In-Cabin Vehicle Carbon Monoxide Concentrations under Different Ventilation Settings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Geographic Setting
2.2. Experimental Routes
2.3. Mobile CO Monitoring
2.4. Data Conditioning
2.5. Statistical Analysis
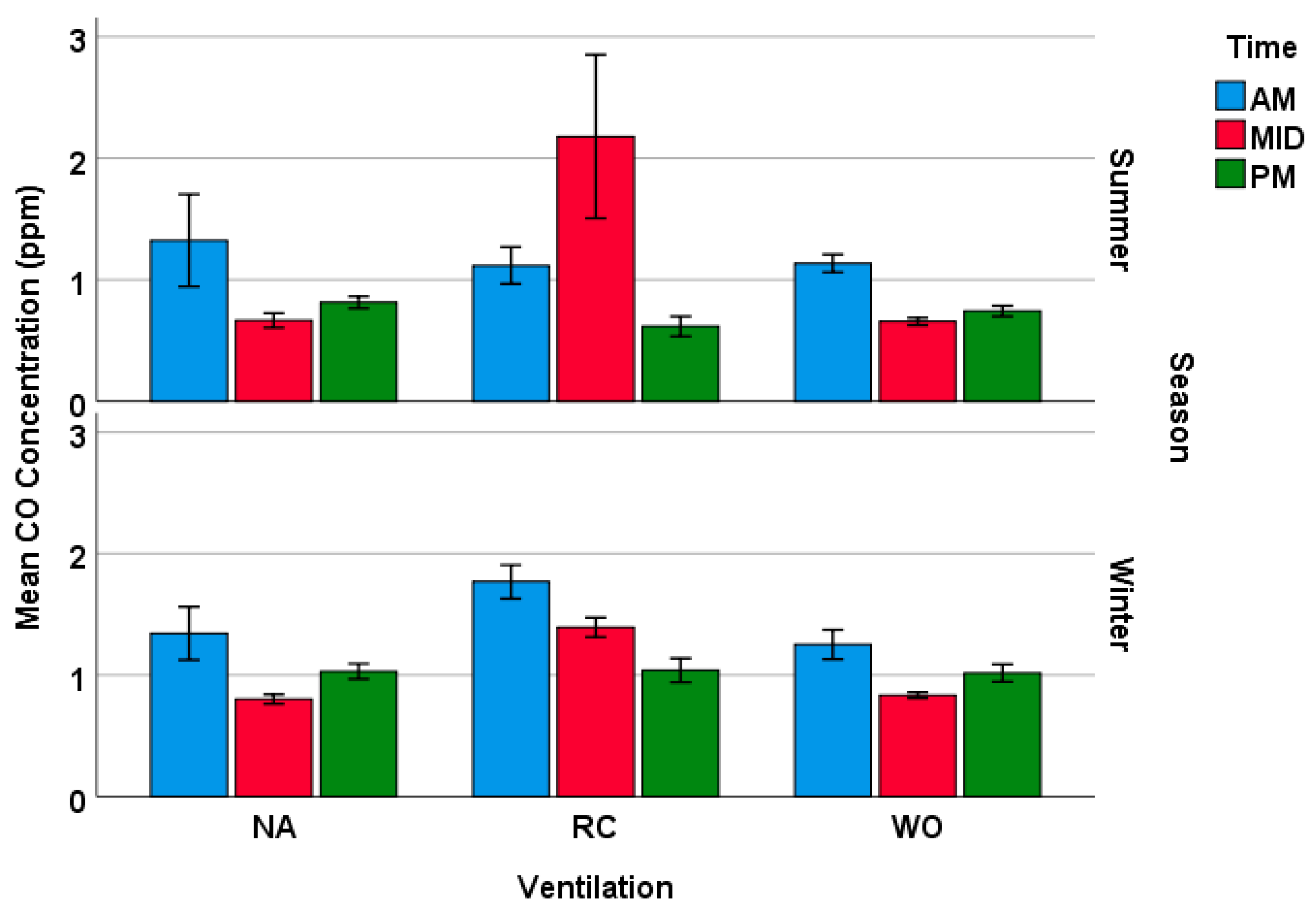
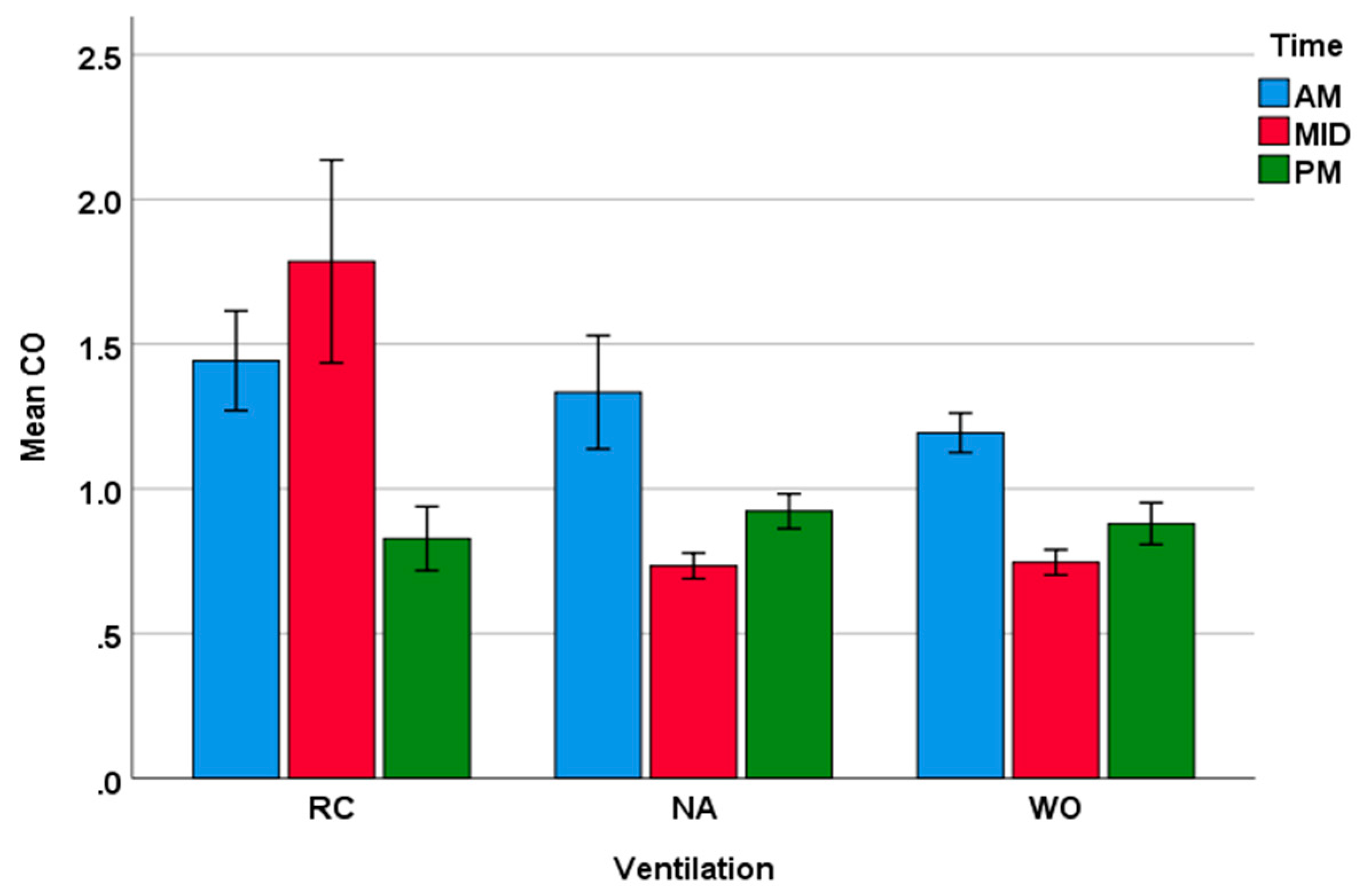
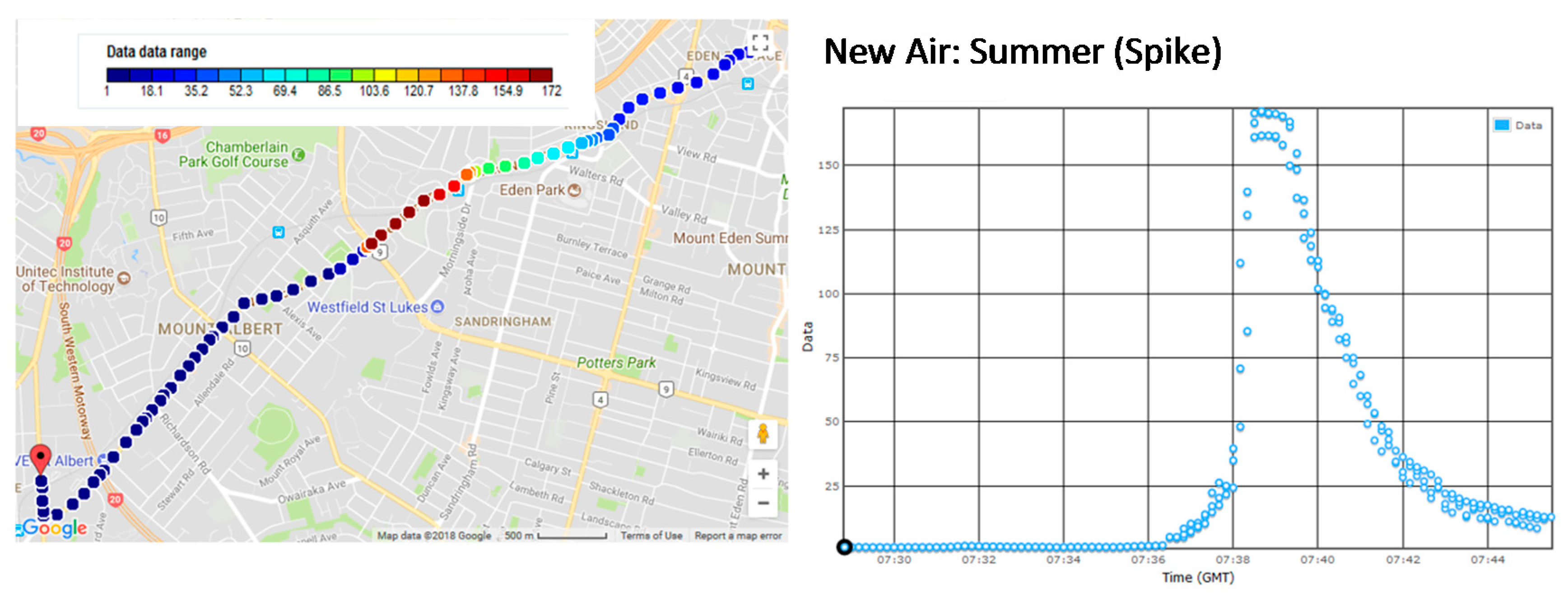
3. Results
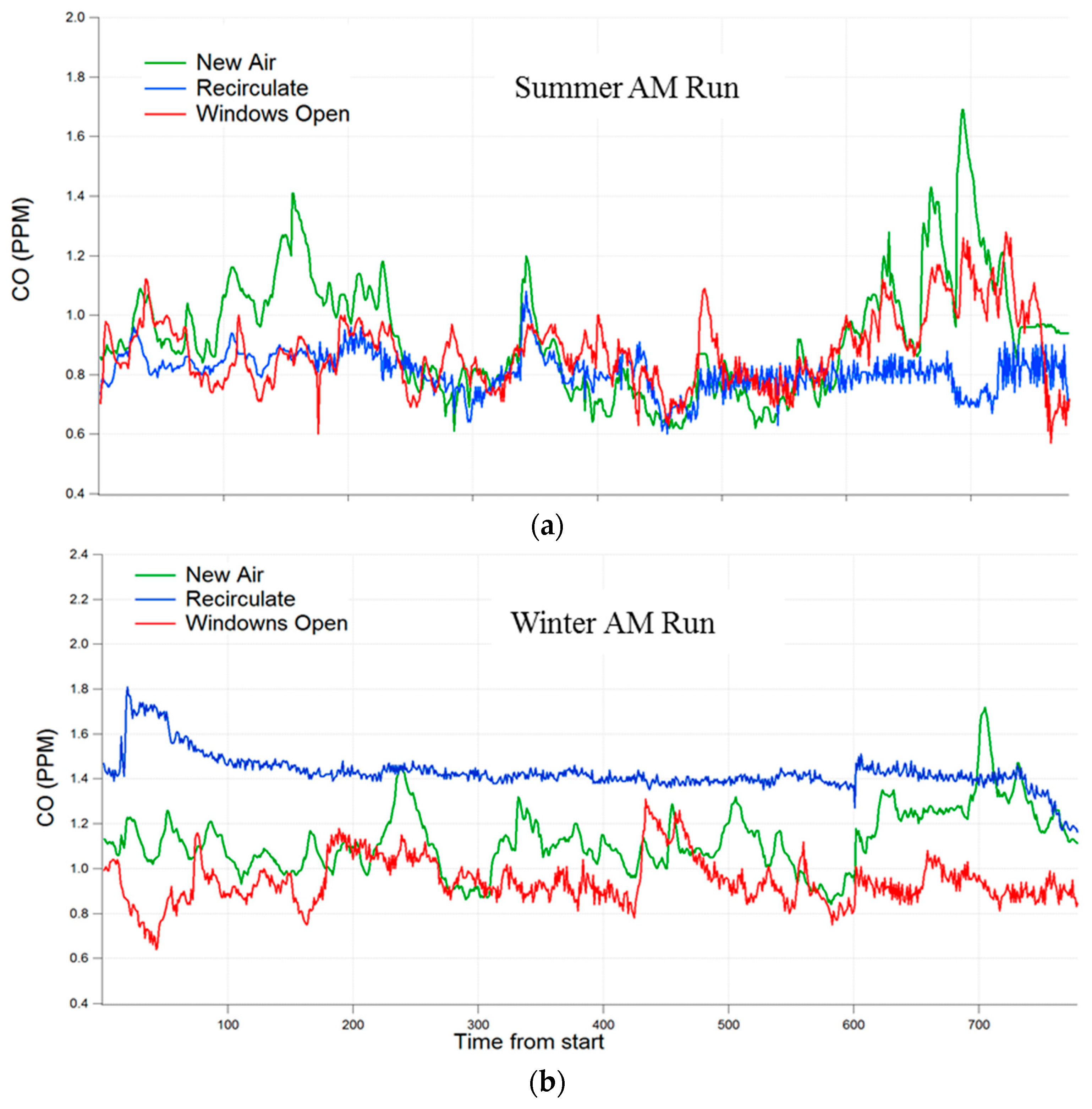
3.1. Time Series Data
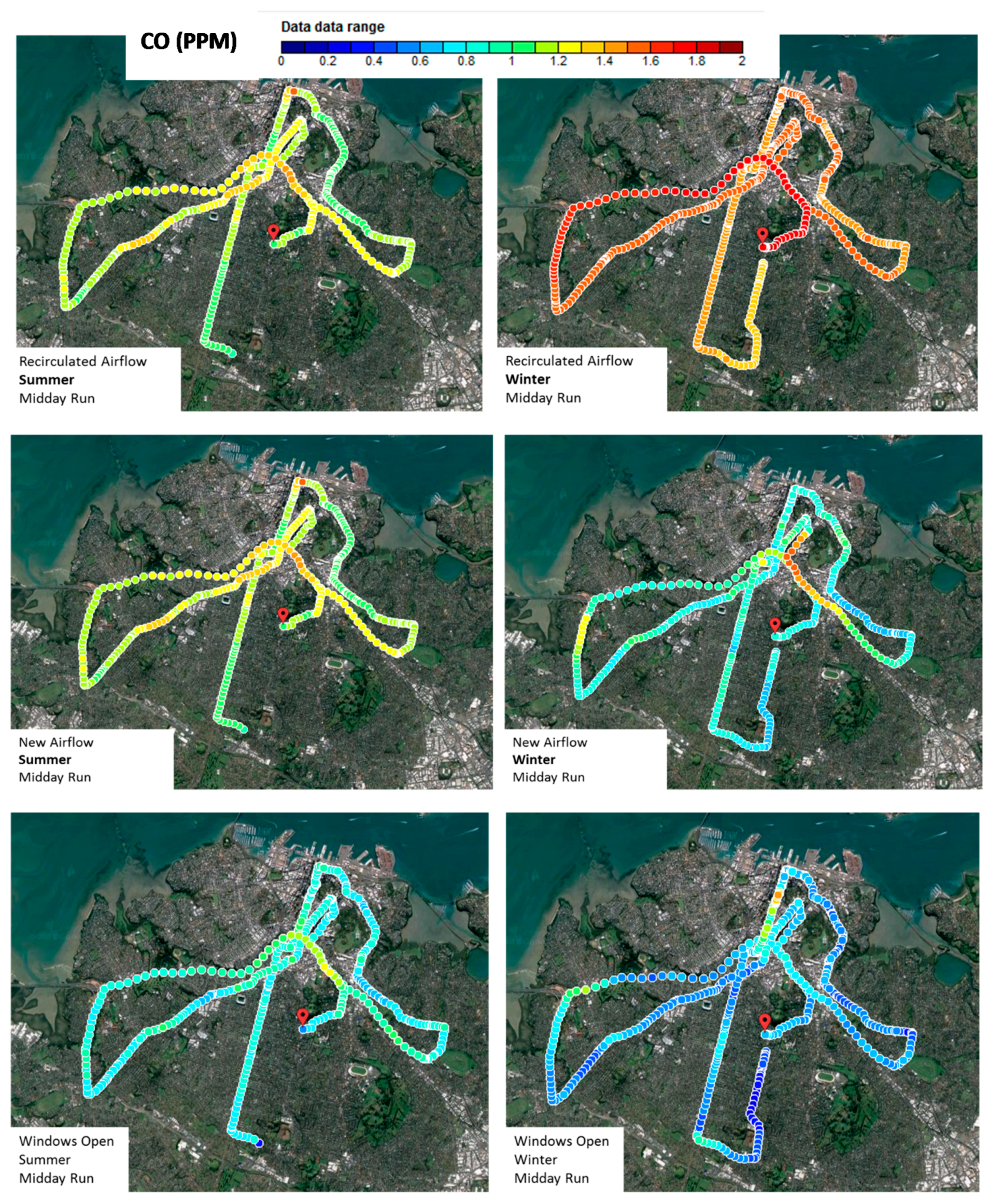
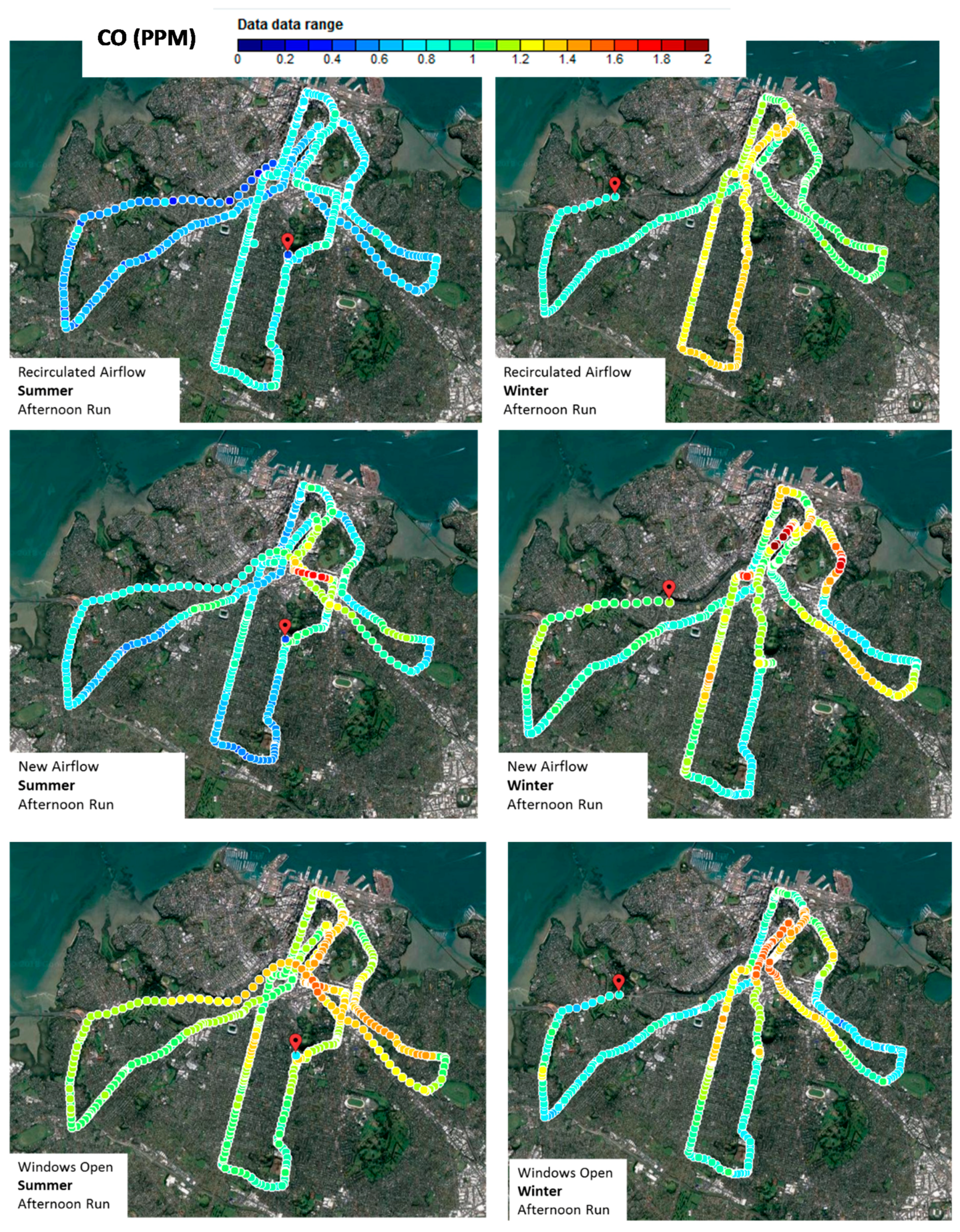
3.2. Analysis of Loop Mean Concentrations
3.3. Analysis of Peak Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayer, H. Air Pollution in Cities. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4029–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Krudysz, M.; Kuhn, T.; Froines, J.; Sioutas, C. Penetration of freeway ultrafine particles into indoor environments. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Fruin, S.A. Models for predicting the ratio of particulate pollutant concentrations inside vehicles to roadways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11048–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.; Hudda, N.; Sioutas, C.; Fruin, S.A.; Delfino, R.J. Modeling the concentrations of on-road air pollutants in Southern California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9291–9299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudda, N.; Kostenidou, E.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Fruin, S.A. Vehicle and driving characteristics that influence in-cabin particle number concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8691–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Hinds, W.C.; Miguel, A.H. In-cabin commuter exposure to ultrafine particles on Los Angeles Freeways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H. Modelling CO2 Concentrations in Vehicle Cabin; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A. Indoor–outdoor relationships of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides under different outdoor meteorological conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirks, K.N.; Sharma, P.; Salmond, J.A.; Costello, S.B. Personal exposure to air pollution for various modes of transport in Auckland, New Zealand. TOASJ 2012, 6, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koushki, P.A.; Al-Dhowalia, K.H.; Niaizi, S.A. Vehicle occupant exposure to carbon monoxide. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1992, 42, 1603–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esber, L.A.; El-Fadel, M.; Nuwayhid, I.; Saliba, N. The effect of different ventilation modes on in-vehicle carbon monoxide exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, S.; Van Ryswyk, K.; Kulka, R.; Sun, L.; Wallace, L.; Joseph, L. In-vehicle exposures to particulate air pollution in Canadian metropolitan areas: The urban transportation exposure study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, S.; Jantunen, M.J.; Vartiainen, M. Urban commuter exposure to particle matter and carbon monoxide inside an automobile. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1999, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saksena, S.; Prasad, R.K.; Shankar, V.R. Daily exposure to air pollutants in indoor, outdoor and in-vehicle micro-environments: A pilot study in Delhi. Indoor Built Environ. 2007, 16, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagury, E.; Le Moullec, Y.; Momas, I. Exposure of Paris taxi drivers to automobile air pollutants within their vehicles. Occup. Environ. Med. 2000, 57, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J.; Morawska, L. Effect of cabin ventilation rate on ultrafine particle exposure inside automobiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, L.B.; Gooch, J. A Multi-City Investigation of Exposure to Diesel Exhaust in Multiple Commuting Modes; CATF Special Report 2007-1; Clean Air Task Force: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Indoor particle dynamics. Indoor Air 2004, 14 (Suppl. 7), 175–183. Available online: http://escholarship.org/uc/item/80f883g7 (accessed on 4 December 2015). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, A.T.; Chung, M.W. Indoor–outdoor air quality relationships in vehicle: Effect of driving environment and ventilation modes. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, X.; Xiong, J. Air quality inside motor vehicles. Indoor Built Environ. 2018, 27, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiyala, A.; Kumar, A. Study of in-vehicle pollutant variation in public transport buses operating on alternative fuels in the city of Toledo, Ohio. Open Environ. Biol. Monit. J. 2011, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachsbart, P.G. Models of exposure to carbon monoxide inside a vehicle on a Honolulu highway. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1999, 9, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kingham, S.; Longley, I.; Salmond, J.; Pattinson, W.; Shrestha, K. Variations in exposure to traffic pollution while travelling by different modes in a low density, less congested city. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 181, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.J.; Clarke, R.; Riffat, S.B. Drivers’ exposure to carbon monoxide in Nottingham, U.K. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1003–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulson, G.; Olivares, G.; Talbot, N. Aerosol Size Distributions in Auckland. Air Qual. Clim. Chang. 2016, 50, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- NZAVS Policy Brief Regional Commute Times. Available online: https://cdn.auckland.ac.nz/assets/psych/about/our-research/nzavs/Feedback%20Reports/NZAVS-Policy-Brief-Regional-Commute-Times.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2018).
- Fruin, S.A.; Hudda, N.; Sioutas, C.; Delifino, R.J. A predictive model for vehicle air exchange rates based on a large, representative sample. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3569–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Colvile, R. Fine particulate matter and carbon monoxide exposure concentrations in urban street transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4781–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auckland Council. Traffic Count Data. Published 2014. Available online: https://at.govt.nz/about-us/reports-publications/traffic-counts/ (accessed on 11 July 2018).
- Marlow, D. Evaluation of Carbon Monoxide Concentration with and without Catalytic Emission Controls from Gasoline Propulsion Engines; Report Number EPHB 289-12a; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
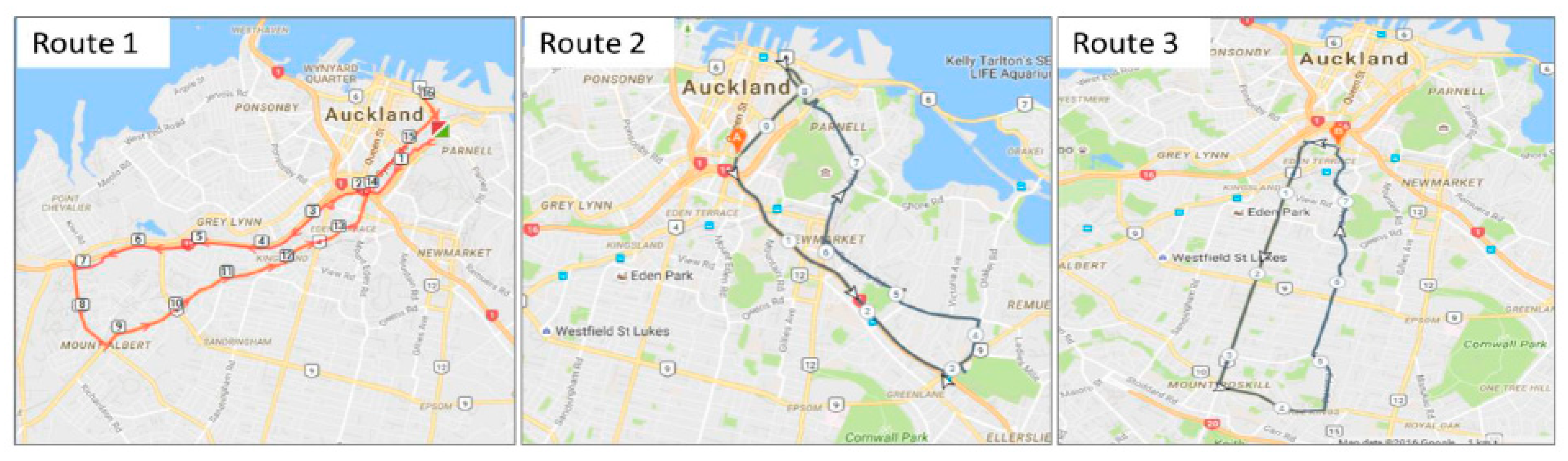

| Route | Road Name | Approximate Segment Range (km) | Average Daily Traffic Count (Vehicles per Day) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Route 1 | SH 16 (Motorway) | 1–7 | 58,000 |
| Great North Road | 7–9 | 16,000 | |
| New North Road | 9–16 | 19,000 | |
| Route 2 | SH 1 (Motorway) | 9–3 | 88,000 |
| Remuera Road | 3–6 | 23,400 | |
| Parnell Road | 6–8 | 18,800 | |
| Upper Queen Street | 8–9 | 17,700 | |
| Route 3 | Dominion Road | 1–3 | 25,900 |
| Balmoral Road | 4 | 24,100 | |
| Mt Eden Road | 5–8 | 15,200 |
| Ventilation | RC AM | RC MID | RC PM | WO AM | WO MID | WO PM | NA AM | NA MID | NA PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| St Dev Summer (ppm) | 0.006 | 0.095 | 0.131 | 0.016 | 0.142 | 0.078 | 0.059 | 0.095 | 0.074 |
| St Dev Winter (ppm) | 0.024 | 0.216 | 0.077 | 0.031 | 0.135 | 0.031 | 0.092 | 0.062 | 0.074 |
| Season | Ventilation | Morning | Midday | Evening | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (ppm) | St Dev (ppm) | Mean (ppm) | St Dev (ppm) | Mean (ppm) | St Dev (ppm) | ||
| Winter | RC | 1.77 | 0.24 | 1.39 | 0.14 | 1.04 | 0.17 |
| NA | 1.34 | 0.38 | 0.80 | 0.68 | 1.03 | 0.11 | |
| WO | 1.25 | 0.21 | 0.84 | 0.04 | 1.02 | 0.13 | |
| Summer | RC | 1.12 | 0.26 | 2.18 | 1.17 | 0.62 | 0.14 |
| NA | 1.32 | 0.66 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 0.08 | |
| WO | 1.13 | 0.12 | 0.66 | 0.05 | 0.74 | 0.07 | |
| Source | Squares | Df | MS | F | Sig |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ventilation | 1.799 | 2 | 0.899 | 6.121 | 0.004 |
| Time | 1.795 | 2 | 0.898 | 6.110 | 0.004 |
| Ventilation × Time | 2.792 | 4 | 0.698 | 4.750 | 0.003 |
| Error | 6.611 | 45 | 0.147 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dirks, K.N.; Talbot, N.; Salmond, J.A.; Costello, S.B. In-Cabin Vehicle Carbon Monoxide Concentrations under Different Ventilation Settings. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090338
Dirks KN, Talbot N, Salmond JA, Costello SB. In-Cabin Vehicle Carbon Monoxide Concentrations under Different Ventilation Settings. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(9):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090338
Chicago/Turabian StyleDirks, Kim N., Nicholas Talbot, Jennifer A. Salmond, and Seosamh B. Costello. 2018. "In-Cabin Vehicle Carbon Monoxide Concentrations under Different Ventilation Settings" Atmosphere 9, no. 9: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090338
APA StyleDirks, K. N., Talbot, N., Salmond, J. A., & Costello, S. B. (2018). In-Cabin Vehicle Carbon Monoxide Concentrations under Different Ventilation Settings. Atmosphere, 9(9), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9090338






