Estimation of Optical Properties for HULIS Aerosols at Anmyeon Island, Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
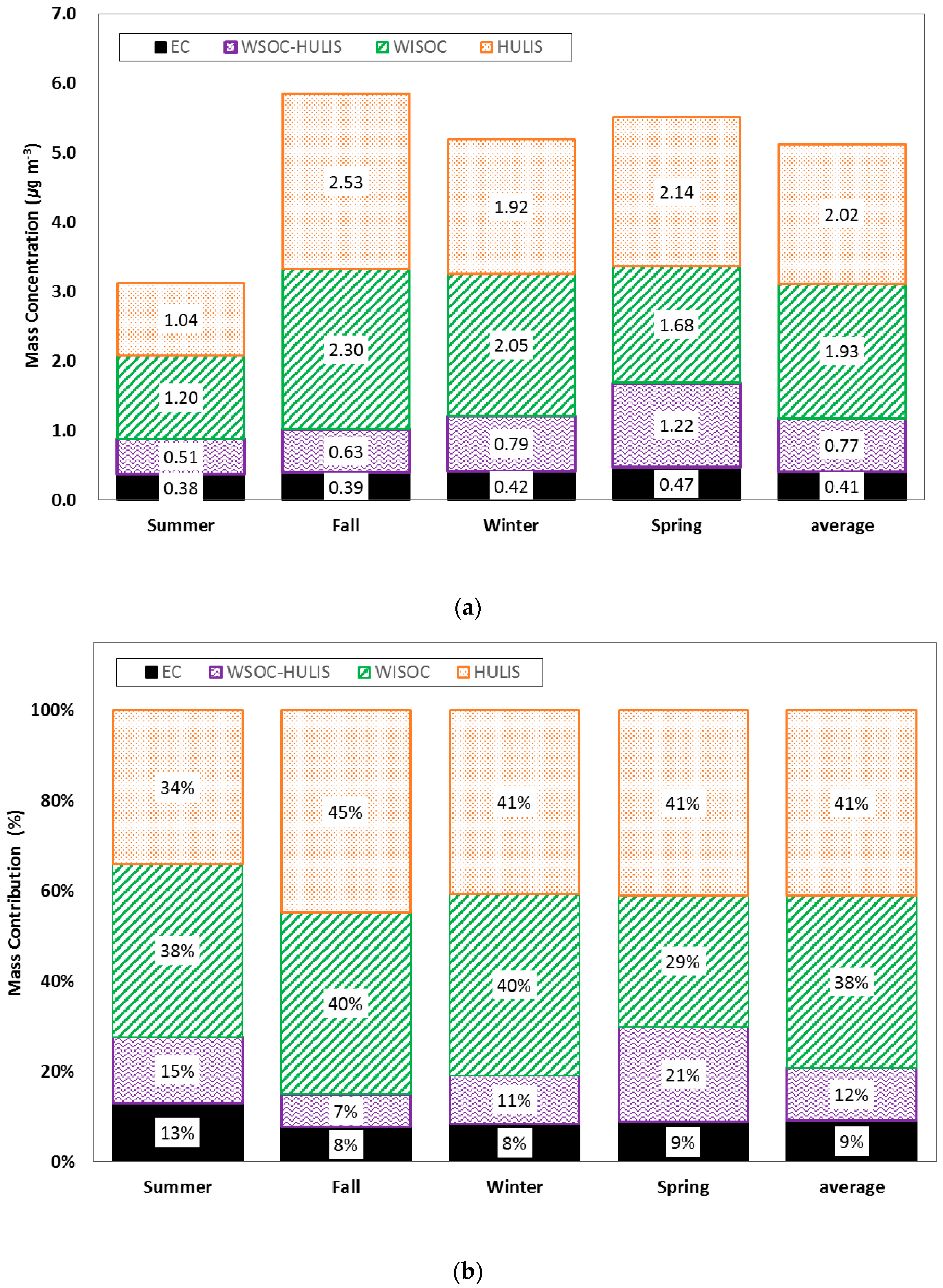
2. Measurement Data
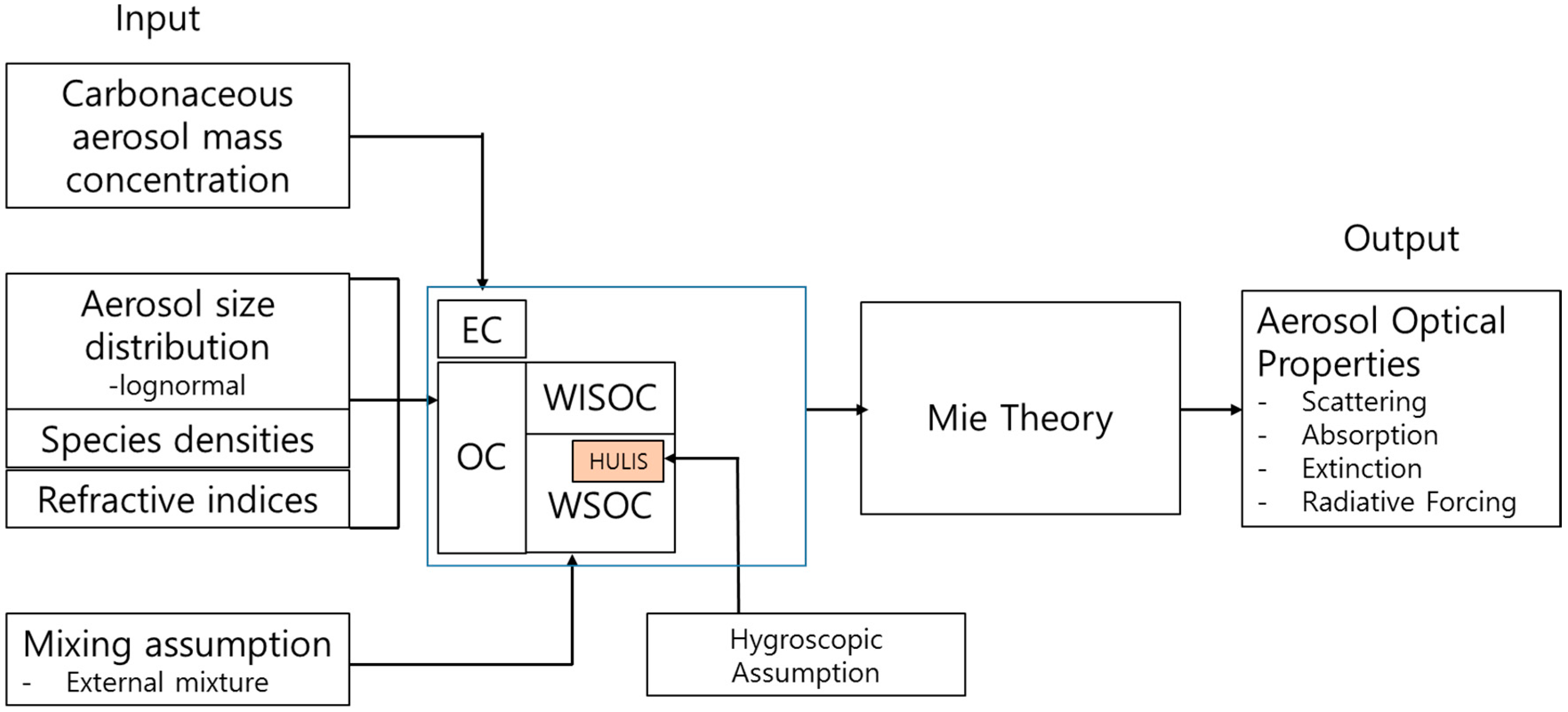
3. Model Description
3.1. Size Distributions
3.2. Hygroscopicity of HULIS
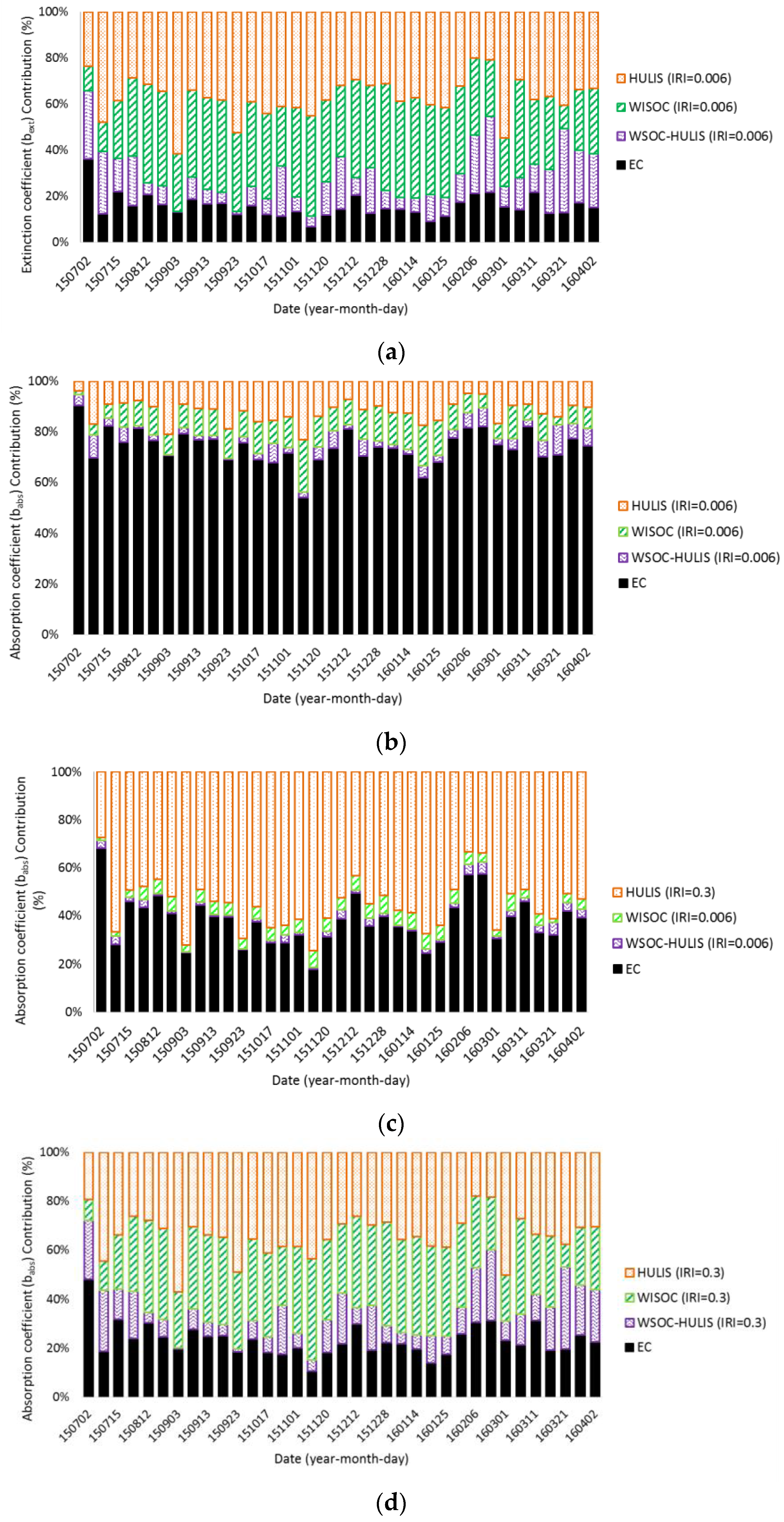
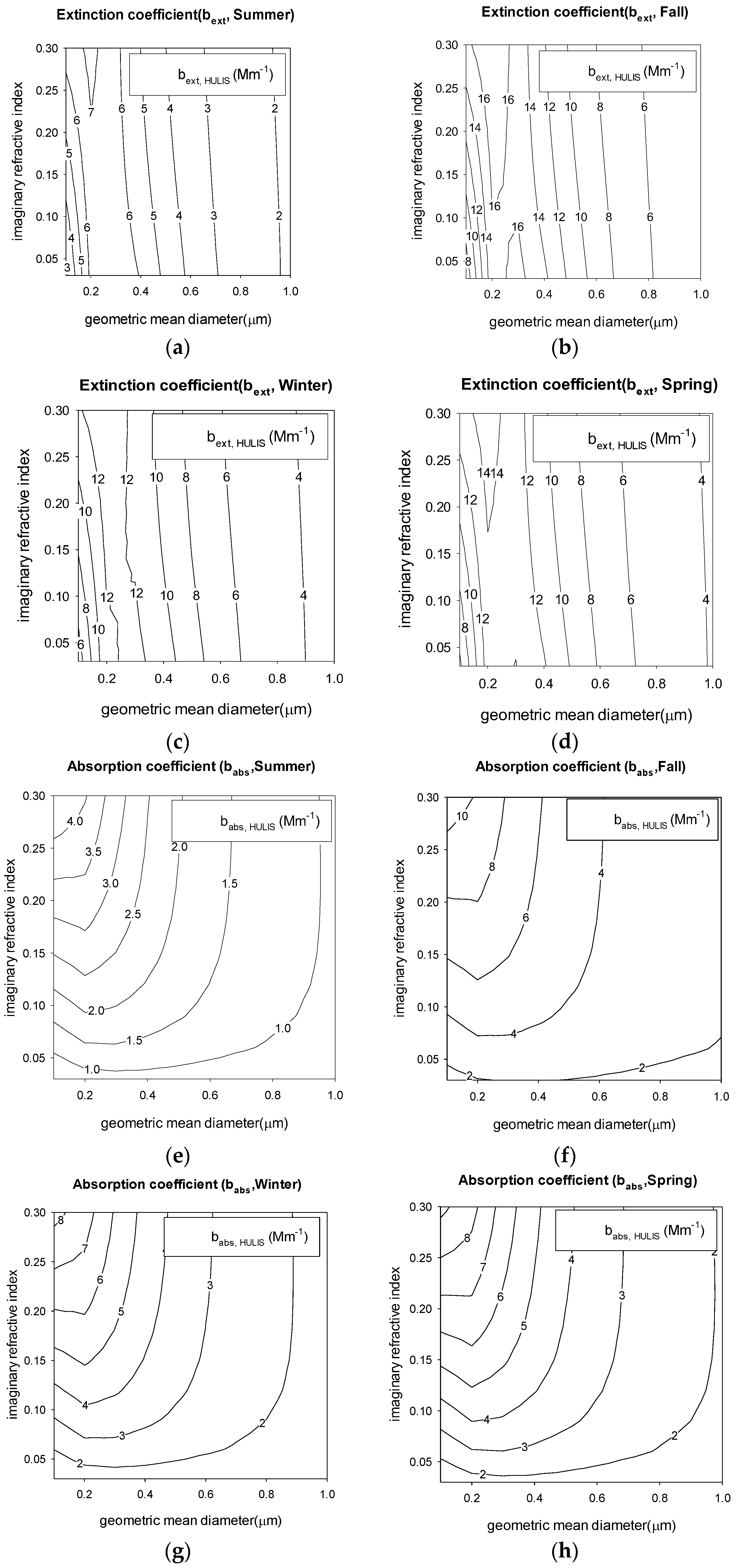
3.3. Light Absorption
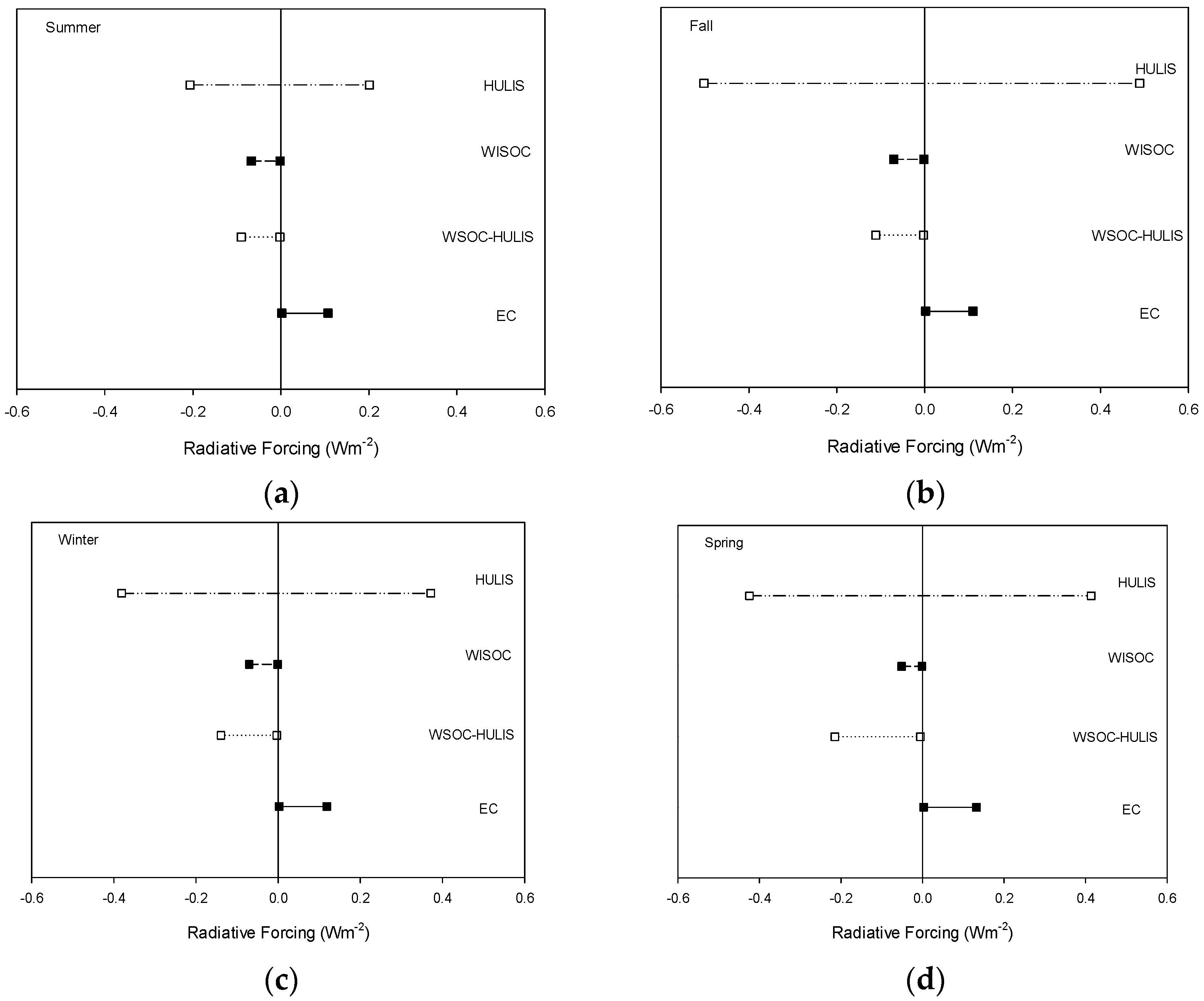
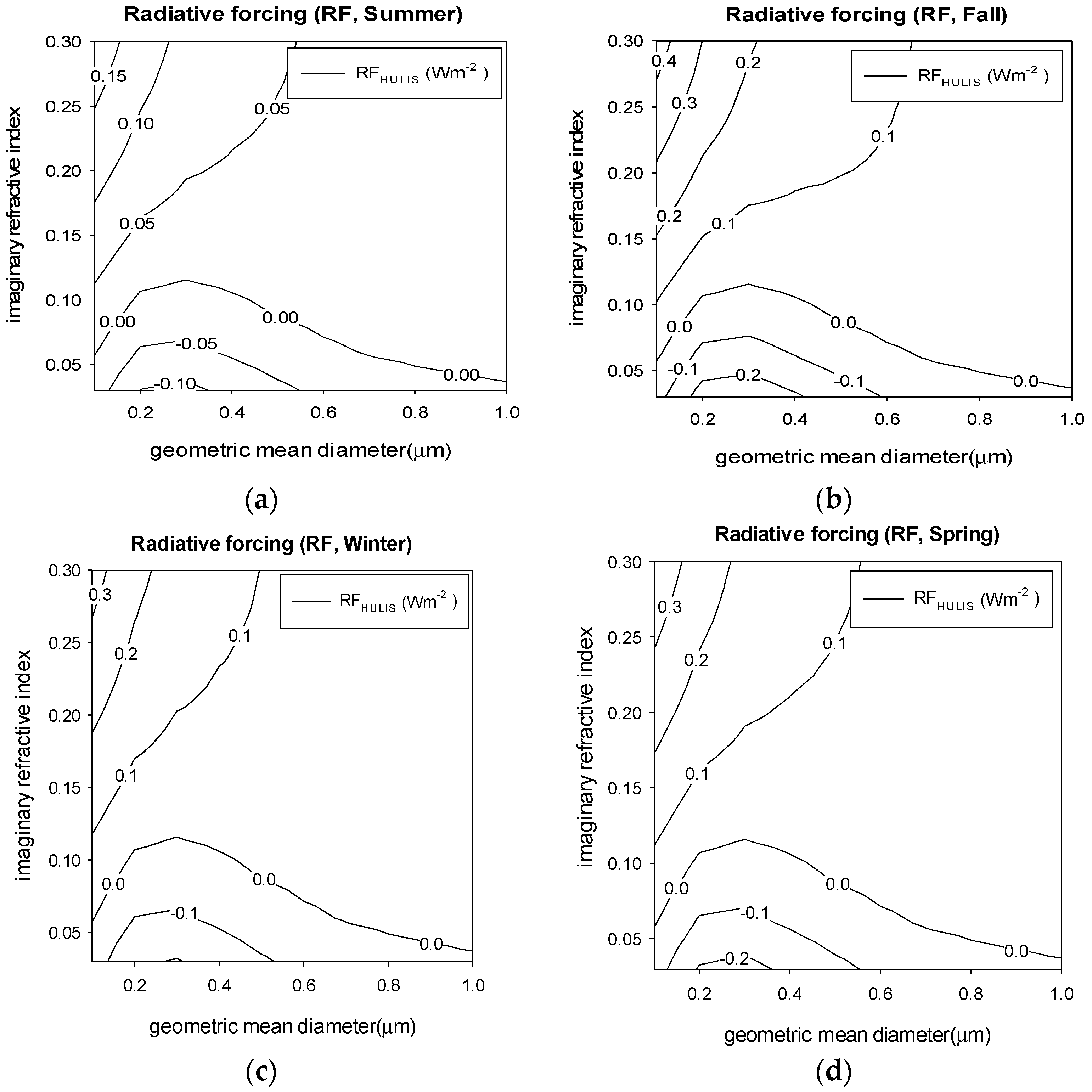
3.4. Aerosol Optical Properties and Radiative Forcing
- S0: solar constant, 1370 (W m−2);
- S0/4: the globally averaged incident solar flux at the top of the atmosphere;
- Tatm: transmittance of the atmosphere above the aerosol layer, 0.76;
- N: fraction of sky covered by clouds (0.6);
- α: albedo of the underlying surface, 0.15;
- β: fraction of the radiation scattered into the upper hemisphere by aerosols, 0.125; and
- : optical depth due to scattering and absorption of the ith component.
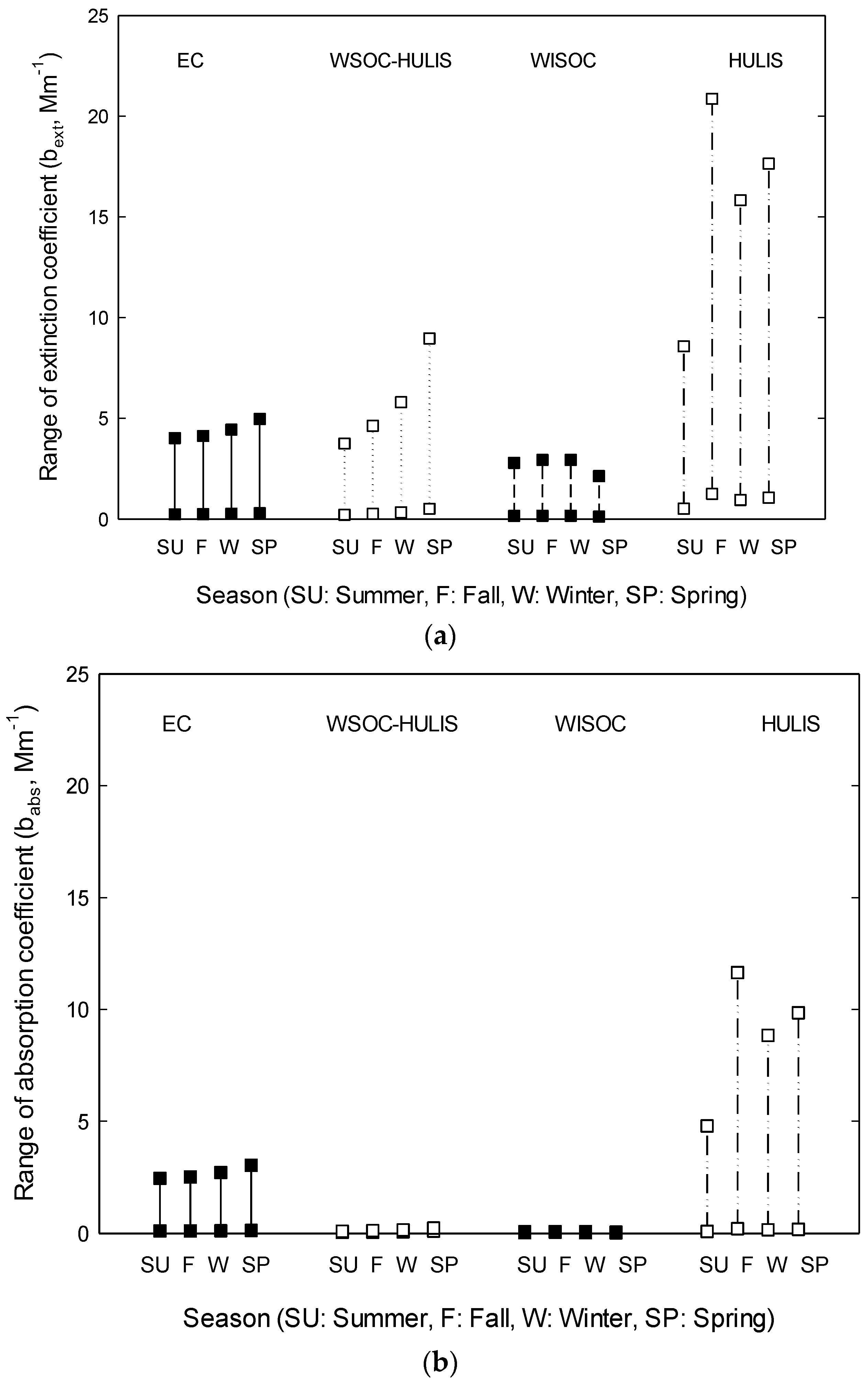
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Putaud, J.P.; Raes, F.; van Dingenen, R.; Brüggemann, E.; Facchini, M.C.; Decesari, S.; Fuzzi, S.; Gehrig, R.; Hüglin, C.; Laj, P.; et al. A European aerosol phenomenology—2: Chemical characteristics of particulate matter at kerbside, urban, rural and background sites in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2579–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N.; Barnes, I.; Dentener, F.J.; Facchini, M.C.; Van Dingenen, R.; Ervens, B.; Nenes, A.; Nielsen, C.J.; et al. Organic aerosol and global climate modeling: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1053–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M. Atmospheric science: Something in the air. Science 2005, 307, 1888–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, R.M.; Santos, E.B.; Pio, C.A.; Duarte, A.C. Comparison of structural features of water-soluble organic matter from atmospheric aerosols with those of aquatic humic substances. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8100–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Hildemann, L.M. Water-soluble organics in atmospheric particles: A critical review of the literature and application of thermodynamics to identify candidate compounds. J. Atmos. Chem. 1996, 24, 57–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, E.R.; Rudich, Y. Atmospheric HULIS: How humic like are they? A comprehensive and critical review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 729–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.; Patel, A.; Singh, A.; Singh, D. Diurnal variability in secondary organic aerosol formation over the Indo-Gangetic plain during winter using online measurement of water-soluble organic carbon. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2225–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermo, P.; Piazzalunga, A.; Tuccillo, F.; Brambilla, L.; Cazzuli, O.; Vecchi, R.; Valli, G. Analytical methods for quantification and characterization of HULIS (humic like substances) in atmospheric aerosol. In Proceedings of the European Aerosol Conference 2009, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–11 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Feczko, T.; Puxbaum, H.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Handler, M.; Limbeck, A.; Gelencser, A.; Pio, C.; Preunkert, S.; Legrand, M. Determination of water and alkaline extractable atmospheric humic-like substances with the TU Vienna HULIS analyzer in samples from six background sites in Europe. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D23S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchstetter, T.W.; Novakov, T.; Hobbs, P.V. Evidence that the spectral dependence of light absorption by aerosols is affected by organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D21208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, A.; Gelencser, A.; Guyon, P.; Kiss, G.; Schmid, O.; Frank, G.P.; Artaxo, P.; Andreae, M.O. Optical properties of Humic-Like Substances (HULIS) in biomass burning aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3563–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, A.; Laskin, J.; Nizkorodov, S.A. Chemistry of atmospheric brown carbon. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4335–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limbeck, A.; Kulmala, M.; Puxbaum, H. Secondary organic aerosol formation in the atmosphere via heterogeneous reaction of gaseous isoprene on acidic particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1996, 30, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Gelencser, A. Black carbon or brown carbon? The nature of light-absorbing carbonaceous aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3131–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, F.; Gilardoni, S.; Barnaba, F.; Ianni, A.D.; Liberto, L.D.; Dionisi, D.; Manigrasso, M.; Paglione, M.; Poluzzi, V.; Rinaldi, M.; et al. Characteristics of brown carbon in the urban Po Valley atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilardoni, S.; Massoli, P.; Paglione, M.; Giulianelli, L.; Carbone, C.; Rinaldi, M.; Decesari, S.; Sandrini, S.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; et al. Direct observation of aqueous secondary organic aerosol from biomass burning emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10013–10018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, M.M.; Chhabra, P.S.; Chan, A.W.H.; Surratt, J.D.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Keutsch, F.N. Glyoxal uptake on ammonium sulphate seed aerosol: Reaction products and reversibility of uptake under dark and irradiated conditions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 3331–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utry, N.; Ajtai, T.; Filep, T.; Pinter, M.; Hoffer, A.; Bozoki, Z.; Szabo, G. Mass specific optical absorption coefficient of HULIS aerosol measured by a four-wavelength photoacoustic spectrometer at NIR, VIS and UV wavelengths. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ikemori, F.; Higo, H.; Asakawa, D.; Mochida, M. Chemical structural characteristics of HULIS and other fractionated organic matter in urban aerosols: Results from mass spectral and FT-IR analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Xiang, P.; Zhou, X.; Duan, J.; Ma, Y.; He, K.; Cheng, Y.; Yu, J.; Querol, X. Chemical characterization of humic-like substances (HULIS) in PM2.5 in Lanzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Chapter 7: Clouds and Aerosols; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, E.; Mentel, T.F.; Rudich, Y. The density of humic acids and humic like substances (HULIS) from fresh and aged wood burning and pollution aerosol particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 5213–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziese, M.; Wex, H.; Nilsson, E.D.; Salma, I.; Ocskay, R.; Hennig, T.; Massling, A.; Stratmann, F. Hygroscopic growth and activation of HULIS particles: Experimental data and a new iterative parameterization scheme for complex aerosol particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1855–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Engling, G.; Yu, J.Z. Humic-like substances in fresh emissions of rice straw burning and in ambient aerosols in the Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6487–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, M.; Roger, J.C.; Despiau, S.; Putaud, J.P.; Dubovik, O. A study of the mixing state of black carbon in urban zone. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, D04202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Koepke, P.; Schult, I. Optical Properties of aerosols and clouds: The software package OPAC. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinne, S.; Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J.; Schulz, M.; Timmreck, C.; Ghan, S.; Easter, R.; Chin, M.; Ginoux, P.; Takemura, T.; et al. Monthly averages of aerosol properties: A global comparison among models, satellite data, and AERONET ground data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, D20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinar, E.; Taraniuk, I.; Graber, E.R.; Anttila, T.; Mentel, T.F.; Rudich, Y. Hygroscopic growth of atmospheric and model humic-like substances. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D05211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.T.L.; Crozier, P.A.; Anderson, J.R. Brown carbon spheres in East Asian outflow and their optical properties. Science 2008, 321, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.P. Estimation of aerosol optical properties considering hygroscopicity and light absorption. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruehl, C.R.; Chuang, P.Y.; Nenes, A. Aerosol hygroscopicity at high (99 to 100%) relative humidities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1329–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, J. How important is organic aerosol hygroscopicity to aerosol indirect forcing? Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 044010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, C.M.; Petters, M.D.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Collett, J.L., Jr.; Engling, G.; Malm, W.C. Aerosol hygroscopicity and cloud droplet activation of extracts of filters from biomass burning experiments. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D08206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gysel, M.; Weingartner, E.; Nyeki, S.; Paulsen, D.; Baltensperger, U.; Galambos, I.; Kiss, G. Hygroscopic properties of water-soluble matter and humic-like organics in atmospheric fine aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2004, 4, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fors, E.O.; Rissler, J.; Massling, A.; Svenningsson, B.; Andreae, M.O.; Dusek, U.; Frank, G.P.; Hoffer, A.; Bilde, M.; Kiss, G.; et al. Hygroscopic properties of Amazonian biomass burning and European background HULIS and investigation of their effects on surface tension with two models linking H-TDMA to CCNC data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 5625–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light absorption by carbonaceous particles: An investigative review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylek, P.; Wong, J. Effect of absorbing aerosol on global radiation budget. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, R.J.; Schwartz, S.E.; Hales, J.M.; Cess, R.D.; Coakley, J.A.; Hansen, J.E.; Hofmann, D.J. Climate forcing by anthropogenic aerosols. Science 1992, 255, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, J.M.; Shine, K.P. The effect of anthropogenic sulfate and soot aerosol on the clear sky planetary radiation budget. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1995, 22, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baduel, C.; Voisin, D.; Jaffrezo, J.-L. Seasonal variations of concentrations and optical properties of water soluble HULIS collected in urban environments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukács, H.; András Gelencsér, A.; Hammer, S.; Puxbaum, H.; Pio, C.; Legrand, M.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Handler, M.; Limbeck, A.; Simpson, D.; et al. Seasonal trends and possible sources of brown carbon based on 2-year aerosol measurements at six sites in Europe. J. Geophy. Res. 2007, 112, D23S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Huang, Z.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xiu, G.; Yu, J. Chemical characterization, the transport pathways and potential sources of PM2.5 in Shanghai: Seasonal variations. Atmos. Res. 2015, 158, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, C.G.; Puppala, S.P.; Panday, A.; Stumm, D.; Shea, J. Black carbon and the Himalayan cryosphere: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 125, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, B.; Ming, J. An overview of the studies on black carbon and mineral dust deposition in snow and ice cores in East Asia. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moise, T.; Flores, J.M.; Rudich, Y. Optical properties of secondary organic aerosols and their changes by chemical processes. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4400–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald, C.L.; Ridley, D.A.; Kroll, J.H.; Barrett, S.R.H.; Cady-Pereira, K.E.; Alvarado, M.J.; Holmes, C.D. Contrasting the direct radiative effect and direct radiative forcing of aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5513–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; Prather, K.A. In-situ measurements of the mixing state and optical properties of soot with implications for radiative forcing estimates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11872–11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.Y.; Lee, S.B.; Bae, G.N.; Park, S.S.; Han, K.M.; Park, R.S.; Song, C.H.; Park, S.H. Distribution and direct radiative forcing of black carbon aerosols over Korean Peninsula. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 58, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.P.; Kang, C.H. Long-term trend of aerosol composition and direct radiative forcing due to aerosols over Gosan: TSP, PM10, and PM2.5 data between 1992 and 2008. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6107–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Composition | Refractive Index (550 nm) | Density (g/cm3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real | Imaginary | ||
| Refractive Index | Refractive Index | ||
| EC | 1.9 | 0.66i | 1.7 |
| HULIS | 1.595 | 0.006i–0.3i | 1.4 |
| WSOC-HULIS | 1.53 | 0.006i * | 1.4 |
| WISOC | 1.53 | 0.006i * | 1.4 |
| Radiative Forcing (W m−2) | Min/Max | Summer | Fall | Winter | Spring | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | Min | 0.0022 | 0.0022 | 0.0024 | 0.0027 | 0.0023 |
| Max | 0.1071 | 0.1099 | 0.1184 | 0.1325 | 0.1156 | |
| WISOC | Min | −0.067 | −0.0705 | −0.0705 | −0.0511 | −0.0667 |
| Max | −0.0016 | −0.0017 | −0.0017 | −0.0012 | −0.0016 | |
| WSOC-HULIS | Min | −0.0899 | −0.1110 | −0.1393 | −0.2151 | −0.1358 |
| Max | −0.0022 | −0.0027 | −0.0034 | −0.0052 | −0.0033 | |
| HULIS | Min | −0.2065 | −0.5023 | −0.3811 | −0.4248 | −0.4010 |
| Max | 0.2011 | 0.4892 | 0.3713 | 0.4138 | 0.3906 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.Y.; Jung, C.H.; Kim, Y.P. Estimation of Optical Properties for HULIS Aerosols at Anmyeon Island, Korea. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8070120
Lee JY, Jung CH, Kim YP. Estimation of Optical Properties for HULIS Aerosols at Anmyeon Island, Korea. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(7):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8070120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Ji Yi, Chang Hoon Jung, and Yong Pyo Kim. 2017. "Estimation of Optical Properties for HULIS Aerosols at Anmyeon Island, Korea" Atmosphere 8, no. 7: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8070120
APA StyleLee, J. Y., Jung, C. H., & Kim, Y. P. (2017). Estimation of Optical Properties for HULIS Aerosols at Anmyeon Island, Korea. Atmosphere, 8(7), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8070120





