Laboratory Investigation on the Evolution of a Sandy Beach Nourishment Protected by a Mixed Soft–Hard System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrodynamics
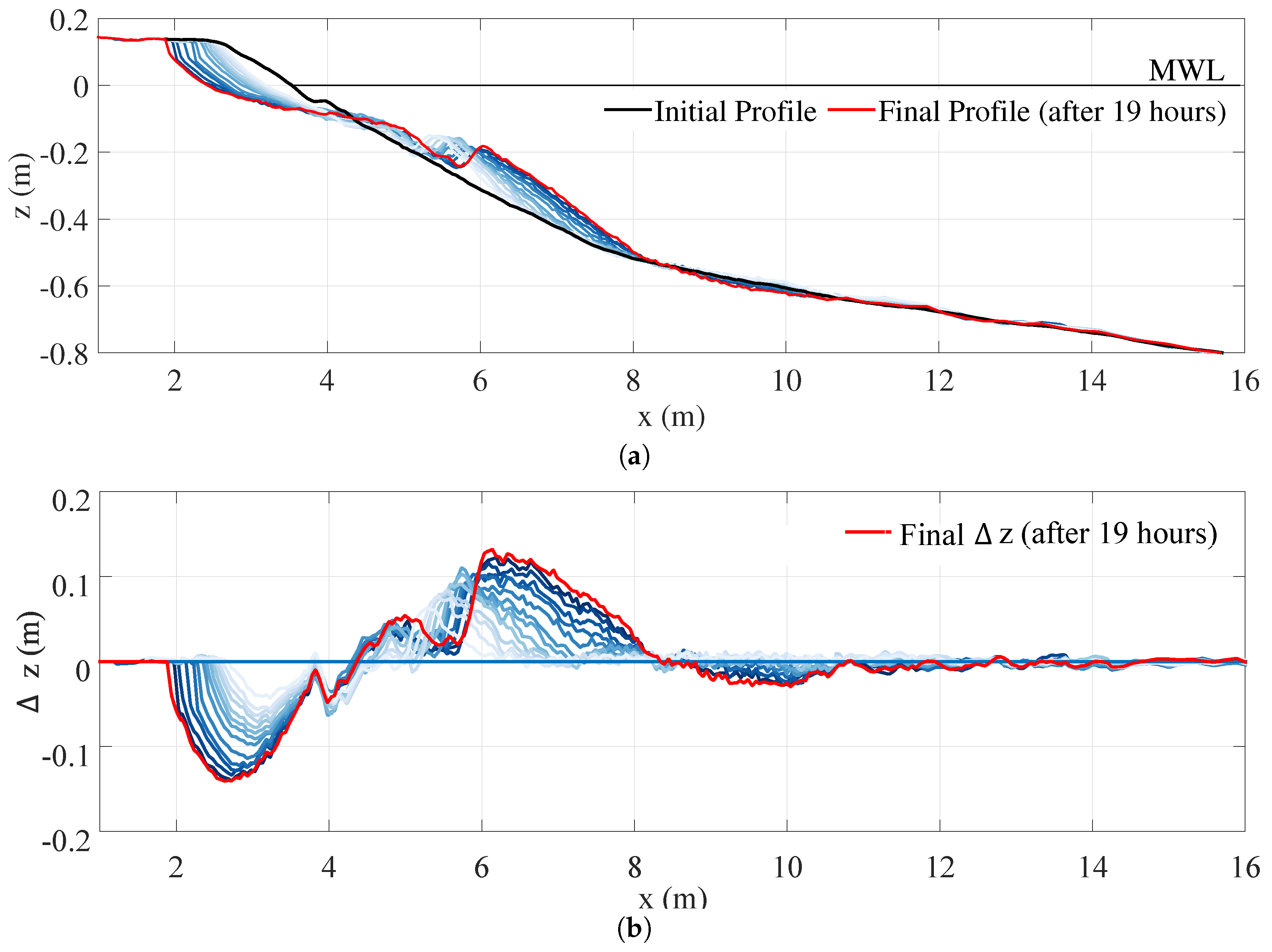
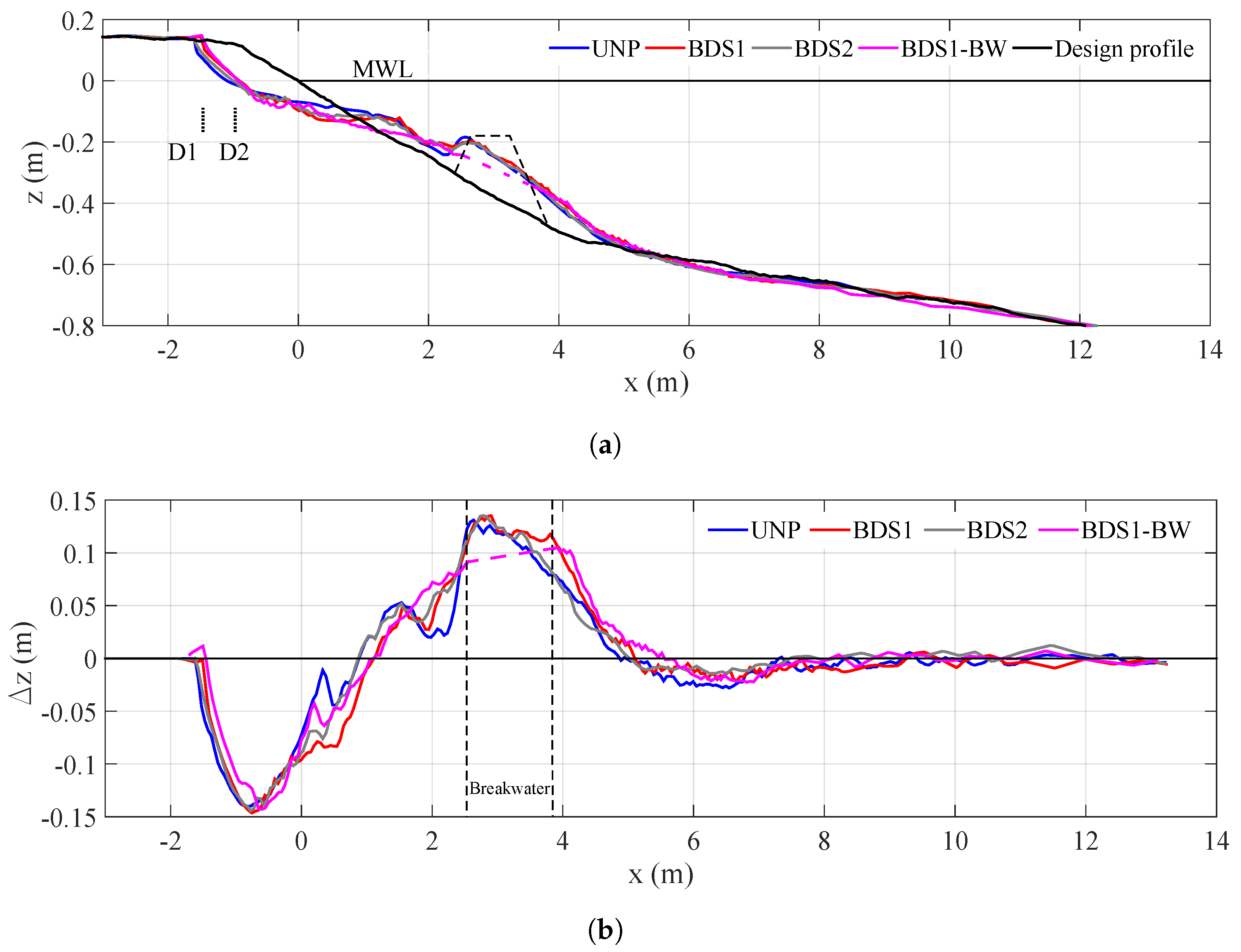
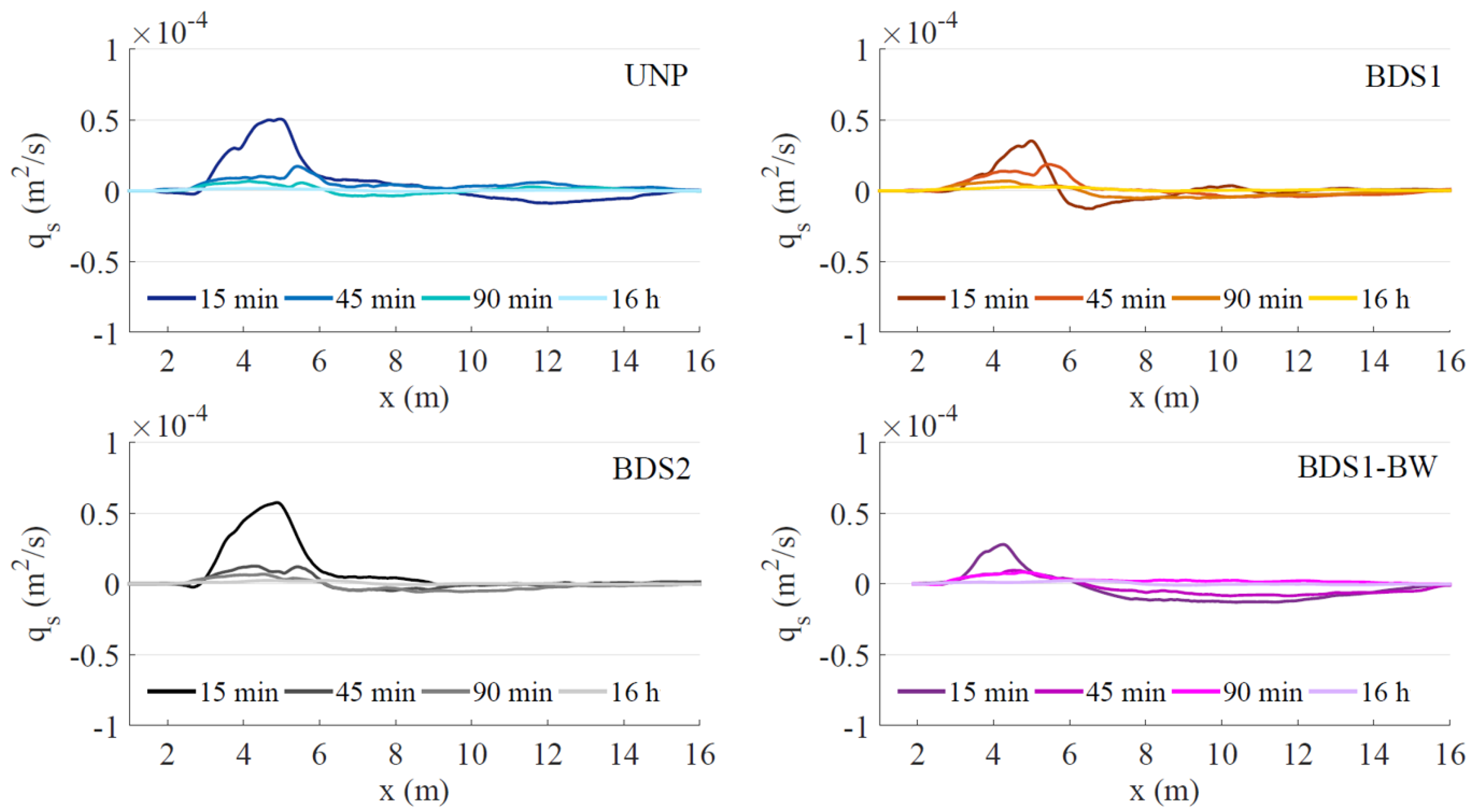
3.2. Morphodynamics
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsvetanov, T.G.; Shah, F.A. The economic value of delaying adaptation to sea-level rise: An application to coastal properties in Connecticut. Climat. Chang. 2013, 121, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruol, P.; Martinelli, L.; Favaretto, C. Vulnerability analysis of the Venetian littoral and adopted mitigation strategy. Water 2018, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, D.; Di Risio, M.; De Girolamo, P. A simplified real time method to forecast semi-enclosed basins storm surge. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 165, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2014–Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Regional Aspects; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lamberti, A.; Archetti, R.; Kramer, M.; Paphitis, D.; Mosso, C.; Di Risio, M. European experience of low crested structures for coastal management. Coast. Eng. J. 2005, 52, 841–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, D.; Pasquali, D.; De Girolamo, P.; Di Risio, M. Effects of submerged berms on the stability of conventional rubble mound breakwaters. Coast. Eng. J. 2018, 136, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnsack, J.A.; Sutherland, D.L. Artificial reef research: A review with recommendations for future priorities. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1985, 37, 11–39. [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco, M.; Hanson, H.; Larson, M.; Steetzel, H.; Stive, M.; Chatelus, Y.; Aarninkhof, S.; Karambas, T. Nourishment design and evaluation: Applicability of model concepts. Coast. Eng. J. 2002, 47, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira da Silva, G.; Toldo, E.; Klein, A.; Short, A.; Tomlinson, R.; Strauss, D. A comparison between natural and artificial headland sand bypassing in Santa Catarina and the Gold Coast. In Proceedings of the Australasian Coasts & Ports 2017 Conference, Cairns, QLD, Australia, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, A.; Taylor, M.D.; Folpp, H.; Lowry, M.B. Managing the development of artificial reef systems: The need for quantitative goals. Fish Fish. 2018, 19, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarczyk, K.W. Design of low-crested (submerged) structures: An overview. In Proceedings of the 6th COPEDEC (International Conference on Coastal and Port Engineering in Developing Countries), Colombo, Sri Lanka, Citeseer, 19 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Di Risio, M.; Lisi, I.; Beltrami, G.; De Girolamo, P. Physical modeling of the cross-shore short-term evolution of protected and unprotected beach nourishments. Ocean Eng. 2010, 37, 777–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaia, G.; Damiani, L.; Petrillo, A. Evolution of a Beach with and without a Submerged Breakwater: Experimental Investigation. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Venice, Italy, 4–9 October 1992; pp. 1959–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Creter, R.E.; Garaffa, T.; Schmidt, C.J. Enhancement of beach fill performance by combination with an artificial submerged reef system. In Proceedings of the 7th National Conference on Beach Preservation Technology, Tallahassee, FL, USA, 9–11 February 1994; pp. 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Buccino, M. Large-scale experiments on the behaviour of low crested and submerged breakwaters in presence of broken waves. In Coastal Engineering 2002: Solving Coastal Conundrums; World Scientific: Sinapore, 2003; pp. 1900–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Armono, H.; Hall, K. Laboratory study of wave transmission on artifical reefs. In Proceedings of the Canadian Coastal Engineering Conference, Kingston, ON, Canada, 15–17 October 2003; Canadian Society for Civil Engineering: Kingston, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Stauble, D.K.; Tabar, J.R. The use of submerged narrow-crested breakwaters for shoreline erosion control. J. Coast. Res. 2003, 19, 684–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wamsley, T.; Hanson, H.; Kraus, N.C. Wave Transmission at Detached Breakwaters for Shoreline Response Modeling; Technical report No. ERDC/CHL-CHETN-II-45; Engineer Research and Development Center Vicksburg MS Coastal and Hydraulics Lab: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Malcangio, D.; Melena, A.; Damiani, L.; Mali, M.; Saponieri, A. Numerical study of water quality improvement in a port through a forced mixing system. In Water Resources Management IX; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2017; pp. 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Mali, M.; Malcangio, D.; Dell’Anna, M.M.; Damiani, L.; Mastrorilli, P. Influence of hydrodynamic features in the transport and fate of hazard contaminants within touristic ports. Case study: Torre a Mare (Italy). Heliyon 2018, 4, e00494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Alsina, J.; Cáceres, I.; González-Marco, D.; Sierra, J.; Pena, C. Morphodynamics on a beach with a submerged detached breakwater. In Coastal Engineering 2004; World Scientific: Sinapore, 2005; pp. 2836–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnold, R. Beach formation by waves: Some model experiments in a wave tank. J. Inst. Civ. Eng. 1940, 15, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, U. Influence of the water table on beach aggradation and degradation. J. Mar. Res. 1948, 7, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, N.; Baldock, T.E.; Nielsen, P.; Jeng, D.S.; Tao, L. Swash-aquifer interaction in the vicinity of the water table exit point on a sandy beach. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponieri, A. Beach Drainage. In Encyclopedia of Coastal Science, 2nd ed.; Finkl, C.W., Makowski, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavola, P.; Vicinanza, D.; Fontana, E. Beach drainage as a form of shoreline stabilization: Case studies in Italy. In Coastal Engineering 2008; World Scientific: Sinapore, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 2646–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Masria, A.; Iskander, M.; Negm, A. Coastal protection measures, case study (Mediterranean zone, Egypt). J. Coast. Conserv. 2015, 19, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, D.P.; Baldock, T.E.; Li, L. The influence of groundwater on profile evolution of fine and coarse sand beaches. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Symposium on Coastal Engineering and Science of Coastal Sediment Process, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 May 2007; pp. 506–519. [Google Scholar]
- Damiani, L.; Petrillo, A.F.; Saponieri, A. Near shore Morphodynamic of drained beaches. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2011, 1, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, L.; Aristodemo, F.; Saponieri, A.; Verbeni, B.; Veltri, P.; Vicinanza, D. Full-scale experiments on a beach drainage system: Hydrodynamic effects inside beach. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, L.; Vicinanza, D.; Aristodemo, F.; Saponieri, A.; Corvaro, S. Experimental investigation on wave set-up and nearshore velocity field in presence of a BDS. J Coast. Res. 2011, SI 64, 55–59. [Google Scholar]
- Aristodemo, F.; Ciavola, P.; Veltri, P.; Saponieri, A. The influence of a Beach Drainage System on wave reflection and surf beat processes. J Coast. Res. 2011, SI 64, 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Saponieri, A.; Damiani, L. Numerical analysis of infiltration in a drained beach. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2015, 10, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavola, P.; Vicinanza, D.; Aristodemo, F.; Contestabile, P. Large-scale morphodynamic experiments on a beach drainage system. J. Hydraul. Res. 2011, 49, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, P.; Aristodemo, F.; Vicinanza, D.; Ciavola, P. Laboratory study on a beach drainage system. Coast. Eng. 2012, 66, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisi, I.; Molfetta, M.; Bruno, M.; Di Risio, M.; Damiani, L. Morphodynamic classification of sandy beaches in enclosed basins: The case study of Alimini (Italy). J. Coast. Res. 2011, SI 64, 180–184. [Google Scholar]
- Krumbein, W.C.; James, W.R. A Lognormal Size Distribution Model for Estimating Stability of Beach Fill Material; Army Coastal Engineering Research Center: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Lisi, I.; Di Risio, M.; De Girolamo, P.; Gabellini, M. Engineering Tools for the Estimation of Dredging-Induced Sediment Resuspension and Coastal Environmental Management. In Applied Studies of Coastal and Marine Environments; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 55–83. [Google Scholar]
- Di Risio, M.; Pasquali, D.; Lisi, I.; Romano, A.; Gabellini, M.; De Girolamo, P. An analytical model for preliminary assessment of dredging-induced sediment plume of far-field evolution for spatial non homogeneous and time varying resuspension sources. Coast. Eng. 2017, 127, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruun, P. Beach scraping—Is it damaging to beach stability? Coast. Eng. 1983, 7, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNinch, J.; Wells, J. Effectiveness of beach scraping as a method of erosion control. Shore Beach 1992, 60, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Henry, R. Preliminary Investigations into the Possible Effects of Beach Scraping on Wooli Beach With Specific Reference to Intertidal Macro-Infauna Diversity and Abundance. Bachelor’s Thesis, Deakin University, Victoria, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Baldock, T.E.; Alsina, J. Impact of beach scraping on near shore sediment transport and bar migration. In Proceedings of the Coasts and Ports 2013: 21st Australasian Coastal and Ocean Engineering Conference and the 14th Australasian Port and Harbour Conference, Sydney, Australia, 11–13 September 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dare, J.L. Alternative Shore Protection Strategies: Innovative Options and Management Issues. Master’s Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Di Risio, M.; Bruschi, A.; Lisi, I.; Pesarino, V.; Pasquali, D. Comparative analysis of coastal flooding vulnerability and hazard assessment at national scale. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R. Standard test methods for determining average grain size (F112). In Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Metal-Mechanical Testing; Elevated and Low Temperature Tests; Metallography; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth, C.K. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, R.G. Heuristic models of sand transport in the surf zone. In First Australian Conference on Coastal Engineering, 1973: Engineering Dynamics of the Coastal Zone; Institution of Engineers: Australia, 1973; p. 215. Available online: https://search.informit.com.au/documentSummary;dn=971703171672500;res=IELENG (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Kriebel, D.; Dally, W.; Dean, R. Undistorted Froude model for surf zone sediment transport. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Taipei, Taiwan, 9–14 November 1986; pp. 1296–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, N.C.; Larson, M. Beach Profile Change Measured in the Tank for Large Waves 1956–1957 and 1962; Technical report; Coastal Engineering Research Center: Vicksburg, MS, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.A. Prediction of storm/normal beach profiles. J. Water. Port Coast. Ocean Eng. 1993, 119, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansard, E.P.; Funke, E. The measurement of incident and reflected spectra using a least squares method. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Sydney, Australia, 23–28 March 1980; pp. 154–172. [Google Scholar]
- Salmon, S.A.; Bryan, K.R.; Coco, G. The use of video systems to measure run-up on beaches. J. Coast. Res. 2007, 50, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, N.; Saponieri, A.; Damiani, L. A new video monitoring system in support of Coastal Zone Management at Apulia Region, Italy. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 142, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, N.; Damiani, L.; Molfetta, M.G.; Saponieri, A. New coastal video-monitoring system achievement and development. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousdoukas, M.I.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Dimou, K.; Zervakis, V.; Conley, D.C. Wave run-up observations in microtidal, sediment-starved pocket beaches of the Eastern Mediterranean. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S37–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentini, N.; Saponieri, A.; Molfetta, M.G.; Damiani, L. New algorithms for shoreline monitoring from coastal video systems. Earth Sci. Inform. 2017, 10, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenaz, P.; Sage, D.; Unser, M. Bi-exponential edge-preserving smoother. IEEE Trans. Image Proc. 2012, 21, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Structured forests for fast edge detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 1841–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Eichentopf, S.; Cáceres, I.; Alsina, J.M. Breaker bar morphodynamics under erosive and accretive wave conditions in large-scale experiments. Coast. Eng. 2018, 138, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, M.; Vicinanza, D.; Buccino, M. 2D wave setup behind submerged breakwaters. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.; Hanson, H.; Kraus, N.C.; Newe, J. Short-and long-term responses of beach fills determined by EOF analysis. J. Water. Port Coastal Ocean Eng. 1999, 125, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goring, D.G.; Nikora, V.I. Despiking acoustic Doppler velocimeter data. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftah, M.B.; Malcangio, D.; De Serio, F.; Mossa, M. Vertical dense jet in flowing current. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2018, 18, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, N.; Nielsen, P.; Jessen, O.Z. Swash zone and near-shore watertable dynamics. In Coastal Engineering 2002: Solving Coastal Conundrums; World Scientific: Singapore, 2003; pp. 1006–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Baldock, T.; Birrien, F.; Atkinson, A.; Shimamoto, T.; Wu, S.; Callaghan, D.; Nielsen, P. Morphological hysteresis in the evolution of beach profiles under sequences of wave climates-Part 1; observations. Coast. Eng. 2017, 128, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldock, T.; Manoonvoravong, P.; Pham, K.S. Sediment transport and beach morphodynamics induced by free long waves, bound long waves and wave groups. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 898–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveless, J.; Debski, D.; MacLeod, A. Sea level set-up behind detached breakwaters. In Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Copenhagen, Denmark, 22–26 June 1998; pp. 1665–1678. [Google Scholar]
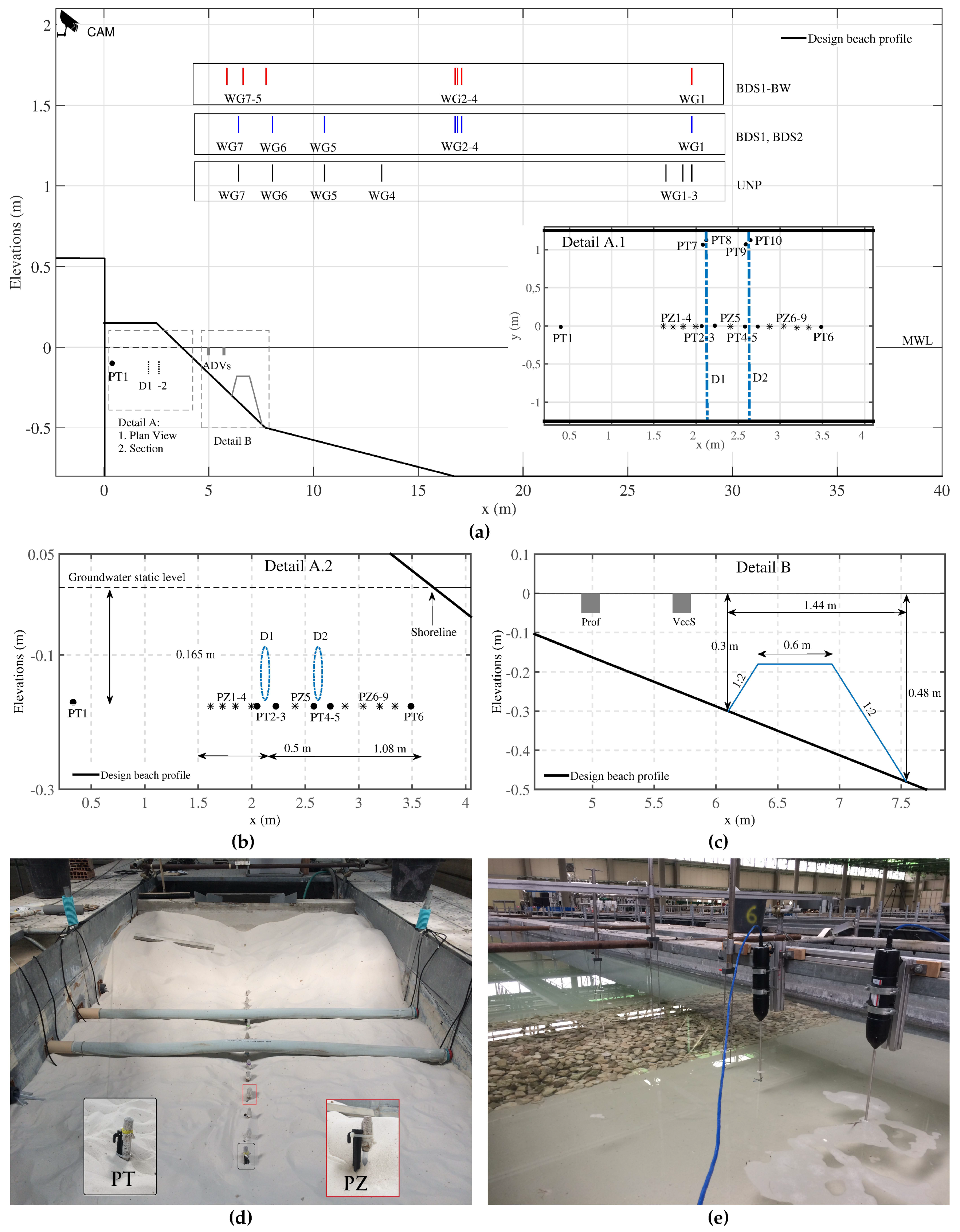
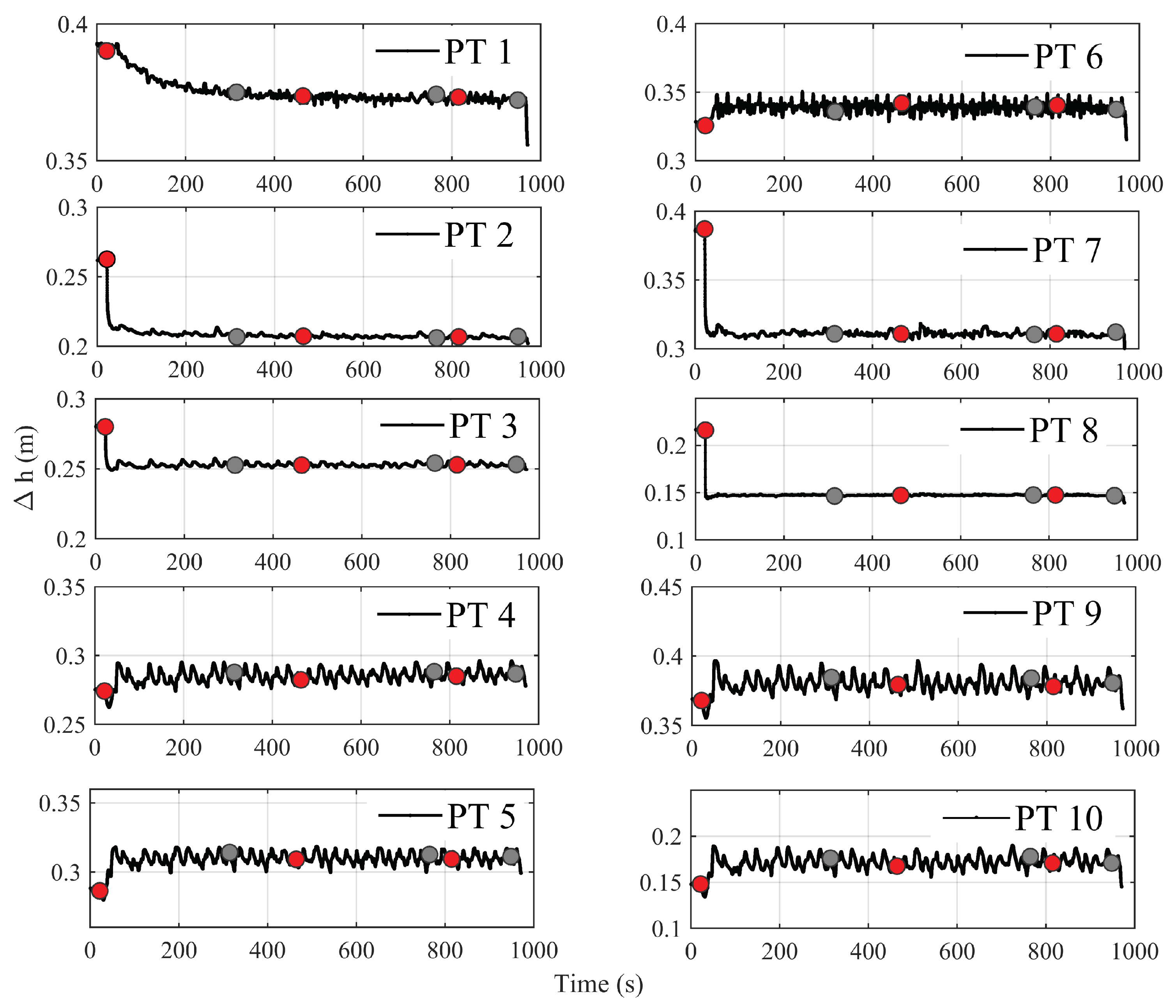

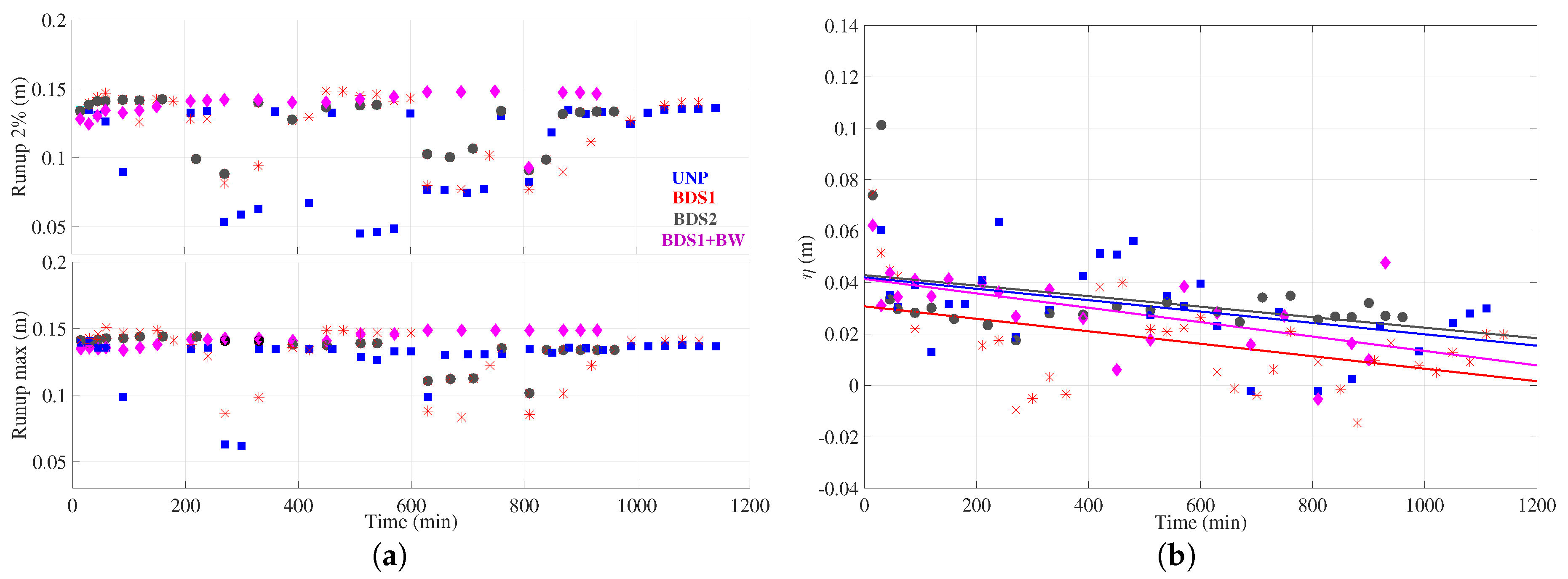
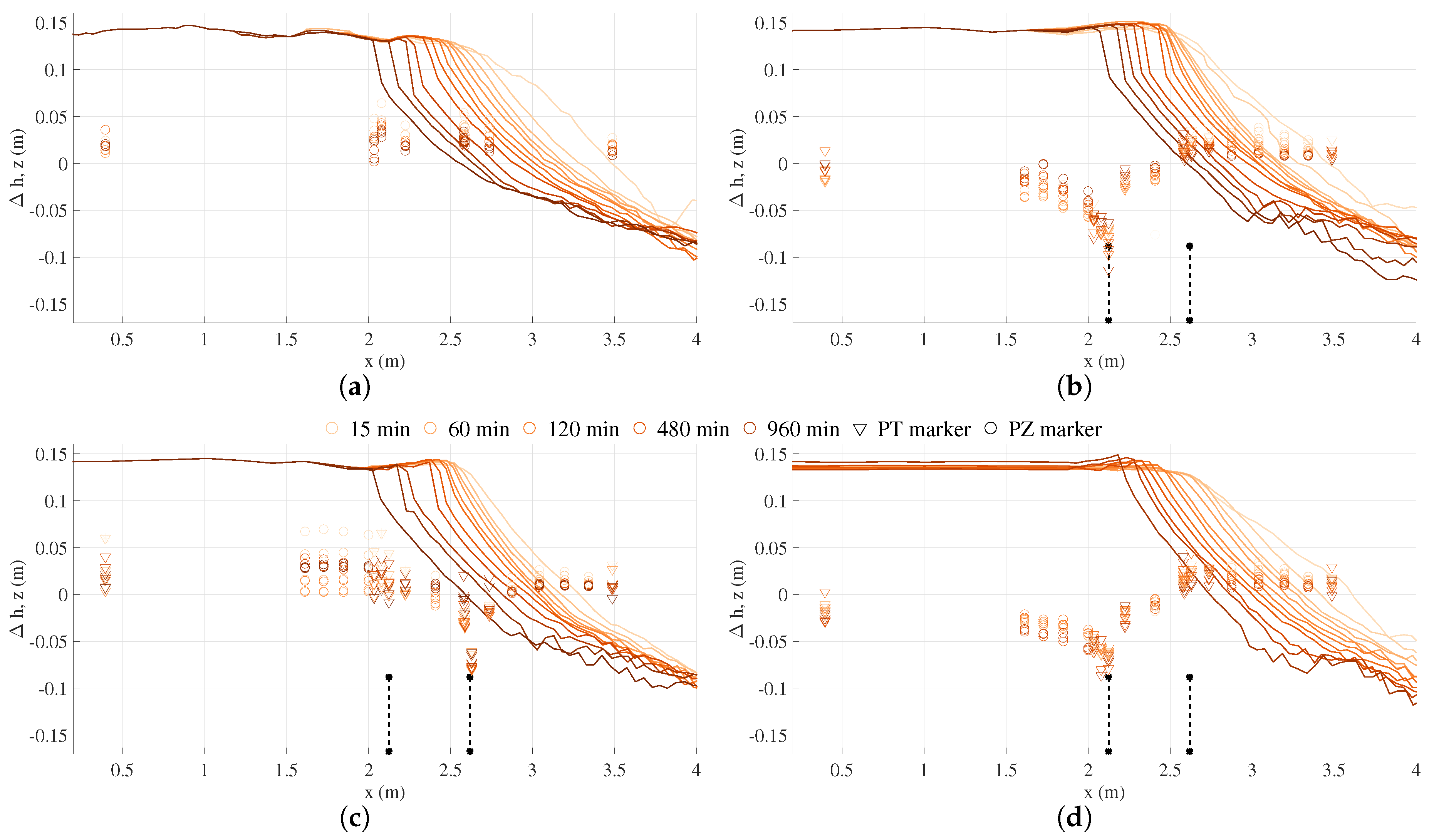
 ); (
); ( ); (
); ( ); and - (
); and - ( ) tests. refers to distances from the bottom, positive upward.
) tests. refers to distances from the bottom, positive upward.
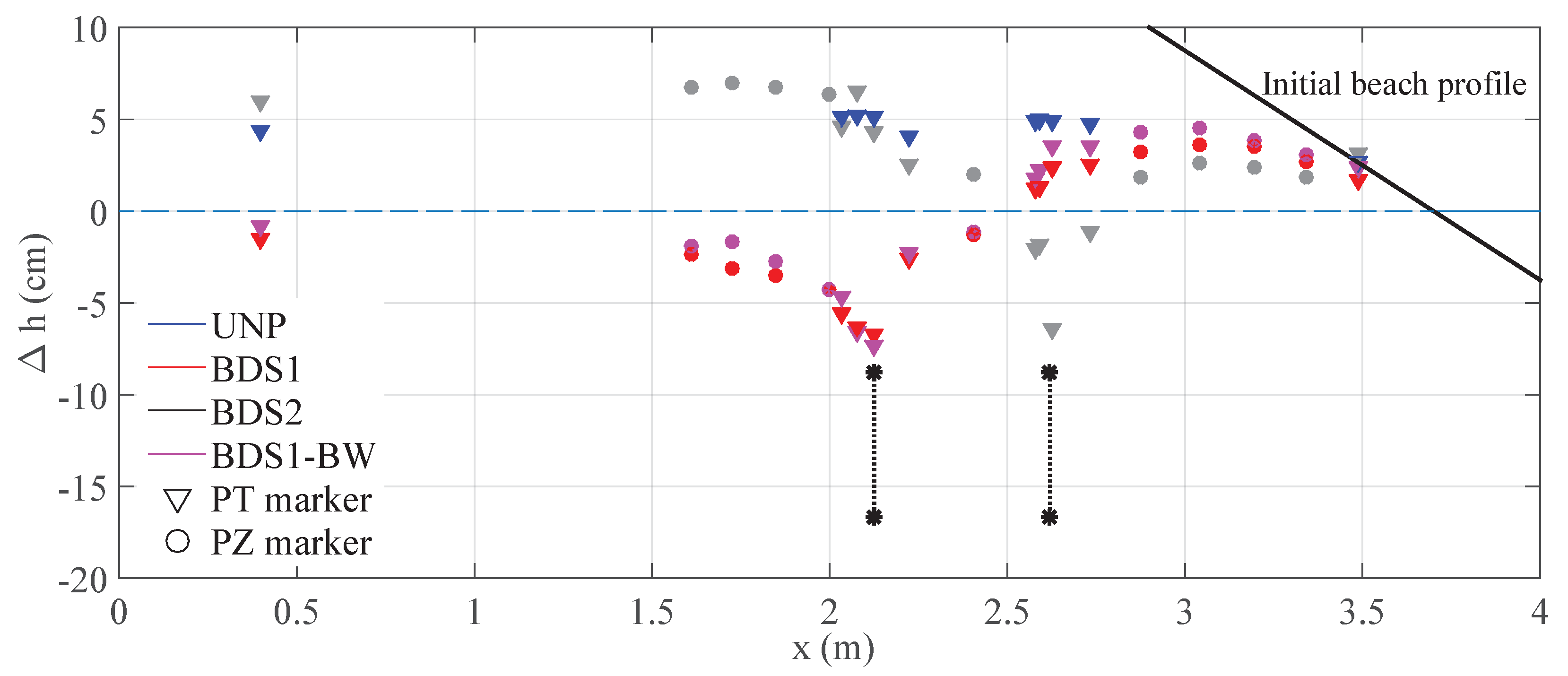
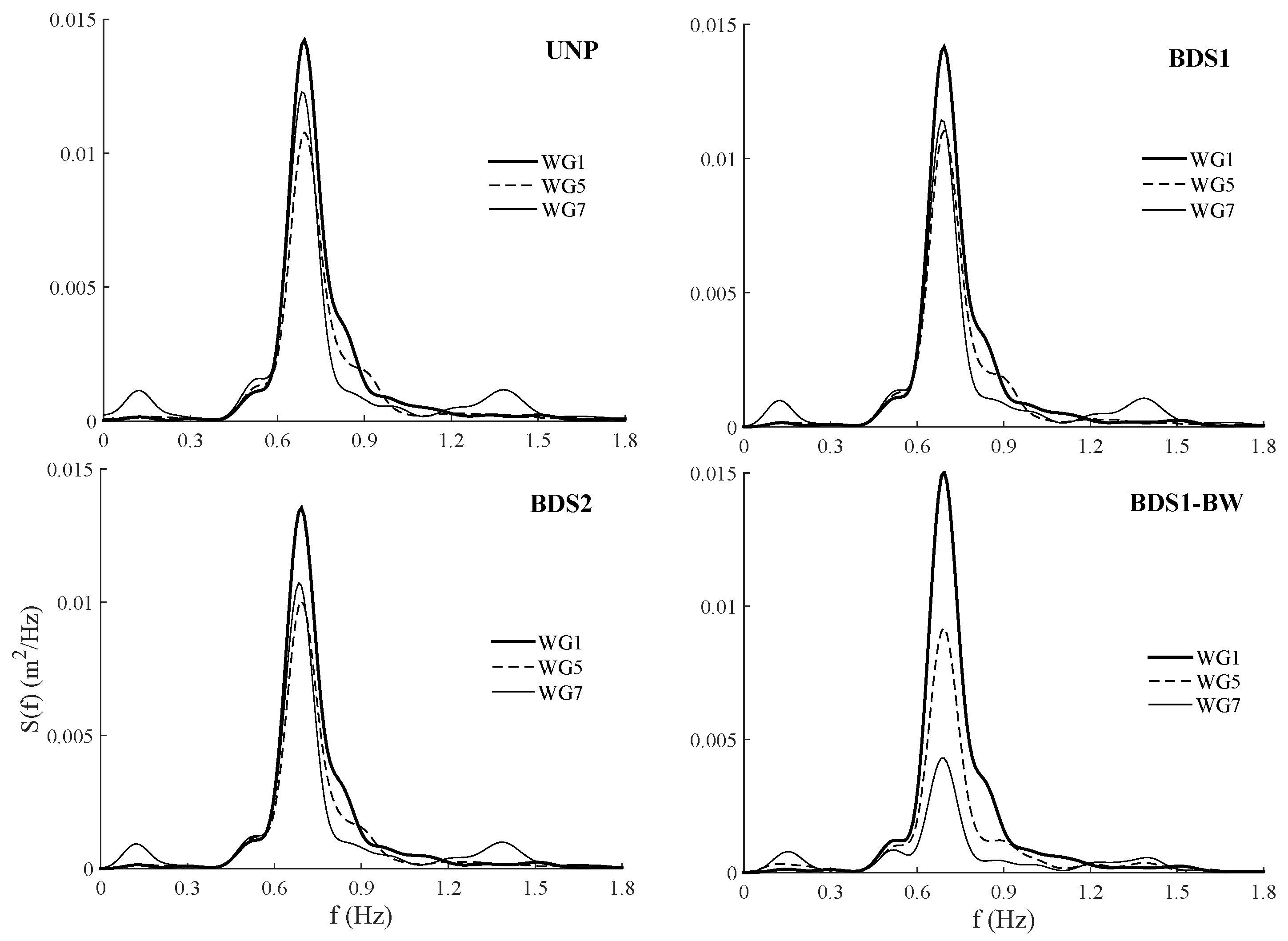
 ); (
); ( ); (
); ( ); and - (
); and - ( ) tests. refers to distances from the bottom, positive upward.
) tests. refers to distances from the bottom, positive upward.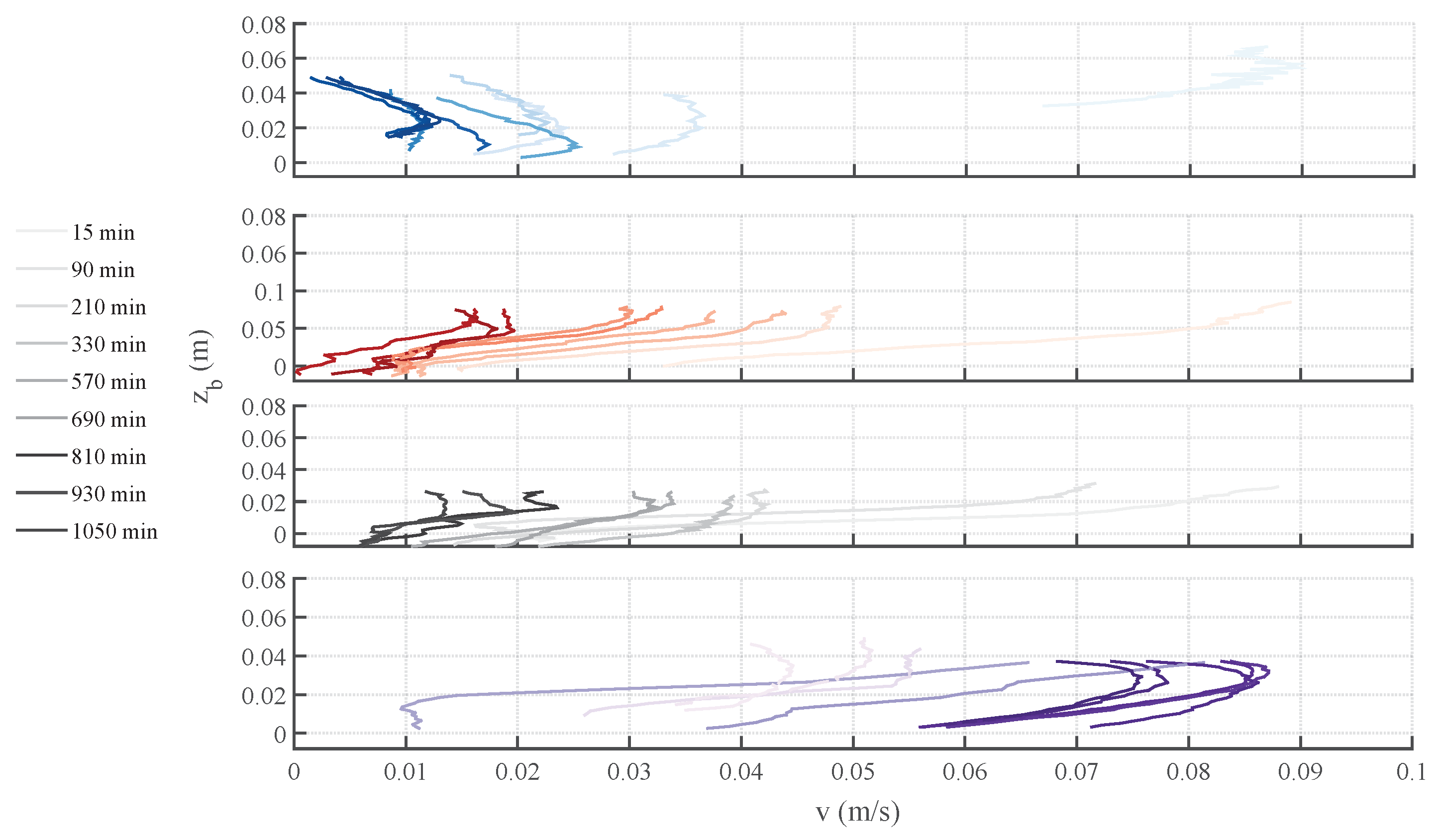
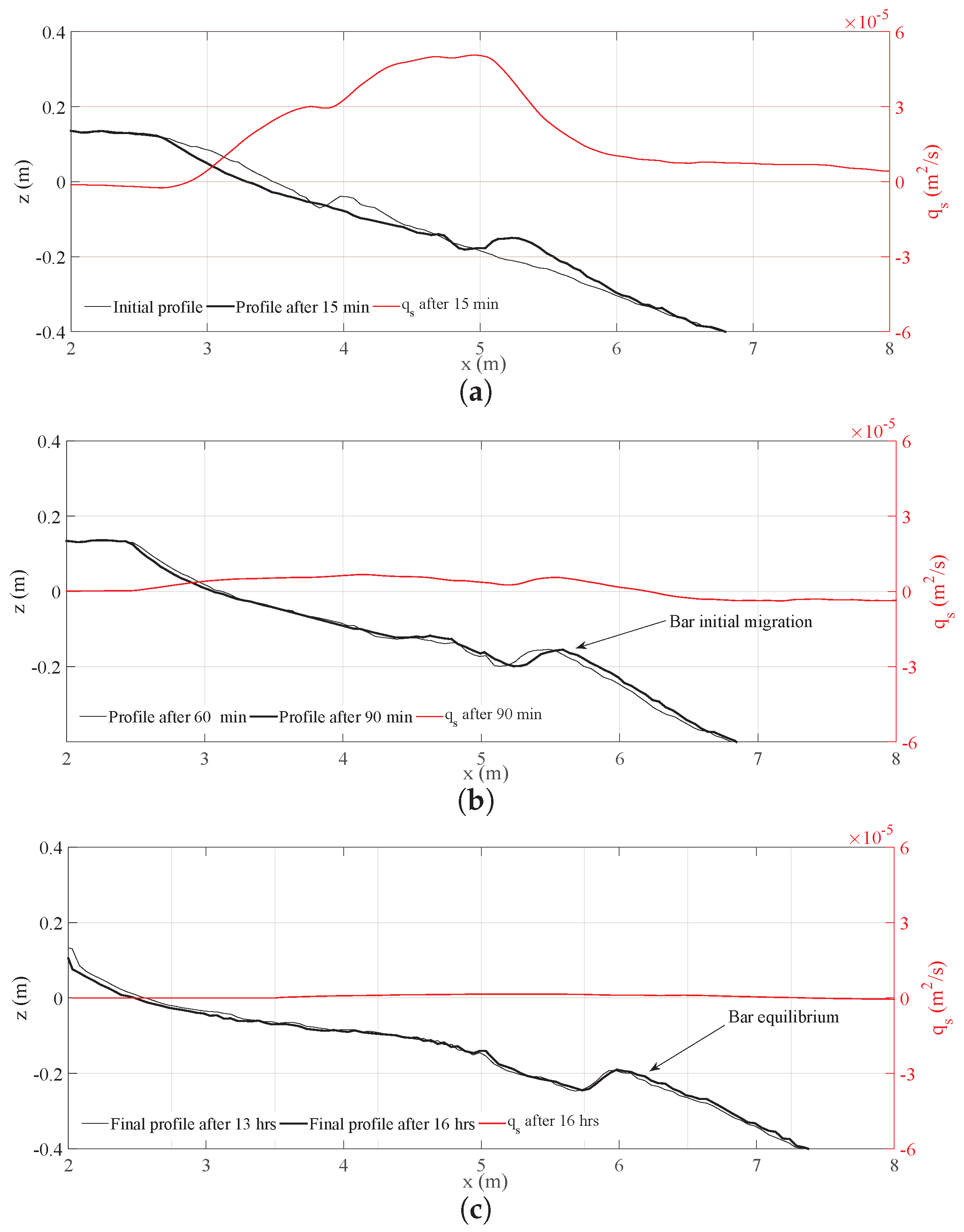
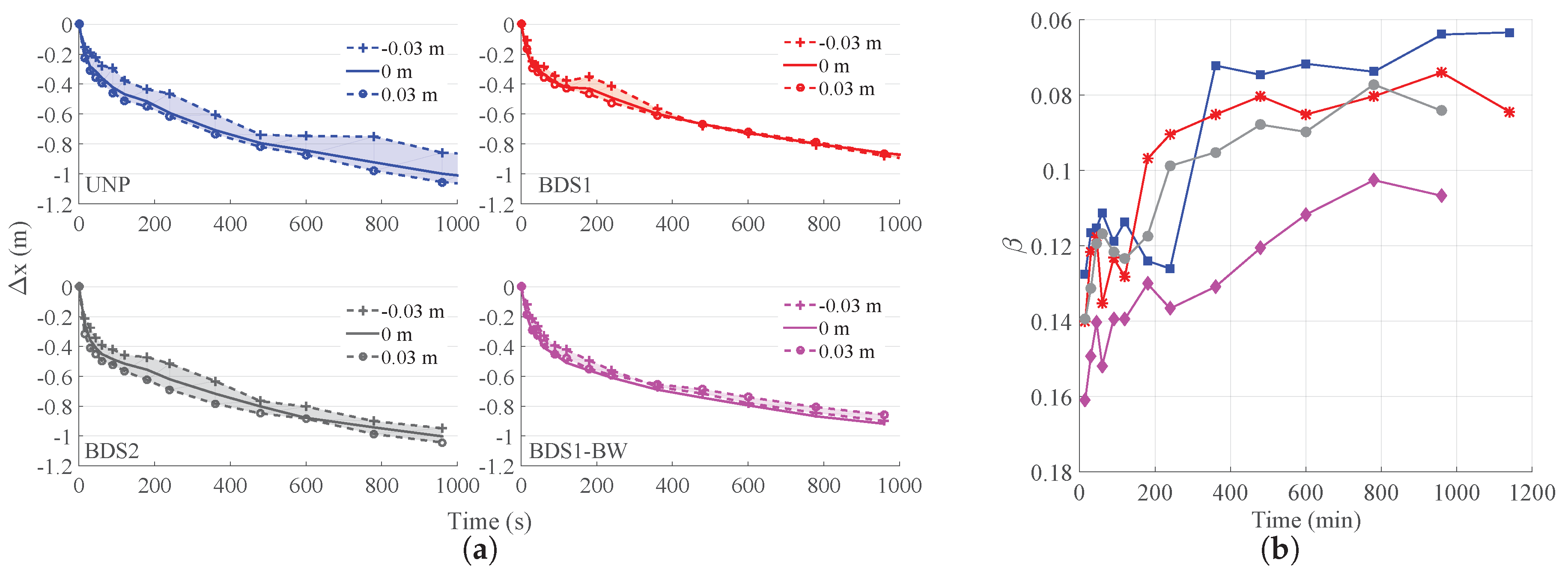
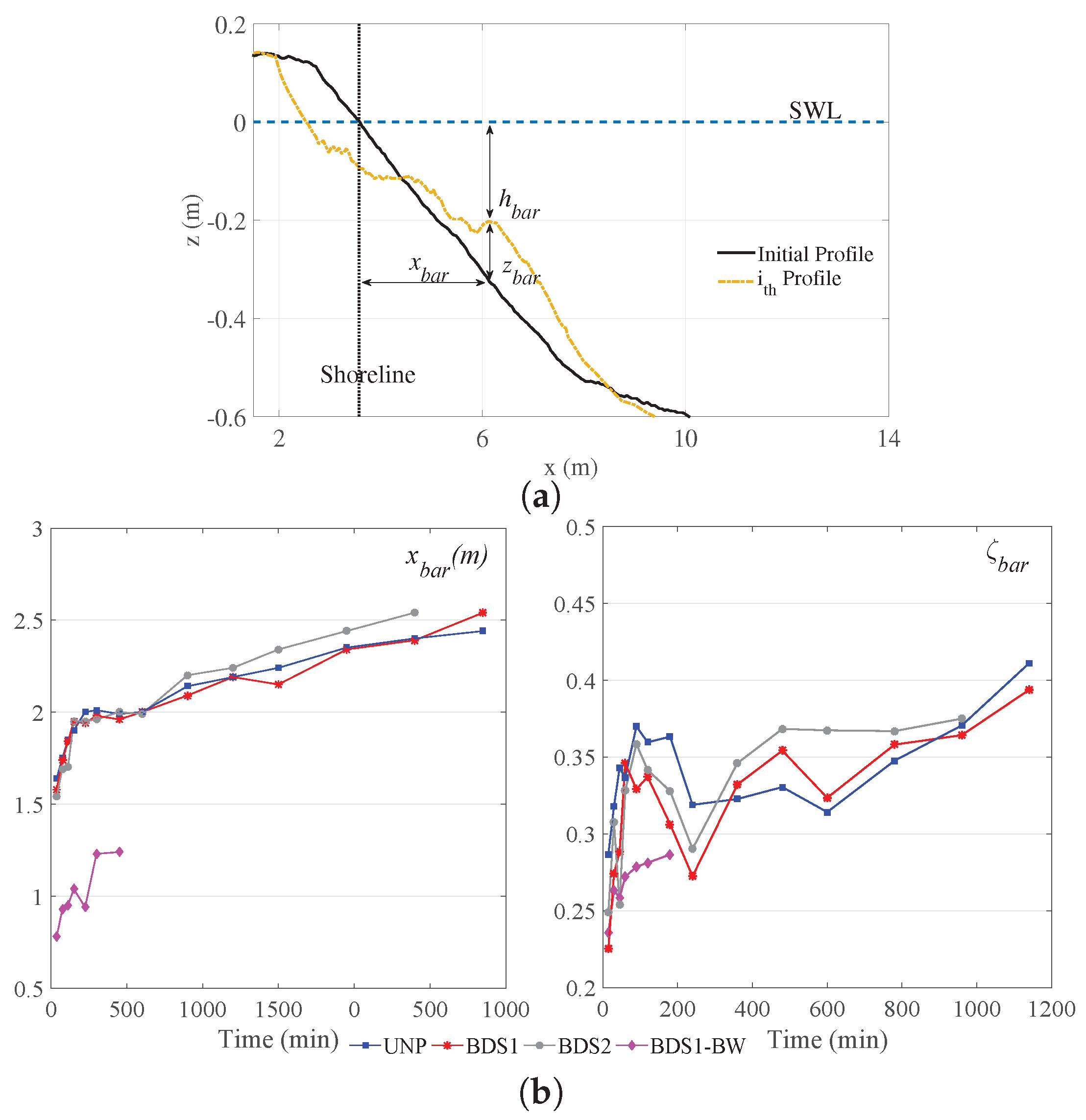
| Test | Test ID | (m) | (m) | (s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unprotected | UNP | 0.187 | 0.206 | 1.47 | 0.0027 |
| Drain 1 | BDS1 | 0.183 | 0.206 | 1.47 | 0.0027 |
| Drain 2 | BDS2 | 0.18 | 0.203 | 1.47 | 0.0026 |
| Drain 1 + Submerged Breakwater | BDS1-BW | 0.19 | 0.212 | 1.47 | 0.0028 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saponieri, A.; Valentini, N.; Di Risio, M.; Pasquali, D.; Damiani, L. Laboratory Investigation on the Evolution of a Sandy Beach Nourishment Protected by a Mixed Soft–Hard System. Water 2018, 10, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091171
Saponieri A, Valentini N, Di Risio M, Pasquali D, Damiani L. Laboratory Investigation on the Evolution of a Sandy Beach Nourishment Protected by a Mixed Soft–Hard System. Water. 2018; 10(9):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091171
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaponieri, Alessandra, Nico Valentini, Marcello Di Risio, Davide Pasquali, and Leonardo Damiani. 2018. "Laboratory Investigation on the Evolution of a Sandy Beach Nourishment Protected by a Mixed Soft–Hard System" Water 10, no. 9: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091171
APA StyleSaponieri, A., Valentini, N., Di Risio, M., Pasquali, D., & Damiani, L. (2018). Laboratory Investigation on the Evolution of a Sandy Beach Nourishment Protected by a Mixed Soft–Hard System. Water, 10(9), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091171









