Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
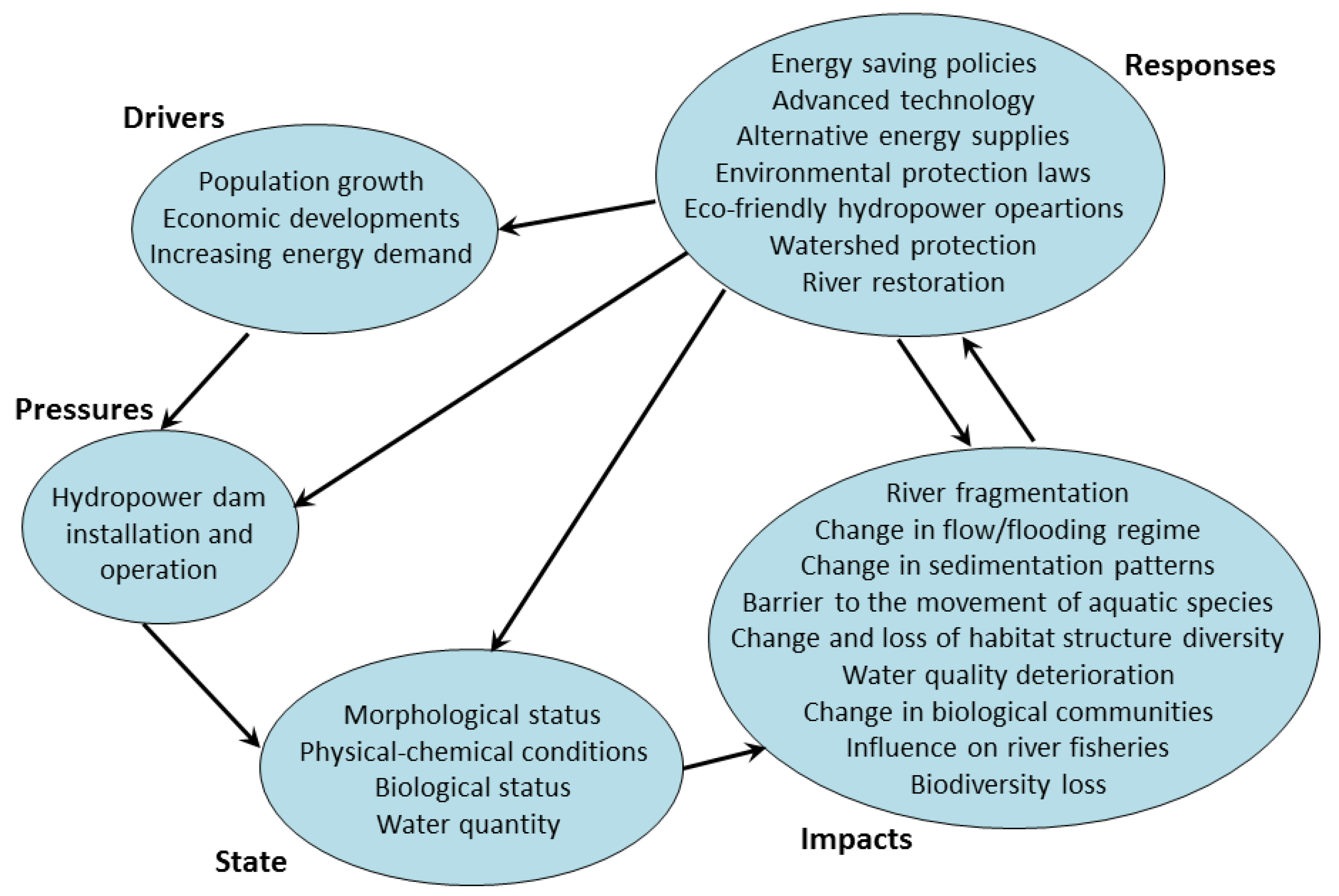
3.1. Impacts of Hydropower Dams on Aquatic Ecosystems
3.1.1. Drivers
3.1.2. Pressures
3.1.3. State
3.1.4. Impacts
3.1.5. Responses
3.2. Models for Hydropower Dam Impact Assessment
3.2.1. Model Approaches and Practical Application
3.2.2. Input Variables
3.2.3. Model Processes and Outputs
3.2.4. Model Validation
3.3. Strengths-Weaknesses-Opportunities-Threats Analysis
3.3.1. Strengths
3.3.2. Weaknesses
3.3.3. Opportunities
3.3.4. Threats
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bratrich, C.; Truffer, B.; Jorde, K.; Markard, J.; Meier, W.; Peter, A.; Schneider, M.; Wehrli, B. Green hydropower: A new assessment procedure for river management. River Res. Appl. 2004, 20, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelletti, A.; Pianosi, F.; Soncini-Sessa, R. Water reservoir control under economic, social and environmental constraints. Automatica 2008, 44, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, H.I.; Smith, B.T. Sustainable reservoir operation: Can we generate hydropower and preserve ecosystem values? River Res. Appl. 2008, 24, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, K. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Commission on Dams. Dams and Development: A Framework for Decision-Making; The Report of the World Commission on Dams; Earthscan Publications Ltd.: London/Sterling, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bartle, A. Hydropower potential and development activities. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Schei, T.; Ahenkorah, A.; Caceres Rodriguez, R.; Devernay, J.-M.; Freitas, M.; Hall, D.; Killingtveit, Å.; Liu, Z. Hydropower. In IPCC Special Report on Renewable Energy Sources and Climate Change Mitigation; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Seyboth, K., Matschoss, P., Kadner, S., Zwickel, T., Eickemeier, P., Hansen, G., Schlömer, S., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Large Dams. World Register of Dams. Available online: http://www.icold-cigb.org (accessed on 25 August 2016).
- Bunn, S.E.; Arthington, A.H. Basic principles and ecological consequences of altered flow regimes for aquatic biodiversity. Environ. Manag. 2002, 30, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonkin, J.D.; Death, R.G.; Joy, M.K. Invertebrate Drift Patterns in a Regulated River: Dams, Periphyton Biomass or Longitudinal Patterns? River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Cui, B.; Hu, B.; Zhang, K. Prediction of river ecological integrity after cascade hydropower dam construction on the mainstream of rivers in Longitudinal Range-Gorge Region (LRGR), China. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkamp, G.; McCartney, M.; Dugan, P.; McNeely, J.; Acreman, M. Dams, Ecosystem Functions and Environmental Restoration Thematic Review II.1 Prepared as an Input to the World Commission on Dams, Cape Town. Available online: http://www. damsreport. org/docs/kbase/thematic/tr21main.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2016).
- Schelle, P.; Collier, U.; Pittock, J. Rivers at risk: Dams and the future of freshwater ecosystems, World wildlife fund (WWF). In Proceedings of the 7th International River Symposium, Brisbane, Australia, 4 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rheinheimer, D.E.; Yarnell, S.M.; Viers, J.H. Hydropower Costs of Environmental Flows and Climate Warming in California’s Upper Yuba River Watershed. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Mulet, R.; Alfredsen, K.; Killingtveit, Å. Modelling of environmental flow options for optimal Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar, embryo survival during hydropeaking. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2014, 21, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolke, A.; Thorbek, P.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Grimm, V. Ecological models supporting environmental decision making: A strategy for the future. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatten, J.R.; Parsley, M.J. A spatial model of white sturgeon rearing habitat in the lower Columbia River, USA. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Jorde, K.; Habit, E.; Caamano, D.; Parra, O. Downstream Environmental Effects of Dam Operations: Changes in Habitat Quality for Native Fish Species. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.M.S.; Martinez-Capel, F.; Munoz-Mas, R.; Alcaraz-Hernandez, J.D.; Garofano-Gomez, V. Habitat Suitability Modelling at Mesohabitat Scale and Effects of Dam Operation on the Endangered Jucar Nase, Parachondrostoma Arrigonis (River Cabriel, Spain). River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fjeldstad, H.P.; Uglem, I.; Diserud, O.H.; Fiske, P.; Forseth, T.; Kvingedal, E.; Hvidsten, N.A.; Okland, F.; Jarnegren, J. A concept for improving Atlantic salmon Salmo salar smolt migration past hydro power intakes. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 81, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, G.; Baran, E.; Nam, S.; Rodríguez-Iturbe, I.; Levin, S.A. Trading-off fish biodiversity, food security, and hydropower in the Mekong River Basin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5609–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatten, J.R.; Tiffan, K.F.; Anglin, D.R.; Haeseker, S.L.; Skalicky, J.J.; Schaller, H. A Spatial Model to Assess the Effects of Hydropower Operations on Columbia River Fall Chinook Salmon Spawning Habitat. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2009, 29, 1379–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, R.; Hehir, G. The use of AUSRIVAS predictive models to assess the response of lotic macroinvertebrates to dams in south-east Australia. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molozzi, J.; Feio, M.J.; Salas, F.; Marques, J.C.; Callisto, M. Development and test of a statistical model for the ecological assessment of tropical reservoirs based on benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 23, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Lee, J.H.W.; Xu, M.Z. Eco-hydraulics and eco-sedimentation studies in China. J. Hydraul. Res. 2013, 51, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnell, S.M.; Lind, A.J.; Mount, J.F. Dynamic flow modelling of riverine amphibian habitat with application to regulated flow management. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjankar, R.; Egger, G.; Jorde, K.; Goodwin, P.; Glenn, N.F. Dynamic floodplain vegetation model development for the Kootenai River, USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 3058–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, G.; Politti, E.; Woo, H.; Cho, K.-H.; Park, M.; Cho, H.; Benjankar, R.; Lee, N.-J.; Lee, H. Dynamic vegetation model as a tool for ecological impact assessments of dam operation. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2012, 6, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, E.d.S.G.; Barbosa, A.M.r.; Waechter, J.L. Occurrence and abundance models of threatened plant species: Applications to mitigate the impact of hydroelectric power dams. Ecol. Model. 2012, 230, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crout, N.; Kokkonen, T.; Jakeman, A.J.; Norton, J.P.; Newham, L.T.H.; Anderson, R.; Assaf, H.; Croke, B.F.W.; Gaber, N.; Gibbons, D.; et al. Chapter Two Good Modelling Practice. In Environmental Modelling, Software and Decision Support; Jakeman, A.J., Voinov, A.A., Rizzoli, A.E., Chen, S.H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 3, pp. 15–31. ISBN 978-0-08-056886-7. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, M.C.; Bowen, Z.H.; Bovee, K.D.; Irwin, E.R. Flow and Habitat Effects on Juvenile Fish Abundance in Natural and Altered Flow Regimes. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruetz, C.R.; Jennings, C.A. Swimming performance of larval robust redhorse Moxostoma robustum and low-velocity habitat modeling in the Oconee River, Georgia. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, J.S.; Campbell, K.; Leung, E.S.; Bernhardt, J.; Post, J. Habitat effects on depth and velocity frequency distributions: Implications for modeling hydraulic variation and fish habitat suitability in streams. Geomorphology 2011, 130, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, M.J.; Wuest, A.; Wehrli, B.; Landert, J.; Senn, D.B. Impact of a large tropical reservoir on riverine transport of sediment, carbon, and nutrients to downstream wetlands. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, J.R. Assessment of Biotic Integrity Using Fish Communities. Fisheries 1981, 6, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, A.H.; Steel, E.A.; Caras, Y.; Sheer, M.; Olson, P.; Kaje, J. Putting watershed restoration in context: Alternative future scenarios influence management outcomes. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gore, J.A.; Hamilton, S.W. Comparison of flow-related habitat evaluations downstream of low-head weirs on small and large fluvial ecosystems. Regul. River 1996, 12, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Tang, T.; Fu, X.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Zhou, S.; Cai, Q.; Fohrer, N. Impacts of cascade run-of-river dams on benthic diatoms in the Xiangxi River, China. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 72, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, C.A.; Yarnell, S.M.; Lind, A.J. Transferability of Habitat Suitability Criteria for a Stream Breeding Frog (Rana Boylii) in the Sierra Nevada, California. Herpetol. Conserv. Biol. 2013, 8, 88–103. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, E.; Weterings, R. Environmental Indicators: Typology and Overview; Technical Report No 25; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1999; Available online: http://www.geogr.uni-jena.de/fileadmin/Geoinformatik/projekte/brahmatwinn/Workshops/FEEM/Indicators/EEA_tech_rep_25_Env_Ind.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2017).
- Arias-Hidalgo, M.E. A Decision Framework for Integrated Wetland-River Basin Management in a Tropical and Data Scarce Environment. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, S. DPSIR = A Problem Structuring Method? An exploration from the “Imagine” approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 222, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekovski, I.; Newton, A.; Dennison, W.C. Megacities in the coastal zone: Using a driver-pressure-state-impact-response framework to address complex environmental problems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermaat, J.E.; Estradivari, E.; Becking, L.E. Present and future environmental impacts on the coastal zone of Berau (East Kalimantan, Indonesia), a deductive scenario analysis. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Frostell, B. The DPSIR Framework and a Pressure-Oriented Water Quality Monitoring Approach to Ecological River Restoration. Water 2012, 4, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spangenberg, J.H.; Martinez-Alier, J.; Omann, I.; Monterroso, I.; Binimelis, R. The DPSIR scheme for analysing biodiversity loss and developing preservation strategies. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, T.; Pinheiro, A. Barbel habitat alterations due to hydropeaking. J. Hydro-Environ. Res. 2015, 9, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Energy. Benefits of Hydropower. Available online: https://energy.gov/eere/water/benefits-hydropower (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Beach, E. Hydro Power vs. Solar Power Advantages. Available online: https://sciencing.com/hydro-power-vs-solar-power-advantages-6513.html (accessed on 5 January 2018).
- Bruno, M.C.; Siviglia, A. Assessing Impacts of Dam Operations-Interdisciplinary Approaches for Sustainable Regulated River Management. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, W.L. Downstream hydrologic and geomorphic effects of large dams on American rivers. Geomorphology 2006, 79, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meile, T.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J. Hydropeaking indicators for characterization of the Upper-Rhone River in Switzerland. Aquat. Sci. 2011, 73, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, E.H.; Holtedahl, T.; Lye, K.A. Hydropower Development. Environmental Effects Assessment; N-7491; Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Department of Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering: Trondheim, Norway, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; Meybeck, M.; Fekete, B.; Sharma, K.; Green, P.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Anthropogenic sediment retention: Major global impact from registered river impoundments. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 39, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand, T.C.; Railsback, S.F.; Hayse, J.W.; Lagory, K.E. A physical habitat model for predicting the effects of flow fluctuations in nursery habitats of the endangered Colorado pikeminnow (Ptychocheilus lucius). River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.E.; Goethals, P.L.M.; Lock, K.; Asio, V.; Bande, M.; Thas, O. Model-based analysis of the relationship between macroinvertebrate traits and environmental river conditions. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forio, M.A.E.; Lock, K.; Radam, E.D.; Bande, M.; Asio, V.; Goethals, P. Assessment and analysis of ecological quality, macroinvertebrate communities and diversity in rivers of a multifunctional tropical island. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 77, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union (EU). Managing Natura 2000 Sites: The Provisions of Article 6 of the ‘Habitats’ Directive 92/43/EEC; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2000; Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/nature/natura2000/management/docs/art6/provision_of_art6_en.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2017).
- Scruton, D.A.; Pennell, C.; Ollerhead, L.M.N.; Alfredsen, K.; Stickler, M.; Harby, A.; Robertson, M.; Clarke, K.D.; LeDrew, L.J. A synopsis of ‘hydropeaking’ studies on the response of juvenile Atlantic salmon to experimental flow alteration. Hydrobiologia 2008, 609, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Tang, T.; Wu, N.; Fu, X.; Jiang, W.; Li, F.; Cai, Q. Impacts of cascaded small hydropower plants on microzooplankton in Xiangxi River, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, J.; Hicks, D.M.; Snelder, T.H.; Arscott, D.B.; Larned, S.T.; Booker, D.; Suren, A.M. Dam Design can Impede Adaptive Management of Environmental Flows: A Case Study from the Opuha Dam, New Zealand. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerny, J.; Copp, G.H.; Kovac, V.; Gozlan, R.; Vilizzi, L. Initial impact of the Gabcikovo hydroelectric scheme on the species richness and composition of 0+fish assemblages in the Slovak flood plain, River Danube. River Res. Appl. 2003, 19, 749–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Merona, B.; Vigouroux, R.; Tejerina-Garro, F.L. Alteration of fish diversity downstream from Petit-Saut Dam in French Guiana. Implication of ecological strategies of fish species. Hydrobiologia 2005, 551, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. Impact of the Gezhouba and Three Gorges Dams on habitat suitability of carps in the Yangtze River. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauble, D.D.; Hanrahan, T.P.; Geist, D.R.; Parsley, M.J. Impacts of the Columbia River Hydroelectric System on Main-Stem Habitats of Fall Chinook Salmon. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2003, 23, 64–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutant, C.C.; Whitney, R.R. Fish Behavior in Relation to Passage through Hydropower Turbines: A Review. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 351–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-Y.; Kwak, S.-J.; Yoo, S.-H. Valuing environmental impacts of large dam construction in Korea: An application of choice experiments. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2008, 28, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrakis, M.C.; Miranda, L.E.; Makrakis, S.; Fontes, H.M.; Morlis, W.G.; Dias, J.H.P.; Garcia, J.O. Diversity in migratory patterns among Neotropical fishes in a highly regulated river basin. J. Fish. Biol. 2012, 81, 866–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.J.; Limburg, K.E.; Waldman, J.R.; Stephenson, K.; Glenn, E.P.; Juanes, F.; Jordaan, A. Fish and hydropower on the US Atlantic coast: Failed fisheries policies from half-way technologies. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, R.S.; Stewardson, M.; Breil, P.; Jalón, D.G.d.; Eisele, M. Hydrological impacts affecting endangered fish species: A Spanish case study. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.; WHO (Eds.) Water Quality Assessments—A Guide to Use of Biota, Sediments and Water in Environmental Monitoring—Second Edition. 1996, p. 651. Available online: http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/resourcesquality/watqualassess.pdf (accessed on 7 January 2016).
- Allesina, S.; Tang, S. Stability criteria for complex ecosystems. Nature 2012, 483, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Zavaleta, E.S.; Eviner, V.T.; Naylor, R.L.; Vitousek, P.M.; Reynolds, H.L.; Hooper, D.U.; Lavorel, S.; Sala, O.E.; Hobbie, S.E.; et al. Consequences of changing biodiversity. Nature 2000, 405, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Käiro, K.; Möls, T.; Timm, H.; Virro, T.; Järvekülg, R. The effect of damming on biological quality according to macroinvertebrates in some Estonian streams, Central—Baltic Europe: A pilot study. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, J.R.; Batt, T.R. Hydraulic Alterations Resulting From Hydropower Development in the Bonneville Reach of the Columbia River. Northwest Sci. 2010, 84, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinokrot, B.A.; Gulliver, J.S. In-stream flow impact on river water temperatures. J. Hydraul. Res. 2000, 38, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, C.W.; Newcomb, T.J.; Orth, D.J. Thermal habitat assessment of alternative flow scenarios in a tailwater fishery. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoub, G.; Westrich, B. Modelling transport dynamics of contaminated sediments in the headwater of a hydropower plant at the Upper Rhine River. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2006, 34, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couillard, C.M.; Macdonald, R.W.; Courtenay, S.C.; Palace, V.P. Chemical-environment interactions affecting the risk of impacts on aquatic organisms: A review with a Canadian perspective-interactions affecting exposure. Environ. Rev. 2008, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jay, D.A.; Leffler, K.; Diefenderfer, H.L.; Borde, A.B. Tidal-Fluvial and Estuarine Processes in the Lower Columbia River: I. Along-Channel Water Level Variations, Pacific Ocean to Bonneville Dam. Estuaries Coasts 2015, 38, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, C.; Holzapfel, P.; Leitner, P.; Graf, W. Longitudinal assessment of hydropeaking impacts on various scales for an improved process understanding and the design of mitigation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Electricity from Hydropower. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/cleanenergy/energy-and-you/affect/hydro.html (accessed on 7 October 2015).
- Torriti, J.; Hassan, M.G.; Leach, M. Demand response experience in Europe: Policies, programmes and implementation. Energy 2010, 35, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M. Energy, environment and sustainable development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 2265–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.K.M.S.; Islam, M.; Rahman, T. Effective renewable energy activities in Bangladesh. Renew. Energy 2006, 11, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. Establishing the Length of License Terms for Hydroelectric Projects. 2016. Available online: https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2016/11/25/2016-28195/establishing-the-length-of-license-terms-for-hydroelectric-projects (accessed on 20 December 2016).
- Dugan, P. Mainstream dams as barriers to fish migration: International learning and implications for the Mekong. Catch Cult 2008, 14, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, R. Hydropower’s future, the environment, and global electricity systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Olden, J.D.; Opperman, J.J.; Miller, W.M.; Fargione, J.; Revenga, C.; Higgins, J.V.; Powell, J. Energy, Water and Fish: Biodiversity Impacts of Energy Sector Water Demand in the United States Depend on Efficiency and Policy Measures. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilt, C.R. Developing fish passage and protection at hydropower dams. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2007, 104, 295–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.A.; Yang, Z.F.; Petts, G.E. Optimizing Environmental Flows Below Dams. River Res. Appl. 2012, 28, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxim, L.; Spangenberg, J.H.; O’Connor, M. An analysis of risks for biodiversity under the DPSIR framework. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 69, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Thomas, G.A. Restoring Environmental Flows by Modifying Dam Operations. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol12/iss1/art12/ (accessed on 20 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- Grill, G.; Dallaire, C.O.; Chouinard, E.F.; Sindorf, N.; Lehner, B. Development of new indicators to evaluate river fragmentation and flow regulation at large scales: A case study for the Mekong River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 45, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragana, I.; Boavida, I.; Cortes, R.; Pinheiro, A. Hydropower Plant Operation Scenarios to Improve Brown Trout Habitat. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezza, P.; Parasiewicz, P.; Spairani, M.; Comoglio, C. Habitat modeling in high-gradient streams: The mesoscale approach and application. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 844–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudgeon, D. River rehabilitation for conservation of fish biodiversity in monsoonal Asia. Ecol. Soc. 2005, 10. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol10/iss2/art15/ (accessed on 20 February 2018). [CrossRef]
- De Groot, S.J. A review of the past and present status of anadromous fish species in the Netherlands: Is restocking the Rhine feasible? Hydrobiologia 2002, 478, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, Q.; Ye, F. Modelling the impacts of reservoir operations on the downstream riparian vegetation and fish habitats in the Lijiang River. J. Hydroinform. 2011, 13, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholow, J.M.; Campbell, S.G.; Flug, M. Predicting the thermal effects of dam removal on the Klamath River. Environ. Manag. 2004, 34, 856–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, W.J.; Gates, T.K.; Flug, M. Variability in perceived satisfaction of reservoir management objectives. J. Water Res. Plan. Manag. 1997, 123, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruokolainen, L.; Lindén, A.; Kaitala, V.; Fowler, M.S. Ecological and evolutionary dynamics under coloured environmental variation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boavida, I.; Dias, V.; Ferreira, M.T.; Santos, J.M. Univariate functions versus fuzzy logic: Implications for fish habitat modeling. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, G.; Holguin, J.E.; Goethals, P.L.M. Selecting relevant predictors: Impact of variable selection on model performance, uncertainty and applicability of models in environmental decision making. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software: Managing Resources of a Limited Planet: Pathways and Visions under Uncertainty, Sixth Biennial Meeting, Leipzig, Germany, 1 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Forio, M.A.E.; Mouton, A.; Lock, K.; Boets, P.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Damanik Ambarita, M.N.; Musonge, P.L.S.; Dominguez-Granda, L.; Goethals, P.L.M. Fuzzy modelling to identify key drivers of ecological water quality to support decision and policy making. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 68, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, I.G. A method for objectively identifying pool, run, and riffle habitats from physical measurements. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1993, 27, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.H.; Lock, K.; Mouton, A.; Goethals, P.L.M. Application of classification trees and support vector machines to model the presence of macroinvertebrates in rivers in Vietnam. Ecol. Inform. 2010, 5, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocovsky, P.M.; Ross, R.M.; Dropkin, D.S. Prioritizing Removal of Dams for Passage of Diadromous Fishes on a Major River System. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, A.P.; Lancelotti, J.L.; Riva-Rossi, C.M.; Tagliaferro, M.; Asorey, M.G.; Pascual, M.A. Dams versus habitat: Predicting the effects of dams on habitat supply and juvenile rainbow trout along the Santa Cruz River, Patagonia. Hydrobiologia 2015, 755, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, F.; Gallerano, F. Multi-objective analysis of dam release flows in rivers downstream from hydropower reservoirs. Appl. Math Model. 2012, 36, 2868–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, Q.; Duan, C. Ecological hydrograph based on Schizothorax chongi habitat conservation in the dewatered river channel between Jinping cascaded dams. Sci. China-Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, E.C.; Scruton, D.A.; Clarke, K.D. The ‘Natural Flow Paradigm’ and Atlantic Salmon-Moving from Concept to Practice. River Res. Appl. 2009, 25, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Cai, Q.; Fu, X.; Liu, J. Construction of habitat suitability models (HSMs) for benthic macroinvertebrate and their applications to instream environmental flows: A case study in Xiangxi River of Three Gorges Reservior region, China. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykiel, E.J.J. Testing ecological models: the meaning of validation. Ecol. Model. 1996, 90, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, D.G.; Butler, D.G. Statistical Validation. Ecol. Model. 1993, 68, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boavida, I.; Santos, J.M.; Katopodis, C.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A. Uncertainty in predicting the fish-response to two-dimensional habitat modeling using field data. River Res. Appl. 2013, 29, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuiller, W.; Munkemuller, T.; Moller, A.P.; Fiedler, W.; Berthold, P. Habitat suitability modelling. In Effects of Climate Change on Birds; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Everaert, G.; Pauwels, I.S.; Boets, P.; Verduin, E.; de la Haye, M.A.A.; Blom, C.; Goethals, P.L.M. Model-based evaluation of ecological bank design and management in the scope of the European Water Framework Directive. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 53, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boets, P.; Pauwels, I.; Lock, K.; Goethals, P. Using an integrated modelling approach for risk assessment of the ‘killer shrimp’ Dikerogammarus villosus. River Res. Appl. 2014, 30, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conallin, J.; Boegh, E.; Jensen, J.K. Instream physical habitat modelling types: An analysis as stream hydromorphological modelling tools for EU water resource managers. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2010, 8, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Nedushan, B.; St-Hilaire, A.; Berube, M.; Robichaud, E.; Thiemonge, N.; Bobee, B. A review of statistical methods for the evaluation of aquatic habitat suitability for instream flow assessment. River Res. Appl. 2006, 22, 503–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E. Overview of the model types available for development of ecological models. Ecol. Model. 2008, 215, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, A.M.; Baets, B.D.; Goethals, P.L.M. Knowledge-based versus data-driven fuzzy habitat suitability models for river management. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, M.; Gonzale, A.; Guichard, F.; Kolasa, J.; Parrott, L. Ecological Systems as Complex Systems: Challenges for an Emerging Science. Diversity 2010, 2, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E.; Chon, T.-S.; Recknagel, F. Handbook of Ecological Modelling and Informatics; WIT Press: Southampton, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Null, S.E.; Medellin’-Azuara, J.; Escriva-Bou, A.; Lent, M.; Lund, J.R. Optimizing the dammed: Water supply losses and fish habitat gains from dam removal in California. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 136, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.; Jones, M.; Lester, N.; Chu, C.; Doka, S.; Netto, J.; Stockwell, J.; Thompson, B.; Minns, C.K.; Shuter, B.; et al. Linking fish population dynamics to habitat conditions: insights from the application of a process-oriented approach to several Great Lakes species. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2009, 19, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pert, E.J.; Erman, D.C. Habitat Use by Adult Rainbow-Trout under Moderate Artificial Fluctuations in Flow. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1994, 123, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.W.; Chen, D.; Li, R.N.; Ma, J.F.; Blanckaert, K. Adapting the operation of two cascaded reservoirs for ecological flow requirement of a de-watered river channel due to diversion-type hydropower stations. Ecol. Model. 2013, 252, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.G.; Werner, A.D.; Xin, P.; Jiang, T.; Barry, D.A. Has the Three-Gorges Dam made the Poyang Lake wetlands wetter and drier? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethals, P.L.M.; Dedecker, A.P.; Gabriels, W.; Lek, S.; De Pauw, N. Applications of artificial neural networks predicting macroinvertebrates in freshwaters. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boets, P.; Lock, K.; Messiaen, M.; Goethals, P.L.M. Combining datadriven methods and lab studies to analyse the ecology of Dikerogammarus villosus. Ecol. Inform. 2010, 5, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.H.; Mouton, A.; Lock, K.; Pauw, N.D.; Goethals, P.L.M. Integrating data-driven ecological models in an expert-based decision support system for water management in the Du river basin (Vietnam). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, L. Hybrid modelling of complex ecological systems for decision support: Recent successes and future perspectives. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin-Gonzalez, J.E.; Everaert, G.; Boets, P.; Galvis, A.; Goethals, P.L.M. Development and application of an integrated ecological modelling framework to analyze the impact of wastewater discharges on the ecological water quality of rivers. Environ. Model. Softw. 2013, 48, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguin-Gonzalez, J.; Boets, P.; Everaert, G.; Pauwels, I.; Lock, K.; Gobeyn, S.; Benedetti, L.; Amerlinck, Y.; Nopens, I.; Goethals, P. Development and assessment of an integrated ecological modelling framework to assess the effect of investments in wastewater treatment on water quality. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Input Variables and Model Validation | Number of Articles | Hydrodynamic Model | Water Quality Model | Habitat Suitability Model | Integrated Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input variables | |||||
| Geomorphology | |||||
| Latitude/longitude | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Elevation | 6 | 2 | 1 | 3 | |
| Stream gradient | 4 | 2 | 2 | ||
| Sinuosity | 1 | 1 | |||
| River width | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| Depth | 16 | 9 | 7 | ||
| Substrate | 13 | 6 | 7 | ||
| Substrate roughness | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Land cover | 2 | 2 | |||
| Tree/canopy cover | 4 | 1 | 3 | ||
| Hydrological | |||||
| Velocity | 16 | 9 | 7 | ||
| Discharge/flow | 19 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Hydrological regime | 1 | 1 | |||
| Meteorological | |||||
| Air temperature | 5 | 2 | 3 | ||
| Air pressure | 1 | 1 | |||
| Cloud cover | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Wind speed | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Humidity | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Rainfall | 1 | 1 | |||
| Solar radiation | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Physical-chemical | |||||
| Water temperature | 11 | 3 | 4 | 4 | |
| Total dissolved solid | 1 | 1 | |||
| Toxicants | 1 | 1 | |||
| Suspended sediment | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| DO | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Conductivity | 2 | 2 | |||
| pH | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Turbidity | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Nutrient | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Chloride | 1 | 1 | |||
| Oxidation-reduction potential | 1 | 1 | |||
| Calcium ion | 1 | 1 | |||
| Salinity | 1 | 1 | |||
| Ligneous structure | 1 | 1 | |||
| Biological components | |||||
| Fish | 16 | 1 | 9 | 6 | |
| Macroinvertebrates | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Amphibians | 1 | 1 | |||
| Algae | 1 | 1 | |||
| Model validation | |||||
| Cross validation | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Single validation | 12 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 4 |
| Total number of articles | 32 | 4 | 3 | 12 | 13 |
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|
|
| Opportunities | Threats |
|
|
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.H.T.; Everaert, G.; Boets, P.; Forio, M.A.E.; Bennetsen, E.; Volk, M.; Hoang, T.H.T.; Goethals, P.L.M. Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams. Water 2018, 10, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030259
Nguyen THT, Everaert G, Boets P, Forio MAE, Bennetsen E, Volk M, Hoang THT, Goethals PLM. Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams. Water. 2018; 10(3):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030259
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Hanh Tien, Gert Everaert, Pieter Boets, Marie Anne Eurie Forio, Elina Bennetsen, Martin Volk, Thu Huong Thi Hoang, and Peter L. M. Goethals. 2018. "Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams" Water 10, no. 3: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030259
APA StyleNguyen, T. H. T., Everaert, G., Boets, P., Forio, M. A. E., Bennetsen, E., Volk, M., Hoang, T. H. T., & Goethals, P. L. M. (2018). Modelling Tools to Analyze and Assess the Ecological Impact of Hydropower Dams. Water, 10(3), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10030259









