra, L.; Billik, P.; Melichová, Z.; Komadel, P. Mechanochemically activated saponite as materials for Cu2+ and Ni2+ removal from aqueous solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igberase, E.; Osifo, P.; Ofomaja, A. The adsorption of copper (II) ions by polyaniline graft chitosan beads from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and desorption studies. J. Eniron. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Ramalingam, S.; Kirupha, S.D.; Murugesan, A.; Vidhyadevi, T.; Sivanesan, S. Adsorption behavior of nickel (II) onto cashew nut shell: Equilibrium, thermodynamics, kinetics, mechanism and process design. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevannan, A.; Mungroo, R.; Niu, C.H. Biosorption of nickel with barley straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuhoglu, Y.; Malkoc, E. Thermodynamic and kinetic studies for environmentaly friendly Ni (II) biosorption using waste pomace of olive oil factory. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2375–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azizi, S.; MahdaviShahri, M.; Mohamad, R. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Enhanced Adsorption of Lead Ions from Aqueous Solutions: Equilibrium, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies. Molecules 2017, 22, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, M.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Noreen, S. Eriobotrya japonica seed biocomposite efficiency for copper adsorption: isotherms, kinetics, thermodynamic and desorption studies. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 176, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).