Effect of Climate Change on Soil Erosion in a Mountainous Mediterranean Catchment (Central Pindus, Greece)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
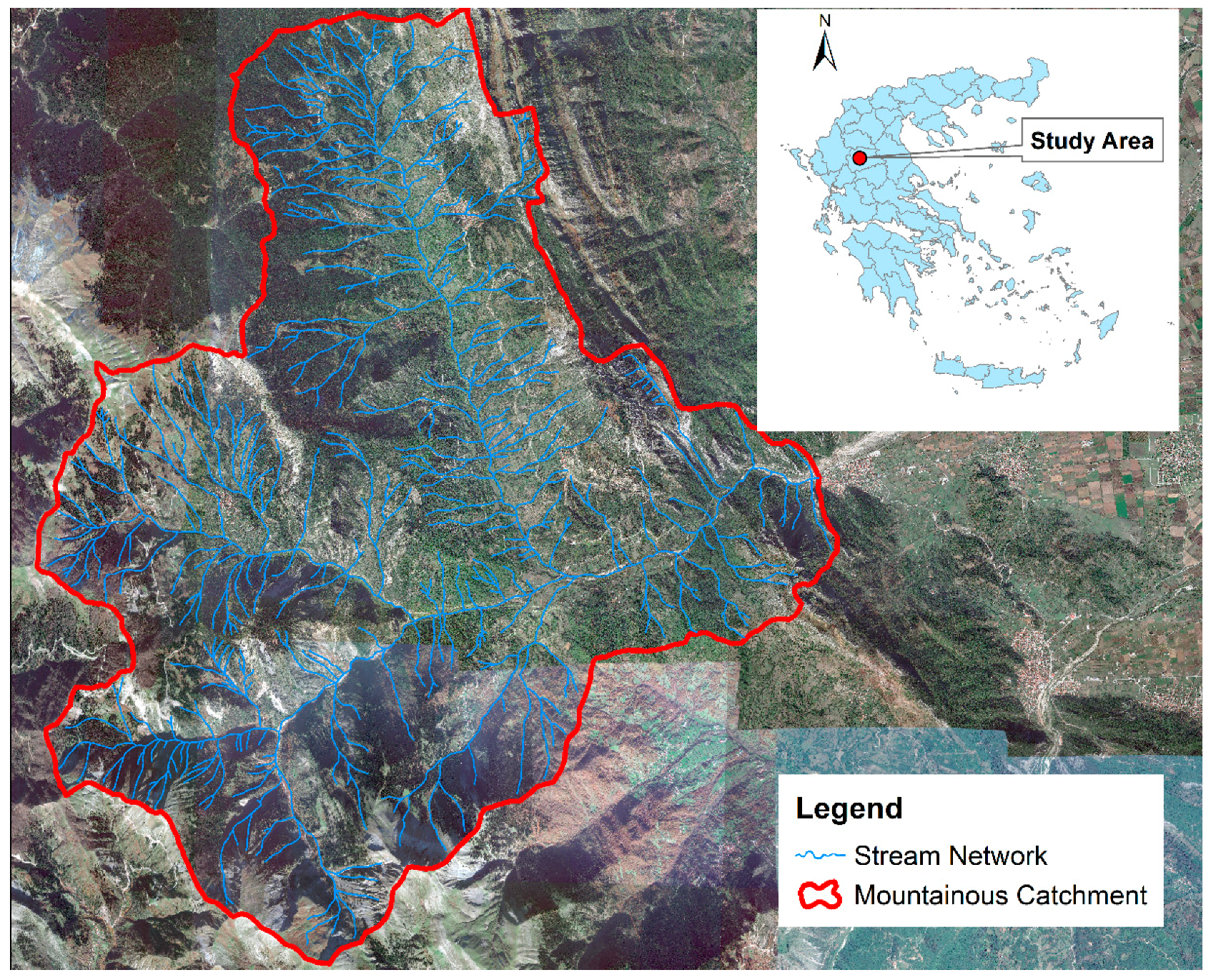
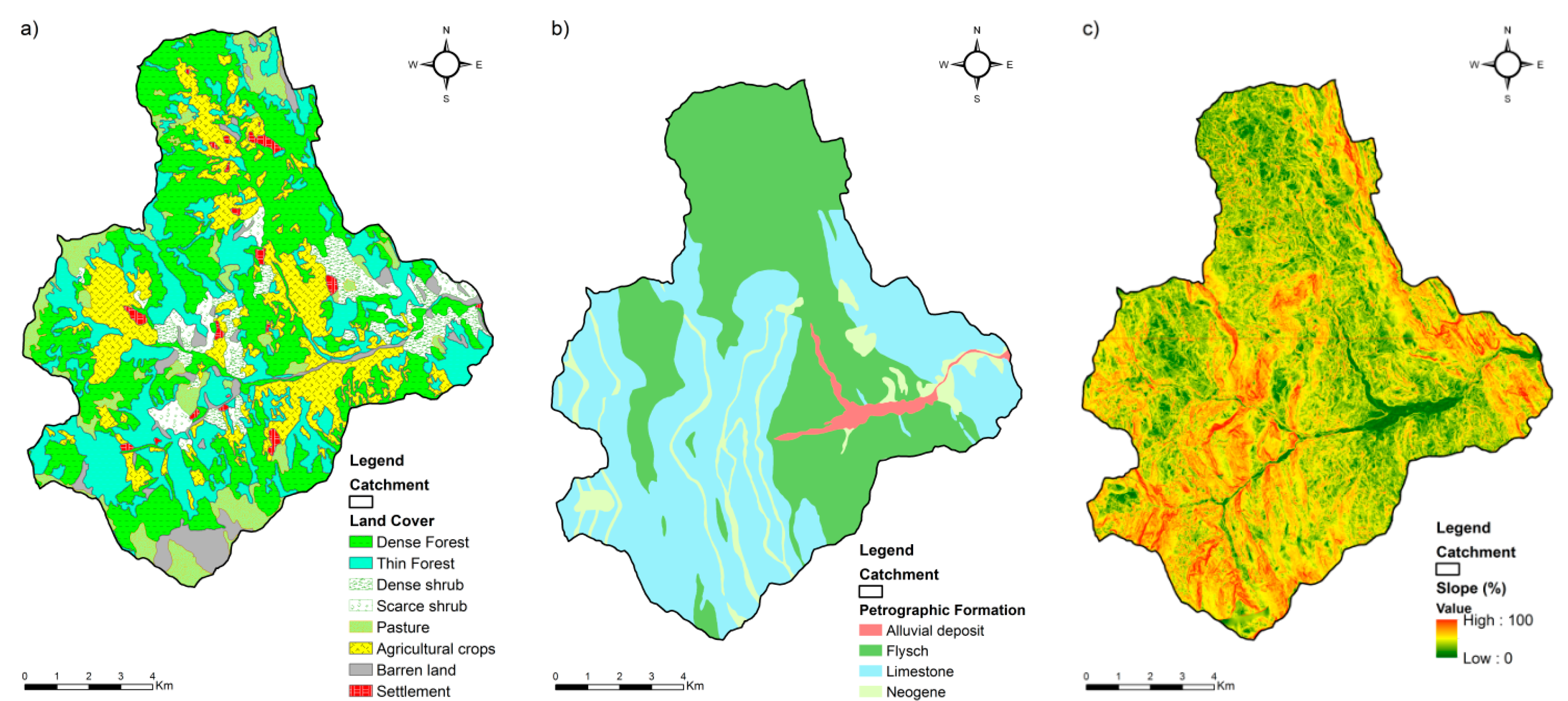
2.1. Study Area
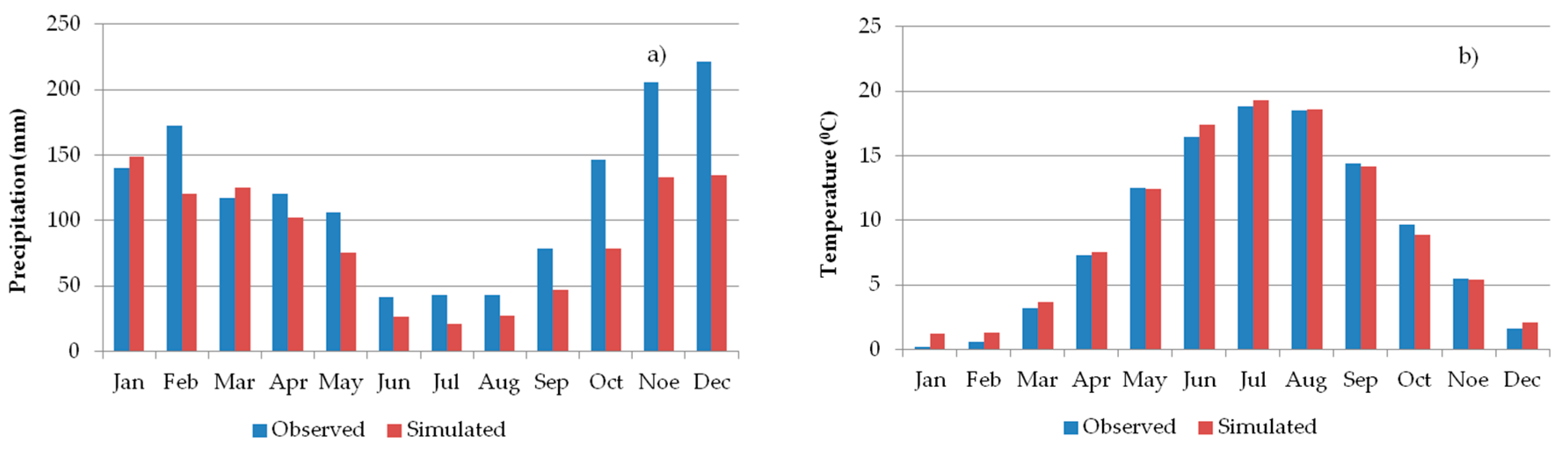
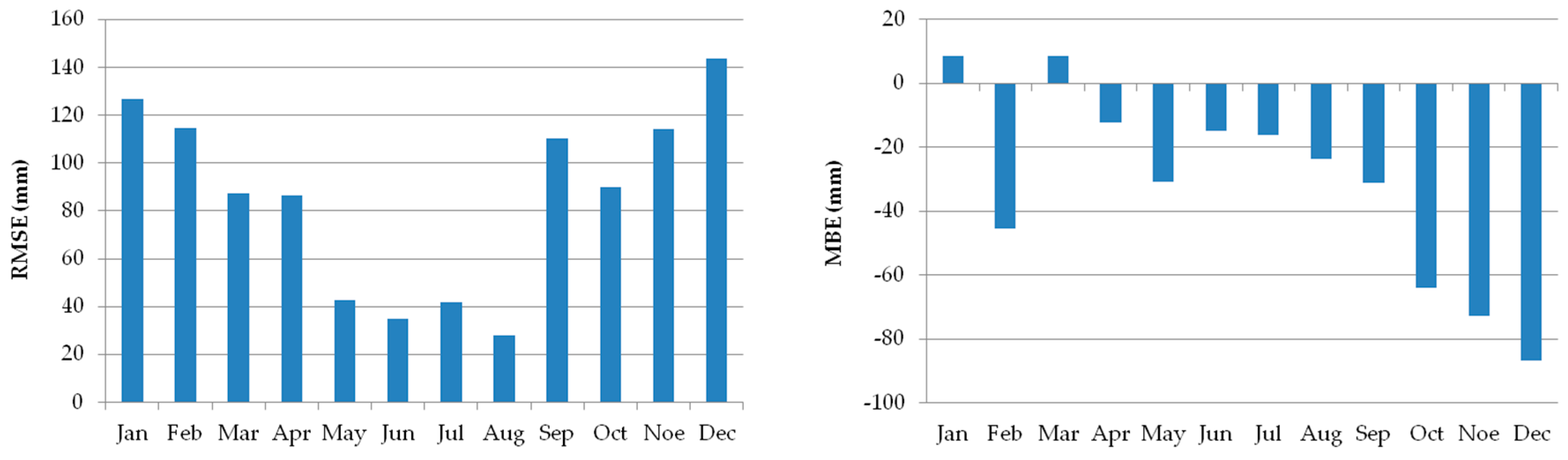
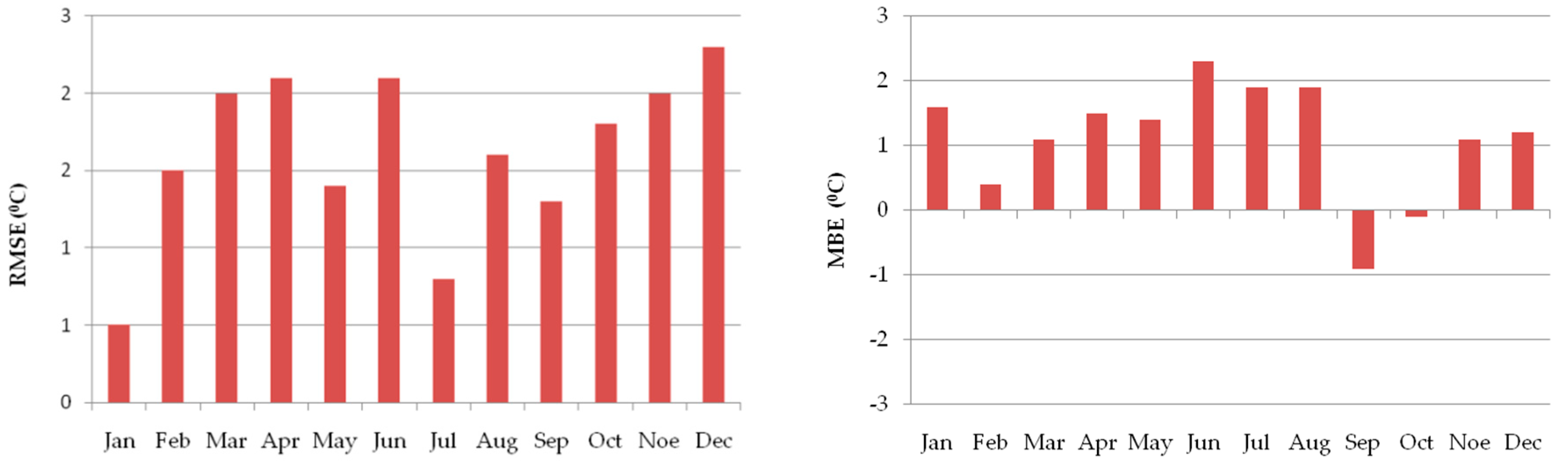
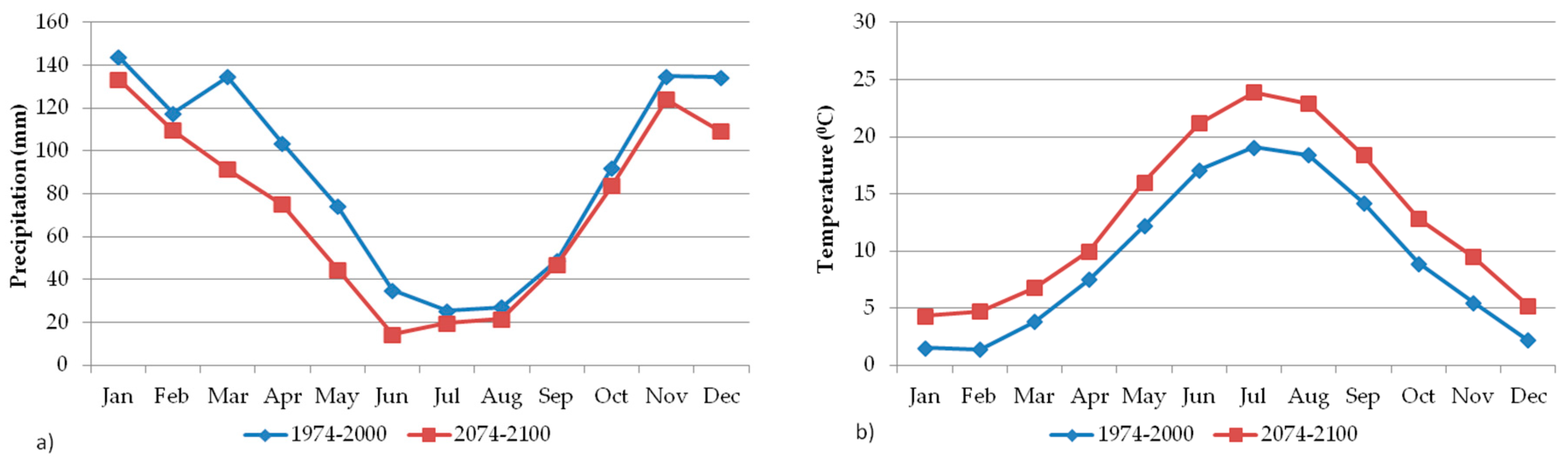
2.2. Climate Simulation
2.3. Methodology
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Annual soil loss was found to be equal to 161,236.5 m3/year, and the erosion rate 1182.1 m3/year/km2, by applying the Gavrilovič erosion prediction model (EPM) in the mountainous catchment of the Portaikos torrent.
- Concerning future climate conditions in the study area, based on RegCM3 data, a decrease (−21.2%) in annual precipitation (mm) and increase (+3.6 °C) in mean annual temperature is expected until the end of the 21st century. The above-mentioned model emphasized a greater decrease in monthly rainfall, especially in spring. As for the temperature, a greater increase in mean monthly temperature should occur in summer.
- Finally, considering the reported changes in climatic condition in the research area, a slight decrease (−4.9%) in erosion rate was estimated. It is suggested that similar surveys should be done all over the Greek mountainous regions so as to identify future erosion-prone areas. Moreover, investigations of the effect of climate change on other hydrometeorological hazards (e.g., flash floods, landslides, etc.) is necessary for adaption and mitigation measures. The EURO-CORDEX project’s comparison of the results of the current study with recent very high-resolution (10 × 10 km) climate change projections [67] could be the target of future research in order to highlight the importance of using the finer-resolution model over complex terrain areas, such as Greece. Simulations of finer timescale data (e.g., daily) could also be examined.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Lionello, P. Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolika, K.; Zanis, P.; Anagnostopoulou, C. Regional climate change scenarios for Greece: Future temperature and precipitation projections from ensembles of RCMs. Glob. NEST J. 2012, 14, 407–421. [Google Scholar]
- Tolika, K.; Maheras, P.; Vafiadis, M.; Flocas, H.A.; Arseni-Papadimitriou, A. Simulation of seasonal precipitation and raindays over Greece: A statistical downscaling technique based on artificial neural networks (ANNs). Int. J. Climatol. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 27, 861–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolika, K.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Maheras, P.; Vafiadis, M. Simulation of future changes in extreme rainfall and temperature conditions over the Greek area: A comparison of two statistical downscaling approaches. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2008, 63, 132–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Pruski, F.F.; O’neal, M.R. Expected climate change impacts on soil erosion rates: A review. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2004, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Nastos, P.; Evelpidou, N.; Vassilopoulos, A. Does climatic change in precipitation drive erosion in Naxos Island, Greece? Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plangoen, P.; Babel, M.S.; Clemente, R.S.; Shrestha, S.; Tripathi, N.K. Simulating the impact of future land use and climate change on soil erosion and deposition in the Mae Nam Nan sub-catchment, Thailand. Sustainability 2013, 5, 3244–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, S.; Chatzichristaki, C. Response of soil erosion in a mountainous watershed to temperature and precipitation trends. Carpath. J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- EC. Proposal for a Establishing a Framework for the Protection of Soil and Amending. Directive 2004/35/EC COM, 232. 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:52006PC0232 (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheras, P.; Anagnostopoulou, C. Circulation types and their influence on the interannual variability and precipitation changes in Greece. In Mediterranean Climate; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 215–239. [Google Scholar]
- García-Orenes, F.; Roldán, A.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Campoy, M.; Arcenegui, V.; Caravaca, F. Soil structural stability and erosion rates influenced by agricultural management practices in a semi-arid Mediterranean agro-ecosystem. Soil Use Manag. 2012, 28, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kairis, O.; Karavitis, C.; Salvati, L.; Kounalaki, A.; Kosmas, K. Exploring the impact of overgrazing on soil erosion and land degradation in a dry Mediterranean agro-forest landscape (Crete, Greece). Arid Land Res. Manag. 2015, 29, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicu, I.C. Is Overgrazing Really Influencing Soil Erosion? Water 2018, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Vega, J.A.; Vieira, D.C.S. Assessing soil erosion after fire and rehabilitation treatments in NW Spain: Performance of RUSLE and revised Morgan–Morgan–Finney models. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronidis, D.I.; Emmanouloudis, D.A.; Mitsopoulos, I.A.; Riggos, E.E. Soil erosion potential after fire and rehabilitation treatments in Greece. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myronidis, D.; Ioannou, K.; Sapountzis, M.; Fotakis, D. Development of a sustainable plan to combat erosion for an island of the Mediterranean region. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2010, 19, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Pradeep, G.S.; Krishnan, M.N.; Vijith, H. Identification of critical soil erosion prone areas and annual average soil loss in an upland agricultural watershed of Western Ghats, using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and RUSLE techniques. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 3697–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanday, M.Y.; Javed, A. Prioritization of sub-watersheds for conservation measures in a semi-arid watershed using remote sensing and GIS. J. Geol. Soc. India 2016, 88, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Díaz, A.; Cammeraat, L.H.; Vacca, A.; Kosmas, C. Soil erosion at three experimental sites in the Mediterranean. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Res. Group 1999, 24, 1243–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidis, P.; Sapountzis, M.; Stathis, D. Sheet erosion after fire at the urban forest of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece). Silva Balc. 2002, 2, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Boix-Fayos, C.; Martínez-Mena, M.; Arnau-Rosalén, E.; Calvo-Cases, A.; Castillo, V.; Albaladejo, J. Measuring soil erosion by field plots: Understanding the sources of variation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 78, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdan, O.; Govers, G.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Van Oost, K.; Poesen, J.; Saby, N.; Gobin, A.; Vacca, A.; Quinton, J.; Auerswald, K.; et al. Rates and spatial variations of soil erosion in Europe: A study based on erosion plot data. Geomorphology 2010, 122, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmadakis, I.; Tsardaklis, P.; Ioannou, K.; Zaimes, G.N. A Novel Fully Automated Soil Erosion Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2015), Kavala, Greece, 17–20 September 2015; pp. 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P.; Gitas, I.Z. A classification of water erosion models according to their geospatial characteristics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2014, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses, a Guide to Conservation Planning; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; Volume 537, p. 62.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.P.C. A simple approach to soil loss prediction: A revised Morgan–Morgan–Finney model. Catena 2001, 44, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A process-based soil erosion model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovič, S. Engineering of Debris Flow and Erosion; Izgradnja: Beograd, Serbia, 1972; p. 292. (In Serbian) [Google Scholar]
- De Vente, J.; Poesen, J. Predicting soil erosion and sediment yield at the basin scale: Scale issue and semi-quantitative models. Earth Sci. Rev. 2005, 71, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapountzis, M.; Myronidis, D.; Stathis, D.; Stefanidis, P. Comparison of the predicted erosion rates by USLE and GAVRILOVIC methods with field measurements. In Proceedings of the 1st Joint Conference EYE-EEDYP, Volos, Greece, 27–30 May 2009; pp. 155–165. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Xanthakis, M. Soil Erosion Study in Mountainous Basins with Modern Technological Tools. Ph.D. Thesis, Harokopio University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2011. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Anastasiou, S. Determination of Degradation and Sediment Sources in Torrents’ Watersheds of Serres, Using GIS. Master’s Thesis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2013. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Efthimiou, N.; Lykoudi, E.; Panagoulia, D.; Karavitis, C. Assessment of soil susceptibility to erosion using the EPM and RUSLE models: The case of Venetikos River Catchment. Glob. NEST J. 2016, 18, 164–179. [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux, V.; Cheggour, A.; Deschamps, C.; Mouillot, F.; Cerdan, O.; Le Bissonnais, Y. Land use and climate change effects on soil erosion in a semi-arid mountainous watershed (High Atlas, Morocco). J. Arid Environ. 2015, 122, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, H.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, Y.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Chappell, A.; Yu, W.; Shi, Z. Current and future assessments of soil erosion by water on the Tibetan Plateau based on RUSLE and CMIP5 climate models. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostopoulos, G.G.; Koutsoyiannis, D.; Christofides, A.; Efstratiadis, A.; Mamassis, N. A comparison of local and aggregated climate model outputs with observed data. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2010, 55, 1094–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Efstratiadis, A.; Georgakakos, K.P. Uncertainty assessment of future hydroclimatic predictions: A comparison of probabilistic and scenario-based approaches. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 261–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoyiannis, D.; Efstratiadis, A.; Mamassis, N.; Christofides, A. On the credibility of climate predictions. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anagnostopoulou, C.; Tolika, K.; Maheras, P.; Reiser, H.; Kutiel, H. Quantifying uncertainties in precipitation: A case study from Greece. Adv. Geosci. 2008, 16, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbantis, I.; Efstratiadis, A.; Rozos, E.; Kopsiafti, M.; Koutsoyiannis, D. Holistic versus monomeric strategies for hydrological modelling of human-modified hydrosystems. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serpa, D.; Nunes, J.P.; Santos, J.; Sampaio, E.; Jacinto, R.; Veiga, S.; Lima, J.C.; Moreira, M.; Corte-Real, J.; Keizer, J.J.; et al. Impacts of climate and land use changes on the hydrological and erosion processes of two contrasting Mediterranean catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stathis, D.; Myronidis, D. Principal component analysis of precipitation in Thessaly region (Central Greece). Glob. NEST J. 2009, 11, 467–476. [Google Scholar]
- Tziaftani, F. The Causes and Mechanism of the Landslides Phenomena in Mountainous Watersheds of Torrents in Greece. Watershed Management and Torrent Control Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 18 February 2013. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Tsitsoni, T.; Zagas, T.; Ganatsas, P. Plant diversity and Nature Conservation in Koziakas Natura 2000 (Network) Site, Central Greece. In Proceedings of the 6st International Conference «Protection and Restoration of the Environment VI», Skiathos, Greece, 1–5 July 2002; Volume 1, pp. 609–616. [Google Scholar]
- Zanis, P.; Katragkou, E.; Ntogras, C.; Marougianni, G.; Tsikerdekis, A.; Feidas, H.; Anadranistakis, E.; Melas, D. Transient high-resolution regional climate simulation for Greece over the period 1960–2100: Evaluation and future projections. Clim. Res. 2015, 64, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummukainen, M. State-of-the-art with Regional Climate Models. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Janjic, Z.; Dudhia, J.; Vasic, R.; De Sales, F. A review on regional dynamical downscaling in intraseasonal to seasonal simulation/prediction and major factors that affect downscaling ability. Atmos. Res. 2014, 147, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefanidis, S. Hydronomy of Mountainous Catchments under Climate Change in Central Pindus. Ph.D. Thesis, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2018. (In Greek). [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, D.; Bärring, L.; Christensen, O.B.; Christensen, J.H.; de Castro, M.; Déqué, M.; Giorgi, F.; Hagemann, S.; Hirschi, M.; Jones, R.; et al. An inter-comparison of regional climate models for Europe: Model performance in present-day climate. Clim. Chang. 2007, 81, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockel, B.; Geyer, B. The performance of the regional climate model CLM in different climate regions, based on the example of precipitation. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias correction of regional climate model simulations for hydrological climate-change impact studies: Review and evaluation of different methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Koehler, A.B. Another look at measures of forecast accuracy. Int. J. Forecast. 2006, 22, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. On the use of dimensioned measures of error to evaluate the performance of spatial interpolators. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J.; Matsuura, K. Advantages of the mean absolute error (MAE) over the root mean square error (RMSE) in assessing average model performance. Clim. Res. 2005, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, T.; Draxler, R. Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)?—Arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazamias, A.P.; Sapountzis, M. Spatial and temporal assessment of potential soil erosion over Greece. Water 2017, 59, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Gallardo, C.; Arribas, A.; Prego, J.A.; Gaertner, M.A.; De Castro, M. Multi-year simulations using a regional-climate model over the Iberian Peninsula: Current climate and doubled CO2 scenario. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 1659–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergant, K.; Belda, M.; Halenka, T. Systematic errors in the simulation of European climate (1961–2000) with RegCM3 driven by NCEP/NCAR reanalysis. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 455–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparrizos, S.; Maris, F.; Matzarakis, A. Integrated analysis of present and future responses of precipitation over selected Greek areas with different climate conditions. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodossiou, N. Assessing the Impacts of Climate Change on the Sustainability of Groundwater Aquifers. Application in Moudania Aquifer in N. Greece. Environ. Process. 2016, 3, 1045–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koufos, G.C.; Mavromatis, T.; Koundouras, S.; Jones, G.V. Response of viticulture-related climatic indices and zoning to historical and future climate conditions in Greece. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2097–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazoglou, G.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Koundouras, S. Climate change projections for Greek viticulture as simulated by a regional climate model. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kling, H.; Fuchs, M.; Paulin, M. Runoff conditions in the upper Danube basin under an ensemble of climate change scenarios. J. Hydrol. 2012, 424, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolika, K.; Anagnostopoulou, C.; Velikou, K.; Vagenas, C. A comparison of the updated very high resolution model RegCM3_10km with the previous version RegCM3_25km over the complex terrain of Greece: Present and future projections. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Coefficient of Land Cover | x |
| Mixed and dense forest | 0.05–0.20 |
| Thin forest with grove | 0.05–0.20 |
| Coniferous forest with little grove, scarce bushes, bushy prairie | 0.20–0.40 |
| Damaged forest and bushes, pasture | 0.40–0.60 |
| Damaged pasture and cultivated land | 0.60–0.80 |
| Areas without vegetal cover | 0.80–1.00 |
| Coefficient of soil erodibility | y |
| Hard rock, erosion resistant | 0.2–0.6 |
| Rock with moderate erosion resistance | 0.6–1.0 |
| Weak rock, schistose, stabilized | 1.0–1.3 |
| Sediments, moraines, clay and other rock with little resistance | 1.3–1.8 |
| Fine sediments and soils without erosion resistance | 1.8–2.0 |
| Coefficient of type and extent of erosion | φ |
| Little erosion on catchment | 0.1–0.2 |
| Erosion in waterways on 20 to 50% of the catchment area | 0.3–0.5 |
| Erosion in rivers, gullies and alluvial deposits, karstic erosion | 0.6–0.7 |
| 50 to 80% of catchment area affected by surface erosion and landslides | 0.8–0.9 |
| Whole catchment affected by erosion | 1.0 |
| Period | Soil Loss (m3/year) | Erosion Rate (m3/year/km2) |
|---|---|---|
| 1974–2000 | 161,236.5 | 1182.1 |
| 2074–2100 | 153316 | 1124 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stefanidis, S.; Stathis, D. Effect of Climate Change on Soil Erosion in a Mountainous Mediterranean Catchment (Central Pindus, Greece). Water 2018, 10, 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101469
Stefanidis S, Stathis D. Effect of Climate Change on Soil Erosion in a Mountainous Mediterranean Catchment (Central Pindus, Greece). Water. 2018; 10(10):1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101469
Chicago/Turabian StyleStefanidis, Stefanos, and Dimitrios Stathis. 2018. "Effect of Climate Change on Soil Erosion in a Mountainous Mediterranean Catchment (Central Pindus, Greece)" Water 10, no. 10: 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101469
APA StyleStefanidis, S., & Stathis, D. (2018). Effect of Climate Change on Soil Erosion in a Mountainous Mediterranean Catchment (Central Pindus, Greece). Water, 10(10), 1469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101469






