Waters from the Djiboutian Afar: A Review of Strontium Isotopic Composition and a Comparison with Ethiopian Waters and Red Sea Brines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Geological Background and the Strontium Isotope Ratio of the Rocks
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
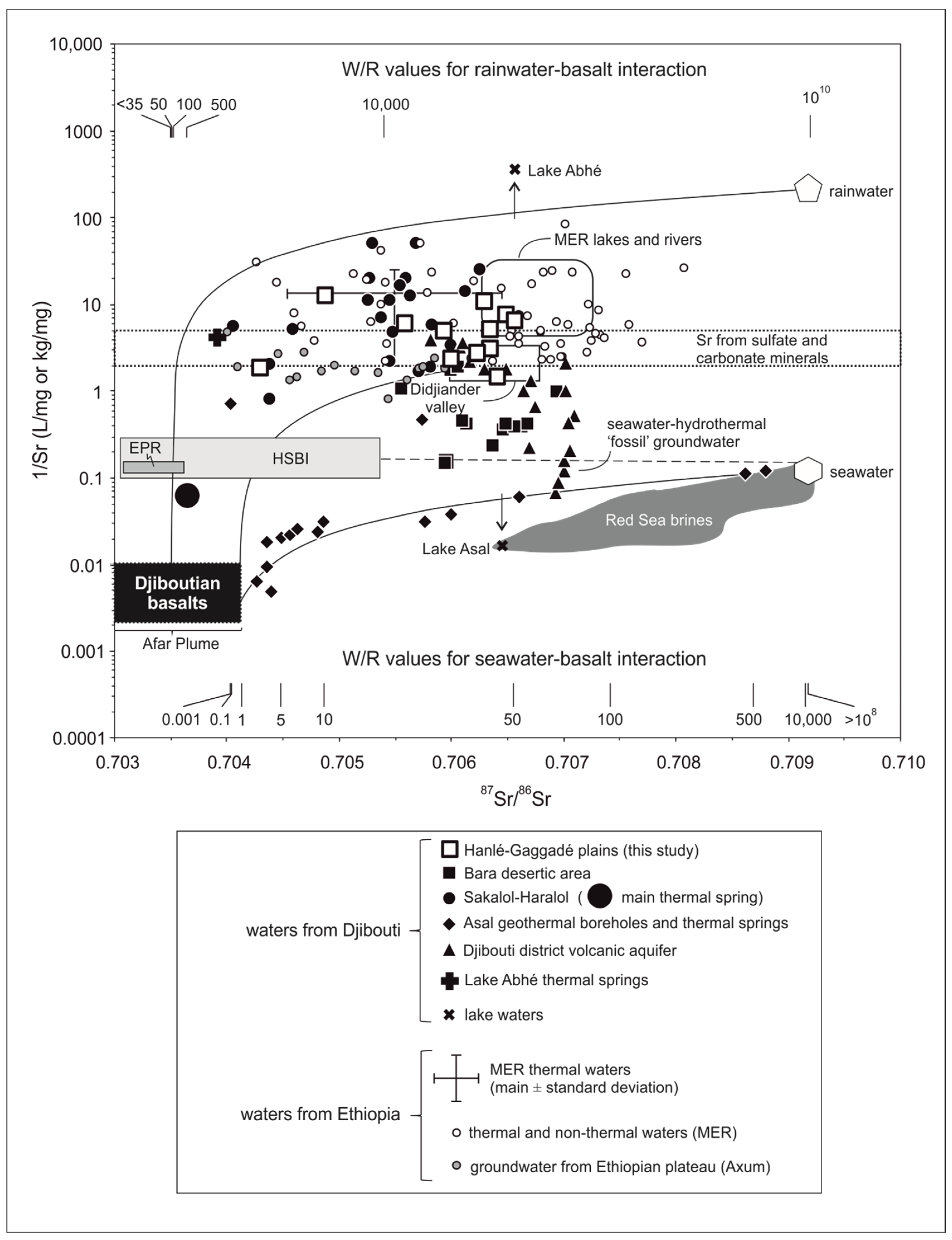
5. Discussion
5.1. Geothermal Waters and the Water/Rock Ratio
5.2. Hydrothermal Waters of Seawater Origin and Red Sea Bottom Brines
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varet, J. Geology of Afar (East Africa); Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Assowe, O.A. Geothermal development in Djibouti Republic. In Proceedings of the ARGeo—6th African Rift Geothermal Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Omenda, P. Geothermal Outlook in East Africa: Perspectives for Geothermal Development. Available online: http://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Events/2018/Jan/Geothermal-financing/S1-p1-IRENA-IGA-Presentation-31-01-2018.pdf?la=en&hash=52618994FFFF6833CFF3B51C6199982BC042741C (accessed on 20 July 2018).
- D’Amore, F.; Giusti, D.; Abdallah, A. Geochemistry of the high-salinity geothermal field of Asal, Republic of Djibouti, Africa. Geothermics 1998, 27, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The World Bank. Djibouti Geothermal Exploration Project—Republic of Djibouti—Draft Final Report; The World Bank Group: San Lorenzo in Campo, Italy, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Data Collection Survey on Geothermal Development in the Republic of Djibouti: Final Report, December 2014; JICA: Tokyo, Japan, 2014.
- Upton, K.; ÓDochartaigh, B.É.; Bellwood-Howard, I. Africa Groundwater Atlas: Hydrogeology of Djibouti. Available online: http://earthwise.bgs.ac.uk/index.php/Hydrogeology_of_Djibouti (accessed on 8 November 2018).
- Jalludin, M.; Razack, M. Assessment of hydraulic properties of sedimentary and volcanic aquifer systems under arid conditions in the Republic of Djibouti (Horn of Africa). Hydrogeol. J. 2004, 12, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellutini, P.; Piguet, P. Djibouti-Itinéraires géologiques; MECAD: Samrand Ave, South Africa, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bamse; Aymatth. Gregory Rift. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gregory_Rift_Topographical.svg (accessed on 9 November 2018).
- Barbieri, M.; Boschetti, T.; Petitta, M.; Tallini, M. Stable isotope (2H, 18O and 87Sr/86Sr) and hydrochemistry monitoring for groundwater hydrodynamics analysis in a karst aquifer (Gran Sasso, Central Italy). Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Morotti, M. Hydrogeochemistry and strontium isotopes of spring and mineral waters from Monte Vulture volcano, Italy. Appl. Geochem. 2003, 18, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.; Nigro, A.; Petitta, M. Groundwater mixing in the discharge area of San Vittorino Plain (Central Italy): Geochemical characterization and implication for drinking uses. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, C.D.; Toner, R.N. Strontium isotopic identification of water-rock interaction and ground water mixing. Groundwater 2004, 42, 418–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naftz, D.L.; Peterman, Z.E.; Spangler, L.E. Using δ87Sr values to identify sources of salinity to a freshwater aquifer, Greater Aneth Oil Field, Utah, USA. Chem. Geol. 1997, 141, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortecci, G.; Boschetti, T.; Mussi, M.; Lameli, C.H.; Mucchino, C.; Barbieri, M. New chemical and original isotopic data on waters from El Tatio geothermal field, northern Chile. Geochem. J. 2005, 39, 547–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Awadh, S.M.; Salvioli-Mariani, E. The origin and MgCl2-NaCl variations in an athalassic sag pond: Insights from chemical and isotopic data. Aquat. Geochem. 2018, 24, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Toscani, L.; Barbieri, M.; Mucchino, C.; Marino, T. Low enthalpy Na-chloride waters from the Lunigiana and Garfagnana grabens, Northern Apennines, Italy: Tracing fluid connections and basement interactions via chemical and isotopic compositions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 348, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, T.; Venturelli, G.; Toscani, L.; Barbieri, M.; Mucchino, C. The Bagni di Lucca thermal waters (Tuscany, Italy): An example of Ca-SO4 waters with high Na/Cl and low Ca/SO4 ratios. J. Hydrol. 2005, 307, 270–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Boschetti, T.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Kim, Y.; Baudron, P.; Kawalieh, A.D.; Ahmed, M.M.; Daoud, M.A.; Dabar, O.A.; Kadieh, I.H.; et al. Geochemical, multi-isotopic studies and geothermal potential evaluation of the complex Djibouti volcanic aquifer (Republic of Djibouti). Appl. Geochem. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, T.L.; Fullagar, P.D.; Spruill, R.K.; Sutton, L.C. Strontium isotopes and major elements as tracers of ground water evolution: Example from the Upper Castle Hayne Aquifer of North Carolina. Groundwater 2000, 38, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, N.O.; Andersen, M.S.; Engesgaard, P. Investigation of a dynamic seawater intrusion event using strontium isotopes (87Sr/86Sr). J. Hydrol. 2008, 348, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, A.; Sappa, G.; Barbieri, M. Strontium isotope as tracers of groundwater contamination. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 17, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.I.; Bickford, M.E.; Orrell, S.E. The use of strontium and lead isotopes to identify sources of water beneath the Fresh Kills landfill, Staten Island, New York, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2000, 15, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilomet, J.D.; Angeletti, B.; Moustier, S.; Ambrosi, J.P.; Wiesner, M.; Bottero, J.Y.; Chatelet-Snidaro, L. Application of strontium isotopes for tracing landfill leachate plumes in groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4675–4679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Baudron, P.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Boschetti, T.; Hoch, F.B.; Egueh, N.M.; Mohamed, J.; Dabar, O.A.; Masse-Dufresne, J.; Gassani, J. Recharge, groundwater flow pattern and contamination processes in an arid volcanic area: Insights from isotopic and geochemical tracers (Bara aquifer system, Republic of Djibouti). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 175, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Boschetti, T.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Baudron, P.; Kawalieh, A.D.; Dabar, O.A.; Ahmed, M.M.; Ahmed, S.I.; Daoud, M.A.; Egueh, N.M.; et al. Geochemical study of the Sakalol-Harralol geothermal field (Republic of Djibouti): Evidences of a low enthalpy aquifer between Manda-Inakir and Asal rift settings. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2017, 331, 26–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awaleh, M.O.; Hoch, F.B.; Boschetti, T.; Soubaneh, Y.D.; Egueh, N.M.; Elmi, S.A.; Jalludin, M.; Khaireh, M.A. The geothermal resources of the Republic of Djibouti—II: Geochemical study of the Lake Abhe geothermal field. J. Geochem. Explor. 2015, 159, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuan, B.; Michard, G.; Michard, A. Origine des substances dissoutes dans les eaux des sources thermales et des forages de la région Asal-Goubhet (République de Djibouti). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1990, 43, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G. Origin of Igneous Rocks: The Isotopic Evidence; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Furman, T.; Bryce, J.; Rooney, T.; Hanan, B.; Yirgu, G.; Ayalew, D. Heads and tails: 30 million years of the Afar plume. In The Afar Volcanic Province within the East African Rift System; Yirgu, G., Ebinger, C.J., Maguire, P.K.H., Eds.; The Geological Society of London: Bath, UK, 2006; Volume 259, pp. 95–119. [Google Scholar]
- Barrat, J.A.; Jahn, B.M.; Fourcade, S.; Joron, J.L. Magma genesis in an ongoing rifting zone: The Tadjoura Gulf (Afar area). Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 2291–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniel, C.; Vidal, P.; Coulon, C.; Vellutini, P.J.; Piguet, P. Temporal evolution of mantle sources during continental rifting: The volcanism of Djibouti (Afar). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1994, 99, 2853–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, P.; Deniel, C.; Vellutini, P.J.; Piguet, P.; Coulon, C.; Vincent, J.; Audin, J. Changes of mantle source in the course of a rift evolution: the Afar case. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1991, 18, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, T.O.; Hanan, B.B.; Graham, D.W.; Furman, T.; Blichert-Toft, J.; Schilling, J.-G. Upper mantle pollution during afar plume–continental rift interaction. J. Petrol. 2012, 53, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, J.G.; Kingsley, R.H.; Hanan, B.B.; McCully, B.L. Nd-Sr-Pb isotopic variations along the Gulf of Aden—Evidence for Afar mantle plume continental lithosphere interaction. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1992, 97, 10927–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trincherini, P.R.; Baffi, C.; Barbero, P.; Pizzoglio, E.; Spalla, S. Precise determination of strontium isotope ratios by TIMS to authenticate tomato geographical origin. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, W.A.; Papanastassiou, D.A.; Tombrello, T.A. Ca isotope fractionation on the Earth and other solar system materials. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1978, 42, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretzler, A.; Osenbrück, K.; Gloaguen, R.; Ruprecht, J.S.; Kebede, S.; Stadler, S. Groundwater origin and flow dynamics in active rift systems—A multi-isotope approach in the Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Hydrol. 2011, 402, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rango, T.; Petrini, R.; Stenni, B.; Bianchini, G.; Slejko, F.; Beccaluva, L.; Ayenew, T. The dynamics of central Main Ethiopian Rift waters: Evidence from δD, δ18O and 87Sr/86Sr ratios. Appl. Geochem. 2010, 25, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamichael, T.A. Water-Rock Interaction and Geochemistry of Groundwater in Axum Area (Northern Ethiopia). Ph.D. Thesis, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pik, R.; Deniel, C.; Coulon, C.; Yirgu, G.; Marty, B. Isotopic and trace element signatures of Ethiopian flood basalts: Evidence for plume–lithosphere interactions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2263–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArthur, J.M. Recent trends in strontium isotope stratigraphy. Terra Nova 1994, 6, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.D.; Griffith, E.M.; Buckley, W.P. Accuracy and precision of 88Sr/86Sr and 87Sr/86Sr measurements by MC-ICPMS compromised by high barium concentrations. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2014, 15, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, J.; Singh, S.K. 87Sr/86Sr and major ion composition of rainwater of Ahmedabad, India: Sources of base cations. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 63, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsellem, E.; Moynier, F.; Day, J.M.; Moreira, M.; Puchtel, I.S.; Teng, F.Z. The stable strontium isotopic composition of ocean island basalts, mid-ocean ridge basalts, and komatiites. Chem. Geol. 2018, 483, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G. Principle of Isotope Geology, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Dekov, V.M.; Egueh, N.M.; Kamenov, G.D.; Bayon, G.; Lalonde, S.V.; Schmidt, M.; Liebetrau, V.; Munnik, F.; Fouquet, Y.; Tanimizu, M.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonate chimneys from a continental rift (Afar Rift): Mineralogy, geochemistry, and mode of formation. Chem. Geol. 2014, 387, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhurst, D.L.; Appelo, C.A.J. Description of Input and Examples for PHREEQC Version 3—A Computer Program for Speciation, Batch-Reaction, One-Dimensional Transport, and Inverse Geochemical Calculations; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2013; p. 497.
- Warren, J.K. Evaporites—A Geological Compendium, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shikazono, N. Geochemical and Tectonic Evolution of Arc-Backarc Hydrothermal Systems—Implication for the Origin of Kuroko and epithermal Vein—Type Mineralizations and the Global Geochemical Cycle; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, T.; Cortecci, G.; Bolognesi, L. Chemical and isotopic compositions of the shallow groundwater system of Vulcano Island, Aeolian Archipelago, Italy: An update. GeoActa 2003, 2, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Boschetti, T.; Toscani, L.; Iacumin, P.; Selmo, E. Oxygen, hydrogen, boron and lithium isotope data of a natural spring water with an extreme composition: A fluid from the dehydrating slab? Aquat. Geochem. 2017, 23, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anschutz, P.; Blanc, G.; Stille, P. Origin of fluids and the evolution of the Atlantis II deep hydrothermal system, Red Sea: Strontium isotope study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 4799–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, G.; Boulègue, J.; Michard, A. Hydrothermal activity in Atlantis II Deep (Red Sea): Chemical and isotopic constraints from May 1985 water sampling. Sci. Géol. Bull. 1994, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Jones, L.M. Anomalous strontium in the Red Sea brines. In Hot Brines and Recent Heavy Metal Deposits in the Red Sea—A Geochemical and Geophysical Account; Degens, E.T., Ross, D.A., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1969; pp. 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- Pierret, M.C.; Clauer, N.; Bosch, D.; Blanc, G.; France-Lanord, C. Chemical and isotopic (87Sr/86Sr, δ18O, δD) constraints to the formation processes of Red-Sea brines. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2001, 65, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierenberg, R.A.; Shanks III, W.C. Isotopic constraints on the origin of the Atlantis II, Suakin and Valdivia brines, Red Sea. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarède, F.; Michard, A.; Minster, J.F.; Michard, G. 87Sr/86Sr ratios in hydrothermal waters and deposits from the East Pacific Rise at 21° N. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1981, 55, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elderfield, H.; Greaves, M.J. Strontium isotope geochemistry of Icelandic geothermal systems and implications for sea water chemistry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Damm, K.L. Seafloor hydrothermal activity: black smoker chemistry and chimneys. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 1990, 18, 173–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, M.; Seyfried Jr, W.E. Basalt-seawater interaction: trace element and strontium isotopic variations in experimentally altered glassy basalt. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1979, 44, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, M. Novel Chemical Tracers for Quantifying Marine Water-Rock Interactions. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, P.D.; Reardon, E.J.; Plummer, L.N.; Busenberg, E. Reaction paths and equilibrium end-points in solid-solution aqueous solution systems. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1990, 54, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, S. Groundwater in Ethiopia—Features, Numbers and Opportunities; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Jaluddin, M. Contribution à l’étude hydrogeologique des systémes aquiféres de la plaine du Hanle. Sci. Environ. 1989. Available online: http://www.scienceetenvironnement.dj/documents/Revue%20n%C2%B01-1989/Contribution%20%C3%A0%20l’%C3%A9tude%20hydrogeologique%20des%20syst%C3%A9mes%20aquif%C3%A9res%20de%20la%20plaine%20du%20Hanle..pdf (accessed on 20 November 2018).
- Fichtner. Projet pour l’évaluation des ressources géothermiques; Projet No. 610-1175; Fichtner GmbH & Co.: Stuttgart, Germany, 1981; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Barberi, F.; Civetta, L.; Varet, J. Sr isotopic composition of Afar volcanics and its implication for mantle evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 50, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, G.; Mensing, T.M. Isotopes: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefs, J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature: Basel, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dickin, A.P. Radiogenic Isotope Geology, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nier, A.O. The isotopic constitution of Strontium, Barium, Bismuth, Thallium and Mercury. Phys. Rev. 1938, 5, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.P. Water/rock interactions and the origin of H2O in granitic batholiths: Thirtieth William Smith lecture. J. Geol. Soc. 1977, 133, 509–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, M.T.; Gregory, R.T.; Wasserburg, G.J.; Taylor Jr, H.P. Sm-Nd, Rb-Sr, and 18O/16O isotopic systematics in an oceanic crustal section: Evidence from the Samail Ophiolite. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1981, 86, 2721–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Nions, R.K.; Carter, S.R.; Evensen, N.M.; Hamilton, P.J. Upper-mantle geochemistry. In The Sea—Ideas and Observations of Progress in the Study of the Seas; Emiliani, C., Ed. John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981; Volume 7, pp. 49–71. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, E. Evoluzione temporale dei Processi di Rifting Continentale ed interazione con un Punto Caldo di Mantello; Università degli Studi di Modena e Reggio-Emilia: Modena, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fouillac, A.M.; Fouillac, C.; Cesbron, F.; Pillard, F.; Legendre, O. Water-rock interaction between basalt and high-salinity fluids in the Asal Rift, Republic of Djibouti. Chem. Geol. 1989, 76, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berndt, M.E.; Seyfried Jr, W.E.; Beck, J.W. Hydrothermal alteration processes at midocean ridges: Experimental and theoretical constraints from Ca and Sr exchange reactions and Sr isotopic ratios. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1988, 93, 4573–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.M.; Sylva, S.P.; Ono, S.; German, C.R.; Seewald, J.S. Geochemistry of fluids from Earth’s deepest ridge-crest hot-springs: Piccard hydrothermal field, Mid-Cayman Rise. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2018, 228, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, B.; Deschamps, J.; Leleu, M.; Lopoukhine, M.; Marce, A.; Vilbert, C. The geothermal zone of Lake Assal (FTAI), geochemical and experimental studies. Geothermics 1977, 5, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafri, U.; Yechieli, Y.; Wollman, S.; Shalev, E. A possible brine supply from the Afar continental endorheic hyper saline lakes to the Red Sea bottom brine pools. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 8, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Name | Latitude N | Longitude E | Sample Type | * Chemical Facies | T (°C) | pH | * TDS (g/L) | Sr (mg/L) | 87Sr/86Sr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oudgini | 11°30.704’ | 41°56.500’ | spring | Na-Cl | 40 | 8.18 | 1.80 | 0.198 | 0.70635 |
| Agna | 11°34.059’ | 41°54.780’ | spring | Na-Cl | 41 | 8.21 | 1.67 | 0.094 | 0.70629 |
| Minkillé | 11°39.253’ | 41°57.032’ | spring | Na-Cl | 52 | 7.81 | 2.07 | 0.533 | 0.70430 |
| Sâgallé | 11°39.151’ | 41°54.646’ | spring | Na-Cl | 39 | 8.39 | 1.53 | 0.131 | 0.70649 |
| Ease-moydo | 11°40.302’ | 41°53.155’ | spring | Na-Cl | 36 | 8.75 | 2.69 | 0.326 | 0.70634 |
| Daggirou | 11°36.447’ | 41°58.613’ | spring | Na-Cl | 38 | 8.19 | 2.29 | 0.167 | 0.70559 |
| Dahotto | 11°37.531’ | 41°57.068’ | spring | Na-Cl | 40 | 8.01 | 2.46 | 0.202 | 0.70593 |
| Galafi | 11°42.203’ | 41°50.985’ | borehole | Na-HCO3 | 36 | 7.96 | 0.68 | 0.081 | 0.70488 |
| Hanlé 1 | 11°21.492’ | 42°8.349’ | borehole | Na-HCO3 | 36 | 7.90 | 0.44 | 0.690 | 0.70641 |
| Hanlé 2 | 11°23.921’ | 42°4.715’ | borehole | Na-HCO3 | 34 | 8.30 | 0.68 | 0.156 | 0.70656 |
| Daoudaouya | 11°45.623’ | 42°8.385’ | borehole | Mg/Na-HCO3 | 40 | 7.16 | 0.29 | 0.367 | 0.70623 |
| Mokoyta | 11°27.083’ | 42°15.991’ | well | Na-Cl | 32 | 7.89 | 1.89 | 0.432 | 0.70600 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boschetti, T.; Awaleh, M.O.; Barbieri, M. Waters from the Djiboutian Afar: A Review of Strontium Isotopic Composition and a Comparison with Ethiopian Waters and Red Sea Brines. Water 2018, 10, 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111700
Boschetti T, Awaleh MO, Barbieri M. Waters from the Djiboutian Afar: A Review of Strontium Isotopic Composition and a Comparison with Ethiopian Waters and Red Sea Brines. Water. 2018; 10(11):1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111700
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoschetti, Tiziano, Mohamed Osman Awaleh, and Maurizio Barbieri. 2018. "Waters from the Djiboutian Afar: A Review of Strontium Isotopic Composition and a Comparison with Ethiopian Waters and Red Sea Brines" Water 10, no. 11: 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111700
APA StyleBoschetti, T., Awaleh, M. O., & Barbieri, M. (2018). Waters from the Djiboutian Afar: A Review of Strontium Isotopic Composition and a Comparison with Ethiopian Waters and Red Sea Brines. Water, 10(11), 1700. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111700






