Abrupt Climate Shift in the Mature Rainy Season of the Philippines in the Mid-1990s
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- With the observed decadal changes in the summer monsoon of the adjacent regions, it is necessary to confirm whether such an interdecadal change can be observed locally over the Philippines. In fact, an inconspicuous rainfall trend can be seen in Figure 1 of Kajikawa et al. [23] using reanalysis datasets over Luzon Island. In particular, the increasing rainfall trend in May (see their Figure 1a) only appears over the central and southern Philippines and the decreasing rainfall trend in June (see their Figure 1b) can only be depicted over the SCS. It is worth mentioning that the complex topography of the Philippines gives rise to four different climate types [8]. The current resolution of available reanalysis datasets present difficulties in representing the correct sub-regional characteristics of rainfall. Thus, to better capture the changes in rainfall in the sub-regional scale, station-based rainfall data are preferred. In this study, we used the station-based rainfall data and supplemented it by the rainfall estimates from the Climate Prediction Center Merged Analysis of Precipitation (CMAP) during 1979–1993 and 1994–2008 following the change point used by Kwon et al. [25] and Kajikawa and Wang [22] around 1993/1994. We also investigated other periods with remarkable changes. Additional tests were performed in both datasets to confirm whether this change point in the mid-1990s is significant or not over the Philippines.
- (2)
- To the best of our knowledge, very few studies have examined the decadal-to-interdecadal changes in rainfall over the Philippines. Previous studies (e.g., by Cruz et al. [2], Villafuerte et al. [12], and Cinco et al. [9]) only focus on long-term trends and variability of seasonal and annual rainfall or temperature. This study is part of our on-going endeavor in understanding the multi-temporal variability of rainfall in the Philippines.
2. Data Sources and Methodology
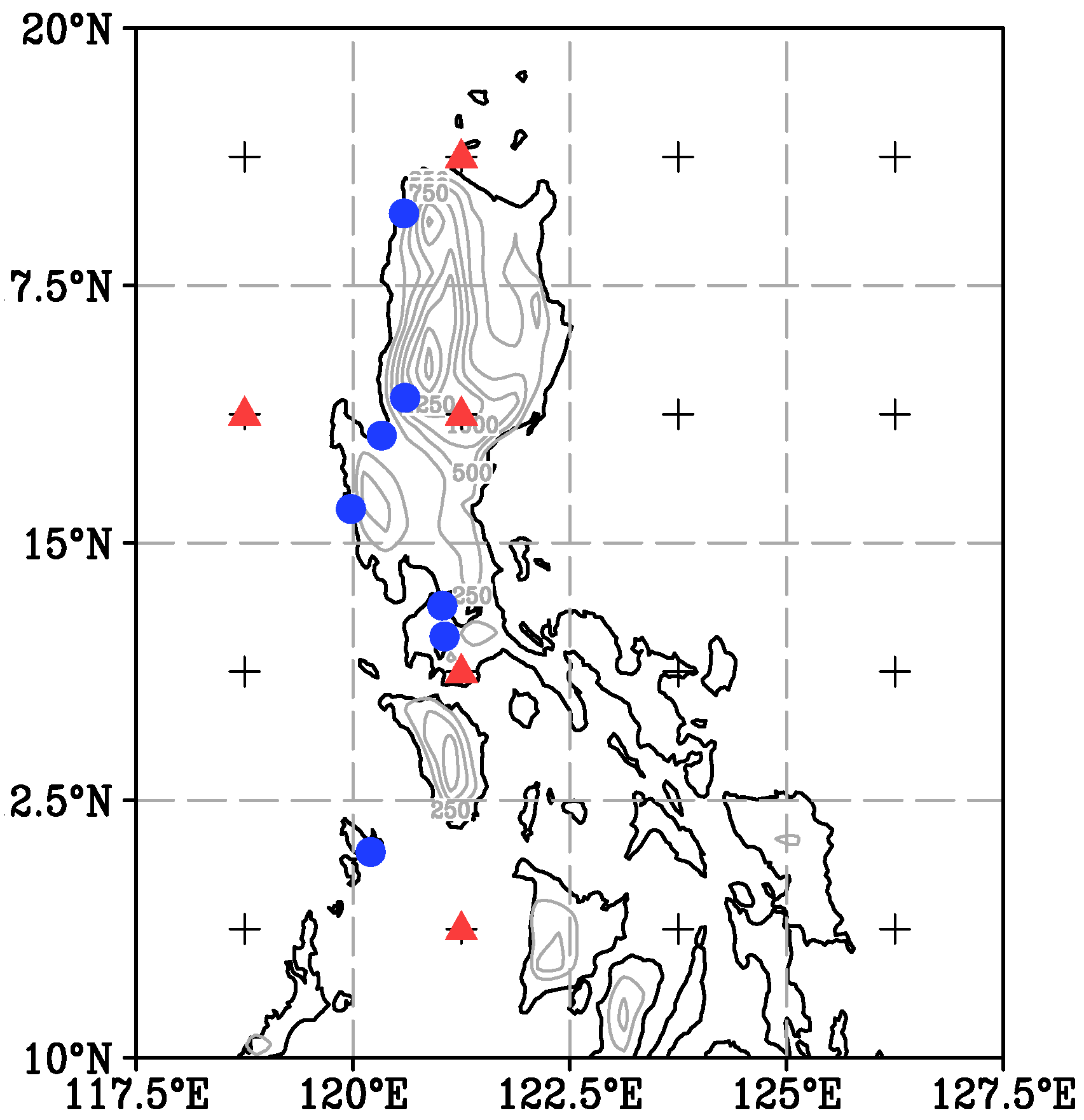
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Methodology
3. Results
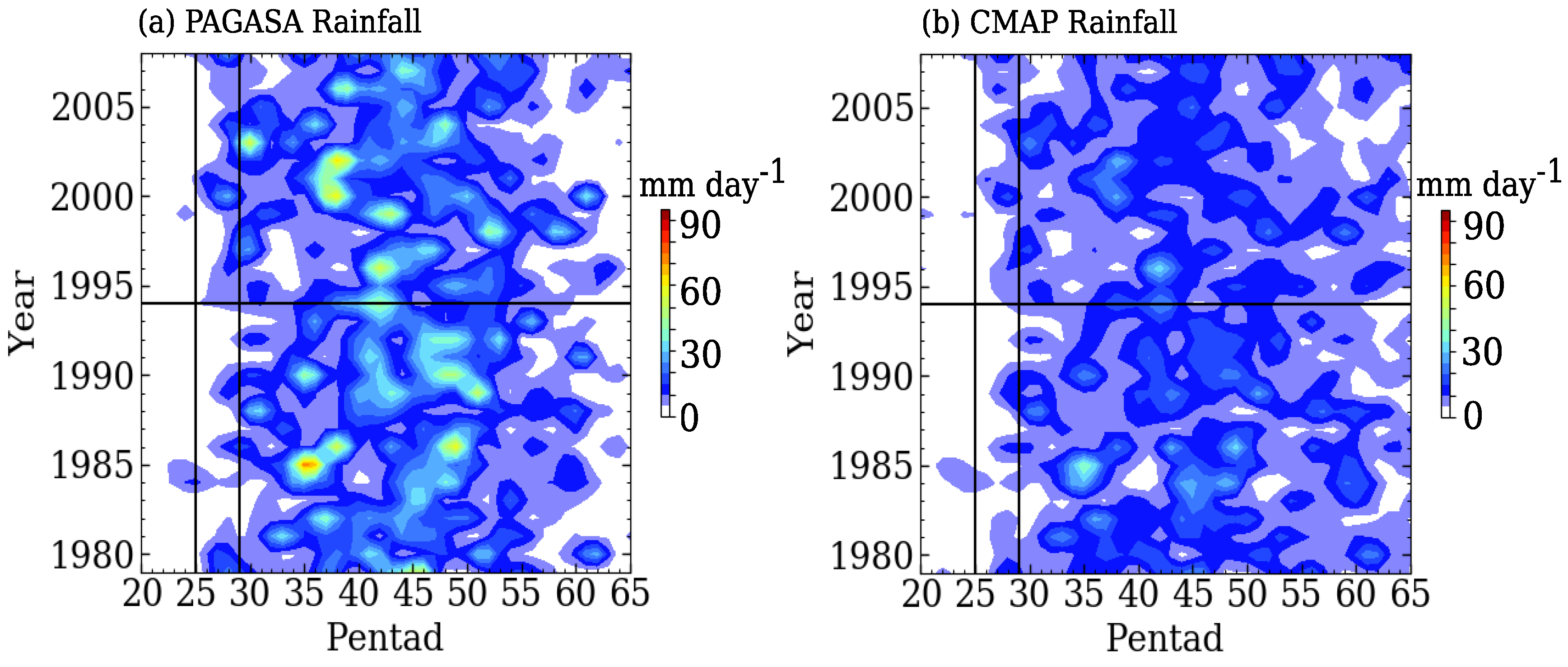
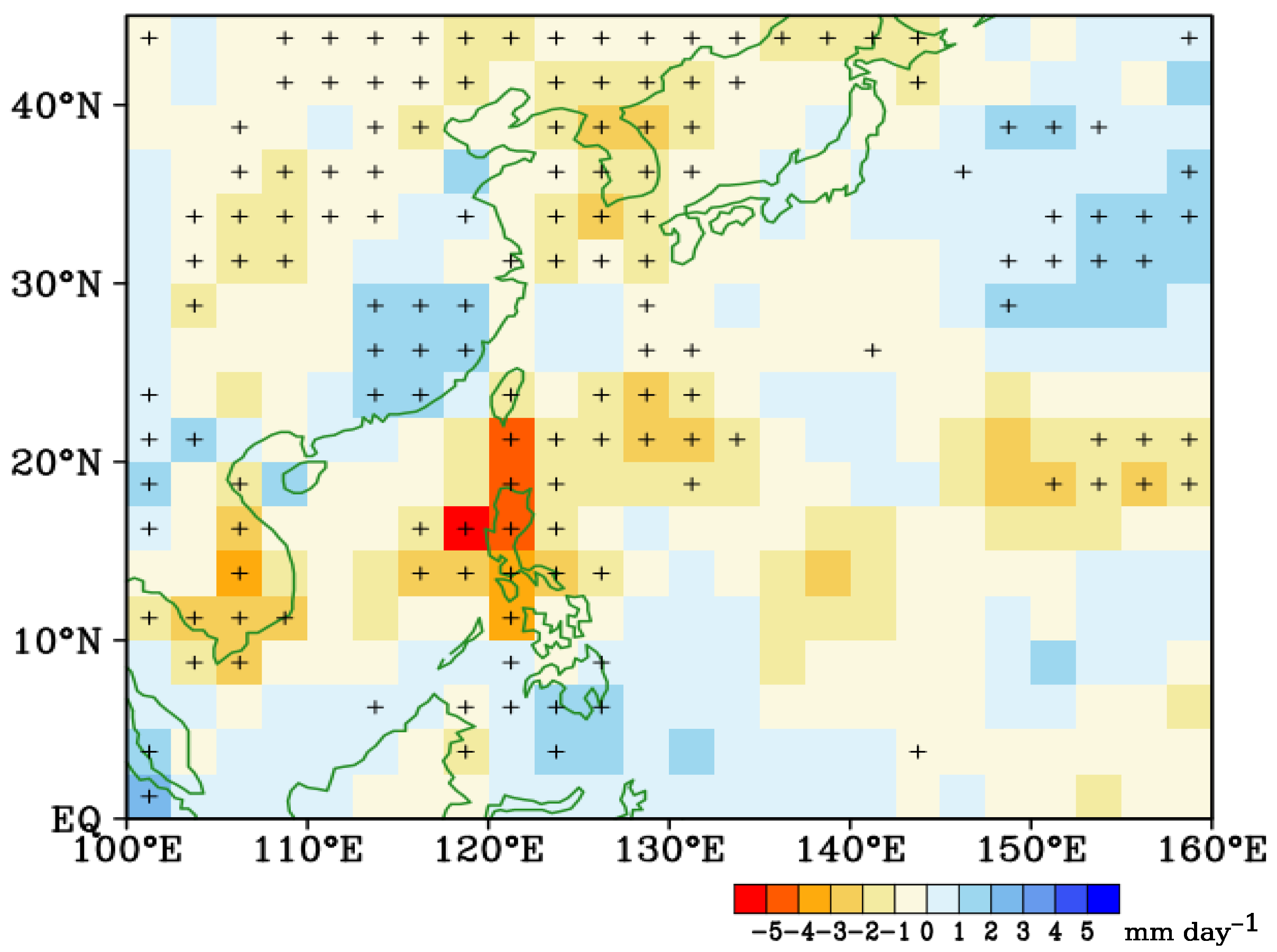
3.1. Changes in Rainfall
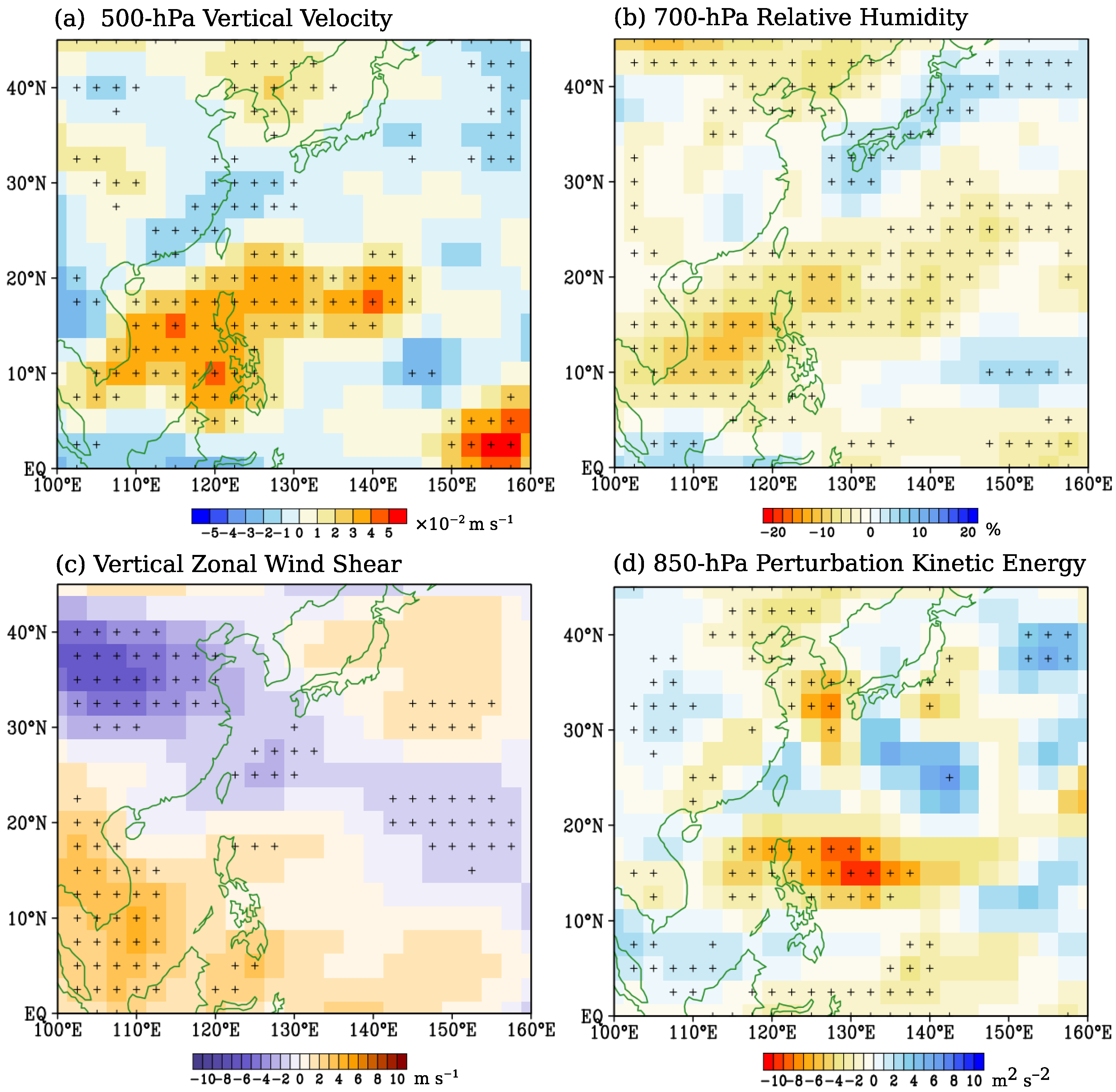
3.2. Possible Influencing Factors
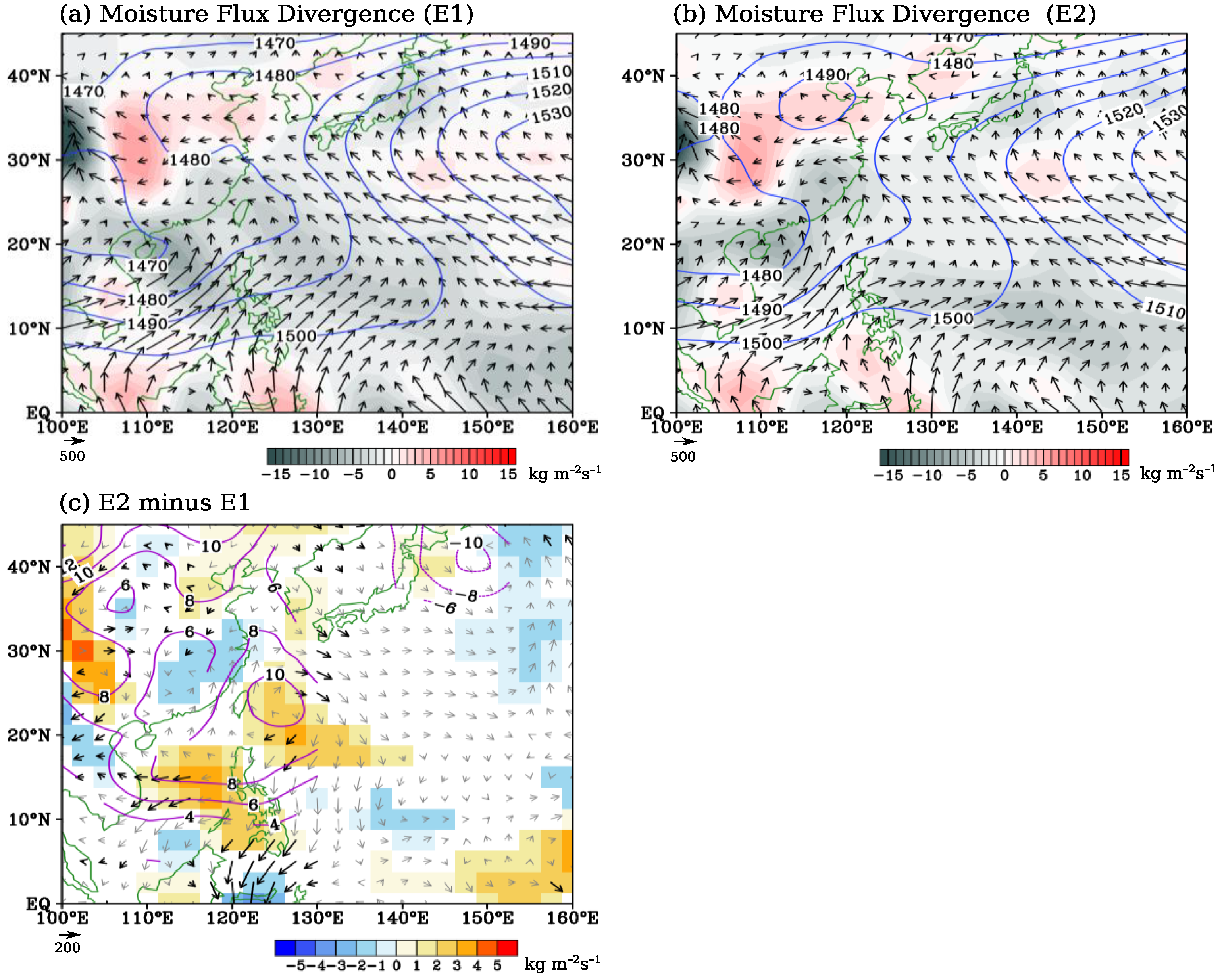
3.2.1. Changes in Moisture Transport
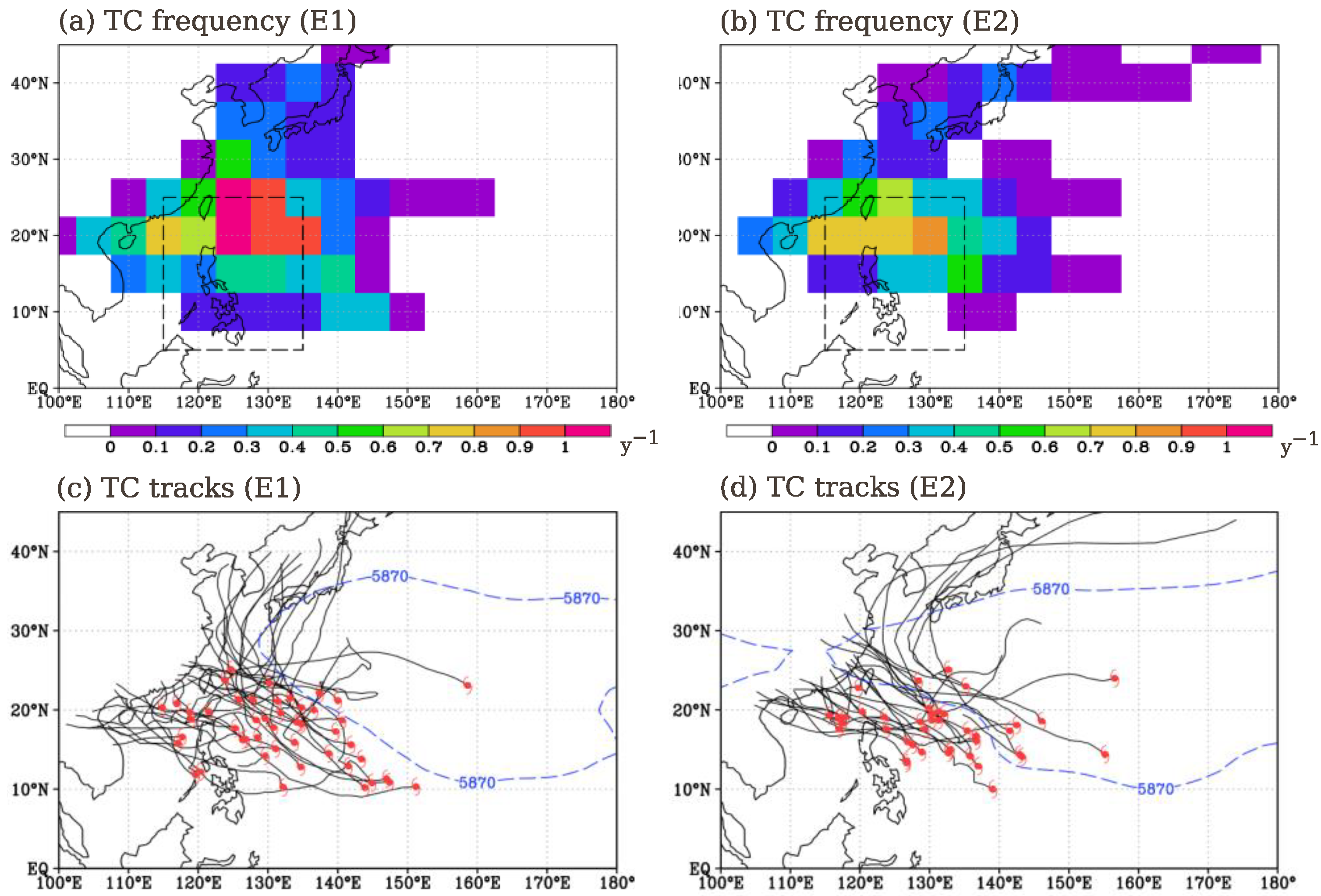
3.2.2. Changes in TC Activity
4. Summary and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cayanan, E.O.; Chen, T.; Argete, J.; Ten, M.; Nilo, P. The effect of tropical cyclones on southwest monsoon rainfall in the Philippines. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 89, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.T.; Narisma, G.T.; Villafuerte, M.Q.; Chua, K.C.; Olaguera, L.M. A climatological analysis of the southwest monsoon rainfall in the Philippines. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B.; Camargo, S.J. The seasonally varying influence of ENSO on rainfall and tropical cyclone activity in the Philippines. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, J. The seasonal changes in Asian Australian monsoon regions. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, J. Seasonal transition of summer rainy season over Indochina and adjacent monsoon region. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 14, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullen, J.; Gordon, A.L.; Flatau, M.; Doyle, J.D.; Villanoy, C.; Cabrera, O. Multiscale influences on extreme winter rainfall in the Philippines. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3292–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akasaka, I. Interannual variations in seasonal march of rainfall in the Philippines. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kintanar, R.L. Climate of the Philippines; PAGASA: Quezon City, Philippines, 1984.
- Cinco, T.A.; de Guzman, R.G.; Hilario, F.D.; Wilson, D.M. Long-term trends and extremes in observed daily precipitation and near surface air temperature in the Philippines for the period 1951–2010. Atmos. Res. 2014, 145, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Y. Interdecadal variation of summer precipitation in east China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1139–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Matsumoto, J. Abrupt climate changes observed in late August over central Japan between 1983 and 1984. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 4957–4967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villafuerte, M.Q.; Matsumoto, J.; Akasaka, I.; Takahashi, H.G.; Kubota, H.; Cinco, T.A. Long-term trends and variability of rainfall extremes in the Philippines. Atmos. Res. 2014, 137, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, K.J.; Yun, K.S.; Jhun, J.G.; Li, J. Circulation changes associated with the interdecadal shift of Korean August rainfall around late 1960s. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nitta, T.; Yamada, S. Recent warming of the tropical sea surface temperature and its relationship to the northern hemisphere circulation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1989, 67, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B. Interdecadal change in El Niño onset in the last four decades. J. Clim. 1995, 8, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J. Weakening of the Asian monsoon circulation after the end of 1970s. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 18, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, T. Convective activities in the tropical western Pacific and their impact on the northern hemisphere summer circulation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 65, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.Y.; Ho, C.H. Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.J.; Li, S.L.; Luo, D.H. Impact of global SST on decadal shift of East Asian summer climate. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y. Interdecadal variation of summer precipitation in east China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part II: Possible causes. Int. J. Climatol. 2009, 29, 1926–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, R.; Wu, R. Interdecadal variability in tropical cyclone frequency over the South China Sea and its association with the Indian Ocean sea surface temperature. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Wang, B. Interdecadal change of the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3207–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Yasunari, T.; Yoshida, S.; Fujinami, H. Advanced Asian summer monsoon onset in recent decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.; Jhun, J.G.; Wang, B.; An, S.I.; Kug, J.S. Decadal change in relationship between East Asian and WNP summer monsoons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.; Jhun, J.G.; Ha, K.J. Decadal change in East Asian summer monsoon circulation in the mid-1990s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, G.; Huang, R. Interdecadal variability of summer rainfall in eastern China detected by Lepage test. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 106, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Wen, Z.; Yang, S.; Li, Y. An interdecadal change in Southern China summer rainfall around 1992/1993. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 2389–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Ma, J. Recent changes in the summer precipitation pattern in East Asia and the background circulation. Clim. Dyn. 2011, 36, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Wu, C.C.; Sui, C.H.; Ho, C.H. Tropical cyclone contribution to interdecadal change in summer rainfall over South China in the early 1990s. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2012, 23, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, R.; Wen, Z. Contribution of the South China Sea tropical cyclones to an increase in Southern China rainfall around 1993. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, Y.; Yasunari, T.; Wang, B. Decadal change in intraseasonal variability over the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.M.; Jhun, J.G.; Ha, K.J.; Kimoto, M. Decadal changes in climatological intraseasonal fluctuation of subseasonal evolution of summer precipitation over the Korean Peninsula in the mid-1990s. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Y. Interdecadal change in the seasonality of rainfall variation in South China. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, T.; Kajikawa, Y. Decadal change in the boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 45, 3003–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Yasunari, T. Decreasing trend in rainfall over Indochina during the late summer monsoon: Impact of tropical cyclones. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2008, 86, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H. Long-term changes in rainfall and tropical cyclone activity over South and Southeast Asia. Adv. Geosci. 2011, 30, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubota, H.; Shirooka, R.; Matsumoto, J.; Cayanan, E.O.; Hilario, F.D. Tropical cyclone influence on the long-term variability of the Philippines summer monsoon onset. Prog. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Tsay, J.D.; Matsumoto, J.; Alpert, J. Impact of summer monsoon westerlies in the South China Sea tropical cyclone genesis in May. Weather Forecast. 2017, 32, 925–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.M.; Yang, S. Climatology and interannual variability of the southeast Asian summer monsoon. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 1997, 14, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Chen, W. Roles of the tropical convective activities over different regions in the earlier onset of the South China Sea summer monsoon after 1993. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.; Wang, B. Mechanisms for the advanced Asian summer monsoon onset since the mid-to-late 1990s. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 1993–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, B. Enhanced western North Pacific tropical cyclone activity in May in recent years. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 2555–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamitsu, M.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Woollen, J.; Yan, S.K.; Hnilo, J.J.; Fiorino, M.; Potter, G.L. NCEP-DOE AMIP-II Reanalysis (R-2). Bull Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2002, 83, 1631–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Ota, Y.; Harada, Y.; Ebita, A.; Moriya, M.; Onoda, H.; Onogi, K.; Kamahori, H.; Kobayashi, C.; Endo, H.; Miyaoka, H.; Takahashi, K. The JRA-55 Reanalysis: General specifications and basic characteristics. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 93, 5–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P. Global precipitation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudeyasu, H.; Iizuka, S.; Matsuura, T. Impact of ENSO on landfall characteristics of tropical cyclones over the western North Pacific during summer monsoon season. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chan, J.C. How strong ENSO events affect tropical storm activity over the western North Pacific. J. Clim. 2002, 13, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Matsumoto, J. Summer monsoon over the Asian Continent and Western North Pacific. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 72, 719–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, B.C.; Chandler, R.E.; Browman, A.W. Trend estimation and change point detection in individual climatic series using flexible regression methods. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ha, K.J.; Ha, E. Climatic change and interannual fluctuations in the long-term record of monthly precipitation for Seoul. Int. J. Climatol. 2006, 26, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallakpour, I.; Villarini, G.A. simulation study to examine the sensitivity of the Pettitt test to detect abrupt changes in mean. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarijazi, M.; Akhond-Ali, A.M.; Adib, A.; Daneshkhah, A. Trend and change-point detection for the annual stream-flow series of the Karun River at the Ahvaz hydrometric station. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2012, 32, 4540–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, R.J. Comments on “Observed trends in indices of daily temperature extremes in south America 1960–2000”. J. Clim. 2010, 24, 2880–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.L. Reply to the comments on “Observed trends in indices of daily temperature extremes in south America 1960–2000”. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 2884–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.F.; Wang, J.; Yeh, H.F.; Lee, C.H. Spatial and temporal streamflow trends in northern Taiwan. Water 2015, 7, 634–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK; Waltham, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 143–144. ISBN 978-0-12-385022-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cinco, T.A.; de Guzman, R.; Ortiz, A.M.; Delfina, R.J.; Lasco, R.D.; Hilario, F.D.; Juanillo, E.L.; Barba, R.; Ares, E.D. Observed trends and impacts of tropical cyclones in the Philippines. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; LinHo. Rainy season of the Asian-Pacific summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2002, 15, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xu, X. Northern Hemisphere summer monsoon singularities and climatological intraseasonal oscillation. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Cha, Y.; Kim, H.D. Interdecadal variation of precipitation days in August in the Korean Peninsula. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2017, 77, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Le, D.; Matsumoto, J.; Ngo-Duc, T. Climatological onset date of summer monsoon in Vietnam. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 3237–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y.; Yamazaki, K. Climatological evolution of the Okinawa Baiu and differences in large-scale features during May and June. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6287–6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Wang, B. How much do tropical cyclones affect seasonal and interannual rainfall variability over the western North Pacific? J. Clim. 2009, 22, 5495–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagtasa, G. Contribution of tropical cyclones to rainfall in the Philippines. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 3621–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yang, J.; Gong, D.; Mao, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, M. Decadal changes in tropical cyclone activity over the western North Pacific in the late 1990s. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 3317–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, M.A.; Chandler, R.E.; Merchant, C.J.; Roberts, F.P. Atlantic hurricanes and NW Pacific typhoon: ENSO spatial impacts on occurrence and landfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2000, 27, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Graf, H.F.; Leung, Y.; Herzog, M. Different El Niño types and tropical cyclone landfall in East Asia. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6510–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Wu, C.C.; Cha, E.J. Change of tropical cyclone activity by Pacific-Japan teleconnection pattern in the western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirata, H.; Kawamura, R. Scale interaction between typhoons and the North Pacific subtropical high and associated remote effects during the Baiu/Mei-yu season. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 5157–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X. Impact of intraseasonal oscillation on the tropical cyclone track in the South China Sea. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1505–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, Y.; Zhong, Z. Decadal change in tropical cyclone activity over the South China Sea around 2002/03. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Sun, F. Impacts of tropical western Pacific on the East Asian summer monsoon. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cui, X. Hadley circulation signal in the tropical cyclone frequency over the western North Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Kosaka, Y.; Xie, S.P. A 117-year long index of the Pacific-Japan pattern with application to interdecadal variability. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 36, 1575–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Y.; Yang, L.; Xie, S.P. Tropical Indian Ocean influence on northwest Pacific tropical cyclones in summer following strong El Nino. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Dickinson, M.J. The intraseasonal oscillation and the energetics of summertime tropical western North Pacific synoptic-scale disturbances. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 2153–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Yasunari, T. A climatological monsoon break in rainfall over Indochina- A singularity in the seasonal march of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Lu, R. Decadal change of the western North Pacific summer monsoon break around 2002/2003. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Karnauskas, K.B. The role of tropical interbasin SST gradients in forcing Walker circulation trends. J. Clim. 2017, 30, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.E. Some simple solutions for heat-induced tropical circulation. Q. J. Royal Meteorol. Soc. 1980, 106, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, N.A.; Parker, D.E.; Horton, E.B.; Folland, C.K.; Alexander, L.V.; Rowell, D.P.; Kent, E.C.; Kaplan, A. Global analysis of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PERIOD | CMAP | PAGASA |
|---|---|---|
| P28–P31 | 1986/1987 | 1995/1996 ** |
| P33–P36 | 1992/1993 ** | 1993/1994 ** |
| P38–P39 | 1998/1999 | 1998/1999 * |
| P43–P44 | 1989/1990 * | 1993/1994 ** |
| P45–P50 | 1993/1994 *** | 1993/1994 ** |
| P52–P54 | 1990/1991 | 1990/1991 ** |
| P59–P60 | 1999/2000 ** | 1999/2000 *** |
| E1 (1979–1993) | E2 (1994–2008) | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTOTAL (mm) | 651.00 | 464.11 | 557.55 |
| PTC (mm) | 352.03 | 160.42 | 256.22 |
| PNOTC (mm) | 298.97 | 303.69 | 301.33 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olaguera, L.M.; Matsumoto, J.; Kubota, H.; Inoue, T.; Cayanan, E.O.; Hilario, F.D. Abrupt Climate Shift in the Mature Rainy Season of the Philippines in the Mid-1990s. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090350
Olaguera LM, Matsumoto J, Kubota H, Inoue T, Cayanan EO, Hilario FD. Abrupt Climate Shift in the Mature Rainy Season of the Philippines in the Mid-1990s. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(9):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090350
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlaguera, Lyndon Mark, Jun Matsumoto, Hisayuki Kubota, Tomoshige Inoue, Esperanza O. Cayanan, and Flaviana D. Hilario. 2018. "Abrupt Climate Shift in the Mature Rainy Season of the Philippines in the Mid-1990s" Atmosphere 9, no. 9: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090350
APA StyleOlaguera, L. M., Matsumoto, J., Kubota, H., Inoue, T., Cayanan, E. O., & Hilario, F. D. (2018). Abrupt Climate Shift in the Mature Rainy Season of the Philippines in the Mid-1990s. Atmosphere, 9(9), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090350






