The Use of a Spectral Nudging Technique to Determine the Impact of Environmental Factors on the Track of Typhoon Megi (2010)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Design and SN
2.1. Experimental Design of Numerical Simulation
2.2. The SN Technique
3. Effect of Different Large-Scale Environmental Factors
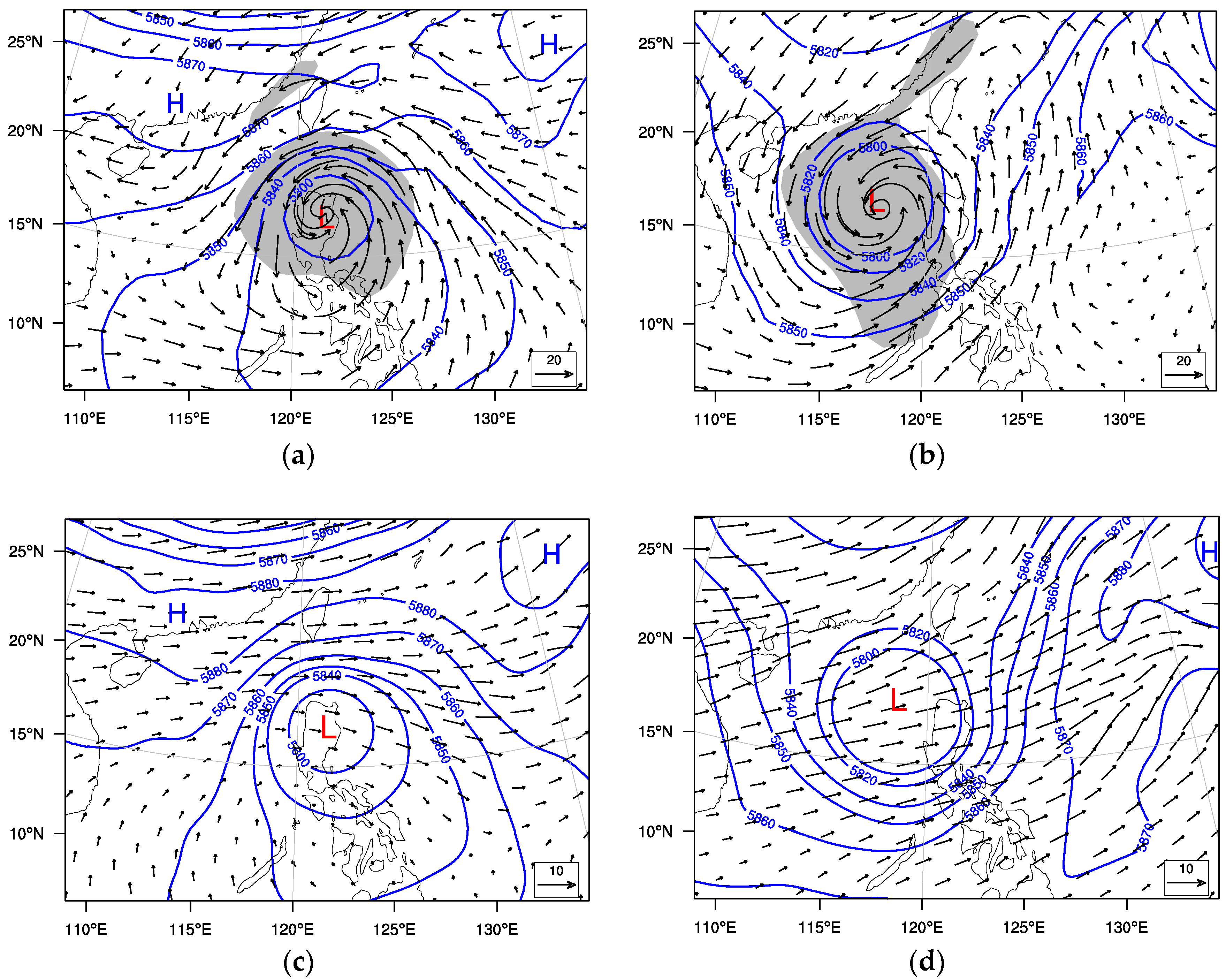
3.1. Sensitivity Tests
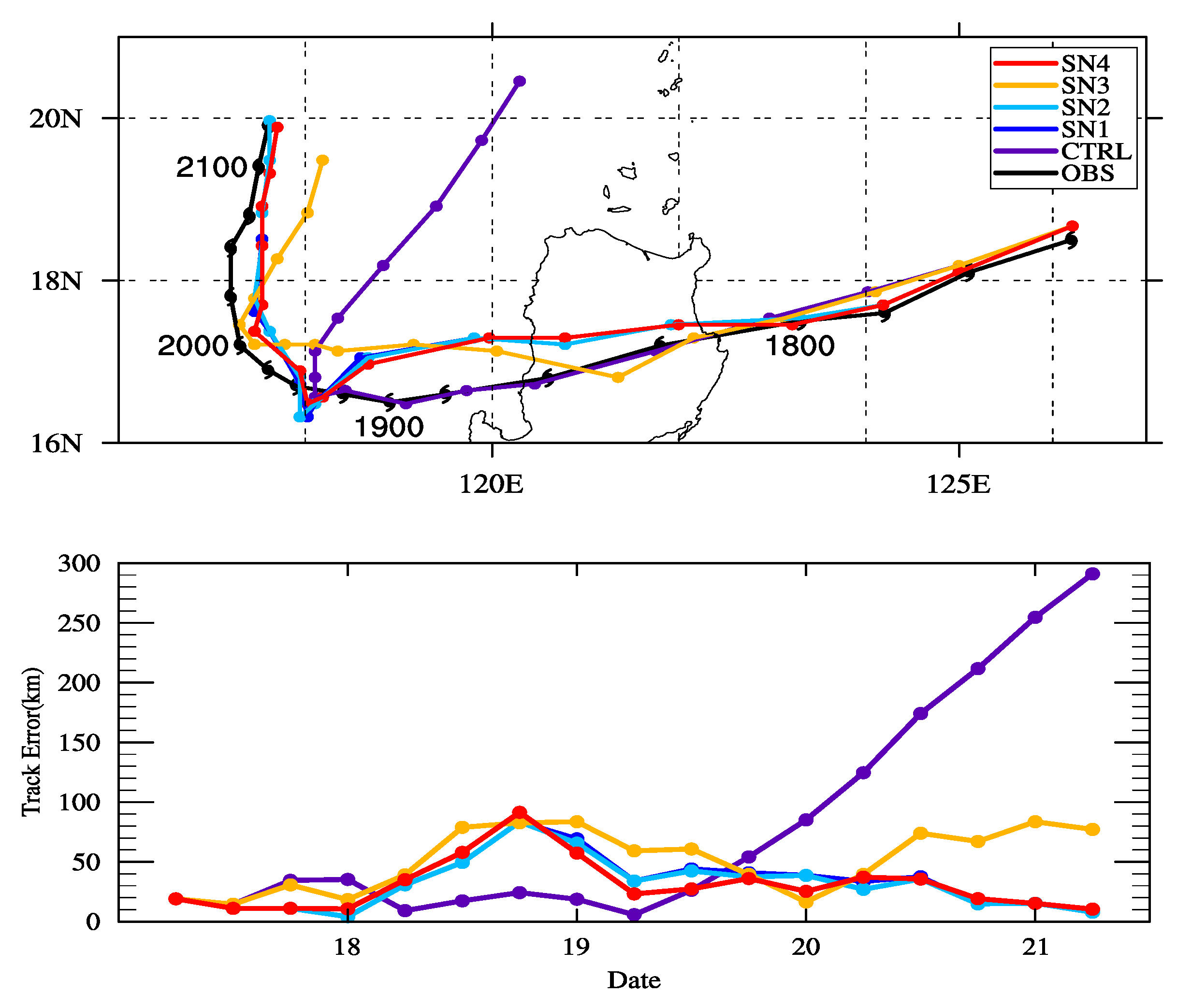
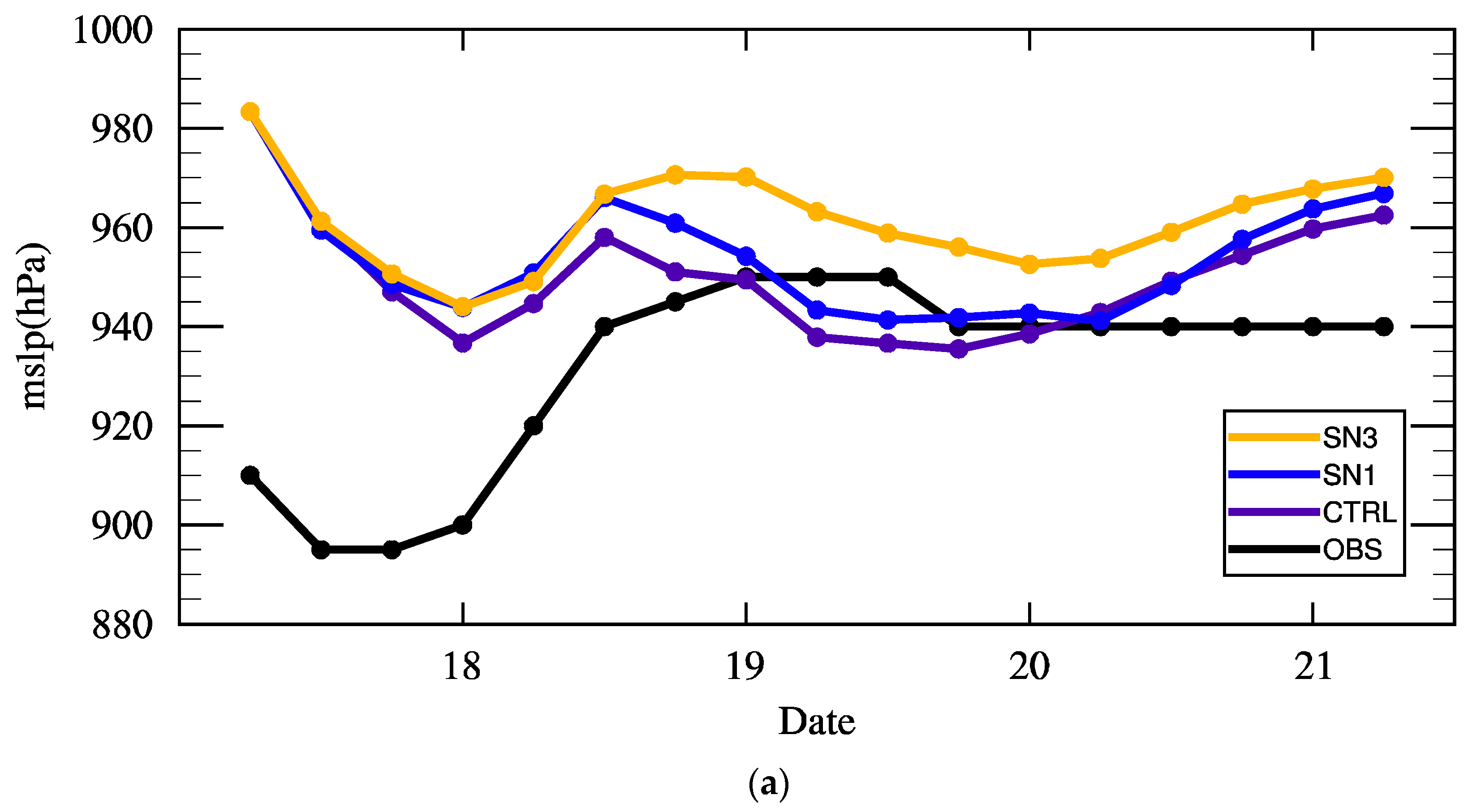
3.2. Simulation Results
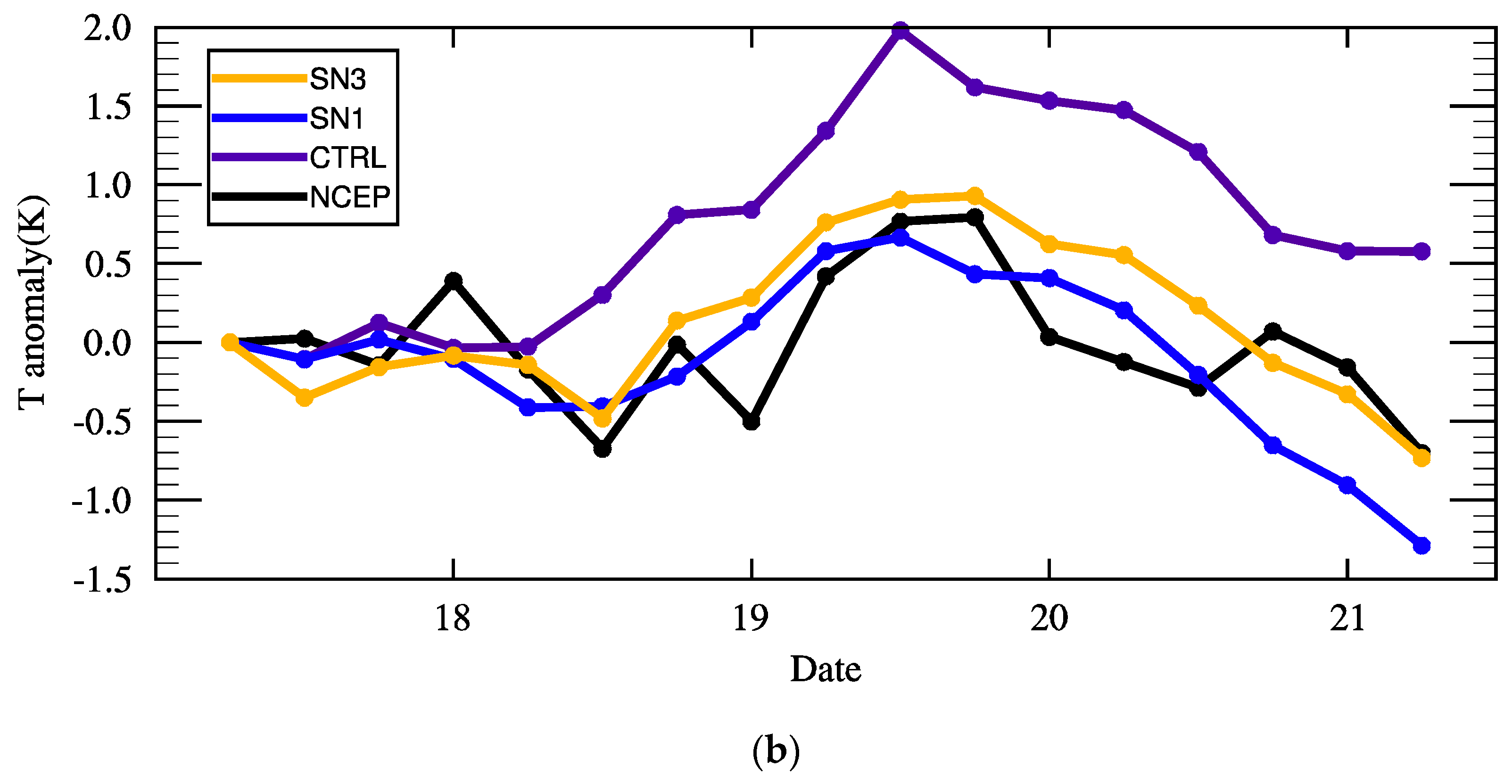
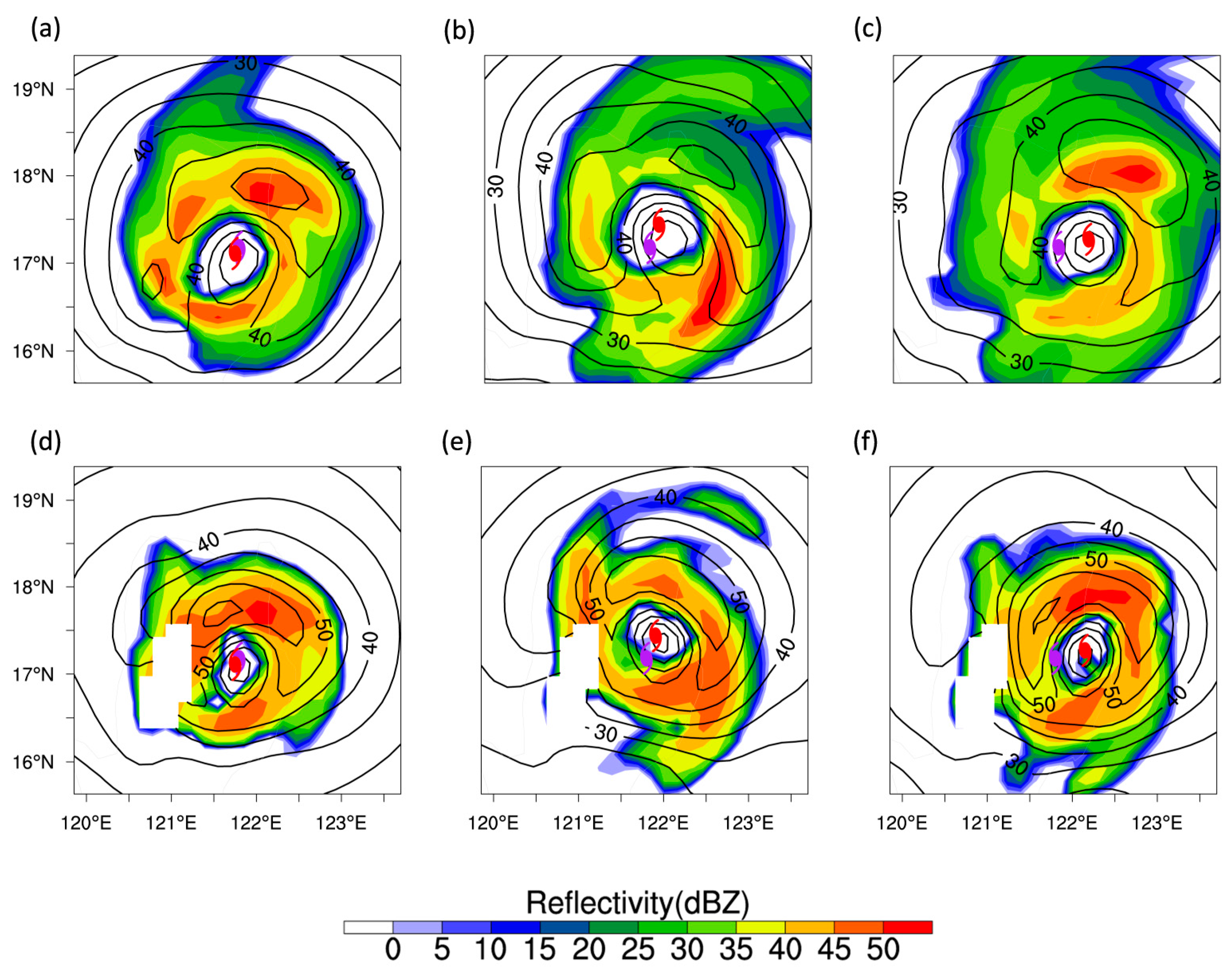
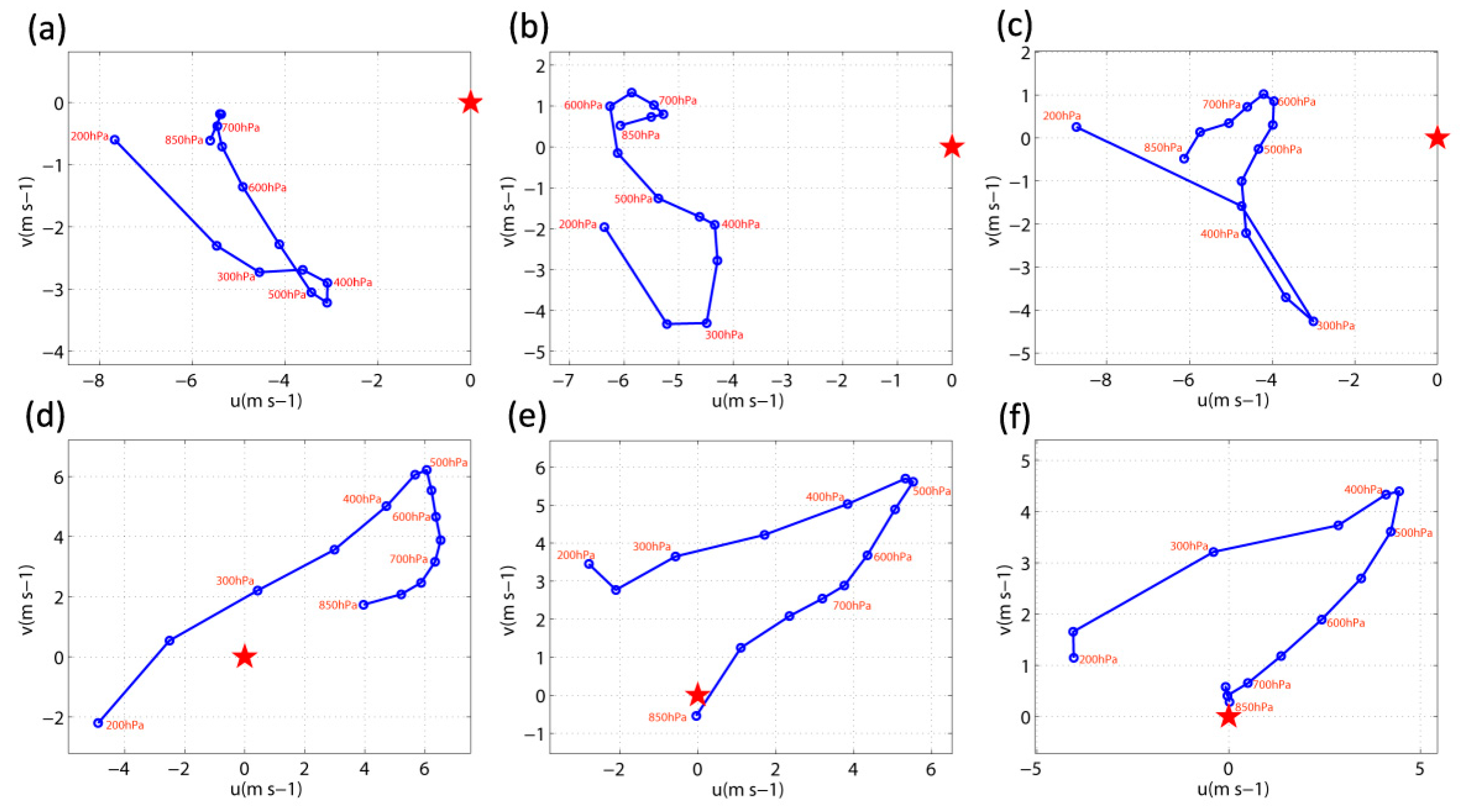
4. Analysis of the Influence of Environmental Variables
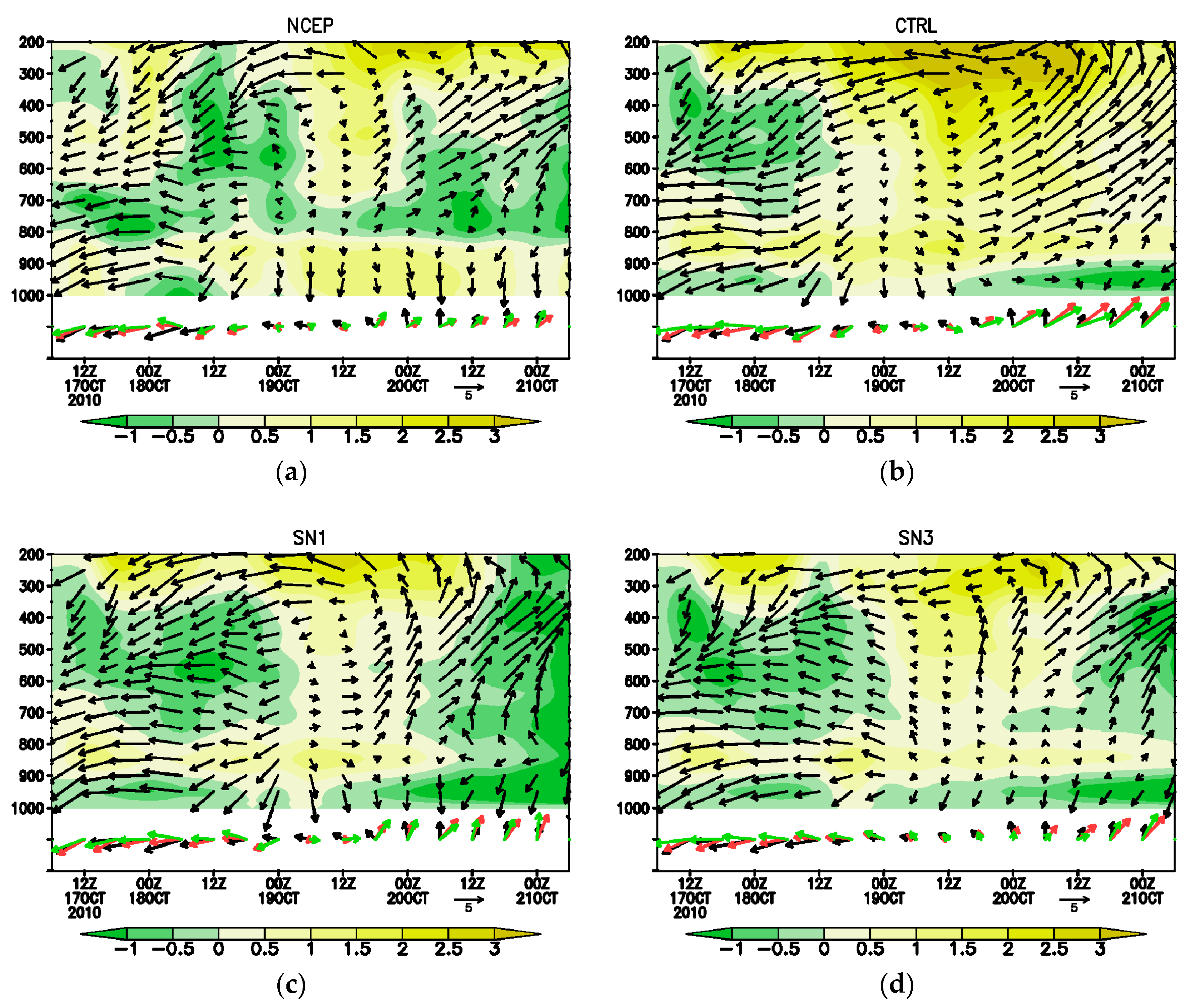
4.1. Effect on the Overall Typhoon System
4.2. Interaction with the Inner Structure of the Typhoon
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rappaport, E.N.; Franklin, J.L.; Avila, L.A.; Baig, S.R.; Beven, J.L.; Blake, E.S.; Burr, C.A.; Jiing, J.G.; Juckins, C.A.; Knabb, R.D.; et al. Advances and challenges at the national hurricane center. Weather Forecast. 2008, 24, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, T.J.J.; Davis, C.A. Diagnosing forecast errors in tropical cyclone motion. Mon. Weather Rev. 2013, 141, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel, R.M.; Sawada, T.; Iwasaki, T. Impacts of Surface Drag Coefficient and Planetary Boundary Layer Schemes on the Structure and Energetics of Typhoon Megi (2010) during Intensification. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 94, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ping, F.; Chen, J.; Xu, L. A simulation study on the rapid intensification of Typhoon Megi (2010) in vertical wind shear. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2016, 17, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y. A Numerical Study of Typhoon Megi (2010). Part I: Rapid Intensification. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieu, C.Q.; Nguyen, T.M.; Hoang, M.T.; Ngo-Duc, T. Sensitivity of the Track and Intensity Forecasts of Typhoon Megi (2010) to Satellite-Derived Atmospheric Motion Vectors with the Ensemble Kalman Filter. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 1794–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Qian, Y.K.; Lai, Z.; Hao, S.; Chen, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Chan, J.C.; Zhou, H.; et al. On the mechanisms of the recurvature of super typhoon Megi. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Zhang, F.; Green, B.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X. Probabilistic evaluation of the dynamics and prediction of Supertyphoon Megi (2010). Weather Forecast. 2013, 28, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.L.; Fei, J.F.; Huang, X.G.; Cheng, X.P.; Ding, J.L.; He, Y.Q. A numerical study on the combined effect of midlatitude and low-latitude systems on the abrupt track deflection of Typhoon Megi (2010). Mon. Weather Rev. 2015, 142, 2483–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.L.; Gray, W.M. Tropical cyclone movement and surrounding flow relationships. Mon. Weather Rev. 1982, 110, 1354–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wu, L. Sudden track changes of tropical cyclones in monsoon gyres: Full-physics, idealized numerical experiments. J. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 72, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, K.M.; Paegle, J.; Horel, J.D. Sensitivity of a spectrally filtered and nudged limited-area model to outer model options. Mon. Weather. Rev. 1996, 124, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, H.V.; Langenberg, H.; Feser, F. A spectral nudging technique for dynamical downscaling purposes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 3664–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, T.R.; Sirutis, J.J.; Garner, S.T.; Held, I.M.; Tuleya, R.E. Simulation of the recent multidecadal increase of atlantic hurricane activity using an 18-km-grid regional model. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1549–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.; Jin, C.; Lee, D.; Kuo, Y. Impact of intermittent spectral nudging on regional climate simulation using weather research and forecasting model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feser, F.; Storch, H.V. Regional modelling of the western pacific typhoon season 2004. Meteorol. Z. 2008, 17, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tang, J.P.; Fang, J. High-resolution numerical simulation of typhoon Longwang (2005) with the spectrum nudging technique. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2015, 21, 311–325. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, H.M. Improving simulation of a tropical cyclone using dynamical initialization and large-scale spectral nudging: A case study of typhoon megi (2010). J. Meteorol. Res. 2013, 27, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, D.; Lee, D. Reduction of systematic errors in regional climate simulations of the summer monsoon over East Asia and the western North Pacific by applying the spectral nudging technique. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 114, 14108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcikowska, M.; Feser, F. The influence of spectral nudging on typhoon formation in regional climate models. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 014024. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, D.K. Impact of spectral nudging on the downscaling of tropical cyclones in regional climate simulations. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2016, 33, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, B.; Miguez-Macho, G. The impact of wave number selection and spin-up time in Spectral Nudging. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 1772–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert-Frisius, M.; Feser, F.; von Storch, H.; Rast, S. Optimal Spectral Nudging for Global Dynamical Downscaling. Mon. Weather Rev. 2017, 145, 909–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguez-Macho, G.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Robock, A. Spectral nudging to eliminate the effects of domain position and geometry in regional climate model simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 1025–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, F.D.J.; Houze, R.A.J.; Gamache, J.F. Dual-aircraft investigation of the inner core of hurricane norbert. Part I: Kinematic structure. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 3221–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.S. Preface some problems of typhoon study. J. Nanjing Univ. 2007, 43, 567–571. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Cui, X.P.; Gao, S.T.; Huang, Y.J. Cause analysis of sudden track change of Typhoon Megi. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 38, 658–669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, D.L.; Carton, J.; Atlas, R. On the rapid intensification of hurricane wilma (2005). Part I: Model prediction and structural changes. Weather Forecast. 2011, 26, 885–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, G.J. Tropical cyclone motion: Environmental interaction plus a beta effect. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 328–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, L.E.; Elsberry, R.L. Analytical tropical cyclone asymmetric circulation for barotropic model initial conditions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1992, 120, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Y. A study on typhoon movement. I: The effect of diabatic heating and horizontal temperature distribution. J. Trop. Meteorol. 1995, 1, 1–9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, R.; Chen, S.; Tenerelli, J.; Willoughby, H. A numerical study of the impact of vertical shear on the distribution of rainfall in hurricane bonnie (1998). Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.L.; Lord, S.J.; Feuer, S.E.; Marks, F.D. The kinematic structure of hurricane gloria (1985) determined from nested analyses of dropwindsonde and doppler radar data. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2433–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.L.M.; Chan, J.C.L. Tropical cyclone intensity in vertical wind shear. J. Atmos. Sci. 2004, 61, 1859–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.C. The evolution of vortices in vertical shear. I: Initially barotropic vortices. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 121, 821–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Holland, G.J. Tropical cyclone motion and evolution in vertical shear. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 3313–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, W.M.; Ritchie, E.A. Effects of environmental flow upon tropical cyclone structure. Mon. Weather Rev. 1999, 127, 2044–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Lu, H.C.; Zhang, D.L. The disgnoses of quasi-balanced flows in asymmetric intense hurricane. Chin. J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 657–677. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Microphysics | WSM6 |
|---|---|
| Longwave Radiation | RRTM |
| Shortwave Radiation | Dudhia |
| Surface Layer | Monin-Obukhov |
| Land Surface | Noah |
| Planetary Boundary layer | MYNN2.5 |
| Cumulus Parameterization | Kain-Fritsch |
| Tests | Variables | Height Range | Wavenumbers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | No | No | No |
| SN1 | (u, v) | all levels | Ja = 4, Ka = 3 |
| SN2 | (u, v) Φ | all levels | Ja = 4, Ka = 3 |
| SN3 | Θ | all levels | Ja = 4, Ka = 3 |
| SN4 | (u, v) Φ θ | all levels | Ja = 4, Ka = 3 |
| Tests | 0–24 h | 0–48 h | 0–72 h | 0–96 h | Landfall Period | Deflection Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTRL | 23 | 20 | 37 | 86 | 17 | 82 |
| SN1 | 15 | 34 | 36 | 32 | 53 | 39 |
| SN2 | 15 | 33 | 35 | 31 | 53 | 37 |
| SN3 | 25 | 47 | 44 | 52 | 69 | 47 |
| SN4 | 17 | 35 | 34 | 31 | 60 | 32 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Zhong, W. The Use of a Spectral Nudging Technique to Determine the Impact of Environmental Factors on the Track of Typhoon Megi (2010). Atmosphere 2017, 8, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120257
Guo X, Zhong W. The Use of a Spectral Nudging Technique to Determine the Impact of Environmental Factors on the Track of Typhoon Megi (2010). Atmosphere. 2017; 8(12):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120257
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xingliang, and Wei Zhong. 2017. "The Use of a Spectral Nudging Technique to Determine the Impact of Environmental Factors on the Track of Typhoon Megi (2010)" Atmosphere 8, no. 12: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120257
APA StyleGuo, X., & Zhong, W. (2017). The Use of a Spectral Nudging Technique to Determine the Impact of Environmental Factors on the Track of Typhoon Megi (2010). Atmosphere, 8(12), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8120257





