Abstract
Observation of the ambient aerosol surface area concentrations is important to understand the aerosol toxicity because an increased surface area may be able to act as an enhanced reaction interface for certain reactions between aerosol particles and biological cells, as well as an extended surface for adsorbing and carrying co-pollutants that are originally in gas phase. In this study, the concentration of aerosol surface area was measured from April 2015 to March 2016 in Fukuoka, Japan. We investigated the monthly and diurnal variations in the correlations between the aerosol surface area and black carbon (BC) and sulfate concentrations. Throughout the year, aerosol surface area concentration was strongly correlated with the concentrations of BC, which has a relatively large surface area since BC particles are usually submicron agglomerates consisting of much smaller (tens of nanometers) sized primary soot particles. The slopes of the regression between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations was highest in August and September 2015. We presented evidence that this was caused by an increase in the proportion of airmasses that originated on the main islands of Japan. This may enhance the introduction of the BC to Fukuoka from the main islands of Japan which we hypothesize to be relatively fresh or “uncoated”, thereby maintaining its larger surface area.
1. Introduction
Many studies investigating the adverse effects, such as respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, of exposure to ambient aerosols on human health have been conducted. This is based on the globally acknowledged possibility that these aerosols are hazardous to humans [1,2,3]. In particular, ultrafine particles with a diameter less than 100 nm (nanoparticles) are considered to be more harmful than larger particles because these exogenous nanoparticles can be inhaled and deposited in the respiratory tract, enter the blood stream, and translocate to other organs [4,5,6,7]. Surface area is considered to be an appropriate indicator as opposed to mass for evaluating pulmonary inflammatory responses for rats and mice caused by exposure to manufactured nanomaterials, such as TiO2, fullerenes, and carbon nanotubes [8,9,10,11]. The surface area measurement is also important to understand the aerosol toxicity because an increased surface area may be able to act as an enhanced reaction interface for certain reactions between aerosol particles and biological cells, as well as an extended surface for adsorbing and carrying co-pollutants that are originally in gas phase [12,13,14].
The most popular method to measure the particle specific surface area is the Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) method [15]. The toxicity led by exposure to manufactured materials related to the specific surface area has been discussed on the basis of the BET specific surface area values [8,9,10]. However, it is challenging to experimentally measure the actual surface area of atmospheric aerosol particles due to low quantity of aerosols that can be collected using ordinary filter sampling methods [16,17,18].
Other practical and continuous techniques are required to measure the concentrations of ambient aerosol surface area. A nanoparticle surface area monitor (NSAM) using the diffusion charging method has been developed for continuous measurement for the concentration of particle surface area [19,20,21,22,23]. Particles introduced in the NSAM first become charged with positive ions emitted by a corona discharger in a mixing chamber. Particle charge is measured by an electrometer installed downstream from the chamber. Surface area is calculated assuming that it is ideally proportional to the particle charge [19]. The actual NSAM output is the lung-deposited surface area (LDSA, the product of particle surface area and lung deposition efficiency) concentration of particles that can be converted to the concentration of ambient aerosol surface area [18,23,24,25,26,27,28].
These previous reports noted that the concentration of aerosol surface area is strongly correlated with the concentrations of black carbon (BC) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in particulate phase. These facts are reasonable since BC (or BC-like) particles are usually submicron agglomerates consisting of much smaller (tens of nanometers) sized primary soot particles [27,29]. However, the ways in which chemical species other than BC and meteorological conditions contribute to the variation in the concentrations of ambient aerosol surface area is not well understood. Particularly, sulfate aerosols may occasionally have a significant effect on aerosol surface area concentration [23].
In this study, we measured the concentration of aerosol surface area together with BC and sulfate, as well as meteorological data for one year at Fukuoka, Japan, and investigated the effect of the aerosol chemical compositions and meteorological conditions on the aerosol surface area. This study is a follow-up experiment of Okuda et al. (2016) [23] in order to perform a year-round investigation of aerosol surface area and some related parameters.
2. Experiments
2.1. Observation Site and Period
The monitoring site for the aerosol surface area, BC, and particle number concentrations was the fourth floor of a building of the Fukuoka Institute for Atmospheric Environment and Health (33.55° N, 130.36° E) at Fukuoka University, Japan [23,30,31,32]. Another monitoring site for the sulfate concentration was the Fukuoka Institute of Health and Environmental Science (33.51° N, 130.48° E). These two sites are ~15 km from each other. Fukuoka City is one of the largest cities in northern Kyushu district, which faces the Asian continent (Figure 1). Generally, sulfate concentrations in this area (northern Kyushu district) are mainly affected by a long-range transport, and exhibit very similar variation over the scale of hundreds of kilometers [30]. For example, sulfate in Fukue and Fukuoka showed very similar concentrations and variations even though these two sites are approximately 200 km from each other [30]. Therefore, we assume that the distance between these observational sites can be ignored. The area and population of Fukuoka City were approximately 340 km2 and 1.5 million, respectively. Aerosols observed in Fukuoka originate on the continent, the ocean, and in the local area. This site is therefore well situated for an examination of differences in aerosol surface area and chemical composition between aerosol sources. PM2.5 concentrations over this site are generally affected by the long-range transport process from the Asian continent [30,33]. The observation period was from 1 April 2015 to 31 March 2016.
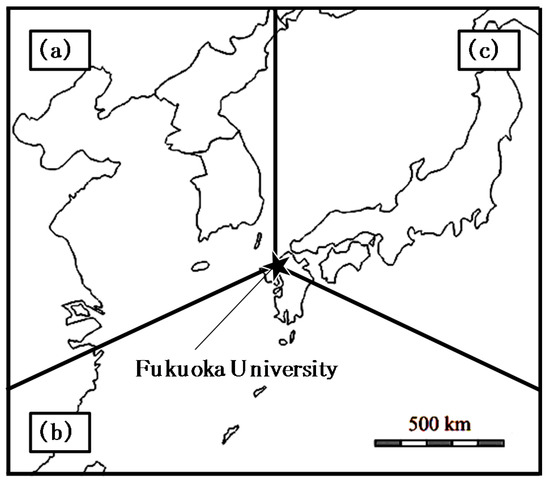
Figure 1.
Map of East Asia showing each sector classified by airmass backward trajectories from the monitoring site (Fukuoka University, Japan): (a) Asian continent, (b) southern part of Kyushu, and (c) main islands of Japan.
2.2. Aerosol Surface Area
The surface area concentration was automatically and continuously measured using an NSAM (Model 3550, TSI Inc., Shoreview, MN, USA). The flow rate of the NSAM was 2.5 L·min−1, and the time resolution was set to 10 min. The NSAM has a cyclone with a 50% cut-off of 1 μm at the inlet. The NSAM can measure reliable LDSA of the particles between the ranges of 20 and 400 nm [26]. The procedure for the conversion from LDSA (the actual NSAM reading) to aerosol surface area has already been described elsewhere [18], but is briefly summarized here. The calibration constant is determined with passing monodisperse aerosols simultaneously through the scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) and the NSAM by the manufacturer (TSI Inc.). Specifically, the total surface area of the 80-nm NaCl particles determined by the SMPS is multiplied by the lung deposition efficiency of 80-nm particles, which is determined using the lung deposition curve for a reference worker reported by the International Commission on Radiological Protection [34]. In this study, we measured tracheobronchial-deposited surface area values using the NSAM, and then converted them into aerosol surface area by dividing them by the ICRP deposition efficiency of 80-nm particles. In order to check the validity of the calibration constant, we measured the total surface area of polydisperse SiO2 particles (sicastar, micromod Partikeltechnologie GmbH, Rostock, Germany) using SMPS and NSAM simultaneously. The geometric surface area concentrations were calculated using particle diameters of the spherical particle. The experiments were conducted for several levels of the particle concentrations by changing the mixing volume of dilution air. The results are shown in Figure 2. The surface area measured by NSAM matched very well with that measured by SMPS. Therefore, we applied this calibration constant to the field measurement results obtained in this study.
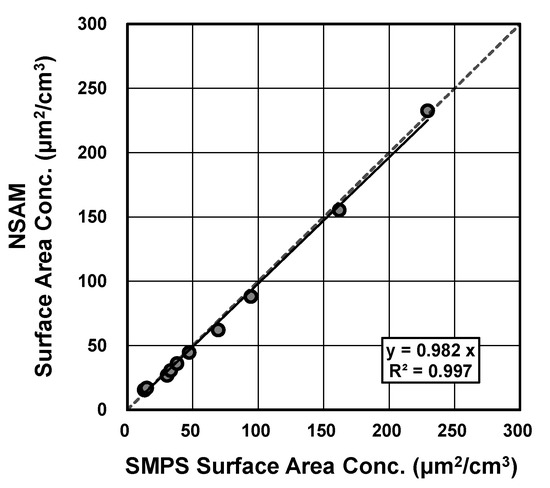
Figure 2.
Total surface area of SiO2 using scanning mobility particle sizer (SMPS) and nanoparticle surface area monitor (NSAM) simultaneously. The geometric surface area concentrations were calculated using particle diameters of the spherical particle.
2.3. Black Carbon, Aerosol Number and Mass, Sulfate Ion Concentration, and Wind Direction and Speed
The mass concentration of BC in PM2.5 was automatically and continuously measured using an aethalometer (AE-16U, Magee Scientific Corp., Berkeley, CA, USA) [33]. A Sharp-Cut Cyclone SCC1.829 (BGI Inc., Butler, NJ, USA) was used as the PM2.5 inlet. The BC concentration measured using an aethalometer based on the rate of absorption of incident light (880 nm) by BC shows reasonable agreement with elemental carbon (EC) measured using the thermal-optical method [35,36]. The flow rate of the aethalometer was 5.0 L·min−1, and the time resolution was set to 15 min.
Sulfate concentrations were automatically measured and analyzed using a continuous dichotomous aerosol chemical speciation analyzer (ACSA-12, Kimoto Electric Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan). The ACSA-12 determines the sulfate ion concentration using the BaSO4-based turbidimetric method after the addition of BaCl2 dissolved in polyvinyl pyrrolidone solution, and the results correspond closely with the values determined using the denuder-filter/ion chromatography method [37]. According to the previous study, sulfate concentration values measured by ACSA were approximately 10% higher than those measured by the denuder-filter/ion chromatography [37]; this might be caused by the effect of organosulfates.
The aerosol number concentrations and particle size distributions (optical equivalent diameter: >0.3, >0.5, >1.0, >2.0, >3.0, and >5.0 μm) were measured using an optical particle counter (OPC, TD100; Sigma Tech., Yokohama, Japan), which was installed on the rooftop of the building in Fukuoka University, and operated in ambient conditions without using a heating drier. The size discriminator of the OPC was calibrated using polystyrene latex spheres with a refractive index of 1.59-0i. The OPC data were corrected for coincidence loss. The flow rate of the OPC was 1.0 L·min−1, and the time resolution was set to 1 min.
PM2.5 mass concentration, wind direction, and wind speed data were obtained from websites operated by national and local governmental offices [38,39].
The time resolution varied according to the instrument or the sources of the downloaded data. As a result, we used 1-h average values for all further analyses in this study. All times are expressed according to the local time zone (JST:UTC + 9 h).
2.4. Airmass Backward Trajectory Analysis
Airmass backward trajectories were calculated for each day of the measurement campaign using the NOAA HYSPLIT model [40,41]. The trajectories were calculated based on the following conditions: start latitude and longitude: 33.55° N, 130.36° E; start altitude: 1500 m above sea level; and calculation time: 72 h (three days). The trajectories were calculated every 3 h (0:00 to 21:00 of local time) and were allocated to one of three sectors ((a) Asian continent, (b) southern Kyushu, and (c) main islands of Japan, see Figure 1) if the trajectory positions for every 6-h interval were within the sector at least 36 h (50% of the time) and if the trajectory positions were within other sectors less than 24 h (33% of the time).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Diurnal Variations
Table 1 shows the mean values of the concentrations of aerosol surface area, PM2.5 mass, BC, sulfate, and particle number measured in this study. The mean concentrations of surface area and other variables measured in this study were not so different from those presented in several previous papers [18,23,24,25,30].

Table 1.
Mean, standard deviation (SD), and number of samples (n) of each variable measured in this study in Fukuoka, Japan (April 2015 to March 2016, 1-h average value). BC, black carbon.
The diurnal variations of each variable were analyzed to investigate the effect of diurnal human activity on the concentration of aerosol surface area (Figure 3). The error bars indicate the standard deviation of the data and reflect the high variability of day to day measurements. In order to establish statistically significant trends, we performed t-tests and found that the concentrations of aerosol surface area and BC in the morning (8:00–10:00) were significantly higher than at other times (p < 0.01). Apparently, concentrated automotive traffic near the monitoring site resulted in the morning peak of aerosol surface area and BC [23,24,25,27,30].
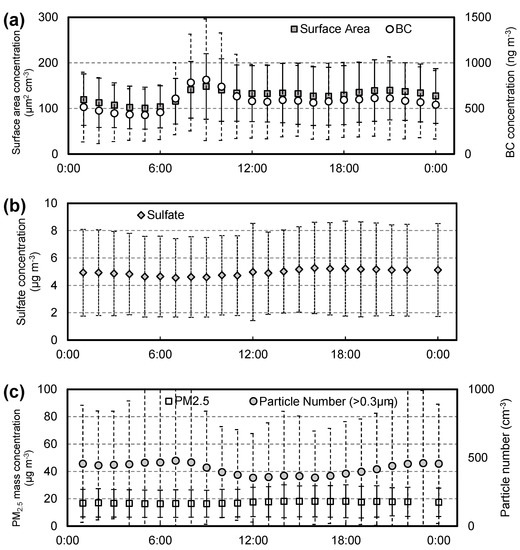
Figure 3.
Diurnal variation in (a) aerosol surface area and BC concentrations; (b) sulfate concentrations; (c) PM2.5 mass concentration and particle number (>0.3 μm), measured from April 2015 to March 2016 in Fukuoka, Japan.
The other variables did not exhibit morning peaks. This finding is supported by a previous study that suggested that the elemental carbon in Fukuoka City originated mainly from local emission sources rather than from long-range transport [30]. Of all the variables, BC was consistently and more strongly correlated with aerosol surface area over the observation site. This fact means that we should pay much more attention to BC when considering the aerosol surface area as a metric of adverse health effects caused by exposure to aerosols.
A detailed investigation of the diurnal variation of the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations are shown in Figure 4. The aerosol surface area and BC concentrations exhibited a clear daily morning peak in winter (October 2015 to March 2016). On the other hand, the morning peak of BC concentration was unclear in summer (April to September). Furthermore, the aerosol surface area concentration in the afternoon was higher than that in the morning in summer. Correlation plots of the aerosol surface area vs. BC concentrations are shown in Figure 5. The correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations was much stronger in winter than summer. The high-surface area-low-BC type plots were found frequently in summer, but not much in winter. Apparently, there are some reasons that the aerosol surface area becomes high other than the BC concentration in the afternoon in summer. The seasonal variations are discussed in the following sections.
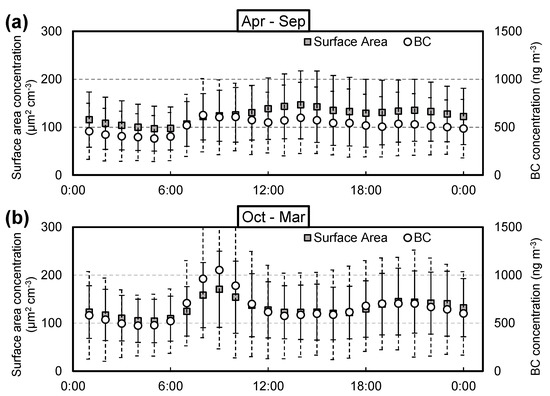
Figure 4.
Diurnal variation in the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations in Fukuoka, Japan, measured from (a) April to September 2015, and (b) October 2015 to March 2016.
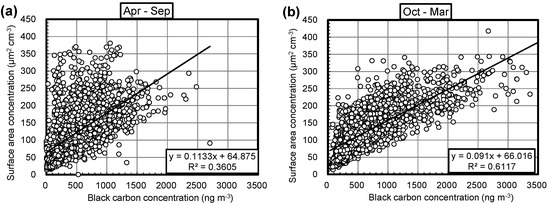
Figure 5.
Correlation plots of the aerosol surface area vs. BC concentrations in Fukuoka, Japan, measured from (a) April to September 2015, and (b) October 2015 to March 2016.
3.2. Monthly Correlations between Aerosol Surface Area and BC Concentrations
The correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations was analyzed on a monthly basis to investigate this relationship in more detail. Table 2 shows the slopes and intercepts of regression lines, the coefficients of determination, and the number of data in the correlation between aerosol surface area and BC or sulfate concentrations for each month through the year. The correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations were relatively strong (R2 = 0.41−0.76) for all months except June and July, for which the coefficient of determination was low (R2 = 0.23). This may have been the result of increasing sulfate concentrations [23], due to the fact that the correlation between the correlation between the aerosol surface area and sulfate concentrations was higher in June (R2 = 0.33) than in other months (R2 = 0.030−0.23; Table 2). The correlations between the aerosol surface area and sulfate concentrations were shown in Figure 6, and that in June (Figure 6a) actually shows that the high concentrations of sulfate increased aerosol surface area concentrations. These events did not appear in other months. For June, the number of data points for which the hourly sulfate concentration was ≥15 μg·m−3 and the aerosol surface area concentration was ≥150 μm2·cm−3 was extremely large (Figure 7). That is, high sulfate concentrations increased aerosol surface area concentrations, which resulted in a weakening of the correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations. According to a previous study, high-sulfate-high-surface area events were possibly caused by volcanic SO2 [23]. However, in this study, SO2 concentrations did not increase in June at Fukuoka, thus the high sulfate concentrations were likely not due to volcanic emissions. Furthermore, the coefficient of determination in the correlation between the aerosol surface area and sulfate concentrations was not high in July (R2 = 0.030; Figure 6b); on the contrary, it was the lowest of the year (Table 2). We therefore surmise that other chemical compounds, such as organic carbon, may have contributed to the July aerosol surface area concentration in Fukuoka.

Table 2.
Linear regressions between black carbon concentration or sulfate concentration and the aerosol surface area concentration for each month from continuous measurements conducted from April 2015 to March 2016.
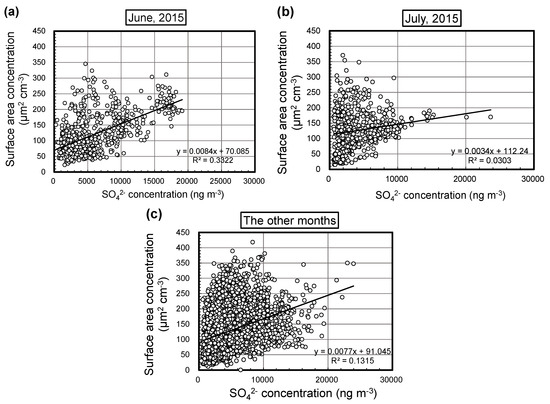
Figure 6.
Comparison between the aerosol surface area and sulfate concentrations recorded in continuous measurements for (a) June, (b) July, and (c) the other months of the study.
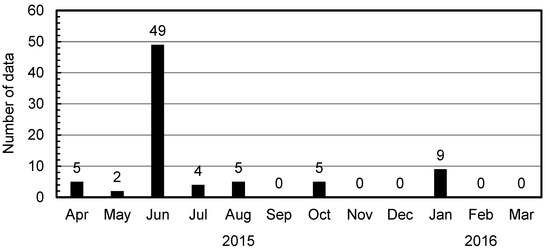
Figure 7.
The monthly number of data points for which the sulfate concentration was ≥15 μg·m−3 and the surface area concentration was ≥150 μm2·cm−3 in Fukuoka.
The slopes of the regression between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations, and thus the ratio of the former to the latter, in August and September was larger than in the other months (Table 2). This appears to have been the result of different airmass sources in summer from the rest of the year. The proportion of the airmass originating in continental Asia was smaller in July, August, and September than in the rest of the year, and the proportion coming from the main islands of Japan was greater in August and September (Figure 8). In Japan, meteorological conditions are generally dominated by the Asian monsoon. As a result, the prevailing wind direction was easterly in August and September 2015 in Fukuoka City. From our results, therefore, we can conclude that the BC from the Asian continent did not have a large surface area but had a high mass concentration, whereas, the mass concentrations of BC transported by easterly wind was low, but that BC had a larger surface area. A possible explanation for this is that some chemical compounds were adsorbed by (or “coated”) the surface of the BC during its long-range transport [42,43,44,45], thereby reducing its surface area. Conversely, the BC from the main islands of Japan was relatively fresh (or “uncoated”), thereby maintaining its larger surface area. For example, China et al. (2015) clearly showed the morphology of soot particles that are thinly and heavily coated [42], and Moffet et al. (2016) reported that all soot particles in urban air were associated with organic carbon, and that soot was frequently at the center of particles as inclusions with thin or thick organic coatings [45]. Apparently this coating would cause the reduction of the surface area of soot particles. This caused the slopes of the regression between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations for August and September to increase, but did not reduce the coefficient of determination.
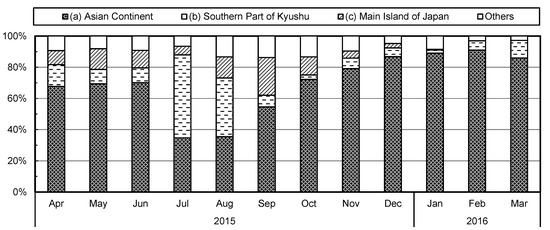
Figure 8.
Monthly airmass backward trajectory analysis, starting at Fukuoka, from April 2015 to March 2016. The sector classification is shown in Figure 1.
3.3. Effect of Land and Sea Breeze on the Correlation between Aerosol Surface Area and Black Carbon Concentrations
As we have seen, the correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations varied from month to month as a result of sulfate input or coating of BC surfaces. In this section, we discuss how this correlation changed with time of day. We divided the day into four segments: (a) night (0:00–6:00), (b) morning (6:00–12:00), (c) afternoon (12:00–18:00), and (d) evening (18:00–24:00). Table 3 shows the correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations in the four time segments. The coefficients of determination for the afternoon (R2 = 0.07–0.71) in particular were lower than that for the other times (night: 0.41–0.87, morning: 0.09–0.84, and evening: 0.29–0.81). This diurnal variation can be related to wind direction and speed. Fukuoka lies on the coast of the Sea of Japan, and is thus often subject to the land and sea breeze. Figure 9 shows a diurnal variation in wind speed and wind direction in Fukuoka from April 2015 to March 2016. In Fukuoka, the direction of sea breezes is northerly (0°) and that of land breezes is southerly (180°). We generally recorded a sea breeze during the afternoon (12:00 to 18:00), which was strongest from 13:00 to 16:00 (~4 m·s−1), and a gentler land breeze (~2 m·s−1) at night and the early morning. This may have caused that BC concentrations to decrease in the afternoon due to the inflow of a clean airmass via the sea breeze. The nocturnal reversal of the wind direction back to the land breeze would then prevent any further decrease in BC concentrations. Figure 10 shows the BC concentrations corresponding to the wind direction and wind speed. These plots clearly show that stronger northerly winds make the BC concentration low. In addition, sulfate concentrations were higher in the afternoon (12:00–18:00) than at other times (t-test, p < 0.01; Figure 3b). Generally, sulfate is formed by the oxidation of SO2, and this reaction is promoted by solar radiation (i.e., during the daytime). The additional sulfate particles formed would thus contribute to the aerosol surface area concentration. This explains the lower coefficients of determination between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations in the afternoon and the reversal of this pattern in the evening (Table 3).

Table 3.
Linear regressions between the aerosol surface area and black carbon (BC) concentrations in the four time segments: (a) night (0:00–6:00), (b) morning (6:00–12:00), (c) afternoon (12:00–18:00), and (d) evening (18:00–24:00). The measurements were conducted from April 2015 to March 2016.
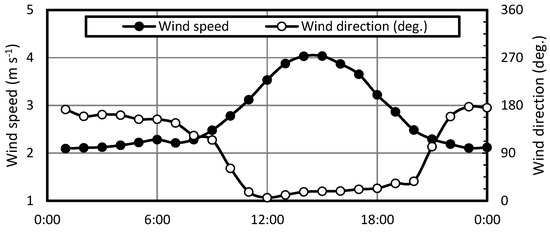
Figure 9.
Diurnal variation in wind speed and wind direction in Fukuoka, measured from April 2015 to March 2016. Wind directions are as follows: 0°: Northerly, 90°; Easterly, 180°; Southerly; and 270°: Westerly.
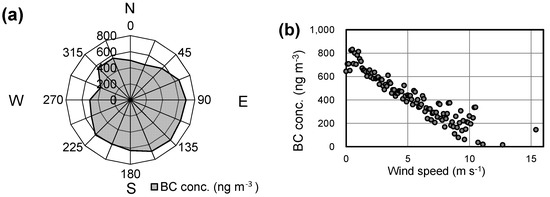
Figure 10.
BC concentrations corresponding to (a) the wind direction, and (b) the wind speed, in Fukuoka, measured from April 2015 to March 2016.
4. Conclusions
We measured the aerosol surface area, black carbon (BC), and sulfate concentrations for one year in Fukuoka, Japan, and investigated the monthly and diurnal variations in the correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations. Throughout the year, the aerosol surface area concentration was strongly correlated with BC concentration. In June 2015, the coefficient of determination for this correlation was lower than in other months, which was evidently due to high sulfate concentrations. In August and September 2015, the slopes of the regression between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations was highest. This appears to have been the result of an increase in the proportion of the airmass that originated on the main islands of Japan. This may enhance the introduction of the BC from the main islands of Japan which is relatively fresh (or “uncoated”), thereby maintaining its larger surface area. In addition, the correlation between the aerosol surface area and BC concentrations was weakest in the afternoon, and this could be because certain secondary formed aerosols increase. This may also be because Fukuoka is generally dominated by the land and sea breeze, and BC concentrations decrease under those conditions due to the afternoon inflow of a clean airmass.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by JSPS/MEXT KAKENHI Grant Numbers 26340010, JP25220101, 17H01864 and 17H04480, Ministry of Environment, Environment Research and Technology Development Fund, Japan (Grant Nos. 5-1452 and 5-1651), Grant for Environmental Research Projects from The Sumitomo Foundation, Steel Foundation for Environmental Protection Technology, and Keio Gijuku Academic Development Funds.
Author Contributions
T.O. conceived and designed the experiments, and wrote the paper; M.K. analyzed the data and wrote the draft of the paper, H.Y. analyzed the data; K.H. (Keio University), K.F., and K.I. installed and operated the NSAM, N.K. performed the BC measurements; I.U. and S.Y. installed and operated the ACSA; A.Y., A.T., C.N., K.H. (Fukuoka University), and M.H. administrated the entire experiments. All authors contributed to revising the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Dockery, D.W.; Pope, C.A., III; Xu, X.; Spengler, J.D.; Ware, J.H.; Fay, M.E.; Ferris, B.G., Jr.; Speizer, F.E. An association between air pollution and mortality in six U.S. cities. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III; Thun, M.J.; Namboodiri, M.M.; Dockery, D.W.; Evans, J.S.; Speizer, F.E.; Heath, C.W., Jr. Particulate air pollution as a predictor of mortality in a prospective study of U.S. adults. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 151, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Air Pollution and Cancer; IARC Scientific Publication: Lyon, France, 2013; No. 161. [Google Scholar]
- Ferin, J.; Oberdörster, G.; Penney, D.P. Pulmonary retention of ultrafine and fine particles in rats. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1992, 6, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdörster, G.; Gelein, R.M.; Ferin, J.; Weiss, B. Association of particulate air pollution and acute mortality: Involvement of ultrafine particles? Inhal. Toxicol. 1995, 7, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donaldson, K.; Li, X.Y.; MacNee, W. Ultrafine (nanometre) particle mediated lung injury. J. Aerosol Sci. 1998, 29, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): Approaches to Safe Nanotechnology; DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 2009-125; The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH): Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdörster, G.; Finkelstein, J.N.; Johnston, C.; Gelein, R.; Cox, C.; Baggs, R.; Elder, A.C.P. Acute pulmonary effects of ultrafine particles in rats and mice. Res. Rep. Health Effects Inst. 2000, 96, 5–74. [Google Scholar]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, J. Risk Assessment of Manufactured Nanomaterials: Carbon Nanotubes (CNT); Final Report Issued on 12 August 2011, Executive Summary; NEDO Project “Research and Development of Nanoparticle Characterization Methods.” (P06041); New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization: Kawasaki, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, O.; Stoeger, T. Surface area is the biologically most effective dose metric for acute nanoparticle toxicity in the lung. J. Aerosol Sci. 2016, 99, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G. Pulmonary effects of inhaled ultrafine particles. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2001, 74, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Alföldy, B.; Drossinos, Y. A metric for health effects studies of diesel exhaust particles. J. Aerosol Sci. 2009, 40, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuland, T.; Øvrevik, J.; Låg, M.; Refsnes, M. Role of size and surface area for pro-inflammatory responses to silica nanoparticles in epithelial lung cells: Importance of exposure conditions. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T. Measurement of the specific surface area and particle size distribution of atmospheric aerosol reference materials. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 75, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Isobe, R.; Nagai, Y.; Okahisa, S.; Funato, K.; Inoue, K. Development of a high-volume PM2.5 particle sampler using impactor and cyclone techniques. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatoya, K.; Okuda, T.; Funato, K.; Inoue, K. On-line measurement of the surface area concentration of aerosols in Yokohama, Japan, using the diffusion charging method. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kittelson, D.B. Characterization of aerosol surface instruments in transition regime. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fissan, H.; Neumann, S.; Trampe, A.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Shin, W.G. Rationale and principle of an instrument measuring lung deposited nanoparticle surface area. J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.G.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Fissan, H.; Neumann, S.; Trampe, A. Calibration and numerical simulation of Nanoparticle Surface Area Monitor (TSI Model 3550 NSAM). J. Nanopart. Res. 2007, 9, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitbrink, W.A.; Evans, D.E.; Ku, B.K.; Maynard, A.D.; Slavin, T.J.; Peters, T.M. Relationships among particle number, surface area, and respirable mass concentrations in automotive engine manufacturing. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, T.; Yamazaki, H.; Hatoya, K.; Kaneyasu, N.; Yoshino, A.; Takami, A.; Funato, K.; Inoue, K.; Nishita, C.; Hara, K.; et al. Factors Controlling the Variation of Aerosol Surface Area Concentrations Measured by a Diffusion Charger in Fukuoka, Japan. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, E.; Siegmann, P.; Siegmann, H.C. Exploratory study of particle-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in different environments of Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4957–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Polidori, A.; Phuleria, H.; Geller, M.D.; Sioutas, C. Application of a diffusion charger for the measurement of particle surface concentration in different environments. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbach, C.; Fissan, H.; Stahlmecke, B.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Pui, D.Y.H. Conceptual limitations and extensions of lung-deposited Nanoparticle Surface Area Monitor (NSAM). J. Nanopart. Res. 2009, 11, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, P.C.; Gomes, J.F.; Bordado, J.C. Assessment of exposure to airborne ultrafine particles in the urban environment of Lisbon, Portugal. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2012, 62, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.F.P.; Albuquerque, P.C.S.; Esteves, H.M.D.S.; Carvalho, P.A. Notice on a methodology for characterizing emissions of ultrafine particles/nanoparticles in microenvironments. Energy Emiss. Cont. Technol. 2013, 1, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Salvadori, N.; Mazzoleni, C. Effect of traffic and driving characteristics on morphology of atmospheric soot particles at freeway on-ramps. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneyasu, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Sato, K.; Takami, A.; Hayashi, M.; Hara, K.; Kawamoto, K.; Okuda, T.; Hatakeyama, S. Impact of long-range transport of aerosols on the PM2.5 composition at a major metropolitan area in the northern Kyushu area of Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, A.; Miyoshi, T.; Irei, S.; Yoshino, A.; Sato, K.; Shimizu, A.; Hayashi, M.; Hara, K.; Kaneyasu, N.; Hatakeyama, S. Analysis of organic aerosol in Fukuoka, Japan using a PMF method. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, A.; Takami, A.; Sato, K.; Shimizu, A.; Kaneyasu, N.; Hatakeyama, S.; Hara, K.; Hayashi, M. Influence of Trans-Boundary Air Pollution on the Urban Atmosphere in Fukuoka, Japan. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneyasu, N.; Takami, A.; Sato, K.; Hatakeyama, S.; Hara, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Yamamoto, S. Year-round behavior of PM2.5 in a remote island and urban site in the northern Kyushu area, Japan. J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 46, 111–118. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Human respiratory tract model for radiological protection. Ann. ICRP 1994, 24, 1–482. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatachari, P.; Zhou, L.; Hopke, P.K.; Schwab, J.J.; Demerjian, K.L.; Weimer, S.; Hogrefe, O.; Felton, D.; Rattigan, O. An intercomparison of measurement methods for carbonaceous aerosol in the ambient air in New York City. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, I.P.; Ma, H.; Kittelson, D.B.; Miller, A.L. Comparing Measurements of Carbon in Diesel Exhaust Aerosols Using the Aethalometer, NIOSH Method 5040, and SMPS; SAE Technical Paper Series 2007-01-0334; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Osada, K.; Kamiguchi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Kuwahara, S.; Pan, X.; Hara, Y.; Uno, I. Comparison of ionic concentrations on size-segregated atmospheric aerosol particles based on a denuder-filter method and a Continuous Dichotomous Aerosol Chemical Speciation Analyzer (ACSA-12). Earozoru Kenkyu 2016, 31, 203–209. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka Prefecture Website. Available online: http://www.fihes.pref.fukuoka.jp/taiki-new/Nipo/OyWbNpKm0151.htm (accessed on 6 May 2017).
- Japan Meteorological Agency Website. Available online: http://www.data.jma.go.jp/obd/stats/etrn/index.php (accessed on 6 May 2017).
- Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.B.; Cohen, M.D.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolph, G.D. Real-Time Environmental Applications and Display sYstem (READY) Website. NOAA Air Resources Laboratory: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2017. Available online: http://ready.arl.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 26 June 2017).
- China, S.; Scarnato, B.; Owen, R.C.; Zhang, B.; Ampadu, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Dzepina, K.; Dziobak, M.P.; Fialho, P.; Perlinger, J.A.; et al. Morphology and mixing state of aged soot particles at a remote marine free troposphere site: Implications for optical properties. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Moteki, N.; Takegawa, N.; Sahu, L.K.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yonemura, S.; Blake, D.R. Radiative impact of mixing state of black carbon aerosol in Asian outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, D24210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takami, A.; Mayama, N.; Sakamoto, T.; Ohishi, K.; Irei, S.; Yoshino, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Murano, K.; Sadanaga, Y.; Bandow, H.; et al. Structural analysis of aerosol particles by microscopic observation using a time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectrometer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6726–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffet, R.C.; O’Brien, R.E.; Alpert, P.A.; Kelly, S.T.; Pham, D.Q.; Gilles, M.K.; Knopf, D.A.; Laskin, A. Morphology and mixing of black carbon particles collected in central California during the CARES field study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14515–14525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).