Assessment of Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Brief Summary of the Main Characteristics of PM in Indoor and Outdoor Environments
4. Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Sampling and Assessment
4.1. Indicators
4.1.1. Total Suspended Particles (TSP)
4.1.2. PM10 and PM2.5
4.1.3. Ultrafine Particles (UFP) and Nanoparticles (NP)
4.1.4. Miscellaneous
4.2. Sampling Methods
4.3. Studies of Site-Specific and Environmental Characteristics
5. Exchange Factors
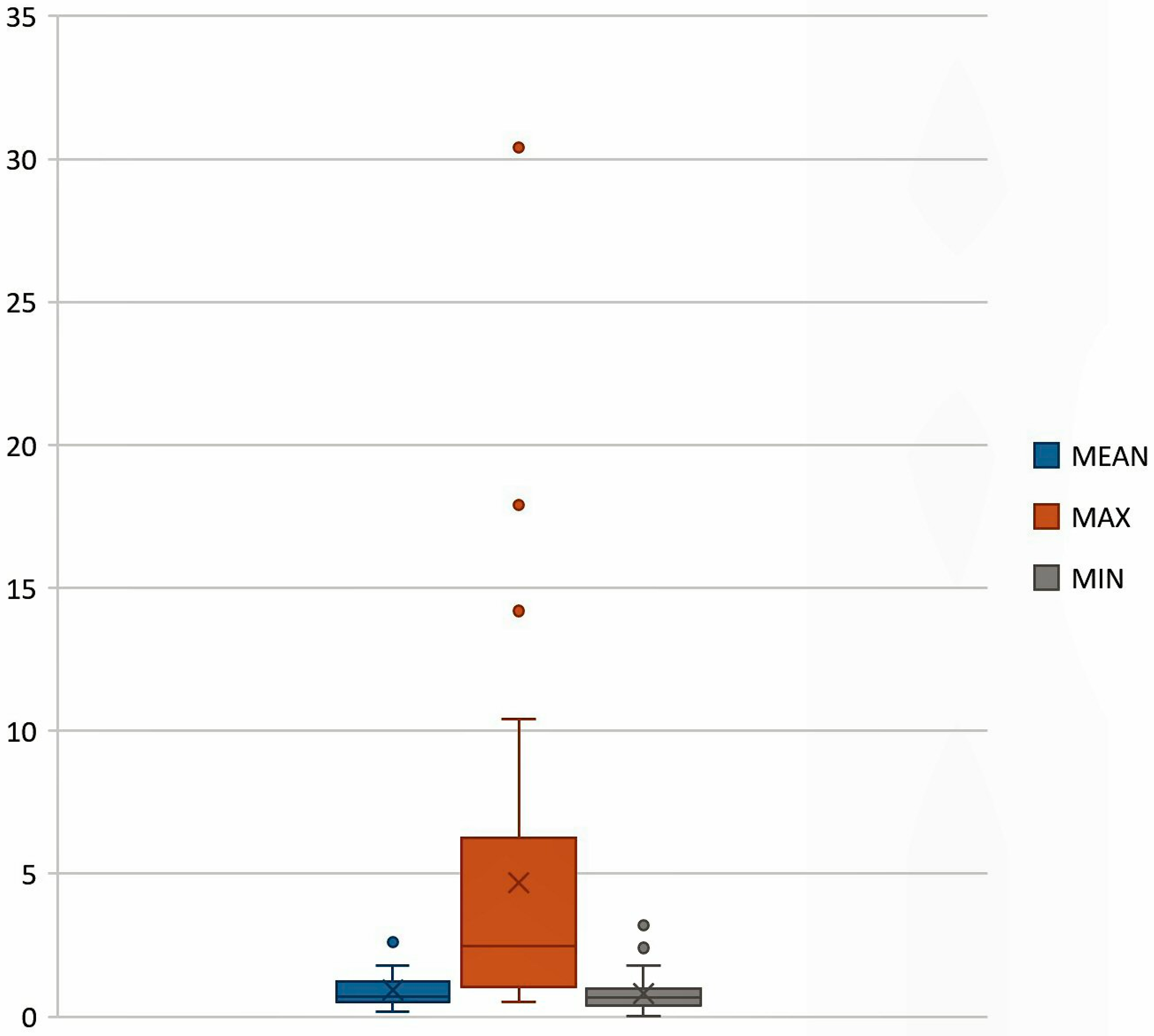
5.1. Indoor/Outdoor Ratio
5.2. Air Exchange Rate (AER)
5.3. Other Approaches
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| I-O | indoor-outdoor |
| Mass concentration | concentration expressed in micrograms per cube meters [μg/m3] |
| NP | nanoparticles |
| PM | (airborne) particulate matter |
| PN | Particle number |
| PNC | Particle number concentration = concentration expressed in number of particles per cubic centimetre [particles/cm3] |
| UFP | ultrafine particles |
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease. Available online: http://www.who.int/phe/publications/air-pollution-global-assessment/en/ (accessed on 11 May 2017).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 109; Outdoor Air Pollution; IARC: Lyon, France, 2015; Available online: http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol109/index.php (accessed on 12 July 2016).
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Guidelines for Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants. 2010. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/environment-and-health/air-quality/publications/2010/who-guidelines-for-indoor-air-quality-selected-pollutants (accessed on 12 May 2017).
- Brunekreef, B.; Holgate, S.T. Air pollution and health. Lancet 2002, 360, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; Andersen, Z.J.; Beelen, R.; Samoli, E.; Stafoggia, M.; Weinmayr, G.; Hoffmann, B.; Fischer, P.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Air pollution and lung cancer incidence in 17 European cohorts: Prospective analyses from the European Study of Cohorts for Air Pollution Effects (ESCAPE). Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, A.; Godden, D.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Particulate air pollution and acute health effects. Lancet 1995, 345, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasche, S.; Bischof, W. Daily time spent indoors in German homes—Baseline data for the assessment of indoor exposure of German occupants. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2005, 208, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monn, C.; Fuchs, A.; Högger, D.; Junker, M.; Kogelschatz, D.; Roth, N.; Wanner, H.U. Particulate matter less than 10 μm (PM10) and fine particles less than 2.5 μm (PM2.5): Relationships between indoor, outdoor and personal concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 208, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkaynak, H.; Xue, J.; Spengler, J.; Wallace, L.; Pellizzari, E.; Jenkins, P. Personal exposure to airborne particles and metals: Results from the Particle TEAM study in Riverside, California. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1996, 6, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wallace, L. Indoor Particles: A Review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1996, 46, 98–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Kan, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, W.; Bai, Z.; Song, G.; Pan, G. Association of Particulate Air Pollution with Daily Mortality: The China Air Pollution and Health Effects Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, M.; Clerico, M.; Pognant, F. Annoyance and disturbance hazard factors related to work and life environments: A review. Geam-Geoing. Ambient. E Mineraria-Geam-Geoengin. Environ. Min. 2016, 149, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kephalopoulos, S.; Koistinen, K.; Paviotti, M.; Schwela, D.; Kotzias, D. Proceedings of the International Workshop on “Combined Environmental Exposure: Noise, Air Pollutants and Chemicals”. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/publication/eur-scientific-and-technical-research-reports/proceedings-international-workshop-combined-environmental-exposure-noise-air-pollutants-and (accessed on 10 May 2017).
- Mohammed, M.O.A.; Song, W.-W.; Ma, W.-L.; Li, W.L.; Ambuchi, J.J.; Thabit, M.; Li, Y.-F. Trends in indoor–outdoor PM2.5 research: A systematic review of studies conducted during the last decade (2003–2013). Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of relationship between indoor and outdoor particles: I/O ratio, infiltration factor and penetration factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Peng, C.-K. Characterization of Indoor PM10, PM2.5, and Ultrafine Particles in Elementary School Classrooms: A Review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, C.A.; Perritt, R.L.; Pellizzari, E.D.; Thomas, K.W.; Whitmore, R.W.; Ozkaynak, H.; Spengler, J.D. Particle Total Exposure Assessment Methodology (PTEAM) study: Distributions of aerosol and elemental concentrations in personal, indoor, and outdoor air samples in a southern California community. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1993, 3, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jantunen, M.J.; Hänninen, O.; Katsouyanni, K.; Knöppel, H.; Kuenzli, N.; Lebret, E.; Maroni, M.; Saarela, K.; Srám, R.; Zmirou, D. Air pollution exposure in European cities: The “EXPOLIS” study. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1998, 8, 495–518. [Google Scholar]
- Lioy, P.J.; Waldman, J.M.; Buckley, T.; Butler, J.; Pietarinen, C. The personal, indoor and outdoor concentrations of PM-10 measured in an industrial community during the winter. Atmos. Environ. Part B Urban Atmos. 1990, 24, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SciVal. Available online: https://www.scival.com/ (accessed on 7 May 2017).
- Karagulian, F.; Belis, C.A.; Dora, C.F.C.; Prüss-Ustün, M.A.; Bonjour, S.; Adair-Rohani, H.; Amann, M. Contributions to cities’ ambient particulate matter (PM): A systematic review of local source contributions at global level. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.; Wu, C.-Y. Nanoparticles and the Environment. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 708–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Amann, M.; Burnett, R.T.; Cohen, A.; Dentener, F.; Ezzati, M.; Henderson, S.B.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Martin, R.V.; Dingenen, R.V.; et al. Exposure Assessment for Estimation of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Outdoor Air Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murr, L.E.; Garza, K.M. Natural and anthropogenic environmental nanoparticulates: Their microstructural characterization and respiratory health implications. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2683–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangchuk, T.; He, C.; Dudzinska, M.R.; Morawska, L. Seasonal variations of outdoor air pollution and factors driving them in the school environment in rural Bhutan. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monn, C. Exposure assessment of air pollutants: A review on spatial heterogeneity and indoor/outdoor/personal exposure to suspended particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide and ozone. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, E.; Suh, H.H.; Allen, G.; Koutrakis, P. Characterization of indoor particle sources: A study conducted in the metropolitan Boston area. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.C.; Thornton, C.A.; Mark, D.; Harrison, R.M. Indoor/outdoor relationships of particulate matter in domestic homes with roadside, urban and rural locations. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.K.; Kendall, M.; Ferrier, H.; Lindup, I.; Alm, S.; Hänninen, O.; Jantunen, M.; Mathys, P.; Colvile, R.; Ashmore, M.R.; et al. Personal exposures and microenvironment concentrations of PM2.5, VOC, NO2 and CO in Oxford, UK. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6399–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yocom, J.E. A Critical Review. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1982, 32, 500–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Indoor particle dynamics. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuoco, F.C.; Stabile, L.; Buonanno, G.; Trassiera, C.V.; Massimo, A.; Russi, A.; Mazaheri, M.; Morawska, L.; Andrade, A. Indoor Air Quality in Naturally Ventilated Italian Classrooms. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1652–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rivas, I.; Viana, N.; Morento, T.; Pandolfi, M.; Amato, F.; Reche, C.; Bouso, L.; Alvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; et al. Child exposure to indoor and outdoor air pollutants in schools in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofful, L.; Perrino, C. Chemical Composition of Indoor and Outdoor PM2.5 in Three Schools in the City of Rome. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1422–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainka, A.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Kaczmarek, K. PM2.5 in Urban and Rural Nursery Schools in Upper Silesia, Poland: Trace Elements Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7990–8008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachenmyer, C. Urban Measurements of Outdoor-Indoor PM2.5 Concentrations and Personal Exposure in the Deep South. Part I. Pilot Study of Mass Concentrations for Nonsmoking Subjects. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 32, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesenfeld, E.; Chalupa, D.; Gibb, F.R.; Oberdörster, G.; Gelein, R.; Morrow, P.E.; Utell, M.J.; Frampton, M.W. Ultrafine Particle Concentrations in a Hospital. Inhal. Toxicol. 2000, 12, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoek, G.; Kos, G.; Harrison, R.; de Hartog, J.; Meliefste, K.; ten Brink, H.; Katsouyanni, K.; Karakatsani, A.; Lianou, M.; Kotronarou, A.; et al. Indoor–outdoor relationships of particle number and mass in four European cities. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Hämeri, K.; Aalto, P.P.; Paatero, P.; Kulmala, M. Modal structure and spatial–temporal variations of urban and suburban aerosols in Helsinki—Finland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.Y.; Turpin, B.J.; Korn, L.; Weisel, C.P.; Morandi, M.; Colome, S.; Zhang, J.; Stock, T.; Spektor, D.; Winer, A. Influence of ambient (outdoor) sources on residential indoor and personal PM2.5 concentrations: Analyses of RIOPA data. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunekreef, B.; Janssen, N.A.H.; de Hartog, J.J.; Oldenwening, M.; Meliefste, K.; Hoek, G.; Lanki, T.; Timonen, K.L.; Vallius, M.; Pekkanen, J.; et al. Personal, indoor, and outdoor exposures to PM2.5 and its components for groups of cardiovascular patients in Amsterdam and Helsinki. Res. Rep. Health Eff. Inst. 2005, 127, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Shilton, V.; Giess, P.; Mitchell, D.; Williams, C. The Relationships between Indoor and Outdoor Respirable Particulate Matter: Meteorology, Chemistry and Personal Exposure. Indoor Built Environ. 2002, 11, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, B.; Guo, X.; Chen, R.; Kan, H. Investigating the geographical heterogeneity in PM10-mortality associations in the China Air Pollution and Health Effects Study (CAPES): A potential role of indoor exposure to PM10 of outdoor origin. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wu, J. Particle deposition in indoor environments: Analysis of influencing factors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazir, R.; Shaheen, N.; Shah, M.H. Indoor/outdoor relationship of trace metals in the atmospheric particulate matter of an industrial area. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krugly, E.; Martuzevicius, D.; Sidaraviciute, R.; Ciuzas, D.; Prasauskas, T.; Kauneliene, V.; Stasiulaitiene, I.; Kliucininkas, L. Characterization of particulate and vapor phase polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in indoor and outdoor air of primary schools. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsall, C.J.; Maher, B.A.; Karloukovski, V.V.; Shah, P.; Watkins, S.J. A novel approach to investigating indoor/outdoor pollution links: Combined magnetic and PAH measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8902–8909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, C.; Duarte, M.; Ferreira, M.; Alves, A.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, Â. Air quality in a school with dampness and mould problems. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2016, 9, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagel, É.C.; Reis, N.C.; Alvarez, C.E.; Santos, J.M.; Conti, M.M.; Boldrini, R.S.; Kerr, A.S. Characterization of the indoor particles and their sources in an Antarctic research station. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraga, D.; Pateraki, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Vasilakos, C.; Maggos, T. Studying the indoor air quality in three non-residential environments of different use: A museum, a printery industry and an office. Build. Environ. 2011, 46, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polednik, B. Particulate matter and student exposure in school classrooms in Lublin, Poland. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worobiec, A.; Samek, L.; Krata, A.; van Meel, K.; Krupinska, B.; Stefaniak, E.A.; Karaszkiewicz, P.; van Grieken, R. Transport and deposition of airborne pollutants in exhibition areas located in historical buildings–study in Wawel Castle Museum in Cracow, Poland. J. Cult. Herit. 2010, 11, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Ondráček, J.; Tesar, O.; Tørseth, K.; Ždímal, V.; Lazaridis, M. Indoor/outdoor particulate matter number and mass concentration in modern offices. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapouli, E.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Karanasiou, A.A.; Vratolis, S.; Hermansen, O.; Colbeck, I.; Lazaridis, M. Indoor and Outdoor Particle Number and Mass Concentrations in Athens. Sources, Sinks and Variability of Aerosol Parameters. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2011, 11, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, E.D.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Custódio, D.; Alves, C.A. Assessment of the indoor air quality in copy centres at Aveiro, Portugal. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braniš, M.; Řezáčová, P.; Domasová, M. The effect of outdoor air and indoor human activity on mass concentrations of PM10, PM2.5, and PM1 in a classroom. Environ. Res. 2005, 99, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, R.; Kumar, P. Indoor-outdoor concentrations of particulate matter in nine microenvironments of a mix-use commercial building in megacity Delhi. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2013, 6, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Shen, X.; Mao, X. Wintertime indoor air levels of PM10, PM2.5 and PM1 at public places and their contributions to TSP. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembari, A.; Triguero-Mas, M.; de Nazelle, A.; Davdand, P.; Vrijheid, M.; Cirach, M.; Martinez, D.; Figueras, F.; Querol, X.; Basagaña, X. Personal, indoor and outdoor air pollution levels among pregnant women. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.J.; Wallace, L.A.; Kearney, J.; van Ryswyk, K.; You, H.; Kulka, R.; Brook, J.R.; Xu, X. Personal, Indoor, and Outdoor Concentrations of Fine and Ultrafine Particles Using Continuous Monitors in Multiple Residences. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajani, S.Z.; Ricciardelli, I.; Trentini, A.; Bacco, D.; Maccone, C.; Castellazzi, S.; Lauriola, P.; Poluzzi, V.; Harrison, R.M. Is particulate air pollution at the front door a good proxy of residential exposure? Environ. Pollut. 2016, 213, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichenthal, S.; Dufresne, A.; Infante-Rivard, C.; Joseph, L. Indoor ultrafine particle exposures and home heating systems: A cross-sectional survey of Canadian homes during the winter months. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2006, 17, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbeck, I.; Nasir, Z.A.; Ali, Z. Characteristics of indoor/outdoor particulate pollution in urban and rural residential environment of Pakistan. Indoor Air 2010, 20, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majewski, G.; Kociszewska, K.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Pyta, H.; Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Mucha, W.; Pastuszka, J. Submicron Particle-Bound Mercury in University Teaching Rooms: A Summer Study from Two Polish Cities. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthel, M.; Pedan, V.; Hahn, O.; Rothhardt, M.; Bresch, H.; Jann, O.; Seeger, S. XRF-Analysis of Fine and Ultrafine Particles Emitted from Laser Printing Devices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7819–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Serfozo, N.; Glytsos, T.; Lazaridis, M. Multi-zone measurement of particle concentrations in a HVAC building with massive printer emissions: Influence of human occupation and particle transport indoors. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-W.; Hsu, D.-J. Measurements of fine and ultrafine particles formation in photocopy centers in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6598–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapouli, E.; Chaloulakou, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Spyrellis, N. Indoor and outdoor PM mass and number concentrations at schools in the Athens area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 136, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlbusch, T.A.; Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Göhler, D.; Stintz, M. Nanoparticle exposure at nanotechnology workplaces: A review. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahm, M.M.; Evans, D.E.; Schubauer-Berigan, M.K.; Birch, M.E.; Deddens, J.A. Occupational Exposure Assessment in Carbon Nanotube and Nanofiber Primary and Secondary Manufacturers: Mobile Direct-Reading Sampling. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2013, 57, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guinot, B.; Shen, Z.; Ho, K.F.; Niu, X.; Xiao, S.; Huang, R.J.; Cao, J. Characteristics of Organic and Elemental Carbon in PM2.5 and PM0.25 in Indoor and Outdoor Environments of a Middle School: Secondary Formation of Organic Carbon and Sources Identification. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.S.; De Carvalho, J.A.; Costa, M.A.M.; Pinheiro, C. An Overview of Particulate Matter Measurement Instruments. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1327–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Doraiswamy, P.; Watson, J.G.; Chen, L.-W.A.; Ho, S.S.H.; Sodeman, D.A. Advances in Integrated and Continuous Measurements for Particle Mass and Chemical Composition. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marple, V.A.; Rubow, K.L.; Turner, W.; Spengler, J.D. Low Flow Rate Sharp Cut Impactors for Indoor Air Sampling: Design and Calibration. JAPCA 1987, 37, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crist, K.C.; Liu, B.; Kim, M.; Deshpande, S.R.; John, K. Characterization of fine particulate matter in Ohio: Indoor, outdoor, and personal exposures. Environ. Res. 2008, 106, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.-W.; Shen, H.-Y. Indoor and outdoor PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations in the air during a dust storm. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinle, S.; Reis, S.; Sabel, C.E.; Semple, S.; Twigg, M.M.; Braban, C.F.; Leeson, S.R.; Heal, M.R.; Harrison, D.; Lin, C.; et al. Personal exposure monitoring of PM2.5 in indoor and outdoor microenvironments. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 508, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA). 2012 National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for Particulate Matter (PM). Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pm-pollution/2012-national-ambient-air-quality-standards-naaqs-particulate-matter-pm (assessed on 16 May 2017).
- Challoner, A.; Gill, L. Indoor/outdoor air pollution relationships in ten commercial buildings: PM2.5 and NO2. Build. Environ. 2014, 80, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, C.P.; Zhang, J.; Turpin, B.J.; Morandi, M.T.; Colome, S.; Stock, T.H.; Spektor, D.M.; Korn, L.; Winer, A.; Alimokhtari, S. Relationship of Indoor, Outdoor and Personal Air (RIOPA) study: Study design, methods and quality assurance/control results. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koistinen, K.J.; Kousa, A.; Tenhola, V.; Hänninen, O.; Jantunen, M.J.; Oglesby, L.; Kuenzli, N.; Georgoulis, L. Fine Particle (PM25) Measurement Methodology, Quality Assurance Procedures, and Pilot Results of the EXPOLIS Study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1999, 49, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Morawska, L.; He, C.; Gilbert, D. Impact of ventilation scenario on air exchange rates and on indoor particle number concentrations in an air-conditioned classroom. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fromme, H.; Diemer, J.; Dietrich, S.; Cyrys, J.; Heinrich, J.; Lang, W.; Kiranoglu, M.; Twardella, D. Chemical and morphological properties of particulate matter (PM10, PM2.5) in school classrooms and outdoor air. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6597–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapouli, E.; Chaloulakou, A.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating the concentration of indoor particles of outdoor origin: A review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 1113–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kousa, A.; Oglesby, L.; Koistinen, K.; Künzli, N.; Jantunen, M. Exposure chain of urban air PM2.5—Associations between ambient fixed site, residential outdoor, indoor, workplace and personal exposures in four European cities in the EXPOLIS-study. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, E.G.; Watkins, T.H.; Solomon, P.A.; Thomas, E.D.; Williams, R.W.; Hagler, G.S.W.; Shelow, D.; Hindin, D.A.; Kilaru, V.J.; Preuss, P.W. The Changing Paradigm of Air Pollution Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11369–11377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, M.; Slezakova, K.; Madureira, J.; de Oliveira Fernandes, E.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; do Carmo Pereira, M. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in primary school environments: Levels and potential risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, P.; Balducci, C.; Perilli, M.; Vichi, F.; Imperiali, A.; Cecinato, A. Indoor air quality at life and work environments in Rome, Italy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3503–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błaszczyk, E.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Fulara, I.; Mielżyńska-Švach, D. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons bound to outdoor and indoor airborne particles (PM2.5) and their mutagenicity and carcinogenicity in Silesian kindergartens, Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogula-Kopiec, P.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Kozielska, B.; Sówka, I. PAH Concentrations Inside a Wood Processing Plant and the Indoor Effects of Outdoor Industrial Emissions. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
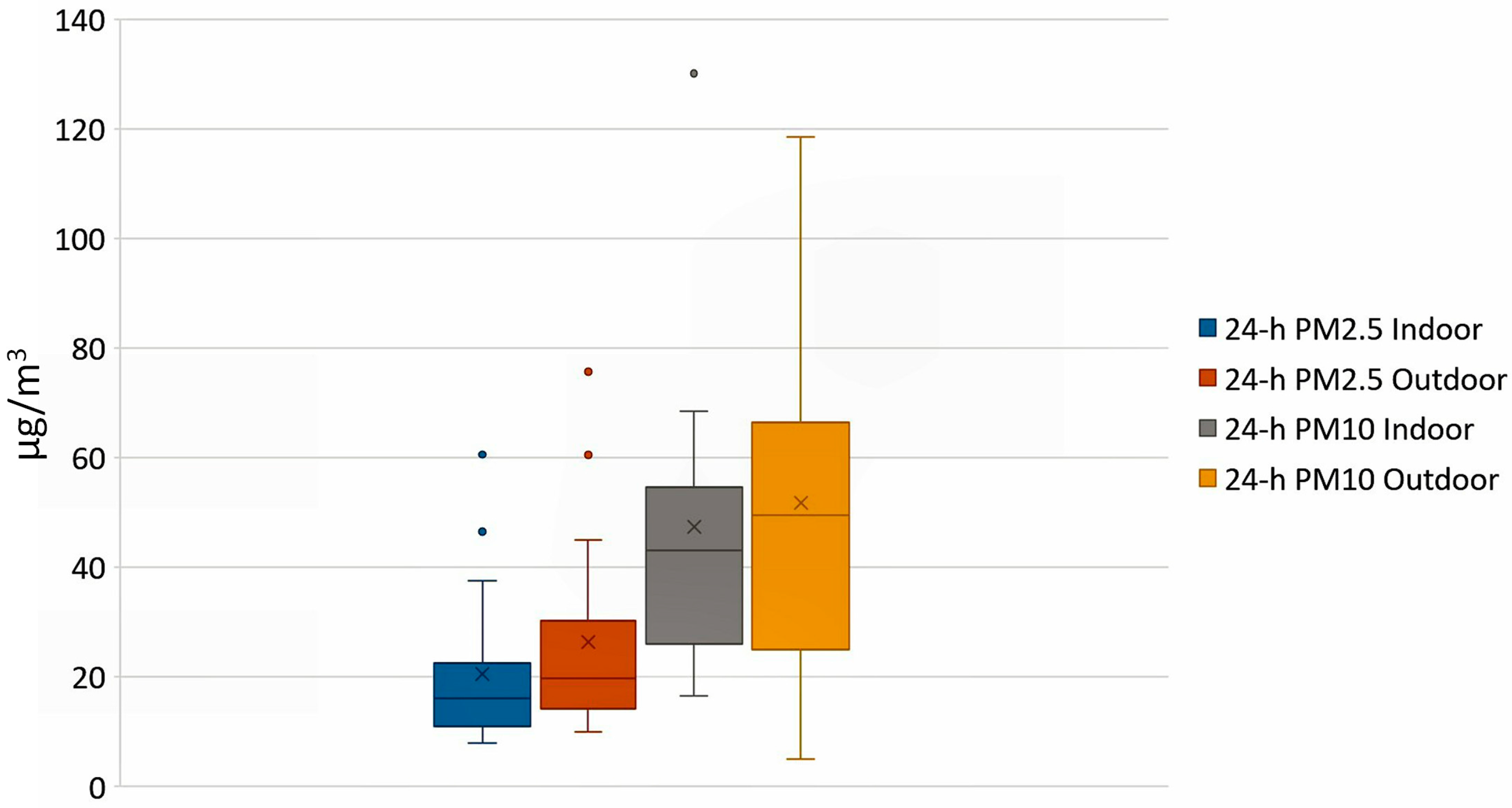
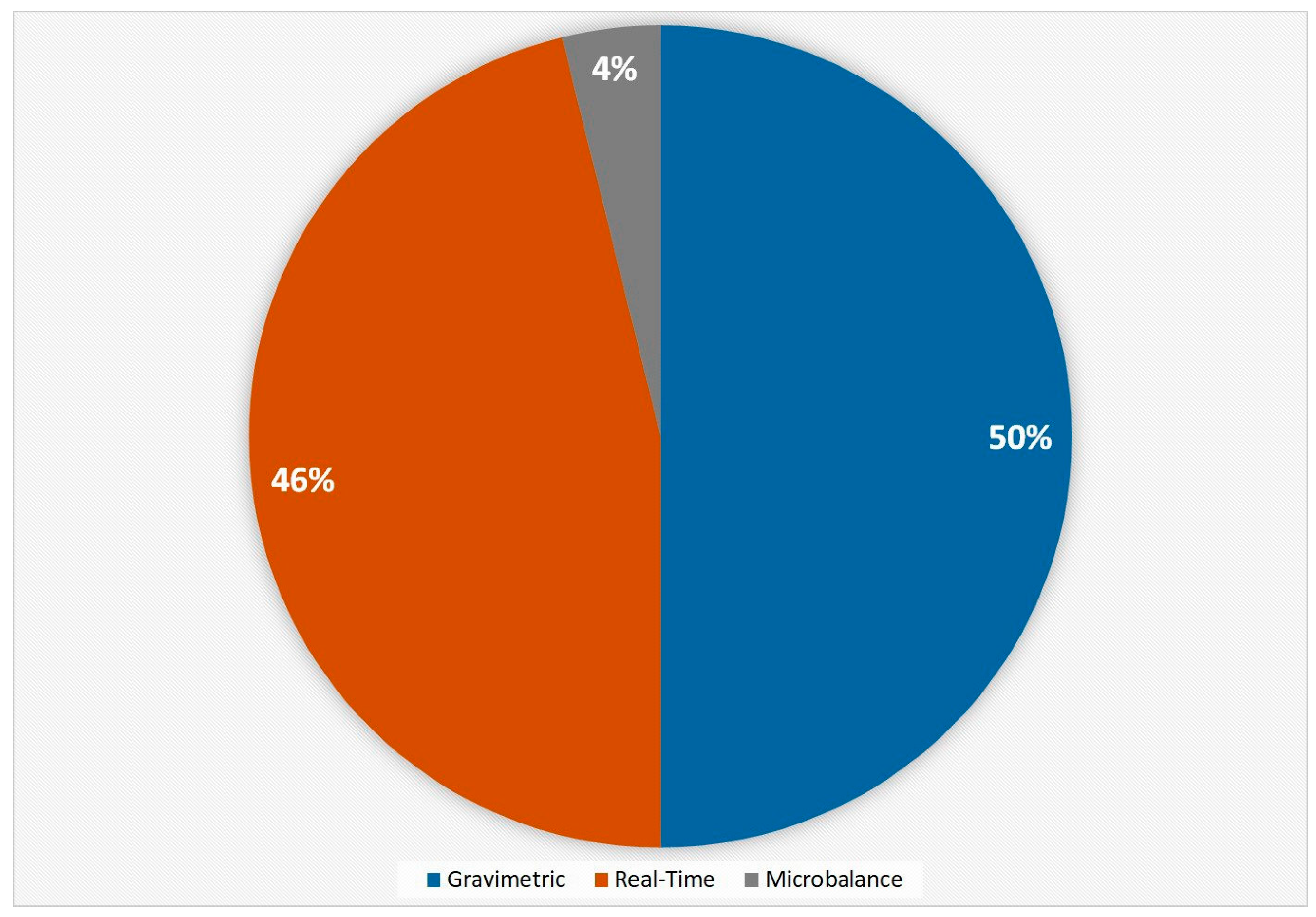
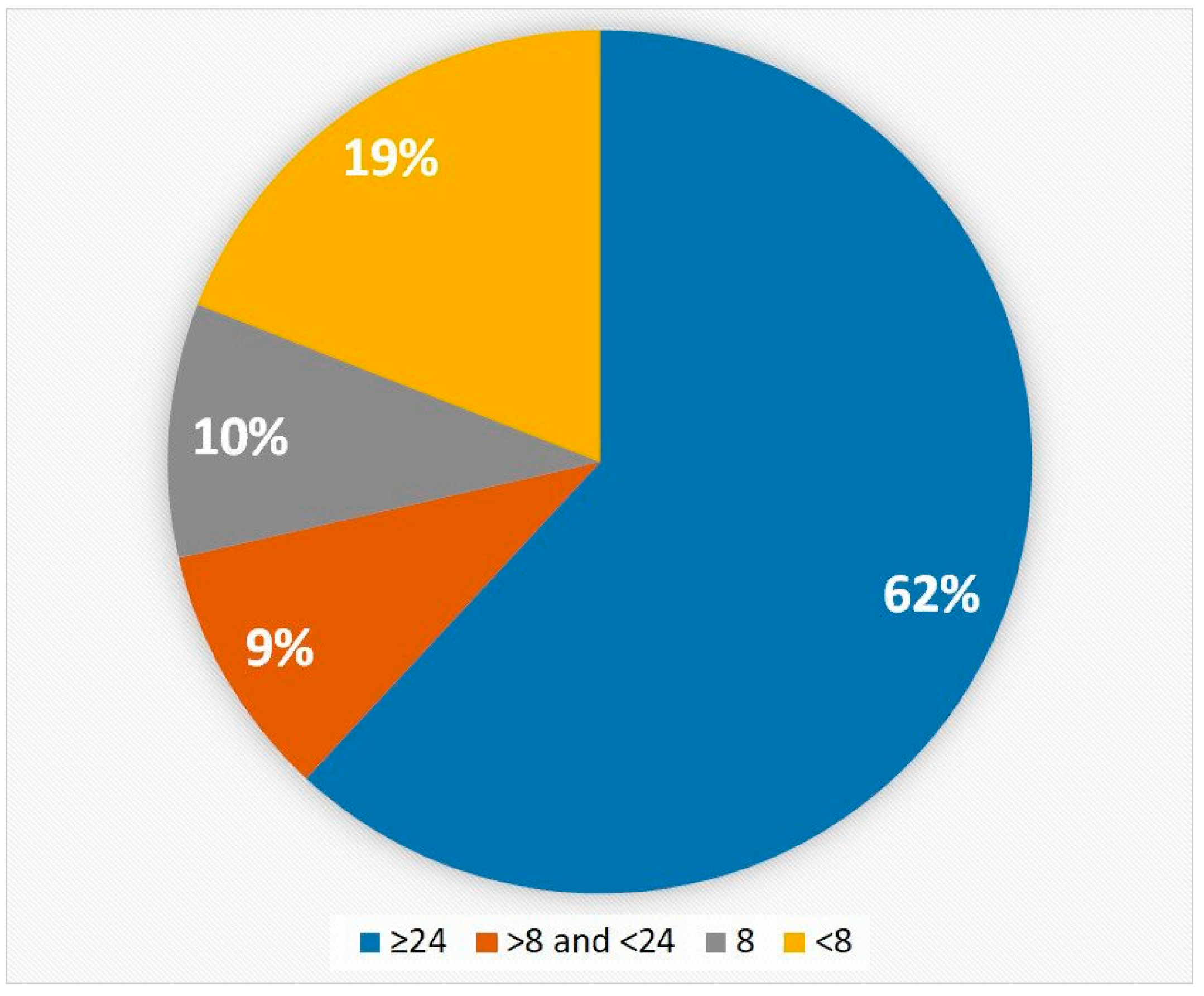
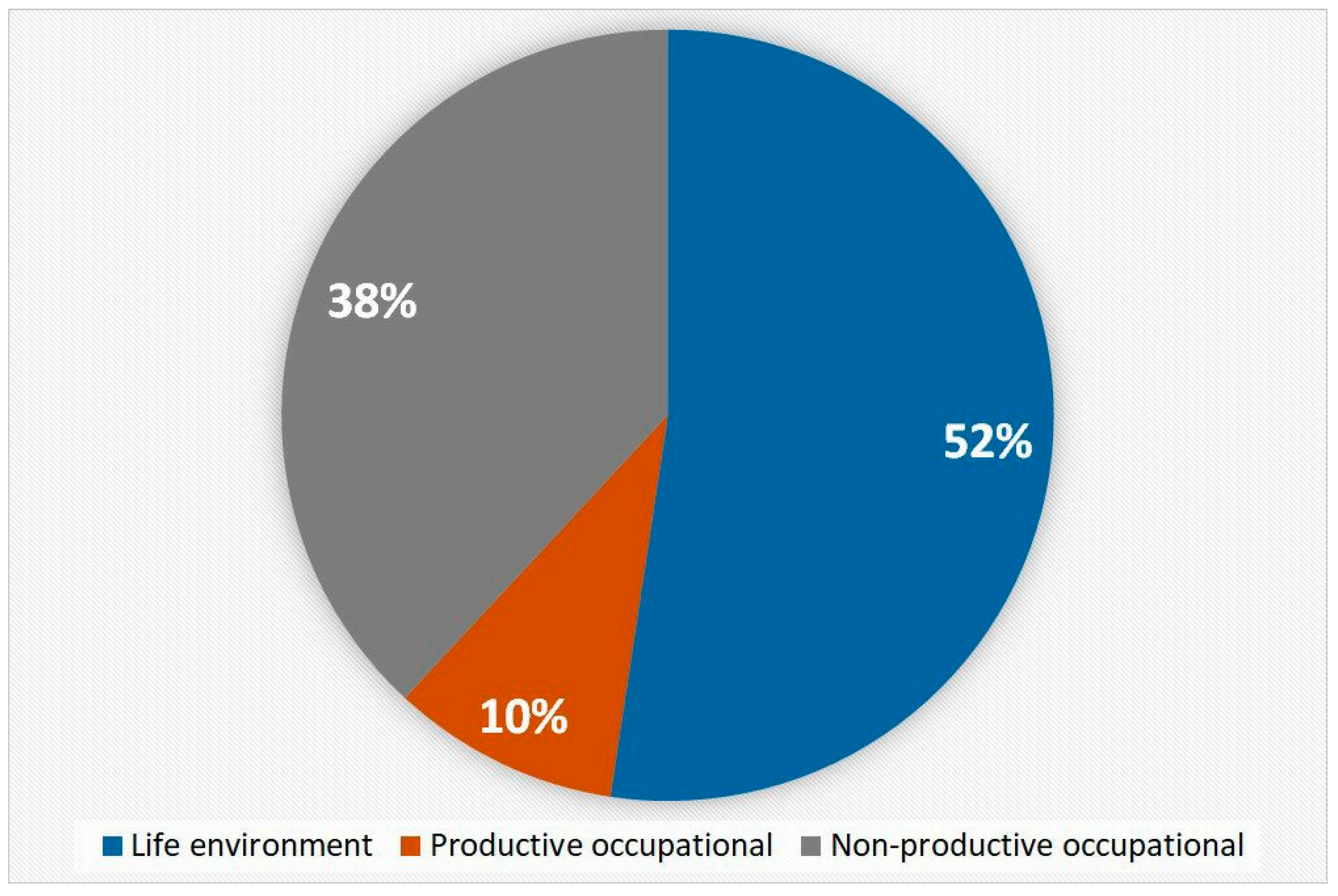
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bo, M.; Salizzoni, P.; Clerico, M.; Buccolieri, R. Assessment of Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution: A Review. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080136
Bo M, Salizzoni P, Clerico M, Buccolieri R. Assessment of Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution: A Review. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(8):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080136
Chicago/Turabian StyleBo, Matteo, Pietro Salizzoni, Marina Clerico, and Riccardo Buccolieri. 2017. "Assessment of Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution: A Review" Atmosphere 8, no. 8: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080136
APA StyleBo, M., Salizzoni, P., Clerico, M., & Buccolieri, R. (2017). Assessment of Indoor-Outdoor Particulate Matter Air Pollution: A Review. Atmosphere, 8(8), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8080136






