Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Instruments
2.1.1. Sample Collection and Preparation of Stock Solutions
2.1.2. Biosorption Studies
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
2.2.1. Adsorbent Dosage and Initial Metal Concentration
2.2.2. Optimization of Agitation Rate and Optimization of pH
2.2.3. Contact Time and Optimization of Temperature
2.2.4. FT-IR Characterization and Sorption Isotherm
3. Results
3.1. Effect Dosage of Adsorbent
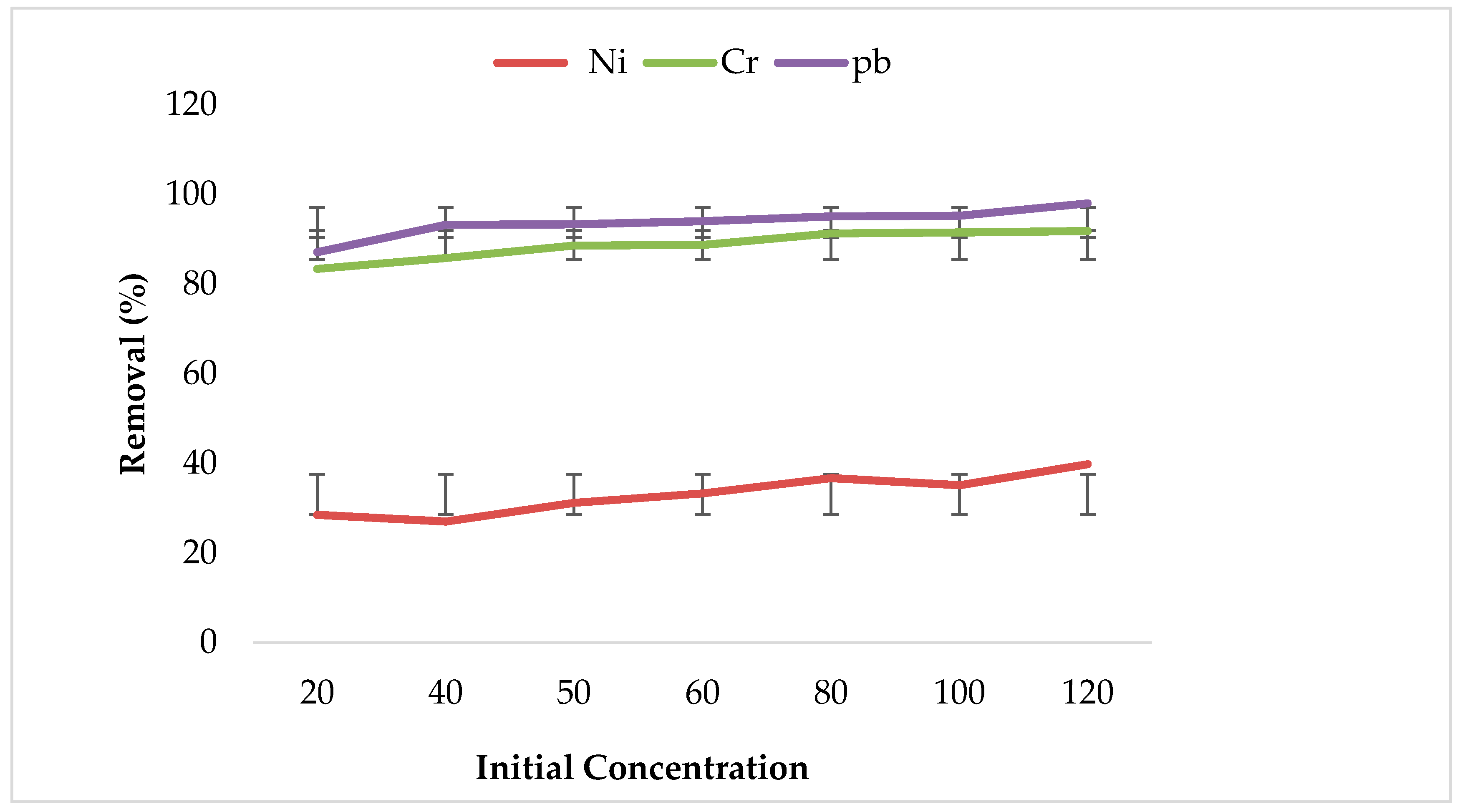
3.2. Effect of Initial Metal Ions Concentration
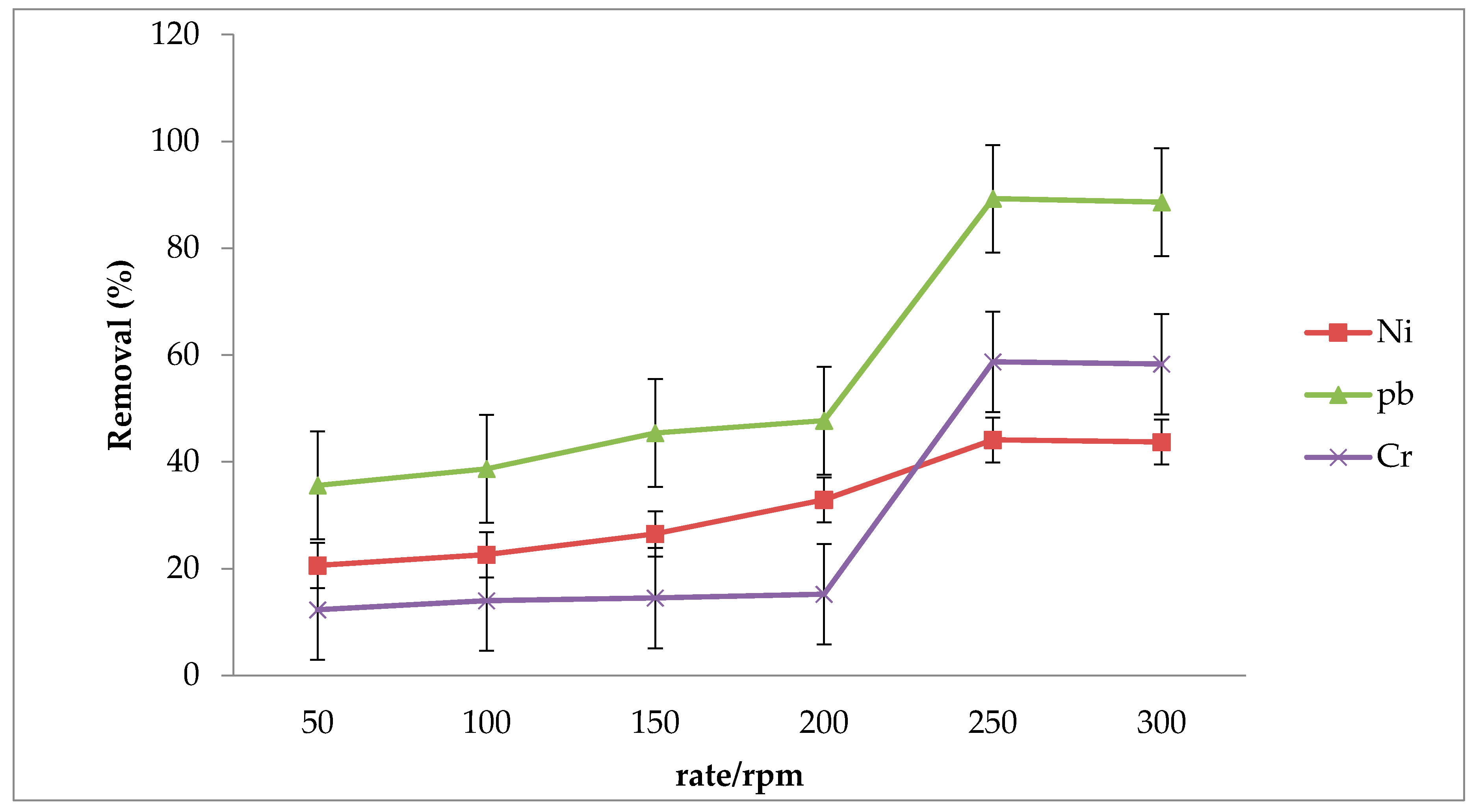
3.3. Effect of Shaking Rate
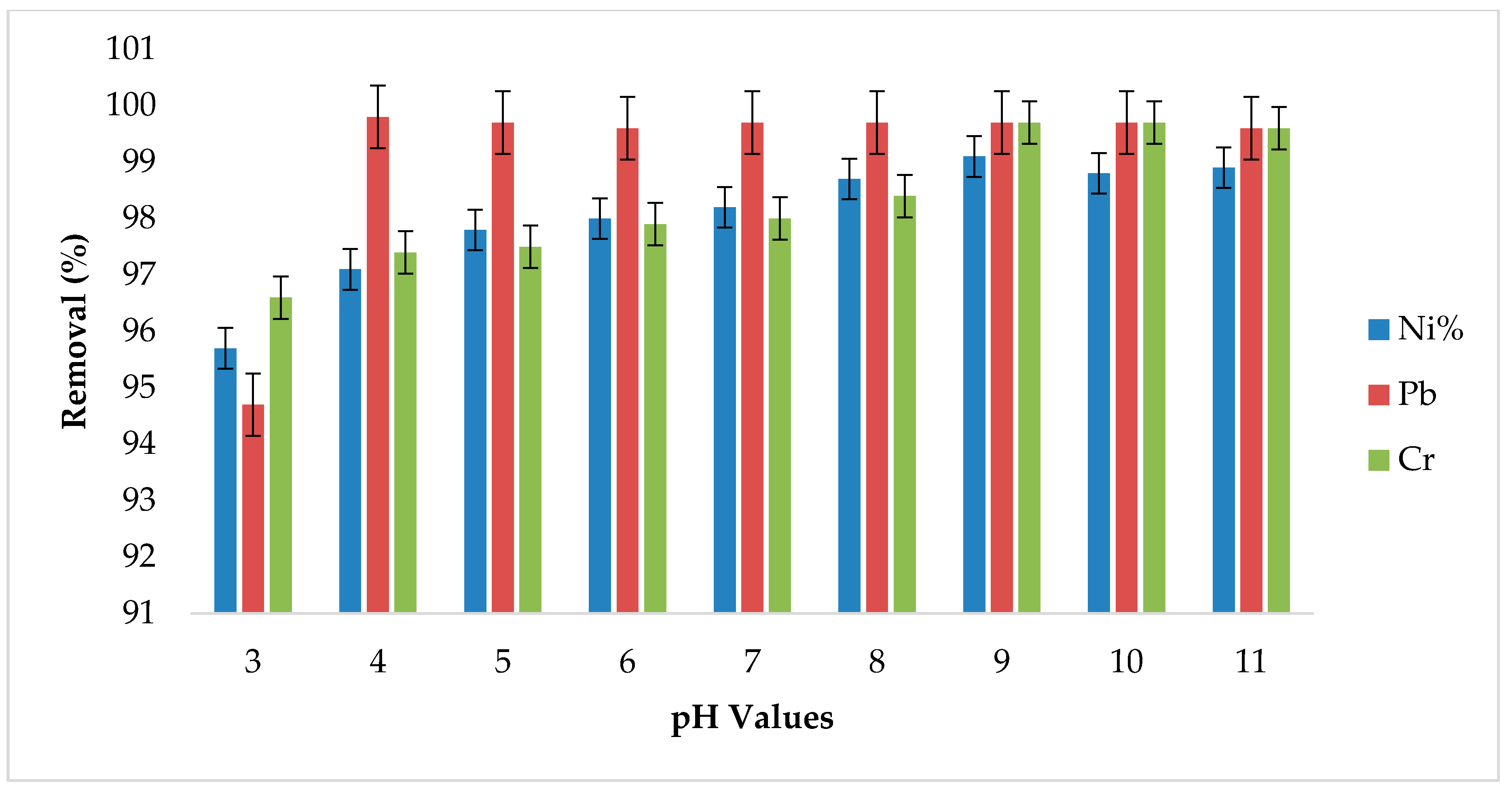
3.4. Effect of pH Variation
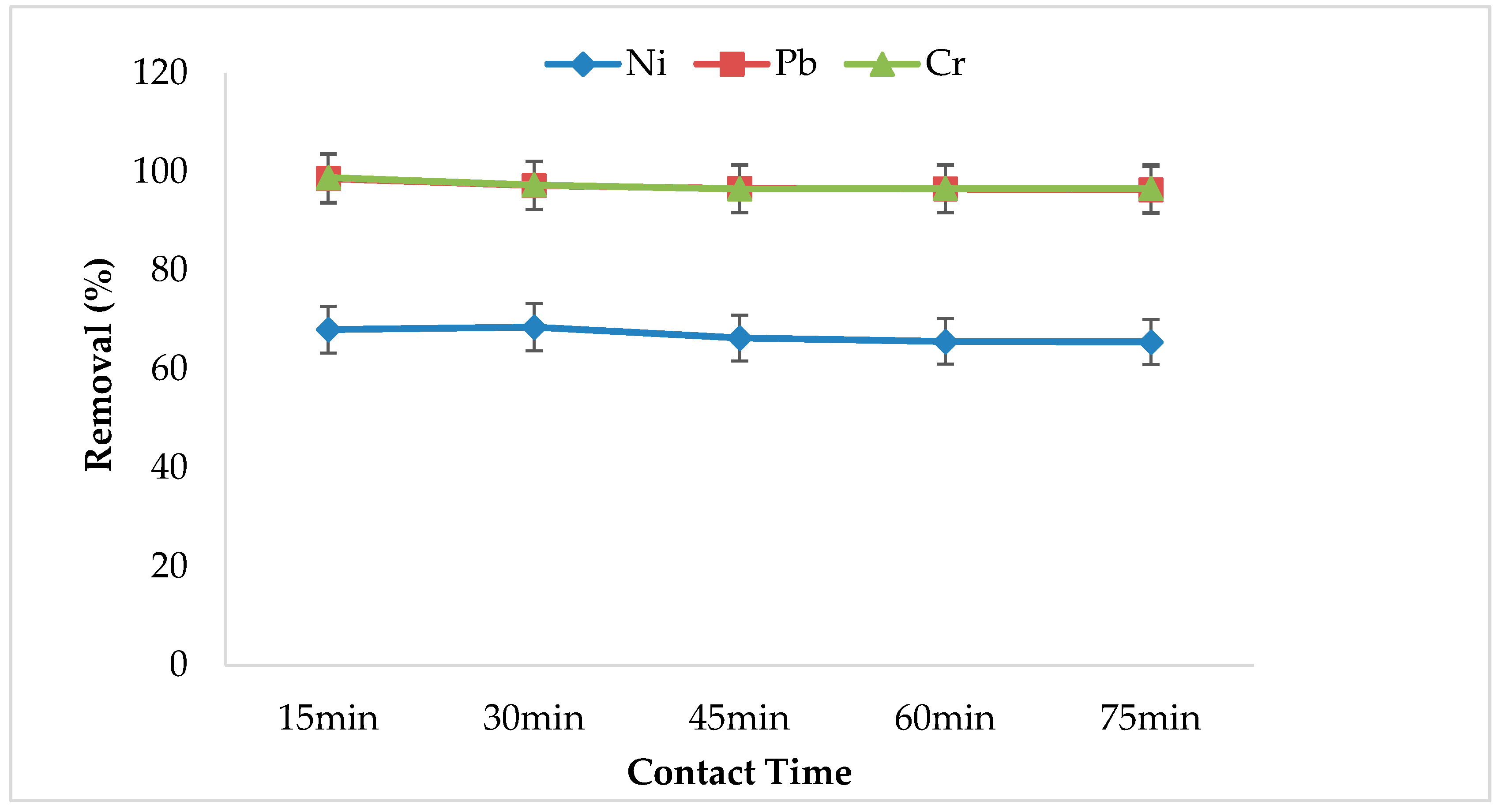
3.5. Effect of Contact Time
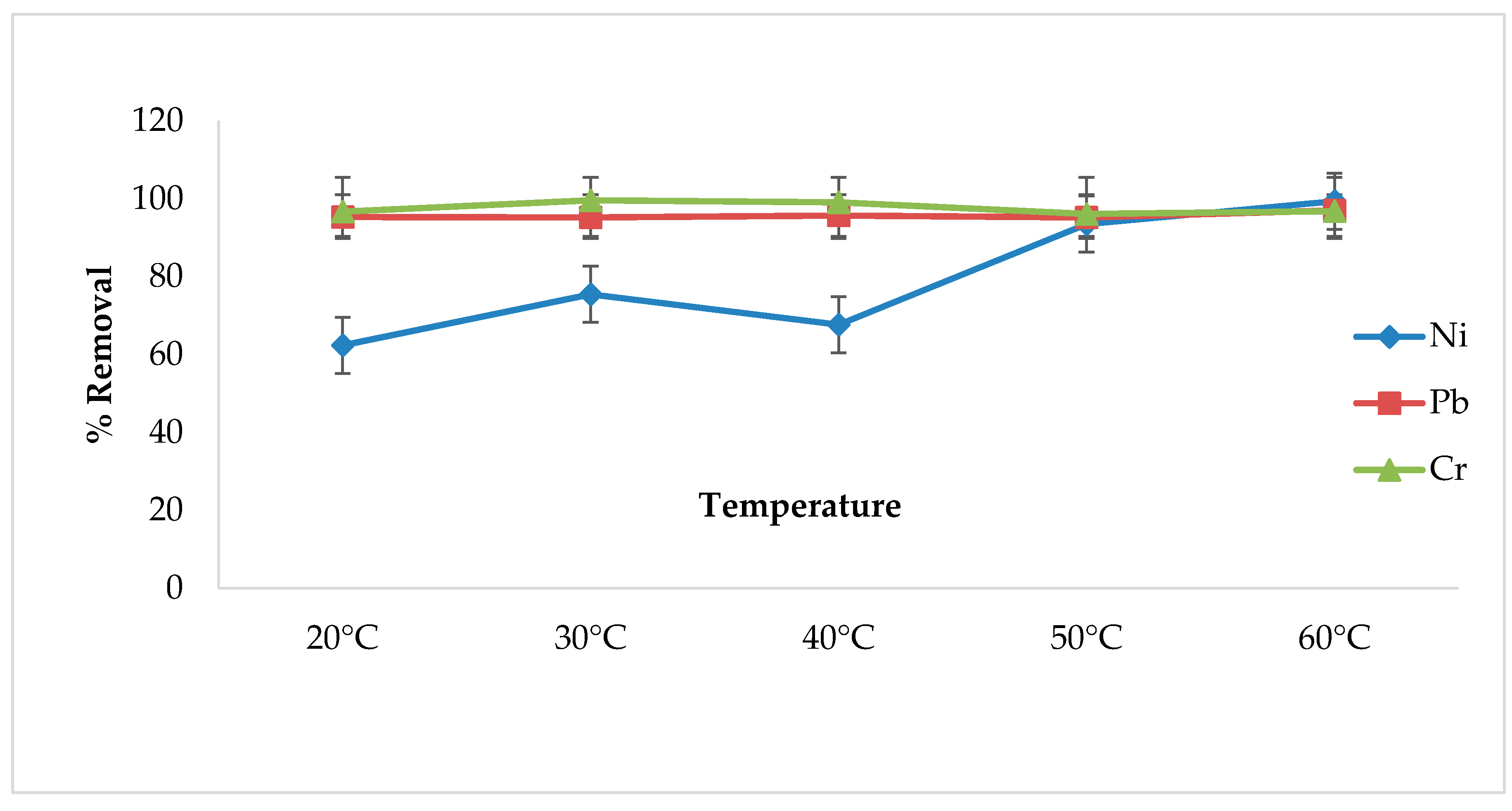
3.6. Effect of Temperature
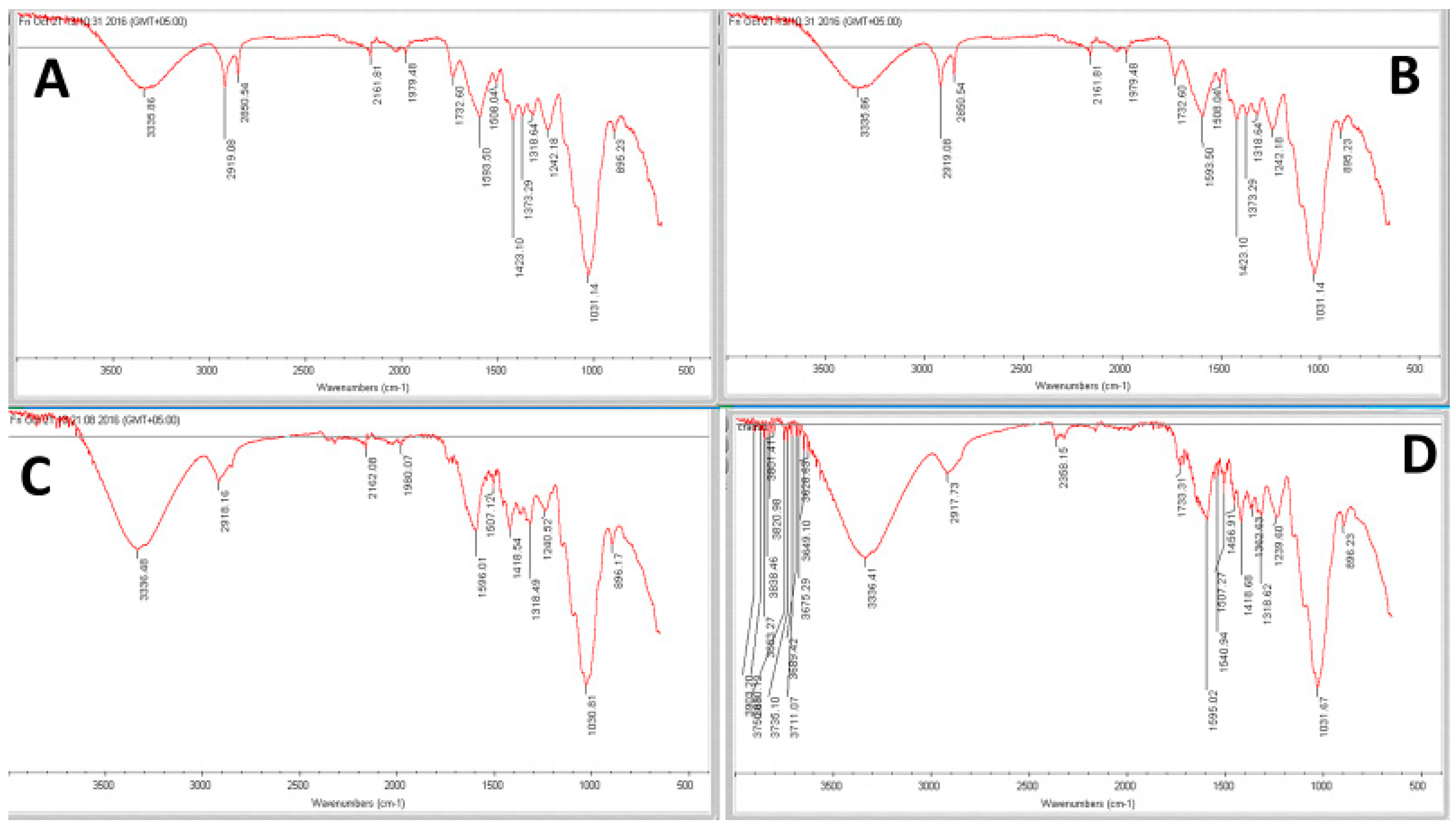
3.7. FTIR Spectroscopic Analysis
3.8. Adsorption Isotherms Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibrahim, W.M.; Hassan, A.F.; Azab, Y.A. Biosorption of toxic heavy metals from aqueous solution by Ulva lactuca activated carbon. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 3, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.M.; Karthik, C.; Saratale, R.G.; Kumar, S.S.; Prabakar, D.; Kadirvelu, K.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biological approaches to tackle heavy metal pollution: A survey of literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Li, X. Ecological risk evaluation of combined pollution of herbicide siduron and heavy metals in soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseem, K.; Farooqi, Z.H.; Ur Rehman, M.Z.; Ur Rehman, M.A.; Begum, R.; Huma, R.; Shahbaz, A.; Najeeb, J.; Irfan, A. A systematic study for removal of heavy metals from aqueous media using Sorghum bicolor: An efficient biosorbent. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 2355–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ravikumar, B.; Bai, G.; Li, X. Studies on seasonal pollution of heavy metals in water, sediment, fish and oyster from the Meiliang Bay of Taihu Lake in China. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosanu, I.; Teodosiu, C.; Paduraru, C.; Ibanescu, D.; Tofan, L. Biosorption of lead ions from aqueous effluents by rapeseed biomass. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaishankar, M.; Tseten, T.; Anbalagan, N.; Mathew, B.B.; Beeregowda, K.N. Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2014, 7, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniz, F.; Karabulut, A. Biosorption of heavy metal ions by chemically modified biomass of coastal seaweed community: Studies on phycoremediation system modeling and design. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 106, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadiani, M.R.; Darani, K.K.; Rahimifard, N.; Younesi, H. Biosorption of low concentration levels of Lead (II) and Cadmium (II) from aqueous solution by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Response surface methodology. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 15, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, A.I.; Peleka, E.N.; Samaras, P. Removal of Toxic Materials from Aqueous Streams. In Mineral Scales and Deposits; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Arsenic contamination, consequences and remediation techniques: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 112, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, B.; Bartacek, J.; Ortega-Bravo, J.C.; Jeison, D. Treatment of acid mine drainage by forward osmosis: Heavy metal rejection and reverse flux of draw solution constituents. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 332, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions based on the optimized dissolution-diffusion-flow forward osmosis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, T.; Li, C.; Bilal, M.; Yu, C.; Iqbal, H.M. Potentially toxic elements and environmentally-related pollutants recognition using colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probes. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 174–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M. Introducing Heavy Metals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahim, S.E.; Hyder, N.H.; Yousif, Y.M. Biosorption of Heavy Metals onto Two Types of Fungi Biomass in Batch Experiments. Assoc. Arab Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2018, 23, 55–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bankar, A.; Nagaraja, G. Recent trends in biosorption of heavy metals by Actinobacteria. New Future Dev. Microb. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2018, 257–275. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y. Fluorescent sensor based models for the detection of environmentally-related toxic heavy metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, M.; Guha, A.K.; Ray, L. Adsorption of Lead on Cucumber Peel. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 151, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabura, M.; Hussain, S.A.; Ghani, W.A.W.A.; Jami, M.S.; Tan, Y.P. Utilization of renewable durian peels for biosorption of zinc from wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2528–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Vigneswaran, S.; Nguyen, T.V. Competitive adsorption of metals on cabbage waste from multi-metal solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.; Sikarwar, S. Adsorptive removal of Erythrosine dye onto activated low cost de-oiled mustard. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonska, B.; Siedlecka, E. Removing heavy metals from wastewaters with use of shales accompanying the coal beds. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 155, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Adil, M.; Yusof, A.M.; Kamaruzzaman, Y.B.; Ansary, R.H. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions with Acid Activated Carbons Derived from Oil Palm and Coconut Shells. Materials 2014, 7, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazer-Rahmati, M.M.; Rabbani, P.; Abdolali, A.; Keshtkar, A.R. Kinetics and equilibrium studies on biosorption of cadmium, lead, and nickel ions from aqueous solutions by intact and chemically modified brown algae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şeker, A.; Shahwan, T.; Eroğlu, A.E.; Yılmaz, S.; Demirel, Z.; Dalay, M.C. Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies for the biosorption of aqueous lead(II), cadmium(II) and nickel(II) ions on Spirulina platensis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Jin, F.; Wang, F.; McMillan, O.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Sorption of lead by Salisbury biochar produced from British broadleaf hardwood. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 193, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertagnolli, C.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Guibal, E. Chromium biosorption using the residue of alginate extraction from Sargassum filipendula. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies of the Biosorption of Ni(II) by Modified Rape Straw. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2016, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşar, Ş.; Kaya, F.; Özer, A. Biosorption of lead(II) ions from aqueous solution by peanut shells: Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Li, H.; Jiang, D.; Luo, D.; Chen, Y.; Xia, J.; Chen, D. Biosorption of strontium(II) from aqueous solutions by Bacillus cereus isolated from strontium hyperaccumulator Andropogon gayanus. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 111, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vendruscolo, F.; da Rocha Ferreira, G.L.; Antoniosi Filho, N.R. Biosorption of hexavalent chromium by microorganisms. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šoštarić, T.D.; Petrović, M.S.; Pastor, F.T.; Lončarević, D.R.; Petrović, J.T.; Milojković, J.V.; Stojanović, M.D. Study of heavy metals biosorption on native and alkali-treated apricot shells and its application in wastewater treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 259, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, S.; Sezer, S.; Apak, R. Characterization and lead(II), cadmium(II), nickel(II) biosorption of dried marine brown macro algae Cystoseira barbata. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2012, 19, 3118–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthi, N.; Srinivasan, K. Adsorptive removal of nickel and lead ions from aqueous solutions using phosphorylated tamarind nut carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 53, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Qin, C.; Hong, X.; Kang, G.; Qin, M.; Yang, D.; Pang, B.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Dick, R.P. Risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metal pollution from lower reaches of Yellow River irrigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, G.; Ge, X.; Xu, G.; Guan, Y. Novel insights into heavy metal pollution of farmland based on reactive heavy metals (RHMs): Pollution characteristics, predictive models, and quantitative source apportionment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 360, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riani, E.; Cordova, M.R.; Arifin, Z. Heavy metal pollution and its relation to the malformation of green mussels cultured in Muara Kamal waters, Jakarta Bay, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Yu, S. Spatio-temporal variational characteristics analysis of heavy metals pollution in water of the typical northern rivers, China. J. Hydrol. 2018, 559, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwinyihija, M. Main Pollutants and Environmental Impacts of the Tanning Industry. In Ecotoxicological Diagnosis in the Tanning Industry; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Schaider, L.A.; Senn, D.B.; Estes, E.R.; Brabander, D.J.; Shine, J.P. Sources and fates of heavy metals in a mining-impacted stream: Temporal variability and the role of iron oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.L. Cadmium and Phosphorous Fertilizers: The Issues and the Science. Procedia Eng. 2014, 83, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanarani, S.; Viswanathan, E.; Piruthiviraj, P.; Arivalagan, P.; Kaliannan, T. Comparative study on the biosorption of aluminum by free and immobilized cells of Bacillus safensis KTSMBNL 26 isolated from explosive contaminated soil. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 69, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Vargas, G.; Sosa-Hernandez, J.E.; Saldarriaga-Hernandez, S.; Villalba-Rodriguez, A.M.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Electrochemical Biosensors: A Solution to Pollution Detection with Reference to Environmental Contaminants. Biosensors 2018, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilal, M.; Rasheed, T.; Sosa-Hernandez, J.E.; Raza, A.; Nabeel, F.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Biosorption: An Interplay between Marine Algae and Potentially Toxic Elements-A Review. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeraatkar, A.K.; Ahmadzadeh, H.; Talebi, A.F.; Moheimani, N.R.; McHenry, M.P. Potential use of algae for heavy metal bioremediation, a critical review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sağ, Y. Biosorption of heavy metals by fungal biomass and modeling of fungal biosorption: A review. Sep. Purif. Method 2001, 30, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Hussain, J.; Akbar, A.; Mehmood, K.; Anwar, M.; Hasni, M.S.; Ullah, S.; Sajid, S.; Ali, I. Biosorption of heavy metals by obligate halophilic fungi. Chemosphere 2018, 199, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Joia, J.; Sood, A.; Sood, R.; Sidhu, C.; Kaur, G. Microbes as potential tool for remediation of heavy metals: A review. J. Microb. Biochem. Technol. 2016, 8, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Martin, J.A.; Gutiérrez, C.; Torrijos, M.; Nanos, N. Wood and bark of Pinus halepensis as archives of heavy metal pollution in the Mediterranean Region. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 239, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezania, S.; Taib, S.M.; Md Din, M.F.; Dahalan, F.A.; Kamyab, H. Comprehensive review on phytotechnology: Heavy metals removal by diverse aquatic plants species from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Song, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, S.; Shao, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, J. Biomass based hydrogel as an adsorbent for the fast removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 3434–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Yang, J.-K.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Koduru, J.R. Low-cost magnetized Lonicera japonica flower biomass for the sorption removal of heavy metals. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

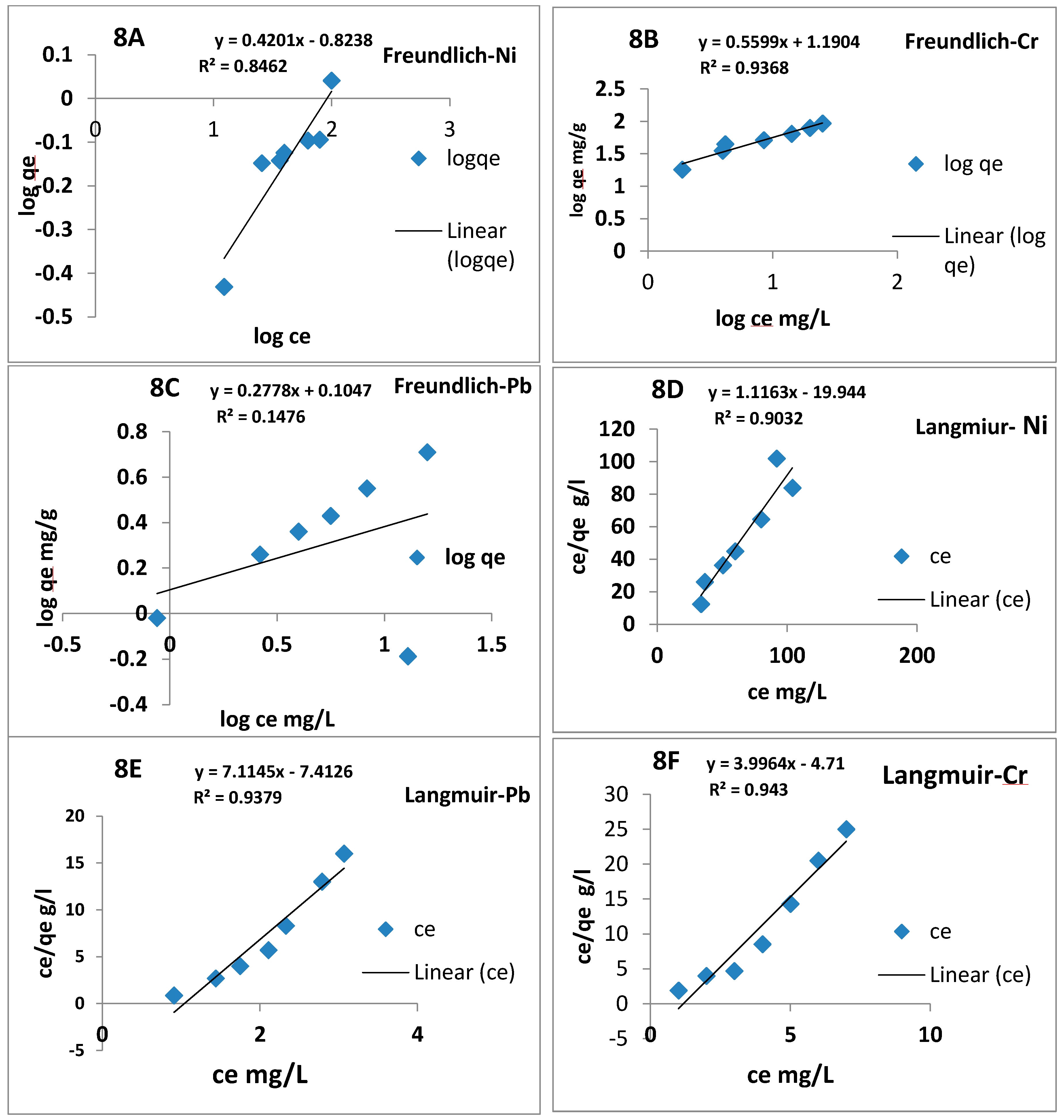
| Metals Ions | BCS Adsorbent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir’s Constant | Freundlich Constant | ||||||
| Qm | b | R2 | qe mg/g | 1/n | Kf | R2 | |
| Ni2+ | 1.1 | 0.9 | 0.56 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 1.8 | 0.887 |
| Cr6+ | 3.9 | 1.2 | 0.91 | 95 | 2.70 | 1.6 | 0.877 |
| Pb2+ | 7.8 | 0.9 | 0.98 | 78.5 | 1.80 | 2.3 | 0.15 |
| S.No | Adsorbent/Agricultural Waste | Metal Ion | Qm mg/gm |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brassica Compestris stem (BCS) | Ni2+ | 1.1 mg/gm |
| 2 | Brassica Compestris Stem (BCS) | Cr6+ | 95 mg/gm |
| 3 | Brassica Compestris Stem (BCS) | Pb2+ | 78 mg/gm |
| 4 | Cashew nut shell (raw) | Ni2+ | 3 gm/L |
| 5 | Brassica satin | Ni2+ | 0.02 mg/kg |
| 6 | Orange peel | Cr3+ | 18.73 mg/gm |
| 7 | Sugarcane bagasse | Cr3+ | 1.76 mg/gm |
| 8 | Neem sawdust | Cr3+ | 58.28 mg/gm |
| 9 | Lentil husk | Pb2+ | 81.73 mg/gm |
| 10 | Cabbage | Pb2+ | 60.57 mg/gm |
| 11 | Cauliflower | Pb2+ | 47.63 mg/gm |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baby Shaikh, R.; Saifullah, B.; Rehman, F.U. Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent. Water 2018, 10, 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101316
Baby Shaikh R, Saifullah B, Rehman FU. Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent. Water. 2018; 10(10):1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101316
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaby Shaikh, Rabia, Bullo Saifullah, and Fawad Ur Rehman. 2018. "Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent" Water 10, no. 10: 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101316
APA StyleBaby Shaikh, R., Saifullah, B., & Rehman, F. U. (2018). Greener Method for the Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from the Wastewater by Application of Agricultural Waste as an Adsorbent. Water, 10(10), 1316. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101316





