On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
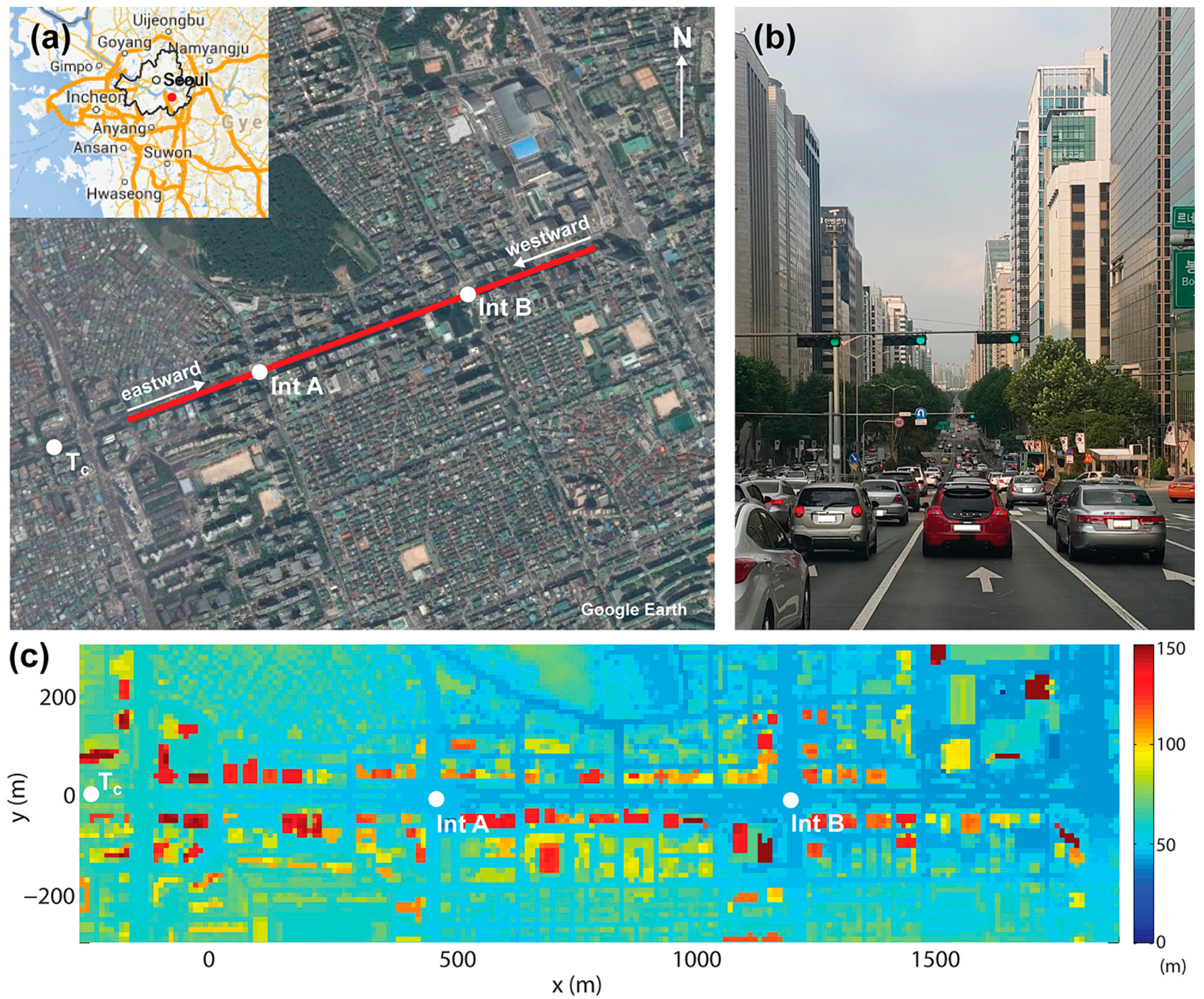
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Mobile Monitoring
2.3. CFD Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
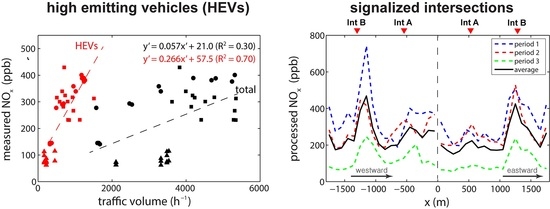
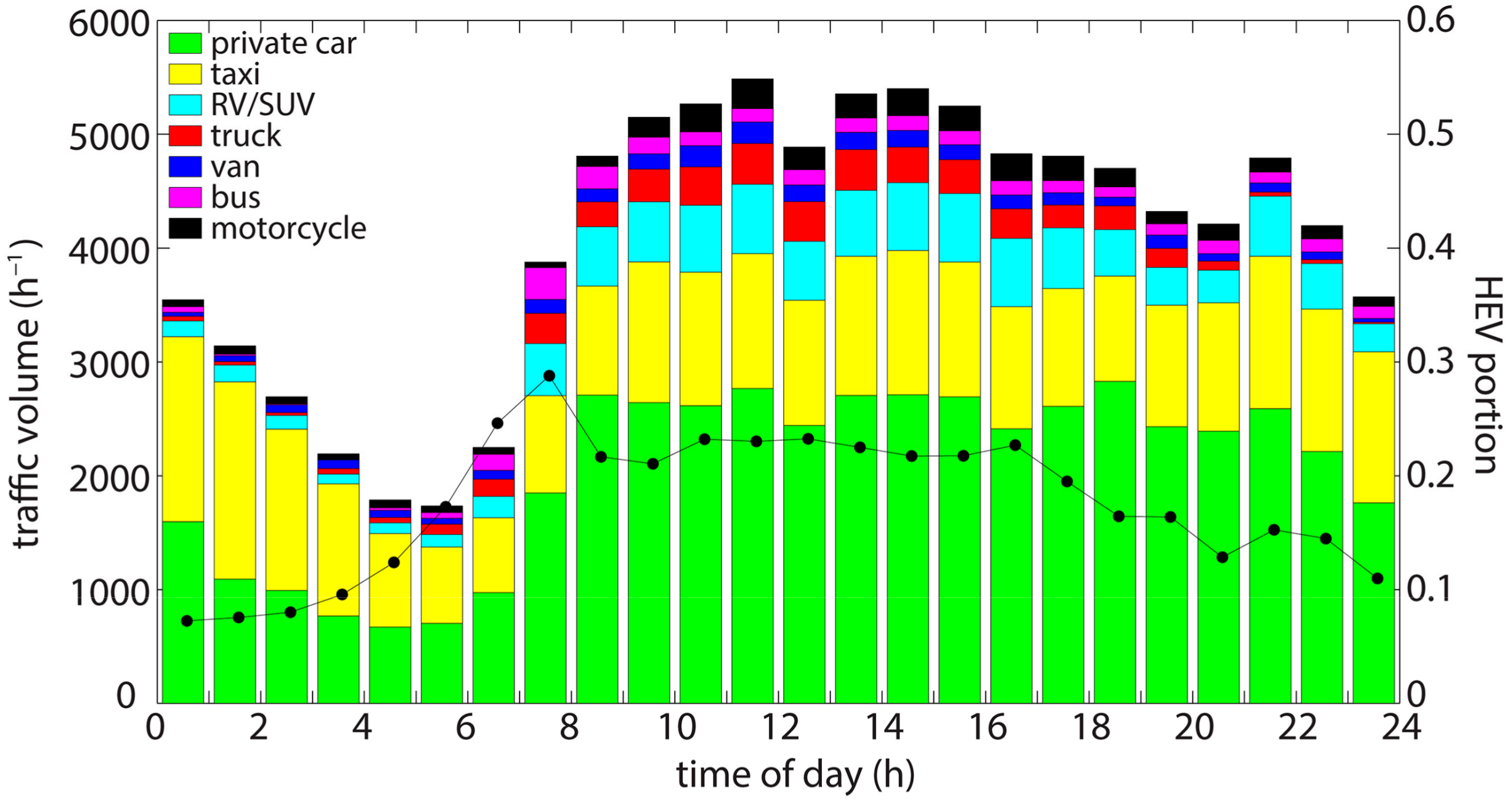
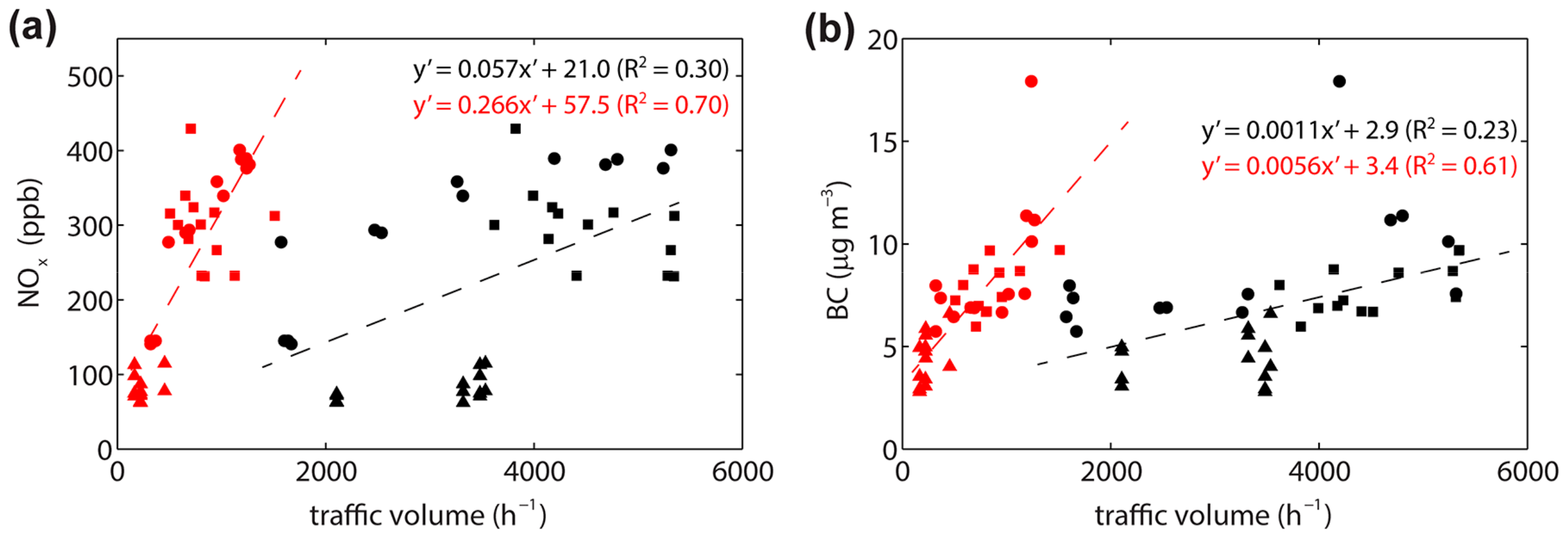
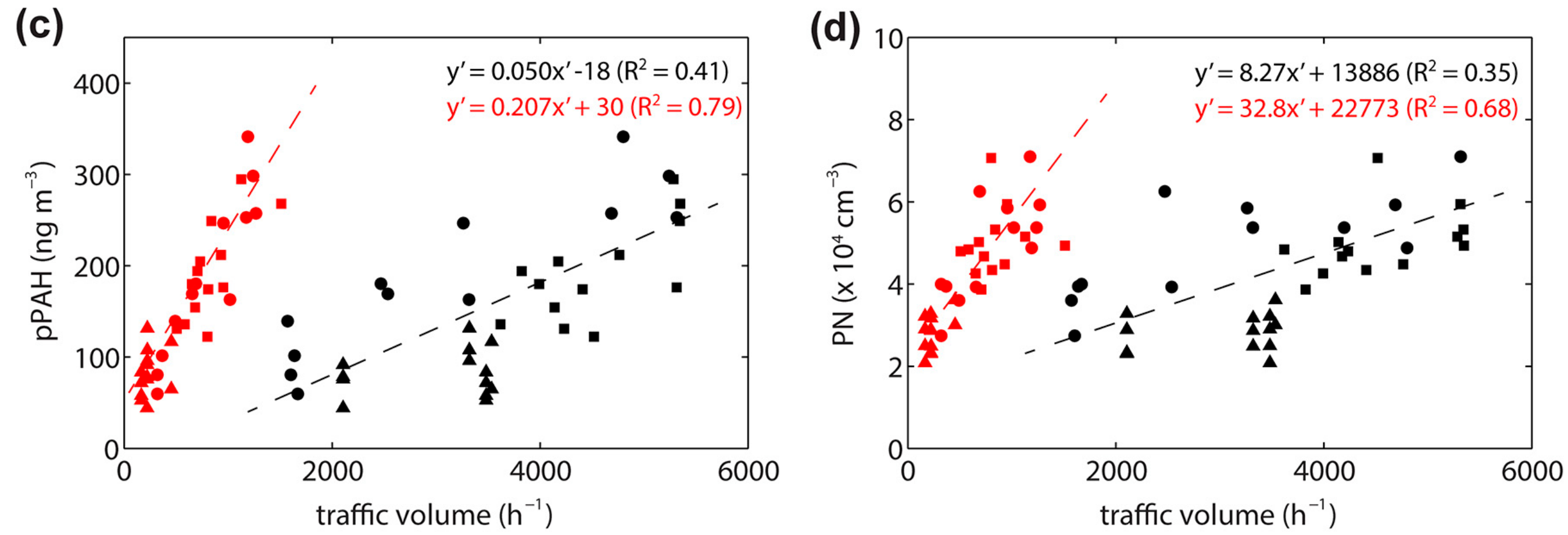
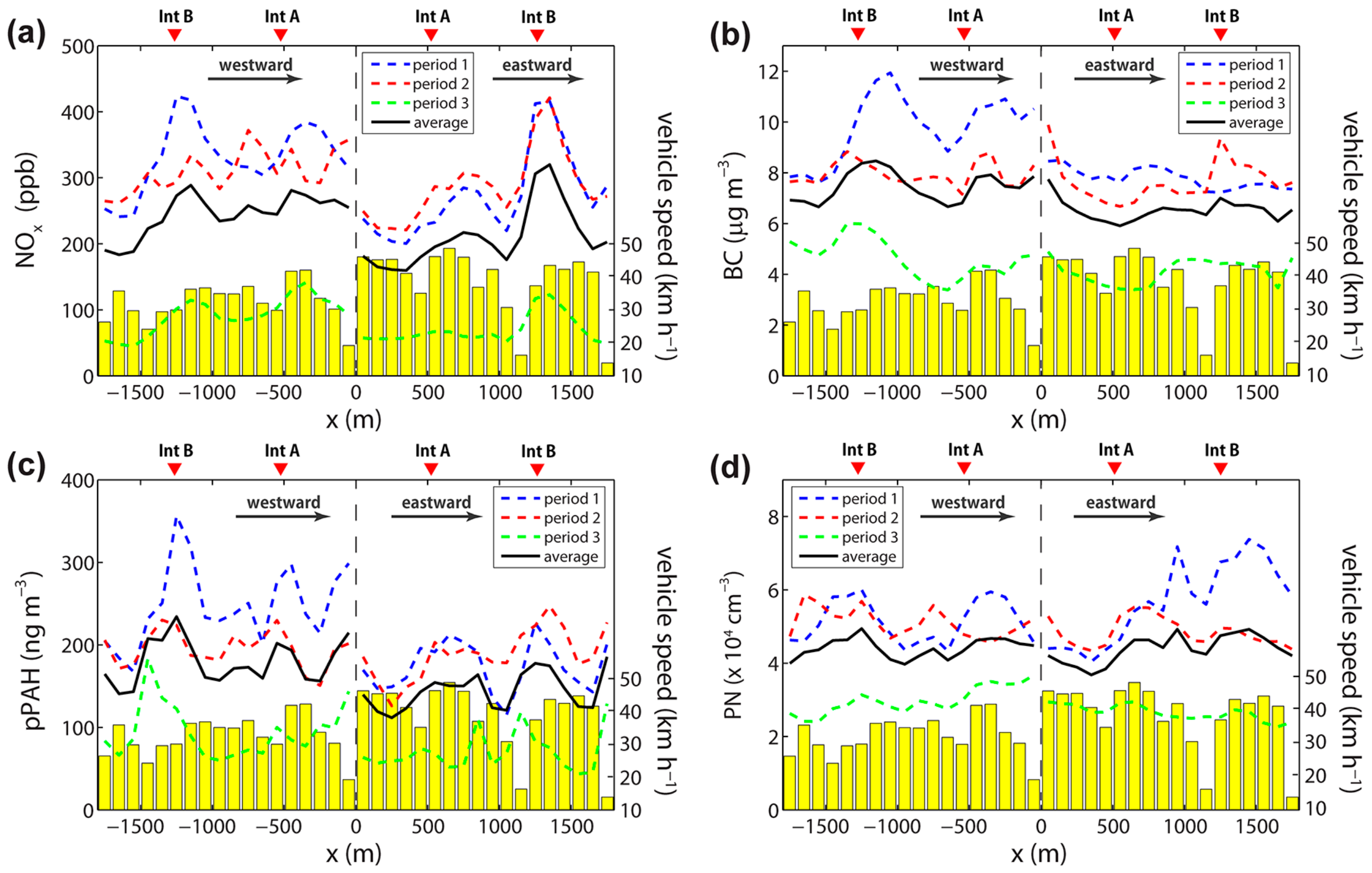
3.1. Association with Traffic Composition
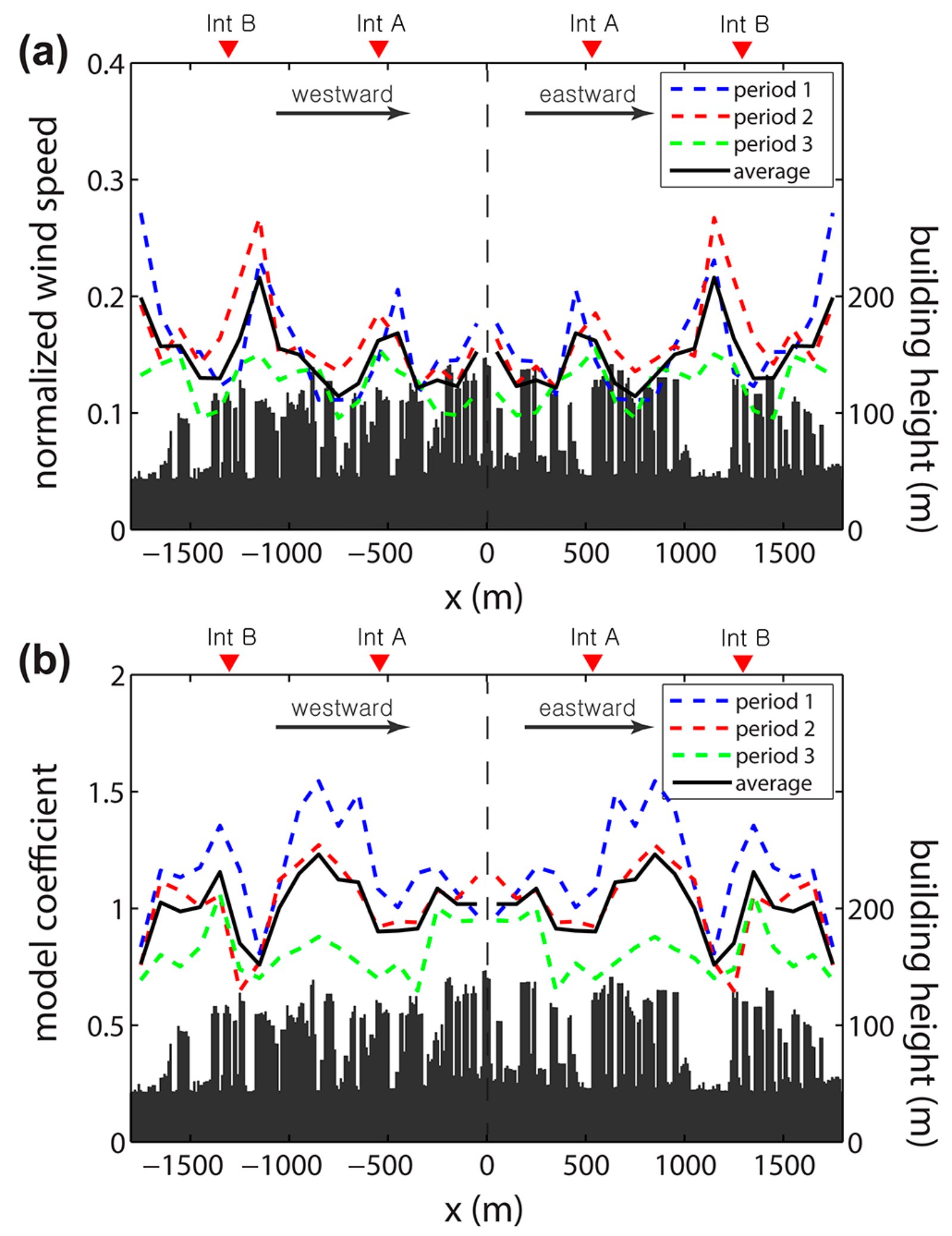
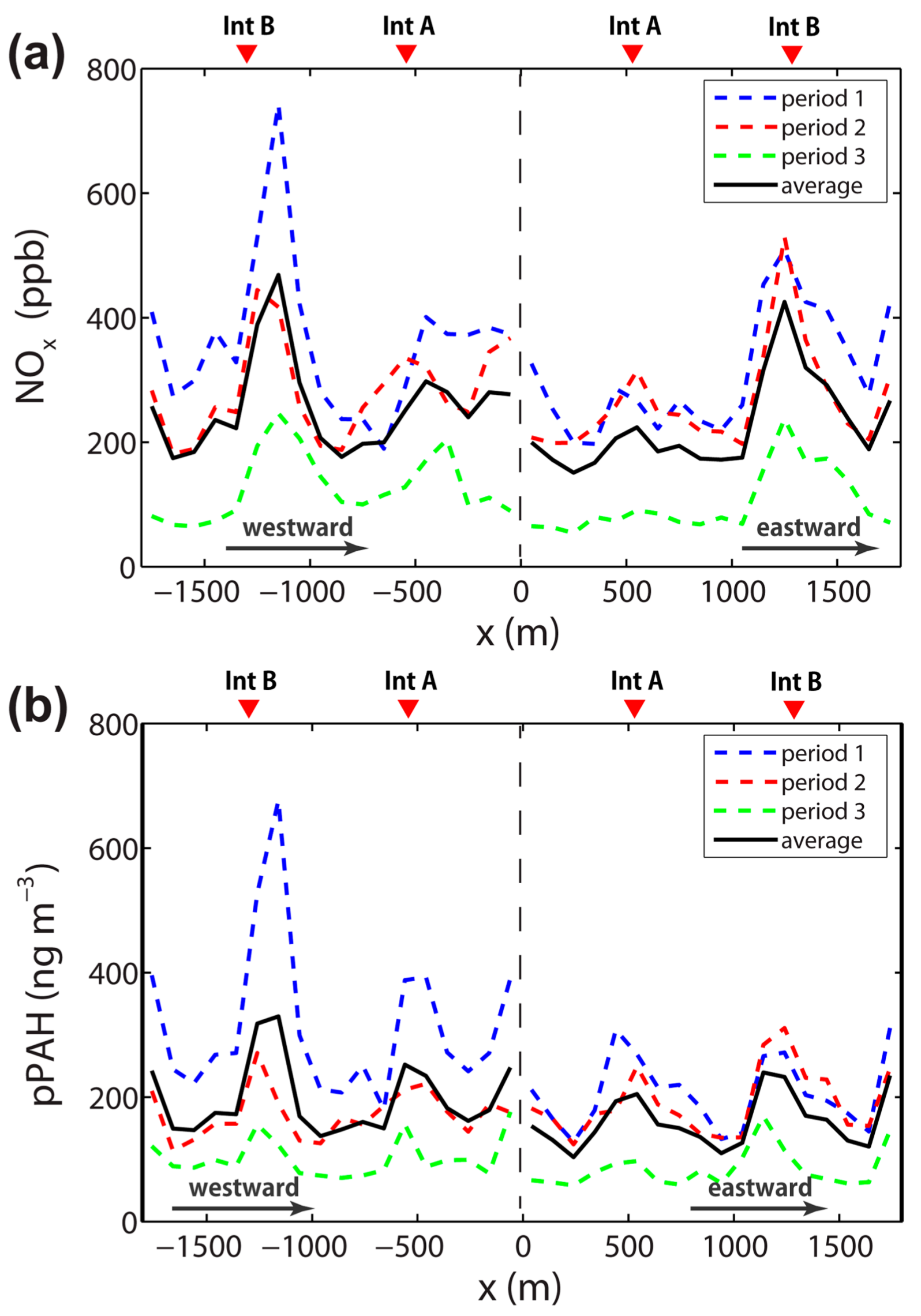
3.2. Association with Street-Canyon Ventilation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernard, S.M.; Samet, J.M.; Grambsch, A.; Ebi, K.L.; Romieu, I. The potential impacts of climate variability and change on air pollution-related health effects in the United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kwon, J.-W.; Jung, Y.-H.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.I.; Kim, H.-Y.; Seo, J.-H.; Kim, H.-B.; Kim, H.-C.; et al. Traffic-related air pollution is associated with airway hyperresponsiveness. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halonen, J.I.; Blangiardo, M.; Toledano, M.B.; Fecht, D.; Gulliver, J.; Anderson, H.R.; Beevers, S.D.; Dajnak, D.; Kelly, F.J.; Tonne, C. Long-term exposure to traffic pollution and hospital admissions in London. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Diesel Engine Exhaust Carcinogenic; International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization: Lyon, France, 2012; Available online: http://www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/pr/2012/pdfs/pr213_E.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Riddle, S.G.; Robert, M.A.; Jakober, C.A.; Hannigan, M.P.; Kleeman, M.J. Size-resolved source apportionment of airborne particle mass in a roadside environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6580–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Wu, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road emission factor distributions of individual diesel vehicles in and around Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Westerdahl, D.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, K.M. On-road diesel vehicle emission factors for nitrogen oxides and black carbon in two Chinese cities. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallmann, T.R.; DeMartini, S.J.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Herndon, S.C.; Onasch, T.B.; Wood, E.C.; Harley, R.A. On-road measurement of gas and particle phase pollutant emission factors for individual heavy-duty diesel trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8511–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Lipsky, E.M.; Saleh, R.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A. Characterizing the spatial variation of air pollutants and the contributions of high emitting vehicles in Pittsburgh, PA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 14186–14194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Townsend, T.; Brimblecombe, P.; Chan, T.L.; Yam, Y.S.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Evaluation of diesel fleet emissions and control policies from plume chasing measurements of on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durbin, T.D.; Johnson, K.; Miller, J.W.; Maldonado, H.; Chernich, D. Emissions from heavy-duty vehicles under actual on-road driving conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 4812–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maness, H.L.; Thurlow, M.E.; McDonald, B.C.; Harley, R.A. Estimates of CO2 traffic emissions from mobile concentration measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2087–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.D.; Johnson, K.C.; Miller, J.W.; Cocker, D.R., III. Emission rates of regulated pollutants from on-road heavy-duty diesel vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Huang, C.; Jing, Q.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Dai, Y.; Huang, H.; Schipper, L.; et al. On-road emission characteristics of heavy-duty diesel vehicles in Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 5334–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Batterman, S. Air pollution and health risks due to vehicle traffic. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 450–451, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Woo, S.H.; Bae, G.-N. NOx profile around a signalized intersection of busy roadway. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Kumar, P. Characterisation of nanoparticle emissions and exposure at traffic intersections through fast–response mobile and sequential measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Tao, L.; Miller, D.J.; Khan, M.A.; Zondlo, M.A. On-road ammonia emissions characterized by mobile, open-path measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3943–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beevers, S.D.; Kitwiroon, N.; Williams, M.L.; Carslaw, D.C. One way coupling of CMAQ and a road source dispersion model for fine scale air pollution predictions. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klompmaker, J.O.; Montagne, D.R.; Meliefste, K.; Hoek, G.; Brunekreef, B. Spatial variation of ultrafine particles and black carbon in two cities: Results from a short-term measurement campaign. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Reis, S.; Lin, C.; Beverland, I.J.; Heal, M.R. Identifying drivers for the intra-urban spatial variability of airborne particulate matter components and their interrelationships. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassoun, Y.; Ruths, M.; Löwner, M.-O.; Weber, S. Intra-urban variation of ultrafine particles as evaluated by process related land use and pollutant driven regression modelling. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.; Ranasinghe, D.; Bunavage, K.; DeShazo, J.R.; Wu, L.; Seguel, R.; Winer, A.M.; Paulson, S.E. The effects of the built environment, traffic patterns, and micrometeorology on street level ultrafine particle concentrations at a block scale: Results from multiple urban sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 553, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittelson, D.B.; Watts, W.F.; Johnson, J.P. Nanoparticle emissions on Minnesota highways. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijers, E.P.; Khlystov, A.Y.; Kos, G.P.A.; Erisman, J.W. Variability of particulate matter concentrations along roads and motorways determined by a moving measurement unit. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerdahl, D.; Fruin, S.; Sax, T.; Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C. Mobile platform measurements of ultrafine particles and associated pollutant concentrations on freeways and residential streets in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3597–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagler, G.S.W.; Thoma, E.D.; Baldauf, R.W. High-resolution mobile monitoring of carbon monoxide and ultrafine particle concentrations in a near-road environment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brantley, H.L.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Kimbrough, E.S.; Williams, R.W.; Mukerjee, S.; Neas, L.M. Mobile air monitoring data-processing strategies and effects on spatial air pollution trends. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, N.; Gilani, O.; Raja, S.; Batterman, S.; Ganguly, R.; Hopke, P.; Berrocal, V.; Robins, T.; Hoogterp, S. Factors affecting pollutant concentrations in the near-road environment. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 115, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwack, L.M.; Paciorek, C.J.; Spengler, J.D.; Levy, J.I. Characterizing local traffic contributions to particulate air pollution in street canyons using mobile monitoring techniques. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2507–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakowska, A.; Wong, K.C.; Townsend, T.; Chan, K.L.; Westerdahl, D.; Ng, S.; Močnik, G.; Drinovec, L.; Ning, Z. Impact of traffic volume and composition on the air quality and pedestrian exposure in urban street canyon. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Woo, D.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N. On-road measurements of ultrafine particles and associated air pollutants in a densely populated area of Seoul, Korea. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, G.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Voliotis, A.; Tsakis, A.; Chasapidis, L.; Konstandopoulos, A.; Eleftheriadis, K. Concentration levels and source apportionment of ultrafine particles in road microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 129, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Fennell, P.; Britter, R. Measurements of particles in the 5–1000 nm range close to road level in an urban street canyon. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 390, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Seo, J.M.; Park, S.-B.; Baik, J.-J. Relationship between rooftop and on-road concentrations of traffic-related pollutants in a busy street canyon: Ambient wind effects. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oanh, N.T.K.; Martel, M.; Pongkiatkul, P.; Berkowicz, R. Determination of fleet hourly emission and on-road vehicle emission factor using integrated monitoring and modeling approach. Atmos. Res. 2008, 89, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solazzo, E.; Vardoulakis, S.; Cai, X. A novel methodology for interpreting air quality measurements from urban streets using CFD modeling. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5230–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Yang, C. Estimating urban roadside emissions with an atmospheric dispersion model based on in-field measurements. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Sandberg, M.; Zhu, W.; Buccolieri, R.; Di Sabatino, S. City breathability in medium density urban-like geometries evaluated through the pollutant transport rate and the net escape velocity. Build. Environ. 2015, 94, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wen, D.; Xiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Ultrafine-particle emission factors as a function of vehicle mode of operation for LDVs based on near-roadway monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.S.; Cui, G.X.; Wang, Z.S.; Zhang, Z.S. Large eddy simulation of wind field and pollutant dispersion in downtown Macao. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2849–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Nguyen, M.T.; Steffens, J.T.; Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hopke, P.K.; Zhang, K.M. Modeling multi-scale aerosol dynamics and micro-environmental air quality near a large highway intersection using the CTAG model. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 443, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Urban air quality simulation in a high-rise building area using a CFD model coupled with mesoscale meteorological and chemistry-transport models. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 100, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterman, S.; Chambliss, S.; Isakov, V. Spatial resolution requirements for traffic-related air pollutant exposure evaluations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.-H.; Kwak, K.-H.; Bae, G.-N.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, C.H.; Yook, S.-J.; Jeon, S.; Kwon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-B. Overestimation of on-road air quality surveying data measured with a mobile laboratory caused by exhaust plumes of a vehicle ahead in dense traffic areas. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-J.; Baik, J.-J. A numerical study of the effects of ambient wind direction on flow and dispersion in urban street canyons using the RNG k–ε turbulence model. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, J.-J.; Kwak, K.-H.; Park, S.-B.; Ryu, Y.-H. Effects of building roof greening on air quality in street canyons. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, K.-H.; Baik, J.-J. Diurnal variation of NOx and ozone exchange between a street canyon and the overlying air. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Lee, S.-B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Bae, G.-N.; Lee, J.Y. A multivariate receptor modeling study of air-borne particulate PAHs: Regional contributions in a roadside environment. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Z.; Wang, Y.J.; Patel, M.; Kinney, P.; Chrillrud, S.; Zhang, K.M. Modeling spatial variations of black carbon particles in an urban highway-building environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, J.-J.; Park, S.-B.; Kim, J.-J. Urban flow and dispersion simulation using a CFD model coupled to a mesoscale model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1667–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S.; Kordowski, K.; Kuttler, W. Variability of particle number concentration and particle size dynamics in an urban street canyon under different meteorological conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 449, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Monitoring Period | Time of Day | Number of Trips | Wind Speed a (m s−1) | Predominant Wind Direction a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 04:21 to 09:00 LT | 13 | 1.4 | ENE (parallel) |
| 2 | 17:13 to 23:00 LT | 13 | 1.7 | WSW (parallel) |
| 3 | 23:02 to 04:00 LT | 13 | 2.0 | WNW (diagonal) |
| Pollutant | Instrument | Flow Rate (L min−1) | Time Resolution (s) | Delay Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx | AC32M, Environmental S.A. | 1 | 5 | 19 |
| BC | AE42, Magee Scientific | 5 | 30 | 28 |
| pPAH | PAS2000, EcoChem Analytics | 2 | 6 | 13 |
| PN | CPC model 5.403, GRIMM | 1.5 | 1 | 18 |
| Pollutant | Private Car | Taxi | RV/SUV | Truck | Van | Bus | Motorcycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOx | 0.36 | 0.27 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.21 | 0.53 | 0.08 |
| BC | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.28 | 0.38 | 0.05 |
| pPAH | 0.41 | 0.14 | 0.62 | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.07 |
| PN | 0.42 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.16 |
| Pollutant | Measured Concentration | Converted Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Btw Int | Int A | Int B | Btw Int | Int A | Int B | |
| NOx (ppb) | 214 | 226 (6) | 265 (24) | 212 | 227 (7) | 333 (57) |
| BC (μg m−3) | 6.98 | 6.57 (–6) | 7.34 (5) | – | – | – |
| pPAH (ng m−3) | 151 | 167 (11) | 189 (25) | 157 | 198 (26) | 225 (43) |
| PN (× 104 cm−3) | 4.32 | 4.30 (–1) | 4.68 (8) | – | – | – |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwak, K.-H.; Woo, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, S.-B.; Bae, G.-N.; Ma, Y.-I.; Sunwoo, Y.; Baik, J.-J. On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
Kwak K-H, Woo SH, Kim KH, Lee S-B, Bae G-N, Ma Y-I, Sunwoo Y, Baik J-J. On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(3):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwak, Kyung-Hwan, Sung Ho Woo, Kyung Hwan Kim, Seung-Bok Lee, Gwi-Nam Bae, Young-Il Ma, Young Sunwoo, and Jong-Jin Baik. 2018. "On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling" Atmosphere 9, no. 3: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092
APA StyleKwak, K.-H., Woo, S. H., Kim, K. H., Lee, S.-B., Bae, G.-N., Ma, Y.-I., Sunwoo, Y., & Baik, J.-J. (2018). On-Road Air Quality Associated with Traffic Composition and Street-Canyon Ventilation: Mobile Monitoring and CFD Modeling. Atmosphere, 9(3), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030092