Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cyclicity of Radon (222Rn) in Groundwater, Giardino Spring, Central Apennines, Italy
Abstract
1. Introduction
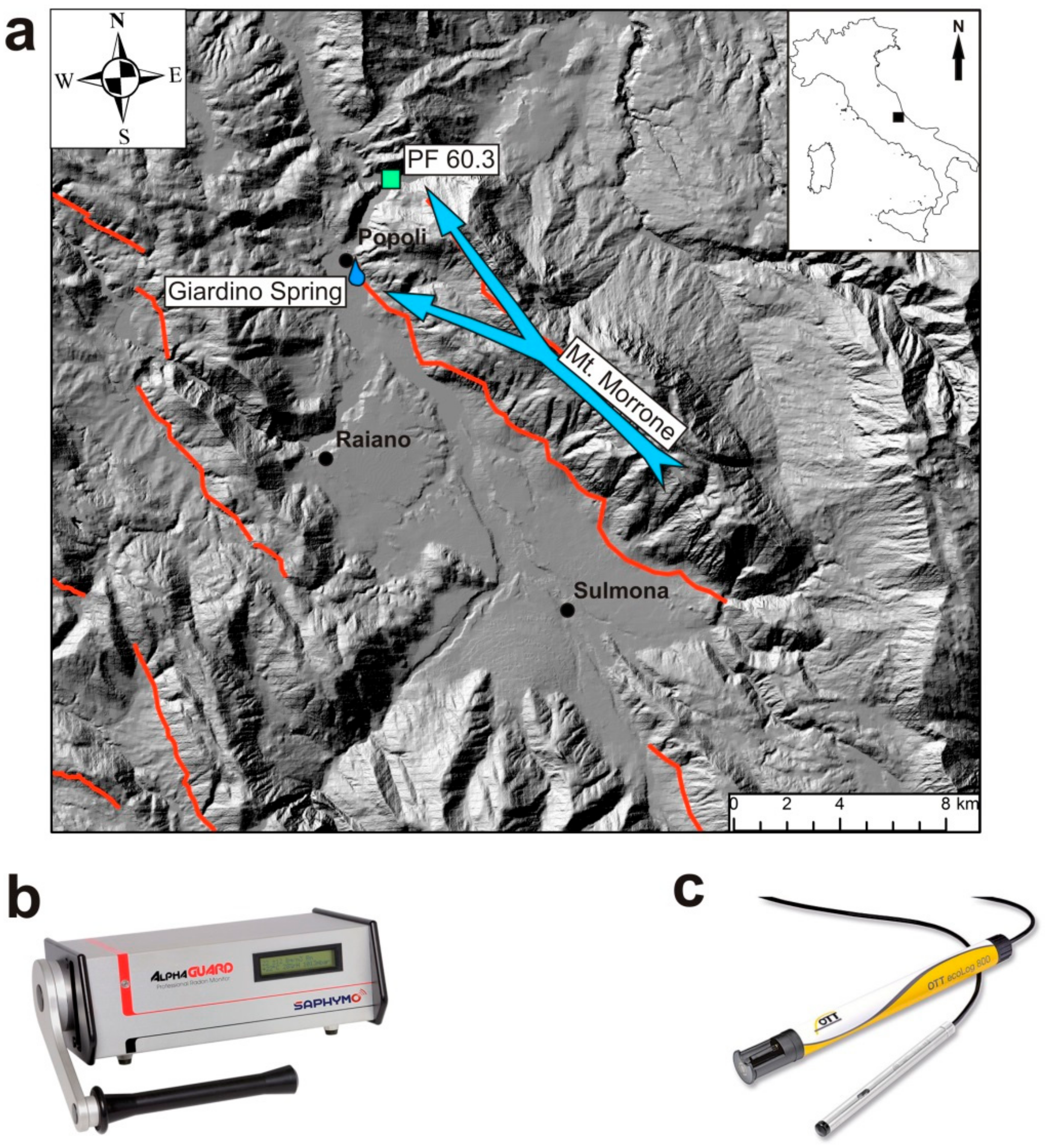
2. Geological and Hydrogeological Settings
3. Materials and Methods
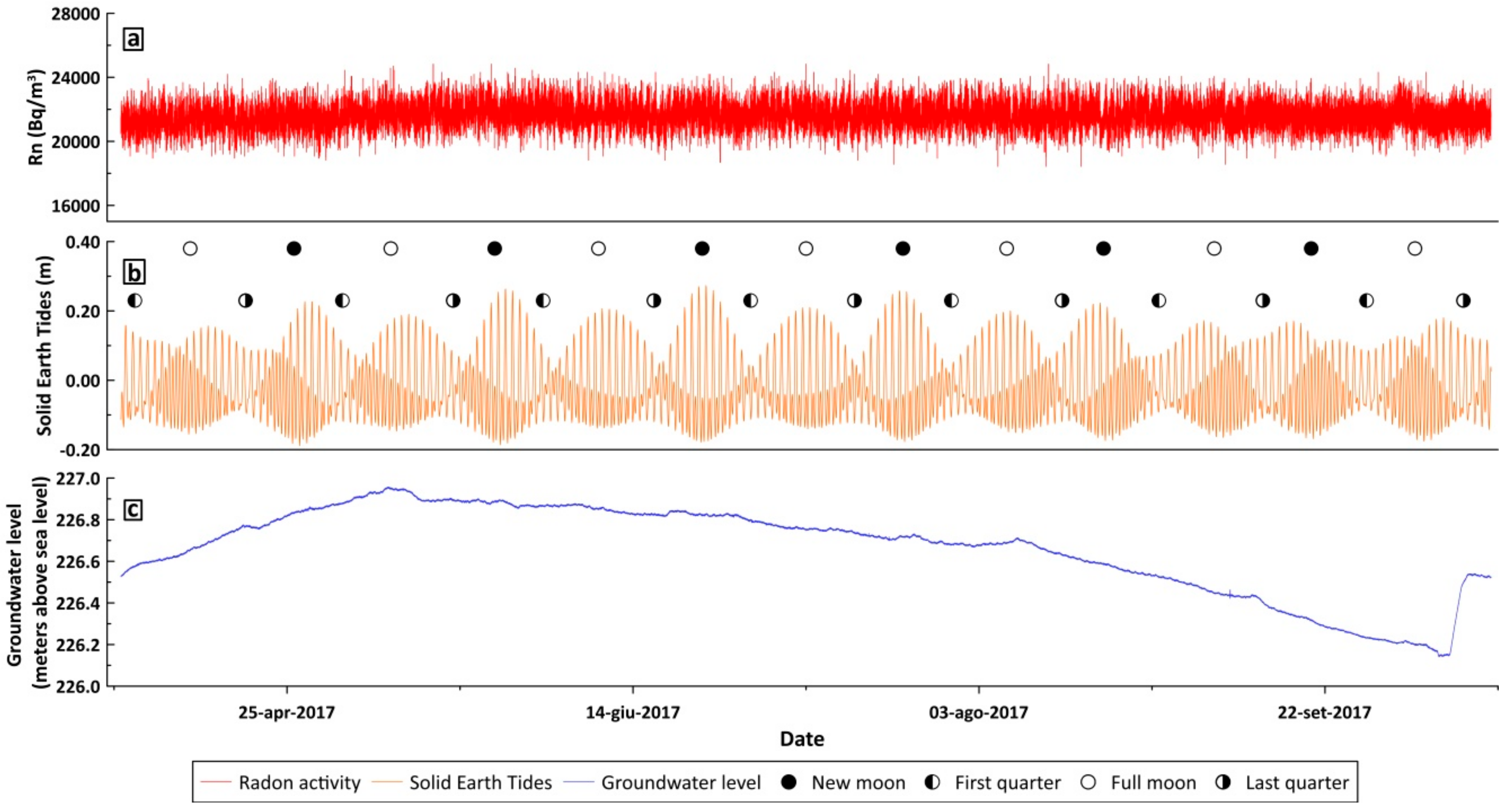
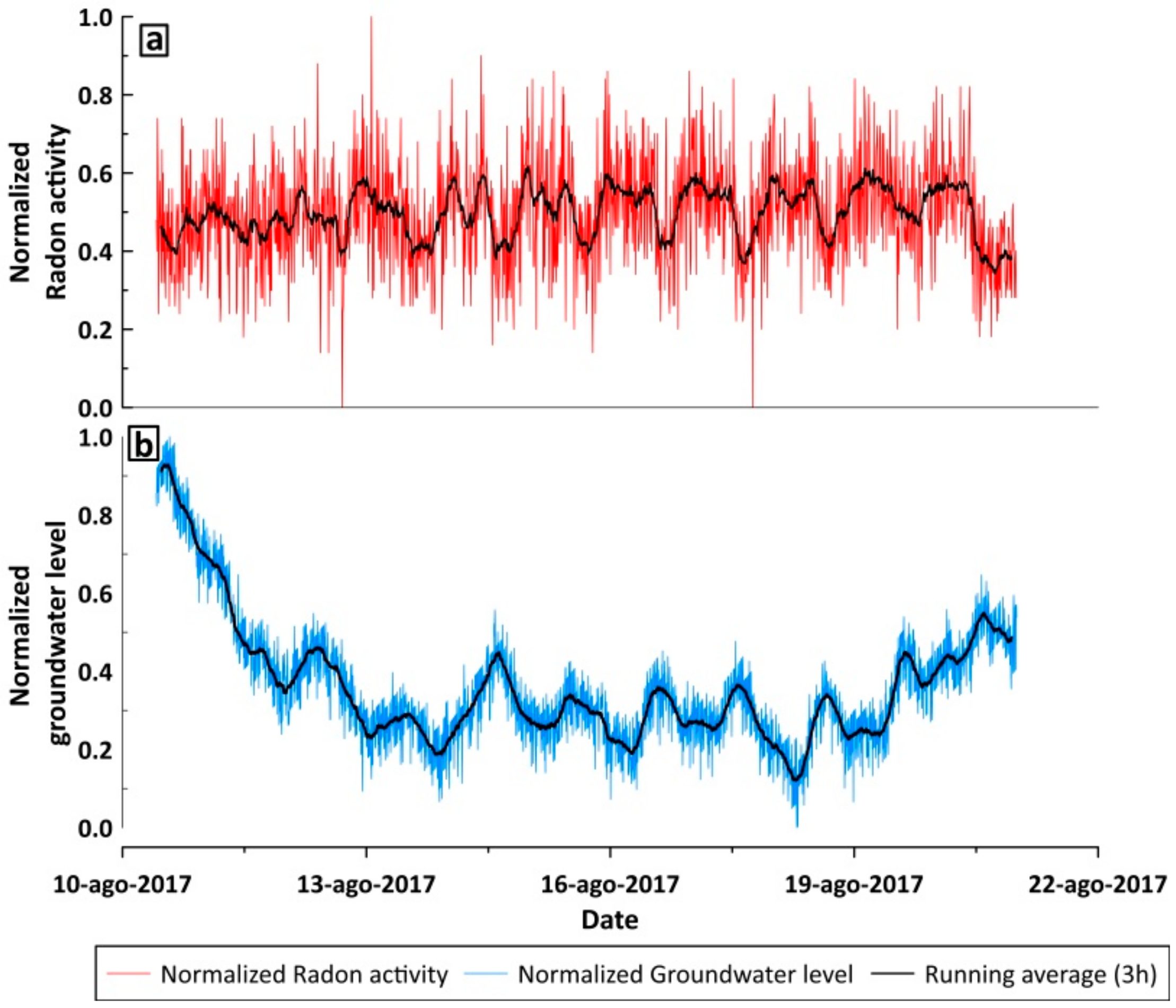
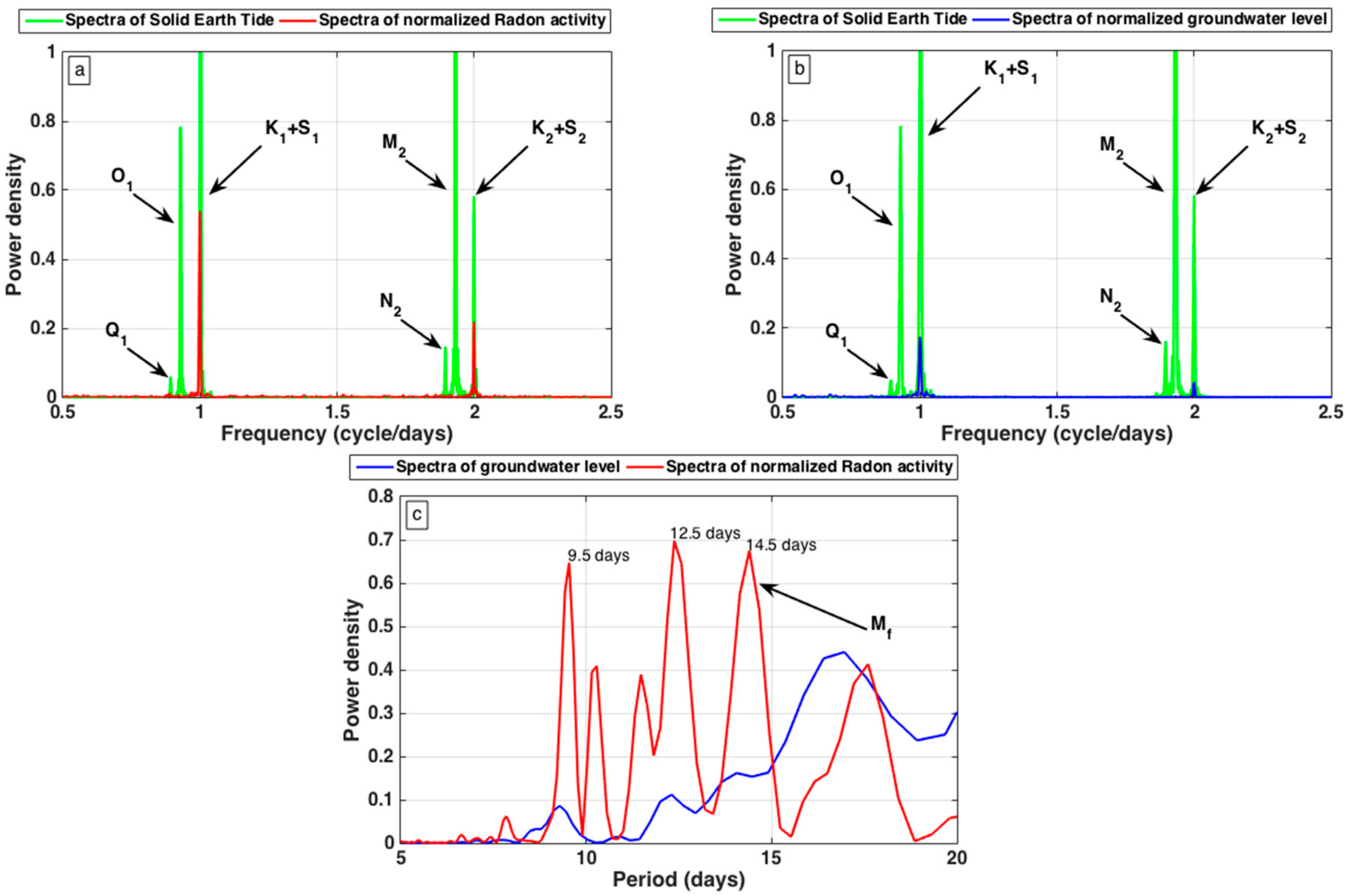
4. Results
5. Data Processing and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundal, A.V.; Henriksen, H.; Soldal, O.; Strand, T. The influence of geological factors on indoor Radon concentrations in Norway. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonollosa, E.; Peñalver, A.; Borrull, F.; Aguilar, C. Radon in spring waters in the south of Catalonia. J. Environ. Radioact. 2016, 151, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, P.T.; Michel, J.; Moore, W.S. Groundwater geochemistry of 228Ra, 226Ra, 222Rn. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinault, J.L.; Baubron, J.C. Signal processing of diurnal and semidiurnal variations in Radon and atmospheric pressure: A new tool for accurate in situ measurement of soil gas velocity, pressure gradient, and tortuosity. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 18101–18120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Phillips, C.R. Dependence of the radon emanation coefficient on radium distribution and internal structure of the material. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1993, 57, 1783–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, A.B. Radon migration in the ground: A supplementary review. Nat. Radiat. Environ. III 1980, 1, 5–56. [Google Scholar]
- Vàrhegyi, A.; Hakl, J.; Monnin, M.; Morin, J.P.; Seidel, J.L. Experimental study of Radon transport in water as test for a transportation microbubble model. J. Appl. Geophys. 1992, 29, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Gunji, Y.; Okuda, T. Mathematical modeling of radon emanation. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2004, 41, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingebritsen, S.E.; Manga, M. Earthquakes: Hydrogeochemical precursors. Nat. Geosci. 2014, 7, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, A.; Santulin, M. Earthquake forecasting: A review of Radon as seismic precursor. Boll. Geofis. Teorica Appl. 2015, 56, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Woith, H. Radon earthquake precursor: A short review. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2015, 224, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.H.; Sykes, L.R.; Aggarwal, Y.P. Earthquake prediction: A physical basis. Science 1973, 181, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakita, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Notsu, K.; Noguchi, M.; Asada, T. Radon anomaly: A possible precursor of the 1978 Izu-Oshima-kinkai Earthquake. Science 1980, 207, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adinolfi Falcone, R.; Carucci, V.; Falgiani, A.; Manetta, M.; Parisse, B.; Petitta, M.; Rusi, S.; Spizzico, M.; Tallini, M. Changes on groundwater flow and hydrochemistry of the Gran Sasso carbonate aquifer after 2009 L’Aquila earthquake. Ital. J. Geosci. 2012, 131, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.J.; Burnett, W.C. Submarine groundwater discharge estimates at a Florida coastal site based on continuous radon measurements. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H. Radon as a tracer of submarine groundwater discharge into a boat basin in Donnalucata, Sicily. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredehoft, J.D. Response of well-aquifer systems to Earth tides. J. Geophys. Res. 1967, 72, 3075–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcaterra, A.; Doglioni, C. The westward drift of the lithosphere: A tidal ratchet? Geosci. Front. 2018, 9, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kies, A.; Majerus, J.; D’Oreye, D.L. Underground radon gas concentrations related to Earth tides. Nuovo Cimento Soc. Ital. Fis. C 1999, 22, 287–293. [Google Scholar]
- Richon, P.; Moreau, L.; Sabroux, J.C.; Pili, E.; Salaün, A. Evidence of both M2 and O1 Earth tide waves in radon-222 air concentration measured in a subglacial laboratory. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, M.H.; Rice, A.; Mendenhall, M.H.; Melvin, J.D.; Tombrello, T.A. Recognition of environmentally caused variations in radon time series. Pure Appl. Geophys. 1984, 122, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinitz, G.; Piatibratova, O.; Kotlarsky, P. Possible effect of solar tides on radon signals. J. Environ. Radioact. 2011, 102, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentes, G.; Eper-Pápai, I. Investigation of temperature and barometric pressure variation effects on radon concentration in the Sopronbánfalva Geodynamic Observatory, Hungary. J. Environ. Radioact. 2015, 149, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinitz, G.; Piatibratova, O.; Barbosa, S.M. Radon daily signals in the Elat Granite, southern Arava, Israel. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richon, P.; Perrier, F.; Pili, E.; Sabroux, J.C. Detectability and significance of 12 h barometric tide in radon-222 signal, dripwater flow rate, air temperature and carbon dioxide concentration in an underground tunnel. Geophys. J. Int. 2009, 176, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinitz, G.; Piatibratova, O.; Kotlarsky, P. Sub-daily periodic radon signals in a confined radon system. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 134, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellotti, E.; Broggini, C.; Di Carlo, G.; Laubenstein, M.; Menegazzo, R. Precise measurement of the 222Rn half-life: A probe to monitor the stability of radioactivity. Phys. Lett. B 2015, 743, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, P.; Galadini, F.; Pantosti, D. Twenty years of paleoseismology in Italy. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2008, 88, 89–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguzzi, F.; Crespi, M.; Devoti, R.; Doglioni, C.; Pietrantonio, G.; Pisani, A.R. Geodetic strain rate and Earthquake size: New clues for seismic hazard studies. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 2012, 206, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberio, M.D.; Barbieri, M.; Billi, A.; Doglioni, C.; Petitta, M. Hydrogeochemical changes before and during the 2016 Amatrice-Norcia seismic sequence (central Italy). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitta, M.; Mastrorillo, L.; Preziosi, E.; Banzato, F.; Barberio, M.D.; Billi, A.; Cambi, C.; De Luca, G.; Di Carlo, G.; Di Curzio, D.; et al. Water-table and discharge changes associated with the 2016–2017 seismic sequence in central Italy: Hydrogeological data and a conceptual model for fractured carbonate aquifers. Hydrogeol. J. 2018, 26, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, G.; Saeki, S.; Takahata, N.; Sumikawa, K.; Tasaka, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Sano, Y. Ground-water radon anomaly before the Kobe earthquake in Japan. Science 1995, 269, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunogai, U.; Wakita, H. Precursory chemical changes in ground water: Kobe earthquake, Japan. Science 1995, 269, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piersanti, A.; Cannelli, V.; Galli, G. The Pollino 2012 seismic sequence: Clues from continuous radon monitoring. Solid Earth 2016, 7, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannelli, V.; Piersanti, A.; Spagnuolo, E.; Galli, G. Preliminary analysis of radon time series before the Ml = 6 Amatrice earthquake: Possible implications for fluid migration. Ann. Geophys. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ithaca (ITaly HAzard from CApable Faults) Database. Available online: http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/en/projects/soil-and-territory/italy-hazards-from-capable-faulting (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- ISPRA Database SINAnet (Rete del Sistema Informativo Nazionale Ambientale). Available online: http://www.sinanet.isprambiente.it/it (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Doglioni, C. A proposal for the kinematic modelling of W-dipping subductions-possible applications to the Tyrrhenian-Apennines system. Terra Nova 1991, 3, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavinato, G.P.; Celles, P.G.D. Extensional basins in the tectonically bimodal central Apennines fold-thrust belt, Italy: Response to corner flow above a subducting slab in retrograde motion. Geology 1999, 27, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, A.; Tiberti, M.M.; Cavinato, G.P.; Cosentino, D.; Di Luzio, E.; Keller, J.V.A.; Kluth, C.; Orlando, L.; Parotto, M.; Praturlon, A.; et al. First results from the CROP-11 deep seismic profile, central Apennines, Italy: Evidence of mid-crustal folding. J. Geol. Soc. 2006, 163, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patacca, E.; Scandone, P.; Di Luzio, E.; Cavinato, G.P.; Parotto, M. Structural architecture of the central Apennines: Interpretation of the CROP 11 seismic profile from the Adriatic coast to the orographic divide. Tectonics 2008, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devoti, R.; D’Agostino, N.; Serpelloni, E.; Pietrantonio, G.; Riguzzi, F.; Avallone, A.; Cavaliere, A.; Cheloni, D.; Cecere, G.; D’Ambrosio, C.; et al. A combined velocity field of the Mediterranean region. Ann. Geophys. 2017, 60, 0215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavinato, G.P.; Carusi, C.; Dall’Asta, M.; Miccadei, E.; Piacentini, T. Sedimentary and tectonic evolution of Plio–Pleistocene alluvial and lacustrine deposits of Fucino Basin (central Italy). Sediment. Geol. 2002, 148, 29–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, S.; Giaccio, B.; Galadini, F.; Falcucci, E.; Messina, P.; Sposato, A.; Dramis, F. Active normal faulting along the Mt. Morrone south-western slopes (central Apennines, Italy). Int. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 100, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, S.; Falcucci, E.; Dramis, F.; Galadini, F.; Galli, P.; Giaccio, B.; Messina, P.; Pizzi, A.; Sposato, A.; Cosentino, D. Deep-seated gravitational slope deformation, large-scale rock failure, and active normal faulting along Mt. Morrone (Sulmona basin, Central Italy): Geomorphological and paleoseismological analyses. Geomorphology 2014, 208, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadini, F.; Galli, P. Archaeoseismology in Italy: Case studies and implications on long-term seismicity. J. Earthq. Eng. 2001, 5, 35–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.A.; Nardis, R.D.; Garbin, M.; Peruzza, L.; Priolo, E.; Lavecchia, G.; Romanelli, M. Temporary seismic monitoring of the Sulmona area (Abruzzo, Italy): A quality study of microearthquake locations. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 13, 2727–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celico, P. Schema idrogeologico dell’Appennino carbonatico centro-meridionale. Mem. Note dell’Ist. Geol. Appl. 1979, 14, 1–97. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, C.; Bono, P.; Capelli, G. Schema Idrogeologico dell’Italia centrale: Note illustrative e carte. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 1986, 35, 991–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Salvati, R. Natural hydrogeological laboratories: A new concept in regional hydrogeology studies. A case history from central Italy. Environ. Geol. 2002, 41, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccadei, E.; Cavinato, G.P.; Vittori, E. Elementi neotettonici della conca di Sulmona. Stud. Geol. Camerti 1992, 1, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Desiderio, G.; Folchi Vici d’Arcevia, C.; Nanni, T.; Rusi, S. Hydrogeological mapping of the highly anthropogenically influenced Peligna Valley intramontane basin (Central Italy). J. Maps 2012, 8, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conese, M.; Nanni, T.; Peila, C.; Rusi, S.; Salvati, R. Idrogeologia della Montagna del Morrone (Appennino Abruzzese): Dati preliminari. Mem. Soc. Geol. Ital. 2001, 56, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Csige, I. Radon and Space Radiation Protection Measurements. Ph.D. Thesis, Lajos Kossuth University, Budapest, Hungary, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- CalSky—Solid Earth Tides Free Resource. Available online: https://www.calsky.com (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Lowrie, W. Fundamentals of Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- MatlabR2017b ‘Mscohere’ Function. Available online: Available online: https://mathworks.com/help/signal/ref/mscohere.html (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Doodson, A.T. The harmonic development of the tide-generating potential. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1921, 100, 305–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schureman, P. Manual of Harmonic Analysis and Prediction of Tides; USA Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Groves-Kirkby, C.J.; Denman, A.R.; Crockett, R.G.M.; Phillips, P.S. Periodicity in Domestic Radon Time Series-Evidence for Earth Tides. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA11e6a27), Madrid, Spain, 23–28 May 2004; pp. 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lomb, N.R. Least-Squares Frequency Analysis of Unequally Spaced Data. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1976, 39, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scargle, J.D. Studies in Astronomical Time Series Analysis. II. Statistical Aspects of Spectral Analysis of Unevenly Spaced Data. Astrophys. J. 1982, 263, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, P. The Earth’s Tides; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, T.K.; Cameron, D.G.; Colma, T.B.; Roberts, P.D. Behavior of Radon in the geological environment: A review. Q. J. Eng. Geol. 1991, 24, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelstein, M.; Eppelbaum, L.V.; Price, C. Analysis of temperature influences on the amplitude frequency characteristics of Radon gas concentration. J. Environ. Radioact. 2006, 86, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Heinkelmann, R.; Park, J. Diurnal and semidiurnal atmospheric tides observed by co-located GPS and VLBI measurements. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2008, 70, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentes, G. Investigation of the relationship between rock strain and radon concentration in the tidal frequency-range. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 155, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugisaki, R. Deep-seated gas emission induced by the earth tide: A basic observation for geochemical earthquake prediction. Science 1981, 212, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, G.; Wakita, H. Tidal responses and earthquake-related changes in the water level of deep wells. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1991, 96, 4269–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumento, F. Radon tides on an active volcanic island: Terceira, Azores. Geofís. Int. 2002, 41, 499–505. [Google Scholar]
- Chanton, J.P.; Burnett, W.C.; Dulaiova, H.; Corbett, D.R.; Taniguchi, M. Seepage rate variability in Florida Bay driven by Atlantic tidal height. Biogeochemistry 2003, 66, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crockett, R.G.; Gillmore, G.K.; Phillips, P.S.; Denman, A.R.; Groves-Kirkby, C.J. Tidal synchronicity of built-environment radon levels in the UK. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L05308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barberio, M.D.; Gori, F.; Barbieri, M.; Billi, A.; Devoti, R.; Doglioni, C.; Petitta, M.; Riguzzi, F.; Rusi, S. Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cyclicity of Radon (222Rn) in Groundwater, Giardino Spring, Central Apennines, Italy. Water 2018, 10, 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091276
Barberio MD, Gori F, Barbieri M, Billi A, Devoti R, Doglioni C, Petitta M, Riguzzi F, Rusi S. Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cyclicity of Radon (222Rn) in Groundwater, Giardino Spring, Central Apennines, Italy. Water. 2018; 10(9):1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091276
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarberio, Marino Domenico, Francesca Gori, Maurizio Barbieri, Andrea Billi, Roberto Devoti, Carlo Doglioni, Marco Petitta, Federica Riguzzi, and Sergio Rusi. 2018. "Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cyclicity of Radon (222Rn) in Groundwater, Giardino Spring, Central Apennines, Italy" Water 10, no. 9: 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091276
APA StyleBarberio, M. D., Gori, F., Barbieri, M., Billi, A., Devoti, R., Doglioni, C., Petitta, M., Riguzzi, F., & Rusi, S. (2018). Diurnal and Semidiurnal Cyclicity of Radon (222Rn) in Groundwater, Giardino Spring, Central Apennines, Italy. Water, 10(9), 1276. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091276








