Differences in Sulfate Aerosol Radiative Forcing between the Daytime and Nighttime over East Asia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model and Observational Data
2.1. WRF-Chem Model
2.2. Observational Data
3. Results
3.1. WRF-Chem Validation
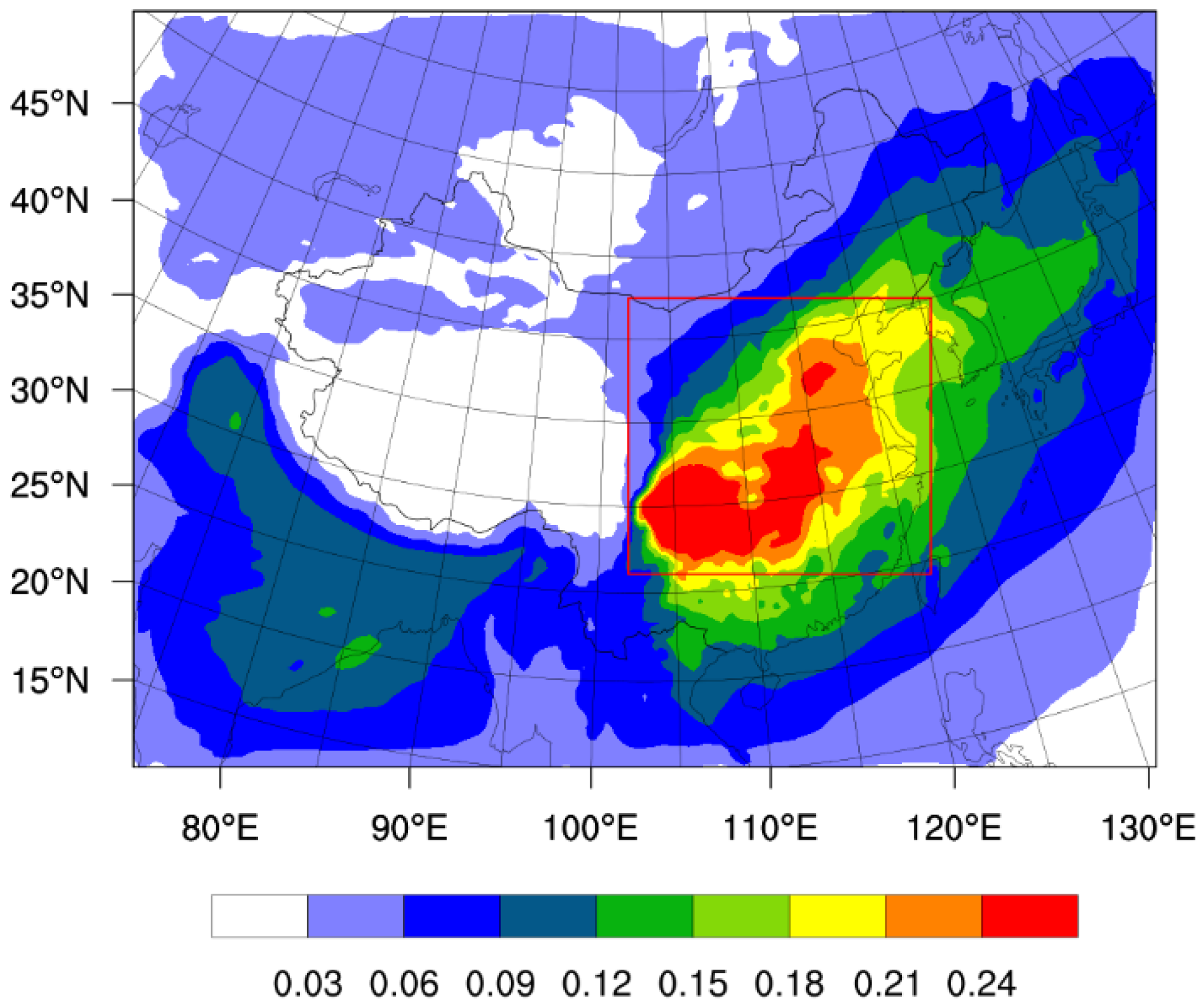
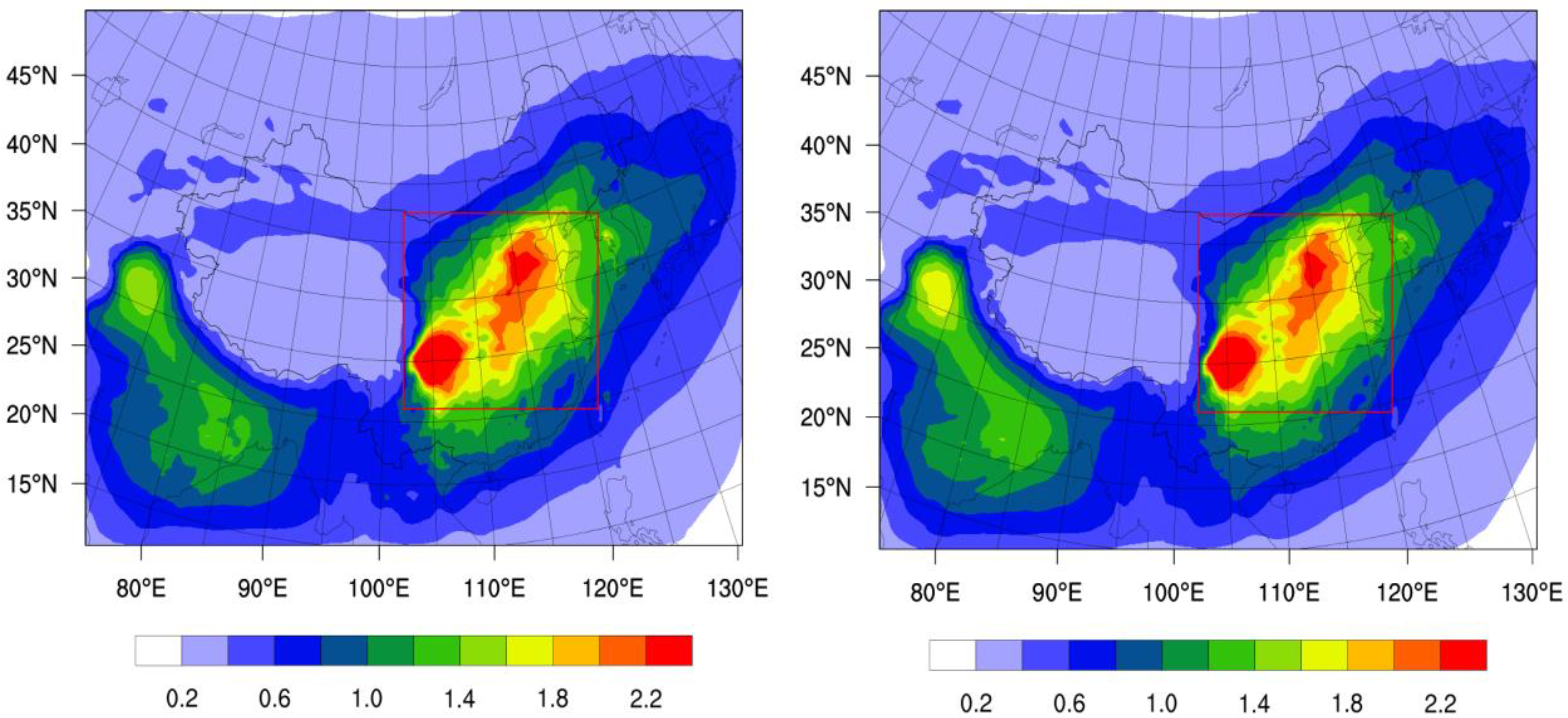
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Distributions of Sulfate Aerosols
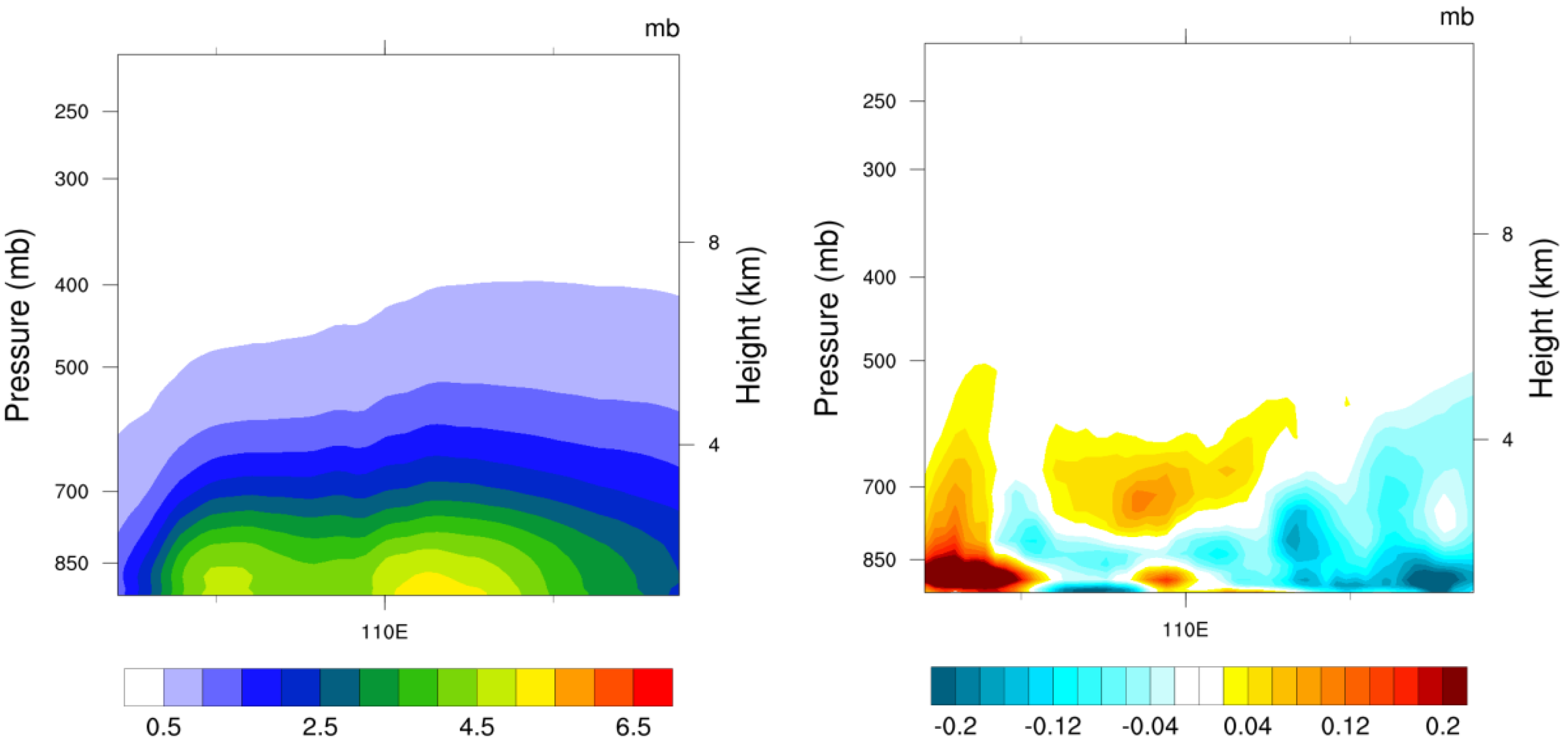
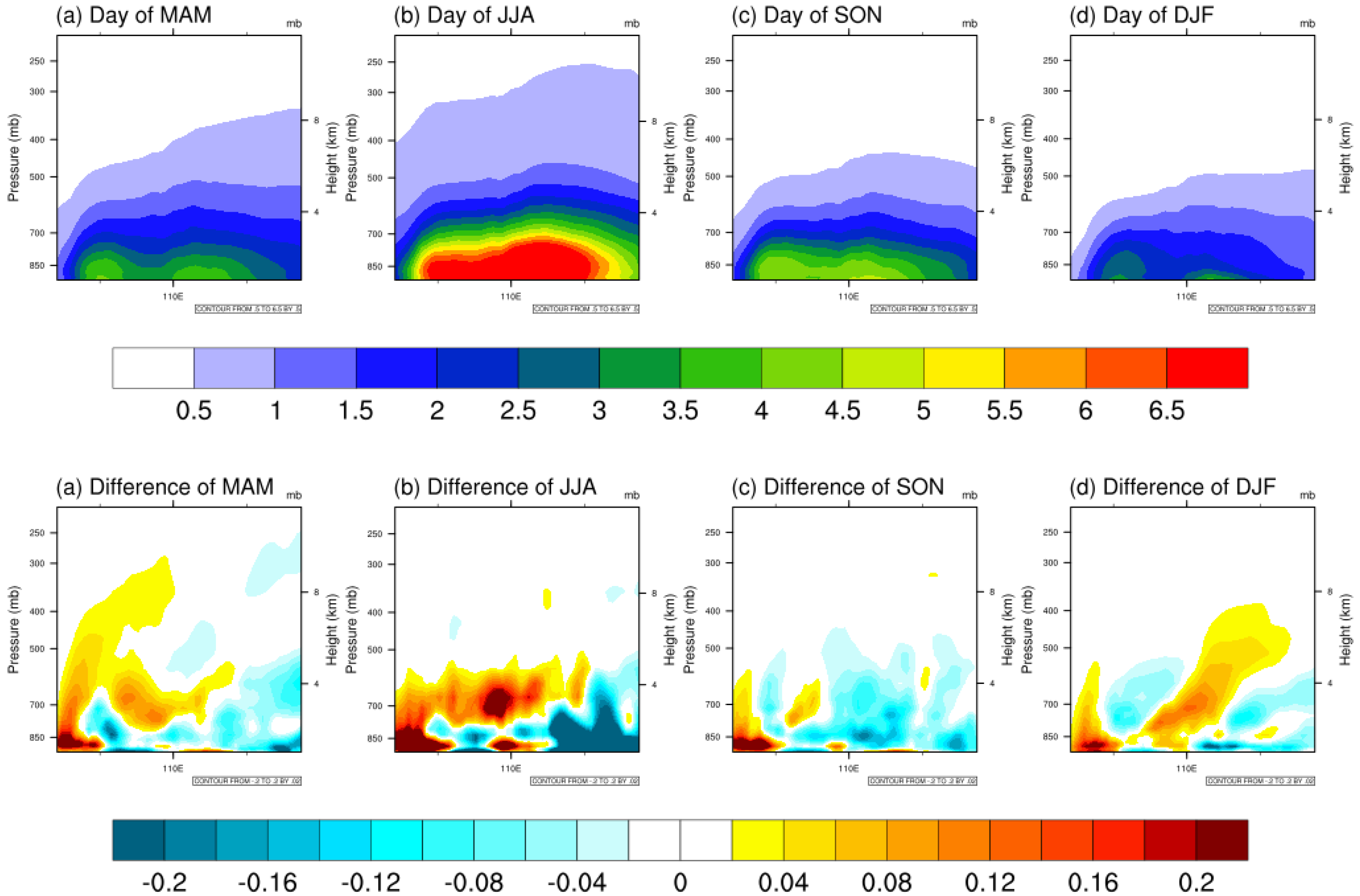
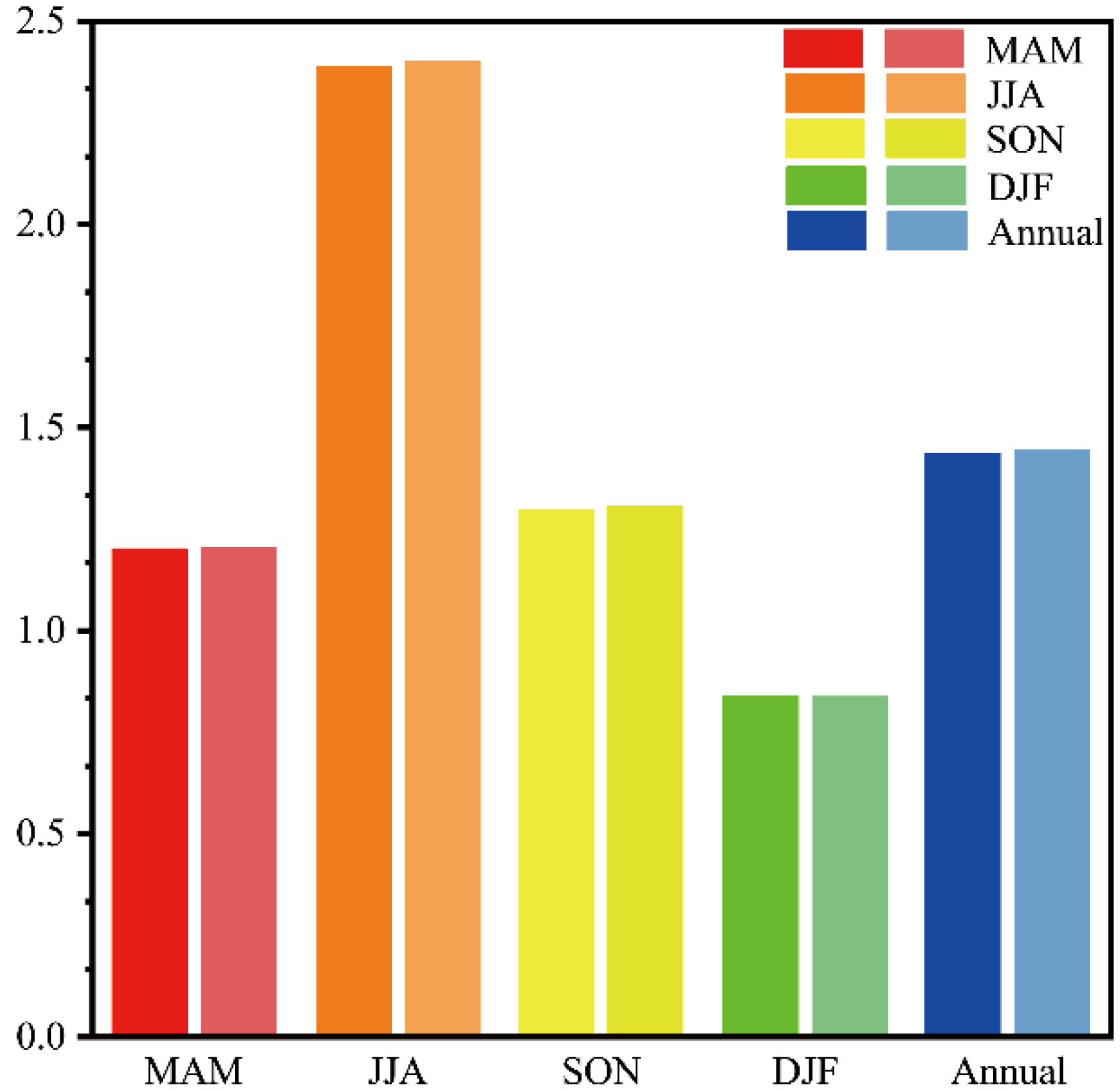
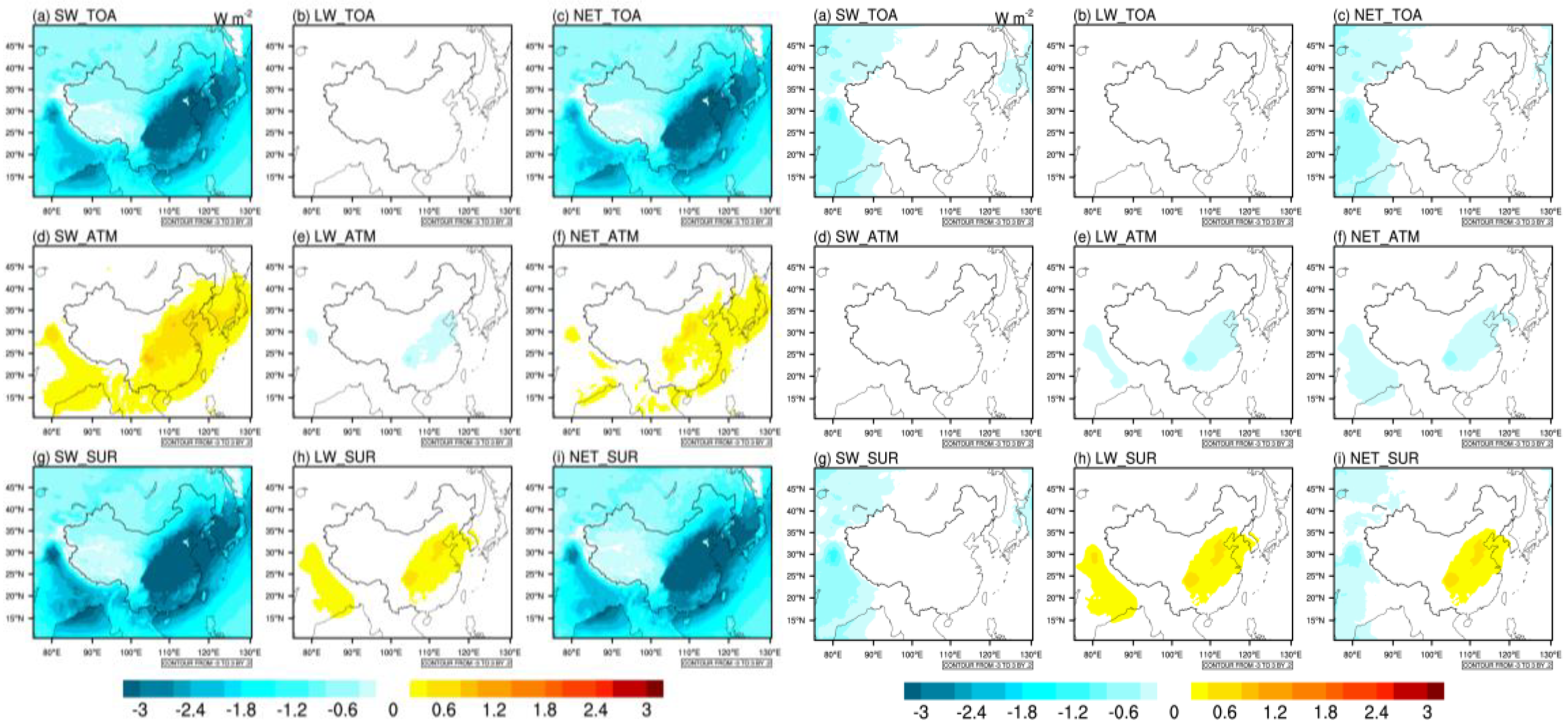
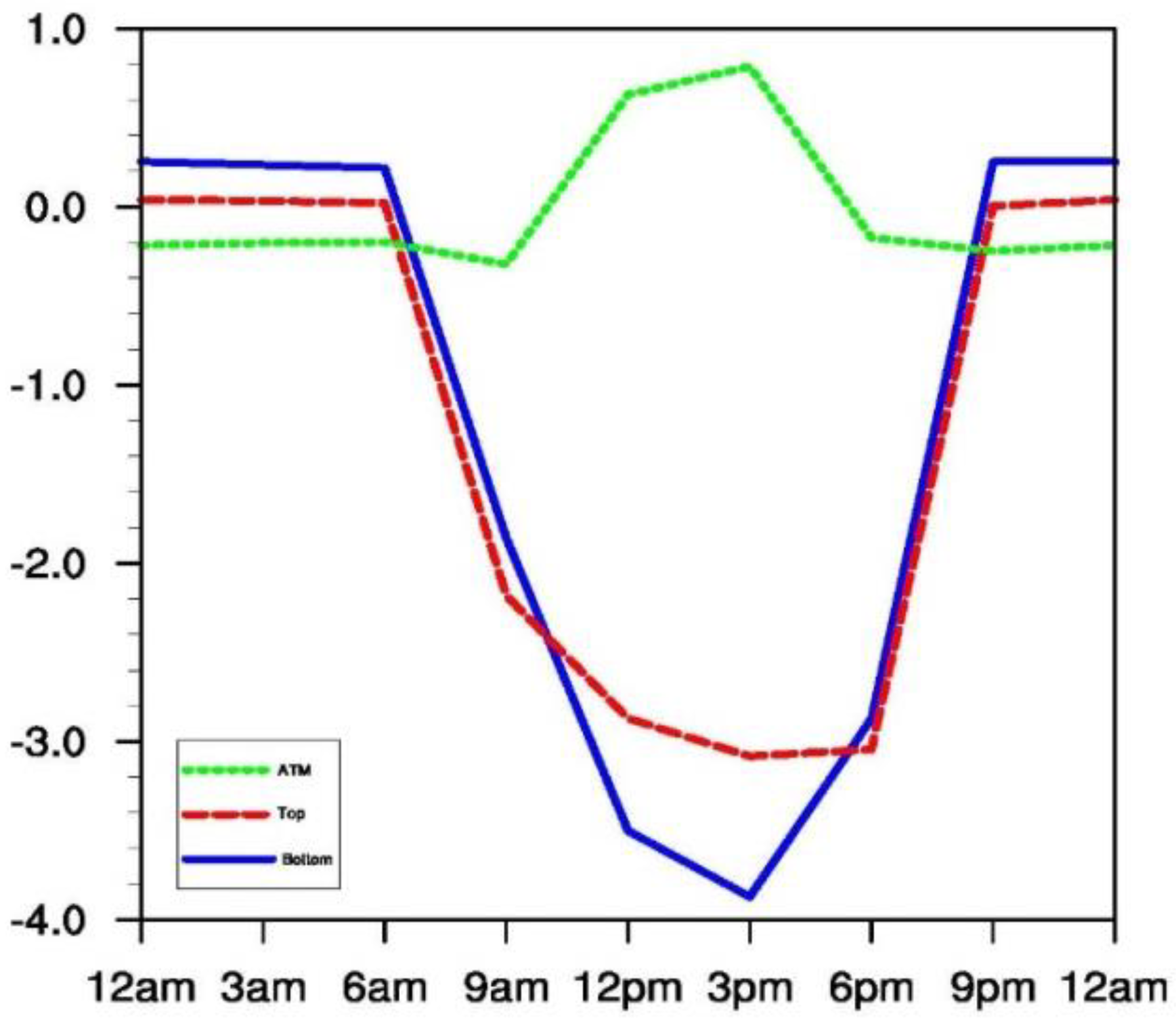
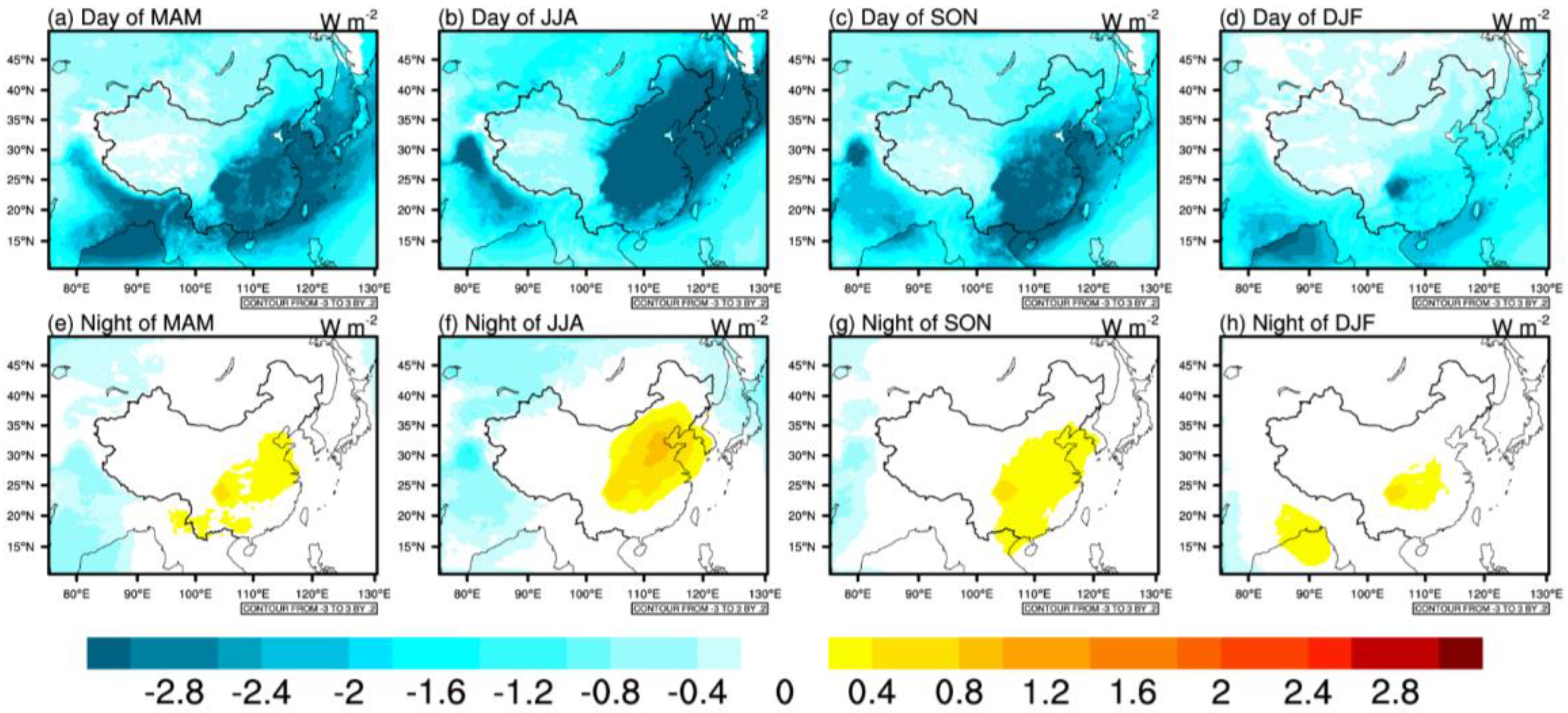
3.3. Sulfate Aerosol Direct Radiative Forcing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.; Tan, S. The radiative and climatic effects of atmospheric aerosols. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 32, 826–840. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Jia, R.; Jiang, N.; Kang, L.; Ma, X.; Xie, T. Comparison of dust emissions, transport, and deposition between the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert from 2007 to 2011. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2017, 60, 1338–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Jiang, N.X.; Huang, J.P.; Xu, X.G.; Zhang, H.W.; Zang, Z.; Huang, K.N.; Xu, X.C.; Wei, Y.; Guan, X.D.; et al. Quantifying contributions of natural and anthropogenic dust emission from different climatic regions. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y. Aerosol over china and their climate effect. Adv. Earth Sci. 2007, 22, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Smith, S.J.; Zhang, R.; Lou, S.; Yun, Q.; Ma, P.L.; Rasch, P.J. Recent intensification of winter haze in China linked to foreign emissions and meteorology. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlson, R.J.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J.; Sato, M.; Ruedy, R. Radiative forcing and climate response. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 6831–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Higuchi, K. Variability of East Asia dust events and their long-term trend. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocker, T.F.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, B.; Midgley, B.M.; et al. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Computat. Geom. 2013, 18, 95–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Shi, G. A Numerical Study on Temporal and Spatial Variations of Anthropogenic Sulfate Column Burden over Eastern Asia. Clim. Environm. Res. 2000, 1, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.; Roberts, D.L.; Slingo, A. A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulphate aerosols. Nature 1994, 370, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, B. Long-term variation of aerosol optical depth over Sichuan Basin of China during 1961–2013 and its relationship with temperature. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2017, 37, 793–802. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Simulation of centennial-scale drought events over eastern china during the past 1500 years. J. Meteorol. Res. 2017, 31, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiyi, S.; Jian, L. A “La Niña-like” state occurring in the second year after tropical volcanic eruptions during the 1500 years. Clim. Dyn. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Russell, L.M.; Yang, Y.; Xu, L.; Lamjiri, M.A.; DeFlorio, M.J.; Miller, A.J.; Ghan, S.J.; Liu, Y.; Singh, B. Impacts of the East Asian Monsoon on springtime dust concentrations over China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 8137–8152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Weaver, A. Factors contributing to diurnal temperature range trends in twentieth and twenty-first century simulations of the CCCMA coupled model. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 20, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Russell, L.M.; Lou, S.; Liao, H.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y.; Singh, B.; Ghan, S.J. Dust-wind interactions can intensify aerosol pollution over eastern China. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, S.; Russell, L.M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Singh, B.; Ghan, S.J. Impacts of interactive dust and its direct radiative forcing on interannual variations of temperature and precipitation in winter over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 8761–8780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Shi, G. The radiative forcing and climate effect due to anthropogenic sulfate aerosols over china. Sci. Atmos. Sin. 1998, 22, 919–925. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Congbin, F.U. Sulfur dioxide emissions, sulfate aerosol and climate change. Adv. Earthences 1997, 12, 440–446. [Google Scholar]
- Penner, J.E.; Hales, J.M.; Laulainen, N.S.; Travis, L.; Leifer, R.; Novakov, T.; Ogren, J.A.; Radke, L.F.; Schwartz, S.E.; Travis, L. Quantifying and minimizing uncertainty of climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 75, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the nasa intex-b mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Giorgi, F. Interactive coupling of regional climate and sulfate aerosol models over eastern Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 6477–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Langner, J.; Rodhe, H.; Leovy, C.B.; Warren, S.G. Perturbation of the northern hemisphere radiative balance by backscattering from anthropogenic sulfate aerosols. Tellus 1991, 43, 152–163. [Google Scholar]
- Charlson, R.J.; Lovelock, J.E.; Andreae, M.O.; Warren, S.G. Sulphate aerosols and climate. Nature 1989, 340, 437–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehl, J.T.; Briegleb, B.P. The relative roles of sulfate aerosols and greenhouse gases in climate forcing. Science 1993, 260, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Shi, G. Estimation of the Direct Radiative Forcing Due to Anthropogenic Sulfate over Eastern Asia. Plateau Meteorol. 2001, 20, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Haywood, J.M.; Shine, K.P. The effect of anthropogenic sulfate and soot aerosol on the clear sky planetary radiation budget. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodore, J. Climate Change 2001; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Chen, S.; Leung, L.R.; Qian, Y.; Kok, J.; Zaveri, R.; Huang, J. Uncertainty in modeling dust mass balance and radiative forcing from size parameterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10733–10753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, W.U.; Luo, Y.; Wang, W.G. The comparison of different simulation methods for the climate responses of the radiative forcing of anthropogenic sulfate aerosol over East Asia. J. Yunnan Univ. 2005, 27, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Jian-Dong, L.I.; Mao, J.Y.; Wang, W.C. Anthropogenic Eastern Asian radiative forcing due to sulfate and black carbon aerosols and their time evolution estimated by an AGCM. Chin. J. Geophys. 2015, 58, 1103–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.F.; Zhou, X.J.; Li, W.L. Advances in the study of atmospheric aerosol radiative forcing and climate change. Adv. Earthences 1998, 13, 572–581. [Google Scholar]
- Nemesure, S.; Wagener, R.; Schwartz, S.E. Direct shortwave forcing of climate by the anthropogenic sulfate aerosol: Sensitivity to particle size, composition, and relative humidity. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1995, 100, 26105–26116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.I.; Song, J.; Sun, L. A numerical study of sulfate aerosol direct effect and its impact on the East Asia climate. J. Meteorol. Res. Appl. 2015, 36, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.; Cui, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Xin, J.Y.; Wang, L.L. Numerical Simulations of Mass Distribution of Aerosols over China in 2006. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 32, 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, G. The Simulation and Estimation of Radiative Properties and Radiative Forcing due to Sulfate and Soot Aerosols. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 25, 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, J.T.; Filho, M.L.G.; Bruce, J.; Lee, H.; Callander, B.A.; Haites, E.; Harris, N.; Maskell, K. Climate Change 1994: Radiative Forcing of Climate Change and an Evaluation of the IPCC IS92 Emissions Scenarios; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Yang, B. Modeling the transport and radiative forcing of Taklimakan dust over the Tibetan Plateau: A case study in the summer of 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, C.; Qian, Y.; Leung, L.R.; Huang, J.; Huang, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Yang, L. Regional modeling of dust mass balance and radiative forcing over East Asia using WRF-Chem. Aeolian Res. 2014, 15, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Kang, L.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; Yuan, T.; Yang, B.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, G. Emission, transport, and radiative effects of mineral dust from the Taklimakan and Gobi deserts: Comparison of measurements and model results. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Schmitz, P.R.; Mckeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled ‘online’ chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, J.D., Jr.; Easter, R.C.; Zaveri, R.A.; Barnard, J.C.; Chapman, E.G.; Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E. Evolution of ozone, particulates, and aerosol direct radiative forcing in the vicinity of Houston using a fully coupled meteorology-chemistry-aerosol model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 5173–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, A.S.; Lurman, F.W.; Seinfeld, J.H. Modeling urban and regional aerosols, I. Model development. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, I.J.; Hass, H.; Memmesheimer, M.; Ebel, A.; Binkowski, F.S.; Shankar, U. Modal aerosol dynamics model for Europe: Development and first applications. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2981–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, B.; Ackermann, I.J.; Hass, H.; Binkowski, F.S.; Ebel, A. Modeling the formation of secondary organic aerosol within a comprehensive air quality model system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 28275–28293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, W.R.; Middleton, P.; Chang, J.S.; Tang, X. The second generation regional acid deposition model chemical mechanism for regional air quality modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 16343–16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, W.R.; Calvert, J.G. The mechanism of the HO-SO2 reaction. Atmos. Environ. 1983, 17, 2231–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margitan, J.J. Cheminform abstract: Mechanism of the atmospheric oxidation of sulfur dioxide. catalysis by hydroxyl radicals. J. Phys. Chem. 1984, 88, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meagher, J.F.; Olszyna, K.J.; Luria, M. The effect of SO2 gas phase oxidation on hydroxyl smog chemistry. Atmos. Environ. 1984, 18, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, J.F.; Sinha, A.; Howard, C.J. Kinetics of the gas-phase reaction HOSO2 + O2 -> HO2 + SO3. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.R.; Seaman, N.L. Use of Four-Dimensional Data Assimilation in a Limited-Area Mesoscale Model. Part I: Experiments with Synoptic-Scale Data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1990, 118, 1250–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.Y.; Noh, Y.; Dudhia, J. A New Vertical Diffusion Package with an Explicit Treatment of Entrainment Processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface Hydrology Model with the Penn State NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, H.; Curry, J.A.; Khvorostyanov, V.I. A New Double-Moment Microphysics Parameterization for Application in Cloud and Climate Models. Part I: Description. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Leung, L.R.; Johnson, B.; McFarlane, S.A.; Gustafson, W.I.; Fast, J.D.; Easter, R. The spatial distribution of mineral dust and its shortwave radiative forcing over North Africa: Modeling sensitivities to dust emissions and aerosol size treatments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8821–8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Sakurai, T.; Streets, D.; Hozumi, Y.; Ueda, H.; Park, S.U. Mics-ASIA II: The model intercomparison study for Asia Phase II methodology and overview of findings. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3468–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Qian, Y.; Ge, J.; Su, J. Effects of aerosols on autumn precipitation over mid-eastern China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2014, 20, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Tanré, D.; Smirnov, A.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Abuhassan, N.; Newcomb, W.W.; Schafer, J.S.; Chatenet, B.; Lavenu, F. An emerging ground-based aerosol climatology: Aerosol optical depth from AERONET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 12067–12097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17051–17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G. The MODIS Aerosol Algorithm, Products, and Validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.; Banerjee, P.; Mcdonald, D. Sensitivity of multiangle imaging to natural mixtures of aerosols over ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 18219–18238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.A.; Li, W.H.; Moroney, C.; Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Fishbein, E. Aerosol source plume physical characteristics from space-based multiangle imaging. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, R.; Banerjee, P.; Mcdonald, D.; Diner, D.J. Sensitivity of Multiangle imaging to Aerosol Optical Depth, and to Pure-Particle Size Distribution and Composition Over Ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32195–32213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Christopher, S.A. Longwave radiative forcing of Saharan dust aerosols estimated from MODIS, MISR, and CERES observations on Terra. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Ramanathan, V. Solar radiation budget and radiative forcing due to aerosols and clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Kahn, R.A.; Rerson, J.T.; Diner, D.J. Quantifying aerosol direct radiative effect with Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer observations: Top-of-atmosphere albedo change by aerosols based on land surface types. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Abdou, W.A.; Bruegge, C.J.; Conel, J.E.; Crean, K.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Helmlinger, M.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Martonchik, J.V.; Pilorz, S.H. MISR aerosol optical depth retrievals over southern Africa during the SAFARI-2000 Dry Season Campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3127–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V.; Diner, D.J.; Kahn, R.; Gaitley, B.; Holben, B.N. Comparison of MISR and AERONET aerosol optical depths over desert sites. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, S.A.; Wang, J. Intercomparison between MISR and Sunphotometer AOT in dust source regions over China: Implication for satellite retrievals and radiative forcing calculations. Tellus Seri. B-Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2004, 56, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Leung, L.R. WRF-Chem simulations of aerosols and anthropogenic aerosol radiative forcing in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liao, H.; Pye, H.O.T.; Wu, S. Projected effect of 2000–2050 changes in climate and emissions on aerosol levels in China and associated transboundary transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7937–7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Min, J.Z.; Sun, Z.B.; Li, Z.K.; Jin, L.S. Characteristics of sulphate aerosol distribution in China. Clim. Environ. Res. 2000, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.J.; Wang, T.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Min, J.Z. Modeling Sulfate Aerosol and Its Radiative Forcing over China. Plateau Meteorol. 2004, 23, 612–619. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Shi, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L. Simulation of Radiative Forcing by Sulfate Aerosols. Clim. Environ. Res. 2004, 9, 454–464. [Google Scholar]
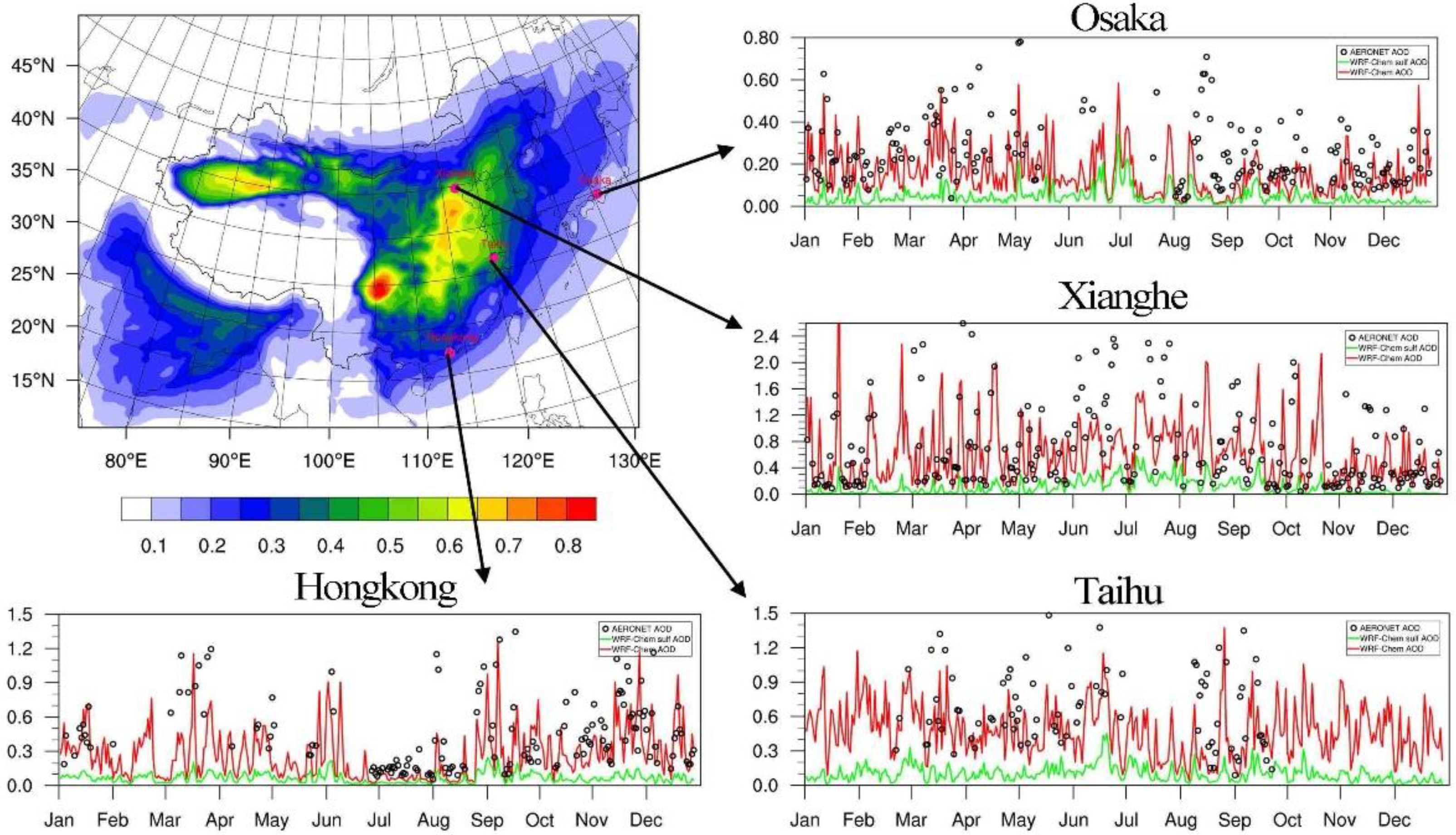
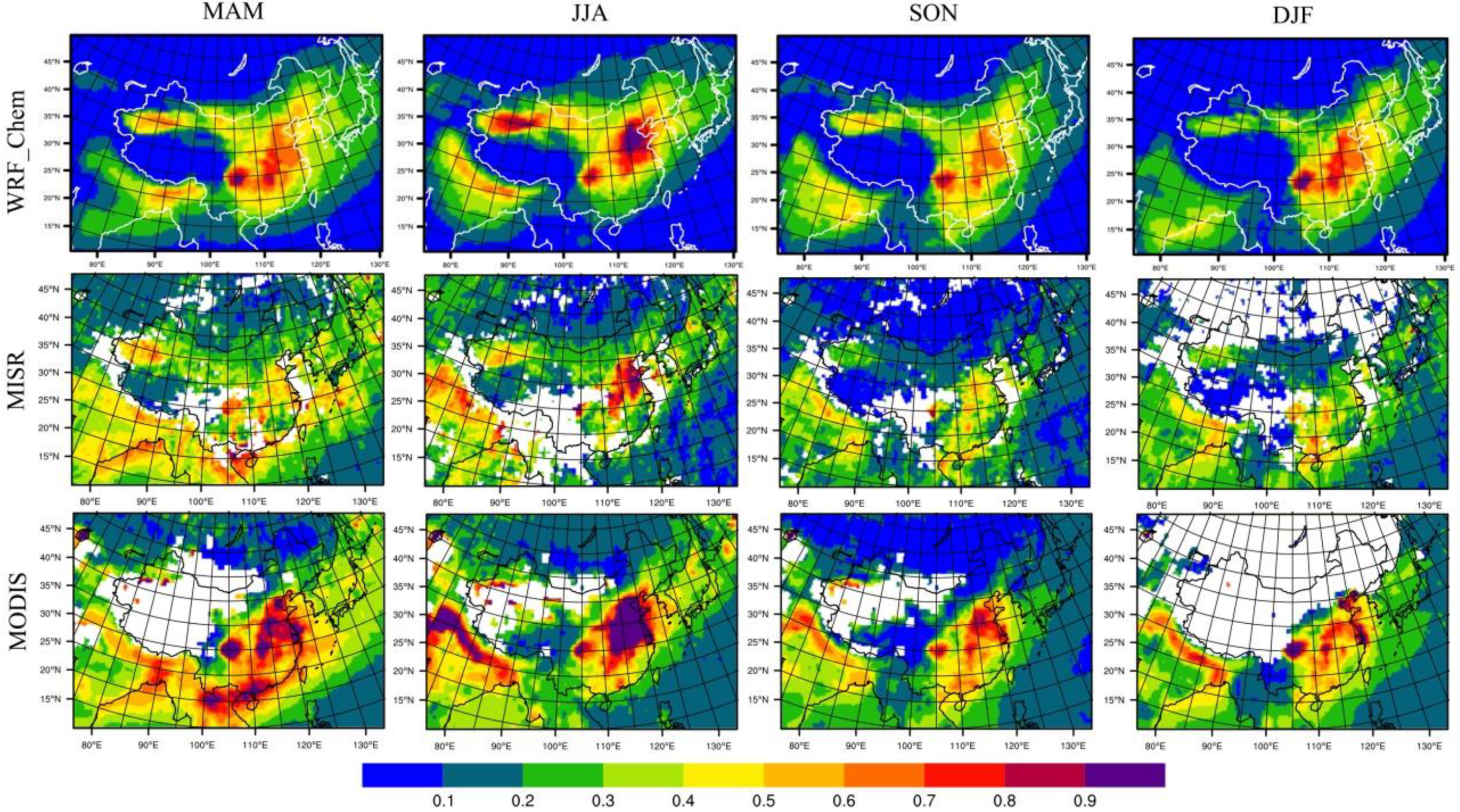
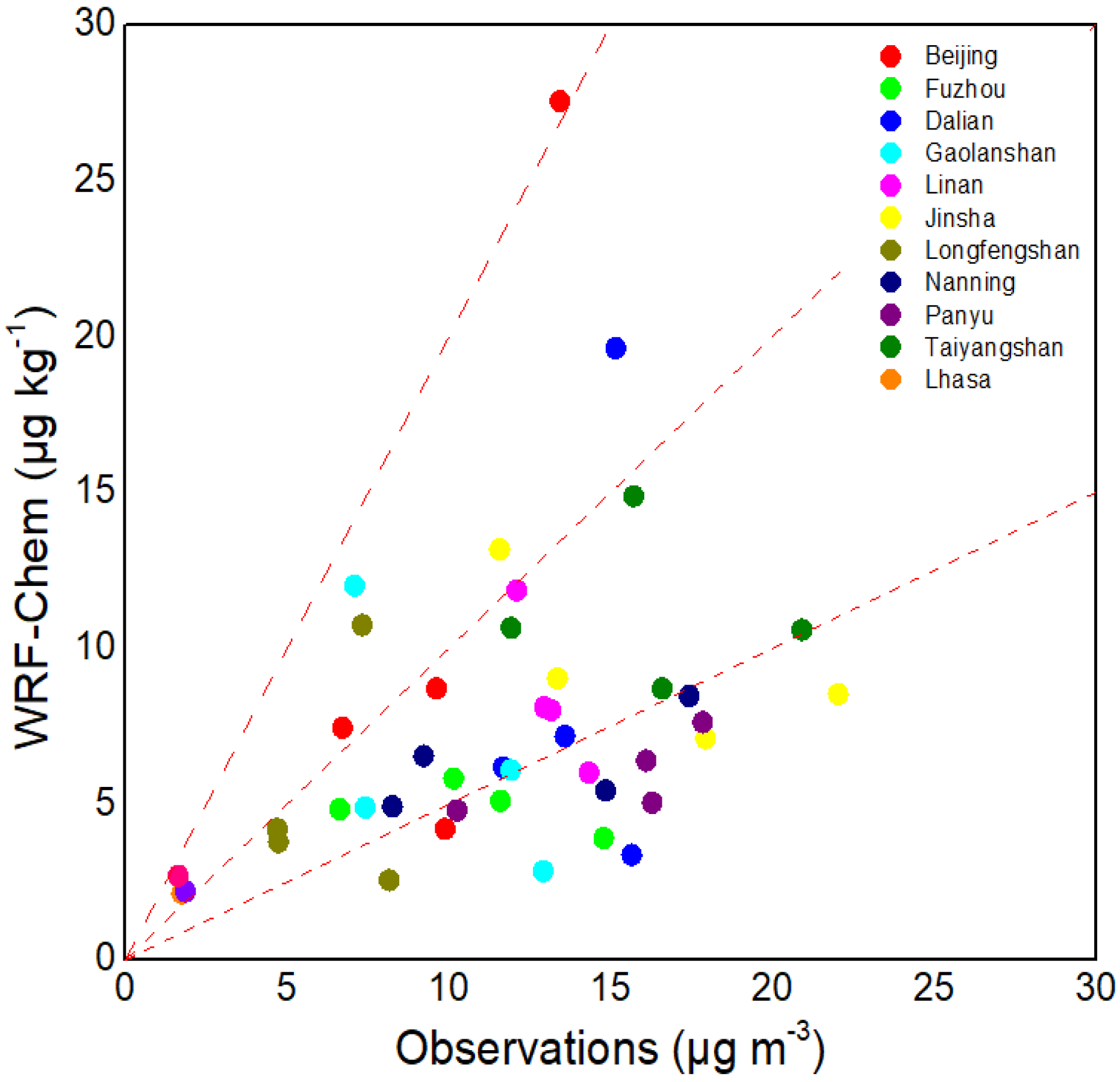

| Name | Latitude (°N) | Longitude (°E) | Elevation (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taihu (China) | 31.42 | 120.21 | 20 |
| Osaka (Japan) | 34.65 | 135.59 | 50 |
| Xianghe (China) | 39.75 | 116.96 | 36 |
| Hong Kong PolyU (China) | 22.30 | 114.18 | 30 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Jiang, N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zang, Z.; Wu, D.; Yuan, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Differences in Sulfate Aerosol Radiative Forcing between the Daytime and Nighttime over East Asia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) Model. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110441
Zhang H, Chen S, Jiang N, Wang X, Zhang X, Liu J, Zang Z, Wu D, Yuan T, Luo Y, et al. Differences in Sulfate Aerosol Radiative Forcing between the Daytime and Nighttime over East Asia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) Model. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(11):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110441
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hongyue, Siyu Chen, Nanxuan Jiang, Xin Wang, Xiaorui Zhang, Jian Liu, Zhou Zang, Dongyou Wu, Tiangang Yuan, Yuan Luo, and et al. 2018. "Differences in Sulfate Aerosol Radiative Forcing between the Daytime and Nighttime over East Asia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) Model" Atmosphere 9, no. 11: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110441
APA StyleZhang, H., Chen, S., Jiang, N., Wang, X., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Zang, Z., Wu, D., Yuan, T., Luo, Y., & Zhao, D. (2018). Differences in Sulfate Aerosol Radiative Forcing between the Daytime and Nighttime over East Asia Using the Weather Research and Forecasting model coupled with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) Model. Atmosphere, 9(11), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110441




