Impact of Madden–Julian Oscillation upon Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China: Observations and Predictability in CFSv2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Observational Data
2.2. Forecast Data
2.3. Methods
3. Impact of MJO upon Extreme Rainfall
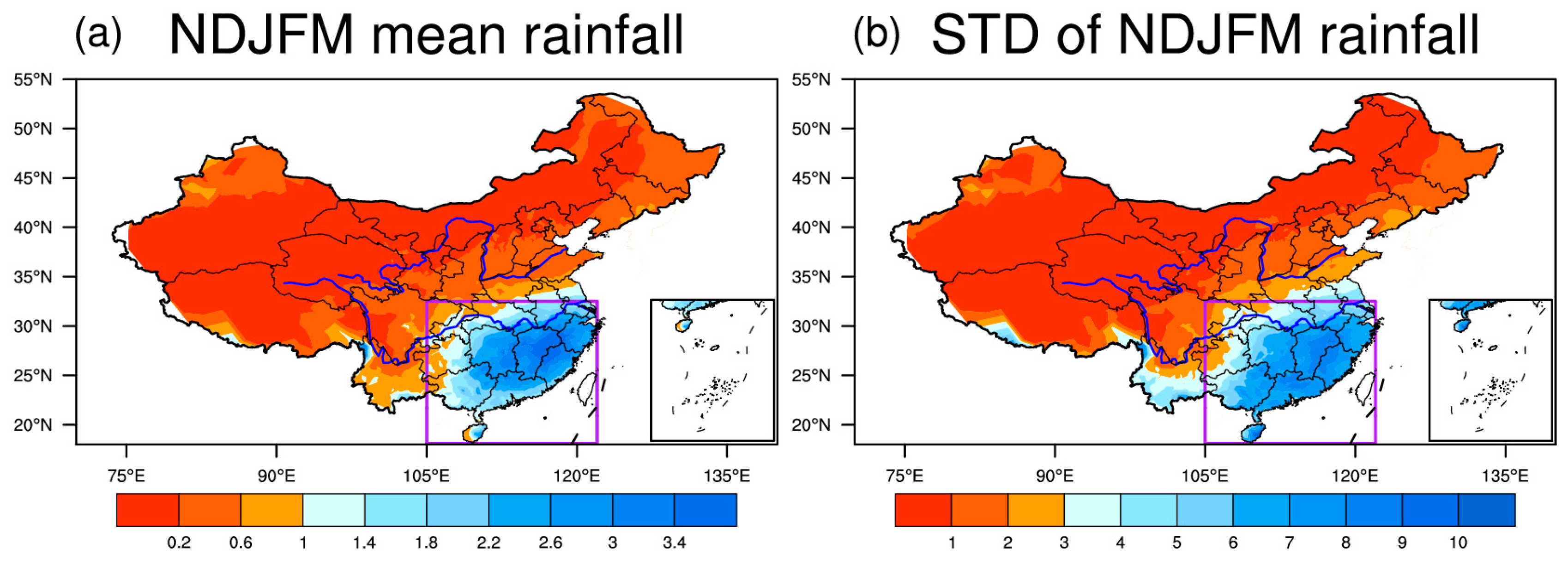
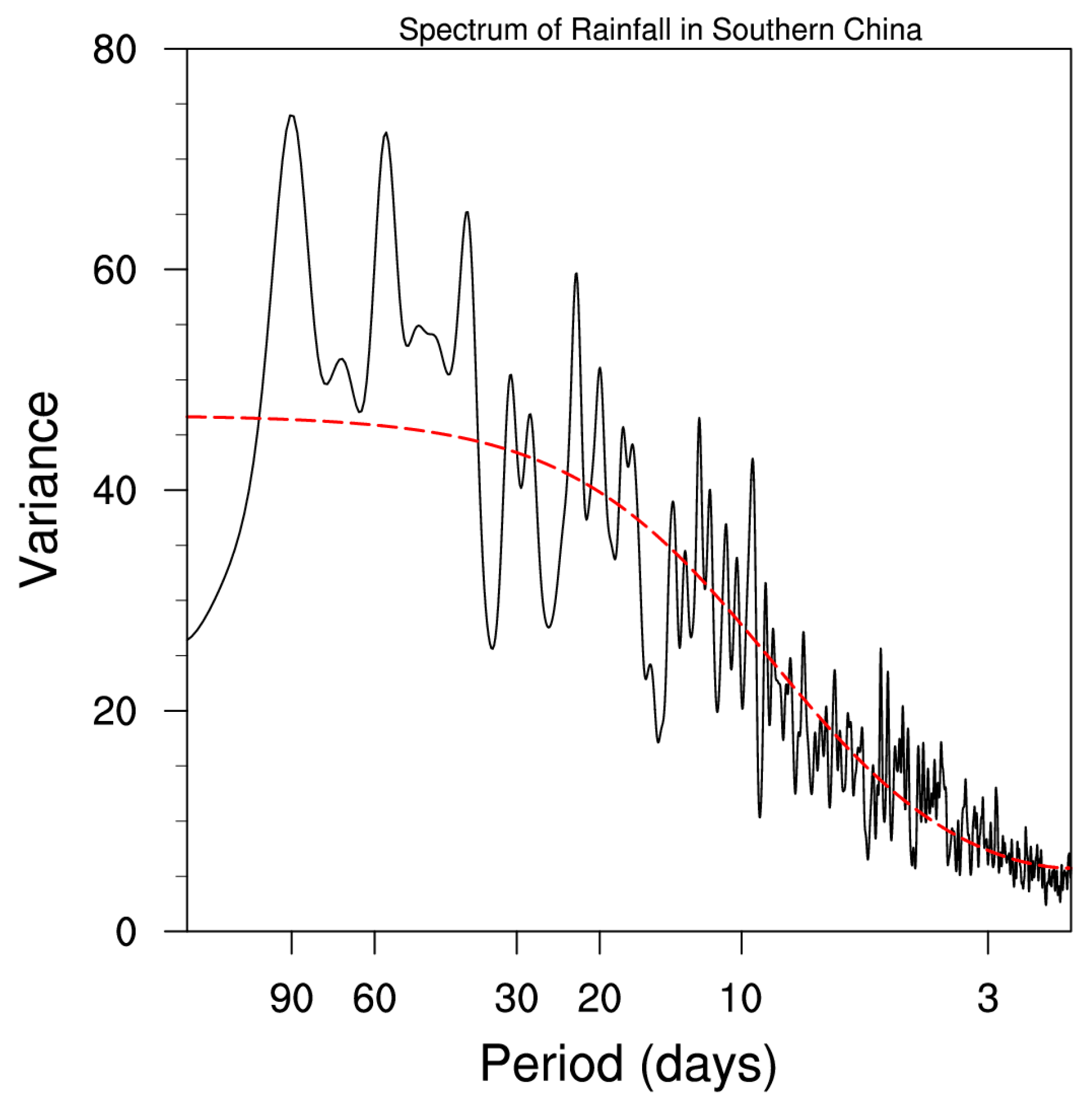
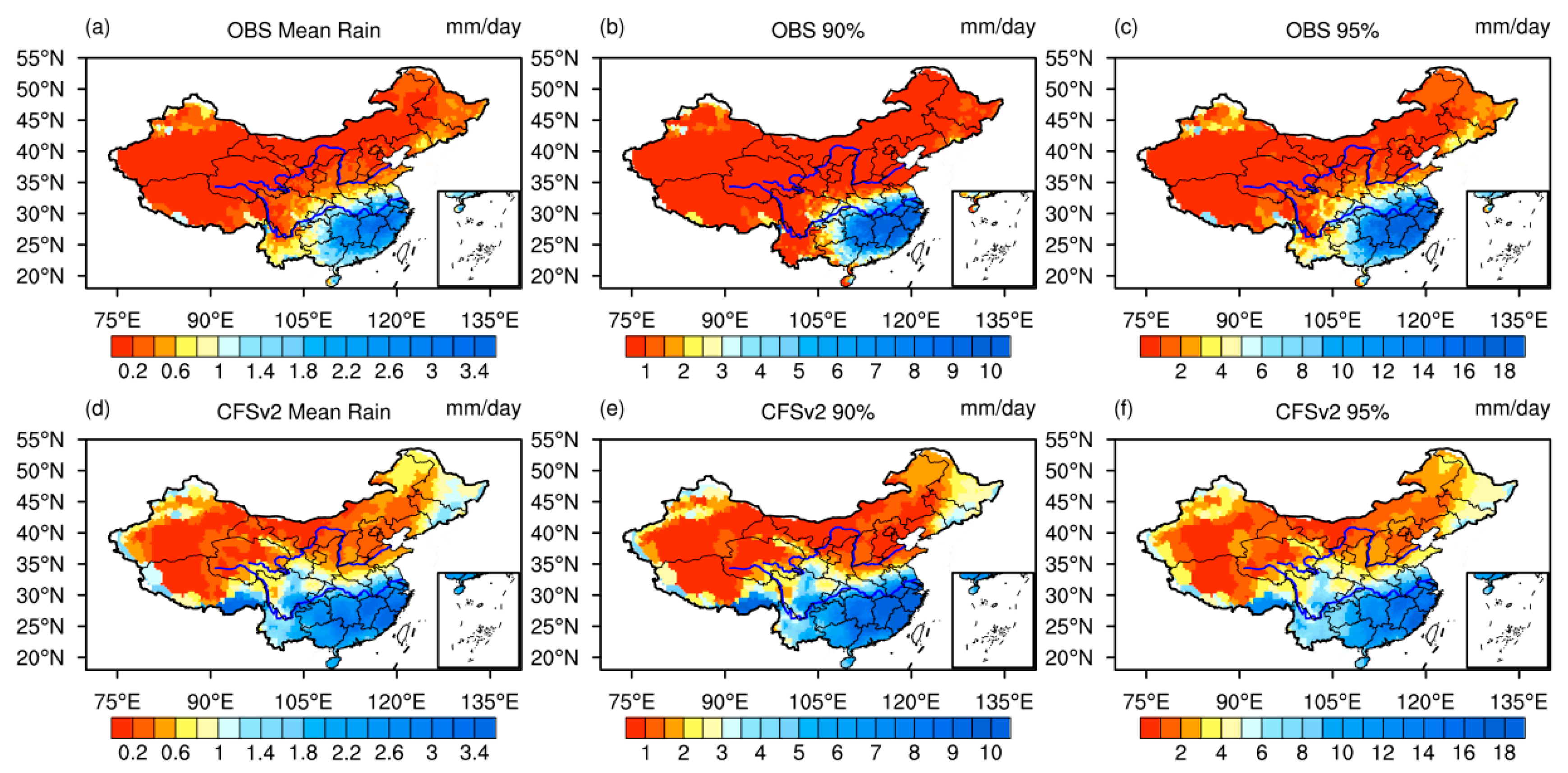
3.1. Rainfall Variability in China during the Winter
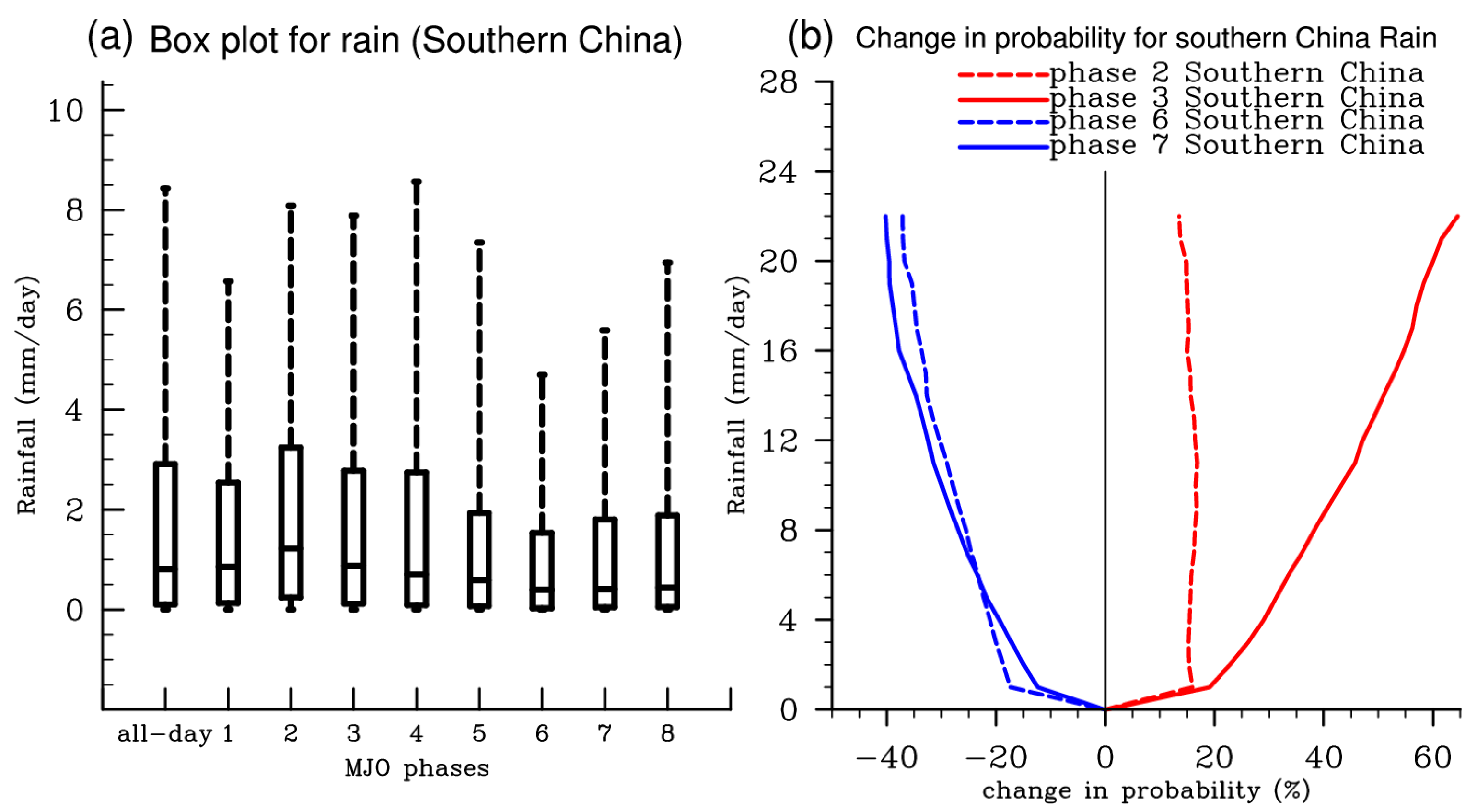
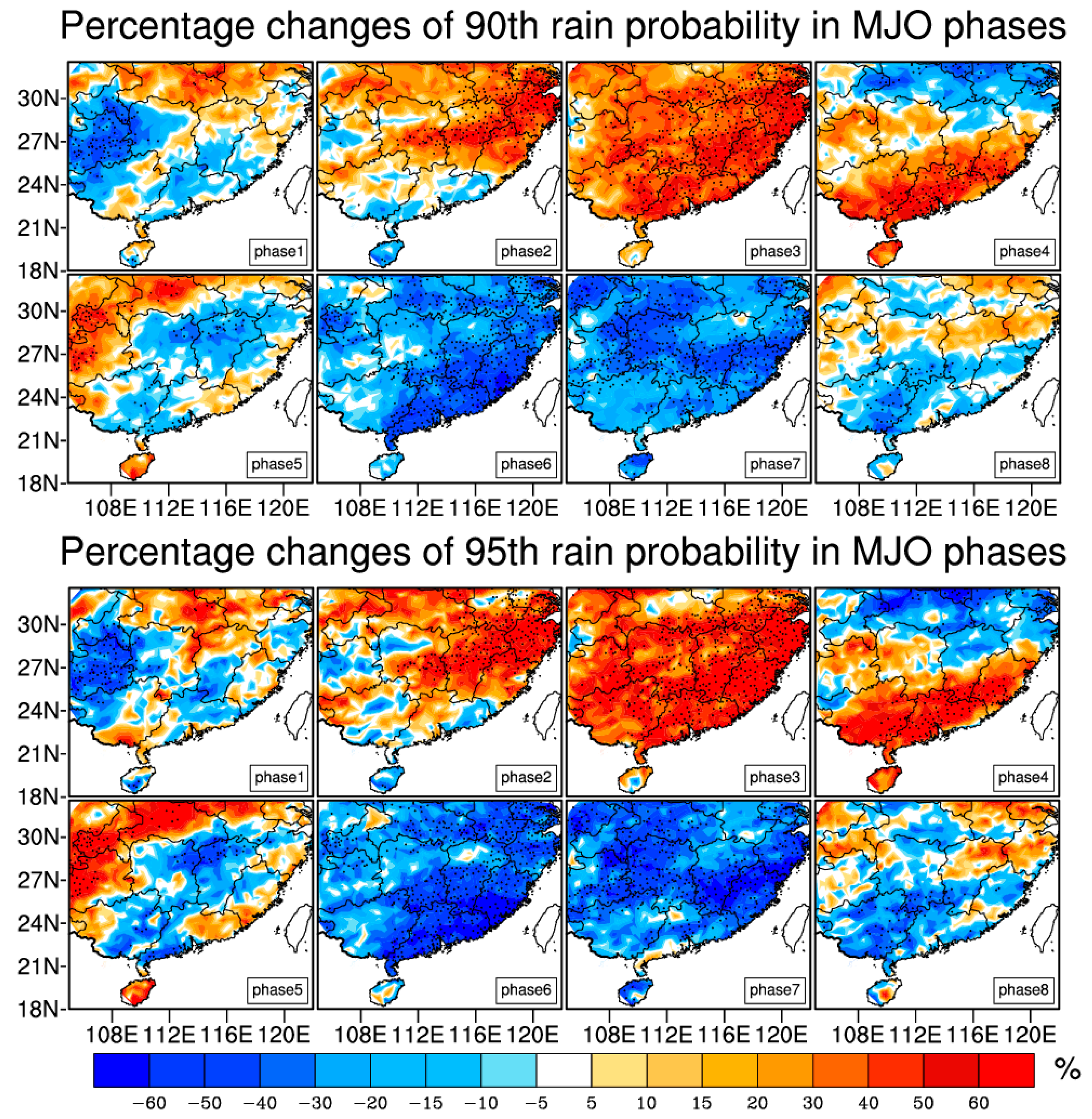
3.2. Modulations of MJO for Extreme Rainfall
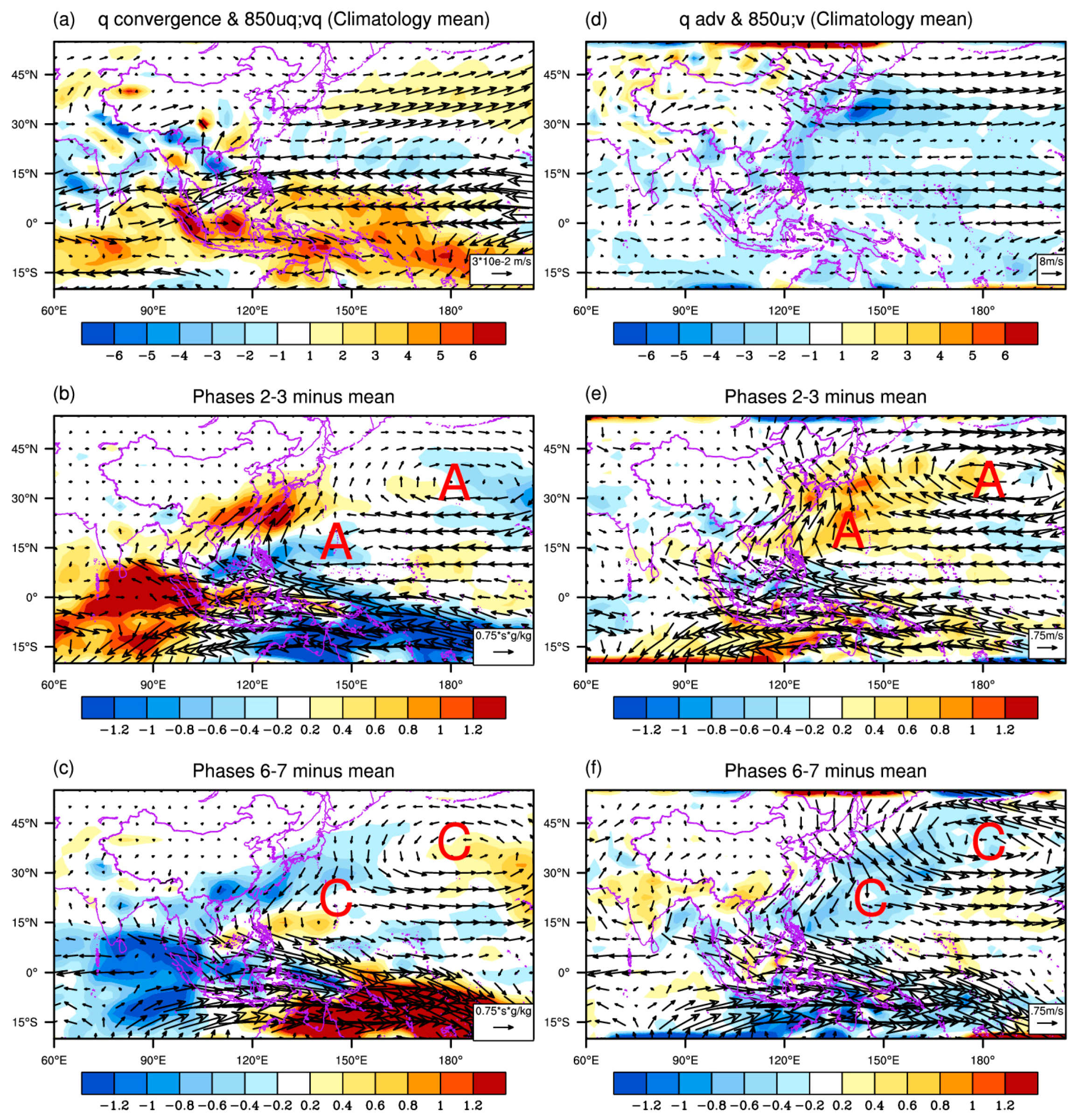
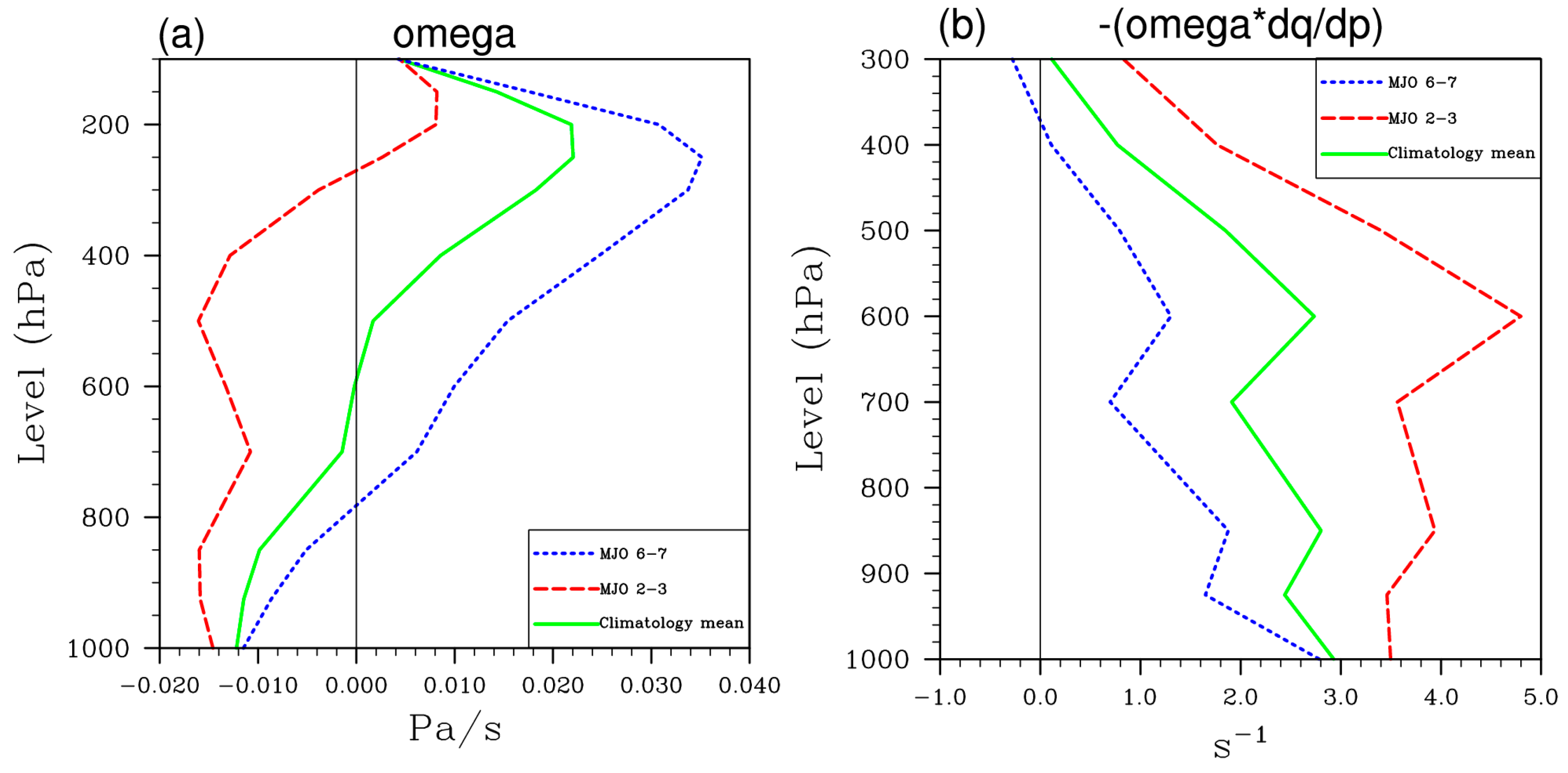
3.3. Physical Basis of Extreme Rainfall Changes
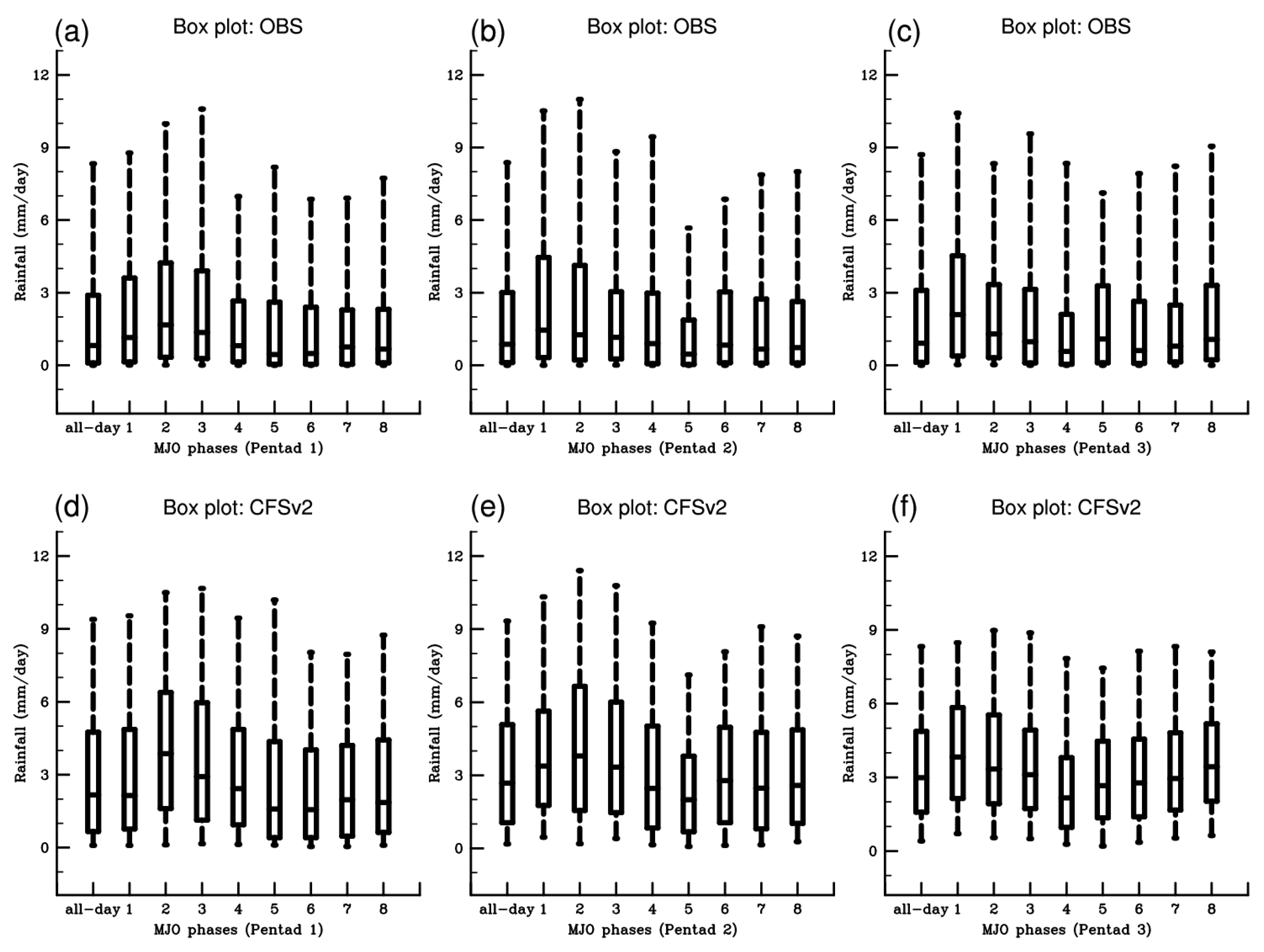
4. Predictability of Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China
5. Summary and Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, P.; Liu, J. Extreme weather/climate events and disaster prevention and mitigation under global warming background. Eng. Sci. 2012, 9, 55–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, L. The Features of Catastrophic Flood over Changjiang River Basin during the Summer of 1998 and Cause Exploration. Clim. Environ. Res. 1998, 4, 13–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Yang, H.; Gu, W. Cause of Severe Weather with Cold Air, Freeezing Rain and Snow over South China in January 2008. Clim. Environ. Res. 2008, 13, 113–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Liang, X. Possible Impacts of the MJO on the Severe Ice-Snow Weather in November of 2009 in China. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2011, 5, 639–648. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Li, J.-P. Impacts and mechanism of diabatic heating on atmospheric perturbation potential energy. Chin. J. Geophys. Chin. Ed. 2013, 56, 3255–3269. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Liang, P. Extended Range Foreeast Basing on MJO. Meteorol. Mon. 2010, 7, 111–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Detection of a 40–50 Day Oscillation in the Zonal Wind in the Tropical Pacific. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Description of Global-Scale Circulation Cells in the Tropics with a 40–50 Day Period. J. Atmos. Sci. 1972, 29, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Rui, H. Synoptic climatology of transient tropical intraseasonal convection anomalies: 1975–1985. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1990, 44, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.A.; Julian, P.R. Observations of the 40–50-Day Tropical Oscillation—A Review. Mon. Weather Rev. 1994, 122, 814–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Madden-Julian Oscillation. Rev. Geophys. 2005, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pan, J.; Song, J. Progress on the MJO Research in Recent Years. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 37, 229–252. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Recent Advance in Understanding the Dynamics of the Madden-Julian Oscillation. Acta. Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 28, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, E.D.; Hartmann, D.L. Modulation of eastern North Pacific hurricanes by the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Chen, D. Variation of tropical cyclone activity in the South Indian Ocean: El Nino-Southern Oscillation and Madden-Julian Oscillation effects. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 5225–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paegle, J.N.; Byerle, L.A.; Mo, K.C. Intraseasonal modulation of South American summer precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2000, 128, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C. Occurrence of extreme precipitation events in California and relationships with the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 3576–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, N.A.; Vecchi, G.A. The influence of the Madden-Julian oscillation on precipitation in Oregon and Washington. Weather For. 2003, 18, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, M.; Wheeler, M.; Lyon, B.; Cullen, H. Modulation of daily precipitation over southwest Asia by the Madden-Julian oscillation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2005, 133, 3579–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.C.; Hendon, H.H.; Cleland, S.; Meinke, H.; Donald, A. Impacts of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on Australian Rainfall and Circulation. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 1482–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Zeng, Q. Impact of the Madden–Julian Oscillation on Summer Rainfall in Southeast China. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, P.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, H. Impact of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on Pre-flood Season Precipitation in South China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 3, 560–570. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, M.C.; Hendon, H.H. An all-season real-time multivariate MJO index: Development of an index for monitoring and prediction. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 1917–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, X. Mechanism responsible for the impact of Madden-Julian Oscillation on the wintertime rainfall over eastern China. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 2010, 30, 684–693. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, H. On the Modulation of MJO to the Precipitation of Southeast China in Winter Season. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Peking 2010, 2, 207–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Chen, L.; Ren, F.; Li, C. Impacts of the MJO on Winter Rainfall and Circulation in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2011, 28, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-L.; Shen, Y. A New Look at Impacts of MJO on Weather and Climate in China. Adv. Meteorol. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 97–105. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, P.; Rahmat, R.; Cheong, W.K.; Wallace, E. Influence of Madden-Julian Oscillation on Southeast Asia rainfall extremes: Observations and predictability. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Ha, K.J. Influence of boreal summer intraseasonal oscillation on rainfall extremes in southern China. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.D. Madden-Julian Oscillation Bridging Weather and Climate. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1849–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.D. Uncertainty of Initial State as a Factor in the Predictability of Large Scale Atmospheric Flow Patterns. Tellus 1957, 9, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. A study of the predictability of a 28-variable atmospheric model. Tellus 1965, 17, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Atmospheric predictability experiments with a large numerical model. Tellus 1982, 34, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N. Extended-range atmospheric prediction and the Lorenz model. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1993, 74, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Dool, H.M. Long-range weather forecasts through numerical and empirical methods. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 1994, 20, 247–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T.N. Predicting uncertainty in forecasts of weather and climate. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2000, 63, 71–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, J.; Anderson, J.; Baumhefner, D.; Brankovic, C.; Chang, Y.; Kalnay, E.; Marx, L.; Palmer, T.; Paolino, D.; Ploshay, J.; et al. Dynamical seasonal prediction. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2000, 81, 2593–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.; Weickmann, K.; Dole, R.; Schubert, S.; Alves, O.; Jones, C.; Newman, M.; Pan, H.L.; Roubicek, A.; Saha, S. The experimental MJO prediction project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 87, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.H.; Wang, W.-Q.; Gottschalck, J.; Zhang, Q.; Schemm, J.-K.E.; Higgins, W.R.; Kumar, A. Evaluation of MJO Forecast Skill from Several Statistical and Dynamical Forecast Models. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2372–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Lee, J.Y.; Hsu, P.C.; Taniguchi, H.; Wang, B.; Wang, W.Q.; Weaver, S. Multi-model MJO forecasting during DYNAMO/CINDY period. Clim. Dynam. 2013, 41, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, W.Q.; Hung, M.P.; Weaver, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Fu, X.H. MJO prediction in the NCEP Climate Forecast System version 2. Clim. Dynam. 2014, 42, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Zhang, P. Progresses of MJO Prediction Researches and Developments. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2015, 26, 658–668. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.B.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, X.W. MJO ensemble prediction in BCC-CSM1.1(m) using different initialization schemes. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2016, 9, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, C.B.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, X.W. Prediction of primary climate variability modes at the Beijing Climate Center. Acta. Meteorol. Sin. 2017, 31, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.B.; Ren, H.L.; Song, L.C.; Wu, J. Madden-Julian Oscillation simulated in BCC climate models. Dynam. Atmos. Ocean. 2015, 72, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.L.; Zuo, J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, L.; Li, Q. MJO prediction skill, predictability, and teleconnection impacts in the Beijing Climate Center Atmospheric General Circulation Model. Dynam. Atmos. Ocean. 2016, 75, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalnay, E. NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.; Chuang, H.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The Ncep Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.D.; Dong, M. Seasonality in the Madden-Julian oscillation. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 3169–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.B.; Alexander, L.; Hegerl, G.C.; Jones, P.; Tank, A.K.; Peterson, T.C.; Trewin, B.; Zwiers, F.W. Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and precipitation data. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2011, 2, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lin, H.; Wu, Z. Another look at influences of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on the wintertime East Asian weather. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 1284–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, P.A.; Schneider, T. The physical basis for increases in precipitation extremes in simulations of 21st-century climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14773–14777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loriaux, J.; Lenderink, G.; Siebesma, A.P. Peak precipitation intensity in relation to atmospheric conditions and large-scale forcing at midlatitudes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5471–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E.; Lau, K.M.; Stern, W.; Jones, C. Potential predictability of the Madden-Julian oscillation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ho, C.H.; Kim, B.M.; Kwon, W.T. Influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation on wintertime surface air temperature and cold surges in east Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, H.-L.; Ren, P. Impact of Madden–Julian Oscillation upon Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China: Observations and Predictability in CFSv2. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100192
Ren H-L, Ren P. Impact of Madden–Julian Oscillation upon Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China: Observations and Predictability in CFSv2. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(10):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100192
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Hong-Li, and Pengfei Ren. 2017. "Impact of Madden–Julian Oscillation upon Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China: Observations and Predictability in CFSv2" Atmosphere 8, no. 10: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100192
APA StyleRen, H.-L., & Ren, P. (2017). Impact of Madden–Julian Oscillation upon Winter Extreme Rainfall in Southern China: Observations and Predictability in CFSv2. Atmosphere, 8(10), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8100192




