A Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming Model for Water Resources Optimization Allocation under Uncertainty
Abstract
:1. Introduction
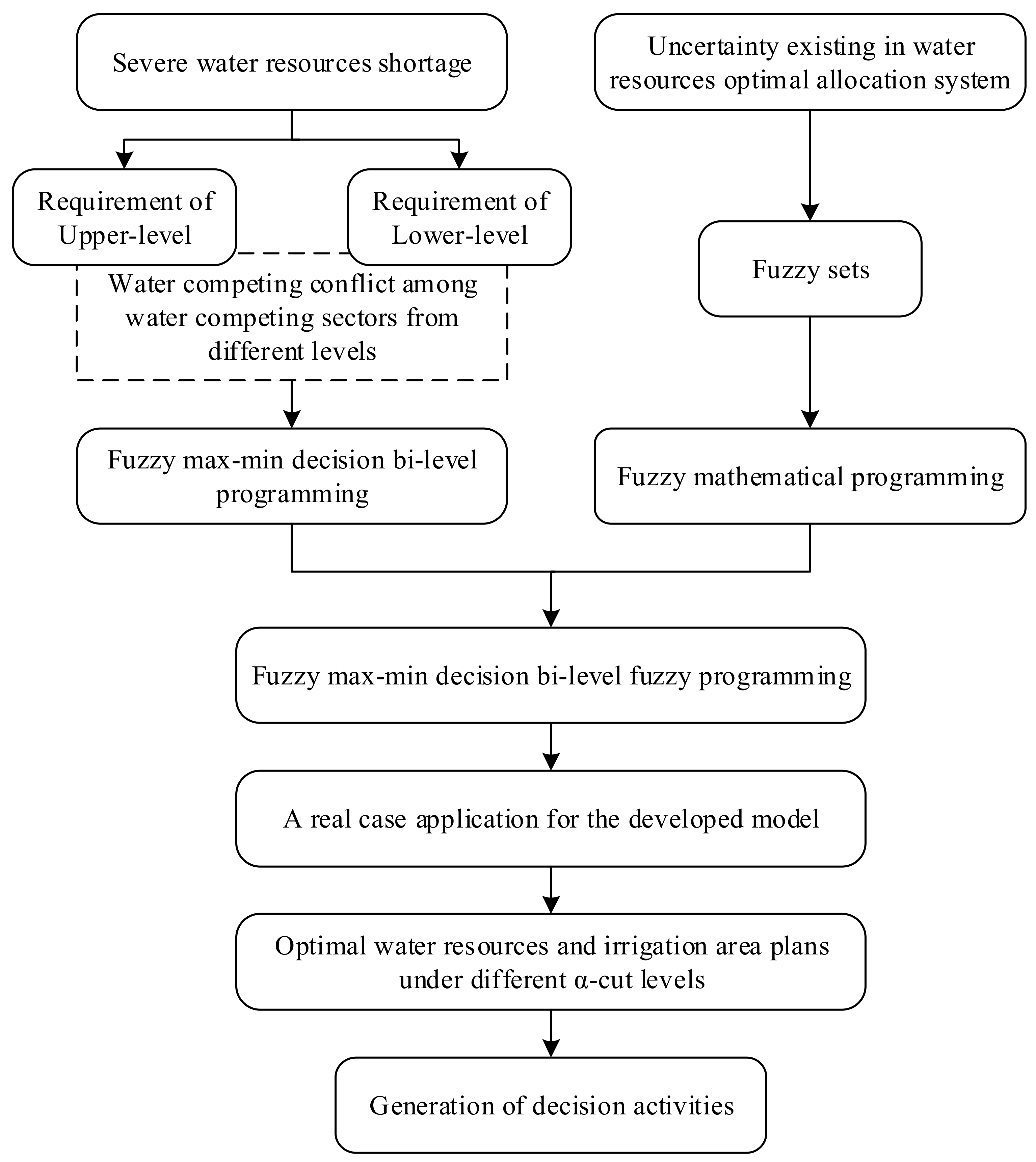
2. Methodology
2.1. Bi-Level Programming
- (The upper-level)where y can be solved from
- (The lower-level)where and . The variables of problem (1) are divided into two classes, namely the upper-level variables and the lower-level variables . Similarly, the functions and are the upper-level and lower-level objective functions, respectively, while the vector-valued functions and are called the upper-level and lower-level constraints, respectively. The upper-level decision-maker (ULDM) controls vector , and the lower-level decision-maker (LLDM) controls vector .
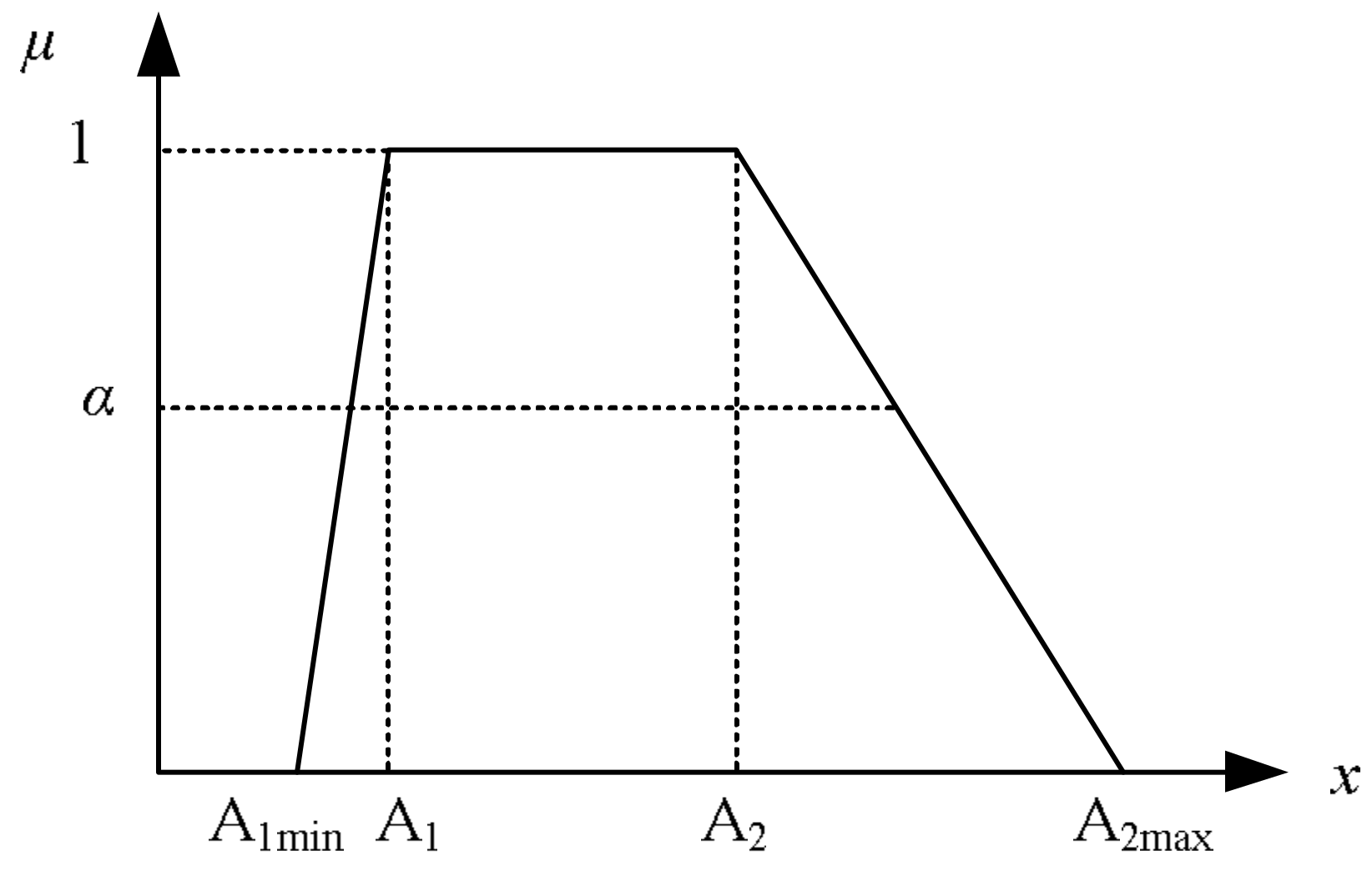
2.2. Fuzzy Set Theory
2.3. Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Programming
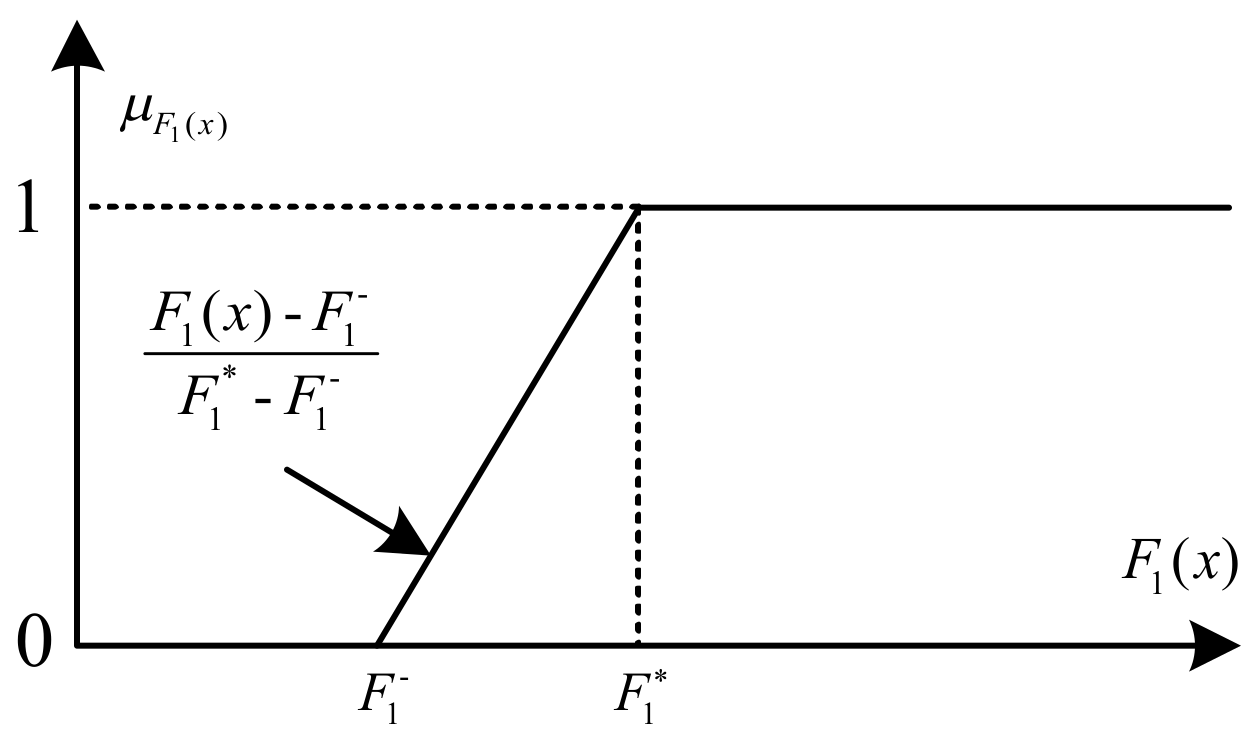
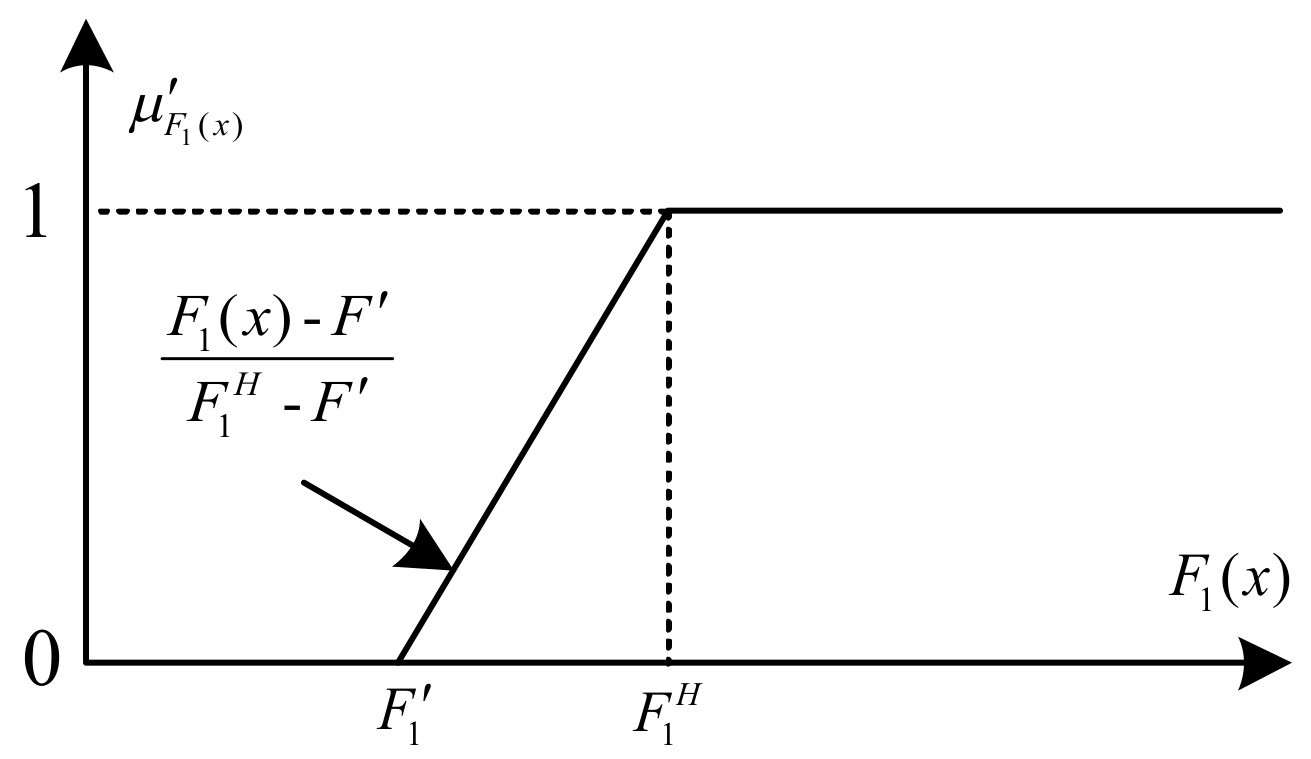
2.4. Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming (FMDBLFP)
- Upper level
- Lower levelwhere denote fuzzy coefficients of the objective and constraints; B and D are crisp numbers constants (fuzzy singletons). The steps of solving the FMDBLFP model are as following:
- Build original FMDBLFP model [Equations (14) and (15)];
- Convert the fuzzy coefficients of [Equations (14) and (15)] into the closed intervals as [Equation (6)] by [Equation (5)];
- Preset the value of and solve the FMDBLFP model by the solving method [Equations (2) and (3)];
- Change the value of and repeat steps 2 and 3;
- Get the optimal solution under different levels.
3. Application
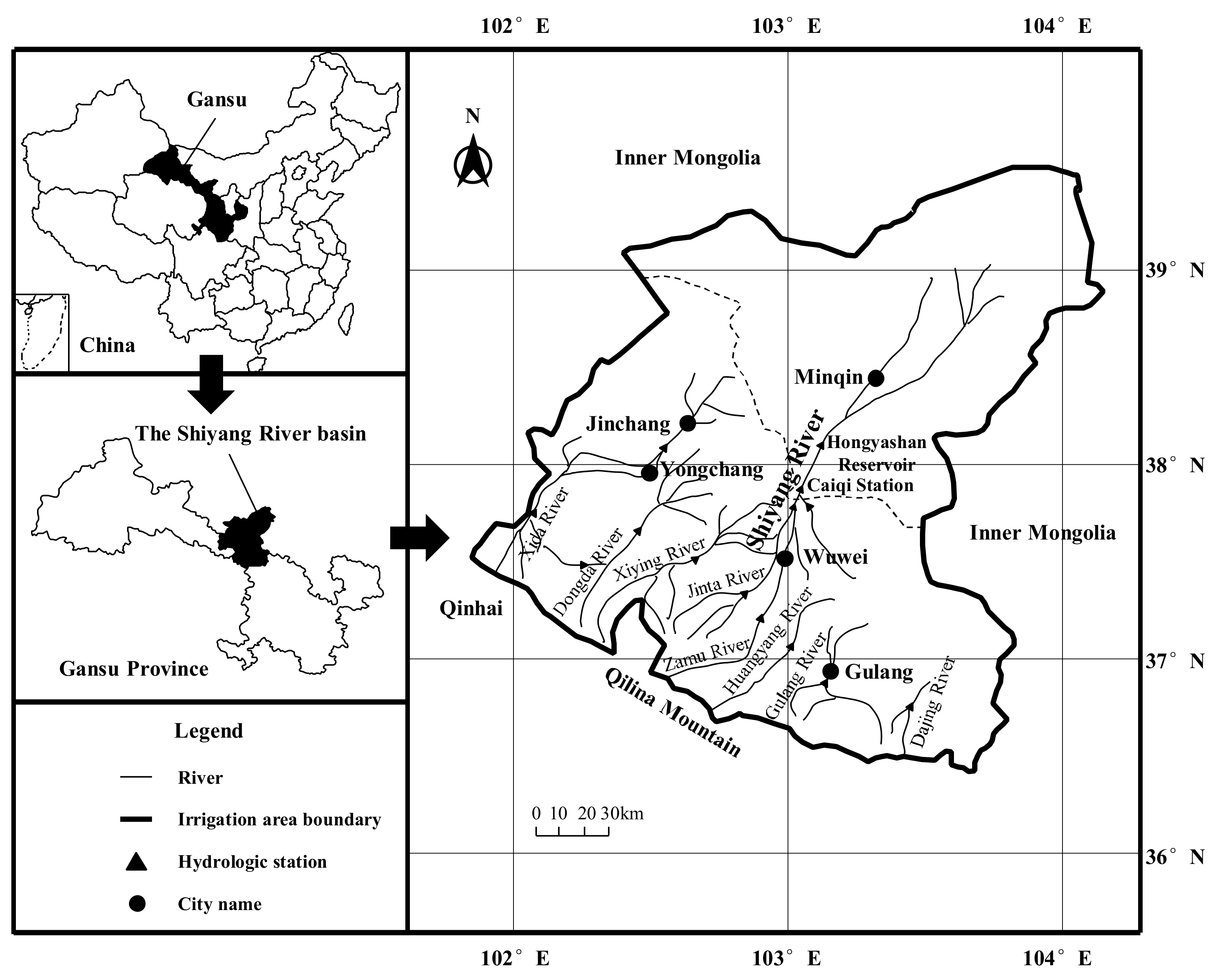
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Model Building
- , : Maximum irrigation areas, irrigation areas of region i (104 mŭ); (mŭ is equal to 614.4 m2);
- : Population of region i (104 p);
- : Food demand per capita of region i (t/p);
- : Irrigation water of per unit irrigation areas in region i (m3/ mŭ);
- , : Water supply for the secondary and tertiary industry of region i (104 m3);
- , : Domestic water and ecological water in region i;
- , , : Per unit of water resources benefit of planting, secondary and tertiary industry in region i (yuan/m3);
- : Yield per unit of region i (t/ mŭ);
- : Water supply for Wuwei City, which is fuzzy sets;
- , : Minimum and maximum water supply for the planting industry of region i (104 m3);
- , : Minimum and maximum water supply for the secondary industry of region i (104 m3);
- , : Minimum and maximum water supply for the tertiary industry of region i (104 m3);
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Solution of the FMDBLFP
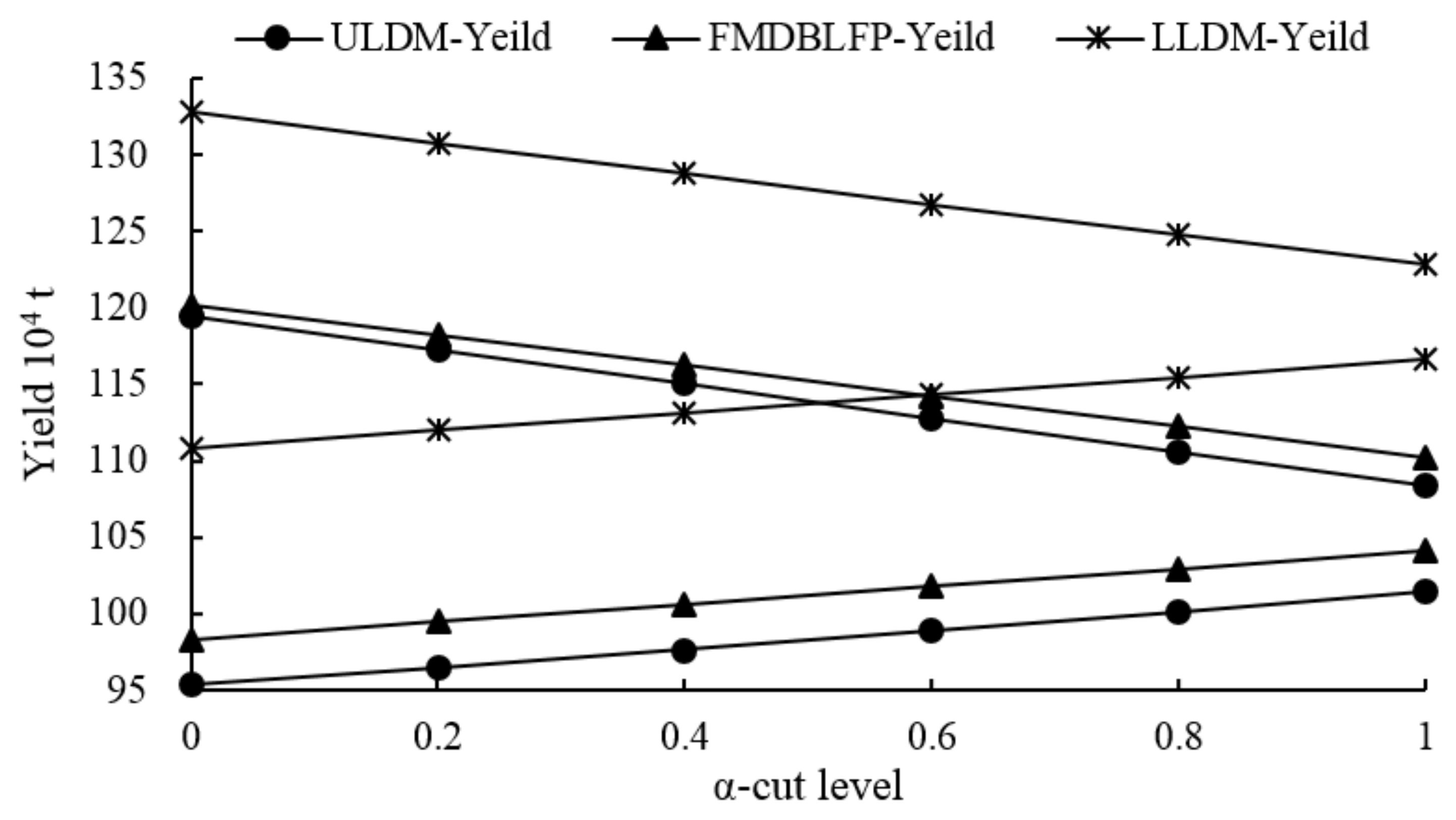
4.2. Comparison of FMDBLFP with ULDM and LLDM
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.H. A multi-level Taguchi-factorial two-stage stochastic programming approach for characterization of parameter uncertainties and their interactions: An application to water resources to water resources management. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 240, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Garizábal, I.; Causapé, J.; Abrahao, R. Application of the irrigation land environmental evaluation tool for flood irrigation management and evaluation of water use. Catena 2011, 87, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.Y.; Li, Y.P. A multistage irrigation water allocation model for agricultural land-use planning under uncertainty. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 129, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.G. Optimization of the irrigation water resources for agricultural sustainability in Tarim river basin, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 107, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, A.Z.; AI-Karablieh, E.K.; Fisher, F.M. An inter-seasonal agricultural water allocation system (SAWAS). Agric. Syst. 2001, 68, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, L.N.; Panda, S.N.; Nayak, M.K. Optimal crop planning and water resources allocation in a coastal groundwater basin, Orissa, India. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 83, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, M.; Gonzalez, I. Applying stochastic goal programming: A case study on water use planning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 196, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.J.; Huang, G.H.; Guo, P.; Shen, N. Interval multistage joint-probabilistic integer programming approach for water resources allocation and management. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 128, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.H.; Guo, P.; Li, M.; Gu, J.J. Optimization of industrial structure considering the uncertainty of water resources. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 3885–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Chen, X.H.; Li, M.; Li, J.B. Fuzzy chance-constrained linear fractional programming approach for optimal water allocation. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, P. A multi-objective optimal allocation model for irrigation water resources under multiple uncertainties. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 4897–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.R.; Huang, G.H.; Huang, K.; Baetz, B.W. Planning water resources allcation under multiple uncertainties through a generalized fuzzy two-stage stochastic programming method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 23, 1488–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, G.H.; Zhou, Y. A fractional-factorial probabilistic-possibilistic optimization framework for planning water resources management systems with multi-level parametric interactions. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 172, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Huang, G.H.; Zhu, H.; Wang, X.L. A two-stage programming approach for water resources management under randomness and fuzziness. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.J.; Guo, P.; Huang, G.H. Inexact stochastic dynamic programming method and application to water resources management in Shandong China under uncertainty. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, P.; Ren, C.H. Water resources management models based on two-level linear fractional programming method under uncertainty. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 05015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davijani, M.H.; Banihabib, M.E.; Anvar, A.N.; Hashemi, S.R. Multi-objective optimization model for the allocation of water resources in arid regions based on the maximization of socioeconomic efficiency. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 927–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.H.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, L.D.; Guo, P. Multiobjective stochastic fractional goal programming model for water resources optimal allocation among industries. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 04016036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Vliet, D.V. A bi-level programming approach for trip matrix estimation and traffic control problems with stochastic user equilibrium link flows. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2001, 35, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, O.E. A fuzzy approach for bi-level integer non-linear programming problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2006, 172, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Huang, G.H.; Nie, S.L. An interval-parameter multi-stage stochastic programming model for water resources management under uncertainty. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 776–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Huang, G.H.; Li, Y.P. Inexact fuzzy-stochastic programming for water resources management under multiple uncertainties. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Haung, G.H.; Guo, P.; Qin, X.S. A fuzzy robust nonlinear programming model for stream water quality management. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 2913–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.P.; Ma, X.F.; Huang, G.H.; Wu, C.Z. An inexact transportation planning model for supporting vehicle emissions management. J. Environ. Inf. 2010, 15, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, B.; Marcotte, P.; Savard, G. Bilevel programming: A survey. 4OR 2005, 3, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Guo, P.; Fang, S.Q.; Zhang, L.D. An inexact fuzzy parameter two-stage stochastic programming model for irrigation water allocation under uncertainty. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2013, 27, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakawa, M. Fuzzy Sets and Interactive Multi-Objective Optimization; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]


| Region | MAi (104 mŭ) | Bi (t/ mŭ) | Ii (m3) | EPi (104 P) | LFi (t/p) | Oi (yuan/m3) | Si (yuan/m3) | Ti (yuan/m3) | WDi (104 m3) | WEi (104 m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liangzhou | 167.12 | 0.41 | 465 | 101.43 | 0.3 | 5.06 | 68.86 | 664.50 | 6303.40 | 9288.40 |
| Minqin | 72.65 | 0.45 | 456 | 24.16 | 0.3 | 4.84 | 131.75 | 689.53 | 1869.30 | 4357.50 |
| Gulang | 91.16 | 0.46 | 425 | 38.95 | 0.3 | 4.82 | 97.21 | 686.07 | 1145.30 | 1603.20 |
| Tianzhu | 33.22 | 0.42 | 475 | 17.62 | 0.3 | 5.04 | 111.05 | 710.48 | 1196.20 | 295.70 |
| Region Districts | Planting Industry (104 m3) | Secondary Industry (104 m3) | Tertiary Industry (104 m3) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWimin | AWimax | SWimin | SWimax | TWimin | TWimax | |
| Liangzhou | 31,393.82 | 73,958.20 | 10,951 | 16,425.50 | 921 | 1555.57 |
| Minqin | 6845.33 | 33,128.40 | 907 | 1360.50 | 172 | 290.51 |
| Gulang | 9449.61 | 38,743.00 | 1253 | 1879.50 | 122 | 206.06 |
| Tianzhu | 5348.93 | 15,779.50 | 1448 | 2172.00 | 124 | 209.44 |
| Region Districts | Ai (104 mŭ) | |||||
| Liangzhou | [105.75, 159.05] | [108.55, 154.14] | [111.34, 149.41] | [114.14, 144.46] | [116.93, 139.73] | [119.73, 134.78] |
| Minqin | [60.65, 60.65] | [60.65, 60.65] | [60.65, 60.65] | [60.65, 60.65] | [60.65, 60.65] | [60.65, 60.65] |
| Gulang | [35.77, 35.77] | [35.77, 35.77] | [35.77, 35.77] | [35.77, 35.77] | [35.77, 35.77] | [35.77, 35.77] |
| Tianzhu | [26.75, 26.55] | [26.75, 26.55] | [26.75, 26.55] | [26.75, 26.55] | [26.75, 26.55] | [26.75, 26.55] |
| Region Districts | ||
| SWi (104 m3) | TWi (104 m3) | |
| Liangzhou | 16426.50 | 1555.57 |
| Minqin | 1360.50 | 290.51 |
| Gulang | 1879.50 | 206.06 |
| Tianzhu | 2172.00 | 209.44 |
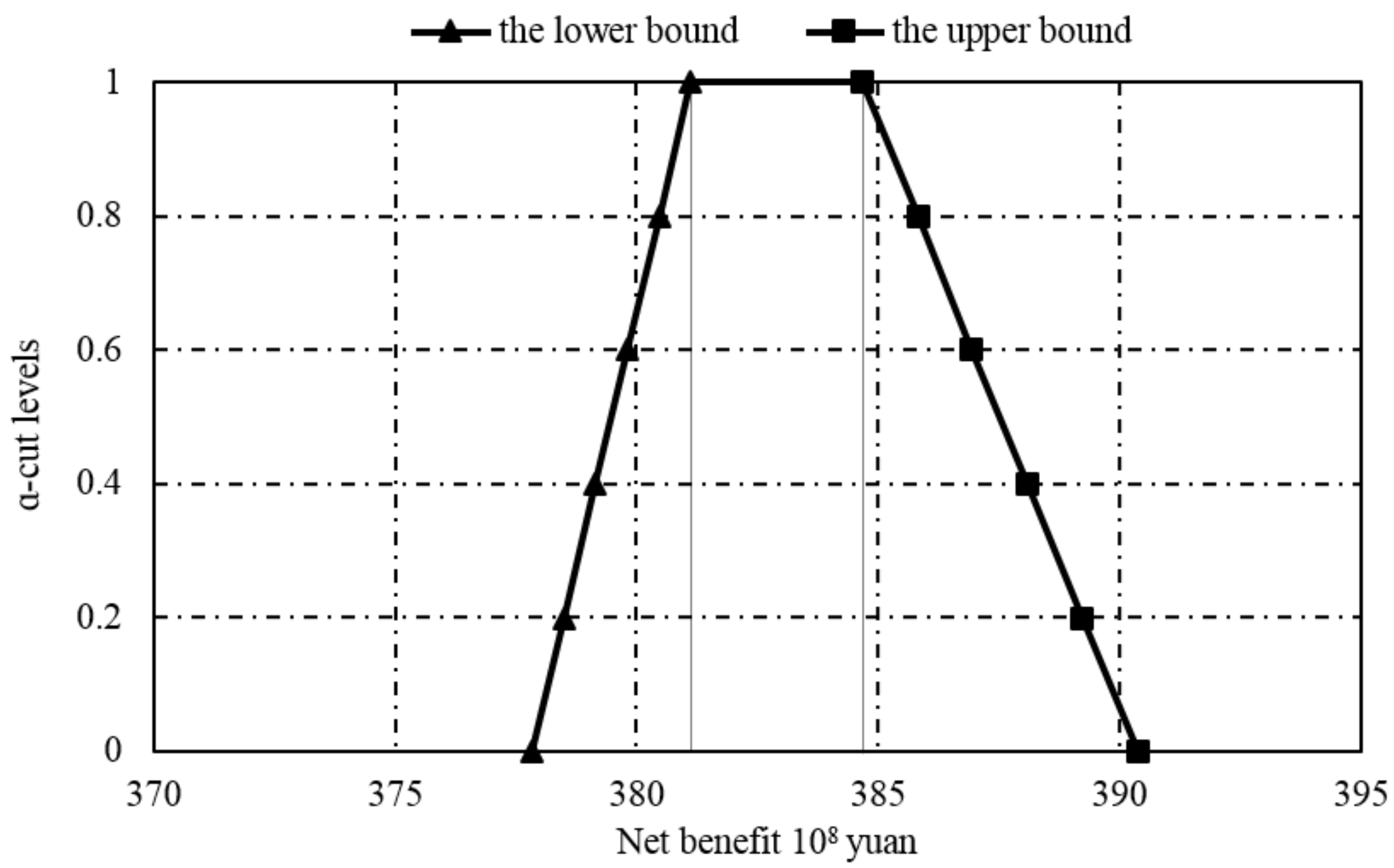
| α-Cut Levels | UBUB (108 yuan) | UBLB (108 yuan) | FBUB (108 yuan) | FBLB (108 yuan) | LBUB (108 yuan) | LBLB (108 yuan) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α = 0 | 390.45 | 378.39 | 390.38 | 377.83 | 273.85 | 261.33 |
| α = 0.2 | 389.34 | 379.05 | 389.22 | 378.49 | 272.69 | 261.98 |
| α = 0.4 | 388.27 | 379.70 | 388.11 | 379.15 | 271.58 | 262.64 |
| α = 0.6 | 387.16 | 380.34 | 386.94 | 379.81 | 270.41 | 263.29 |
| α = 0.8 | 386.10 | 380.97 | 385.83 | 380.47 | 269.30 | 263.95 |
| α = 1 | 384.98 | 381.60 | 384.67 | 381.12 | 268.14 | 264.60 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, C.; Zhang, H. A Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming Model for Water Resources Optimization Allocation under Uncertainty. Water 2018, 10, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040488
Ren C, Zhang H. A Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming Model for Water Resources Optimization Allocation under Uncertainty. Water. 2018; 10(4):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040488
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Chongfeng, and Hongbo Zhang. 2018. "A Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming Model for Water Resources Optimization Allocation under Uncertainty" Water 10, no. 4: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040488
APA StyleRen, C., & Zhang, H. (2018). A Fuzzy Max–Min Decision Bi-Level Fuzzy Programming Model for Water Resources Optimization Allocation under Uncertainty. Water, 10(4), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10040488






