Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Urumqi, China: Temporal Variations, Health Risk, and Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Pretreatment and Analysis of Samples
2.3. GC/MS Analysis
2.4. Quality Control and Quality Assurance (QA/QC)
2.5. Source Apportionment with Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
3. Results and Discussion
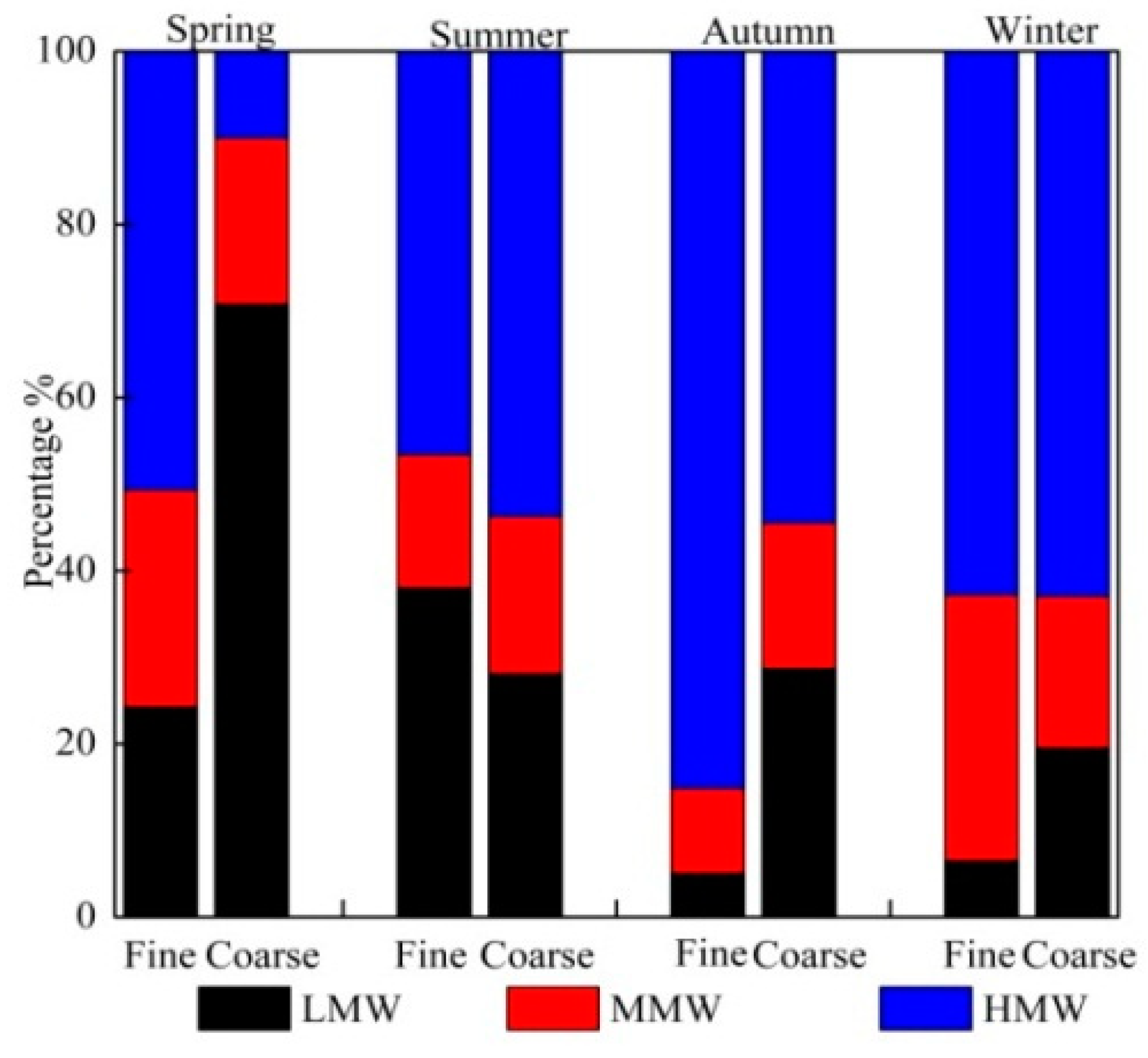
3.1. Size Distributions of PAHs in Aerosols
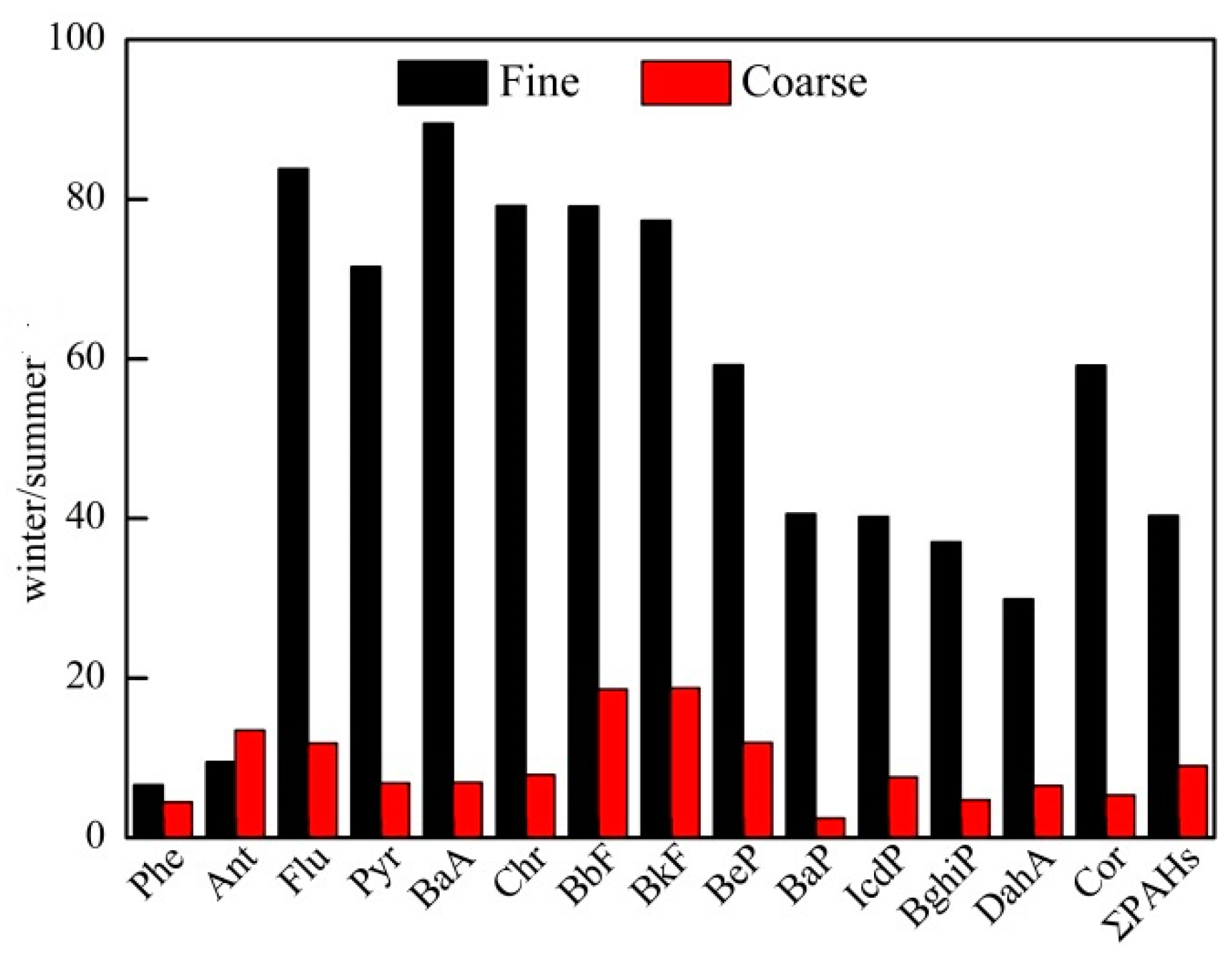
3.2. Seasonal Variations of PAHs in Aerosols
3.3. Risk Assessment of PAHs Exposure
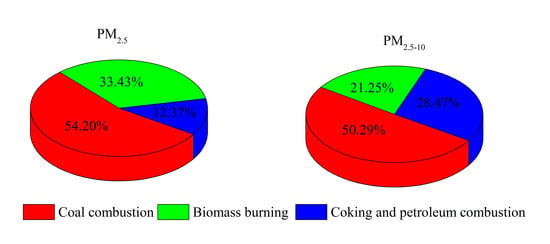
3.4. Sources of Particulate PAHs
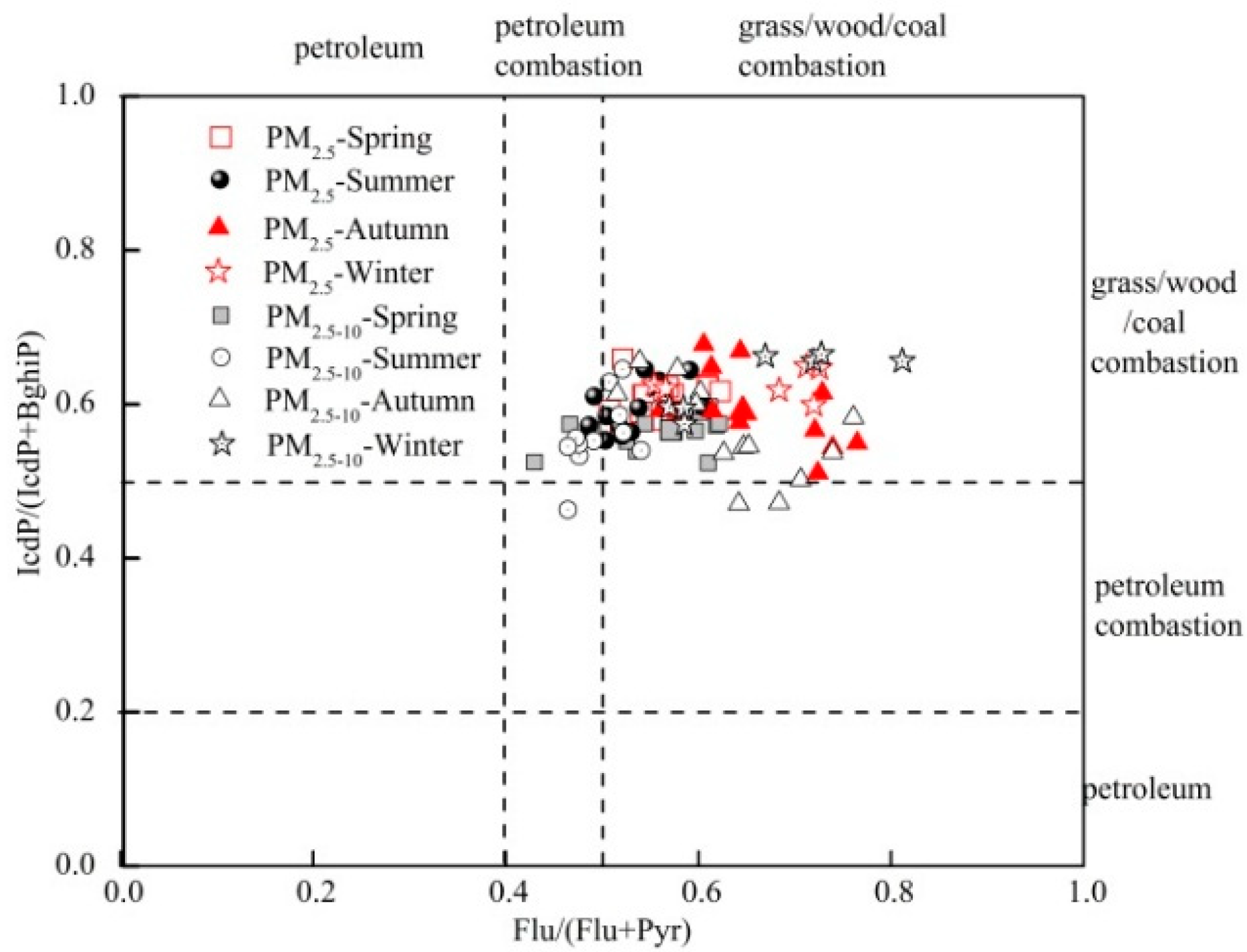
3.4.1. Diagnostic Ratios (DR) Analysis
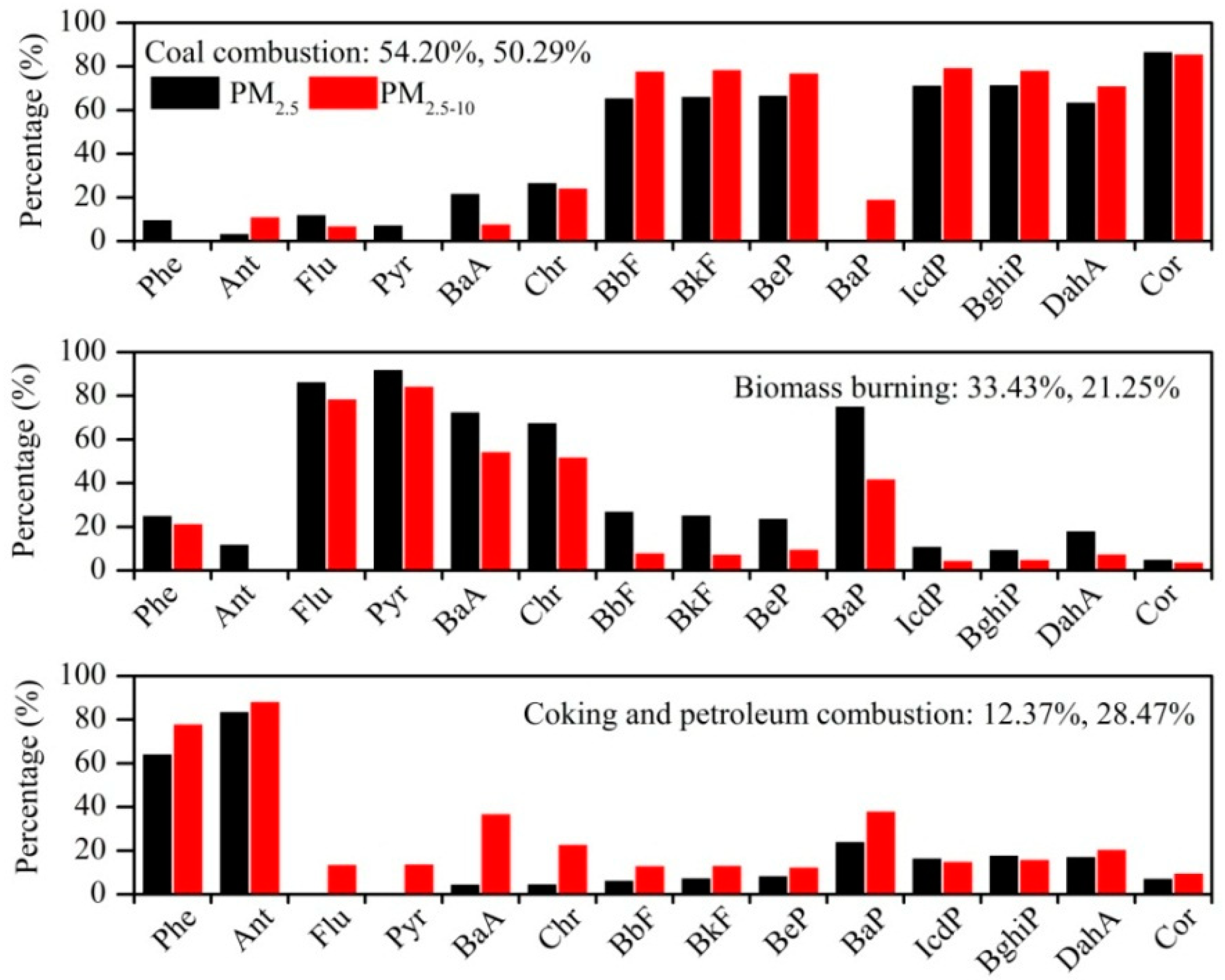
3.4.2. Sources of PAHs with Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Listed, N. Polynuclear aromatic compounds, Part 1, Chemical, environmental and experimental data. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog Risk Chem. Hum. 1983, 32, 1–453. [Google Scholar]
- Moeller, M.; Alfheim, I.; Larssen, S.; Mikalsen, A. Mutagenicity of airborne particles in relation to traffic and air pollution parameters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1982, 16, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.I. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, from Air Pollution to Climate Change. Atmos. Chem. 2000, 37, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.H.; Wu, S.H.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, H.; Li, B.J.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.N.; Shi, Y.X. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from urban to rural areas in Nanjing: Concentration, source, spatial distribution, and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 527–528, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haritash, A.K.; Kaushik, C.P. Biodegradation aspects of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs): A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, G.; Huang, K.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, S. Characteristics and sources of air-borne particulate in Urumqi, China, the upstream area of Asia dust. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 776–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limu, Y.L.M.A.B.D.; Lifu, D.L.N.T.; Miti, A.B.L.Y.; Wang, X.; Ding, X. Autumn and wintertime polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 from Urumqi, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Cao, C.; Cao, J. Changes in concentration, composition and source contribution of atmospheric organic aerosols by shifting coal to natural gas in Urumqi. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 148, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.M.; Xie, Z.Q.; Xiang, C.H.; Mai, B.X.; Sun, L.G.; Zheng, M.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Pöschl, U. Atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons observed over the North Pacific Ocean and the Arctic area: Spatial distribution and source identification. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2061–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yu, J.Z.; Li, S.X.; Ding, X.; He, Q.F.; Wang, X.M. Roadside and rooftop measurements of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in urban Guangzhou: Evaluation of vehicular and regional combustion source contributions. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7184–7191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, M.; Bi, X.; Chaemfa, C.; Ren, Z.; Wang, X.; Sheng, G.; Fu, J. Phase distribution, sources and risk assessment of PAHs, NPAHs and OPAHs in a rural site of Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.P.; Sun, R.H.; Cui, H.X.; Yang, C.; Jin, J.; Chu, Y.P.; Xia, Q. Spatial-Temporal Distribution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 of Shanghai Pudong New Area. Adm. Tech. Environ. Monit. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, S.; Yin, Y.; Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Li, Q.; Xiao, H.; Chen, K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric PM2.5 around 2013 Asian Youth Games period in Nanjing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174–175, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Jeppesen, E.; Gu, X.; Mao, Z.; Chen, H. Distribution, fate and risk assessment of PAHs in water and sediments from an aquaculture- and shipping-impacted subtropical lake, China. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, C.N. GC-MS analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aerosol in Urumuqi aeras. Environ. Monit. China 2005, 21, 45–48. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guzizaeri, M.; Dilinuer, T.; Wang, X.M.; Ding, X. Gaseous Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Southern part of Urumqi Air. Arid Environ. Monit. 2015, 29, 11–17. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Talip, D.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, G. Gas-Particle Partitioning of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Urban Area of Urumqi City, China. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1408–1416. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ular, K.; Xue, J.; Dilinuer, T. Correlation Research on the PAHs in Particulate Matter and Specific Surface Area, meteorological parameters in Urumqi’s Aerosphere. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2014, 41, 27–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wulaer, H.; Dilinuer, T.; Mailikezati, M.; Wang, X.M. Source apportionment of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in inhalable particulate matter at heating and non-heating periods in Urumqi, China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2015, 37, 35–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; You, Y.; Zhu, T.; Bai, Z.P.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.C. Analysis of the source and the composition of PAHs carbon isotope in atmospheric particles of Urumchi city. China Environ. Sci. 2006, 26, 542–545. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Z.H.; Duan, X.L.; Qiu, W.X.; Liu, D.; Wang, B.; Tao, S.; Jiang, Q.J.; Lu, B.; Song, Y.X.; Hu, X.X. Health risk assessment on dietary exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Taiyuan, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2010, 408, 5331–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Q.; Alharbi, B.; Collett, J., Jr.; Kreidenweis, S.; Pasha, M.J. Measurements and source apportionment of particle-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callén, M.S.; Iturmendi, A.; López, J.M. Source apportionment of atmospheric PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a PMF receptor model assessment of potential risk for human health. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Qiu, X.; Zheng, M. Sources and spatial distribution of particulate polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 584–585, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Guo, H.; Wang, X.M.; Zhao, X.H.; Ling, Z.H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Tracer-based source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Guangzhou, southern China, using positive matrix factorization (PMF). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2398–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.F.; Ding, X.; Bai, Z.P.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; Shi, J.W.; Li, Z.Y. A seasonal study of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in five typical cities of Liaoning Province, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slezakova, K.; Castro, D.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; Pereira, M.D.C. Impact of vehicular traffic emissions on particulate-bound PAHs: Levels and associated health risks. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zhuang, Y.H.; Wang, X.K.; Hao, Z.P. Characterization of PM2.5/PM2.5–10 and source tracking in the juncture belt between urban and rural areas of Beijing. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y. Seasonal variation and source apportionment of organic and inorganic compounds in PM2.5 and PM10 particulates in Beijing, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Yin, S.; Li, X.; Yu, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, R. Carbonaceous species in PM2.5 and PM10 in urban area of Zhengzhou in China: Seasonal variations and source apportionment. Atmos. Res. 2017, 191, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, R.; Xue, H.; Hu, R.; Liu, G. Characteristic and Source of Atmospheric PM10- and PM2.5-bound PAHs in a Typical Metallurgic City Near Yangtze River in China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2018, 100, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazquiarán, M.A.B.; Pinedo, L.C.O.D. Organic composition of atmospheric urban aerosol: Variations and sources of aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Res. 2007, 85, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, E.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C. Chemical characterization and source identification/apportionment of fine and coarse air particles in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Wang, X.M.; Zou, S.C. Particle-associated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in urban air of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5307–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaganoreña, H.; Lópezmárquez, R.; Murillotovar, M.; Hernándezmena, L.; Ospinanoreña, E.; Sánchezsalinas, E.; Waliszewski, S.; Montiel-Palma, S. Analysis of PAHs Associated with Particulate Matter PM2.5 in Two Places at the City of Cuernavaca, Morelos, México. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet, I.C.; Lagoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Stone, D.; Wang, W.; Schrlau, J.; Tao, S.; Simonich, S.L.M. Estimated Reduction in Cancer Risk due to PAH Exposures If Source Control Measures during the 2008 Beijing Olympics Were Sustained. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, G.; Wang, X.; Yao, T. Ambient distribution of particulate- and gas-phase n-alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Mastral, A.M.; López, J.M.; Callén, M.S.; García, T.; Murillo, R.; Navarro, M.V. Spatial and temporal PAH concentrations in Zaragoza, Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 307, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B. Pollution Characteristics and Sources of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 in Guangzhou; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Air Quality Guidelines for Europe; European Series No. 23; WHO Regional Publication: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Deng, W.; Huang, Z.; Ding, X.; Hu, Q.; Huang, Z. Attributing risk burden of PM2.5-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to major emission sources: Case study in Guangzhou, south China. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B. Concentrations, sources and human health risk of inhalation exposure to air toxics in Edmonton, Canada. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Man, R.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Peng, J. Atmospheric levels and health risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) bound to PM2.5 in Guangzhou, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 100, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behymer, T.D.; Hites, R.A. Photolysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons adsorbed on simulated atmospheric particulates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1985, 19, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclet, P.; Mouvier, G.; Nikolaou, K. Relative decay index and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Atmos. Environ. 1986, 20, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oros, D.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Identification and emission rates of molecular tracers in coal smoke particulate matter. Fuel 2000, 79, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, Z.X.; Zeng, Y.L.; Liu, F.B.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Y.L.; Xu, H.M.; Cao, J.J.; Yang, L. Day-Night Differences, Seasonal Variations and Source Apportionment of PM10-Bound PAHs over Xi’an, Northwest China. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, N.R.; Scheff, P.A.; Holsen, T.M. PAH source fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and, gasoline engines, highway tunnels, and wood combustion emissions. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ho, S.S.H.; Huang, R.; Gao, M.; Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Cao, J.; Wang, G.; Shen, Z.; Han, Y. Characterization of parent and oxygenated-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Xi’an, China during heating period: An investigation of spatial distribution and transformation. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, M.P.; Takada, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ohno, K.; Yamada, J.; Kouno, E.; Kumata, H. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in rivers and estuaries in Malaysia: A widespread input of petrogenic PAHs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Spring (n = 30) | Summer (n = 24) | Autumn (n = 26) | Winter (n = 17) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | −4~20 (8.5) a | 16~30 (22) | 3~24 (12) | −20~−8 (−14) | ||||||||
| RH (%) | 37~72 (53) | 22~83 (50) | 30~77 (52) | 77~84 (80) | ||||||||
| Name | Fine | Coarse | ρ2.5/(ρ2.5 + ρ2.5–10) (%) | Fine | Coarse | ρ2.5/(ρ2.5 + ρ2.5–10) (%) | Fine | Coarse | ρ2.5/(ρ2.5 + ρ2.5–10) (%) | Fine | Coarse | ρ2.5/(ρ2.5 + ρ2.5–10) (%) |
| Phe | 30.47 | 44.50 | 40.64 | 7.58 | 4.68 | 61.72 | 8.05 | 5.59 | 59.04 | 47.07 | 19.66 | 70.54 |
| Ant | 2.07 | 3.33 | 38.27 | 0.83 | 1.10 | 42.96 | 2.76 | 1.44 | 65.66 | 7.87 | 14.81 | 34.69 |
| Flu | 10.99 | 6.13 | 64.19 | 1.11 | 1.10 | 50.08 | 4.89 | 1.42 | 77.49 | 92.71 | 13.07 | 87.65 |
| Pyr | 7.93 | 4.09 | 65.98 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 45.79 | 3.19 | 0.84 | 79.24 | 58.37 | 6.60 | 89.84 |
| BaA | 5.76 | 1.02 | 84.92 | 0.55 | 0.62 | 46.82 | 4.71 | 0.71 | 86.83 | 48.73 | 4.28 | 91.93 |
| Chr | 8.88 | 1.74 | 83.64 | 0.75 | 0.89 | 45.82 | 8.27 | 1.14 | 87.90 | 59.25 | 6.96 | 89.49 |
| BbF | 21.52 | 1.93 | 91.76 | 1.88 | 1.87 | 50.12 | 50.18 | 3.84 | 92.90 | 148.68 | 34.77 | 81.04 |
| BkF | 12.45 | 1.27 | 90.76 | 1.17 | 1.30 | 47.36 | 33.70 | 2.76 | 92.43 | 90.29 | 24.33 | 78.77 |
| BeP | 12.38 | 1.53 | 88.98 | 1.40 | 1.70 | 45.05 | 31.31 | 2.80 | 91.80 | 82.73 | 20.27 | 80.32 |
| BaP | 3.58 | 0.33 | 91.55 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 44.37 | 3.12 | 0.28 | 91.73 | 31.04 | 2.34 | 92.99 |
| IcdP | 9.57 | 0.82 | 92.13 | 2.33 | 2.16 | 51.88 | 33.25 | 1.74 | 95.03 | 93.50 | 16.34 | 85.13 |
| BghiP | 6.03 | 0.61 | 90.80 | 1.51 | 1.82 | 45.31 | 22.61 | 1.26 | 94.72 | 55.88 | 8.63 | 86.62 |
| DahA | 1.76 | 0.20 | 89.99 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 53.09 | 4.30 | 0.48 | 89.90 | 13.93 | 2.68 | 83.85 |
| Cor | 0.66 | 0.09 | 87.56 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 41.80 | 3.99 | 0.19 | 95.54 | 14.17 | 1.77 | 88.90 |
| Σ14PAHs | 134.05 | 67.59 | 66.48 | 20.90 | 19.65 | 51.57 | 214.30 | 24.48 | 89.75 | 844.22 | 176.50 | 82.71 |
| PAH | TEF | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse | Fine | Coarse | ||
| Phe | 0.001 | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.008 | 0.005 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.047 | 0.020 |
| Ant | 0.01 | 0.021 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.011 | 0.028 | 0.015 | 0.079 | 0.148 |
| Flu | 0.001 | 0.011 | 0.006 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.093 | 0.013 |
| Pyr | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.0008 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.058 | 0.007 |
| BaA | 0.10 | 0.58 | 0.10 | 0.055 | 0.062 | 0.47 | 0.071 | 4.87 | 0.43 |
| Chr | 0.01 | 0.089 | 0.017 | 0.0075 | 0.009 | 0.083 | 0.011 | 0.59 | 0.07 |
| BbF | 0.10 | 2.15 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 5.02 | 0.38 | 14.87 | 3.48 |
| BkF | 0.10 | 1.25 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 3.37 | 0.28 | 9.03 | 2.43 |
| BaP | 1.00 | 3.58 | 0.33 | 0.77 | 0.96 | 3.12 | 0.28 | 31.04 | 2.34 |
| IcdP | 0.10 | 0.96 | 0.082 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 3.33 | 0.17 | 9.35 | 1.63 |
| BghiP | 0.01 | 0.060 | 0.006 | 0.015 | 0.018 | 0.23 | 0.013 | 0.56 | 0.086 |
| DahA | 1.00 | 1.76 | 0.20 | 0.47 | 0.41 | 4.30 | 0.48 | 13.93 | 2.68 |
| BaPeq | 10.50 | 1.14 | 1.88 | 2.02 | 19.97 | 1.71 | 84.52 | 13.33 | |
| BaP/BaPeq (%) | 34.10 | 28.87 | 41.06 | 47.60 | 15.63 | 16.38 | 36.73 | 17.55 | |
| CANPAHs/BaPeq (%) * | 63.81 | 61.42 | 56.79 | 50.17 | 82.58 | 80.81 | 61.59 | 79.87 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rekefu, S.; Talifu, D.; Gao, B.; Turap, Y.; Maihemuti, M.; Wang, X.; Abulizi, A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Urumqi, China: Temporal Variations, Health Risk, and Sources. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100412
Rekefu S, Talifu D, Gao B, Turap Y, Maihemuti M, Wang X, Abulizi A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Urumqi, China: Temporal Variations, Health Risk, and Sources. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(10):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100412
Chicago/Turabian StyleRekefu, Suwubinuer, Dilinuer Talifu, Bo Gao, Yusan Turap, Mailikezhati Maihemuti, Xinming Wang, and Abulikemu Abulizi. 2018. "Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Urumqi, China: Temporal Variations, Health Risk, and Sources" Atmosphere 9, no. 10: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100412
APA StyleRekefu, S., Talifu, D., Gao, B., Turap, Y., Maihemuti, M., Wang, X., & Abulizi, A. (2018). Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM2.5 and PM2.5–10 in Urumqi, China: Temporal Variations, Health Risk, and Sources. Atmosphere, 9(10), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9100412