Quantitative Analysis of Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Involved in Microfiltration of Humic Acid–Protein Mixtures at Different Solution Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microfiltration Membrane and Model Foulants
2.2. xDLVO Theory
2.2.1. Surface Thermodynamic Parameters
2.2.2. Interfacial Interaction Energy
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Fouling Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of the PES Membrane and Foulants
3.2. Surface Tension Parameters of the PES Membrane and Foulants
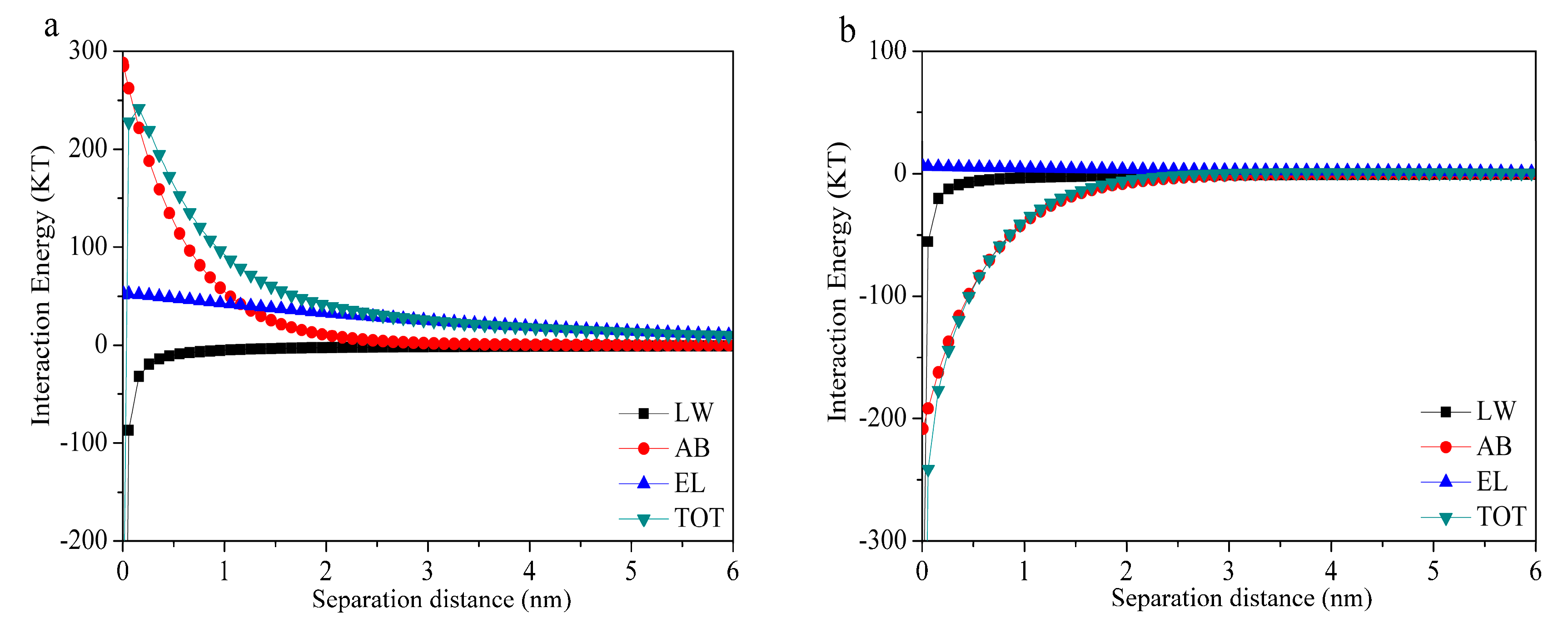
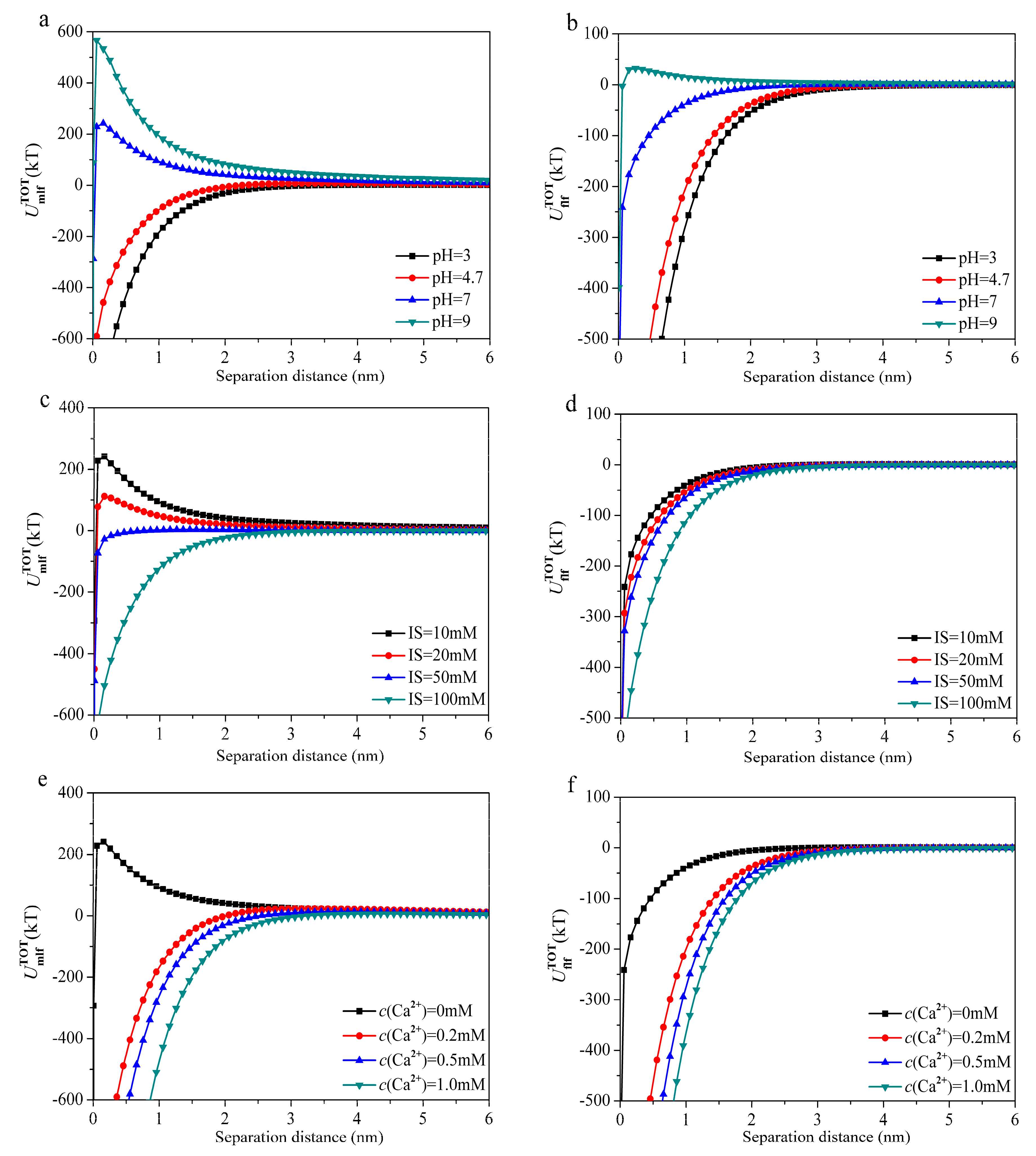
3.3. Interfacial Interaction Energies of Membrane–Foulant and Foulant–Foulant Combinations
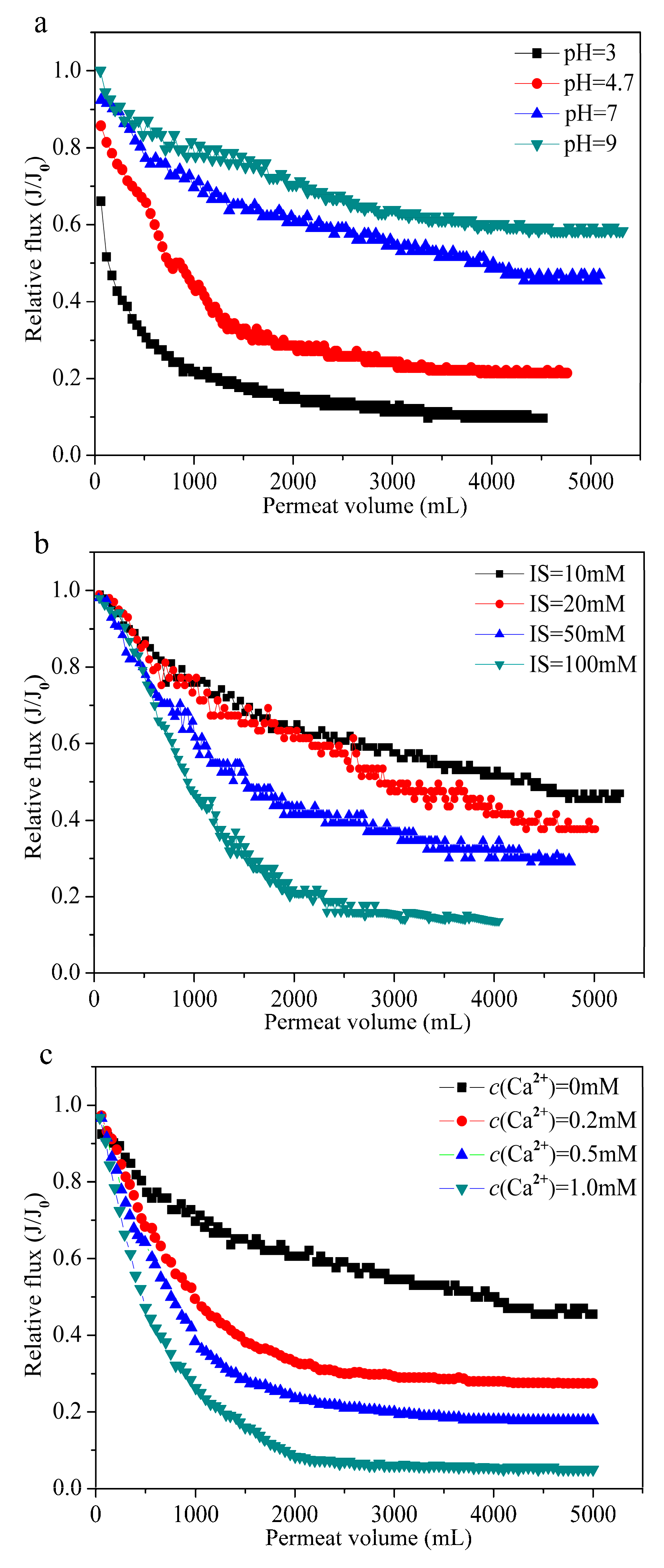
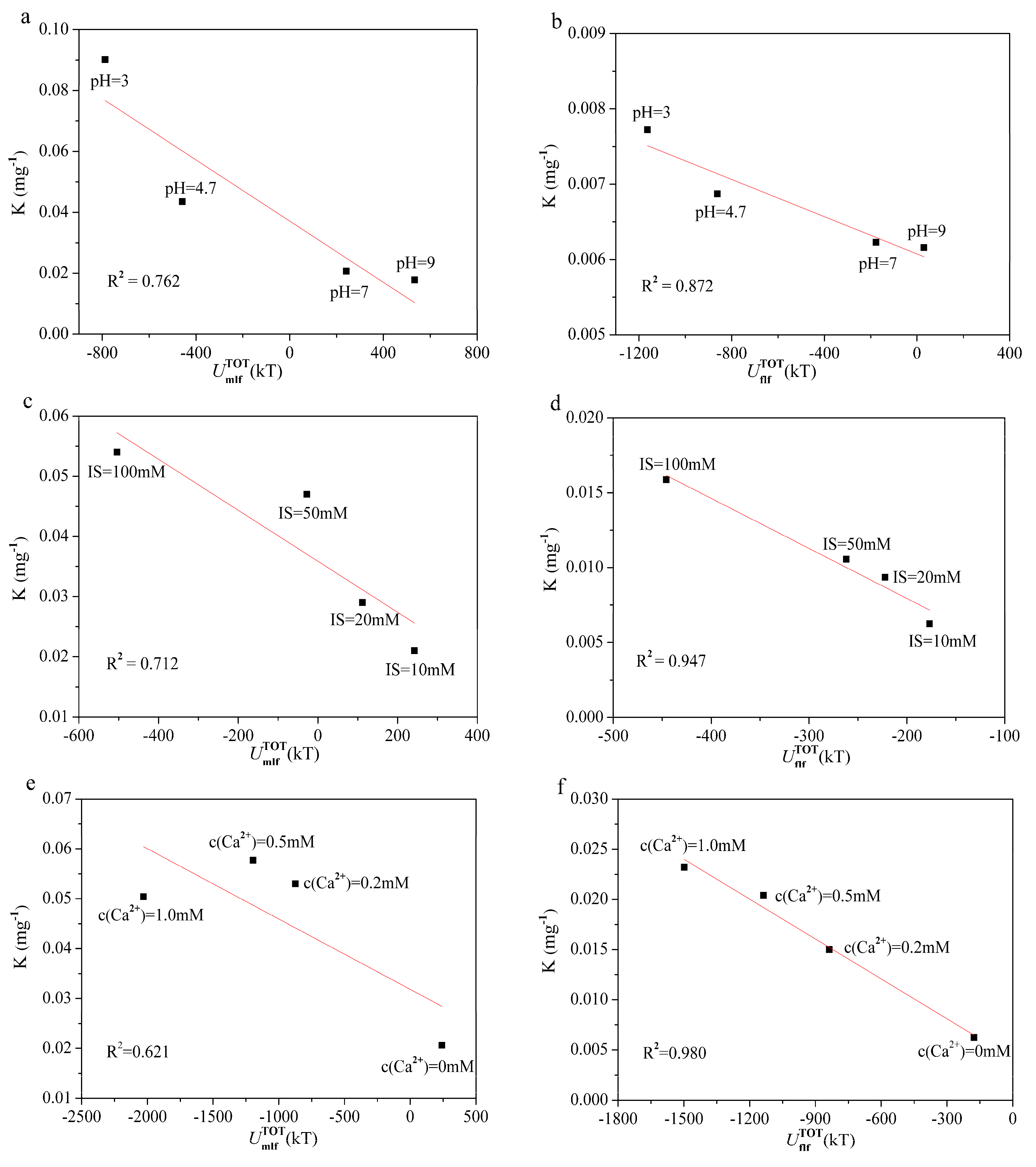
3.4. Experimental Verification
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, H.; Wyart, Y.; Perot, J.; Nauleau, F.; Moulin, P. Low-pressure membrane integrity tests for drinking water treatment: A review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, L.; Roddick, F.A. Influence of the characteristics of soluble algal organic matter released from Microcystis aeruginosa on the fouling of a ceramic microfiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 425, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashino, M.; Hirami, K.; Katagiri, T.; Kubota, N.; Ohmukai, Y.; Ishigami, T.; Maruyama, T.; Matsuyama, H. Effects of three natural organic matter types on cellulose acetate butyrate microfiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 379, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Gao, B.; Sun, Y.; Shi, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, J. Effects of humic acid and solution chemistry on the retention and transport of cerium dioxide nanoparticles in saturated porous media. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Sun, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Floc properties and membrane fouling of polyferric silicate chloride and polyferric chloride: The role of polysilicic acid. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4566–4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Li, L.; Deng, J.; Tan, C.; Zhu, M. Influence of hydrophobic/hydrophilic fractions of extracellular organic matters of Microcystis aeruginosa on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, S.R.; Ritchie, C.; Tran, T.; Bolto, B. Effect of NOM characteristics and membrane type on microfiltration performance. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3833–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Zietzschmann, F.; Plume, S.; Paar, H.; Ernst, M.; Wang, Z.; Jekel, M. Understanding and Control of Biopolymer Fouling in Ultrafiltration of Different Water Types. Water 2017, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Hou, J.; Song, H. Comparison of humic acid rejection and flux decline during filtration with negatively charged and uncharged ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.P.; Mohammad, A.W. Effect of solution chemistry on flux decline during high concentration protein ultrafiltration through a hydrophilic membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 159, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaeni, S.; Sedeh, S.N.; De Nobili, M. Ultrafiltration of humic substances in the presence of protein and metal ions. Transp. Porous Media 2006, 65, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, E.; Madaeni, S. Adsorption of humic acid onto ultrafiltration membranes in the presence of protein and metal ions. Desalination 2010, 263, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myat, D.T.; Stewart, M.B.; Mergen, M.; Zhao, O.; Orbell, J.D.; Gray, S. Experimental and computational investigations of the interactions between model organic compounds and subsequent membrane fouling. Water Res. 2014, 48, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.G.; Lei, Q.; Chen, J.-R.; Hong, H.-C.; He, Y.-M.; Lin, H.-J. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor: Impacts of floc size. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 269, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Interaction mechanisms of humic acid combined with calcium ions on membrane fouling at different conditions in an ultrafiltration system. Desalination 2015, 357, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lu, Z.; Chen, W. Interaction mechanisms and predictions on membrane fouling in an ultrafiltration system, using the XDLVO approach. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 461, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Interaction energy evaluation of the role of solution chemistry and organic foulant composition on polysaccharide fouling of microfiltration membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 104, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishijima, W.; Speitle, G.E., Jr. Fate of biodegradable dissolved organic carbon produced by ozonation on biological activated carbon. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Qu, F.; Liu, B.; Yu, H.; Li, K.; Shao, S.; Li, G.; Liang, H. Hydraulic irreversibility of ultrafiltration membrane fouling by humic acid: Effects of membrane properties and backwash water composition. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oss, C. Acid—Base interfacial interactions in aqueous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 78, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; Huang, X.; Hoek, E.M. Direct observation of bacterial deposition onto clean and organic-fouled polyamide membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 336, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Tan, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Chang, Y.-I.; Zhong, C.-J.; He, N. Effect of surface physicochemical properties on the flocculation behavior of Bacillus licheniformis. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16049–16056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brant, J.A.; Childress, A.E. Assessing short-range membrane–colloid interactions using surface energetics. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 203, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.; Agarwal, G.K. Extended DLVO interactions between spherical particles and rough surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, J.; Hoek, E.M. Natural organic matter fouling due to foulant–membrane physicochemical interactions. Desalination 2007, 202, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Song, L. Effect of solution chemistry on the fouling potential of dissolved organic matter in membrane bioreactor systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Le Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, A.G.; Jefferson, B. Fouling mechanisms of alginate solutions as model extracellular polymeric substances. Desalination 2005, 175, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, Y.; Cao, C.Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.N. Interaction energy evaluation of soluble microbial products (SMP) on different membrane surfaces: Role of the reconstructed membrane topology. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2693–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Yu, H.; Hong, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, J.; Liao, B.-Q. Physicochemical correlations between membrane surface hydrophilicity and adhesive fouling in membrane bioreactors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Mechanism analysis of membrane fouling behavior by humic acid using atomic force microscopy: Effect of solution pH and hydrophilicity of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane interface. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 487, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, M.; Meng, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, D. Effect of protein on PVDF ultrafiltration membrane fouling behavior under different pH conditions: Interface adhesion force and XDLVO theory analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Tay, K.G.; Ng, H.Y. Fouling of reverse osmosis membrane by protein (BSA): Effects of pH, calcium, magnesium, ionic strength and temperature. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Mei, X.; Wu, Z. Assessment of SMP fouling by foulant–membrane interaction energy analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; He, Y.; Wang, F.; Weng, X.; Yu, H.; Lin, H. Thermodynamic analysis of membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor and its implications. Biores. Technol. 2013, 146, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Chen, L. Microfiltration (MF) membrane fouling potential evaluation of protein with different ion strengths and divalent cations based on extended DLVO theory. Desalination 2013, 331, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoudh, S.; Othmane, A.; Mora, L.; Ouada, H.B. Assessing bacterial adhesion using DLVO and XDLVO theories and the jet impingement technique. Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces 2009, 73, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, H.; Okimoto, K.; Kimura, K.; Watanabe, Y. Hydrophilic fraction of natural organic matter causing irreversible fouling of microfiltration and ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2014, 54, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bower, M.J.D.; Bank, T.L.; Giese, R.F.; Oss, C.J.V. Nanoscale forces of interaction between glass in aqueous and non-aqueous media: A theoretical and empirical study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2010, 362, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, A.; Hoek, E.M. Direct observation of initial microbial deposition onto reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 319, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redman, J.A.; Walker, S.L.; Elimelech, M. Bacterial adhesion and transport in porous media: Role of the secondary energy minimum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, E.M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Elimelech, M. Effect of Membrane Surface Roughness on Colloid−Membrane DLVO Interactions. Langmuir 2003, 19, 4836–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Miao, R.; Wang, X.; Lv, Y.; Meng, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Feng, L.; Liu, Z.; Ju, K. Fouling behavior of typical organic foulants in polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes: Characterization from microforces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 3708–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Pinnau, I. Fouling of reverse osmosis membranes by biopolymers in wastewater secondary effluent: Role of membrane surface properties and initial permeate flux. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 290, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. Control of protein (BSA) fouling in RO system by antiscalants. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling and chemical cleaning of nanofiltration membranes: Measurements and mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4683–4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Hoek, E.M. Interactions controlling biopolymer fouling of reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2007, 202, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Huang, X.; Hoek, E.M. Role of specific ion interactions in seawater RO membrane fouling by alginic acid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3580–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Solution Conditions | PES Membrane | HA–BSA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| θW (°) | θG (°) | θD (°) | Zeta (mV) | θW (°) | θG (°) | θD (°) | Zeta (mV) | |
| pH = 3.0 | 37.7 ± 1.9 a | 44.4 ± 2.1 | 40.0 ± 2.5 | −16.8 ± 2.1 | 90.2 ± 2.1 | 72.9 ± 3.1 | 30.4 ± 1.0 | −16.5 ± 2.5 |
| pH = 4.7 | 32.0 ± 2.2 | 43.4 ± 2.0 | 37.7 ± 1.8 | −21.8 ± 1.8 | 84.6 ± 3.0 | 72.0 ± 0.9 | 41.9 ± 2.9 | −28.4 ± 2.7 |
| pH = 7.0 | 27.5 ± 1.6 | 42.8 ± 1.8 | 36.9 ± 1.5 | −37.8 ± 2.3 | 69.1 ± 1.2 | 71.9 ± 2.7 | 39.0 ± 2.1 | −32.2 ± 1.9 |
| pH = 9.0 | 23.0 ± 2.5 | 41.8 ± 1.9 | 40.5 ± 2.2 | −51.8 ± 1.5 | 62.6 ± 1.5 | 70.1 ± 2.7 | 35.8 ± 1.6 | −43.0 ± 2.1 |
| IS = 10 mM | 27.5 ± 1.6 | 42.8 ± 1.8 | 36.9 ± 1.5 | −37.8 ± 2.3 | 69.1 ± 1.2 | 71.9 ± 2.7 | 39.0 ± 2.1 | −32.2 ± 1.9 |
| IS = 20 mM | 34.1 ± 1.4 | 46.4 ± 1.1 | 36.4 ± 1.8 | −31.3 ± 1.9 | 70.4 ± 2.1 | 72.3 ± 1.3 | 39.8 ± 1.6 | −26.3 ± 1.2 |
| IS = 50 mM | 41.8 ± 2.3 | 50.6 ± 1.5 | 36.8 ± 1.5 | −23.1 ± 1.3 | 71.9 ± 2.3 | 72.8 ± 2.2 | 47.9 ± 1.5 | −19.2 ± 2.4 |
| IS = 100 mM | 53.7 ± 2.1 | 51.5 ± 2.9 | 38.5 ± 2.3 | −13.8 ± 2.7 | 76.3 ± 2.0 | 73.5 ± 2.1 | 50.2 ± 2.3 | −10.9 ± 2.6 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0 mM | 27.5 ± 1.6 | 42.8 ± 1.8 | 36.9 ± 1.5 | −37.8 ± 2.3 | 69.1 ± 1.2 | 71.9 ± 2.7 | 39.0 ± 2.1 | −32.2 ± 1.9 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.2 mM | 53.4 ± 2.6 | 55.3 ± 2.0 | 29.3 ± 1.3 | −34.9 ± 2.4 | 76.8 ± 2.8 | 72.8 ± 0.7 | 36.5 ± 1.0 | −29.3 ± 2.3 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.5 mM | 54.5 ± 0.9 | 55.3 ± 2.2 | 30.2 ± 0.5 | −32.4 ± 1.4 | 81.1 ± 2.3 | 73.8 ± 1.2 | 43.0 ± 0.8 | −22.2 ± 1.8 |
| c(Ca2+) = 1.0 mM | 64.7 ± 3.5 | 58.3 ± 2.9 | 32.2 ± 2.2 | −30.7 ± 1.2 | 85.3 ± 2.1 | 74.1 ± 1.9 | 40.6 ± 2.7 | −16.9 ± 2.6 |
| Solution Conditions | PES Membrane | HA–BSA | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ+ | γ− | γAB | γLW | γTOT | ΔGsls | γ+ | γ− | γAB | γLW | γTOT | ΔGsls | |
| pH = 3.0 | 0.52 | 34.53 | 8.51 | 34.47 | 42.98 | 11.42 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.21 | 44.06 | 44.27 | −89.16 |
| pH = 4.7 | 0.37 | 39.32 | 7.60 | 35.37 | 42.97 | 18.42 | 0.06 | 3.56 | 0.95 | 38.64 | 39.59 | −65.58 |
| pH = 7.0 | 0.29 | 42.93 | 7.06 | 35.67 | 42.73 | 23.71 | 0.24 | 19.47 | 4.31 | 40.11 | 44.42 | −17.16 |
| pH = 9.0 | 0.37 | 46.18 | 8.27 | 34.27 | 42.54 | 28.21 | 0.45 | 27.31 | 6.98 | 41.66 | 48.64 | −3.29 |
| IS = 10 mM | 0.29 | 42.93 | 7.06 | 35.67 | 42.73 | 23.71 | 0.24 | 19.47 | 4.31 | 40.11 | 44.42 | −17.16 |
| IS = 20 mM | 0.19 | 39.38 | 5.54 | 35.86 | 41.40 | 19.20 | 0.20 | 18.06 | 3.82 | 39.71 | 43.53 | −20.12 |
| IS = 50 mM | 0.13 | 34.37 | 4.25 | 35.71 | 39.96 | 11.77 | 0.03 | 17.05 | 1.53 | 35.44 | 36.97 | −21.33 |
| IS = 100 mM | 0.45 | 21.79 | 6.28 | 35.06 | 41.34 | −9.92 | 0.001 | 12.24 | 0.09 | 34.16 | 34.25 | −34.02 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0 mM | 0.29 | 42.93 | 7.06 | 35.67 | 42.73 | 23.71 | 0.24 | 19.47 | 4.31 | 40.11 | 44.42 | −17.16 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.2 mM | 0.05 | 24.05 | 2.09 | 38.33 | 40.42 | −7.45 | 0.10 | 10.41 | 2.04 | 41.32 | 43.36 | −40.71 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.5 mM | 0.07 | 22.86 | 2.52 | 38.04 | 40.56 | −9.63 | 0.002 | 7.07 | 0.21 | 38.07 | 38.28 | −52.37 |
| c(Ca2+) = 1.0 mM | 0.18 | 13.99 | 3.14 | 37.37 | 40.51 | −28.40 | 0.06 | 3.12 | 0.83 | 39.31 | 40.14 | −68.23 |
| Solution Conditions | PES–Foulant | Foulant–Foulant | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH = 3.0 | −34.56 | −765.35 | 12.04 | −787.87 | −28.49 | −1136.38 | 1.50 | −1163.37 |
| pH = 4.7 | −28.68 | −455.13 | 25.26 | −458.55 | −17.61 | −848.66 | 4.44 | −861.83 |
| pH = 7.0 | −31.91 | 221.98 | 51.71 | 241.78 | −20.37 | −162.22 | 5.74 | −176.85 |
| pH = 9.0 | −30.88 | 470.49 | 93.88 | 533.49 | −23.53 | 43.14 | 10.17 | 29.78 |
| IS = 10 mM | −31.91 | 221.98 | 51.71 | 241.78 | −20.37 | −162.22 | 5.74 | −176.85 |
| IS = 20 mM | −31.62 | 108.90 | 34.41 | 111.69 | −19.59 | −206.47 | 3.75 | −222.31 |
| IS = 50 mM | −24.26 | −21.50 | 18.00 | −27.76 | −12.13 | −251.71 | 1.93 | −261.91 |
| IS = 100 mM | −21.32 | −488.64 | 5.84 | −504.12 | −10.18 | −436.26 | 0.60 | −445.84 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0 mM | −31.91 | 221.98 | 51.71 | 241.78 | −20.37 | −162.22 | 5.74 | −176.85 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.2 mM | −66.18 | −879.55 | 72.03 | −873.70 | −37.93 | −803.19 | 4.72 | −836.40 |
| c(Ca2+) = 0.5 mM | −53.92 | −1186.69 | 45.60 | −1195.01 | −27.63 | −1113.58 | 4.51 | −1136.70 |
| c(Ca2+) = 1.0 mM | −56.37 | −1999.22 | 26.05 | −2029.54 | −31.37 | −1468.17 | 1.56 | −1497.98 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, F.; Ke, G.; Song, L.; Liu, X.; Liang, S. Quantitative Analysis of Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Involved in Microfiltration of Humic Acid–Protein Mixtures at Different Solution Conditions. Water 2018, 10, 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101306
Sun C, Zhang N, Li F, Ke G, Song L, Liu X, Liang S. Quantitative Analysis of Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Involved in Microfiltration of Humic Acid–Protein Mixtures at Different Solution Conditions. Water. 2018; 10(10):1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101306
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Chunyi, Na Zhang, Fazhan Li, Guoyi Ke, Lianfa Song, Xiaoqian Liu, and Shuang Liang. 2018. "Quantitative Analysis of Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Involved in Microfiltration of Humic Acid–Protein Mixtures at Different Solution Conditions" Water 10, no. 10: 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101306
APA StyleSun, C., Zhang, N., Li, F., Ke, G., Song, L., Liu, X., & Liang, S. (2018). Quantitative Analysis of Membrane Fouling Mechanisms Involved in Microfiltration of Humic Acid–Protein Mixtures at Different Solution Conditions. Water, 10(10), 1306. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101306






