Effect of Saturated Zone on Nitrogen Removal Processes in Stormwater Bioretention Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
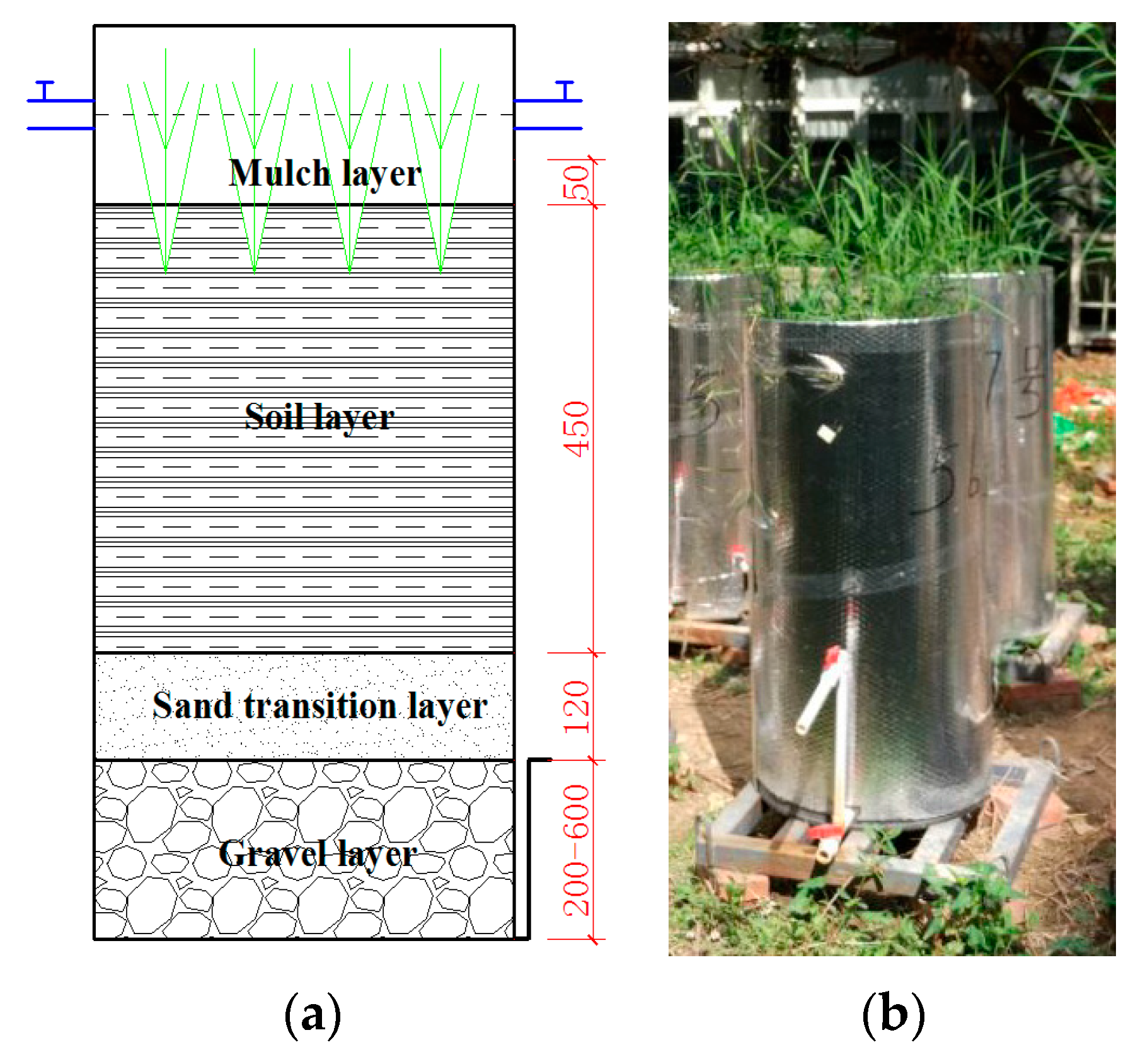
2.1. Experimental Set-up
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Mesocosm Bioretention Systems
2.2.2. Small-Scale Bioretention Systems
2.3. Sample Analysis
3. Results
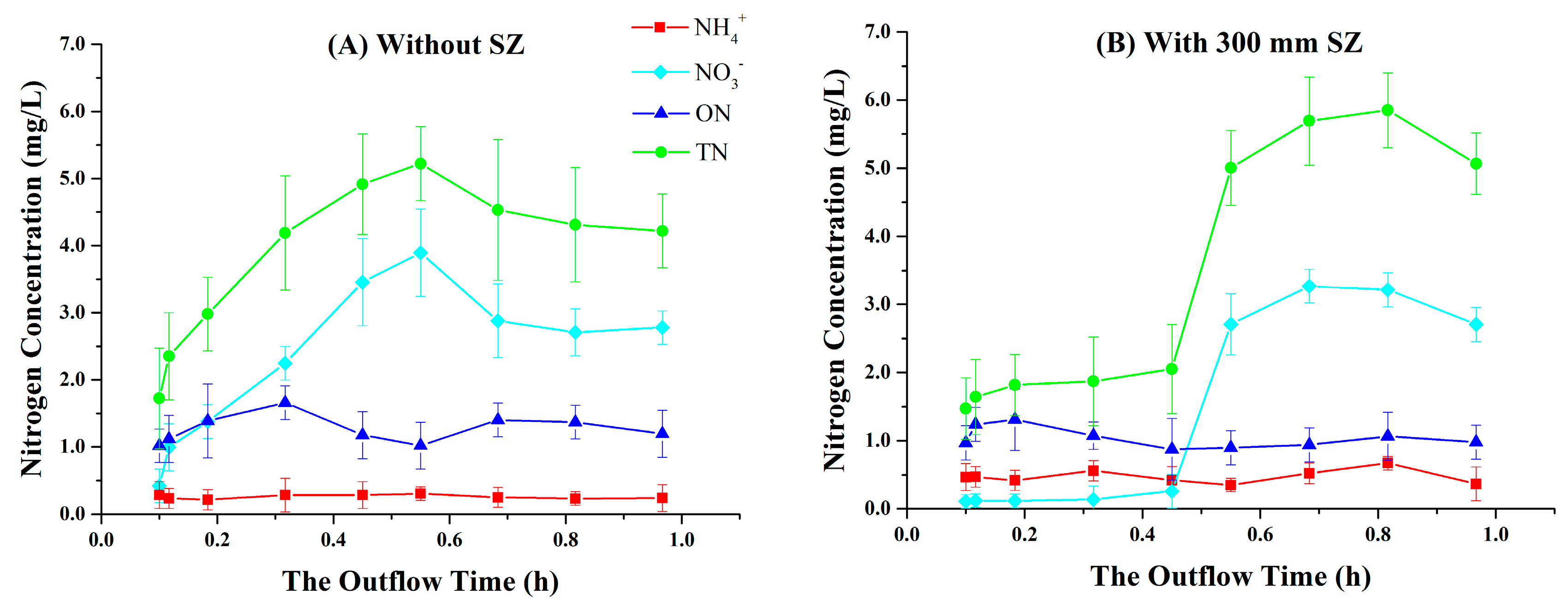
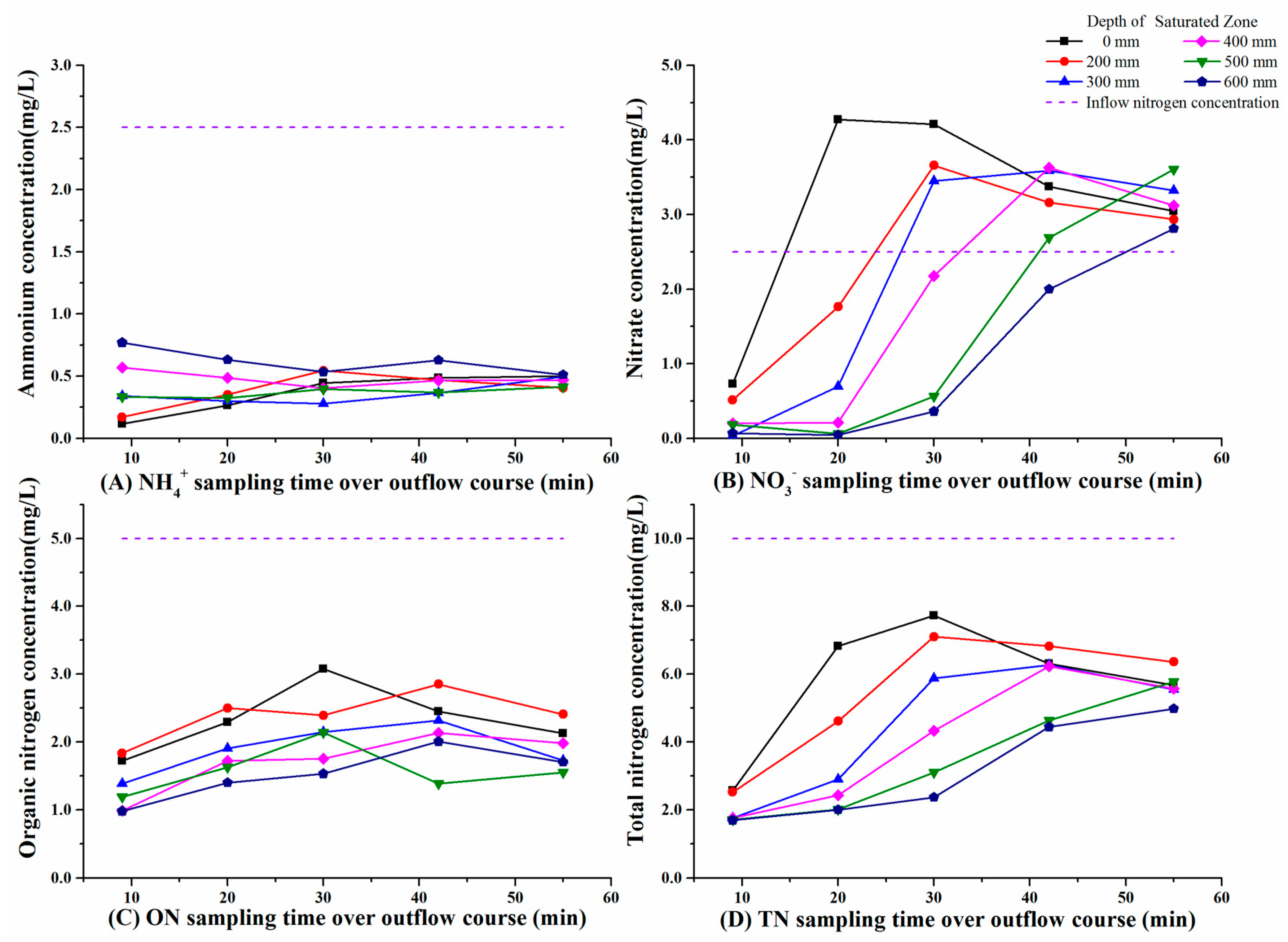
3.1. Variations in Nitrogen Concentrations over the Outflow Process
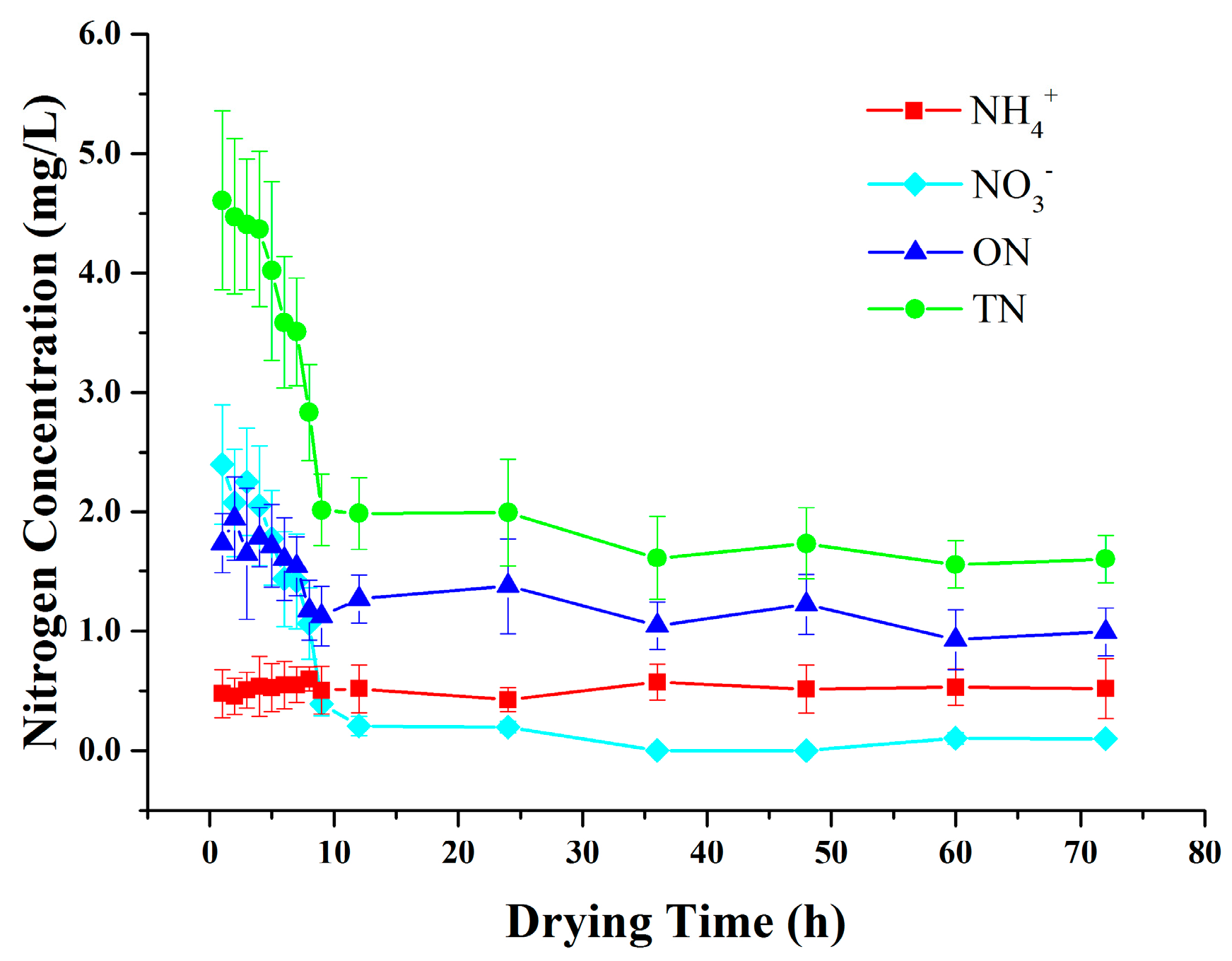
3.2. Variations in Nitrogen Concentrations in SZ during Drying Periods
3.3. Effect of the Presence of SZ on Nitrogen Removal
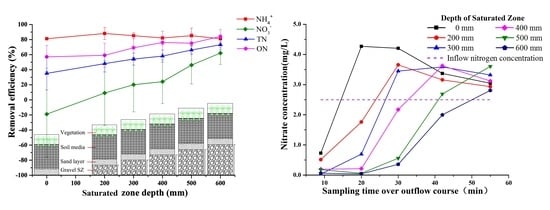
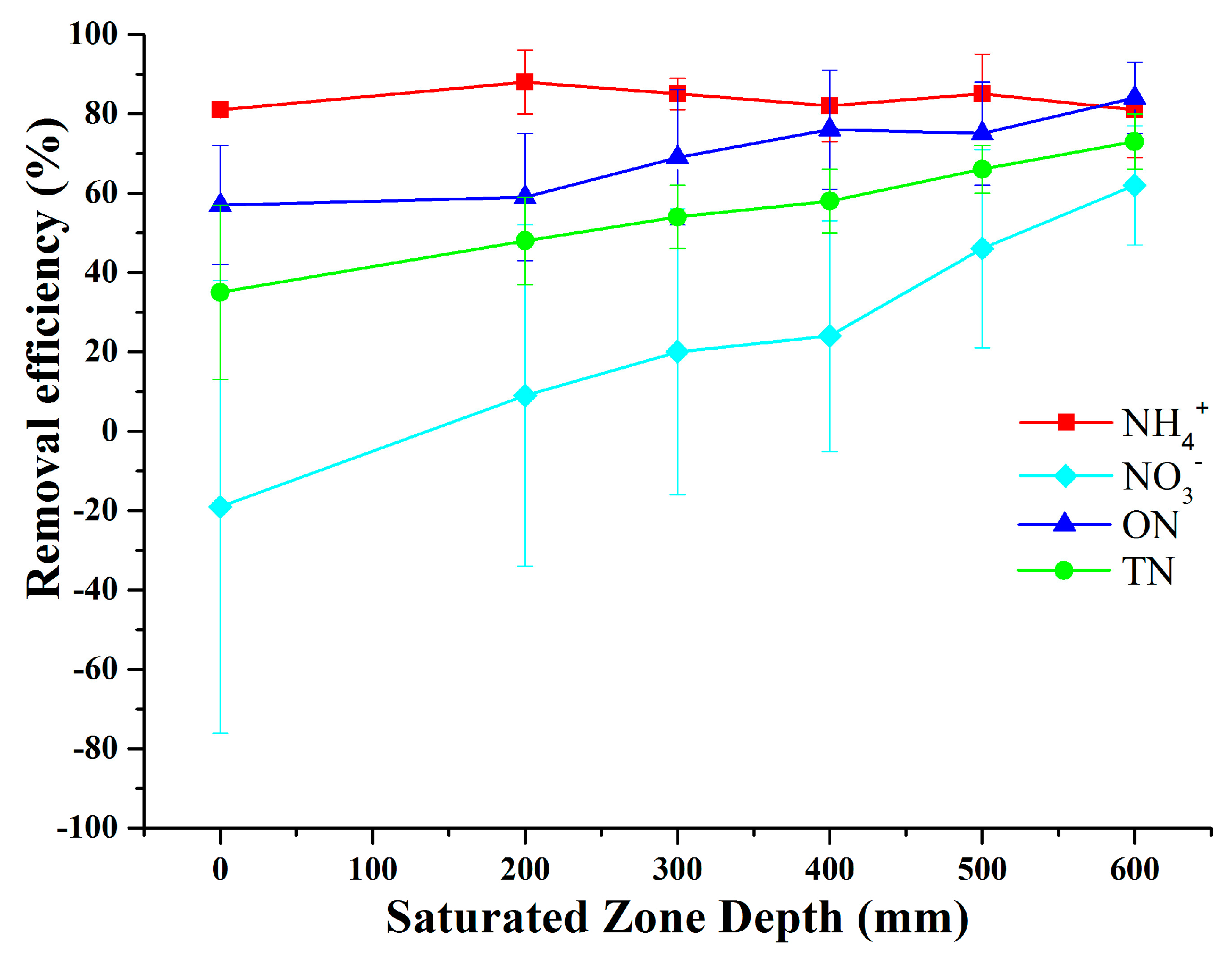
3.4. Effect of SZ Depths on Nitrogen Removal
4. Discussion
4.1. Ammonium Removal
4.2. Nitrate Removal
4.3. Organic Nitrogen Removal
4.4. Total Nitrogen Removal
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). Renewed Call to Action to Reduce Nutrient Pollution and Support for Incremental Actions to Protect Water Quality and Public Health; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-09/documents/renewed-call-nutrient-memo-2016.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2016).
- Driscoll, C.T.; Whitall, D.R.; Aber, J.D.; Boyer, E.W.; Castro, M.S.; Cronan, C.S.; Groffman, P.; Hopkinson, C.; Lambert, K.; Lambert, K.; et al. Nitrogen Pollution in the Northeastern United States: Sources, Effects, and Management Options. BioScience 2003, 53, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.D.; Fletcher, T.D.; Wong, T.H.F.; Breen, P.F.; Duncan, H.P. Nitrogen composition in urban runoff: Implications for stormwater management. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sample, D.J.; Bell, C.; Guan, Y. Review and Research Needs of Bioretention Used for the Treatment of Urban Stormwater. Water 2014, 6, 1069–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Yao, H.; Shaw, L.Y. Advances in LID BMPs research and practice for urban runoff control in China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C.; Winogradoff, D.A. Water quality improvement through bioretention: Lead, copper, and zinc removal. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Shokouhian, M.; Sharma, H.; Minami, C. Water quality improvement through bioretention media: Nitrogen and phosphorus removal. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, B.E.; Fletcher, T.; Deletic, A. Hydraulic and Pollutant Removal Performance of Fine Media Stormwater Filtration Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2535–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, W.F.; Davis, A.P.; Traver, R.G. Meeting Hydrologic and Water Quality Goals through Targeted Bioretention Design. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 138, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, T.J.; Yeh, D.H.; Ergas, S.J. Performance and longevity of denitrifying wood-chip biofilters for stormwater treatment: A microcosm study. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2015, 32, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, E.T.; Poor, C.J.; Hinman, C.; Stark, J.D. Nitrate and phosphate removal through enhanced bioretention media: Mesocosm study. Water Environ. Res. 2013, 85, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rycewicz-Borecki, M.; Mclean, J.E.; Dupont, R.R. Nitrogen and phosphorus mass balance, retention and uptake in six plant species grown in stormwater bioretention microcosms. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 99, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.; Jarrett, A.; Smith, J.; Sharkey, L. Evaluating Bioretention Hydrology and Nutrient Removal at Three Field Sites in North Carolina. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratieres, K.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Zinger, Y.A. Nutrient and sediment removal by stormwater biofilters: A large-scale design optimisation study. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3930–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.P.; Hunt, W.F.; Traver, R.G.; Clar, M. Bioretention technology: Overview of current practice and future needs. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.A.; Lawrence, T.J.; Stander, E.K.; Jontos, R.J.; Kaushale, S.S.; Newcomer, T.A.; Grimmg, N.B.; Ekberg, M.C. Opportunities and challenges for managing nitrogen in urban stormwater: A review and synthesis. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, L.J.; Hunt, W.F. Hydrologic and water quality performance of four bioretention cells in central North Carolina. In Proceedings of the Watershed Management Conference—Managing Watersheds for Human and Natural Impacts: Engineering, Ecological, and Economic Challenges, Williamsburg, VA, USA, 19–22 July 2005; pp. 833–842. [Google Scholar]
- Blecken, G.; Zinger, Y.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.; Hedstrom, A.; Viklander, M. Laboratory study on stormwater biofiltration: Nutrient and sediment removal in cold temperatures. J. Hydrol. 2010, 394, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinger, T.; Fletcher, T.D.; Deletic, A.; Blecken, G.T.; Viklander, M. Optimisation of the nitrogen retention capacity of stormwater biofiltration systems. Presented at the 6th International Conference on Sustainable Techniques and Strategies in Urban Water Management, Lyon, France, 24–28 June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zinger, Y.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.D. The effect of various intermittent wet-dry cycles on nitrogen removal capacity in biofilters systems. Presented at the 13th International Rainwater Catchment Systems Conference and 5th International Water Sensitive Urban Design Conference, Sydney, Australia, 21–23 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zinger, Y.; Blecken, G.; Fletcher, T.D.; Viklander, M.; Deletic, A. Optimising nitrogen removal in existing stormwater biofilters: Benefits and tradeoffs of a retrofitted saturated zone. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soberg, L.C.; Viklander, M.; Blecken, G. Do salt and low temperature impair metal treatment in stormwater bioretention cells with or without a submerged zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 579, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amir, A.; Asher, B. Use of Cotton as a Carbon Source for Denitrification in Biofilters for Groundwater Remediation. Water 2017, 9, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, M.E.; Clausen, J.C. Saturation to Improve Pollutant Retention in a Rain Garden. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1335–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Liaghati, T.; Antoniette, T.; Meney, K. Influence of plant species and submerged zone with carbon addition on nutrient removal in stormwater biofilter. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1833–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Rengel, Z.; Meney, K. Interactive effects of nitrogen and phosphorus loadings on nutrient removal from simulated wastewater using Schoenoplectus validus in wetland microcosms. Chemosphere 2008, 72, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passeport, E.; Hunt, W.F.; Line, D.E. Field study of the ability of two grassed bioretention cells to reduce storm-water runoff pollution. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2009, 135, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monash University. Adoption Guidelines for Stormwater Biofiltration Systems: Facility for Advancing Water Biofiltration; Monash University: Melbourne, Australia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Melbourne Water. WSUD Engineering Procedures: Stromwater; CSIRO Publishing: Melbourne, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environmental Resources. Bioretention Manual. Environmental Services Division; Department of Environmental Resources: The Prince George’s County, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blecken, G.; Zinger, Y.; Deletic, A.; Fletcher, T.; Viklander, M. Impact of a submerged zone and a carbon source on heavy metal removal in stormwater biofilters. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Du, P.; Ao, C.T.; Lei, M.H.; Zhao, D.Q.; Ho, M.; Wang, Z. Characterization of surface runoff from a subtropics urban catchment. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, E.G.; Fletcher, T.D.; Cook, P.L.; Deletic, A.; Hatt, B.E. Processes and drivers of nitrogen removal in stormwater biofiltration. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 44, 796–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geronimo, F.K.F.; Maniquiz-Redillas, M.C.; Kim, L.H. Fate and removal of nutrients in bioretention systems. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, I.J.; Igielski, S.; Davis, A.P. Enhanced denitrification in bioretention using woodchips as an organic carbon source. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.A.; Hunt, W.F. Underdrain configuration to enhance bioretention exfiltration to reduce pollutant loads. J. Environ. Eng. 2011, 137, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, D.; Mather, P.B.; Russell, S.; Rajapakse, J. Dynamics of Nitrate-Nitrogen Removal in Experimental Stormwater Biofilters under Intermittent Wetting and Drying. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Media Layer | Depth (mm) | Material |
|---|---|---|
| Mulch | 50 | Wood chips |
| Soil layer | 450 | Sandy loam |
| Transition layer | 120 | River sand (1–2 mm) |
| Saturated zone | 0, 200, 300, 400, 500, 600 | Gravel and Carbon source |
| Pollutant | Mean Inflow Concentration | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Oxygen Demand | 200 mg/L | Glucose (C6H12O6) |
| NO3−-N | 2.5 mg/L | Potassium Nitrate (KNO3) |
| NH4+-N | 2.5 mg/L | Ammonium Chloride (NH4Cl) |
| ON | 5.0 mg/L | 3-Aminopropanoic (C3H7NO2) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Qin, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, X.; Yu, S.-L. Effect of Saturated Zone on Nitrogen Removal Processes in Stormwater Bioretention Systems. Water 2018, 10, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020162
Wang C, Wang F, Qin H, Zeng X, Li X, Yu S-L. Effect of Saturated Zone on Nitrogen Removal Processes in Stormwater Bioretention Systems. Water. 2018; 10(2):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020162
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chuansheng, Fan Wang, Huapeng Qin, Xiangfei Zeng, Xueran Li, and Shaw-Lei Yu. 2018. "Effect of Saturated Zone on Nitrogen Removal Processes in Stormwater Bioretention Systems" Water 10, no. 2: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020162
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, F., Qin, H., Zeng, X., Li, X., & Yu, S.-L. (2018). Effect of Saturated Zone on Nitrogen Removal Processes in Stormwater Bioretention Systems. Water, 10(2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020162