Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Industrial City—Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China: Size Distributions, Seasonal Variations, and Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Instruments and Experiments
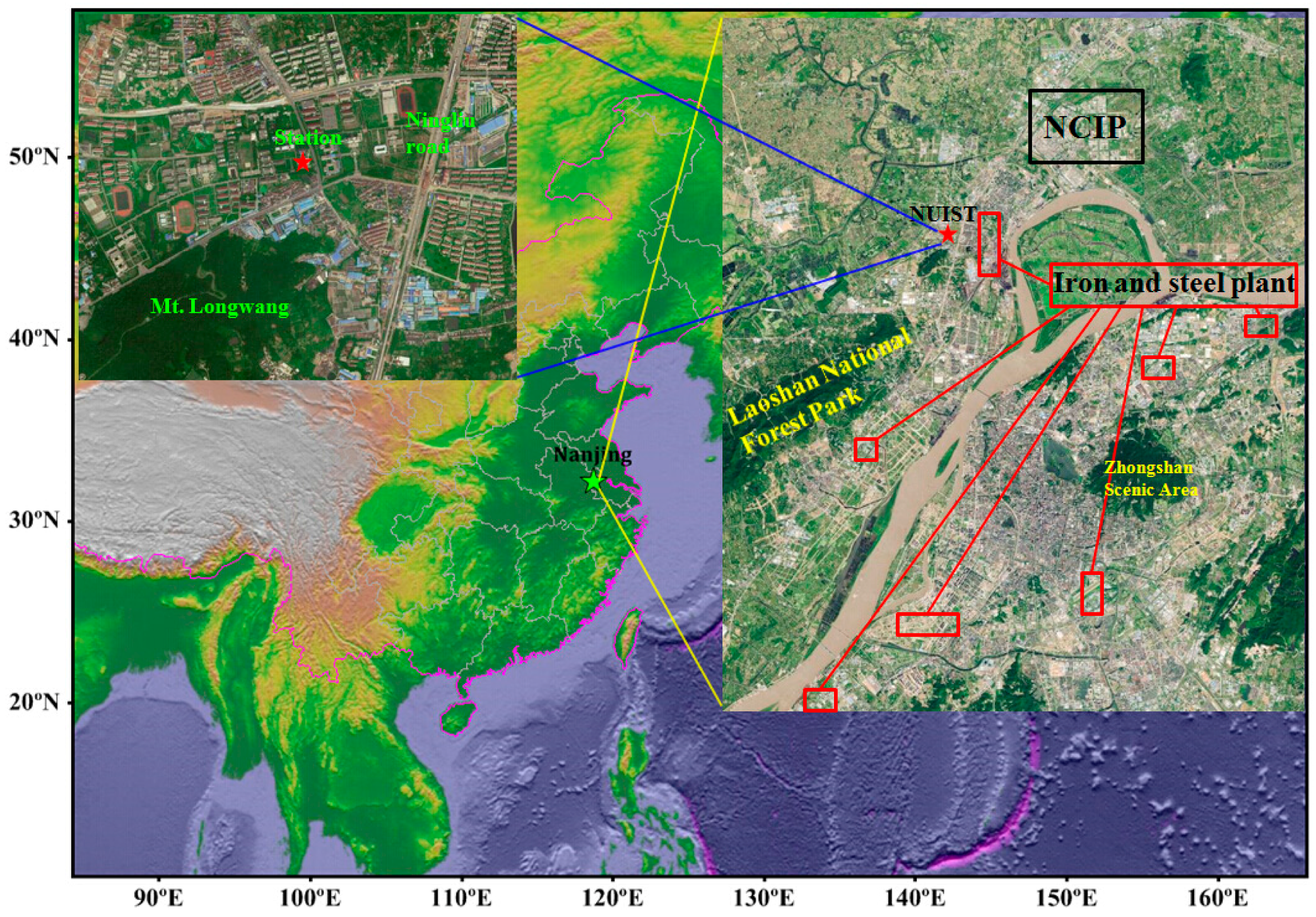
2.1. Observation Stations and Experiment Descriptions
2.2. Instrumentation
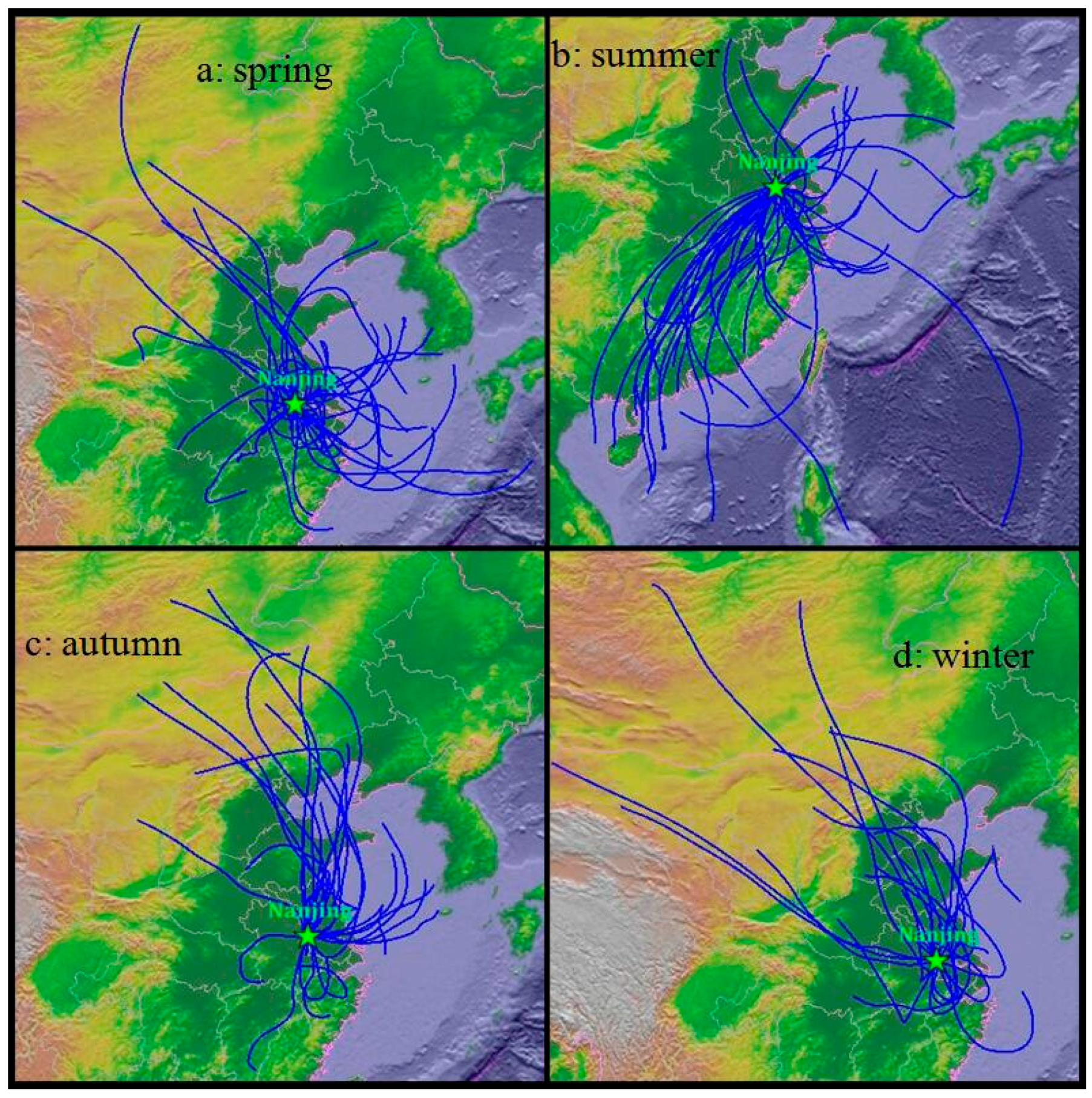
2.3. Air Mass Backward Trajectories
3. Results and Discussion
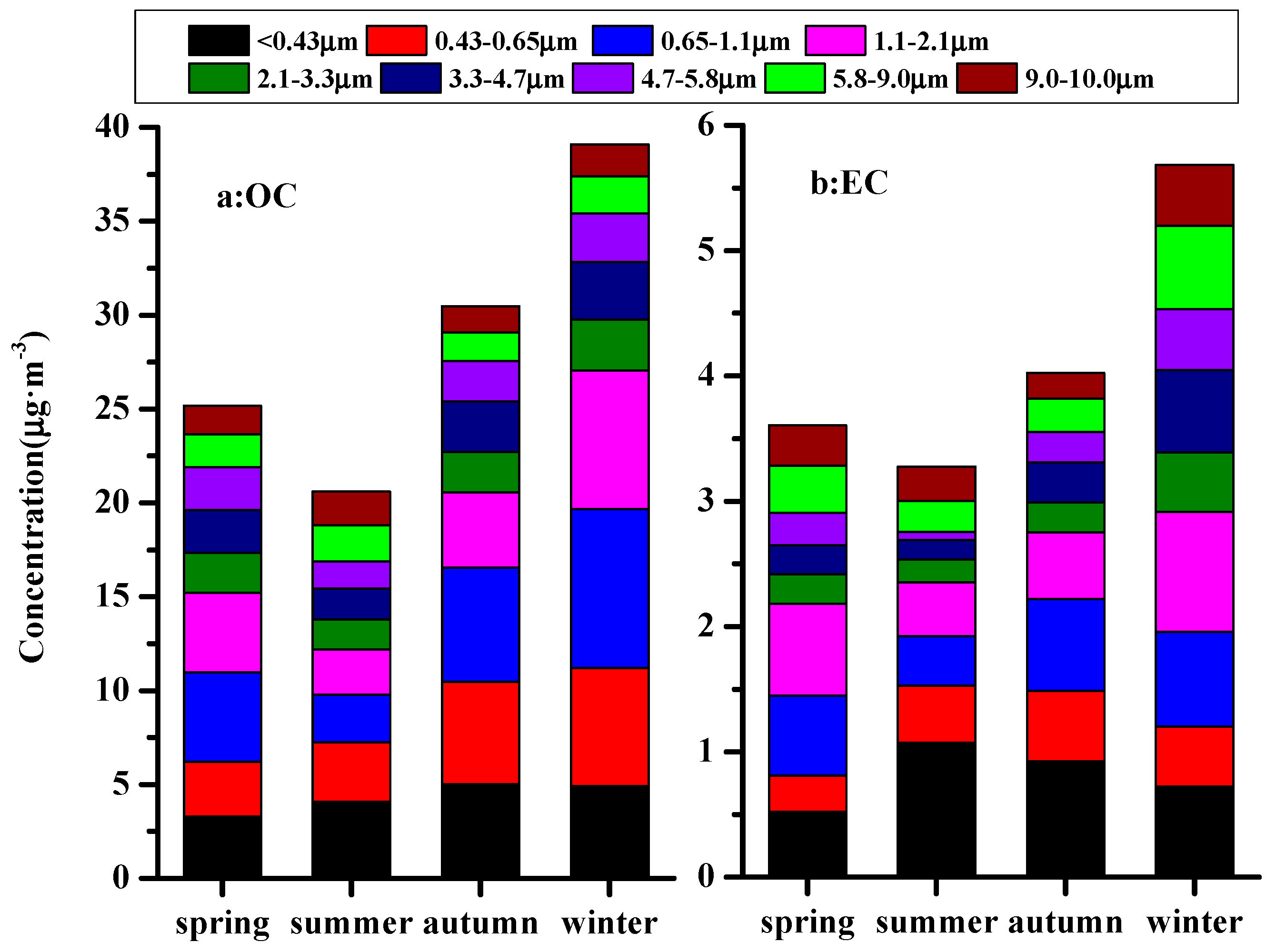
3.1. Seasonal Variations of the Carbonaceous Aerosol
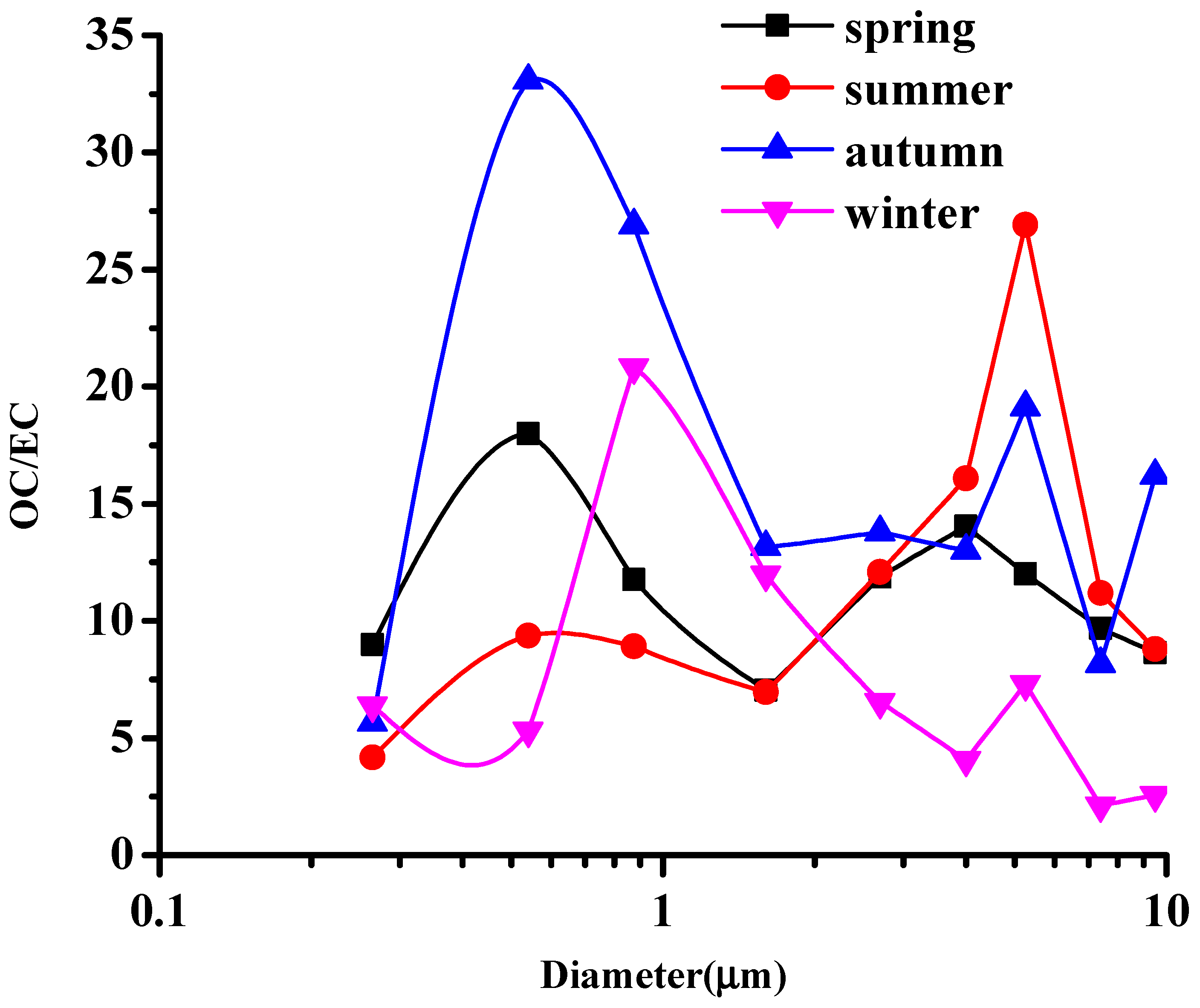
3.2. Size Distributions of OC and EC
3.3. The Characteristics of SOC and POC
3.4. Source Analysis of OC and EC
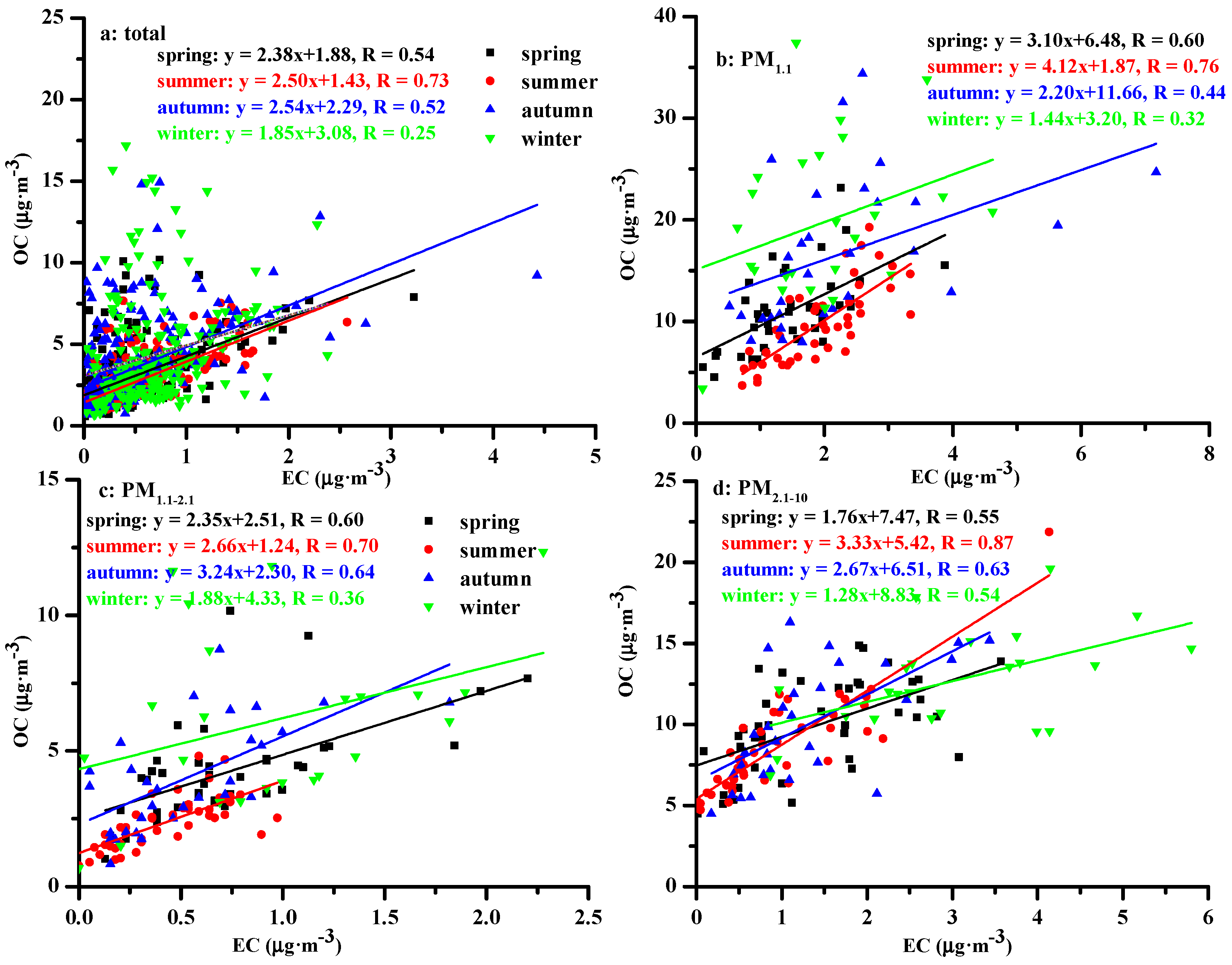
3.4.1. Relationships between OC and EC
3.4.2. Implications of the OC/EC Ratios
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.J.; Shen, Z.; Chow, J.C.; Qi, G.; Watson, J.G. Seasonal variations and sources of mass and chemical composition for PM 10 aerosol in Hangzhou, China. Particuology 2009, 7, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Wu, F.; Chow, J.C.; Lee, S.C.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.W.; An, Z.S.; Fung, K.K.; Watson, J.G.; Zhu, C.S.; et al. Characterization and source apportionment of atmospheric organic and elemental carbon during fall and winter of 2003 in Xi'an, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Ho, K.F.; Han, Y.M.; Shen, Z.X.; Zhan, C.L.; Zhang, J.Q. Light attenuation cross-section of black carbon in an urban atmosphere in northern China. Particuology 2015, 18, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. PM2.5 carbonate concentrations at regionally representative Interagency Monitoring of Protected Visual Environment sites. J. Geophys. Res. 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Doraiswamy, P.; Chen, L.W.A.; Sodeman, D.A.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Park, K.; Arnott, W.P.; Motallebi, N. Aerosol light absorption, black carbon, and elemental carbon at the Fresno Supersite, California. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrezo, J.L.; Aymoz, G.; Cozic, J. Size distribution of EC and OC in the aerosol of Alpine valleys during summer and winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 2915–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Identification of secondary organic aerosol episodes and quantization of primary and secondary organic aerosol concentrations during SCAQS. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3527–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Lim, H.J. Species contributions to PM2.5 mass concentrations: Revisiting common assumptions for estimating organic mass. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, K.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zou, S.C.; Fung, K.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in Pearl River Delta Region, China during 2001 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Cho, S.Y. Tracking sources and behaviors of water-soluble organic carbon in fine particulate matter measured at an urban site in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Li, Y.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Fung, K. Variability of Organic and Elemental Carbon, Water Soluble Organic Carbon, and Isotopes in Hong Kong. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 4569–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhi, G.; Feng, Y.; Fu, J.; Feng, J.; Sheng, G.; Simoneit, B.R. Measurement of Emission Factors for Primary Carbonaceous Particles from Residential Raw-Coal Combustion in China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Edgerton, S.A.; Vega, E. Chemical composition of PM2.5 and PM10 in Mexico City during winter 1997. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 287, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, F.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Jia, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Okuta, T. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosols in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandis, S.N.; Wexler, A.S.; Seinfeld, J.H. Secondary organic aerosol formation and transport-II. Predicting the ambient secondary organic aerosol size distribution. Atmos. Environ. 1993, 27, 2403–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Huntzicker, J.J. Secondary formation of organic aerosol in the Los Angeles Basin: a descriptive analysis of organic and elemental carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1991, 25, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, S.; Li, J.; Lang, J.; Wen, W.; Yang, X.; Tian, L. Source apportionment and seasonal variation of PM2.5 carbonaceous aerosol in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region of China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Kawamura, K.; Liu, B.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Fu, P. Carbonaceous aerosols on the south edge of the Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, seasonality and sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Q.; Shen, G.; Wu, H. Seasonal variation of urban carbonaceous aerosols in a typical city Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.; Martin, R.V.; Pierce, J.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Spracklen, D.V.; Nowlan, C.R.; Lamsal, L.N.; Cooper, M.J.; et al. Spatially and seasonally resolved estimate of the ratio of organic matter to organic carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, L. Pollution characteristics of organic and elemental carbon in PM2.5 in Xiamen, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.J.; Chen, D.L.; Li, X.; Huang, X.F.; He, L.Y.; Deng, Y.G.; Feng, N.; Hu, M. Modal characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol size distribution in an urban atmosphere of South China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.H.; Han, B.; Huo, J.; Lu, B.; Ding, X.; Chen, L.; Kong, S.; Bai, Z.; Wang, B. Characterization, meteorological influences and source identification of carbonaceous aerosols during the autumn-winter period in Tianjin, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, B.J.; Cary, R.A.; Huntzicker, J.J. An in situ, time-resolved analyzer for aerosol organic and elemental carbon. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1990, 12, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Kang, S.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Wen, T.; Zhang, G.; Cong, Z. Size distribution of carbonaceous aerosols at a high-altitude site on the central Tibetan Plateau (Nam Co Station, 4730ma.s.l.). Atmos. Res. 2015, 153, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Schmid, O.; Yang, H.; Chand, D.; Yu, J.Z.; Zeng, L.M.; Zhang, Y.H. Optical properties and chemical composition of the atmospheric aerosol in urban Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6335–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, G.H.; Shen, Z.X.; An, Z.S. Black carbon relationships with emissions and meteorology in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C. Measurement methods to determine compliance with ambient air quality standards for suspended particles. J. Air Waste Manag. 1995, 45, 320–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Han, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.W.A.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Emission characteristics of carbonaceous particles and trace gases from open burning of crop residues in China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreae, M.O.; Merlet, P. Emission of trace gases and aerosols from biomass burning. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 2001, 15, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.Y.; Hu, M.; Huang, X.F.; Yu, B.D.; Zhang, Y.H.; Liu, D.Q. Measurement of Emissions of Fine Particulate Organic Matter from Chinese Cooking. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6557–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R. Measurement of Emissions from Air Pollution Sources: 2. C1 through C30 Organic Compounds from Medium Duty Diesel Trucks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R. Measurement of Emissions from Air Pollution Sources: 5.C1-C32 organic Compounds from Gasoline-Powered Motor Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; He, L.; Zhu, B.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, X. Source profiles of particulate organic matters emitted from cereal straw burnings. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.C.; Tan, J.H.; Cheng, D.X.; Bi, X.H.; Deng, W.J.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M.; Wong, M.H. Sources and characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in two largest cities in Pearl River Delta Region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2895–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhou, B.; Cheng, C.; Cao, J.; Li, J.; Meng, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, R.; Fu, P. Impact of Gobi desert dust on aerosol chemistry of Xi'an, inland China during spring 2009: differences in composition and size distribution between the urban ground surface and the mountain atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; An, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, B.; Pan, C.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Duan, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Mechanism for the formation and microphysical characteristics of submicron aerosol during heavy haze pollution episode in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.F.; Xue, L.; Tian, X.D.; Shao, W.W.; Sun, T.L.; Gong, Z.H.; Ju, W.W.; Jiang, B.; Hu, M.; He, L.Y. Highly time-resolved carbonaceous aerosol characterization in Yangtze River Delta of China: Composition, mixing state and secondary formation. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 64, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Chen, Y.J.; Guo, H.; Zhi, G.R.; Xiong, S.C.; Li, J.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. Characteristics of organic and elemental carbon in PM2.5 samples in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Res. 2009, 92, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Xing, J.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Hao, J. Emission inventory of primary pollutants and chemical speciation in 2010 for the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, R.; Liu, T.; Guo, Z.; Chen, Y. The implication of carbonaceous aerosol to the formation of haze: Revealed from the characteristics and sources of OC/EC over a mega-city in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Crow, D.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Merrifield, T. Comparison of IMPROVE and NIOSH carbon measurements. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 34, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Cao, J.J.; An, Z.S.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Jin, Z.; Fung, K.; Liu, S. Evaluation of the thermal/optical reflectance method for quantification of elemental carbon in sediments. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L. Particulate and trace gas emissions from open burning of wheat straw and corn stover in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6052–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pósfai, M.; Simonics, R.; Li, J.; Hobbs, P.V.; Buseck, P.R. Individual aerosol particles from biomass burning in southern Africa: 1. Compositions and size distributions of carbonaceous particles. J. Geophys. Res. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, B.; Shen, L.; Kang, H. Size distributions of aerosol and water-soluble ions in Nanjing during a crop residual burning event. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, A.H.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Jaques, P.A.; Jaques, P.A.; Froines, J.R.; Grant, B.L.; Mayo, P.R.; Sioutas, C. Seasonal variation of the particle size distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and of major aerosol species in Claremont, California. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Carmichael, G.R.; Arimoto, R.; Conant, W.C. ACE-ASIA-Regional climatic and atmospheric chemical effects of Asian dust and pollution. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2004, 85, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupiainen, K.; Klimont, Z. Primary emissions of fine carbonaceous particles in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentner, D.R.; Isaacman, G.; Worton, D.R.; Chan, A.W.H.; Dallmann, T.R.; Davis, L.; Liu, S.; Day, D.A.; Russell, L.M.; Wilson, K.R.; et al. Elucidating secondary organic aerosol from diesel and gasoline vehicles through detailed characterization of organic carbon emissions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18318–18323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Tsang, P.K.; Ho, S.; Zou, C.W.; Zou, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Xu, H.M. Characteristics of carbonaceous aerosol in PM2.5: Pearl Delta River region, China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 104, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Rogge, W.F.; Hildemann, L.M.; Mazurek, M.A.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R. Source apportionment of airborne particulate matter using organic compounds as tracers. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3837–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachier, H.; Liousse, C.; Pertuisot, M.H.; Gaudichet, A.; Echalar, F.; Lacaux, J.P. African fire particulate emissions and atmospheric influence. Biomass Burning Global Change 1996, 1, 428–440. [Google Scholar]
- Ram, K.; Sarin, M.M. Spatio-temporal variability in atmospheric abundances of EC, OC and WSOC over Northern India. J. Aerosol Sci. 2010, 41, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Lu, Z.; Fujita, E.M.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Lawson, D.R.; Ashbaugh, L.L. Chemical mass balance source apportionment of PM10 during the Southern California Air Quality Study. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1994, 21, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]

| Season | Observation Period | Temperature (°C) | RH (%) | Wind Speed (m·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 2014.4.17–5.22 | 19.2±4.3 | 61.5 ± 22.1 | 2.2 ± 1.2 |
| Summer | 2013.6.1–7.17 | 26.4 ± 4.5 | 67.3 ± 16.2 | 2.5 ± 1.1 |
| Autumn | 2013.10.15–11.13 | 15.0 ± 3.7 | 63.4 ± 18.1 | 1.8 ± 1.1 |
| Winter | 2013.12.30–2014.1.23 | 5.0 ± 3.7 | 53.2 ± 21.8 | 1.9 ± 1.0 |
| Size | Component | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM1.1 | OC (μg·m−3) | 11.0 ± 3.9 | 9.8 ± 3.9 | 16.6 ± 7.2 | 19.7 ± 7.7 |
| EC (μg·m−3) | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | 2.2 ± 1.4 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | |
| SOC (μg·m−3) | 6.3 ± 3.1 | 5.3 ± 2.8 | 11.2 ± 6.3 | 12.6 ± 7.4 | |
| POC (μg·m−3) | 4.1 ± 2.0 | 4.4 ± 1.8 | 4.9 ± 2.4 | 6.4 ± 3.5 | |
| PM1.1–2.1 | OC (μg·m−3) | 4.2 ± 1.9 | 2.4 ± 1.0 | 4.0 ± 2.0 | 7.4 ± 5.4 |
| EC (μg·m−3) | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.4 | 1.0 ± 0.6 | |
| SOC (μg·m−3) | 1.4 ± 1.5 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 1.5 | 4.2 ± 5.2 | |
| POC (μg·m−3) | 2.0 ± 1.4 | 0.9 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 3.0 ± 2.0 | |
| PM2.1–10 | OC (μg·m−3) | 10.0 ± 2.9 | 8.4 ± 3.1 | 9.9 ± 3.5 | 12.1 ± 3.7 |
| EC (μg·m−3) | 1.4 ± 0.9 | 0.9 ± 0.8 | 1.3 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 1.5 | |
| SOC (μg·m−3) | 6.2 ± 2.4 | 5.2 ± 1.5 | 6.4 ± 2.5 | 6.8 ± 2.6 | |
| POC (μg·m−3) | 3.5 ± 2.2 | 3.0 ± 2.7 | 3.2 ± 1.9 | 4.7 ± 2.4 |
| Diameter (μm) | 0–0.43 | 0.43–0.65 | 0.65–1.1 | 1.1–2.1 | 2.1–3.3 | 3.3–4.7 | 4.7–5.8 | 5.8–9.0 | 9.0–10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | 2.83 | 4.53 | 3.03 | 4.00 | 4.29 | 3.09 | 3.73 | 1.35 | 1.99 |
| Summer | 2.35 | 2.12 | 2.65 | 2.14 | 3.73 | 2.88 | 4.70 | 4.14 | 2.88 |
| Autumn | 2.81 | 2.20 | 2.08 | 3.73 | 4.72 | 3.39 | 0.97 | 2.67 | 1.82 |
| Winter | 3.70 | 3.32 | 3.69 | 3.35 | 3.23 | 1.70 | 1.89 | 1.25 | 1.69 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; An, J.; Zhu, B.; Shen, L.; Duan, Q.; Shi, Y. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Industrial City—Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China: Size Distributions, Seasonal Variations, and Sources. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8040073
Wang H, An J, Zhu B, Shen L, Duan Q, Shi Y. Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Industrial City—Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China: Size Distributions, Seasonal Variations, and Sources. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(4):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8040073
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Honglei, Junlin An, Bin Zhu, Lijuan Shen, Qing Duan, and Yuanzhe Shi. 2017. "Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Industrial City—Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China: Size Distributions, Seasonal Variations, and Sources" Atmosphere 8, no. 4: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8040073
APA StyleWang, H., An, J., Zhu, B., Shen, L., Duan, Q., & Shi, Y. (2017). Characteristics of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a Typical Industrial City—Nanjing in Yangtze River Delta, China: Size Distributions, Seasonal Variations, and Sources. Atmosphere, 8(4), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8040073






