Characterization and Seasonal Variations of Organic and Elemental Carbon and Levoglucosan in PM10 in Krynica Zdroj, Poland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Sampling Point
2.2. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
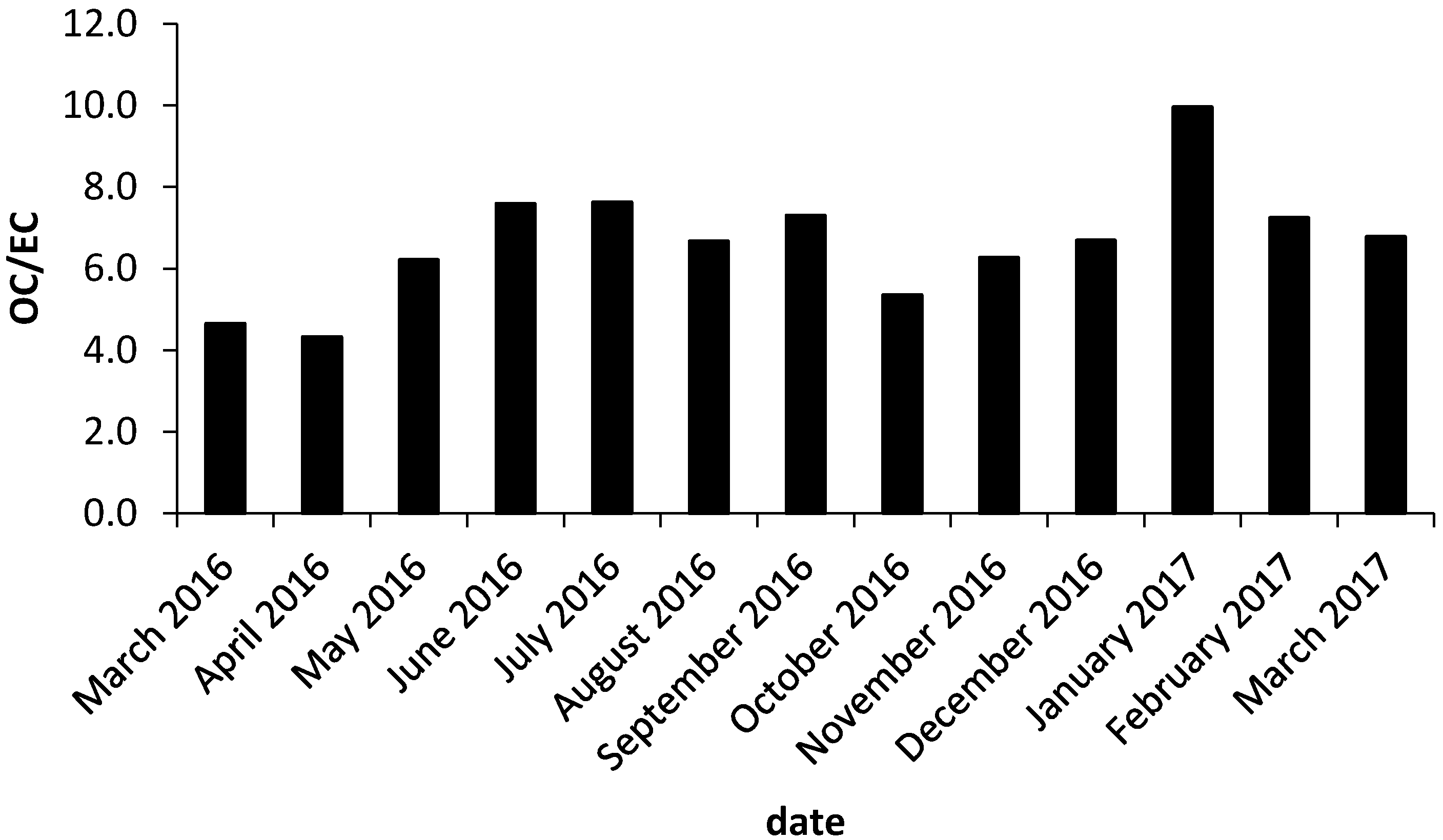
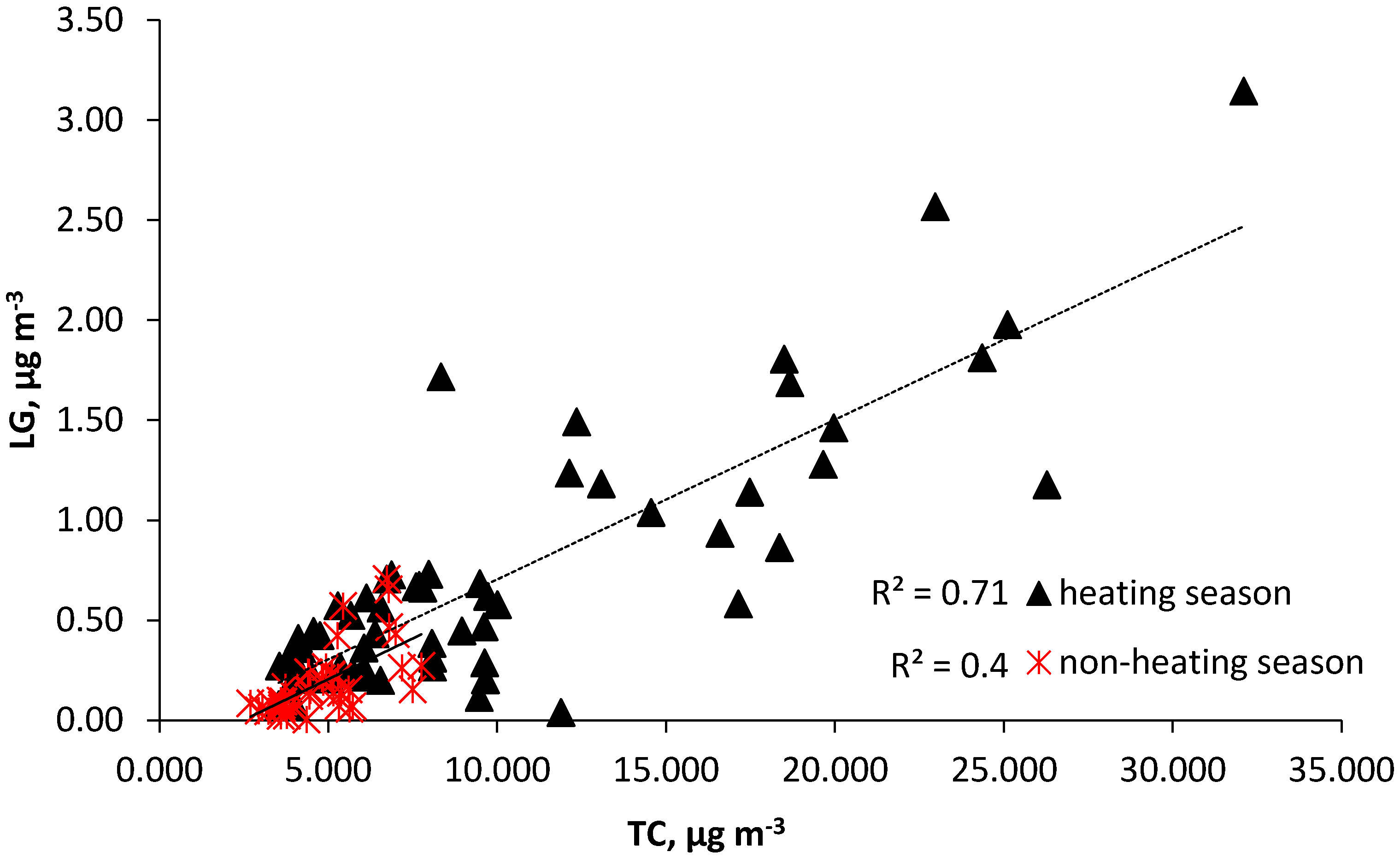
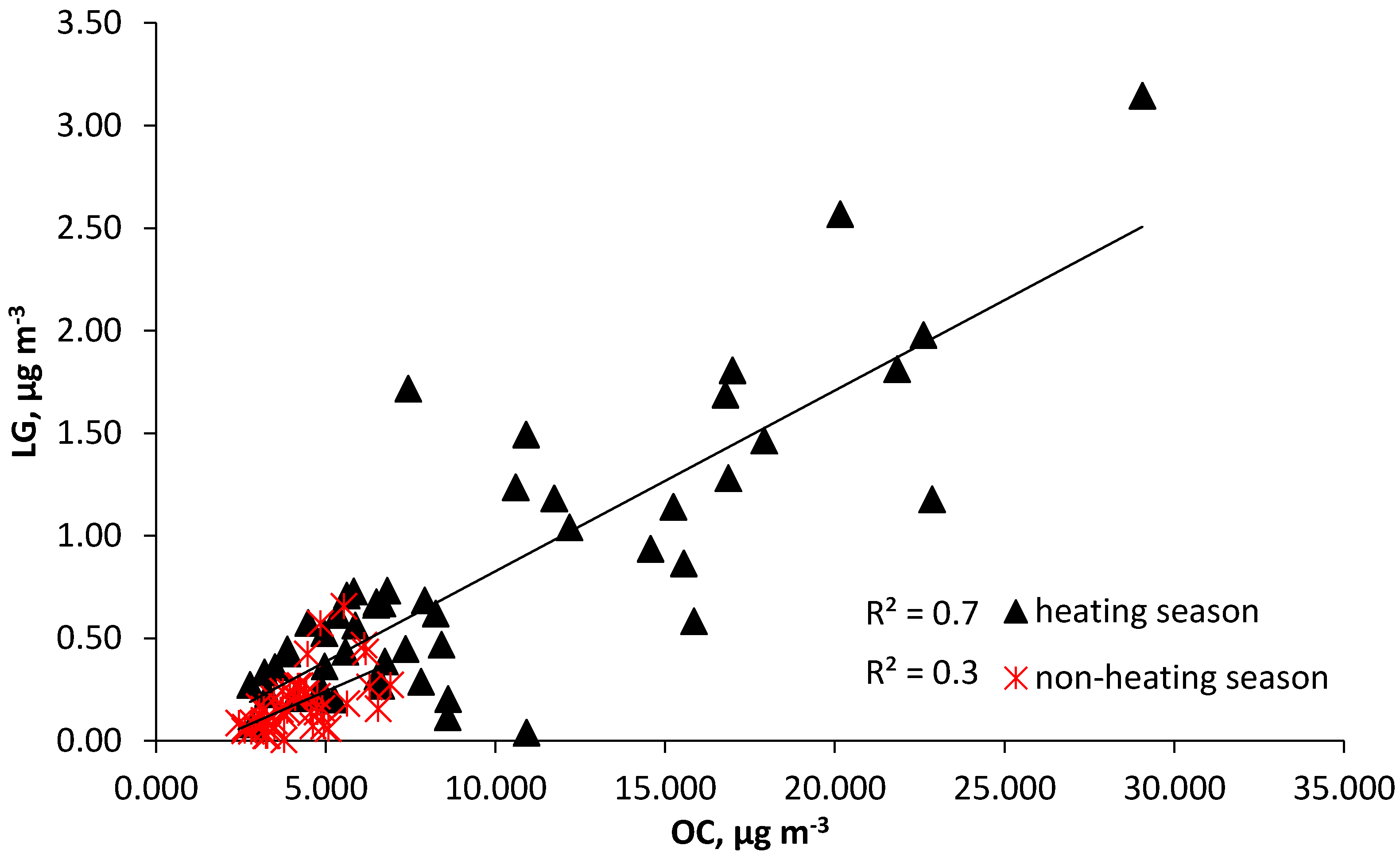
Correlation between Total Carbon (TC), Elemental Carbon (EC), and Organic Carbon (OC)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calvo, A.I.; Alves, C.; Castro, A.; Pont, V.; Vicente, A.M.; Fraile, R. Research on aerosol sources and chemical composition: Past, current and emerging issues. Atmos. Res. 2013, 120, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, M.; Kawamura, K.; Fu, P.; Takemura, T. Seasonal variation of levoglucosan in aerosols over the western North Pacific and its assessment as a biomass-burning tracer. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 3511–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pio, C.; Cerqueira, M.; Harrison, R.M.; Nunes, T.; Mirante, F.; Alves, C.; Oliveira, C.; Sanchez de la Campa, A.; Artíñano, B.; Matos, M. OC/EC ratio observations in Europe: Re-thinking the approach for apportionment between primary and secondary organic carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6121–6132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.D.; Allan, D.E.; Young, H.; Coe, D.; Beddows, Z.L.; Fleming, M.J.; Flynn, M.W.; Gallagher, R.M.; Harrison, J.; Lee, A.S.H.; et al. Size distribution, mixing state and source apportionment of black carbon aerosol in London during wintertime. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10061–10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.M.; Sciare, J.; Poulain, L.; Kamili, K.; Merkel, M.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Sarda-Estève, R.; et al. Sources and mixing state of size-resolved elemental carbon particles in a European megacity: Paris. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 1681–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 1326. [Google Scholar]
- Berent-Kowalska, G.; Dąbrowska-Ładno, J.; Dziedzina, K.; Gontarczuk, W.; Peryt, S.; Roman, W.; Ciszewska, A.; Kossak, E.; Gilecki, R.; Kacprowska, J.; et al. Energy Consumption in Households; Central Statistical Office: Warsaw, Poland, 2015.
- Allan, D.; Williams, P.I.; Morgan, W.T.; Martin, C.L.; Flynn, M.J.; Lee, J.; Nemitz, E.; Phillips, G.J.; Gallagher, M.W.; Coe, H. Contributions from transport, solid fuel burning and cooking to primary organic aerosols in two UK cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 647–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, C.R.M.; Hellebust, S.; Kourtchev, I.; Allanic, A.; O’Connor, I.P.; Bell, J.M.; Healy, D.A.; Sodeau, J.R.; Wenger, J.C. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in Cork Harbour, Ireland using a combination of single particle mass spectrometry and quantitative semi-continuous measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 9593–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of emissions from air pollution sources. 3. C1–C29 organic compounds from fireplace combustion of wood. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 1716–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.M.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Hu, L.; Yin, J. Comparison of methods for evaluation of wood smoke and estimation of UK ambient concentrations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 8271–8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, T. Size-resolved organic speciation of wintertime aerosols in California’s Central Valley. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandradewi, J.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Szidat, S.; Perron, N.; Alfarra, M.R.; Lanz, V.A.; Weingartner, E.; Baltensperger, U. Using Aerosol Light Absorption Measurements for the Quantitative Determination of Wood Burning and Traffic Emission Contributions to Particulate Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 3316–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Cao, J.J.; Chow, J.C.; Shen, Z.-X.; Ho, K.-F.; Sai, S.; Ho, H. Characterization and seasonal variations of levoglucosan in fine particulate matter in Xi’an, China. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche, C.; Viana, M.; Amato, F.; Alastuey, A.; Moreno, T.; Hillamo, R.; Teinilä, K.; Saarnio, K.; Seco, R.; Peñuelas, J.; et al. Biomass burning contributions to urban aerosols in a coastal Mediterranean City. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holnicki, P.; Kałuszko, A.; Nahorski, Z.; Stankiewicz, K.; Trapp, W. Air quality modeling for Warsaw agglomeration. Arch. Environ. Protect. 2017, 43, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J. Sources and processes affecting carbonaceous aerosol in central England. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, V.A.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Alfarra, M.R.; Weimer, S.; Mohr, C.; DeCarlo, P.F.; Gianini, M.F.D.; Hueglin, C.; Schneider, J.; Favez, O.; et al. Characterization of aerosol chemical composition with aerosol mass spectrometry in Central Europe: An overview. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10453–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauraitė, J.; Mordas, G.; Byčenkienė, S.; Ulevicius, V. Spatial and temporal analysis of organic and black carbon mass concentrations in Lithuania. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarnio, K.; Aurela, M.; Timonen, H.; Saarikoski, S.; Teinilä, K.; Mäkelä, T.; Sofiev, M.; Koskinen, J.; Aalto, P.P.; Kulmala, M.; et al. Chemical composition of fine particles in fresh smoke plumes from boreal wild-land fires in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 405, 2527–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Air Quality Guidelines: Global Update 2005: Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide; World Health Organization: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalli, F.; Viana, M.; Yttri, K.E.; Genberg, J.; Putaud, J.-P. Toward a standardized thermal-optical protocol for measuring atmospheric organic and elemental carbon: The EUSAAR Protocol. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, D.; Del Genio, A.D. Black carbon semi-direct effects on cloud cover: Review and synthesis. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 7685–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, M.; Crippa, M.; Tritscher, T.; Jurányi, Z.; Decarlo, P.F.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Marchand, N.; Eckhardt, S.; Stohl, A.; Baltensperger, U.; et al. Black carbon physical properties and mixing state in the European megacity Paris. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5831–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yttri1, K.E.; Aas, W.; Bjerke, A.; Cape, J.N.; Cavalli, F.; Ceburnis, D.; Dye, C.; Emblico, L.M.; Facchini, C.; Forster, C.; et al. Elemental and organic carbon in PM10: A one year measurement campaign within the European Monitoring and Evaluation Programme EMEP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5711–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Warnke, J. Organic Aerosols. In Volatile Organic Compounds in the Atmosphere; Koppmann, R., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 342–387. [Google Scholar]
- Gelencsér, A.; May, B.; Simpson, D.; Sánchez-Ochoa, A.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Puxbaum, H.; Caseiro, A.; Pio, C.; Legrand, M. Source apportionment of PM2.5 organic aerosol over Europe: Primary/secondary, natural/anthropogenic, fossil/biogenic origin. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Houck, J.E. PM2.5 chemical source profiles for vehicle exhaust, vegetative burning, geological material, and coal burning in northwestern Colorado during 1995. Chemosphere 2001, 43, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeman, M.J.; Schauer, J.J.; Cass, G.R. Size and composition distribution of fine particulate matter emitted from motor vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funasaka, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Tsuruho, K.; Tamura, K.; Mizuno, T.; Kuroda, K. Relationship between indoor and outdoor carbonaceous particulates in roadside households. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 110, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szidat, S.; Jenk, T.M.; Synal, H.; Kalberer, M.; Wacker, L.; Hajdas, I.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Baltensperger, U. Contributions of fossil fuel, biomass burning, and biogenic emissions to carbonaceous aerosols in Zürich as traced by 14C. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.; Kang, S.; Kawamura, K.; Liu, B.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, S.; Fu, P. Carbonaceous aerosols on the south edge of the Tibetan Plateau: Concentrations, seasonality and sources. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.; Martin, R.V.; Pierce, J.R.; Jimenez, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Canagaratna, M.R.; Spracklen, D.V.; Nowlan, C.R.; Lamsal, L.N.; Cooper, M.J.; et al. Spatially and seasonally resolved estimate of the ratio of organic matter to organic carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Han, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, L.W.A.; Tian, J.; Wang, X.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; et al. Emission characteristics of carbonaceous particles and trace gases from open burning of crop residues in China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Harrison, R.M.; Smith, D.J.T. Carbonaceous aerosol in urban and rural European atmospheres: Estimation of secondary organic carbon concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2771–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianoni, M.; Martellini, T.; Del Bubba, M.; Gambaro, A.; Zangrando, R.; Chiari, M.; Lepri, L.; Cincinelli, A. The use of levoglucosan for tracing biomass burning in PM2.5 samples in Tuscany (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2012, 167, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, R.C.; Lima-Souza, M.; Caetano-Silva, L.; Queiroz, M.E.C.; Nogueira, R.F.P.; Allen, A.G.; Cardoso, A.A.; Held, G.; Campos, M.L.A.M. Use of levoglucosan, potassium, and water-soluble organic carbon to characterize the origins of biomass-burning aerosols. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engling, G.; Lee, J.J.; Sie, H.-J.; Wu, Y.-C.; Yet-Pole, I. Anhydrosugar characteristics in biomass smoke aerosoldcase study of environmental influence on particle-size of rice straw burning aerosol. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2013, 56, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtchev, I.; Hellebust, S.; Bell, J.M.; O’Connor, I.P.; Healy, R.M.; Allanic, A.; Healy, D.; Wenger, J.C.; Sodeau, J.R. The use of polar organic compounds to estimate the contribution of domestic solid fuel combustion and biogenic sources to ambient levels of organic carbon and PM2.5 in Cork Harbour, Ireland. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2143–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennigan, C.J.; Sullivan, A.P.; Collett, J.L.; Robinson, A.L. Levoglucosan stability in biomass burning particles exposed to hydroxyl radicals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.; Tilgner, A.; Iinuma, Y.; Hermann, H. Atmospheric stability of levoglucosan: A detailed laboratory and modeling study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, Q.; He, H. Degradation kinetics of levoglucosan initiated by hydroxyl radical under different environmental conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 91, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, A.P.; Holden, A.S.; Patterson, L.A.; McMeeking, G.R.; Kreidenweis, S.M.; Malm, W.C.; Hao, W.M.; Wold, C.E.; Collett, J.L. A method for smoke marker measurements and its potential application for determining the contribution of biomass burning from wildfires and prescribed fires to ambient PM2.5 organic carbon. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxbaum, H.; Caseiro, A.; Sanchez-Ochoa, A.; Kasper-Giebl, A.; Claeys, M.; Gelencser, A.; Legrand, M.; Preunkert, S.; Pio, C. Levoglucosan levels at background sites in Europe for assessing the impact of biomass combustion on the European aerosol background. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

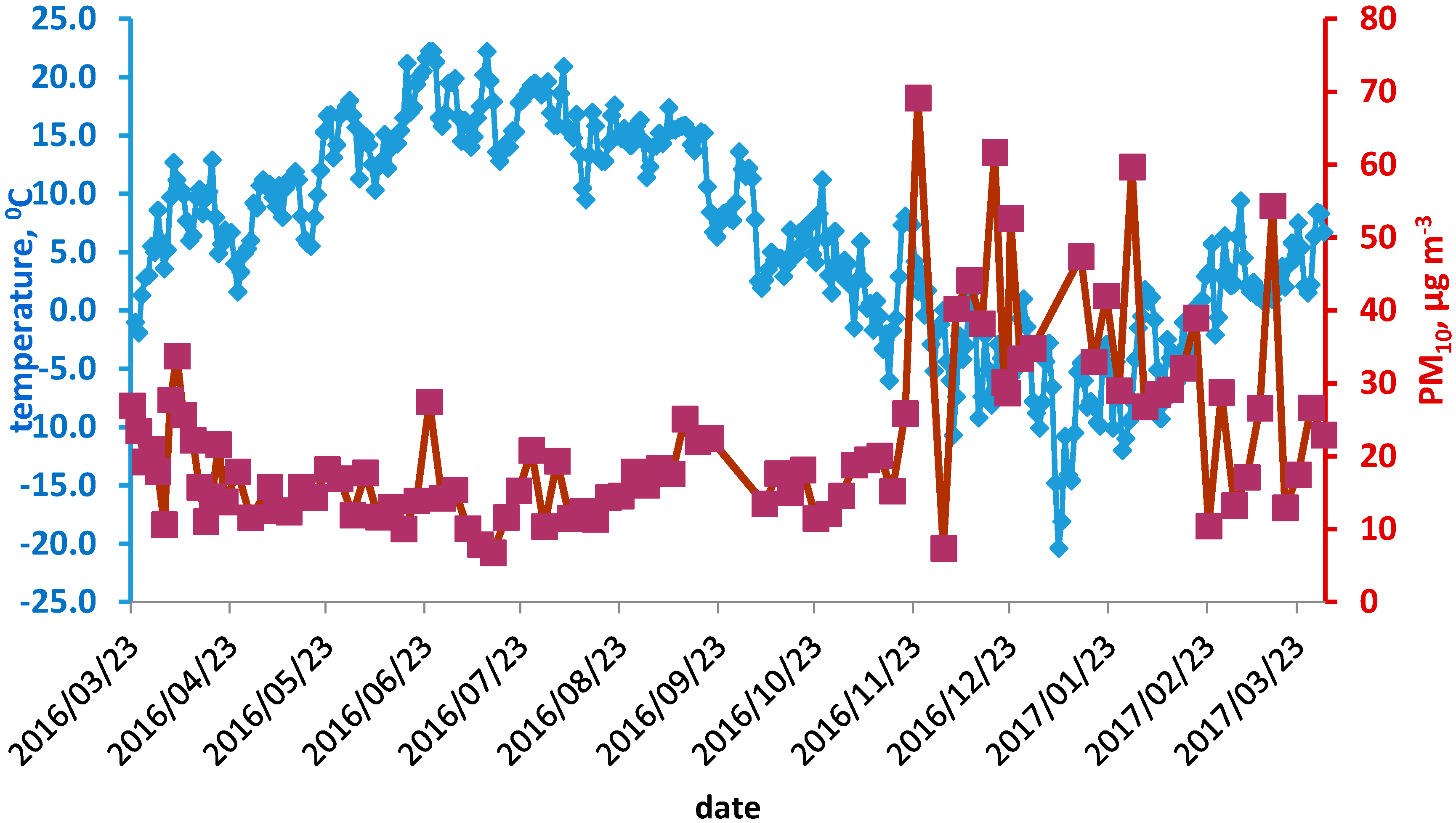
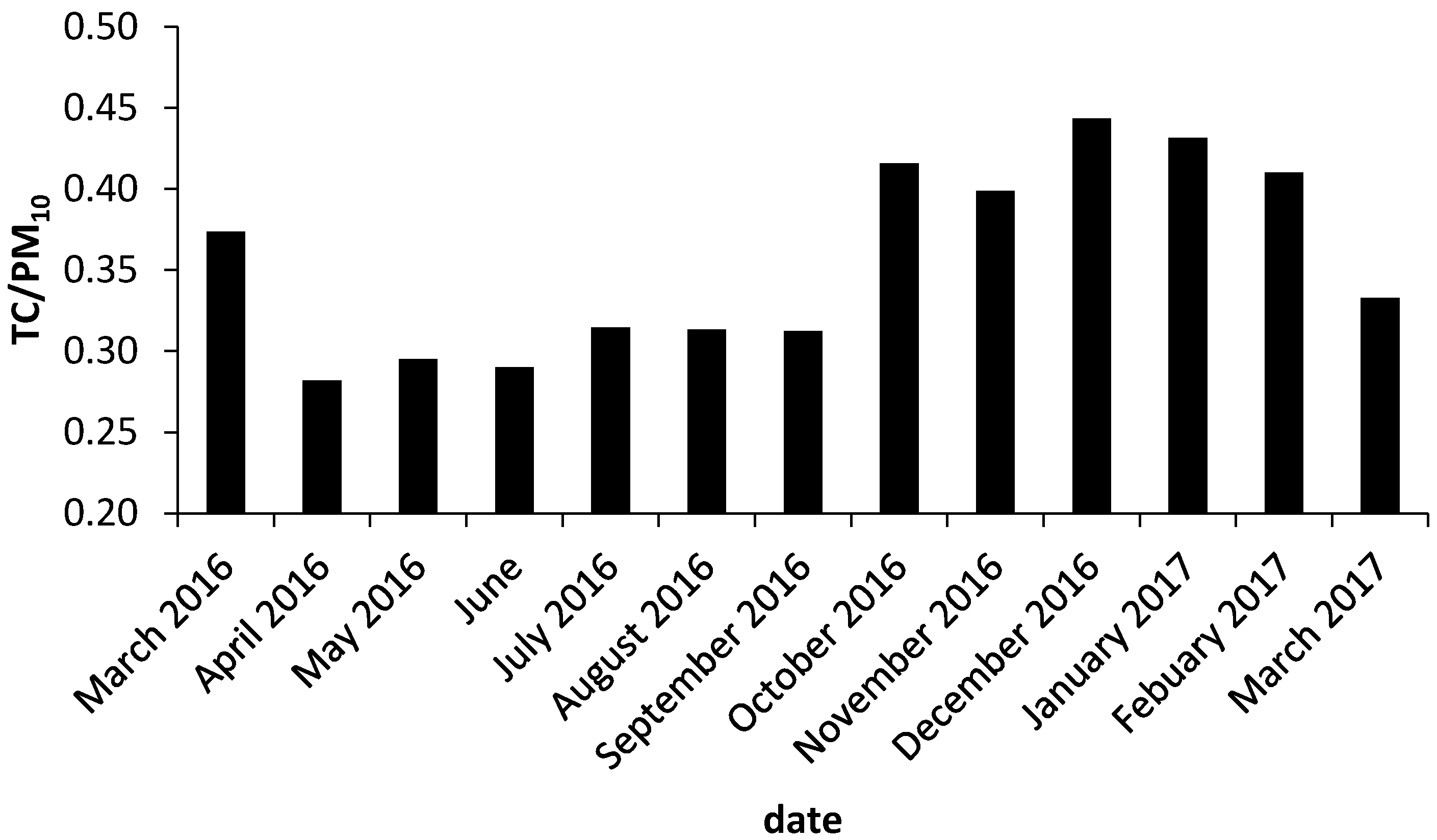
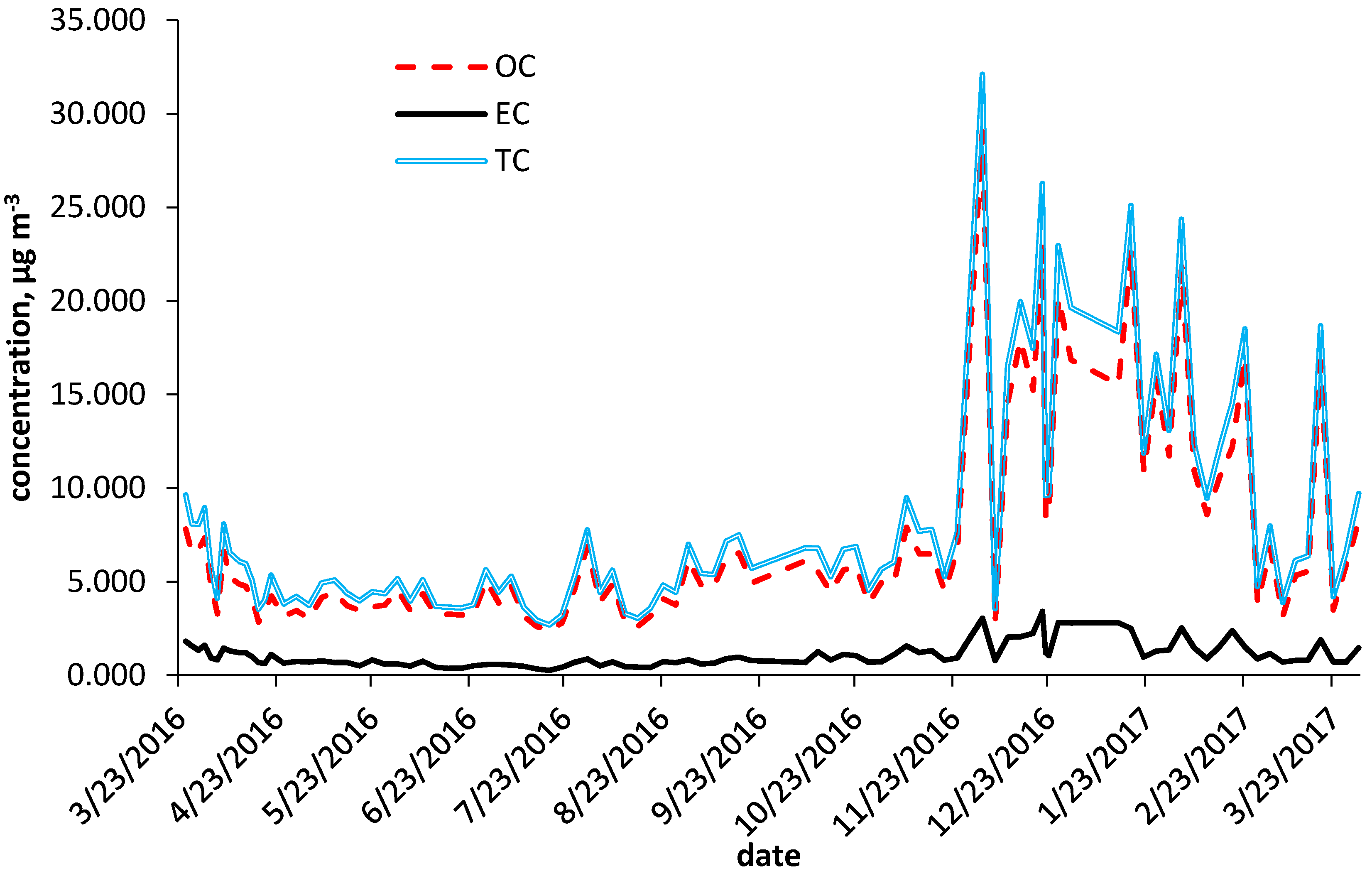
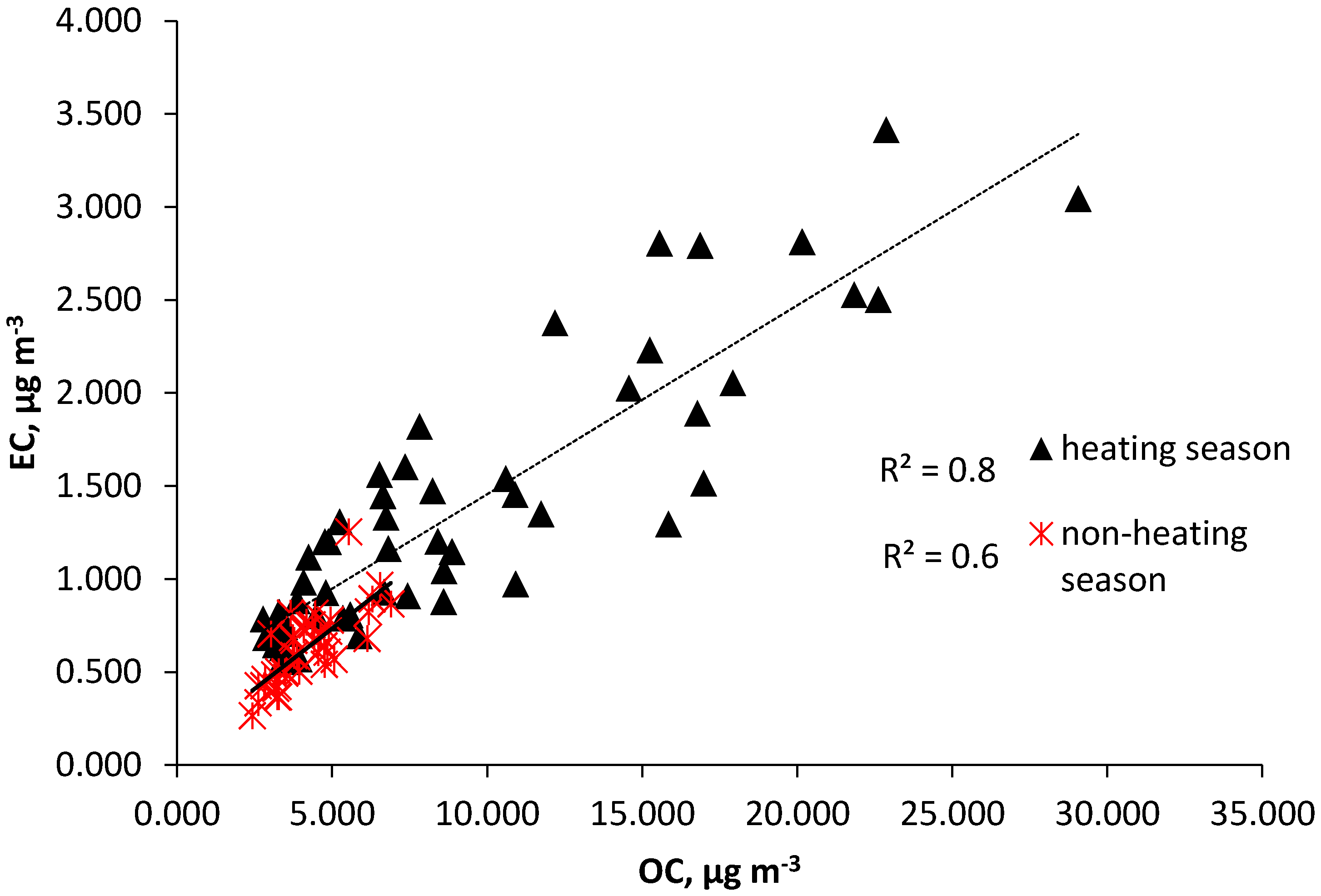
| Parameter | Heating Season 25 March 2016–21 April 2016 and 26 September 2016–30 March 2017 | Non-Heating Season 22 April 2016–25 September 2016 |
|---|---|---|
| Average air temperature, T (°C) | 0.6 ± 6.4 | 14.1 ± 4.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 84.0 ± 5.1 | 77.6 ± 4.7 |
| Average wind speed (m/s) | 1.8 ± 1.2 | 1.6 ± 0.9 |
| Cumulative rainfall (mm) | 447.9 (108 rain days) | 437.4 (77 rain days) |
| Parameter | Mean (SD) | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 21.9 (12.3) | 69.2 | 6.7 |
| Heating season | 31.0 (15.2) | 69.2 | 7.4 |
| Non-heating season | 15.3 (4.5) | 25.1 | 6.7 |
| EC | 1.1 (0.66) | 3.42 | 0.26 |
| Heating season | 1.34 (0.69) | 3.42 | 0.63 |
| Non-heating season | 0.64 (0.21) | 1.11 | 0.26 |
| OC | 7.00 (5.28) | 29.10 | 2.61 |
| Heating season | 8.82 (6.18) | 29.10 | 2.77 |
| Non-heating season | 4.21 (1.14) | 6.54 | 2.61 |
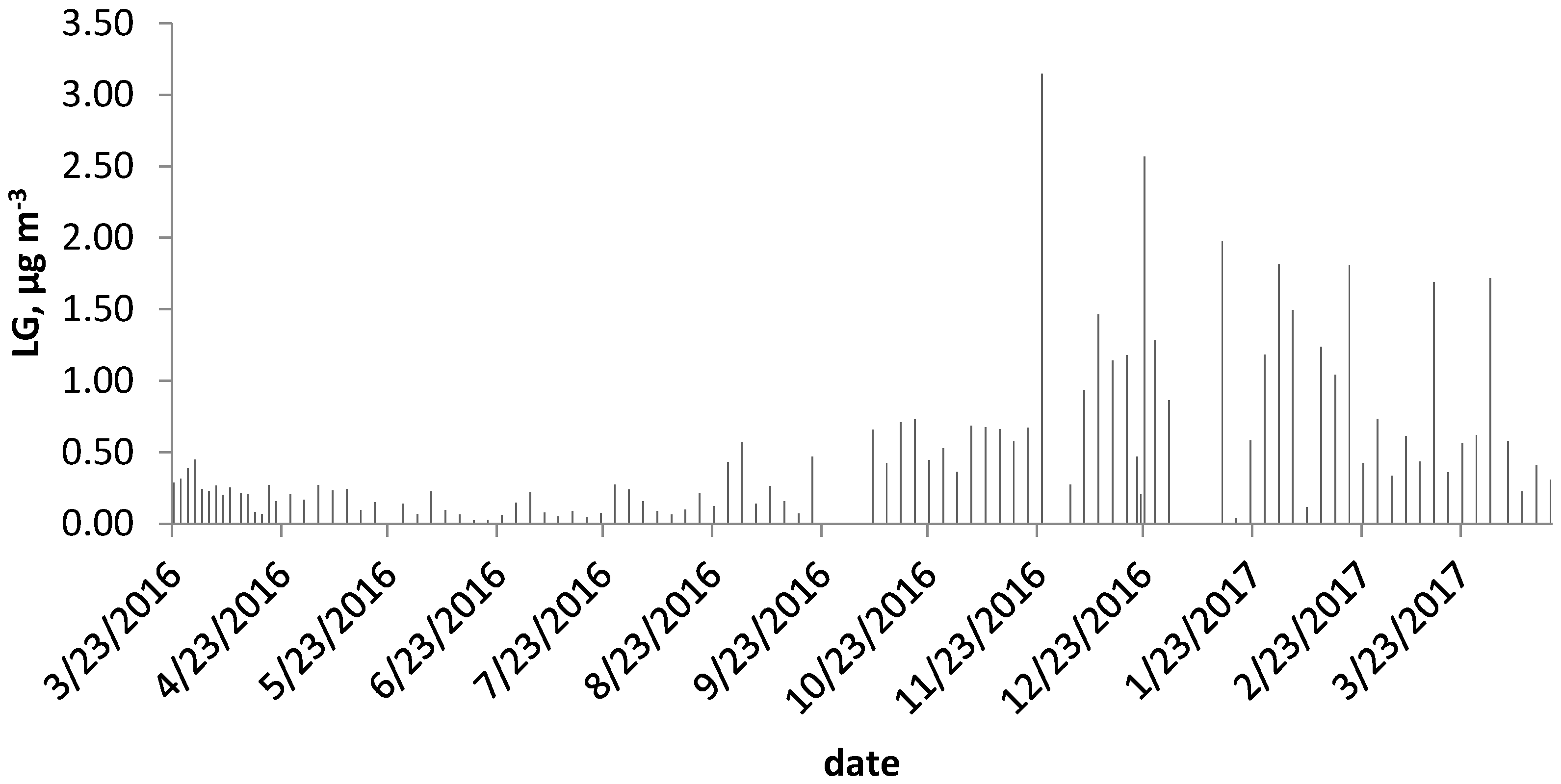
| Levoglucosan | 0.51 (0.57) | 1.72 | 0.02 |
| Heating season | 0.78 (0.65) | 1.72 | 0.04 |
| Non-heating season | 0.18 (0.15) | 0.66 | 0.02 |
| Ratio | Mean | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|
| TC/PM10 | 0.35 | 0.59 | 0.19 |
| EC/TC | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.08 |
| OC/TC | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.79 |
| OC/EC | 6.7 | 12.2 | 4.3 |
| LG/OC | 0.070 | 0.065 | 0.043 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klejnowski, K.; Janoszka, K.; Czaplicka, M. Characterization and Seasonal Variations of Organic and Elemental Carbon and Levoglucosan in PM10 in Krynica Zdroj, Poland. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100190
Klejnowski K, Janoszka K, Czaplicka M. Characterization and Seasonal Variations of Organic and Elemental Carbon and Levoglucosan in PM10 in Krynica Zdroj, Poland. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(10):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100190
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlejnowski, Krzysztof, Katarzyna Janoszka, and Marianna Czaplicka. 2017. "Characterization and Seasonal Variations of Organic and Elemental Carbon and Levoglucosan in PM10 in Krynica Zdroj, Poland" Atmosphere 8, no. 10: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100190
APA StyleKlejnowski, K., Janoszka, K., & Czaplicka, M. (2017). Characterization and Seasonal Variations of Organic and Elemental Carbon and Levoglucosan in PM10 in Krynica Zdroj, Poland. Atmosphere, 8(10), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100190




