Extreme Wave Storms and Atmospheric Variability at the Spanish Coast of the Bay of Biscay
Abstract
1. Introduction
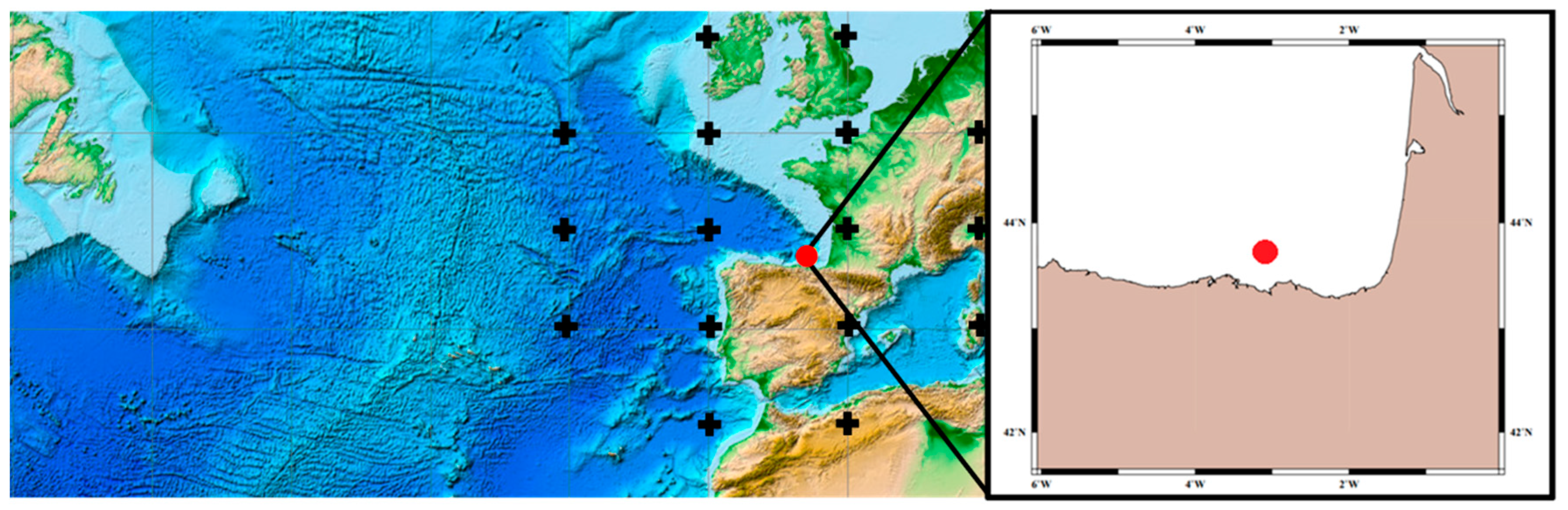
2. Study Area, Material and Methods
3. Results
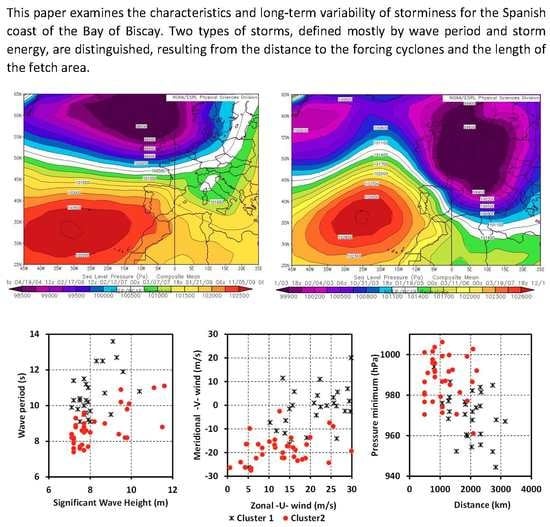
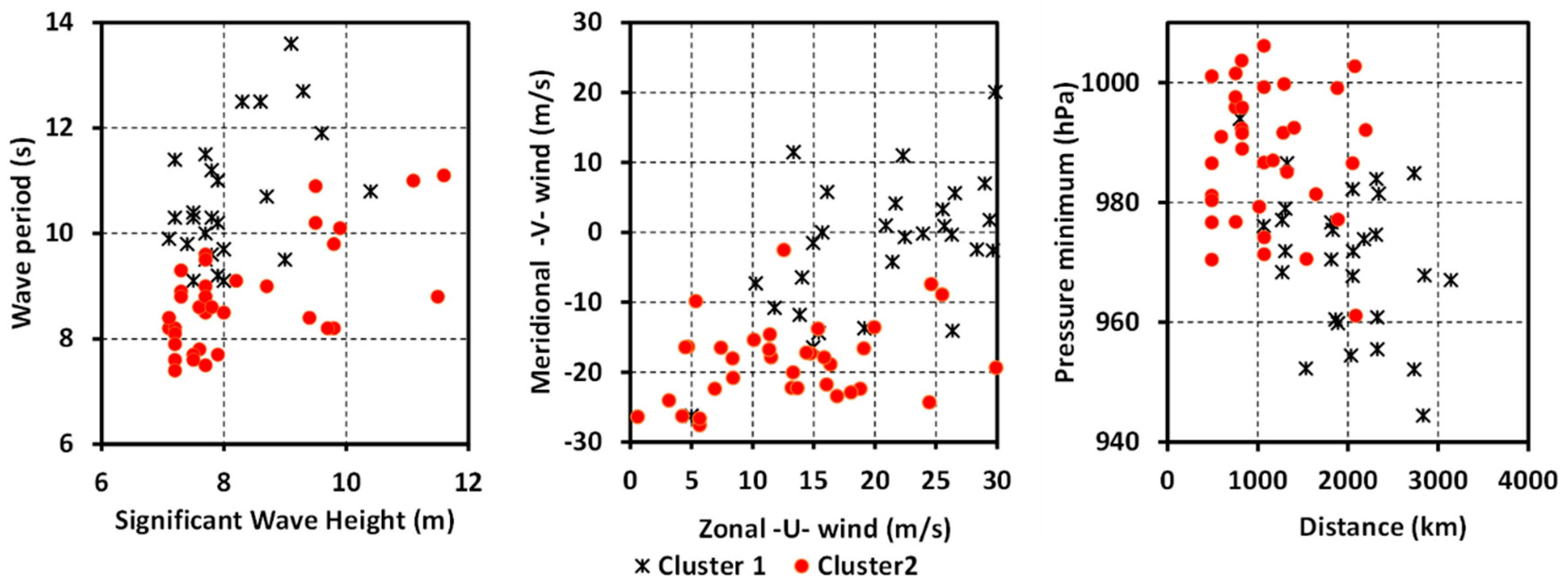
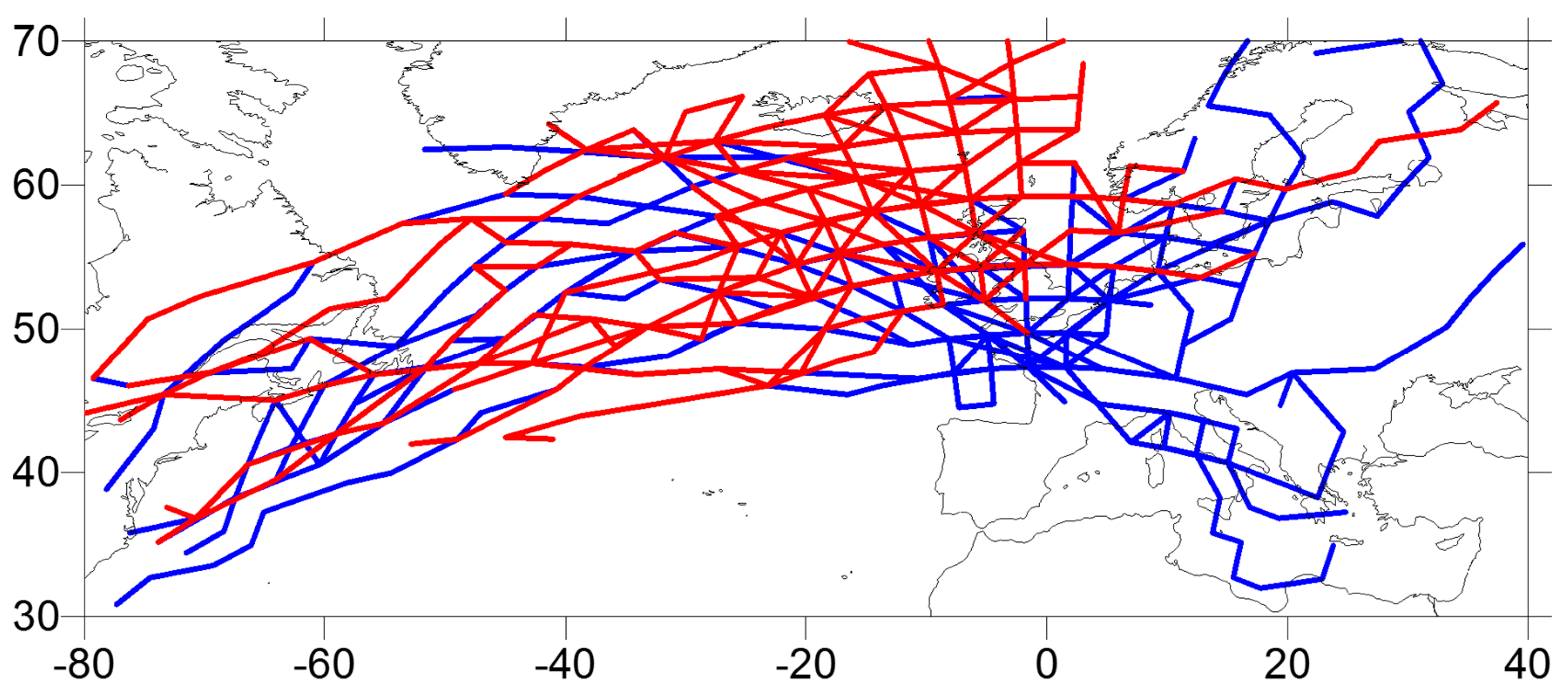
3.1. Identification, Characterization, and Classification of Extreme Wave Events
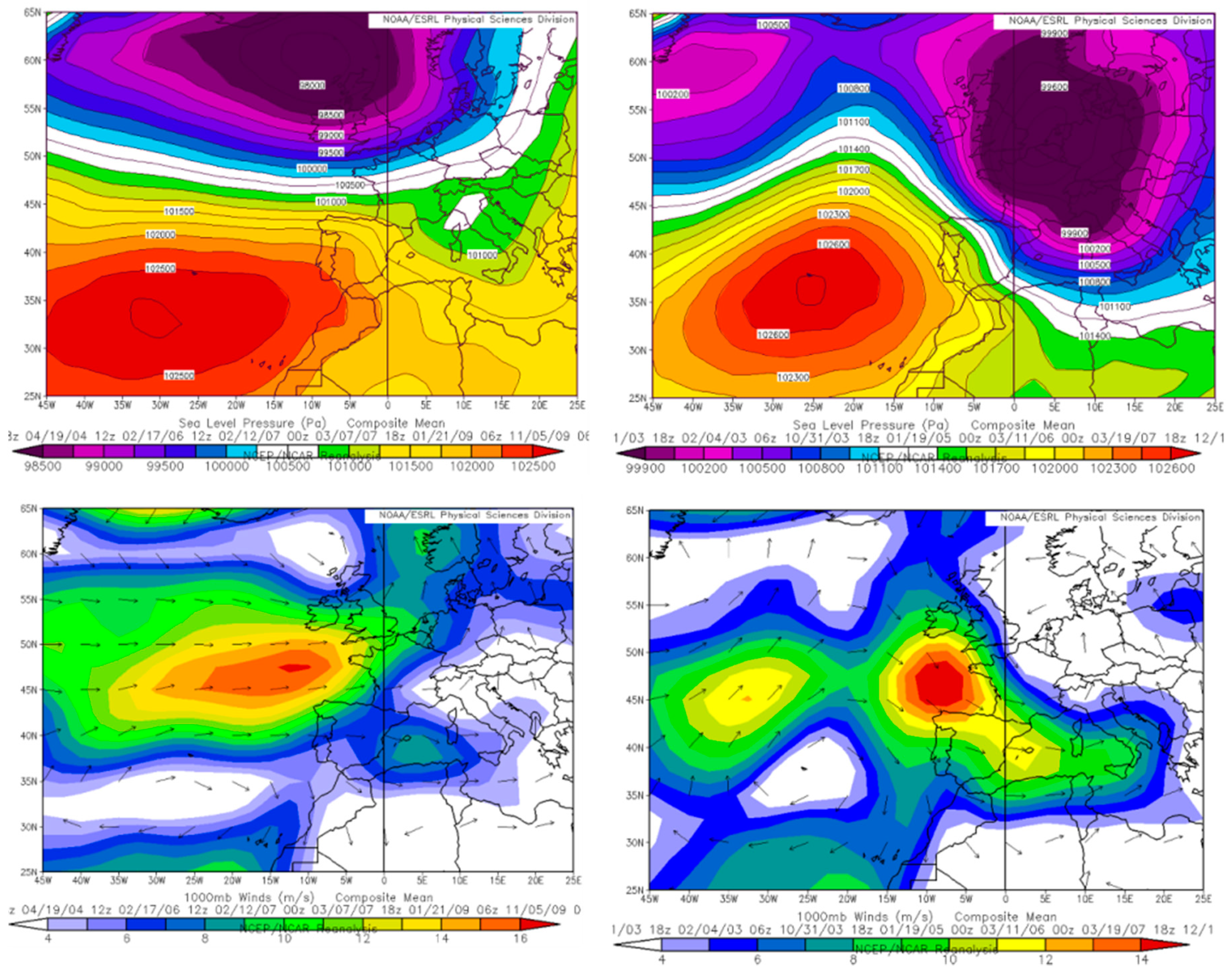
3.2. Atmospheric Controls Upon Wave Storms
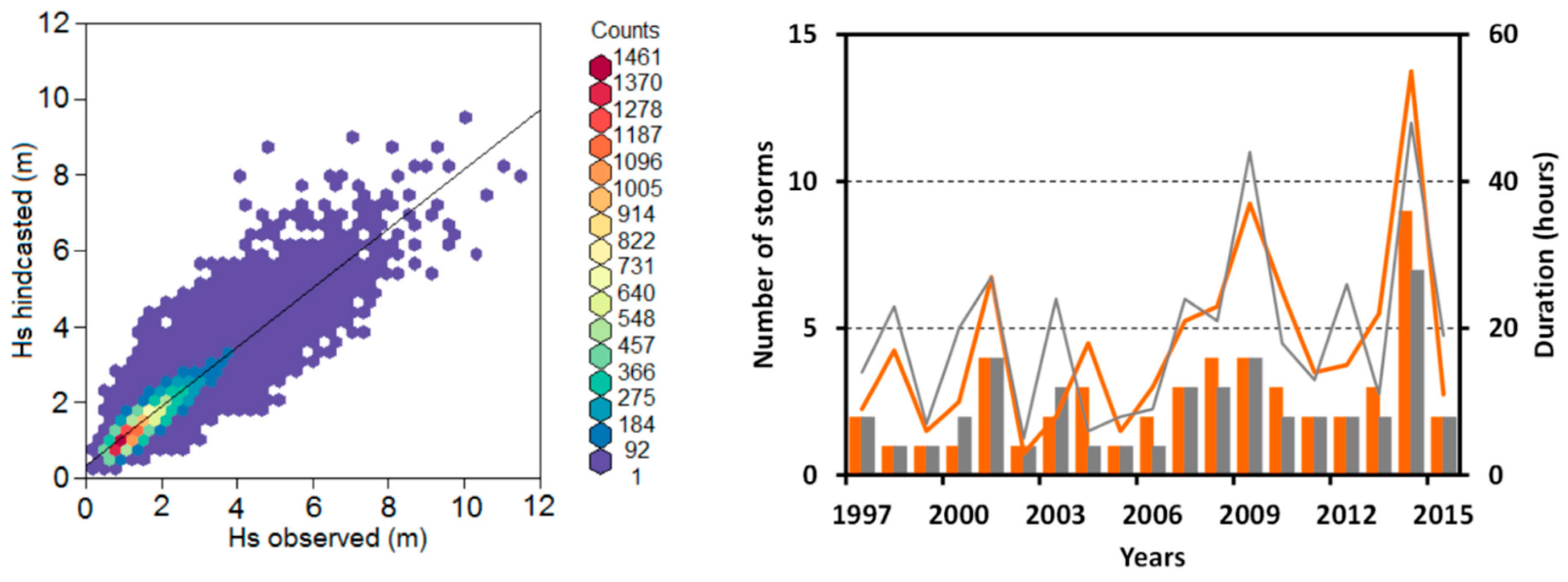
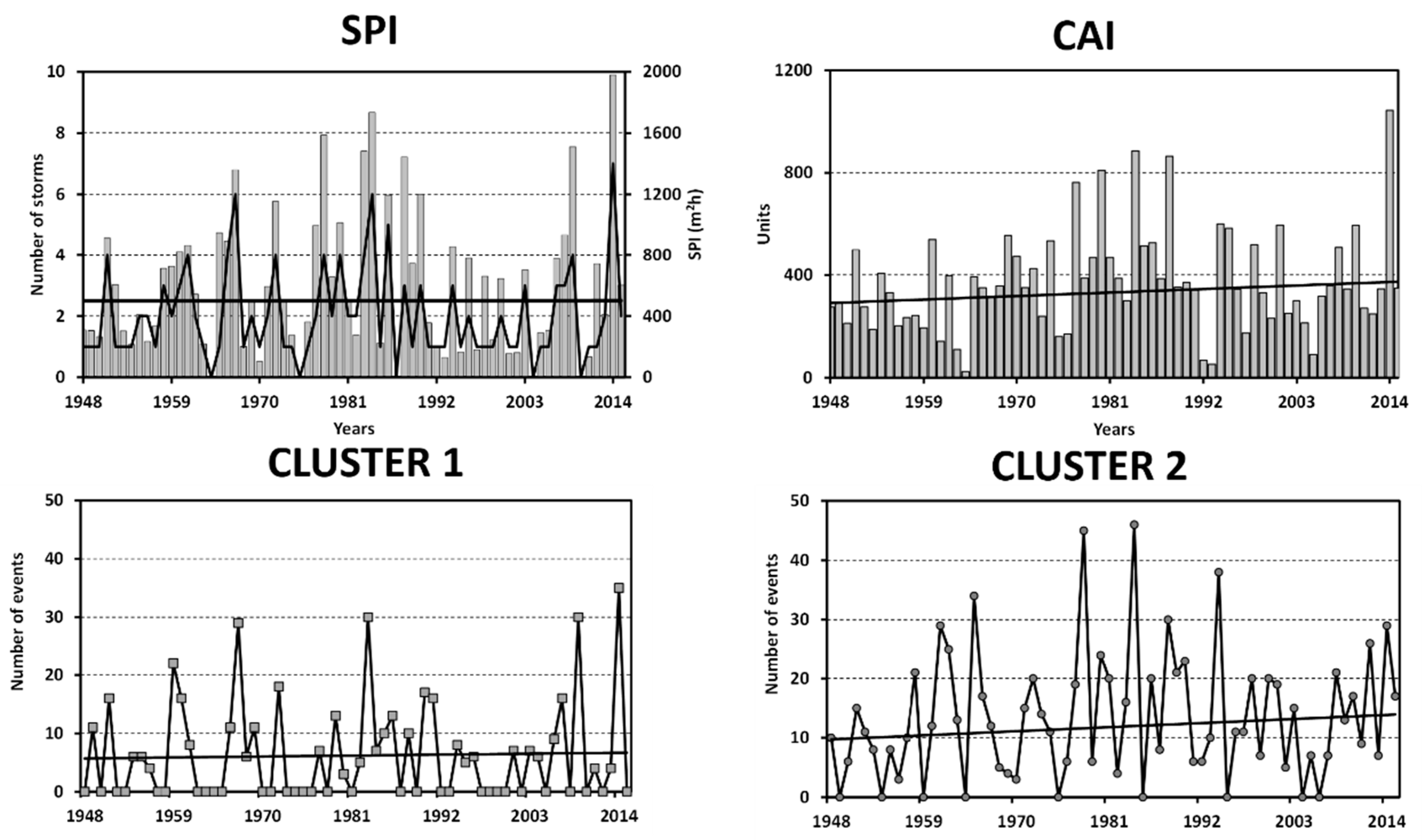
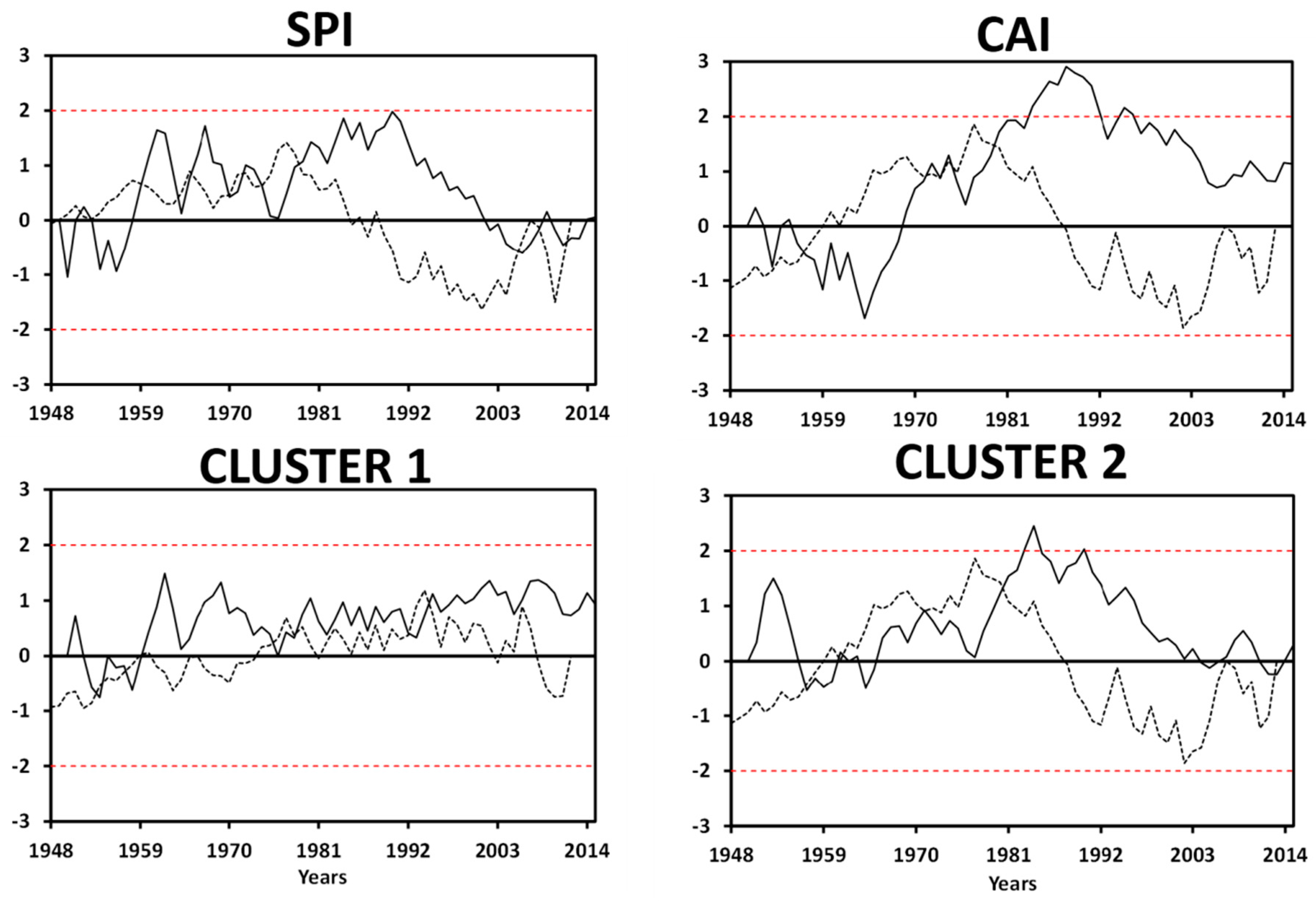
3.3. Analysis of Long-Term Variability in Storminess
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, R.A.; Gibeaut, J.C.; Paine, J.G. Meso-scale transfer of sand during and after storms: Implications for prediction of shoreline movement. Mar. Geol. 1995, 126, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouws, E.; Jannink, D.; Komen, G.J. The increasing wave height in the North Atlantic Ocean. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 2275–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, D.K.; Challenor, P.G.; Cotton, P.D. Variability and predictability of the North Atlantic wave climate. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, C.; Méndez, F.J.; Menéndez, M.; Losada, I.J. Global extreme wave height variability based on satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodet, G.; Bertin, X.; Taborda, R. Wave climate variability in the North-East Atlantic Ocean over the last six decades. Ocean Model. 2010, 31, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semedo, A.; Suselj, K.; Rutgersson, A.; Sterl, A. A global view on the wind sea and swell climate and variability from ERA-40. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, X.; Prouteau, E.; Letetrel, C. A significant increase in wave height in the North Atlantic Ocean over the 20th century. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2013, 106, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Dodet, G.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T. Increased winter-mean wave height, variability, and periodicity in the northeast Atlantic over 1949–2017. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3586–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupuis, H.; Michel, D.; Sottolichio, A. Wave climate evolution in the Bay of Biscay over two decades. J. Mar. Syst. 2006, 63, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.; Idier, D.; Thiebot, J.; Le Cozannet, G.; Pedreros, R. Present wave climate of the Bay of Biscay: Spatiotemporal variability and trends from 1958 to 2001. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 2020–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, F.; Lecacheux, S.; Idier, D.; Charles, E. Assessing wave climate trends in the Bay of Biscay through an intercomparison of wave hindcasts and reanalyses. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerma, A.N.; Bulteau, T.; Lecacheux, S.; Idier, D. Spatial variability of extreme wave height along the Atlantic and channel French coast. Ocean Eng. 2015, 97, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulazia, A.; Penalba, M.; Ibarra-Berastegui, G.; Ringwood, J.; Saénz, J. Wave energy trends over the Bay of Biscay and the consequences for wave energy converters. Energy 2017, 141, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cozannet, G.; Lecacheux, S.; Delvallée, E.; Desramaut, N.; Oliveros, C.; Pedreros, R. Teleconnection pattern influence on sea-wave climate in the Bay of Biscay. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromirski, P.D.; Cayan, D.R. Wave power variability and trends across the North Atlantic influenced by decadal climate patterns. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 3419–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Asensio, A.; Tsimplis, M.N.; Marcos, M.; Feng, X.; Gomis, D.; Jordà, G.; Josey, S.A. Response of the North Atlantic wave climate to atmospheric modes of variability. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1210–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, V.; Cendrero, A. Human influence in a low-hazard coastal area: An approach to risk assessment and proposal of mitigation strategies. J. Coast. Res. 1994, SI 12, 289–298. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/ stable/25735605 (accessed on 14 June 2018).
- García Codron, J.C.; Rasilla Álvarez, D.F. Coastline retreat, sea level variability and atmospheric circulation in Cantabria (Northern Spain). J. Coast. Res. 2006, SI 48, 49–54. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/25737381 (accessed on 14 June 2018).
- Chust, G.; Caballero, A.; Marcos, M.; Liria, P.; Hernández, C.; Borja, Á. Regional scenarios of sea level rise and impacts on Basque (Bay of Biscay) coastal habitats, throughout the 21st century. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 87, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmendia Pedraja, C.; Rasilla Álvarez, D.F.; Rivas Mantecón, V. Distribución espacial de los daños producidos por los temporales de invierno 2014 en la costa norte de España: Peligrosidad. vulnerabilidad y exposición. Estudios Geográficos 2017, 78, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, A.F.; Collison, F.P. An Initial Climatology of Gales over the North Sea. In Synoptic Climatology Branch Memorandum, No. 62; Meteorological Office: Bracknell, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Masselink, G.; Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Dodet, G.; Suanez, S.; Jackson, D.; Floc’h, F. Extreme wave activity during 2013/2014 winter and morphological impacts along the Atlantic coast of Europe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavola, P.; Coco, G. Coastal Storms: Processes and Impacts; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.C.; Leatherman, S.P. Twentieth-Century Storm Activity along the U.S. East Coast. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1748–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, R.; Davis, R.E. An Intensity Scale for Atlantic Coast Northeast Storms. J. Coast. Res. 1992, 8, 840–853. [Google Scholar]
- Serreze, M.C. Climatological aspects of cyclone development and decay in the Arctic. Atmos. Ocean 1995, 33, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Swail, V.R.; Zwiers, F.W. Climatology and Changes of Extratropical Cyclone Activity: Comparison of ERA-40 with NCEP–NCAR Reanalysis for 1958–2001. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3145–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E.; Kanamitsu, M.; Kistler, R.; Collins, W.; Deaven, D.; Gandin, L.; Iredell, M.; Saha, S.; White, G.; Woollen, J.; et al. The NCEP/NCAR 40-Year Reanalysis Project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarnal, B. Synoptic Climatology in Environmental Analysis; Belhaven Press: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Wilks, D. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 100, Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/bookseries/international-geophysics/vol/100 (accessed on 9 August 2018).
- Castelle, B.; Dodet, G.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T. A new climate index controlling winter wave activity along the Atlantic coast of Europe: The West Europe Pressure Anomaly. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneyers, R. On the Statistical Analysis of Series of Observations; World Meteorological Organization (WMO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1990; No. 143; Available online: https://library.wmo.int/pmb_ged/wmo_415.pdf (accessed on 14 June 2018).
- Luo, Y.; Liu, S.; Fu, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Zhou, G. Trends of precipitation in Beijiang River Basin. Guangdong Province. China. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, R.J.; Gray, S.L.; Jones, O.P. North Atlantic storm driving of extreme wave heights in the North Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans. 2017, 122, 3253–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Kushnir, Y.; Battisti, D.; Chang, P.; Czaja, A.; Dickson, R.; Hurrell, J.; McCartney, M.; Saravanan, R.; Visbeck, M. North Atlantic climate variability: Phenomena, impacts and mechanisms. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1863–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigo, R.M.; Valente, M.A.; Trigo, I.F.; Miranda, P.M.; Ramos, A.M.; Paredes, D.; García-Herrera, R. The Impact of North Atlantic Wind and Cyclone Trends on European Precipitation and Significant Wave Height in the Atlantic. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1146, 212–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butel, R.; Dupuis, H.; Bonneton, P. Spatial variability of wave conditions on the French Atlantic coast using in-situ data. J. Coast. Res. 2002, SI 36, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, X.; Castelle, B.; Chaumillon, E.; Butel, R.; Quique, R. Longshore transport estimation and inter-annual variability at a high-energy dissipative beach: St. Trojan beach. SW Oléron Island. France. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1316–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.T.; Jimenez, J.A.; Mateo, J. A coastal storms intensity scale for the Catalan sea (NW Mediterranean). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Buitrago, N.; Anfuso, G. Winter wave climate. storms and regional cycles: The SW Spanish Atlantic coast. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 2142–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.P.; Ferreira, O.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Dodet, G. Historical variation and trends in storminess along the Portuguese South Coast. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 11, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plomaritis, T.A.; Benavente, J.; Laiz, I.; del Rio, R. Variability in storm climate along the Gulf of Cadiz: The role of large scale atmospheric forcing and implications to coastal hazards. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2499–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, S.; Carter, D.J. A connection between mean wave height and atmospheric pressure gradient in the North Atlantic. Int. J. Climatol. 1993, 13, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.C.; Cooper, J.A.G.; Jackson, D.W.T. Decadal behavior of tidal inlet-associated beach systems, Northwest Ireland, in relation to climate forcing. J. Sediment. Res. 2011, 81, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feser, F.; Barcikowska, M.; Krueger, O.; Schenk, F.; Weisse, R.; Xia, L. Storminess over the North Atlantic and northwestern Europe—A review. Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 141, 350–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, T.; Murphy, C.; Wilby, R.L.; Harrigan, S. Stormiest winter on record for Ireland and UK. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 738–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Poate, T.; Russell, P.; Davidson, M.; Conley, D. The extreme 2013/2014 winter storms: Hydrodynamic forcing and coastal response along the southwest coast of England. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2016, 41, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, A.; Castelle, B.; Idier, D.; Le Cozannet, G.; Déqué, M. Charles E. Statistical modeling of interannual shoreline change driven by North Atlantic climate variability spanning 2000–2014 in the Bay of Biscay. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2016, 36, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bengtsson, L.; Hodges, K.I.; Roeckner, E. Storm tracks and climate change. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 3518–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, U.; Pinto, J.G.; Kupfer, H.; Leckebusch, G.C.; Spangehl, T.; Reyers, M. Northern Hemisphere storm tracks in an ensemble of IPCC climate change simulations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, U.; Leckebusch, G.C.; Pinto, J.G. Extra-tropical cyclones in the present and future climate: A review. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 96, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, E.; Idier, D.; Delecluse, P.; Déqué, M.; Le Cozannet, G. Climate change impact on waves in the Bay of Biscay France. Ocean Dyn. 2012, 62, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Oceanographic | Atmospheric |
|---|---|
| Significant wave height (Hs, m) 1,2 | Sea level pressure (slp, hPa) 3 |
| Wave period (Tp, s) 1 | Zonal wind component (U, m/s) 3 |
| Wave direction (θ, degrees) 1 | Meridional wind component (V, m/s) 3 |
| Geostrophic wind (FF, m/s) 3 | |
| Vorticity (Z, units of hPa) 3 | |
| Cyclone depth (depth, hPa) 3 | |
| Cyclone distance (distance, km) 3 |
| Duration | SPI (Storm Power Index) | Distance | Depth | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hs | 0.36 ** | 0.71 ** | 0.03 | −0.25 * |
| Tp | 0.35 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.23 * | −0.49 ** |
| Parameters and Indices | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hs (Significant wave height) (m) | 8.02 | 8.49 | |
| Tp (Wave period) (s) | 10.61 | 8.88 | ** |
| θ (Wave direction) (degrees) | 317 | 335 | * |
| Duration (h × 6) | 48.3 | 31.2 | ** |
| SPI (Storm Power Index) (m2 h) | 538.83 | 415.63 | * |
| SLP (Sea Level Pressure) (hPa) | 1008.79 | 1007.86 | |
| U (Zonal wind component) (m/s) | 21.11 | 12.47 | ** |
| V (Meridional wind component) (m/s) | –1.29 | –19.38 | ** |
| Z (Vorticity) (hPa) | –10.83 | 10.21 | ** |
| FF (Geostrophic wind) (m/s) | 22.95 | 24.32 | |
| Depth (Cyclone depth) (slp) | 969.84 | 987.76 | ** |
| Distance (Cyclone distance) (km) | 1950.68 | 1156.58 | ** |
| SPI | CAI | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sen’s estimator | |||||||
| Z-statistics | p-value | Z-statistics | p-value | Z-statistics | p-value | Z-statistics | p-value |
| 0.06 | 0.9536 | 1.14 | 0.255 | 0.93 | 0.351 | 0.30 | 0.76 |
| Sen’s slope | |||||||
| 0.025 | 1.24 | 0.066 | 0.008 | ||||
| Mann-Kendall test | |||||||
| S-statistic | p-value | S statistic | p-value | S statistic | p-value | S statistic | p-value |
| 12 | 0.95 | 216 | 0.25 | 177 | 0.35 | 5.8 | 0.76 |
| Number of Storms | SPI | CAI | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAO | 0.14 | 0.19 | −0.05 | 0.17 | 0.25 * |
| EA | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.33 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.08 |
| EA/WR | −0.34 ** | −0.35 ** | −0.44 ** | −0.26 * | −0.31 * |
| SCAND | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.40 ** | 0.06 | −0.14 |
| WEPI | 0.48 ** | 0.37 ** | 0.63 ** | 0.56 ** | 0.41 ** |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasilla, D.; García-Codron, J.C.; Garmendia, C.; Herrera, S.; Rivas, V. Extreme Wave Storms and Atmospheric Variability at the Spanish Coast of the Bay of Biscay. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080316
Rasilla D, García-Codron JC, Garmendia C, Herrera S, Rivas V. Extreme Wave Storms and Atmospheric Variability at the Spanish Coast of the Bay of Biscay. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(8):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080316
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasilla, Domingo, Juan Carlos García-Codron, Carolina Garmendia, Sixto Herrera, and Victoria Rivas. 2018. "Extreme Wave Storms and Atmospheric Variability at the Spanish Coast of the Bay of Biscay" Atmosphere 9, no. 8: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080316
APA StyleRasilla, D., García-Codron, J. C., Garmendia, C., Herrera, S., & Rivas, V. (2018). Extreme Wave Storms and Atmospheric Variability at the Spanish Coast of the Bay of Biscay. Atmosphere, 9(8), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080316