A Case Study of the Stratospheric and Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm in Northern China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data
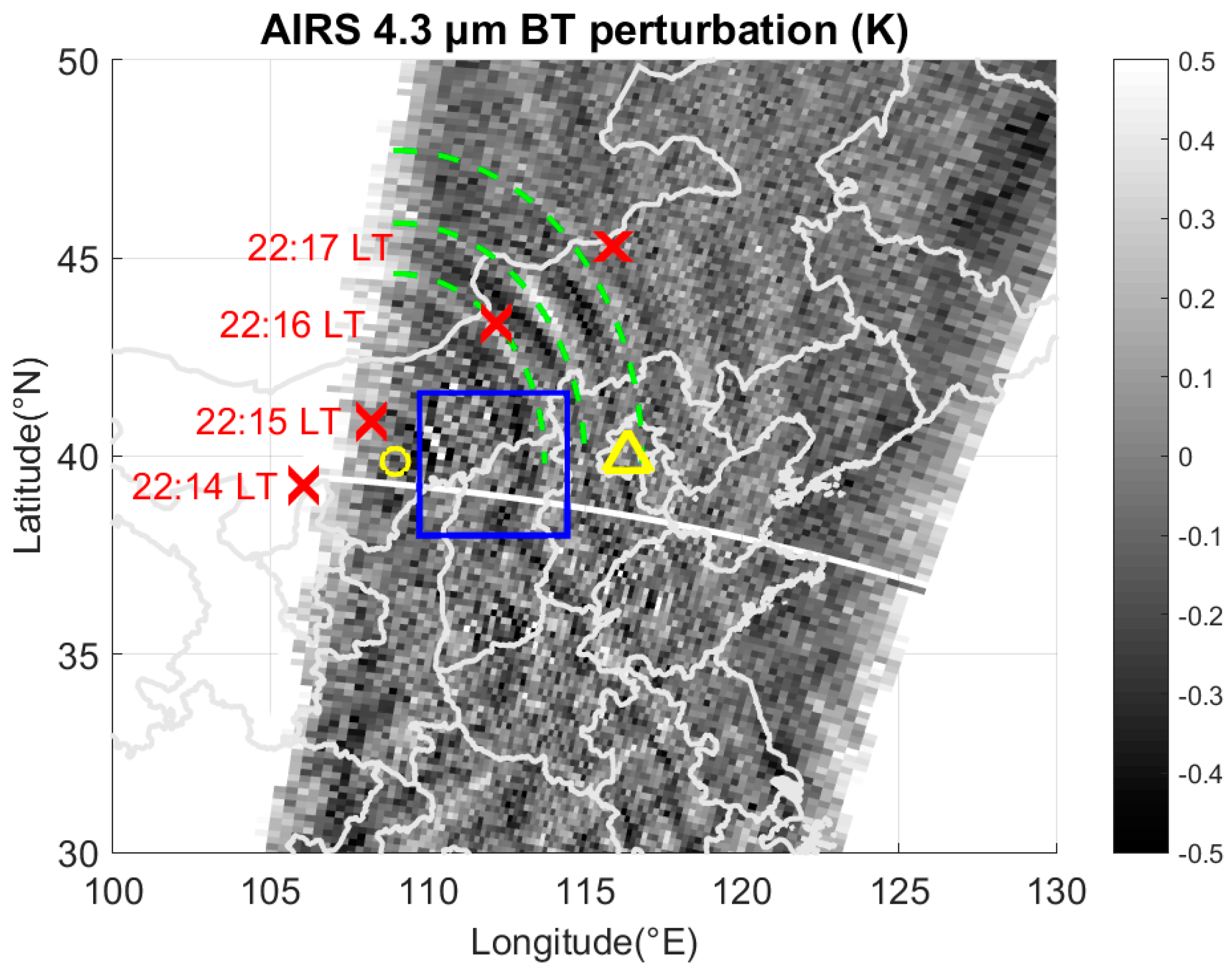
2.1. AIRS Radiation Variation
2.2. OH All-Sky Airglow Image
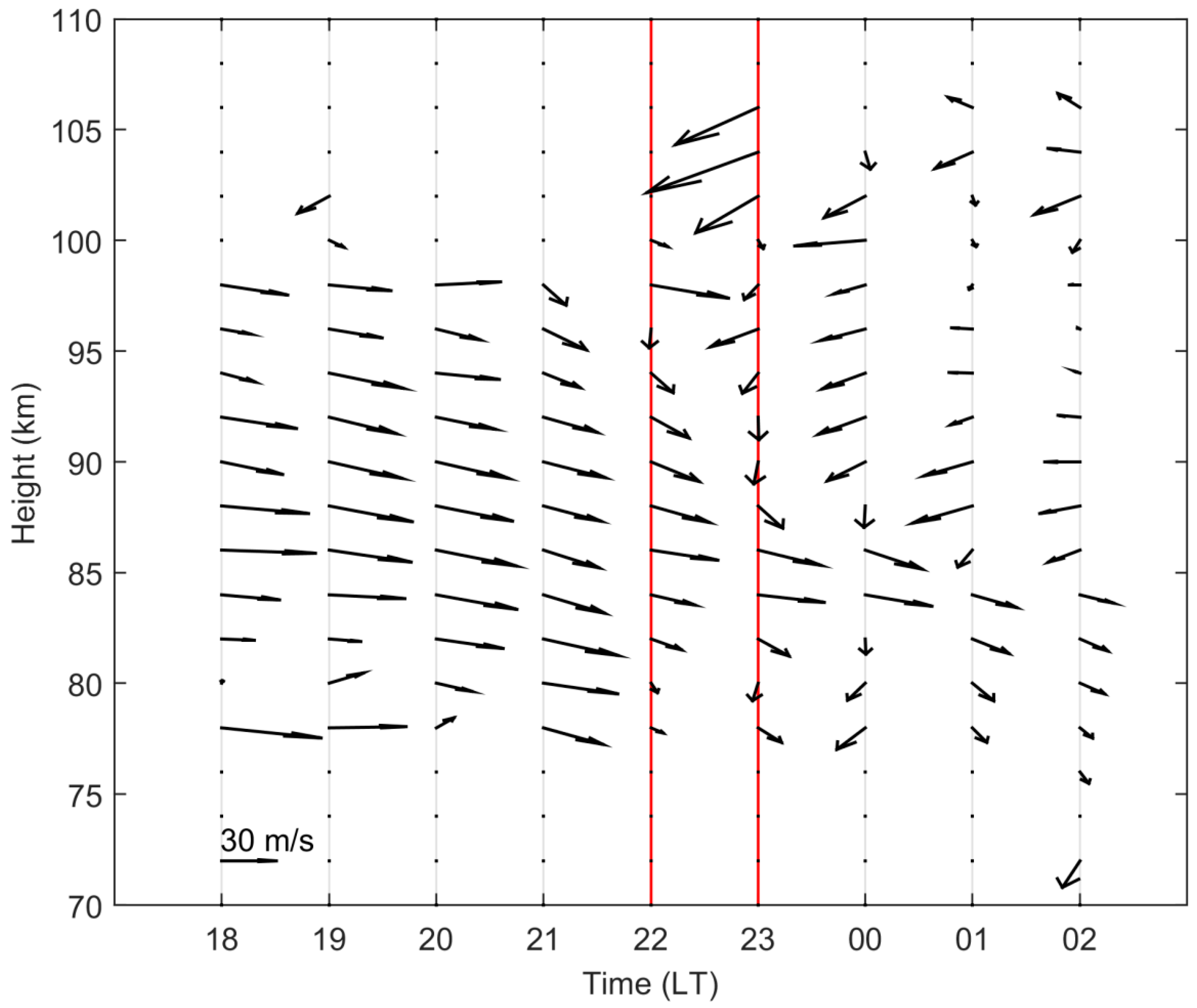
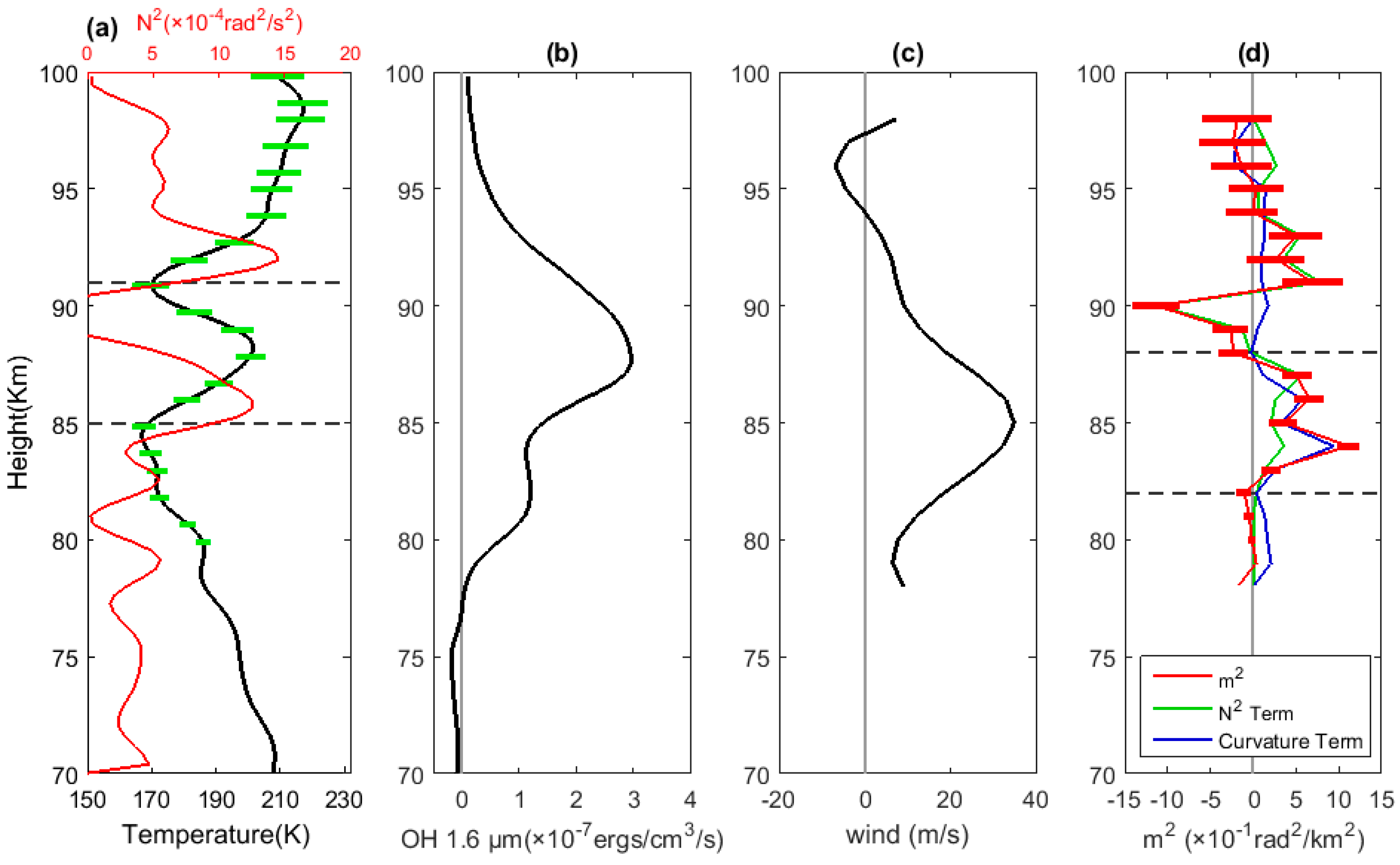
2.3. TIMED/SABER and Meteor Doppler Radar Data
3. Method
3.1. Processing of All-Sky Image Data
3.2. Boussinesq GW Dispersion Relation
4. CGW Characteristics
4.1. Mesospheric CGW
4.2. Stratospheric CGWs
5. CGWs Excitation Source
6. Propagation Background Circumstances
7. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fritts, D.C.; Alexander, M.J. Gravity wave dynamics and effects in the middle atmosphere. Rev. Geophys. 2003, 41, 1–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holton, J.R.; Alexander, M.J. Gravity waves in the mesosphere generated by tropospheric convention. Tellus Ser. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 1999, 51, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, T.P.; Reeder, M.J.; Clark, T.L. Numerical modeling of gravity wave generation by deep tropical convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 1249–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Holton, J.R.; Durran, D.R. The gravity wave response above deep convection in a squall line simulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, R.E.; Alexander, M.J. Linear stratospheric gravity waves above convective thermal forcing. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 2434–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, T.P.; Sharman, R.D.; Clark, T.L.; Hsu, H.M. An Investigation of Turbulence Generation Mechanisms above Deep Convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 60, 1297–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Fritts, D.C. Reconstruction of the gravity wave field from convective plumes via ray tracing. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 147–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.L.; Yue, J.; She, C.-Y.; Stamus, P.A.; Liu, A.Z. A model study of the effects of winds on concentric rings of gravity waves from a convective plume near Fort Collins on 11 May 2004. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-J.; Chun, H.-Y.; Song, I.-S. Characteristics and Momentum Flux Spectrum of Convectively Forced Internal Gravity Waves in Ensemble Numerical Simulations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2007, 64, 3723–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, A.; Coroniti, S. A mechanism for the generation of acoustic-gravity waves during thunderstorm formation. Nature 1966, 210, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, J. Nonlinear interactions between gravity waves and different mean winds. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2006, 16, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrasse, C.M.; Nakamura, T.; Tsuda, T.; Takahashi, H.; Medeiros, A.F.; Taylor, M.J.; Gobbi, D.; Salatun, A.; Suratno; Achmad, E.; et al. Reverse ray tracing of the mesospheric gravity waves observed at 23° S (Brazil) and 7° S (Indonesia) in airglow imagers. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2006, 68, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechine, J.; Wrasse, C.; Takahashi, H.; Medeiros, A.; Batista, P.; Clemesha, B.; Lima, L.; Fritts, D.; Laughman, B.; Taylor, M.J. First observation of an undular mesospheric bore in a Doppler duct. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, E.M.; Picard, R.H.; O’Neil, R.R.; Gardiner, H.A.; Gibson, J.; Mill, J.D.; Richards, E.; Kendra, M.; Gallery, W.O. MSX satellite observations of thunderstorm-generated gravity waves in mid-wave infrared images of the upper stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 939–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Alexander, M.J. Retrieval of stratospheric temperatures from Atmospheric Infrared Sounder radiance measurements for gravity wave studies. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, H.H.; Chahine, M.T.; Gautier, C.; Goldberg, M.D.; Kalnay, E.; McMillin, L.M.; Revercomb, H.; Rosenkranz, P.W.; Smith, W.L.; Staelin, D.H.; et al. AIRS/AMSU/HSB on the aqua mission: Design, science objectives, data products, and processing systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimsdell, A.W.; Alexander, M.J.; May, P.T.; Hoffmann, L. Model Study of Waves Generated by Convection with Direct Validation via Satellite. J. Atmos. Sci. 2010, 67, 1617–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Alexander, M.J. Occurrence frequency of convective gravity waves during the North American thunderstorm season. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.H.; Alexander, M.J.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Gelinas, L.J.; Vincent, R.A.; MacKinnon, A.D.; Woithe, J.M.; May, P.T.; Skinner, W.R.; Mlynczak, M.G.; et al. Imaging of atmospheric gravity waves in the stratosphere and upper mesosphere using satellite and ground-based observations over Australia during the TWPICE campaign. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Hong, S.-Y. Interaction between the orography-induced gravity wave drag and boundary layer processes in a global atmospheric model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, T.P.; Sharman, R.D. Gravity wave breaking, secondary wave generation, and mixing above deep convection in a three-dimensional cloud model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, J.H.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Ross, M.N. First measurements of the two-dimensional horizontal wave number spectrum from CCD images of the nightglow. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 11449–11460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Bishop, M.; Taylor, V. All-sky measurements of short period waves imaged in the OI (557.7 nm), Na (589.2 nm) and near infrared OH and O2 (0, 1) nightglow emissions during the ALOHA-93 campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 2833–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.J.; Pautet, P.D.; Medeiros, A.F.; Buriti, R.; Fechine, J.; Fritts, D.C.; Vadas, S.L.; Takahashi, H.; Sabbas, F.T.S.O. Characteristics of mesospheric gravity waves near the magnetic equator, Brazil, during the SpreadFEx campaign. Ann. Geophys. 2009, 27, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Mendillo, M.; Baumgardner, J.; Clark, R.R. Mesospheric gravity wave imaging at a subauroral site: First results from Millstone Hill. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2000, 105, 27119–27130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Yue, J.; Yuan, W.; Liu, X. Statistical characteristics of gravity wave activities observed by an OH airglow imager at Xinglong, in northern China. Ann. Geophys. 2011, 29, 1401–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, G.R.; Mende, S.B. OH emission and gravity waves (including a breaking wave) in all-sky imagery from Bear Lake, UT. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1994, 21, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentman, D.D.; Wescott, E.M.; Picard, R.H.; Winick, J.R.; Stenbaek-Nielsen, H.C.; Dewan, E.M.; Moudry, D.R.; São Sabbas, F.T.; Heavner, M.J.; Morrill, J. Simultaneous observations of mesospheric gravity waves and sprites generated by a midwestern thunderstorm. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2003, 65, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Vadas, S.L.; Shiokawa, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Kawamura, S.; Murayama, Y. Typhoon-induced concentric airglow structures in the mesopause region. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 5983–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, J.; Vadas, S.L.; She, C.-Y.; Nakamura, T.; Reising, S.C.; Liu, H.-L.; Stamus, P.; Krueger, D.A.; Lyons, W.; Li, T. Concentric gravity waves in the mesosphere generated by deep convective plumes in the lower atmosphere near Fort Collins, Colorado. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O.; Tarasick, D.W. On the detection and utilization of gravity waves in airglow studies. Planet. Space Sci. 1987, 35, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.P.; Walterscheid, R.L.; Taylor, M.J.; Ward, W.; Schubert, G.; Zhou, Q.; Garcia, F.; Kelly, M.C.; Shepherd, G.G. Numerical simulations of gravity waves imaged over Arecibo during the 10-day January 1993 campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 11475–11489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G.; Walterscheid, R.L. Wave-driven fluctuations in OH nightglow from an extended source region. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 9903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, G.R.; Gardner, C.S. Analytical models for the responses of the mesospheric OH* and Na layers to atmospheric gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 6271–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.Z. A modeling study of O2 and OH airglow perturbations induced by atmospheric gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, Z.; Lü, D. Simulation of the stratospheric gravity waves generated by the Typhoon Matsa in 2005. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 55, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritts, D.C.; Nastrom, G.D. Sources of mesoscale variability of gravity waves. Part II: Frontal, convective, and jet stream excitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Xu, J.; Yue, J.; Liu, X.; Yuan, W.; Ning, B.; Guan, S.; Younger, J.P. Investigation of a mesospheric bore event over northern China. Ann. Geophys. 2013, 31, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Smith, A.K.; Jiang, G.; Gao, H.; Wei, Y.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Russell, J.M. Strong longitudinal variations in the OH nightglow. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadas, S.; Yue, J.; Nakamura, T. Mesospheric concentric gravity waves generated by multiple convective storms over the North American Great Plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perwitasari, S.; Sakanoi, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Otsuka, Y.; Hozumi, Y.; Akiya, Y.; Saito, A.; Shiokawa, K.; Kawamura, S. Coordinated airglow observations between IMAP/VISI and a ground-based all-sky imager on concentric gravity wave in the mesopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2015, 120, 9706–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, F.; Swenson, G.; Liu, A.; Pautet, D. Evidence of the excitation of a ring-like gravity wave in the mesosphere over the Andes Lidar Observatory. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 8896–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Yue, J.; Hoffmann, L.; Straka, W.C.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Yuan, W.; Han, S.; Miller, S.D. Concentric gravity waves over northern China observed by an airglow imager network and satellites. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.M.; Qinzeng, L.I.; Jiyao, X.U.; Sun, L.C.; Yuan, W. A study of wave sources of gravity wave events observer by OH airglow imager located at Donggang station. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Wu, X.; Alexander, M.J. Satellite Observations of Stratospheric Gravity Waves Associated with the Intensification of Tropical Cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock Theory of the interaction of gravity waves with O2(1Σ) airglow. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1978, 83, 5175–5185. [CrossRef]
- Moreels, G.; Herse, M. Photographic evidence of waves around the 85 km level. Planet. Space Sci. 1977, 25, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Fukushima, T.; Tsuda, T.; She, C.Y.; Williams, B.P.; Krueger, D.; Lyons, W. Simultaneous observation of dual-site airglow imagers and a sodium temperature-wind lidar, and effect of atmospheric stability on the airglow structure. Adv. Space Res. 2005, 35, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yue, J.; Xu, J.; Garcia, R.R.; Russell, J.M.; Mlynczak, M.; Wu, D.L.; Nakamura, T. Variations of global gravity waves derived from 14 years of SABER temperature observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 6231–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynczak, M.G. Energetics of the mesosphere and lower thermosphere and the SABER experiment. Adv. Space Res. 1997, 20, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Kamalabadi, F.; Rumsey, L.G.; Swenson, G.R. Point-source suppression for atmospheric wave extraction from airglow imaging measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Shiokawa, K.; Otsuka, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Kubota, M.; Tsutsumi, M.; Nakamura, T.; Fritts, D.C. Gravity wave momentum flux in the upper mesosphere derived from OH airglow imaging measurements. Earth Planets Space 2007, 59, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.J.; Stair, A.T., Jr. Rocket measurements of the altitude distributions of the hydroxyl airglow. Phys. Scr. 1988, 37, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Heale, C.J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, A.Z.; Snively, J.B. Observation and modeling of gravity wave propagation through reflection and critical layers above Andes Lidar Observatory at Cerro Pachón, Chile. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12737–12750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowling, D.H.; Webb, H.D.; Yeh, K.C. Group rays of internal gravity waves in a wind-stratified atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 1971, 76, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldock, J.A.; Jones, T.B. The effects of neutral winds on the propagation of medium-scale atmospheric gravity waves at mid-latitudes. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1984, 46, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzog, A.; Vial, F. A study of the dynamics of the equatorial lower stratosphere by use of ultra-long-duration balloons: 2. Gravity waves. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 22745–22761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertin, F.; Testud, J.; Kersley, L.; Rees, P.R. The meteorological jet stream as a source of medium scale gravity waves in the thermosphere: An experimental study. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 1978, 40, 1161–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, C.O. Internal atmospheric gravity waves at ionospheric heights. Can. J. Phys. 1960, 38, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewan, E.M.; Picard, R.H. Mesospheric bores. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 6295–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isler, J.R.; Taylor, M.J.; Fritts, D.C. Observational evidence of wave ducting and evanescence in the mesosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 26301–26313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapgood, M.A.; Taylor, M.J. Analysis of airglow image data. Ann. Geophys. 1982, 38, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, Q.; Gao, H. The Propagation Characteristics of Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm. Chin. J. Geophys. 2018. (In Chinese) (accepted) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Wu, D.L.; Eckermann, S.D. Gravity wave variances and propagation derived from AIRS radiances. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1701–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fovell, R.; Durran, D.; Holton, J. Numerical simulations of convectively generated stratospheric gravity waves. J. Atmos. Sci. 1992, 49, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, M.Y.; Lin, C.C.H.; Huba, J.D.; Lien, C.P.; Chen, C.H.; Yue, J.; Chang, L.C.; Rajesh, P.K. Numerical modeling of the concentric gravity wave seeding of low-latitude nighttime medium-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.F. An investigation of gravity wave activity in the low-latitude upper mesosphere: Propagation direction and wind filtering. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Taylor, M.J.; Swenson, G.R.; She, C.-Y.; Hocking, W.; Baumgardner, J.; Mendillo, M. A multidiagnostic investigation of the mesospheric bore phenomenon. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2003, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, C.Y.; Li, T.; Williams, B.P.; Yuan, T.; Picard, R.H. Concurrent OH imager and sodium temperature/wind lidar observation of a mesopause region undular bore event over Fort Collins/Platteville, Colorado. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bageston, J.V.; Wrasse, C.M.; Batista, P.P.; Hibbins, R.E.; C Fritts, D.; Gobbi, D.; Andrioli, V.F. Observation of a mesospheric front in a thermal-doppler duct over King George Island, Antarctica. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12137–12147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remsberg, E.E.; Marshall, B.T.; Garcia-Comas, M.; Krueger, D.; Lingenfelser, G.S.; Martin-Torres, J.; Mlynczak, M.G.; Russell, J.M.; Smith, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Assessment of the quality of the Version 1.07 temperature-versus-pressure profiles of the middle atmosphere from TIMED/SABER. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Q. A Case Study of the Stratospheric and Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm in Northern China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9120489
Wen Y, Zhang Q, Gao H, Xu J, Li Q. A Case Study of the Stratospheric and Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm in Northern China. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(12):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9120489
Chicago/Turabian StyleWen, Ying, Qilin Zhang, Haiyang Gao, Jiyao Xu, and Qinzeng Li. 2018. "A Case Study of the Stratospheric and Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm in Northern China" Atmosphere 9, no. 12: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9120489
APA StyleWen, Y., Zhang, Q., Gao, H., Xu, J., & Li, Q. (2018). A Case Study of the Stratospheric and Mesospheric Concentric Gravity Waves Excited by Thunderstorm in Northern China. Atmosphere, 9(12), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9120489



