Influence of Proteins on Transport of Ferrihydrite Particles Formed during Recharge of Groundwater Containing Fe with Reclaimed Water
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Column Experiments
2.3. Transport Experiments
2.3.1. Ferrihydrite Synthesis
2.3.2. Preparation of Ferrihydrite Suspensions
2.3.3. Ferrihydrite Transport in Porous Medium
2.4. Batch Experiments
2.5. Characteristics
2.6. Transport Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Ferrihydrite Formation
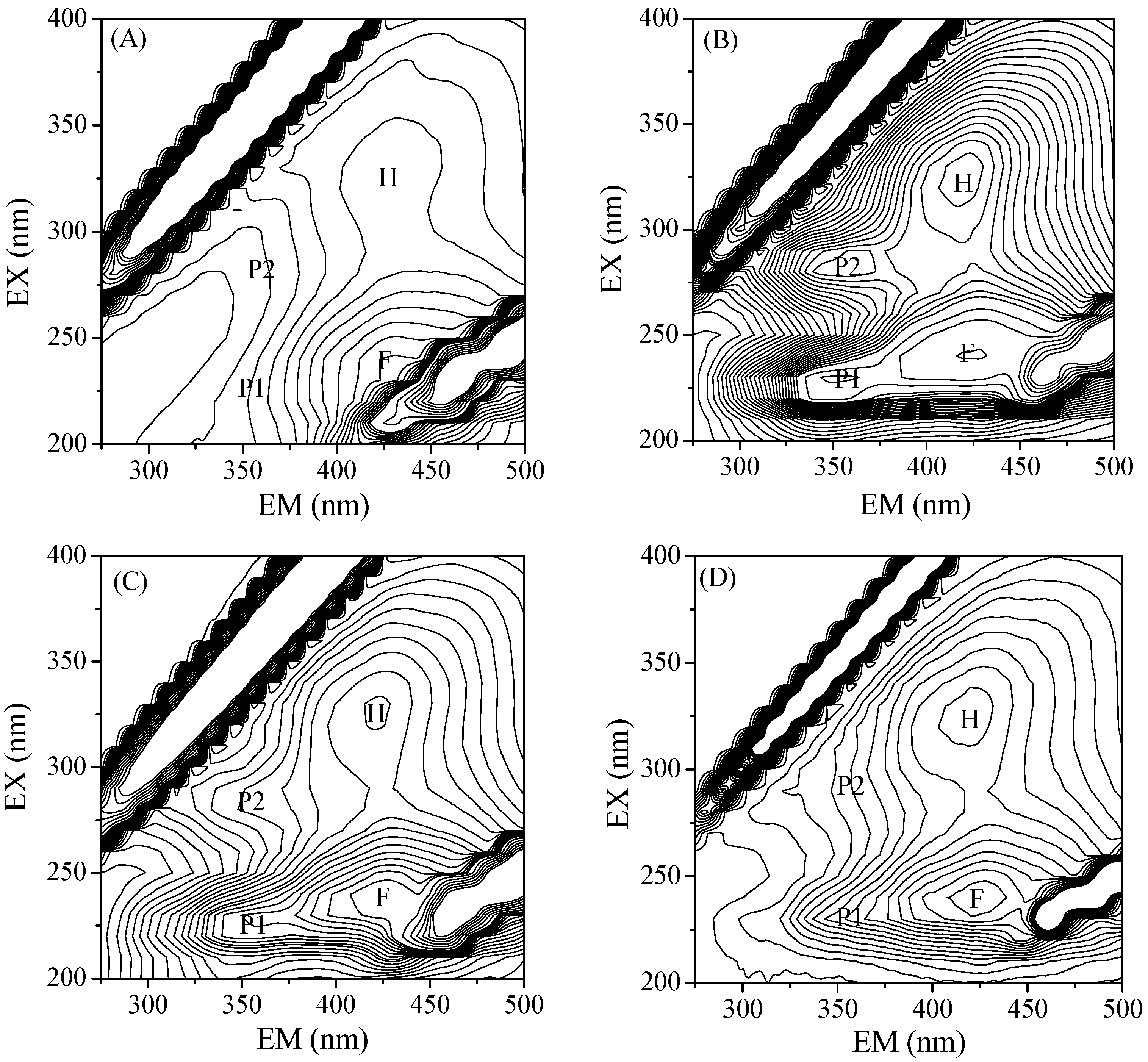
3.2. Organics Adsorbed onto the Ferrihydrite Particles
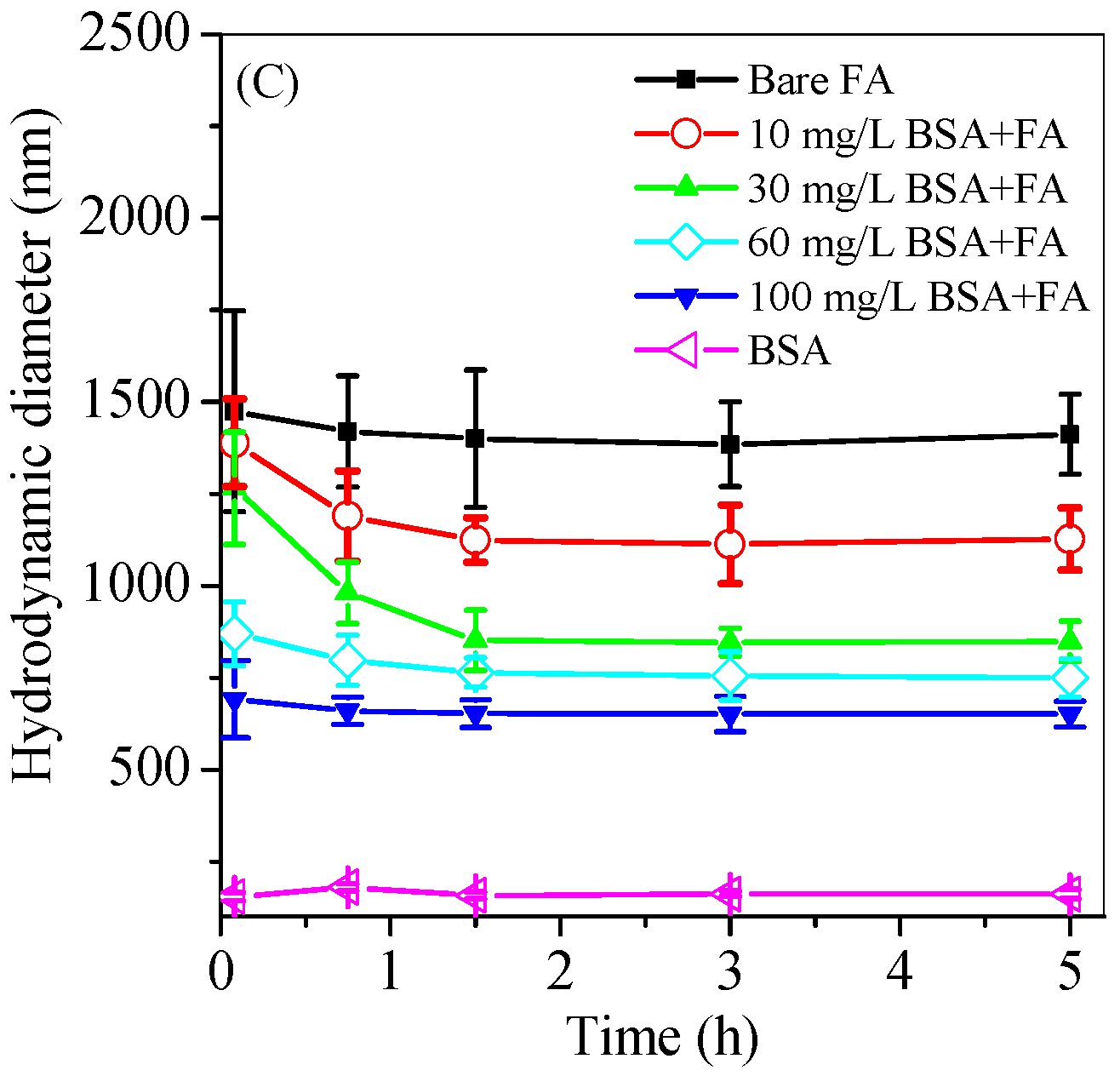
3.3. Effect of Protein on the Ferrihydrite Transport
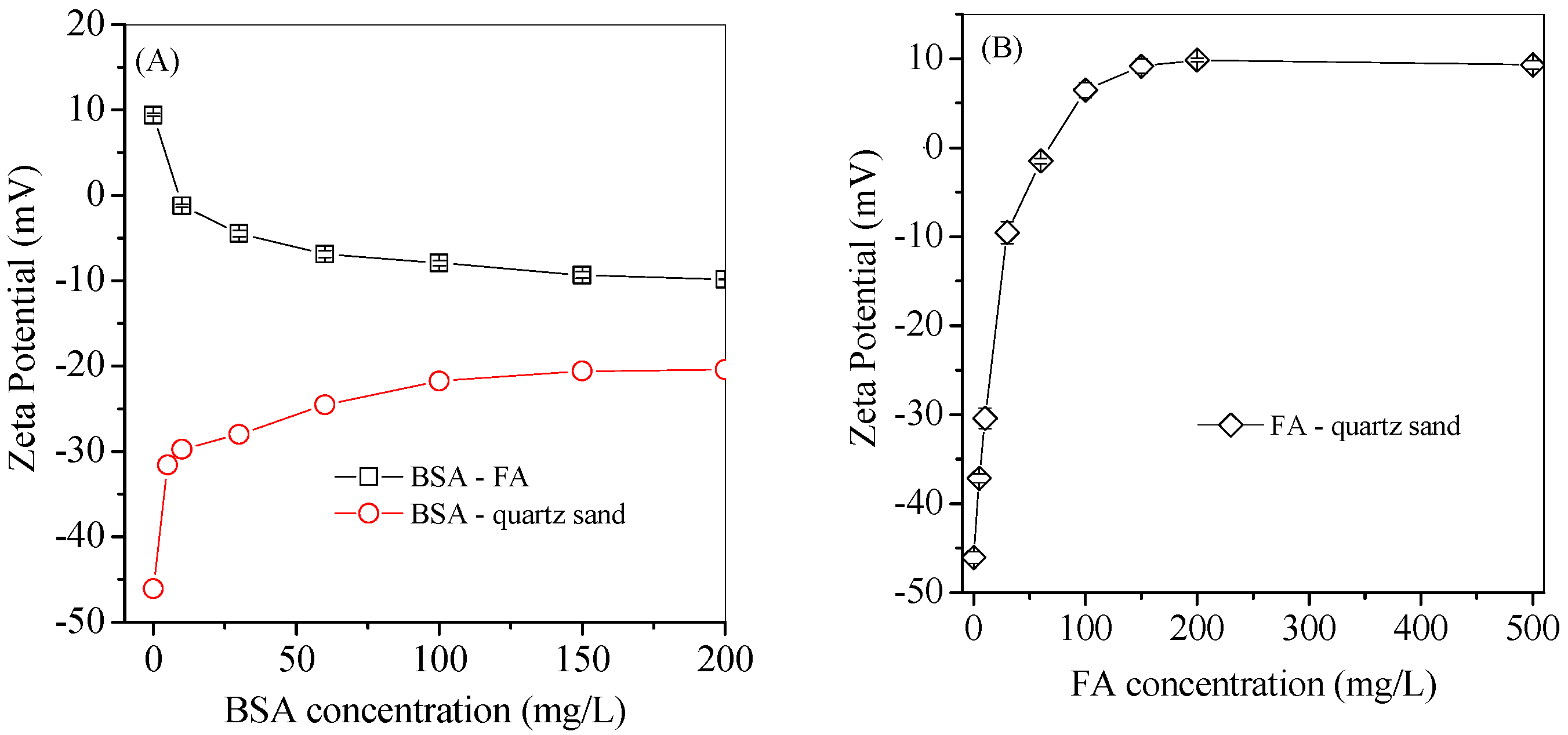
3.4. Protein Adsorption
3.5. Mechanism of Transport of Protein-Mediated Ferrihydrite Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Overacre, R.; Clinton, T.; Pyne, D.; Snyder, S.; Dillon, P. Reclaimed water aquifer storage and recovery: Potential changes in water quality. Proc. Water Environ. Fed. 2006, 2006, 1339–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderzalm, J.; Le Gal La Salle, C.; Hutson, J.; Dillon, P. Behaviour of metals during reclaimed water aquifer storage and recovery. In Proceedings of the EGS-AGU-EUG Joint Assembly, Nice, France, 6–11 April 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shareef, A.; Page, D.; Vanderzalm, J.; Williams, M.; Gupta, V.V.; Dillon, P.; Kookana, R. Biodegradation of simazine and diuron herbicides under aerobic and anoxic conditions relevant to managed aquifer recharge of storm water. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Bettahar, M. Concentration dependent transport of colloids in saturated porous media. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2006, 82, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, T.; Persson, P. Complexes with aquatic organic matter suppress hydrolysis and precipitation of Fe(III). Chem. Geol. 2012, 322, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Ceglie, A.; He, J.Z.; Liu, Y.R.; Palumbo, G.; Colombo, C. Particle size, charge and colloidal stability of humic acids coprecipitated with ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, A.; Yan, W.; Koel, B.E.; Jaffé, P.R. Poly(acrylic acid) coating induced 2-line ferrihydrite nanoparticle transport in saturated porous media. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenari, S.L.D.; Barbeau, B. Size and zeta potential of oxidized iron and manganese in water treatment: Influence of pH, ionic strength, and hardness. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokoro, C.; Yatsugi, Y.; Koga, H.; Owada, S. Sorption mechanisms of arsenate during coprecipitation with ferrihydrite in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosco, T.; Bosch, J.; Meckenstock, R.U.; Sethi, R. Transport of ferrihydrite nanoparticles in saturated porous media: Role of ionic strength and flow rate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4008–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.Y.; Du, Y.; Wu, Q.Y.; Zhao, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, Z. Differences in dissolved organic matter between reclaimed water source and drinking water source. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, P.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Jiang, Y.; Pan, C.; Fortner, J.D.; Yuan, S. Effect of reduced humic acid on the transport of ferrihydrite nanoparticles under anoxic conditions. Water. Res. 2017, 109, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, S. Influence of humic acid on the transport and deposition of colloidal silica under different hydrogeochemical conditions. Water 2016, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.; Douglas, T.; Nest, D.; Schoonen, M.; Strongin, D. Charge development on ferritin: An electrokinetic study of a protein containing a ferrihydrite nanoparticle. ACS Symp. Ser. 2005, 890, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Zhou, D.; Fan, W.; Huo, M.; Crittenden, J.C.; Yu, Z.; Ju, P.; Wang, Y. The effectiveness of coagulation for water reclamation from a wastewater treatment plant that has a long hydraulic and sludge retention times: A case study. Chemosphere 2016, 157, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Paradelo, M.; Bradford, S.A.; Peijnenburg, W.J.; Chu, L.; Zhou, D. Facilitated transport of Cu with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in saturated sand: Effects of solution ionic strength and composition. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5905–5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurences and Uses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Yan, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Chow, C.W.; Chong, M.N. Multistep, microvolume resin fractionation combined with 3D fluorescence spectroscopy for improved DOM characterization and water quality monitoring. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezwan, K.; Meier, L.P.; Rezwan, M.; Vörös, J.; Textor, M.; Gauckler, L.J. Bovine serum albumin adsorption onto colloidal Al2O3 particles: A new model based on zeta potential and UV-vis measurements. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10055–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Gao, B.; Wu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Z. Effects of surfactant type and concentration on graphene retention and transport in saturated porous media. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 1187–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Simunek, J.; Bettahar, M.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Yates, S.R. Modeling colloid attachment, straining, and exclusion in saturated porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chistyakova, N.I.; Rusakov, V.S.; Shapkin, A.A.; Starokurov, Y.V.; Kazakov, A.P.; Zavarzina, D.G.; Zhilina, T.N.; Lančok, A.; Kohout, J. Mössbauer study of biogenic formation processes of iron minerals. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mössbauer Spectroscopy in Materials Science, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 11–15 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Huggins, F.E.; Feng, Z.; Huffman, G.P. Ferrihydrite: Surface structure and its effects on phase transformation. Clays Clay Miner. 1994, 42, 737–746. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, S.; Benning, L.G.; Terrill, N.J.; Davidson, L. Nucleation and growth of iron oxyhydroxide nanoparticles from solution: An in situ time-resolved Small Angle X-ray Scattering (SAXS) study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2004, 68, A158. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.; Zhu, C.; Rule, J.; Nuhfer, N.T.; Ford, R.; Hedges, S.; Soong, Y. A high-resolution TEM-AEM, pH titration, and modeling study of Zn2+ coprecipitation with ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2005, 69, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi-Chuan, K.; Wen-Hsiang, C.; Meng-Wei, W.; Piaw, P.; Jatuporn, W.; Kun-Feng, L. The preliminary study of iron and manganese removal from groundwater by NaOCl oxidation and MF filtration. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2012, 22, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Guo, H.; Lei, M.; Li, Y.; Weng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.; Deng, Y.; Feng, X.; Xiu, W. Enhanced transport of ferrihydrite colloid by chain-shaped humic acid colloid in saturated porous media. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Huang, G.; An, C.; Xin, X.; Huang, C.; Rosendahl, S. Removal of Tetrabromobisphenol A by Adsorption on Pinecone-Derived Activated Charcoals: Synchrotron FTIR, Kinetics and Surface Functionality Analyses. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z. Hydrolysis and coagulation behavior of polyferric sulfate and ferric sulfate. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voegelin, A.; Kaegi, R.; Berg, M.; Nitzsche, K.S.; Kappler, A.; Lan, V.M.; Trang, P.T.; Göttlicher, J.; Steininger, R. Solid-phase characterisation of an effective household sand filter for As, Fe and Mn removal from groundwater in Vietnam. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seda, N.N.; Koenigsmark, F.; Vadas, T.M. Sorption and coprecipitation of copper to ferrihydrite and humic acid organomineral complexes and controls on copper availability. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ajmal, Z.; Muhmood, A.; Usman, M.; Kizito, S.; Lu, J.; Dong, R.; Wu, S. Phosphate removal from aqueous solution using iron oxides: Adsorption, desorption and regeneration characteristics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 528, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saalfield, S.L.; Bostick, B.C. Synergistic effect of calcium and bicarbonate in enhancing arsenate release from ferrihydrite. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 5171–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eusterhues, K.; Rennert, T.; Knicker, H.; Totsche, K.U. Association of organic matter and ferrihydrite: Adsorption versus coprecipitation. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 19–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.N.; Li, B.; Liu, R.X.; Song, Y.H.; Wu, W. Fluorescence characteristics of fractionated colloidal organic matter in freshwater from Hunhe and Taizihe watersheds. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2014, 35, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Norde, W.; Tan, W.; Koopal, L. Protein Adsorption at Solid Surfaces and Protein Complexation with Humic Acids. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2008, 8, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Sun, C.; Yang, X. Adsorption and zeta potential studies relevant to hematite ore reverse froth flotation. Miner. Metall. Process. 2012, 29, 148–155. [Google Scholar]




| Elements | Reclaimed Water | Groundwater | Effluent A | Mass Loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 0.27 | 8.48 | 0.03 | 99.3 |
| Zn | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 93.3 |
| Mn | 0.005 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 92.2 |
| Al | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 88.2 |
| Protein-like compounds | 8.6 | 0.02 | 1.14 | 73.5 |
| COD | 25.58 | 9.53 | 10.3 | 41.6 |
| Si | 1.68 | 9.57 | 3.31 | 41.2 |
| Mg | 11.49 | 0.26 | 3.89 | 33.8 |
| Ca | 15.43 | 5.19 | 7.98 | 22.6 |
| Na | 166.65 | 54.54 | 101.4 | 8.3 |
| pH | 6.7 | 7.3 | 7.2 |
| Experiment Number | Rd | katt (/min) | Kdet (/min) | Smax (mg/g) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mg/L BSA | 54.0% | 0.420 | 0 | 1.264 | 0.97 |
| 5 mg/L FA * in 10 mg/L of BSA solution | 48.5% | 0.718 | 8 × 10−4 | 5.494 | 0.92 |
| 150 mg/L FA * in 30 mg/L of BSA solution | 78.7% | 1.433 | 8 × 10−4 | 27.087 | 0.93 |
| 150 mg/L FA * in 60 mg/L of BSA solution | 76.9% | 1.159 | 8 × 10−4 | 21.742 | 0.95 |
| 150 mg/L FA * in 100 mg/L of BSA solution | 75.0% | 1.036 | 8 × 10−4 | 17.460 | 0.96 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, S.; Zhu, J.; Fan, W.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhang, L.; Bian, D. Influence of Proteins on Transport of Ferrihydrite Particles Formed during Recharge of Groundwater Containing Fe with Reclaimed Water. Water 2018, 10, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101329
Zhu S, Zhu J, Fan W, Yu Y, Yang J, Chang Y, Huo M, Zhang L, Bian D. Influence of Proteins on Transport of Ferrihydrite Particles Formed during Recharge of Groundwater Containing Fe with Reclaimed Water. Water. 2018; 10(10):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101329
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Suiyi, Junna Zhu, Wei Fan, Yang Yu, Jiakuan Yang, Ying Chang, Mingxin Huo, Leilei Zhang, and Dejun Bian. 2018. "Influence of Proteins on Transport of Ferrihydrite Particles Formed during Recharge of Groundwater Containing Fe with Reclaimed Water" Water 10, no. 10: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101329
APA StyleZhu, S., Zhu, J., Fan, W., Yu, Y., Yang, J., Chang, Y., Huo, M., Zhang, L., & Bian, D. (2018). Influence of Proteins on Transport of Ferrihydrite Particles Formed during Recharge of Groundwater Containing Fe with Reclaimed Water. Water, 10(10), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101329




