High-Frequency Water Isotopic Analysis Using an Automatic Water Sampling System in Rice-Based Cropping Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- There are seasonal and crop effects on isotopic compositions in groundwater and surface water.
- The isotopic differences in water sources are driven by the evaporation fractionation process.
- Meteorological conditions control evaporation so that a day-night cycle is apparent for stable isotopes of ponding water, while this cannot be found for groundwater.
2. Materials and Methods
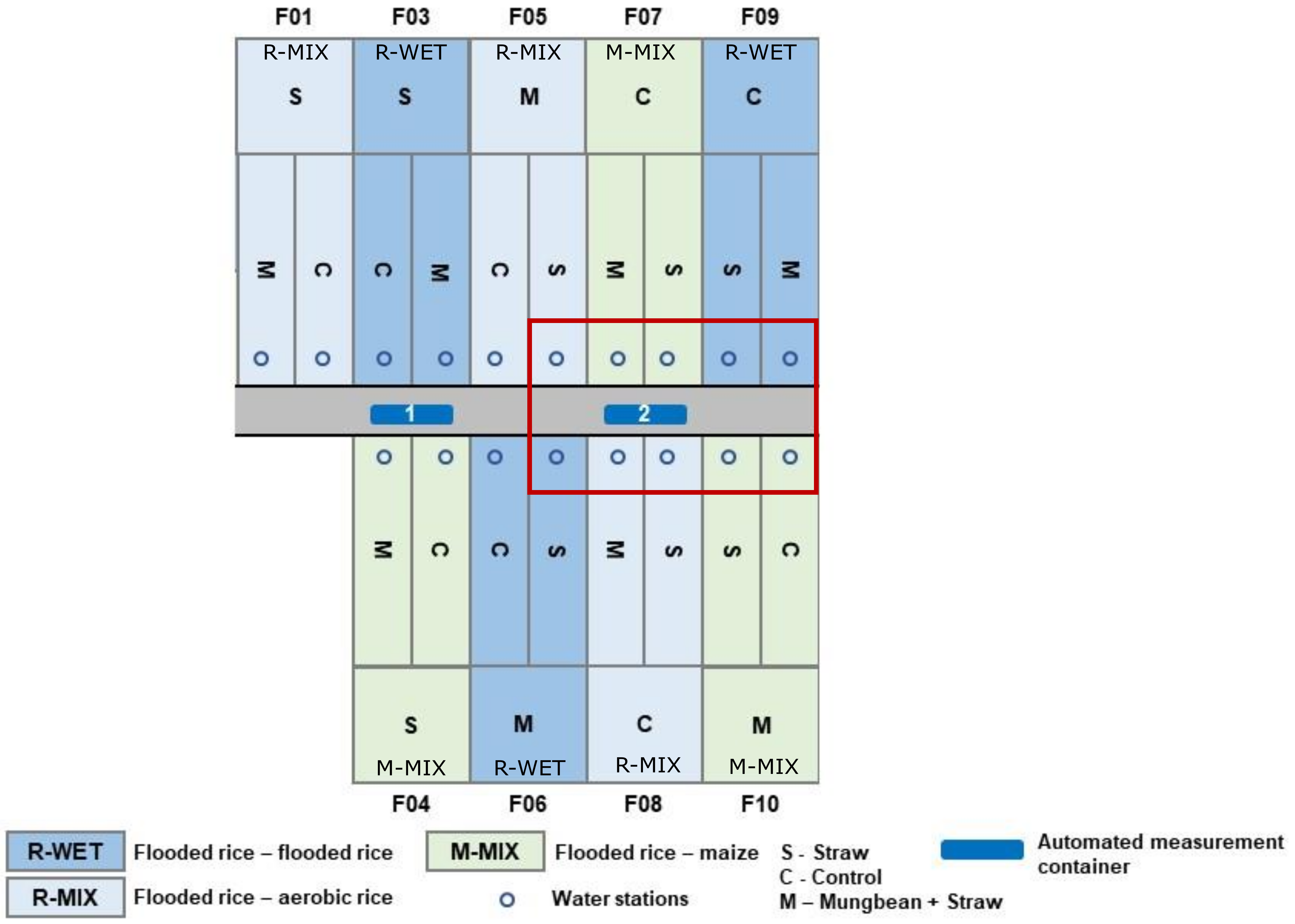
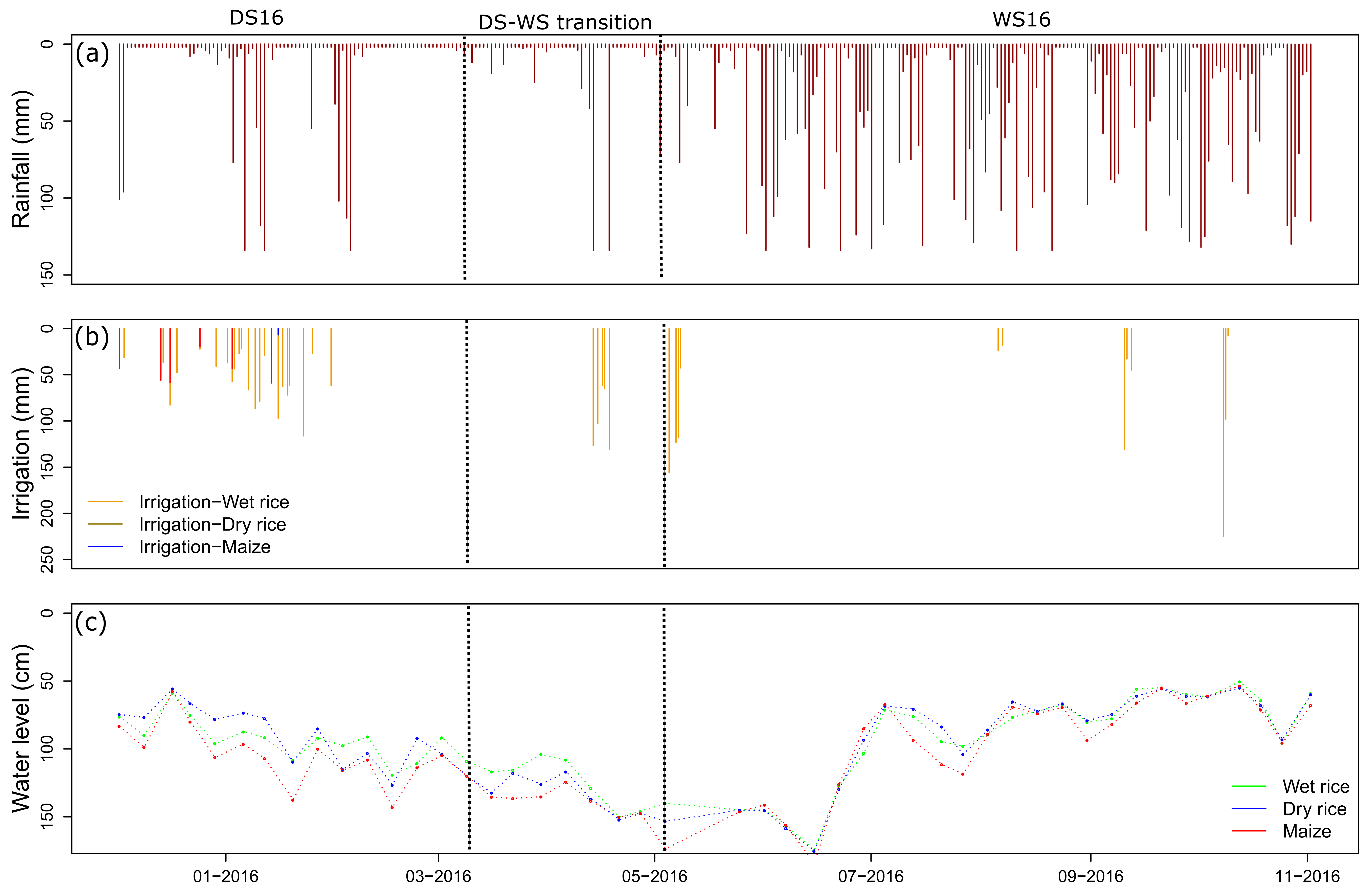
2.1. Field Site and Management
2.2. Automatic Analytical System
2.3. Isotopic Analysis
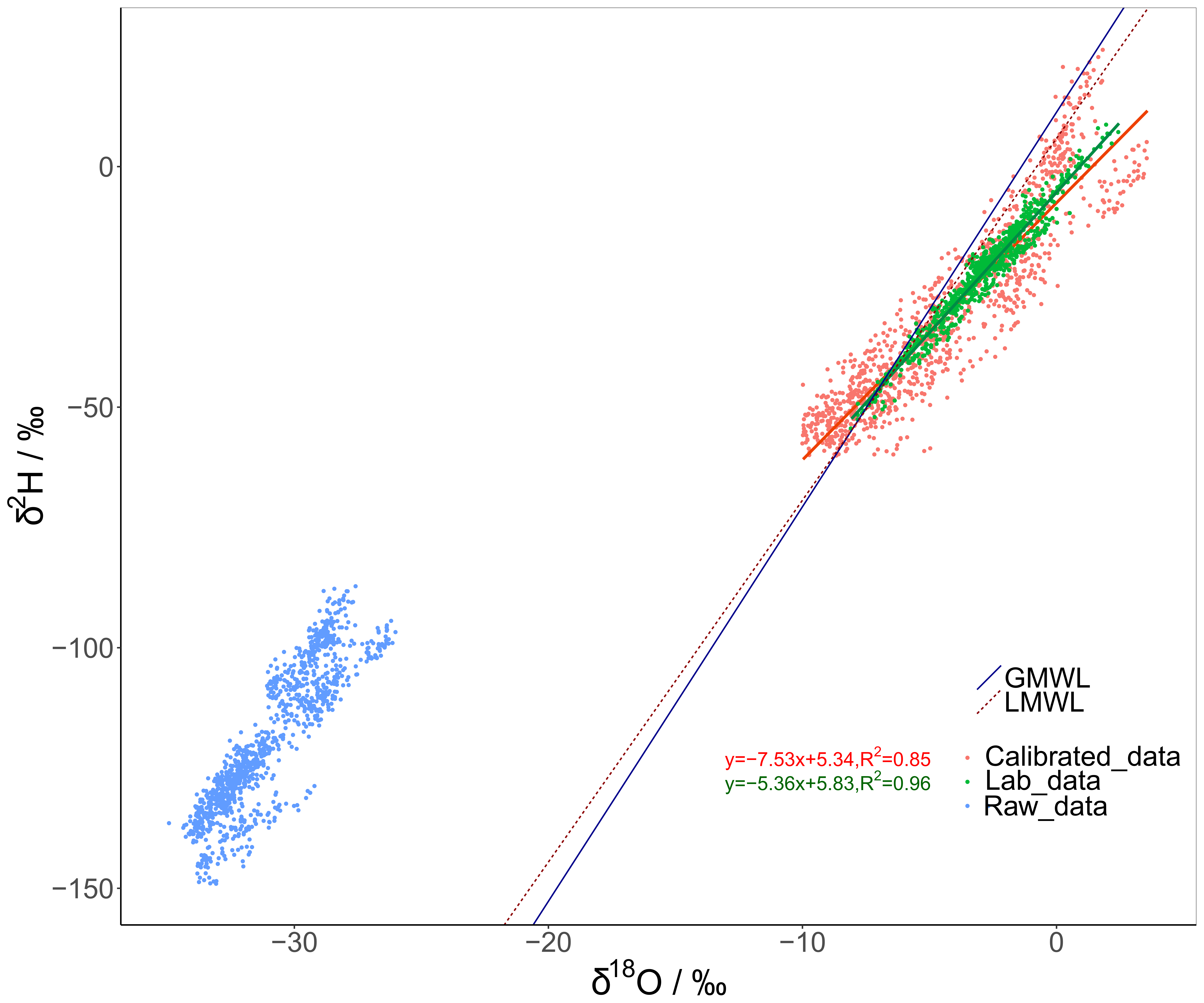
2.4. Raw Data Correction and Calibration
- The sample has already been in the diffusion cell for at least 300 s (and therefore safely beyond the lag time).
- The slope of a linear regression for the δ signals as a function of time is less than 0.002‰ s−1 for 2H and 0.005‰ s−1 for 18O.
- The coefficient of determination (R2) of the δ signals is less than 0.05 over plateau time.
- The vapor content is above 15,000 ppm.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Estimation of the Relative Extent of Evaporation
2.7. Assessing Water Provenance of Surface and Groundwater
2.8. Daily Variation of Isotopic Values
3. Results
3.1. System Calibrated Data and Lab Data Comparison
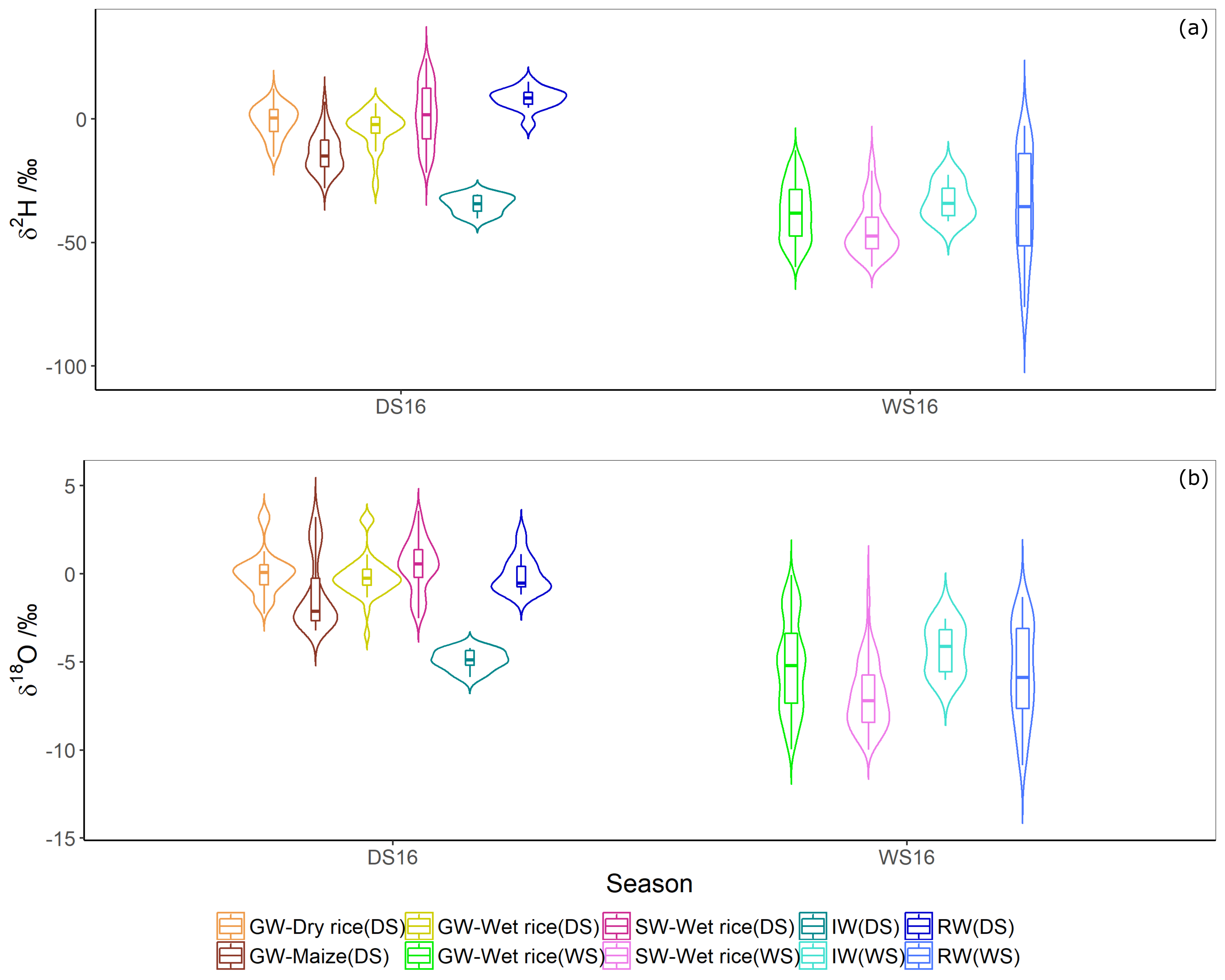
3.2. Isotope Composition of Crops
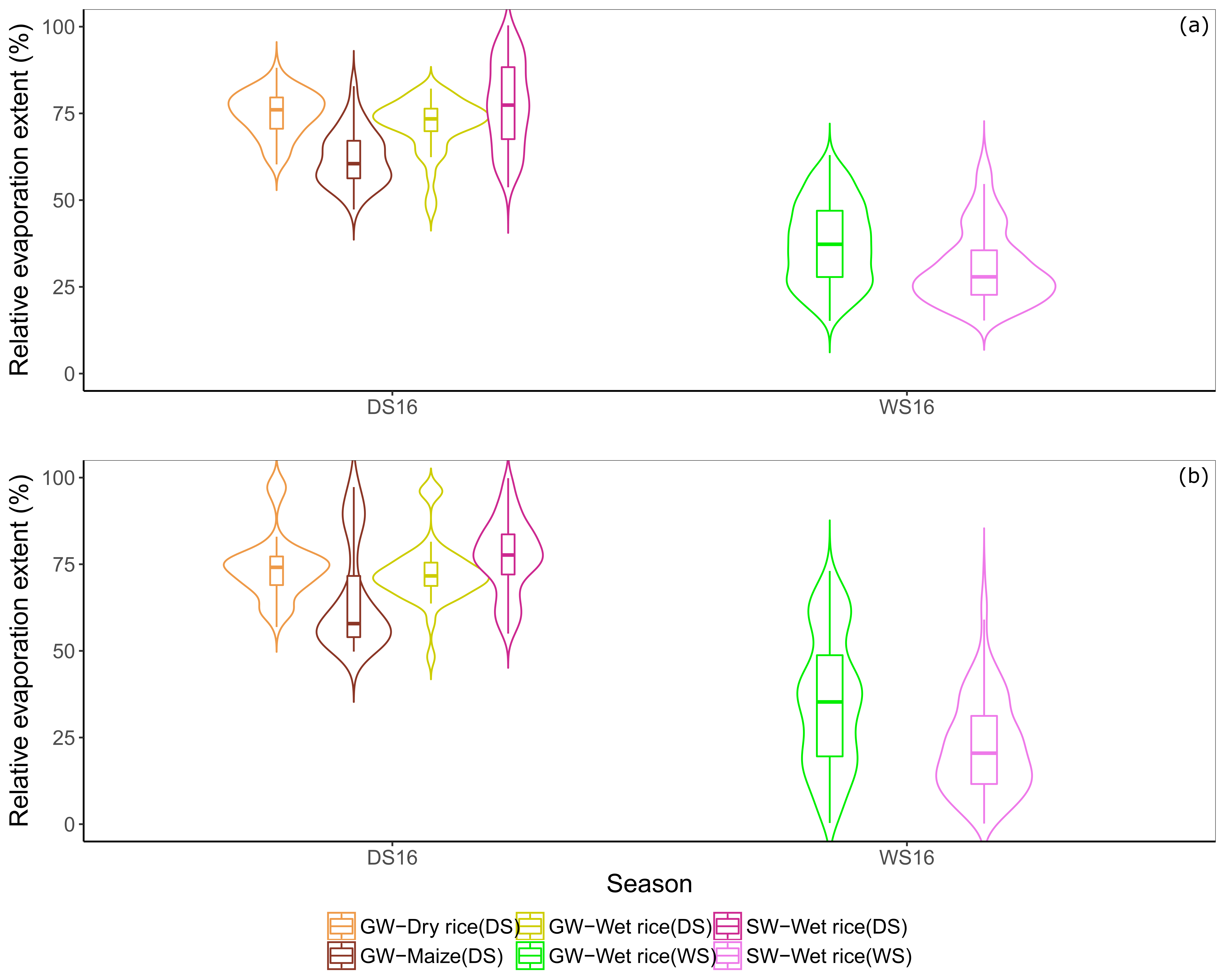
3.3. Estimation of the Relative Extent of Evaporation
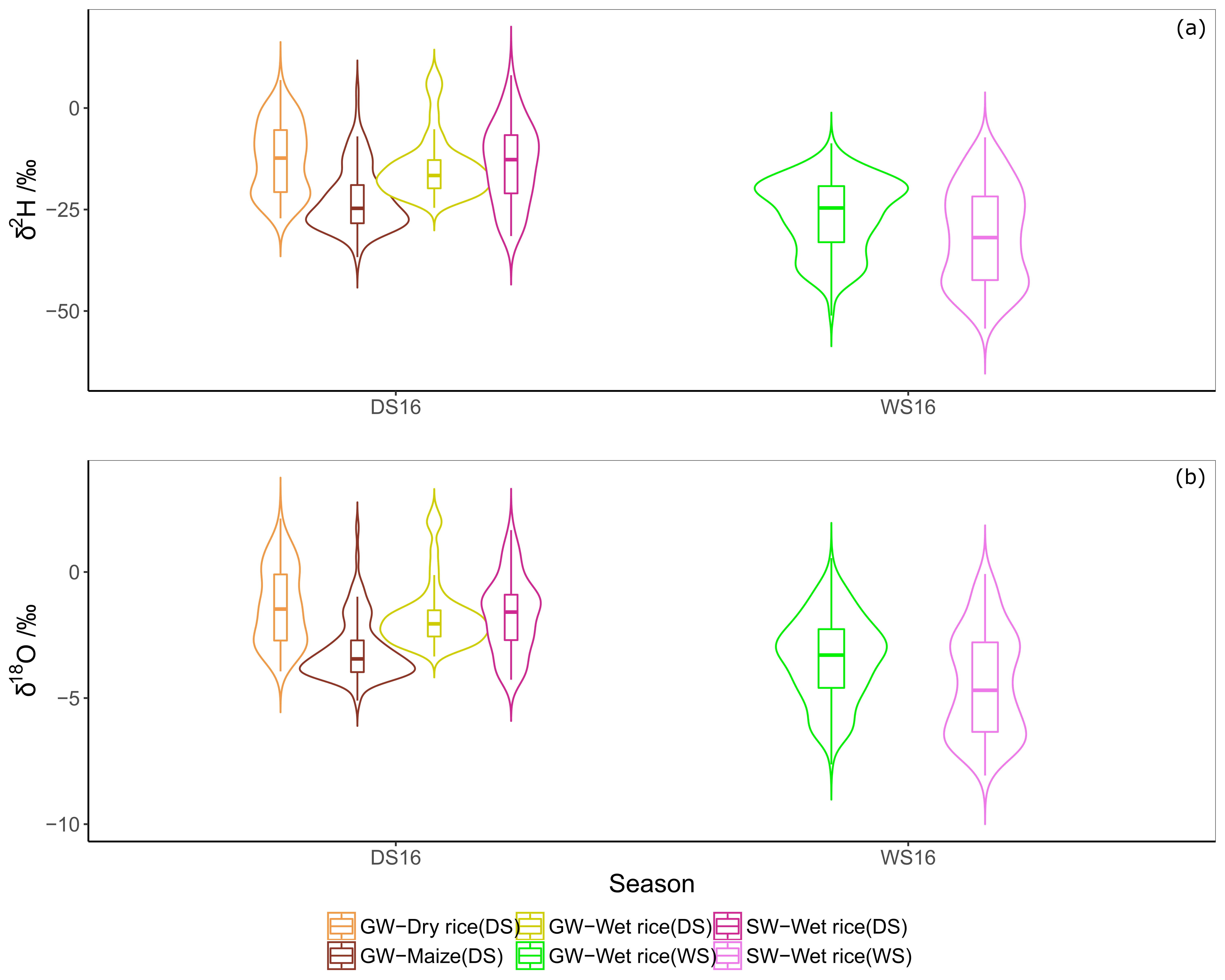
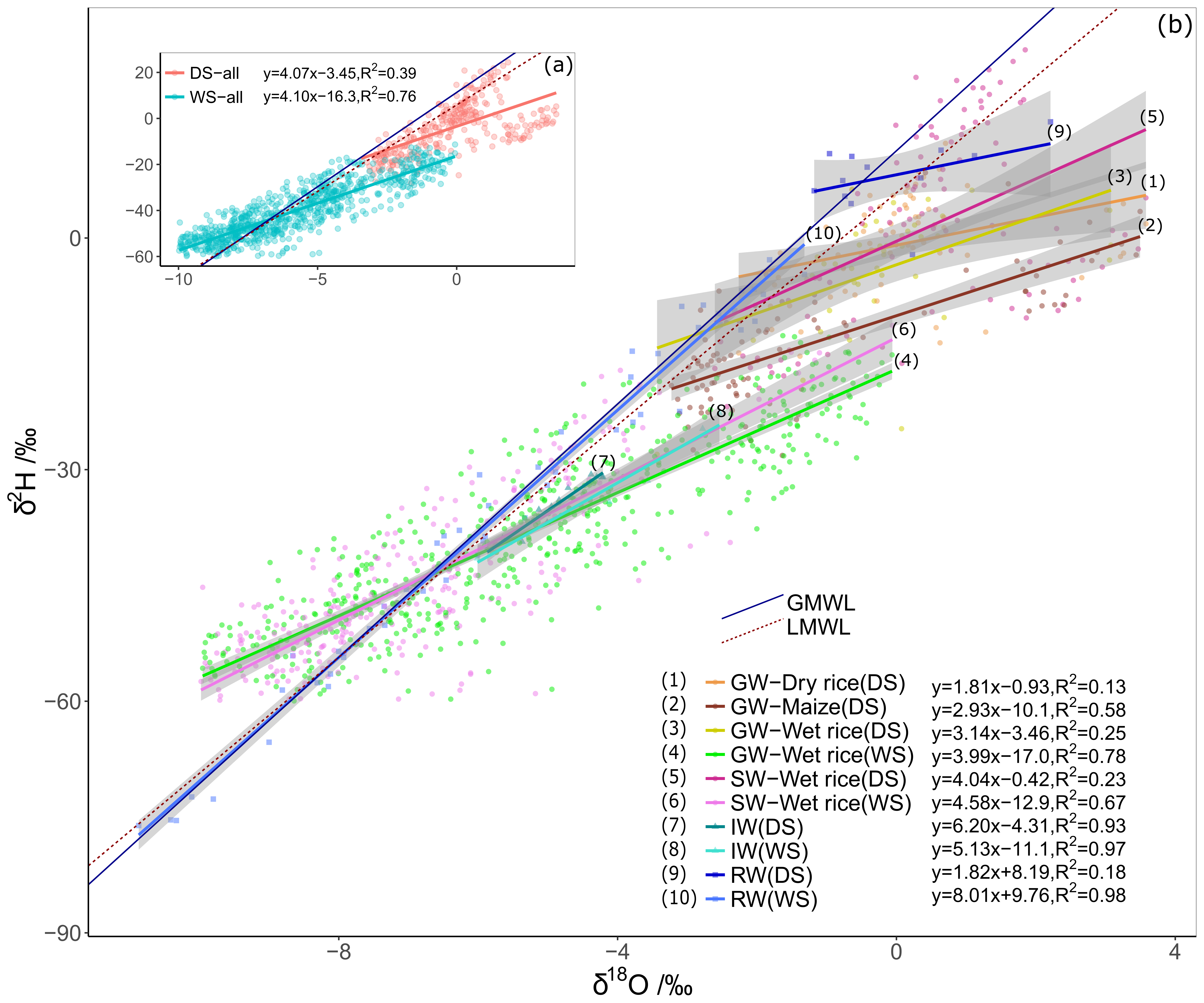
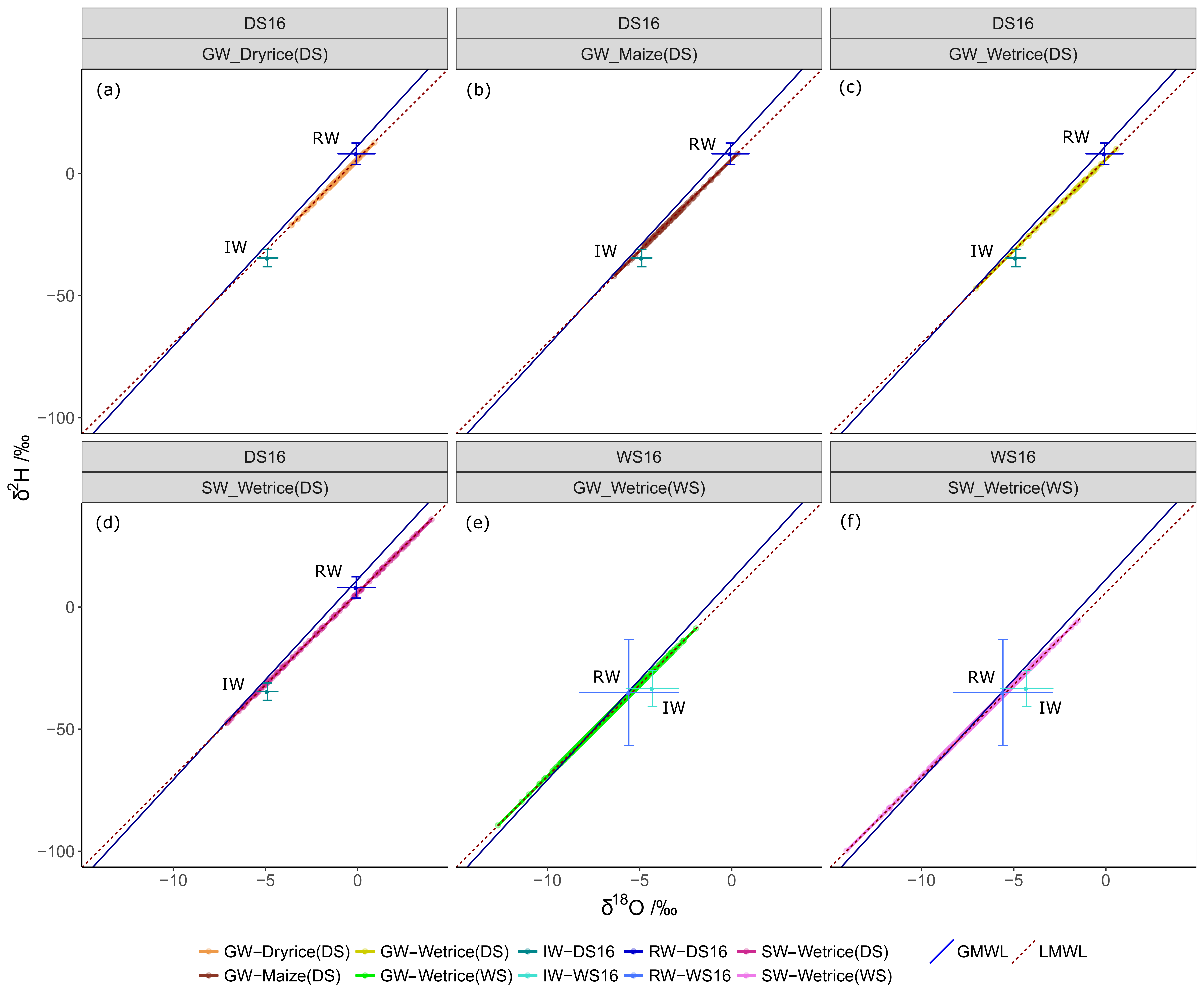
3.4. Assessment of Water Provenance in Surface and Groundwater
3.5. Daily Variation of Isotopic Values
4. Discussion
4.1. Isotope Composition of Water Sources
4.2. Relative Evaporation Extent
4.3. Origin of Water Sources
4.4. Sub-Daily Fluctuation of Surface and Groundwater
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclean, J.L.; Dawe, D.C.; Hettel, G.P. Rice Almanac: Source Book for the Most Important Economic Activity on Earth, 3rd ed.; International Rice Research Institute, Ed.; CABI Publishing: Oxon, UK, 2002; ISBN 978-0-85199-636-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bouman, B.A.M.; Tuong, T.P. Field water management to save water and increase its productivity in irrigated lowland rice. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 49, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, S.J.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. Review of measured crop water productivity values for irrigated wheat, rice, cotton and maize. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 69, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, H.J.; Herczeg, A.L.; Meyer, W.S. Stable isotope ratios in irrigation water can estimate rice crop evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, J.; Song, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; He, B. Spatial and temporal patterns of stable water isotopes along the Yangtze River during two drought years. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I. Stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures. In Spoleto; Tongiorgi, T., Ed.; Laboratory of Geology and Nuclear Science: Spoleto, Italy, 1965; pp. 9–130. [Google Scholar]
- Klaus, J.; Zehe, E.; Elsner, M.; Külls, C.; McDonnell, J.J. Macropore flow of old water revisited: Experimental insights from a tile-drained hillslope. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, T.H.M.; Weiler, M. Continual in situ monitoring of pore water stable isotopes in the subsurface. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 1819–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.J.; Beven, K. Debates—The future of hydrological sciences: A (common) path forward? A call to action aimed at understanding velocities, celerities and residence time distributions of the headwater hydrograph. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 5342–5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narancic, B.; Wolfe, B.B.; Pienitz, R.; Meyer, H.; Lamhonwah, D. Landscape-gradient assessment of thermokarst lake hydrology using water isotope tracers. J. Hydrol. 2017, 545, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Tetzlaff, D.; Soulsby, C. Stable isotopes reveal evaporation dynamics at the soil-plant-atmosphere interface of the critical zone. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, W.G.; Bowes, M.J. A long-term study of stable isotopes as tracers of processes governing water flow and quality in a lowland river basin: The upper Thames, UK. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 2178–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, K.J.; McDonnell, J.J. Tracer advances in catchment hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 5135–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Prabakaran, M.; Yang, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H. Authenticity of rice (Oryza sativa L.) geographical origin based on analysis of C, N, O and S stable isotope ratios: A preliminary case report in Korea, China and Philippine. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, R.; Ghosh, P. Stable Oxygen and Carbon Isotopic Composition of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Grains as Recorder of Relative Humidity. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakashita, R.; Korenaga, T. Responses of carbon and oxygen stable isotopes in rice grain (Oryza sativa L.) to an increase in air temperature during grain filling in the Japanese archipelago. Ecol. Res. 2014, 29, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahindawansha, A.; Orlowski, N.; Kraft, P.; Rothfuss, Y.; Racela, H.; Breuer, L. Quantification of plant water uptake by water stable isotopes in rice paddy systems. Plant Soil 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lee, X.; Wen, X.; Xiao, W. Evapotranspiration partitioning for three agro-ecosystems with contrasting moisture conditions: A comparison of an isotope method and a two-source model calculation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 252, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, J.P.; Simpson, H.J.; Herczeg, A.L.; Whitehead, R.; Walker, G.R. Stable isotope composition of water vapor as an indicator of transpiration fluxes from rice crops. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Li, F.; Li, S.; Ding, R.; Tong, L. Quantification of maize water uptake from different layers and root zones under alternate furrow irrigation using stable oxygen isotope. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 168, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, X. Using stable isotopes to determine seasonal variations in water uptake of summer maize under different fertilization treatments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, F.; Ai, Z.; Li, J.; Gu, C. Stable isotope evidences for identifying crop water uptake in a typical winter wheat-summer maize rotation field in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCool, W.C.; Coltrain, J.B. A Potential Oxygen Isotope Signature of Maize Beer Consumption: An Experimental Pilot Study. Ethnoarchaeology 2018, 10, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, T.; Ding, R.; Tong, L.; Li, S.; Wang, L. Multiple Methods to Partition Evapotranspiration in a Maize Field. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Cui, Y.L. Real-time forecasting of irrigation water requirements of paddy fields. Agric. Water Manag. 1996, 31, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trout, T.J.; DeJonge, K.C. Crop Water Use and Crop Coefficients of Maize in the Great Plains. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2018, 144, 04018009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouman, B.A.M. Water Management in Irrigated Rice: Coping with Water Scarcity; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2007; ISBN 978-971-22-0219-3.
- Tabbal, D.F.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Bhuiyan, S.I.; Sibayan, E.B.; Sattar, M.A. On-farm strategies for reducing water input in irrigated rice; case studies in the Philippines. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 56, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuong, T.P.; Bhuiyan, S.I. Increasing water-use efficiency in rice production: Farm-level perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 1999, 40, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, M.; Bamouh, A.; Karrou, M.; El Mourid, M. Estimation of rice evapotranspiration using a microlysimeter technique and comparison with FAO Penman-Monteith and Pan evaporation methods under Moroccan conditions. Agronomie 2003, 23, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Cui, J.-Y.; Zhang, T.-H.; Zhao, H.-L. Measurement of evapotranspiration of irrigated spring wheat and maize in a semi-arid region of north China. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 61, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freyberg, J.; Studer, B.; Kirchner, J.W. A lab in the field: High-frequency analysis of water quality and stable isotopes in stream water and precipitation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1721–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, E.S.F.; Gupta, M.; Gabrielli, C.; Garland, T.; McDonnell, J.J. High-frequency field-deployable isotope analyzer for hydrological applications. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W.; Feng, X.; Neal, C.; Robson, A.J. The fine structure of water-quality dynamics: The (high-frequency) wave of the future. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhorst, D.; Kraft, P.; Timbe, E.; Frede, H.-G.; Breuer, L. Stable water isotope tracing through hydrological models for disentangling runoff generation processes at the hillslope scale. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 4113–4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.; Ford, W.; Fox, J.; Husic, A. Improving In-Stream Nutrient Routines in Water Quality Models Using Stable Isotope Tracers: A Review and Synthesis. Trans. ASABE 2018, 61, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Coplen, T.B.; Aggarwal, P.K. Approaches for Achieving Long-Term Accuracy and Precision of δ18O and δ2H for Waters Analyzed using Laser Absorption Spectrometers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbstritt, B.; Gralher, B.; Weiler, M. Continuous in situ measurements of stable isotopes in liquid water. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W03601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangle, L.A.; Klaus, J.; Berman, E.S.F.; Gupta, M.; McDonnell, J.J. A new multisource and high-frequency approach to measuring δ2H and δ18O in hydrological field studies. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 7797–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, E.; Kraft, P.; Buchen, C.; Frede, H.-G.; Aquino, E.; Breuer, L. Set up of an Automatic Water Quality Sampling System in Irrigation Agriculture. Sensors 2013, 14, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, S.W.; Desilets, S.L.E.; Troch, P.A. Characterizing the response of a catchment to an extreme rainfall event using hydrometric and isotopic data. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W06413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, K.; Boll, J.; Sánchez-Murillo, R.; Roupsard, O. Isotope hydrology of a tropical coffee agroforestry watershed: Seasonal and event-based analyses. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 1965–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munksgaard, N.C.; Wurster, C.M.; Bird, M.I. Continuous analysis of δ18O and δD values of water by diffusion sampling cavity ring-down spectrometry: A novel sampling device for unattended field monitoring of precipitation, ground and surface waters. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 3706–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassenaar, L.I.; Athanasopoulos, P.; Hendry, M.J. Isotope hydrology of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Okanagan Valley, British Columbia, Canada. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.M.; Munksgaard, N.C.; O’Grady, D.; Williams, M.J.M.; Bostock, H.C.; Rintoul, S.R.; Bird, M.I. Continuous shipboard measurements of oceanic δ18O, δD and δ13CDIC along a transect from New Zealand to Antarctica using cavity ring-down isotope spectrometry. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 137, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munksgaard, N.C.; Zwart, C.; Kurita, N.; Bass, A.; Nott, J.; Bird, M.I. Stable Isotope Anatomy of Tropical Cyclone Ita, North-Eastern Australia, April 2014. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tweed, S.; Munksgaard, N.; Marc, V.; Rockett, N.; Bass, A.; Forsythe, A.J.; Bird, M.I.; Leblanc, M. Continuous monitoring of stream δ18O and δ2H and stormflow hydrograph separation using laser spectrometry in an agricultural catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, M.C.R.; Quilty, J.R.; Buresh, R.J.; Wassmann, R.; Haidar, S.; Correa, T.Q.; Sandro, J.M. Actual evapotranspiration and dual crop coefficients for dry-seeded rice and hybrid maize grown with overhead sprinkler irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 136, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.K.D. Principles and Practices of Rice Production; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 1981; pp. 259–297. ISBN 978-0-471-09760-0. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Siemens, J.; Amelung, W.; Goldbach, H.; Wassmann, R.; Alberto, M.C.R.; Lücke, A.; Lehndorff, E. Carbon release from rice roots under paddy rice and maize–paddy rice cropping. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 210, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, B.; Tanweer, A.; Kurttas, T. IAEA Standard Operating Procedure for the Liquid-Water Stable Isotope Analyser; Laser Proced IAEA Water Resour Programme: Vienna, Austria, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rozanski, K.; Araguás-Araguás, L.; Gonfiantini, R. Isotopic Patterns in Modern Global Precipitation. In Climate Change in Continental Isotopic Records; Swart, P.K., Lohmann, K.C., Mckenzie, J., Savin, S., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 1–36. ISBN 978-1-118-66402-5. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, H. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science 1961, 133, 1702–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Statistical Treatment of Data on Environmental Isotopes in Precipitation; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 1992.
- Crawford, J.; Hughes, C.E.; Lykoudis, S. Alternative least squares methods for determining the meteoric water line, demonstrated using GNIP data. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2331–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Geldern, R.; Barth, J.A.C. Optimization of instrument setup and post-run corrections for oxygen and hydrogen stable isotope measurements of water by isotope ratio infrared spectroscopy (IRIS). Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 1024–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, W.A.; Coplen, T.B.; Aerts-Bijma, A.T.; Böhlke, J.K.; Gehre, M.; Geilmann, H.; Gröning, M.; Jansen, H.G.; Meijer, H.A.J.; Mroczkowski, S.J.; et al. Comprehensive inter-laboratory calibration of reference materials for δ18O versus VSMOW using various on-line high-temperature conversion techniques. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 999–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple Comparisons Using Rank Sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 5th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall Up: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A.; Magnone, D.; Boyce, A.J.; Casanueva-Marenco, M.J.; van Dongen, B.E.; Ballentine, C.J.; Polya, D.A. Delineating sources of groundwater recharge in an arsenic-affected Holocene aquifer in Cambodia using stable isotope-based mixing models. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Külls, C. Environmental Tracers. In Tracers in Hydrology; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 13–56. ISBN 978-0-470-74714-8. [Google Scholar]
- Geyh, M.A.; Ploethner, D. Isotope Hydrological Study in Eastern Owambo, Etosha Pan, Otavi Mountain Land and Central Omatako Catchment Including Waterberg Plateau; German-Namibian Groundwater Exploration Project. Technical Cooperation Project No. 89 2034. 0., Follow-up report, 2,34 p; Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources Hannover: Hannover, Germany, 1997.
- Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Johnsen, S.J.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Stenni, B.; Risi, C.; Sodemann, H.; Balslev-Clausen, D.; Blunier, T.; Dahl-Jensen, D.; Ellehøj, M.D.; et al. Continuous monitoring of summer surface water vapor isotopic composition above the Greenland Ice Sheet. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4815–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, W.G. Hydrological factors in the interpretation of stable isotopic proxy data present and past: A European perspective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2004, 23, 743–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benettin, P.; Volkmann, T.H.; von Freyberg, J.; Frentress, J.; Penna, D.; Dawson, T.E.; Kirchner, J.W. Effects of climatic seasonality on the isotopic composition of evaporating soil waters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, C.; Coplen, T.B. Distribution of oxygen-18 and deuterium in river waters across the United States. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 1363–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helliker, B.R.; Ehleringer, J.R. Grass blades as tree rings: Environmentally induced changes in the oxygen isotope ratio of cellulose along the length of grass blades. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbour, M.M.; Farquhar, G.D. Relative humidity- and ABA-induced variation in carbon and oxygen isotope ratios of cotton leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2000, 23, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonfiantini, R. On the isotopic composition of precipitation in tropical stations (*). Acta Amaz. 1985, 15, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, C.J.; Allison, G.B. Tracing of water movement in the unsaturated zone using stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen. J. Hydrol. 1988, 100, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Herczeg, A.L.; Barnes, C. Isotope Engineering—Using Stable Isotopes of the Water Molecule to Solve Practical Problems. In Environmental Tracers in Subsurface Hydrology; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; pp. 79–110. ISBN 978-1-4613-7057-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; da SL Sternberg, L. Hydrogen Isotopic Fractionation by Plant Roots during Water Uptake in Coastal Wetland Plants. In Stable Isotopes and Plant Carbon-Water Relations; Ehleringer, J.R., Hall, A.E., Farquhar, G.D., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 497–510. ISBN 978-0-12-233380-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ellsworth, P.Z.; Williams, D.G. Hydrogen isotope fractionation during water uptake by woody xerophytes. Plant Soil 2007, 291, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplen, T.B.; Hanshaw, B.B. Ultrafiltration by a compacted clay membrane—I. Oxygen and hydrogen isotopic fractionation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1973, 37, 2295–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerter, E.; Finstad, K.; Schaefer, J.; Goldsmith, G.R.; Dawson, T.; Amundson, R. Oxygen isotope fractionation effects in soil water via interaction with cations (Mg, Ca, K, Na) adsorbed to phyllosilicate clay minerals. J. Hydrol. 2014, 515, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Horita, J. An experimental study on isotope fractionation in a mesoporous silica-water system with implications for vadose-zone hydrology. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2016, 184, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.; Dubois, K.; Veizer, J. Carbon and oxygen dynamics in the Laurentian Great Lakes: Implications for the CO2 flux from terrestrial aquatic systems to the atmosphere. Chem. Geol. 2011, 281, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danvi, A.; Giertz, S.; Zwart, S.J.; Diekkrüger, B. Rice Intensification in a Changing Environment: Impact on Water Availability in Inland Valley Landscapes in Benin. Water 2018, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, P.; Zhou, S.; Han, Z.; Tu, H.; Zhang, S. Seasonal variability of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in a wetland system of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, southwest China: A quantitative assessment of groundwater inflow fluxes. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liang, L.L.; Wang, L.; Jenerette, G.D.; McCabe, M.F.; Grantz, D.A. Partitioning of evapotranspiration using a stable isotope technique in an arid and high temperature agricultural production system. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuong, T.P.; Cabangon, R.J.; Wopereis, M.C.S. Quantifying Flow Processes during Land Soaking of Cracked Rice Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Tang, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, C. Using stable isotopes and major ions to identify hydrological processes and geochemical characteristics in a typical karstic basin, Guizhou, southwest China. Isotopes Environ. Health Stud. 2014, 50, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froehlich, K.F.O.; Gonfiantini, R.; Rozanski, K. Isotopes in Lake Studies: A Historical Perspective. In Isotopes in the Water Cycle; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 139–150. ISBN 978-1-4020-3010-9. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Lehndorff, E.; Amelung, W.; Wassmann, R.; Alberto, M.C.; von Unold, G.; Siemens, J. Drainage and leaching losses of nitrogen and dissolved organic carbon after introducing maize into a continuous paddy-rice crop rotation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 249, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, H.; Gordon, L.I. Deuterium and oxygen 18 variations in the ocean and the marine atmosphere. 1965, 17, 277–374. [Google Scholar]
- Skrzypek, G.; Mydłowski, A.; Dogramaci, S.; Hedley, P.; Gibson, J.J.; Grierson, P.F. Estimation of evaporative loss based on the stable isotope composition of water using Hydrocalculator. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkel, C.; Soulsby, C.; Tetzlaff, D.; Dunn, S.; Spezia, L. High-frequency storm event isotope sampling reveals time-variant transit time distributions and influence of diurnal cycles. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, B.; Barkan, E.; Yam, R.; Shemesh, A. Fractionation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in evaporating water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 6697–6703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.M.; Condon, L.E. Connections between groundwater flow and transpiration partitioning. Science 2016, 353, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
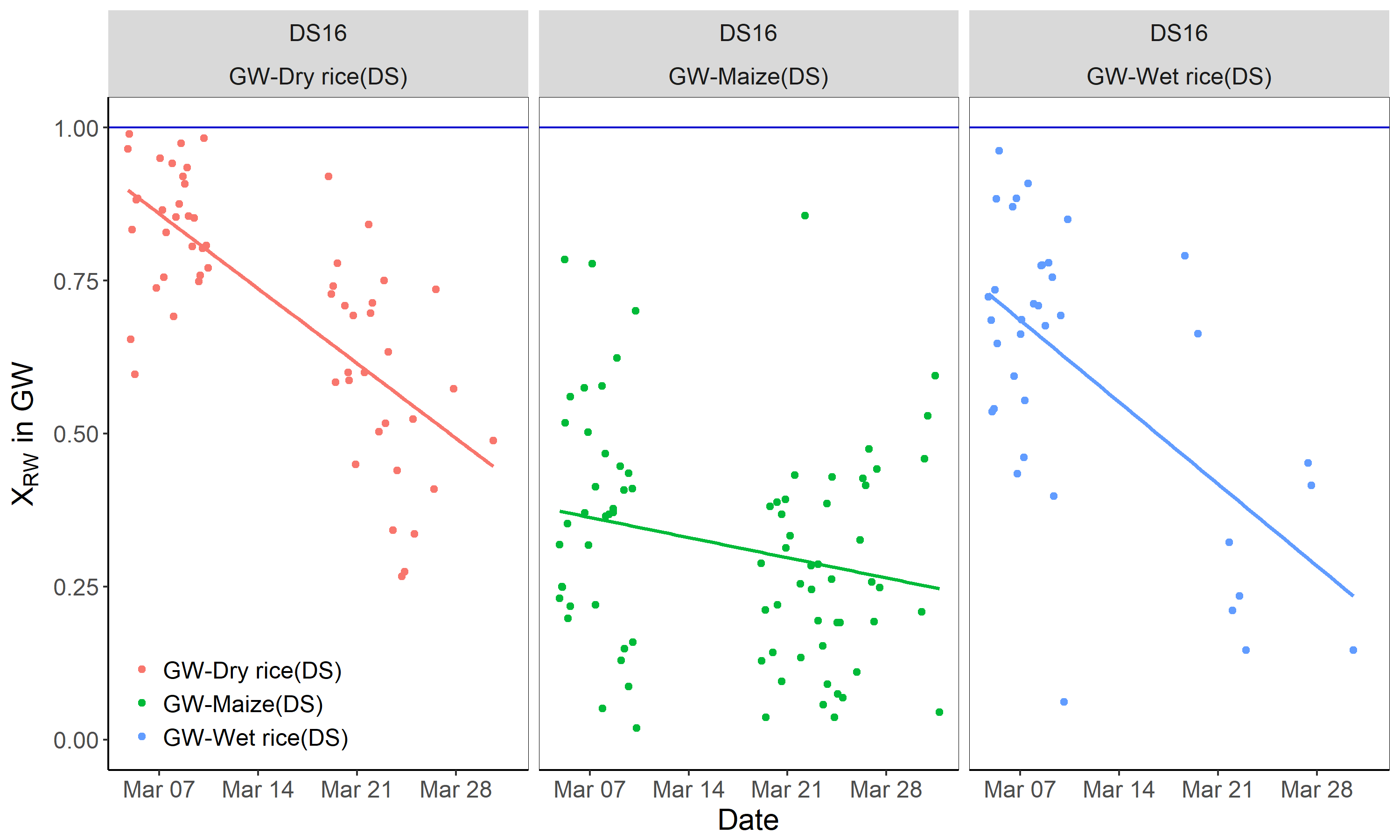
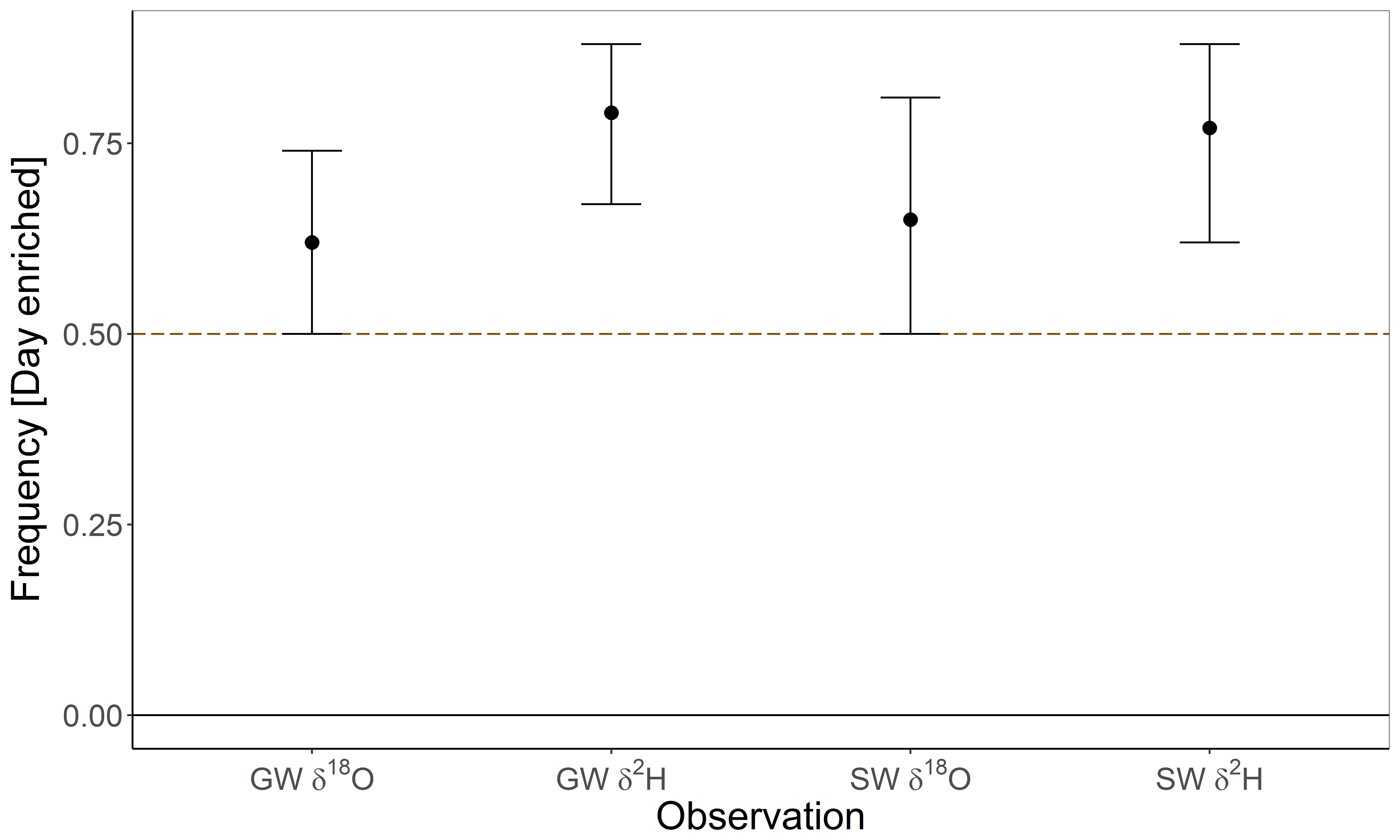
| Season | Water Type | Number of Observations | Calibrated Isotopic Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ2H ± SD [‰] | δ18O ± SD [‰] | |||
| DS | GW-Wet rice | 40 | −3.92 ± 7.6 | −0.14 ± 1.2 |
| GW-Dry rice | 67 | −0.80 ± 6.3 | 0.07 ± 1.2 | |
| GW-Maize | 88 | −13.5 ± 7.8 | −1.16 ± 2.0 | |
| SW-Wet rice | 101 | 1.54 ± 12.1 | 0.48 ± 1.4 | |
| WS | GW-Wet rice | 517 | −37.8 ± 11.6 | −5.2 ± 2.6 |
| SW-Wet rice | 269 | −44.6 ± 10.6 | −6.9 ± 1.9 | |
| (a) | ||||||
| GW | δ2Hday | δ2Hnight | δ18Oday | δ18Onight | δ2Hday− δ2Hnight | δ18Oday−δ18Onight |
| RHday | −0.618 ** | −0.639 ** | −0.675 ** | −0.658 ** | (0.008) | (−0.083) |
| RHnight | −0.530 ** | −0.547 ** | −0.547 ** | −0.551 ** | (−0.001) | (0.044) |
| RHday − RHnight | −0.471 ** | −0.490 ** | −0.567 ** | −0.523 ** | (0.020) | (−0.256) |
| Tday | 0.395 ** | 0.408 ** | 0.491 ** | 0.471 ** | (−0.002) | (0.106) |
| Tnight | (0.086) | (0.088) | (0.133) | (0.146) | (0.004) | (−0.086) |
| Tday − Tnight | 0.471 ** | 0.487 ** | 0.550 ** | 0.506 ** | (−0.008) | (0.263) |
| (b) | ||||||
| SW | δ2Hday | δ2Hnight | δ18Oday | δ18Onight | δ2Hday − δ2Hnight | δ18Oday − δ18Onight |
| RHday | −0.679 ** | −0.682 ** | −0.797 ** | −0.785 ** | (0.081) | (−0.097) |
| RHnight | −0.651 ** | −0.661 ** | −0.781 ** | −0.793 ** | (0.155) | (0.091) |
| RHday − RHnight | (−0.331) | (−0.317) | (−0.351) | (−0.292) | (−0.135) | −0.466 * |
| Tday | (0.345) | (0.354) | 0.465 * | 0.442 * | (−0.133) | (0.178) |
| Tnight | (0.123) | (0.138) | (0.261) | (0.271) | (−0.175) | (−0.079) |
| Tday − Tnight | (0.356) | (0.349) | (0.326) | (0.274) | (0.070) | 0.416 * |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahindawansha, A.; Breuer, L.; Chamorro, A.; Kraft, P. High-Frequency Water Isotopic Analysis Using an Automatic Water Sampling System in Rice-Based Cropping Systems. Water 2018, 10, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101327
Mahindawansha A, Breuer L, Chamorro A, Kraft P. High-Frequency Water Isotopic Analysis Using an Automatic Water Sampling System in Rice-Based Cropping Systems. Water. 2018; 10(10):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101327
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahindawansha, Amani, Lutz Breuer, Alejandro Chamorro, and Philipp Kraft. 2018. "High-Frequency Water Isotopic Analysis Using an Automatic Water Sampling System in Rice-Based Cropping Systems" Water 10, no. 10: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101327
APA StyleMahindawansha, A., Breuer, L., Chamorro, A., & Kraft, P. (2018). High-Frequency Water Isotopic Analysis Using an Automatic Water Sampling System in Rice-Based Cropping Systems. Water, 10(10), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101327





