Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data Source Acquisition
2.2. Methodology
3. Results, Analysis, and Discussion
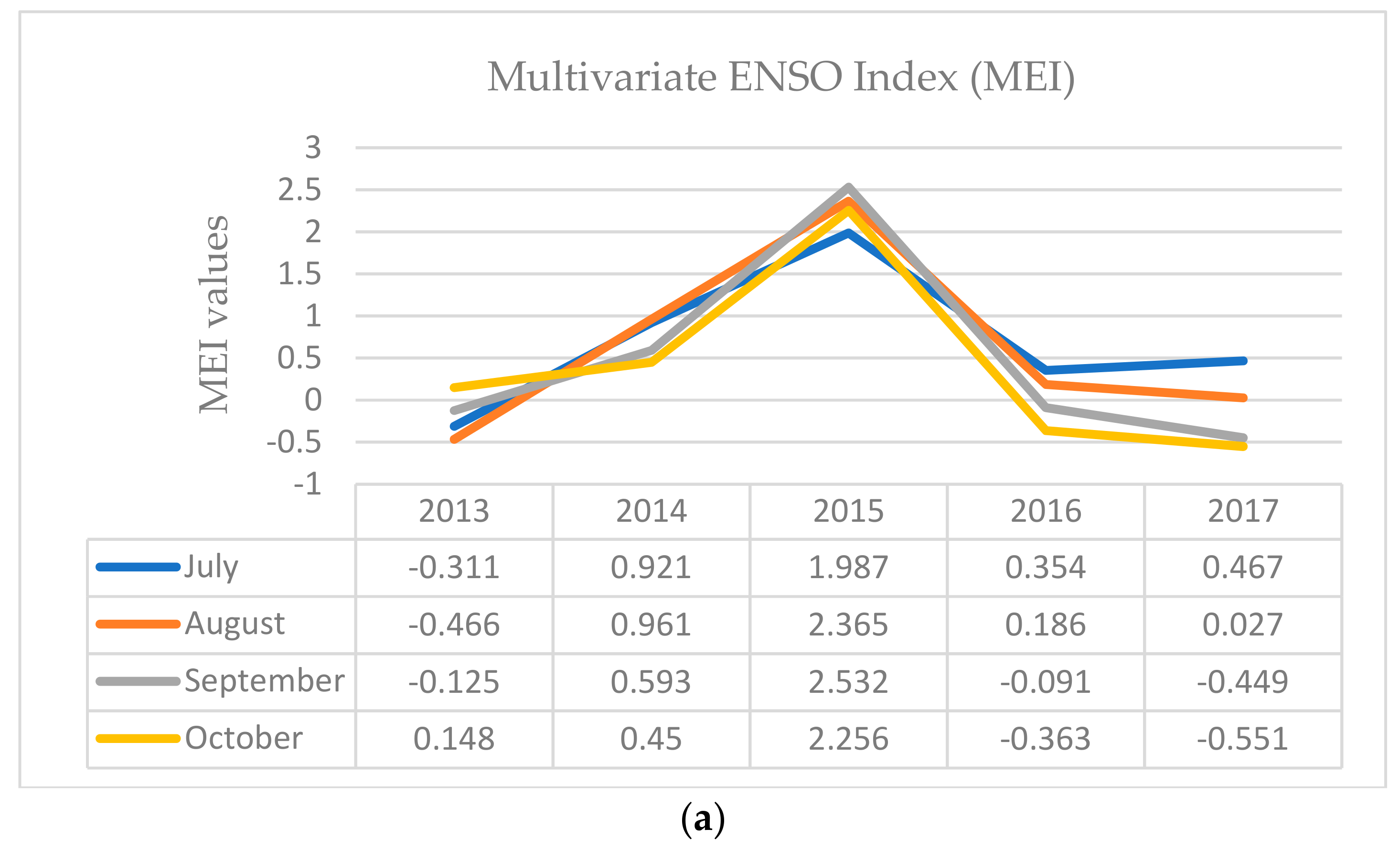
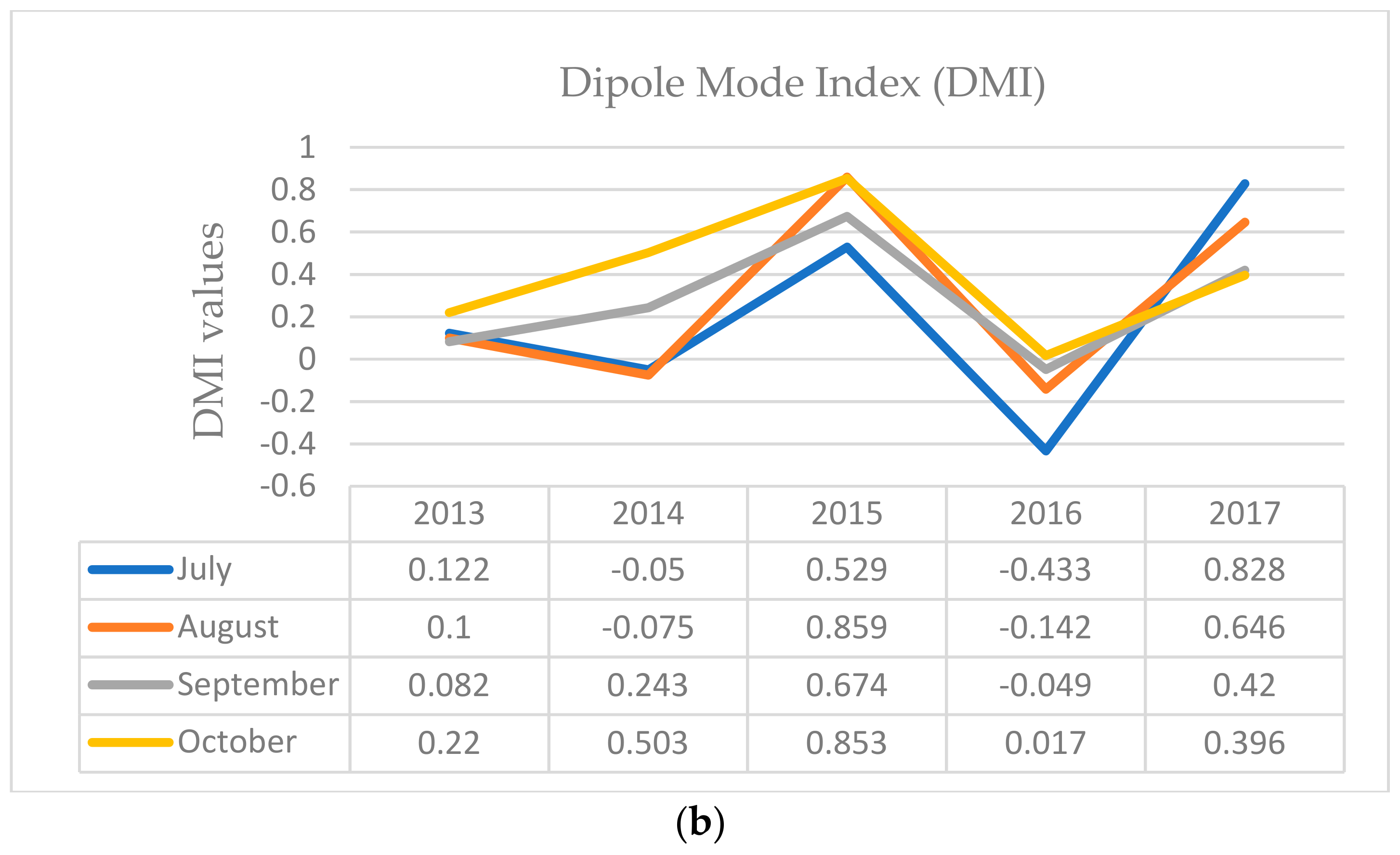
3.1. Concurrent ENSO and Positive IOD in 2015
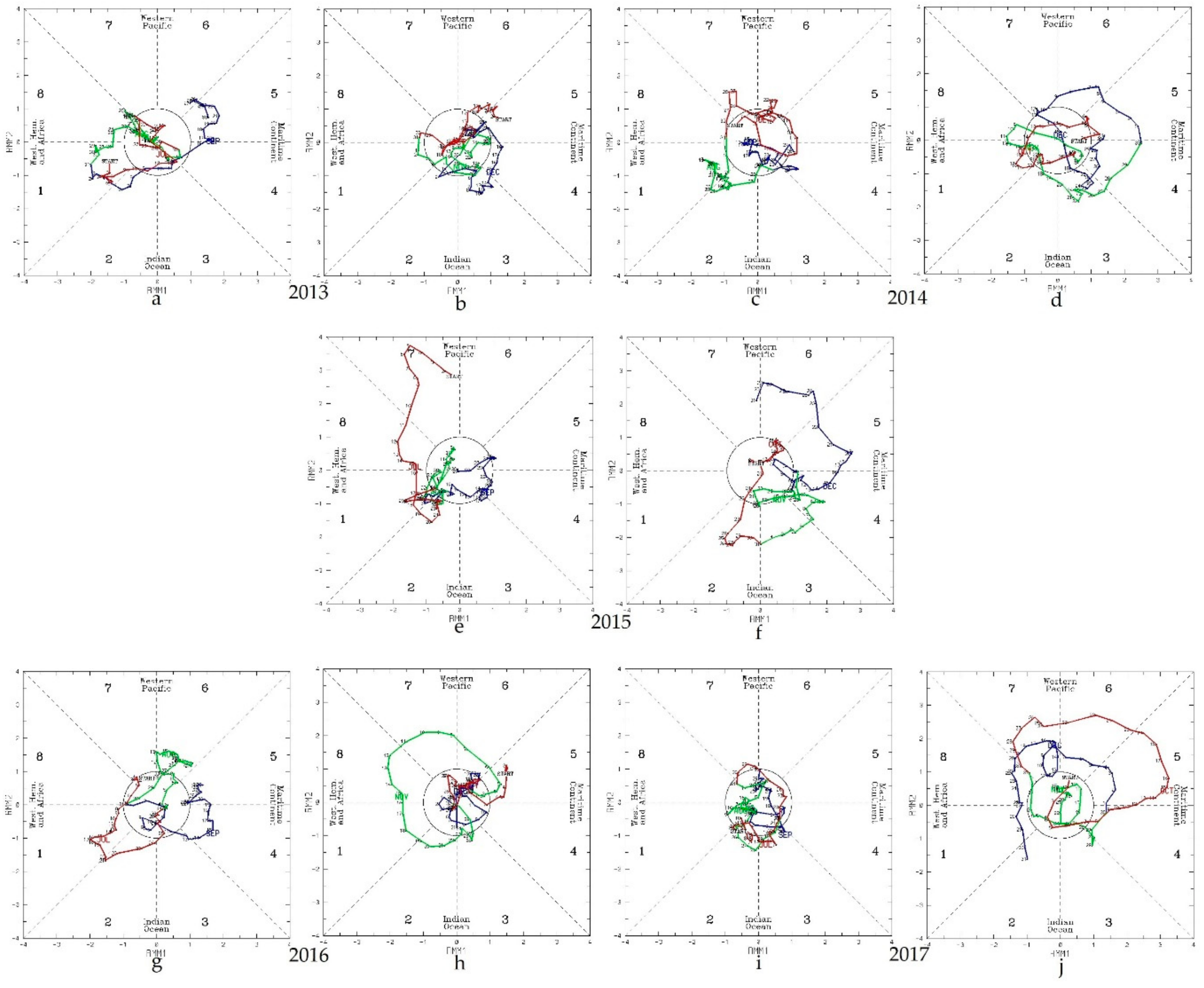
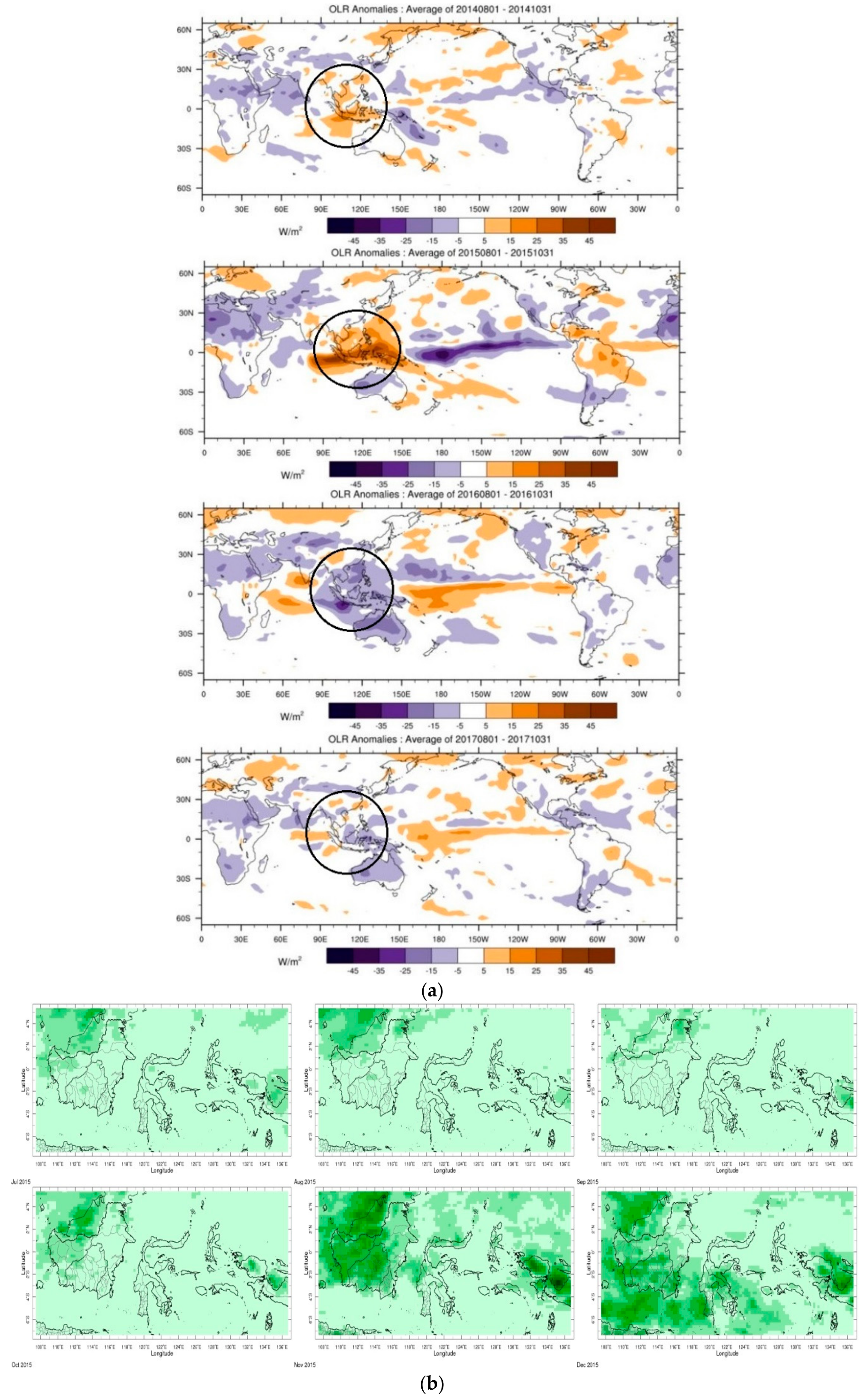
3.2. MJO, OLR, and Suppressed Rainfall during the 2015 BB Episode
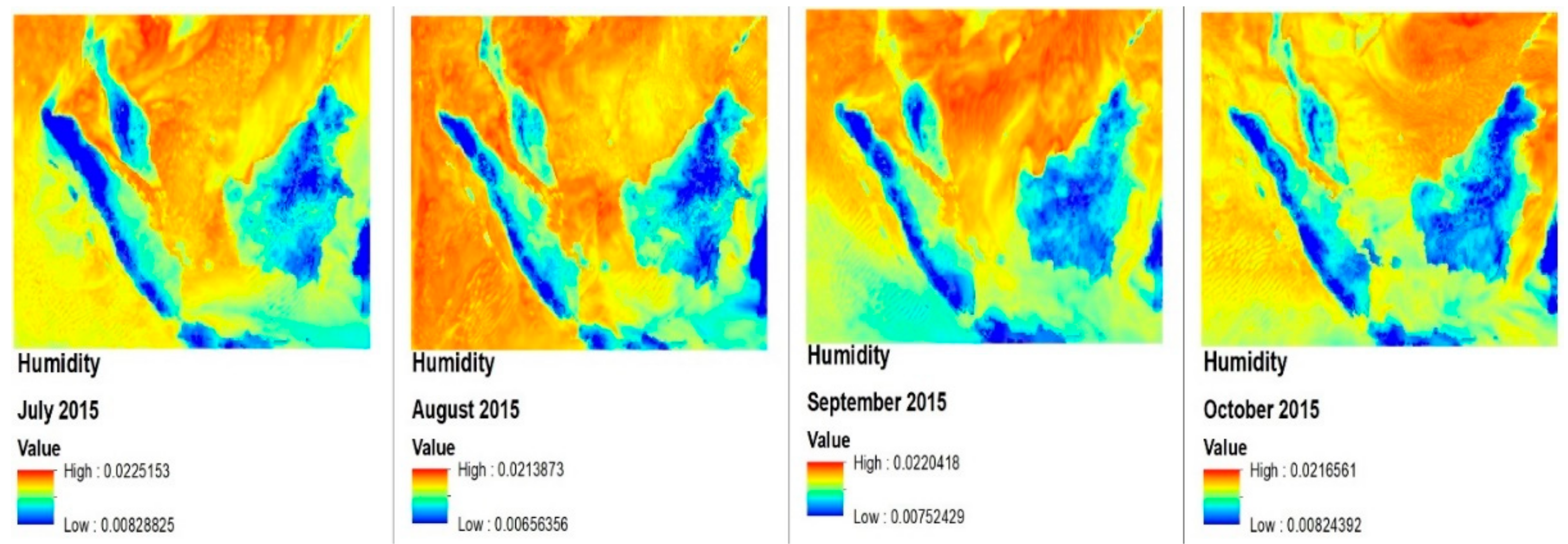
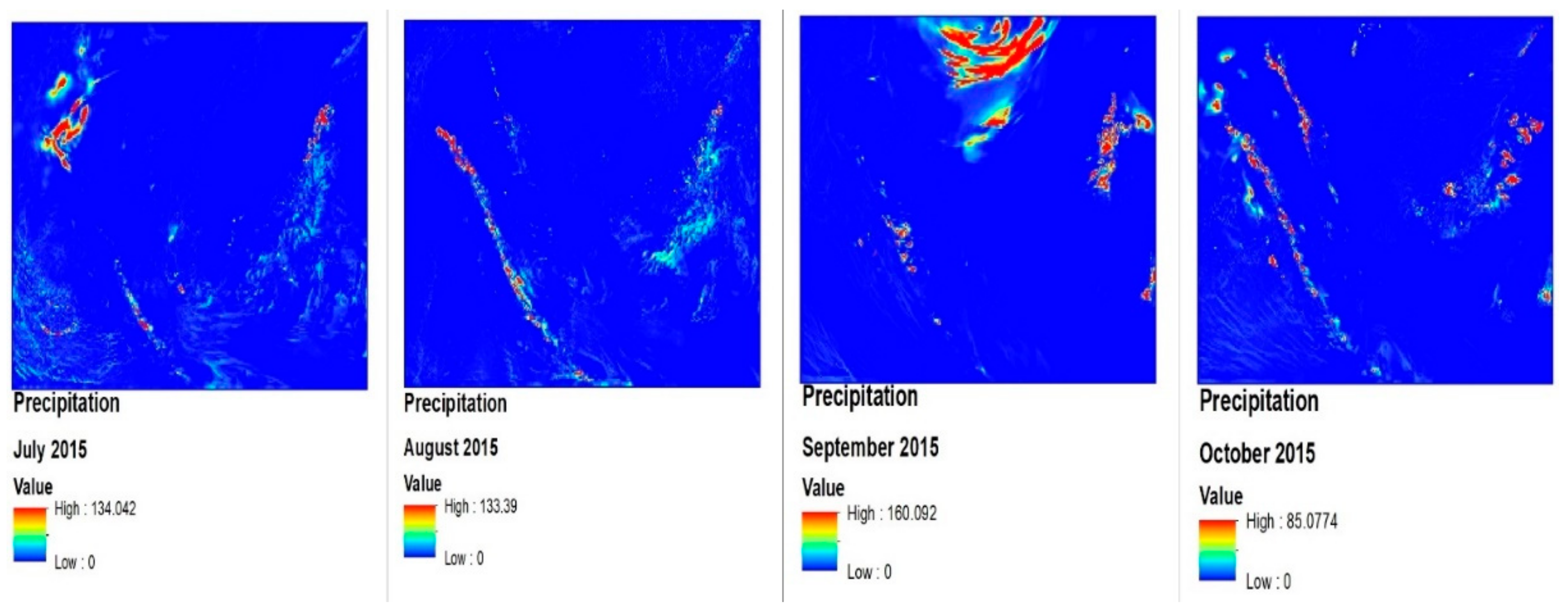
3.3. Model Data (Surface Air Temparature, Humidity, and Precipitation) Analysis from MEI, DMI, MJO, and OLR Viewpoints
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramage, C.S. Role of a tropical maritime continent in the atmospheric circulation 1. Mon. Weather Rev. 1968, 96, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, N.; Jilia, S. The Maritime Continent and Its Role in the Global Climate: A GCM Study. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-P.; Zhuo, W. Annual Cycle of Southeast Asia—Maritime Continent Rainfall and the Asymmetric Monsoon Transition. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, J.-H. Why Precipitation Is Mostly Concentrated over Islands in the Maritime Continent. J. Atmosp. Sci. 2008, 67, 3509–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.C. Intertropical convergence zone studied with an interacting atmosphere and ocean model. Mon. Weather Rev. 1971, 99, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianotti, R.L. Assessment of the Regional Climate Model Version 3 over the Maritime Continent Using Different Cumulus Parameterization and Land Surface Schemes. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 638–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrian, E.; Susanto, R.D. Identification of three dominant rainfall regions within Indonesia and their relationship to sea surface temperature. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakhmat, P.; As-Syakur, R.A.; Takahiro, O. Validation of TRMM Precipitation Radar satellite data over Indonesian region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 12, 575–587. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L. Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Precipitation Data and Services for Research and Applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 92, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, A.; Robertson, A.W.; Qian, J.H. A role for tropical tropospheric temperature adjustment to El-Niño Southern Oscillation in the seasonality of monsoonal Indonesia precipitation predictability. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmosp. 2007, 112, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, P.J.; Crutzen, M.O. Biomass burning in the tropics: Impact on atmospheric chemistry and biogeochemical cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Collatz, G.J.; Mu, M.; Kasibhatla, P.S.; Morton, D.C.; DeFries, R.S.; Jin, Y.; van Leeuwen, T.T. Global fire emissions and the contribution of deforestation, savanna, forest, agricultural, and peat fires (1997–2009). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 11707–11735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Field, R.D.; der werf, G.R.V.; Fanin, T.; Fetzer, E.J.; Fuller, R.; Jethva, H.; Levy, R.; Livesey, N.J.; Luo, M.; Torres, O.; et al. Indonesian fire activity and smoke pollution in 2015 show persistent nonlinear sensitivity to El-Niño induced drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9204–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Pei, Y.H.; Mangharam, S. Trans-Boundary Haze Pollution in Southeast Asia: Sustainability through Plural Environmental Governance. Sustainability 2016, 8, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okimori, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Takahashi, F. Potential of Co2 emission reductions by carbonizing biomass waste from industrial tree plantation in South Sumatra, Indonesia. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2003, 8, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Schaaf, E.; Olivier, J.; Peters, J.; Schure, K. Fossil CO2 & GHG Emissions of All World Countries; JRC (Joint Research Centre) Science for Policy Report; JRC (Joint Research Centre): Ispra, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-79-73207-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z. Breakdown of the relationship between Australian summer rainfall and ENSO caused by tropical Indian Ocean SST warming. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 2321–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, T.; He, J. Out-of-Phase Relationship between Boreal Spring and Summer Decadal Rainfall Changes in Southern China. J. Clim. 2013, 27, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K. Tropical Circulation Systems and Monsoons; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Li, T. Why rainfall response to El Niño over Maritime Continent is weaker and non-uniform in boreal winter than in boreal summer. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1465–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, J.L.; Haylock, M.R.; Nicholls, N. Relationships between the Maritime Continent Heat Source and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation Phenomenon. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haylock, M.; McBride, J. Spatial Coherence and Predictability of Indonesian Wet Season Rainfall. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 3882–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden–Julian Oscillation: Bridging Weather and Climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1849–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Song, H.J.; Lim, G.H. The impact of the diurnal cycle on the MJO over the Maritime Continent: A modeling study assimilating TRMM rain rate into global analysis. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 40, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarella, A.; Giuliacci, A.; Scafetta, N. Quantifying the Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI) coupling to CO2 concentration and to the length of day variations. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2012, 111, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, K.; Timlin, M.S. Monitoring ENSO in COADS with a Seasonally Adjusted Principal Component Index. University of Oklahoma, School of Meteorology. Norman: Oklahoma Climate Survey. Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/enso/mei/WT1.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Saji, N.H.; Yamagata, T. Possible impacts of Indian Ocean Dipole mode events on global climate. Clim. Res. 2003, 25, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ESRL/NOAA. (12 September 2017). Dipole Mode Index (DMI). Retrieved from Global Climate Observing System (GCOS). Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/gcos_wgsp/Timeseries/Data/dmi.long.data (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Wheeler, M.C.; Harry, H.H. An All-Season Real-Time Multivariate MJO Index: Development of an Index for Monitoring and Prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bureau of Meteorology, Australia. Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO). Retrieved from Bureau of Meteorology, Australia. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/#tabs=MJO-phase (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Petty, G.W. A First Course in Atmospheric Radiation, 2nd ed.; Sundog Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Meteorology, Australia. Global Maps of Outgoing Longwave Radiation (OLR). Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/mjo/#tabs=Cloudiness (accessed on 1 May 2018).
- NASA Earthdata-EOSDIS. Global Fire Maps. Retrieved from NASA Worldview. Available online: https://worldview.earthdata.nasa.gov/?p=geographic&l=MODIS_Aqua_SurfaceReflectance_Bands143,MODIS_Aqua_SurfaceReflectance_Bands721,MODIS_Terra_SurfaceReflectance_Bands143,MODIS_Terra_SurfaceReflectance_Bands721,VIIRS_SNPP_CorrectedReflectance_TrueColor(hi (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Joyce, R.J.; Janowiak, J.E.; Arkin, P.A.; Xie, P. CMORPH: A Method that Produces Global Precipitation Estimates from Passive Microwave and Infrared Data at High Spatial and Temporal Resolution. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Weather Service/NOAA/U.S. Department of Commerce (2015): NCEP GDAS/FNL 0.25 Degree Global Tropospheric Analyses and Forecast Grids. Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory. Dataset. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5065/D65Q4T4Z (accessed on 10 May 2018).
- NOAA. Bimonthly MEI Values. Retrieved from Multivariate ENSO Index (MEI). Available online: https://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/enso/mei/table.html (accessed on 17 May 2018).
- Hong, S.-Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.-H. A Revised Approach to Ice Microphysical Processes for the Bulk Parameterization of Clouds and Precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.F.M. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Contrib. Geophys. Inst. Acad. Sci. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Mitchell, K.E.; Chen, F.; Ek, M.B.; Barlage, M.; Kumar, A.; Manning, K.; Niyogi, D.; Rosero, E.; et al. The community Noah land surface model with multiparameterization options (Noah-MP): 1. Model description and evaluation with local-scale measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Guan, Z. Individual and Combined Influences of ENSO and the Indian Ocean Dipole on the Indian Summer Monsoon. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3141–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, G.; McIntosh, P.; Pigot, L.; Pook, M. The Years of El Niño, La Niña, and interactions with the tropical Indian Ocean. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-julian oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Physics (Processes) | Schemes Description |
|---|---|
| Microphysics scheme | WRF single-Moment (WSM) 3-class [38] |
| Long-wave radiation scheme | RRTM (Rapid Radiative Transfer Model) scheme [39] |
| Short-wave radiation scheme | Dudhia scheme [40] |
| Surface layer scheme | Monin-Obukhov similarity scheme [41] |
| Land surface model | Noah-MP Land Surface model [42] |
| Planetary boundary layer (PBL) scheme | Yonsei University scheme (YSU) [43] |
| Cumulus parameterization scheme | Kain-Fritsch (new Eta) scheme [44] |
| 2015 (SST) K | Observed Value (Mean) Oi | Model Value (Mean) Mi | Absolute Error |(Oi−Mi)| | Square of the Absolute Error |(Oi−Mi)|2 | MSE | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Months | 5.9 | ≈2.43 | ||||
| JUL | 303.48 | 300.9 | 2.5 | 6.25 | ||
| AUG | 303.65 | 301.2 | 2.5 | 6.07 | ||
| SEP | 303.38 | 300.9 | 2.5 | 6.18 | ||
| OCT | 303.85 | 301.6 | 2.3 | 5.19 | ||
| 2015 (Precipitation) mm | Observed Value (Mean) Oi | Model Value (Mean) Mi | Absolute Error |(Oi−Mi)| | Square of the Absolute Error |(Oi−Mi)|2 | MSE | RMSE |
| Months | 0.24 | ≈0.49 | ||||
| JUL | 1.74 | 1.15 | 0.59 | 0.35 | ||
| AUG | 1.38 | 1.17 | 0.21 | 0.04 | ||
| SEP | 1.90 | 1.30 | 0.63 | 0.40 | ||
| OCT | 2.63 | 2.25 | 0.38 | 0.15 | ||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.A.; Chan, A.; Ashfold, M.J.; Ooi, C.G.; Azari, M. Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090352
Islam MA, Chan A, Ashfold MJ, Ooi CG, Azari M. Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(9):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090352
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, M. Amirul, Andy Chan, Matthew J. Ashfold, Chel Gee Ooi, and Majid Azari. 2018. "Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015" Atmosphere 9, no. 9: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090352
APA StyleIslam, M. A., Chan, A., Ashfold, M. J., Ooi, C. G., & Azari, M. (2018). Effects of El-Niño, Indian Ocean Dipole, and Madden-Julian Oscillation on Surface Air Temperature and Rainfall Anomalies over Southeast Asia in 2015. Atmosphere, 9(9), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090352





