Importance of Ship Emissions to Local Summertime Ozone Production in the Mediterranean Marine Boundary Layer: A Modeling Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
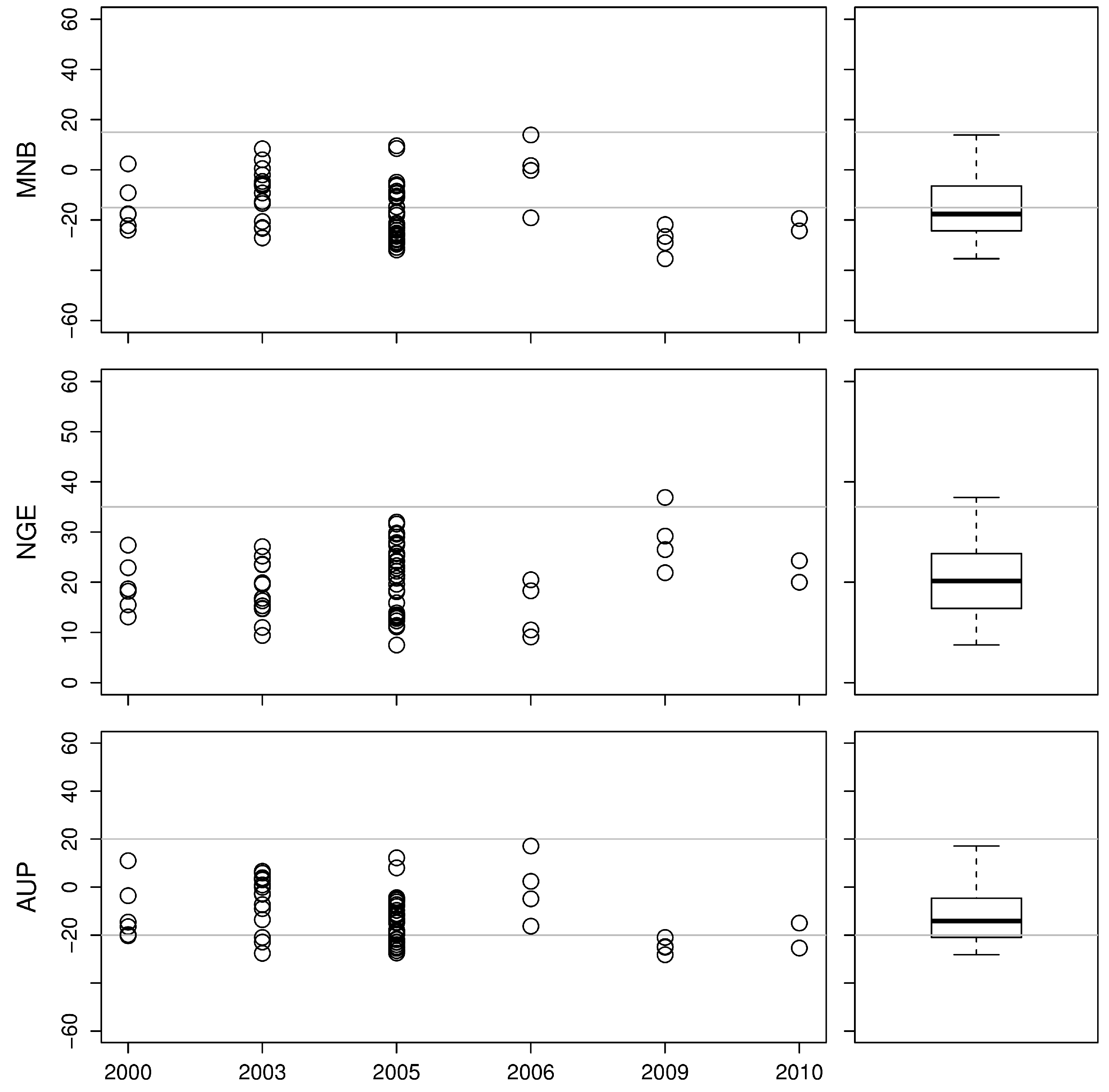
2. Measurements
| Year | Start | End | Route |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | Palermo 14 July | Civitavecchia 9 August | Strait of Messina, South of Crete, Sicily, Gulf of Naples, Sardinia |
| 2003 | Palermo 5 August | Livorno 28 August | Strait of Sicily, towards Crete, Ionian Sea, Naples, Alboran Sea |
| 2005 | Naples 17 June | Naples 3 July | Sicily, Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea Gulf of Trieste |
| 2006 | Civitavecchia 4 July | Messina 20 July | Sicily, Eastern Mediterranean, Ionian Sea |
| 2009 | Civitavecchia 4 June | Messina 30 June | Corsica, Sardinia, Naples, Strait of Sicily, Ionian Sea |
| 2010 | Naples 27 August | Palermo 12 September | Palermo Strait of Messina, Ionian sea, Gulf of Taranto, Eastern Mediterranean, Strait of Sicily |

3. Modeling
3.1. Modeling Domains
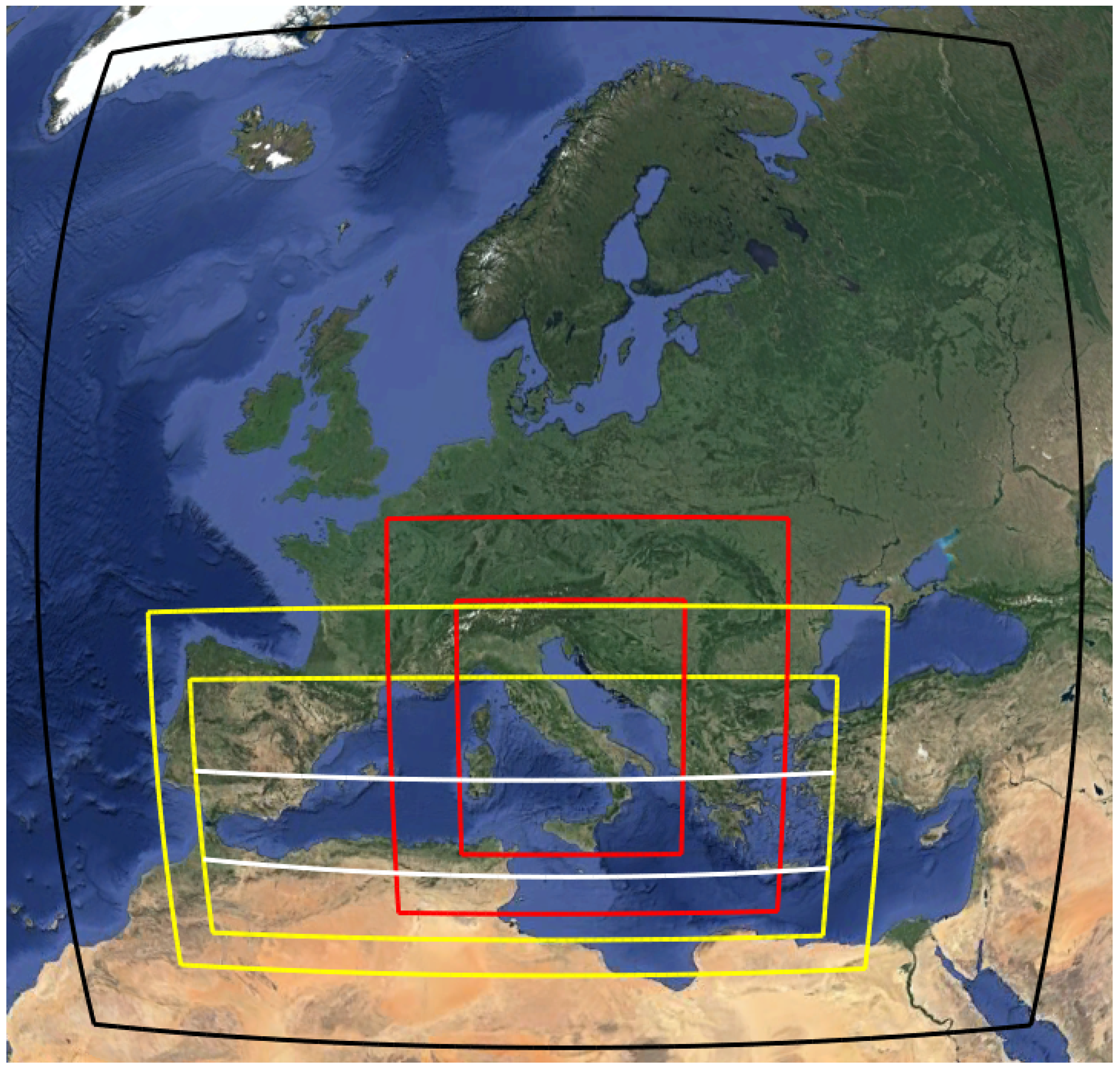
3.2. Physics, Chemistry and Initialization
3.3. Emissions
3.4. In-Plume Chemistry and Artificial Plume Dilution
3.5. The Simulations Performed
4. Results and Discussion
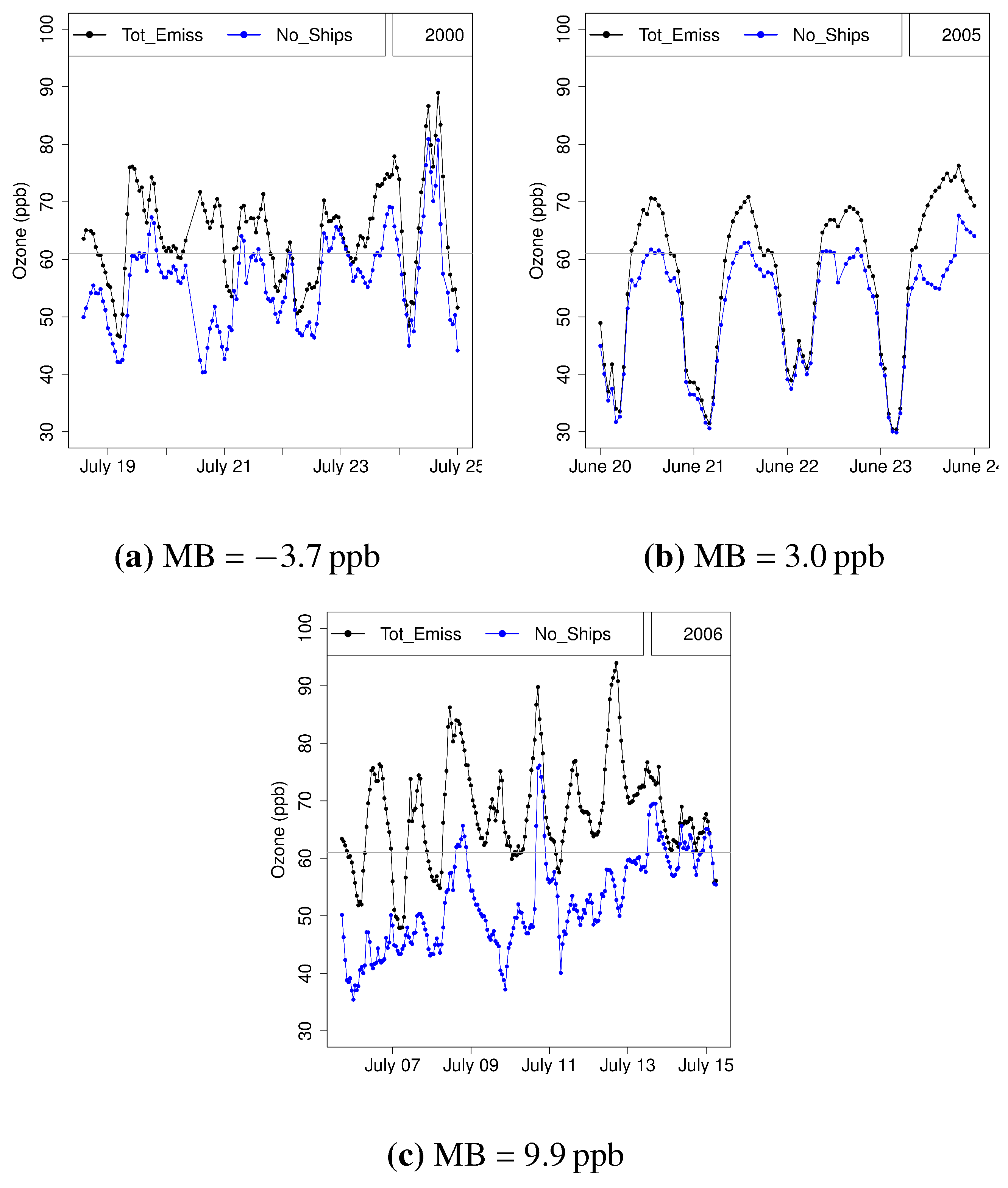
4.1. Model Validation
4.2. Ozone Concentration Validations
| Year | MB (ppb) | R | RMSE (ppb) | UF | IOA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| low | hi | low | hi | low | hi | low | hi | low | hi | |
| 2000 | −3.7 | 0.7 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 11.0 | 9.6 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.76 |
| 2003 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 14.7 | 14.7 | 0.47 | 0.48 | 0.55 | 0.54 |
| 2005 | 3.0 | 4.6 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 13.8 | 13.5 | 0.80 | 0.69 | 0.73 | 0.72 |
| 2006 | 9.9 | −8.8 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 14.5 | 14.3 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.48 | 0.49 |
| 2009 | 7.8 | 7.9 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 14.9 | 15.3 | 0.55 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 0.52 |
| 2010 | −0.7 | −1.2 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 10.7 | 10.9 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.63 |

4.3. The Influence of Ship Emission Height in the Model
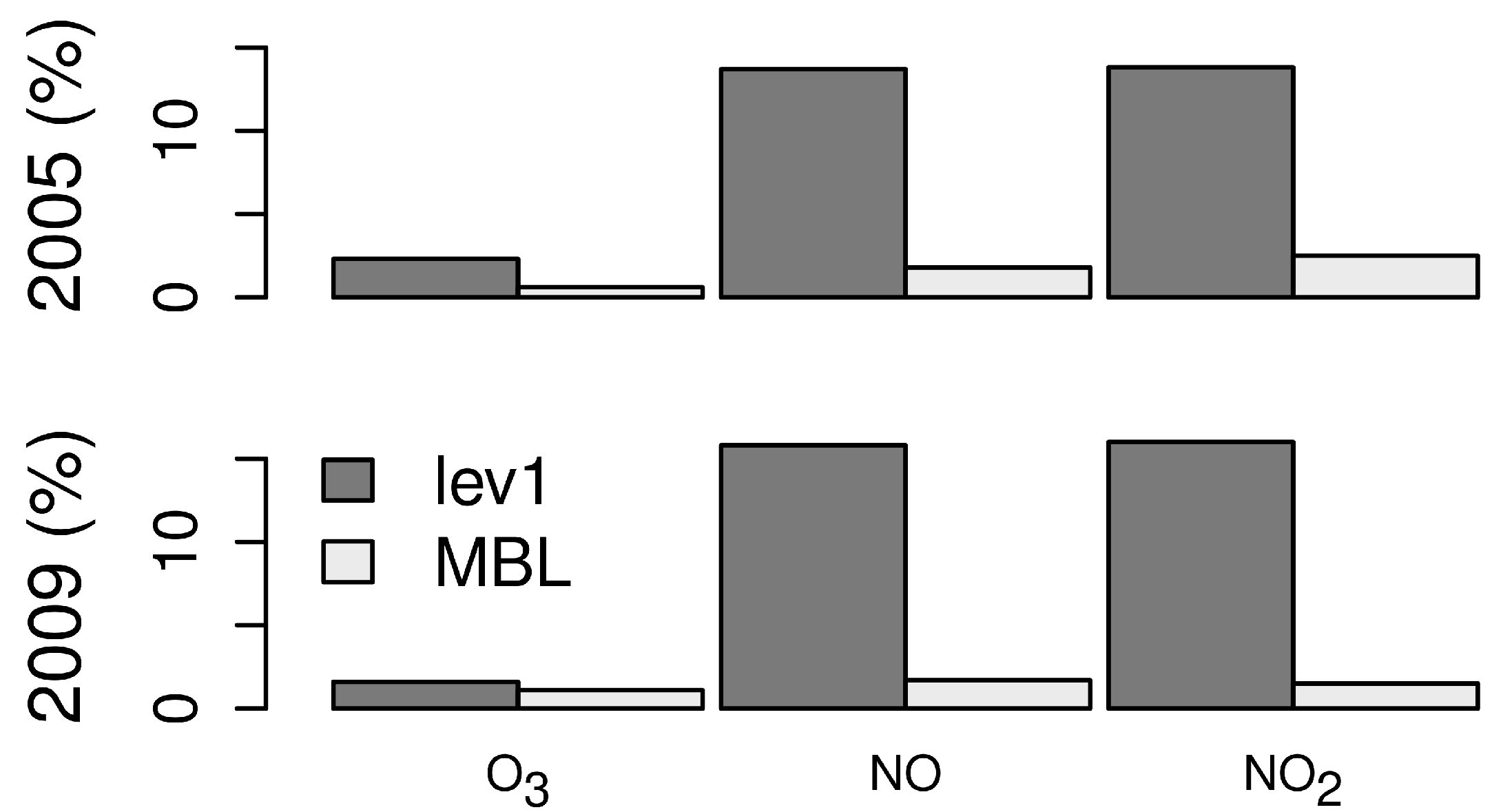
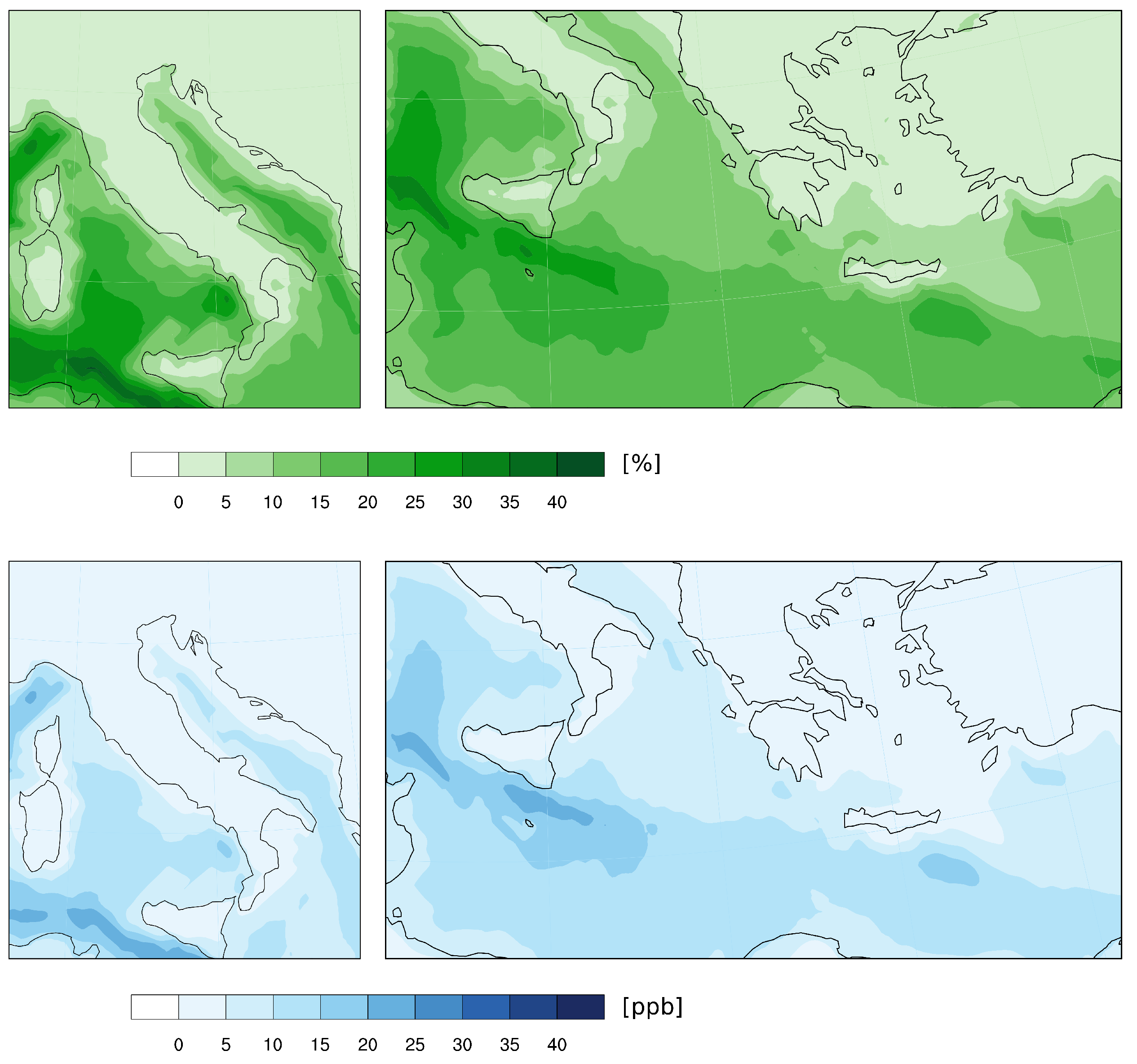
4.4. The Influence of Ship Emissions
| Year | Whole Domain | Mediterranean Sea | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O3 | NO | NO2 | O3 | NO | NO2 | |
| 2000 | 5.5 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 6.2 | 20.0 | 23.2 |
| 2003 | 7.0 | 10.3 | 11.0 | 8.2 | 24.9 | 28.9 |
| 2005 | 4.5 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 25.0 | 27.7 |
| 2006 | 5.3 | 12.2 | 13.1 | 8.3 | 26.9 | 30.9 |
| 2009 | 9.1 | 20.2 | 21.8 | 11.6 | 42.6 | 46.0 |
| 2010 | 7.7 | 15.9 | 13.8 | 9.8 | 30.1 | 32.7 |
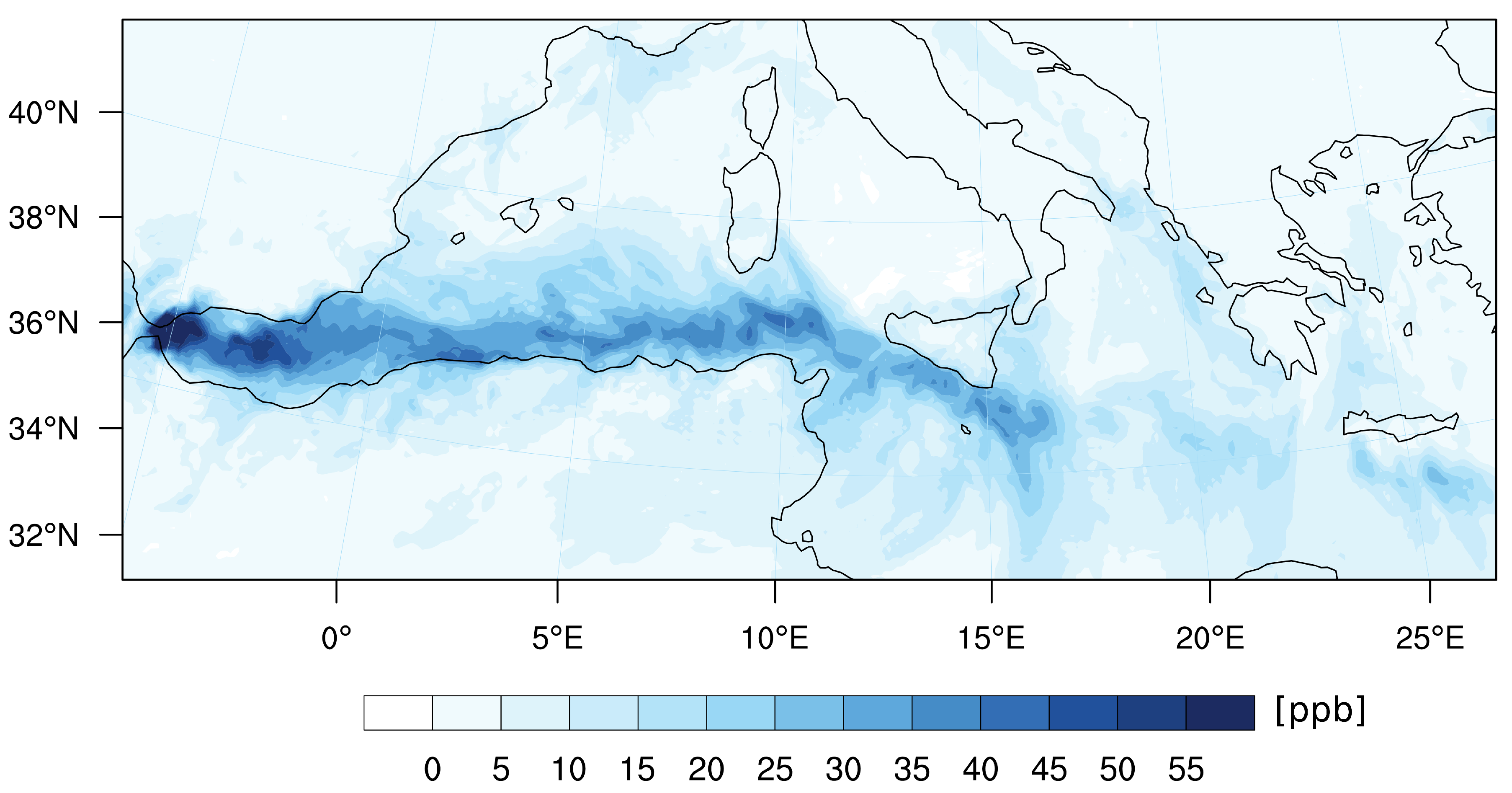

5. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary Information (PDF, 28138 KB)Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Millán, M.M.; Sanz, M.J.; Salvador, R.; Mantilla, E. Atmospheric dynamics and ozone cycles related to nitrogen deposition in the western Mediterranean. Environ. Poll. 2002, 118, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Berresheim, H.; Borrmann, S.; Crutzen, P.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Fischer, H.; Feichter, J.; Flatau, P.J.; Heland, J.; Holzinger, R.; et al. Global Air Pollution Crossroads over the Mediterranean. Science 2002, 298, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristofanelli, P.; Bonasoni, P. Background ozone in the southern Europe and Mediterranean area: Influence of the transport processes. Environ. Poll. 2009, 157, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolle, M.; Ellul, R.; Heinrich, G.; Güsten, H. A long-term study of background ozone concentrations in the central Mediterranean—Diurnal and seasonal variations on the island of Gozo. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, M.; Ellul, R.; Camilleri, L.; Güsten, H. A 10-year study of background surface ozone concentrations on the island of Gozo in the Central Mediterranean. J. Atmos. Chem. 2008, 60, 117–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Kouvarakis, G.; Vrekoussis, M.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. Ozone variability in the marine boundary layer of the eastern Mediterranean based on 7-year observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D15309. [Google Scholar]
- Velchev, K.; Cavalli, F.; Hjorth, J.; Marmer, E.; Vignati, E.; Dentener, F.; Raes, F. Ozone over the Western Mediterranean Sea—Results from two years of shipborne measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2010, 10, 6129–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adame, J.A.; Serrano, E.; Bolívar, J.P.; de la Morena, B.A. On the tropospheric ozone variations in a coastal area of southwestern Europe under a mesoscale circulation. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol. 2009, 49, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabokas, P.D.; Cammas, J.P.; Thouret, V.; Volz-Thomas, A.; Boulanger, D.; Repapis, C.C. Examination of the atmospheric conditions associated with high and low summer ozone levels in the lower troposphere over the eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10339–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kindap, T.; Im, U.; Vrekoussis, M.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Dermitzaki, E.; Unal, A.; Koçak, M.; Markakis, K.; et al. Megacities as hot spots of air pollution in the East Mediterranean. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, U.; Kanakidou, M. Summertime impacts of Eastern Mediterranean megacity emissions on air quality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 26657–26690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonasoni, P.; Stohl, A.; Cristofanelli, P.; Calzolari, F.; Colombo, T.; Evangelisti, F. Background ozone variations at Mt. Cimone Station. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 5183–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanelli, P.; Bonasoni, P.; Carboni, G.; Calzolari, F.; Casarola, L.; Sajani, S.Z.; Santaguida, R. Anomalous high ozone concentrations recorded at a high mountain station in Italy in summer 2003. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worden, H.M.; Bowman, K.W.; Kulawik, S.S.; Aghedo, A.M. Sensitivity of outgoing longwave radiative flux to the global vertical distribution of ozone characterized by instantaneous radiative kernels from Aura-TES. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, D14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, N.A.D.; Arnold, S.R.; Chipperfield, M.P.; Miles, G.; Rap, A.; Siddans, R.; Monks, S.A.; Hollaway, M.J. The Mediterranean summertime ozone maximum: Global emission sensitivities and radiative impacts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2331–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis, the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC. Available online: http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/publications_ipcc_fourth_assessment_report_wg1_report_the_physical_science_basis.htm (accessed on 24 November 2014).
- Viana, M.; Hammingh, P.; Colette, A.; Querol, X.; Degraeuwe, B.; Vlieger, I.D.; van Aardenne, J. Impact of maritime transport emissions on coastal air quality in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 90, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Köhler, H.W.; van Aardenne, J.; Lauer, A. Emissions from international shipping: 1. The last 50 years. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, D17305. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, V.; Stevenson, D.S.; Lauer, A.; Dentener, F.J.; Butler, T.; Collins, W.J.; Ellingsen, K.; Gauss, M.; Hauglustaine, D.A.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; et al. Multi-model simulations of the impact of international shipping on atmospheric chemistry and climate in 2000 and 2030. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 757–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Isaksen, I.S.; Berntsen, T.; Collins, W.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Endresen, O.; Grainger, R.G.; Moldanova, J.; Schlager, H.; Stevenson, D.S. Transport impacts on atmosphere and climate: Shipping. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 4735–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmer, E.; Langmann, B. Impact of ship emissions on the Mediterranean summertime pollution and climate: A regional model study. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4659–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J.; Green, E.H.; Kasibhatla, P.; Eyring, V.; Lauer, A. Mortality from Ship Emissions: A Global Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, V.; Bewersdorff, I.; Aulinger, A.; Quante, M. The contribution of ship emissions to air pollution in the North Sea regions. Environ. Poll. 2010, 158, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miola, A.; Ciuffo, B. Estimating air emissions from ships: Meta-analysis of modelling approaches and available data sources. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2242–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schembari, C.; Cavalli, F.; Cuccia, E.; Hjorth, J.; Calzolai, G.; Pérez, N.; Pey, J.; Prati, P.; Raes, F. Impact of a European directive on ship emissions on air quality in Mediterranean harbours. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derwent, R.G.; Stevenson, D.S.; Doherty, R.M.; Collins, W.J.; Sanderson, M.G.; Johnson, C.E.; Cofala, J.; Mechler, R.; Amann, M.; Dentener, F.J. The contribution from shipping emissions to air quality and acid deposition in Europe. AMBIO: J. Hum. Environ. 2005, 34, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dalsøren, S.B.; Eide, M.S.; Endresen, Ø.; Mjelde, A.; Gravir, G.; Isaksen, I.S.A. Update on emissions and environmental impacts from the international fleet of ships: The contribution from major ship types and ports. Atmos. Chem. .Phys. 2009, 9, 2171–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Pirrone, N. An investigation of the origins of reactive gaseous mercury in the Mediterranean marine boundary layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Sommar, J. Mercury speciation in the marine boundary layer along a 6000 km cruise path around the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.E.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Wängberg, I.; Sprovieri, F.; Pirrone, N.; Lindqvist, O. Reprint of “Seasonal and daily variation of mercury evasion at coastal and off shore sites from the Mediterranean Sea”. Marine Chem. 2007, 107, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, J.; Horvat, M.; Tessier, E.; Ogrinc, N.; Monperrus, M.; Amouroux, D.; Fajon, V.; Gibičar, D.; Žižek, S.; Sprovieri, F.; et al. Mercury speciation in surface and deep waters of the Mediterranean Sea. Marine Chem. 2007, 107, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Ceccarini, C.; Lanzillotta, E.; Gårdfeldt, K.; Sommar, J.; Horvat, M.; Logar, M.; Fajon, V.; Kotnik, J. Profiles of dissolved gaseous mercury concentration in the Mediterranean seawater. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gårdfeldt, K.; Sommar, J.; Ferrara, R.; Ceccarini, C.; Lanzillotta, E.; Munthe, J.; Wängberg, I.; Lindqvist, O.; Pirrone, N.; Sprovieri, F.; et al. Evasion of mercury from coastal and open waters of the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjellbrekke, A.G.; Solberg, S.; Fjæraa, A.M. Ozone Measurements 2009, EMEP/CCC-Report 2/2011. Available online: http://www.nilu.no/projects/ccc/reports.html (accessed on 20 November 2014).
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF; Version 3; Technical Report; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stockwell, W.R.; Middleton, P.; Chang, J.S.; Taang, X. The second-generation regional acid deposition model chemical mechanism for regional air quality modelling. J. Geophy. Res. 1990, 95, 16343–16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madronich, S. Photodissociation in the atmosphere 1. actinic flux and the effects of ground reflections and clouds. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 9740–9752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMEP/CEIP 2014. Present State of Emissions as Used in EMEP Models. Available online: http://www.ceip.at/webdab_emepdatabase/emissions_emepmodels/ (accessed on 20 November 2014).
- Vestreng, V.; Mareckova, K.; Kakareka, S.; Malchykhina, A.; Kukharchyk, T. Inventory Review 2007; Emission Data Reported to LRTAP Convention and NEC Directive, MSC-W TechnicalReport 1/07; The Norwegian Meteorological Institute: Oslo, Norway, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schürmann, G.J.; Algieri, A.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Manna, G.; Pirrone, N.; Sprovieri, F. Modelling local and synoptic scale influences on ozone concentrations in a topographically complex region of Southern Italy. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4424–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.; Fagerli, H.; Jonson, J.; Tsyro, S.; Wind, P.; Tuovinen, J. Trans-boundary Acidification and Eutrophication and Ground Level Ozone in Europe: Unified EMEP Model Description; EMEP/MSC-W Report; EMEP/MSC-W: Oslo, Norway, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Marmer, E.; Dentener, F.; Aardenne, J.V.; Cavalli, F.; Vignati, E.; Velchev, K.; Hjorth, J.; Boersma, F.; Vinken, G.; Mihalopoulos, N.; et al. What can we learn about ship emission inventories from measurements of air pollutants over the Mediterranean Sea? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6815–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Zimmerman, P.R.; Harley, P.C.; Monson, R.K.; Fall, R. Isoprene and Monoterpene emission rate variability: Model evaluations and sensitivity analyses. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 12609–12617. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, A.; Zimmerman, P.; Wildermuth, M. Natural volatile organic compound emission rate estimates for U.S. woodland landscapes. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.; Guenther, A.; Hewitt, C.N.; Steinbrecher, R. Biogenic emissions in Europe 1. Estimates and uncertainties. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 22875–22890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of emissions of gases and aerosols from nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.G.; Crutzen, P.J. Influence of NOx emissions from ships on tropospheric photochemistry and climate. Nature 1999, 402, 167–170. [Google Scholar]
- Capaldo, K.; Corbett, J.J.; Kasibhatla, P.; Fischbeck, P.; Pandis, S.N. Effects of ship emissions on sulphur cycling and radiative climate forcing over the ocean. Nature 1999, 400, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton-Perez, C.L.; Evans, M.J.; Marsham, J.H.; Esler, J.G. The impact of resolution on ship plume simulations with NOx chemistry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7505–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszar, P.; Cariolle, D.; Paoli, R.; Halenka, T.; Belda, M.; Schlager, H.; Miksovsky, J.; Pisoft, P. Modeling the regional impact of ship emissions on NOx and ozone levels over the Eastern Atlantic and Western Europe using ship plume parameterization. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6645–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, G.C.M.; Boersma, K.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Meijer, E.W. Accounting for non-linear chemistry of ship plumes in the GEOS-Chem global chemistry transport model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2011, 11, 17789–17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chosson, F.; Paoli, R.; Cuenot, B. Ship plume dispersion rates in convective boundary layers for chemistry models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 4841–4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.C.; Hanna, S.R. Air quality model performance evaluation. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2004, 87, 167–196. [Google Scholar]
- Willmott, C.J.; Davis, R.E.; Feddema, J.J.; Klink, K.M.; Legates, D.R.; Rowe, C.M.; Ackleson, S.G.; O’Donnell, J. Statistics for the evaluation and comparison of models. J. Geophys. Res 1985, 90, 8995–9005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.H.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Kleeman, M.; Ying, Q. Evaluation of a seven-year air quality simulation using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF)/Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) models in the eastern United States. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Support Center for Regulatory Atmospheric Modeling. Available online: http://www.epa.gov/ttn/scram/guidance_sip.htm (accessed on 20 November 2014).
- Tie, X.; Madronich, S.; Li, G.H.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, R.; Garcia, A.; Lee-Taylor, J.; Liu, Y. Characterizations of chemical oxidants in Mexico City: A regional chemical dynamical model (WRF-Chem) study. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1989–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuccella, P.; Curci, G.; Visconti, G.; Bessagnet, B.; Menut, L.; Park, R.J. Modeling of gas and aerosol with WRF/Chem over Europe: Evaluation and sensitivity study. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D03303. [Google Scholar]
- Fast, J.D.; William, I.; Easter, R.C.; Zaveri, R.A.; Barnard, J.C.; Chapman, E.G.; Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E. Evolution of ozone, particulates, and aerosol direct radiative forcing in the vicinity of Houston using a fully coupled meteorology-chemistry-aerosol model. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D21305. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, F.; Zhao, C.; Tang, X.; Lu, G.; Tie, X. Analysis of ozone and VOCs measured in Shanghai: A case study. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y. Implementation and testing of a new aerosol module in WRF/Chem. In Proceedings of 14th Joint Conference on the Applications of Air Pollution Meteorology with the Air and Waste Management Assoc, Atlanta, GA, USA, 28 January–2 February 2006.
- Zhang, Y. Online-coupled meteorology and chemistry models: History, current status, and outlook. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 2895–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misenis, C.; Zhang, Y. An examination of sensitivity of WRF/Chem predictions to physical parameterizations, horizontal grid spacing, and nesting options. Atmos. Res. 2010, 97, 315–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, K.; Wang, K.; Gudoshava, M.; Glotfelty, T.; Zhang, Y. Application of WRF/Chem over North America under the AQMEII Phase 2: Part I. Comprehensive evaluation of 2006 simulation. Atmos. Environ. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Dubey, M.K. Comparisons of WRF/Chem simulated O3 concentrations in Mexico City with ground-based RAMA measurements during the MILAGRO period. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4622–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meij, A.; Gzella, A.; Cuvelier, C.; Thunis, P.; Bessagnet, B.; Vinuesa, J.F.; Menut, L.; Kelder, H.M. The impact of MM5 and WRF meteorology over complex terrain on CHIMERE model calculations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6611–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menut, L.; Goussebaile, A.; Bessagnet, B.; Khvorostiyanov, D.; Ung, A. Impact of realistic hourly emissions profiles on air pollutants concentrations modelled with CHIMERE. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gencarelli, C.N.; Hedgecock, I.M.; Sprovieri, F.; Schürmann, G.J.; Pirrone, N. Importance of Ship Emissions to Local Summertime Ozone Production in the Mediterranean Marine Boundary Layer: A Modeling Study. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 937-958. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040937
Gencarelli CN, Hedgecock IM, Sprovieri F, Schürmann GJ, Pirrone N. Importance of Ship Emissions to Local Summertime Ozone Production in the Mediterranean Marine Boundary Layer: A Modeling Study. Atmosphere. 2014; 5(4):937-958. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040937
Chicago/Turabian StyleGencarelli, Christian N., Ian M. Hedgecock, Francesca Sprovieri, Gregor J. Schürmann, and Nicola Pirrone. 2014. "Importance of Ship Emissions to Local Summertime Ozone Production in the Mediterranean Marine Boundary Layer: A Modeling Study" Atmosphere 5, no. 4: 937-958. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040937
APA StyleGencarelli, C. N., Hedgecock, I. M., Sprovieri, F., Schürmann, G. J., & Pirrone, N. (2014). Importance of Ship Emissions to Local Summertime Ozone Production in the Mediterranean Marine Boundary Layer: A Modeling Study. Atmosphere, 5(4), 937-958. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040937





