Tracing Sources of Total Gaseous Mercury to Yongheung Island off the Coast of Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
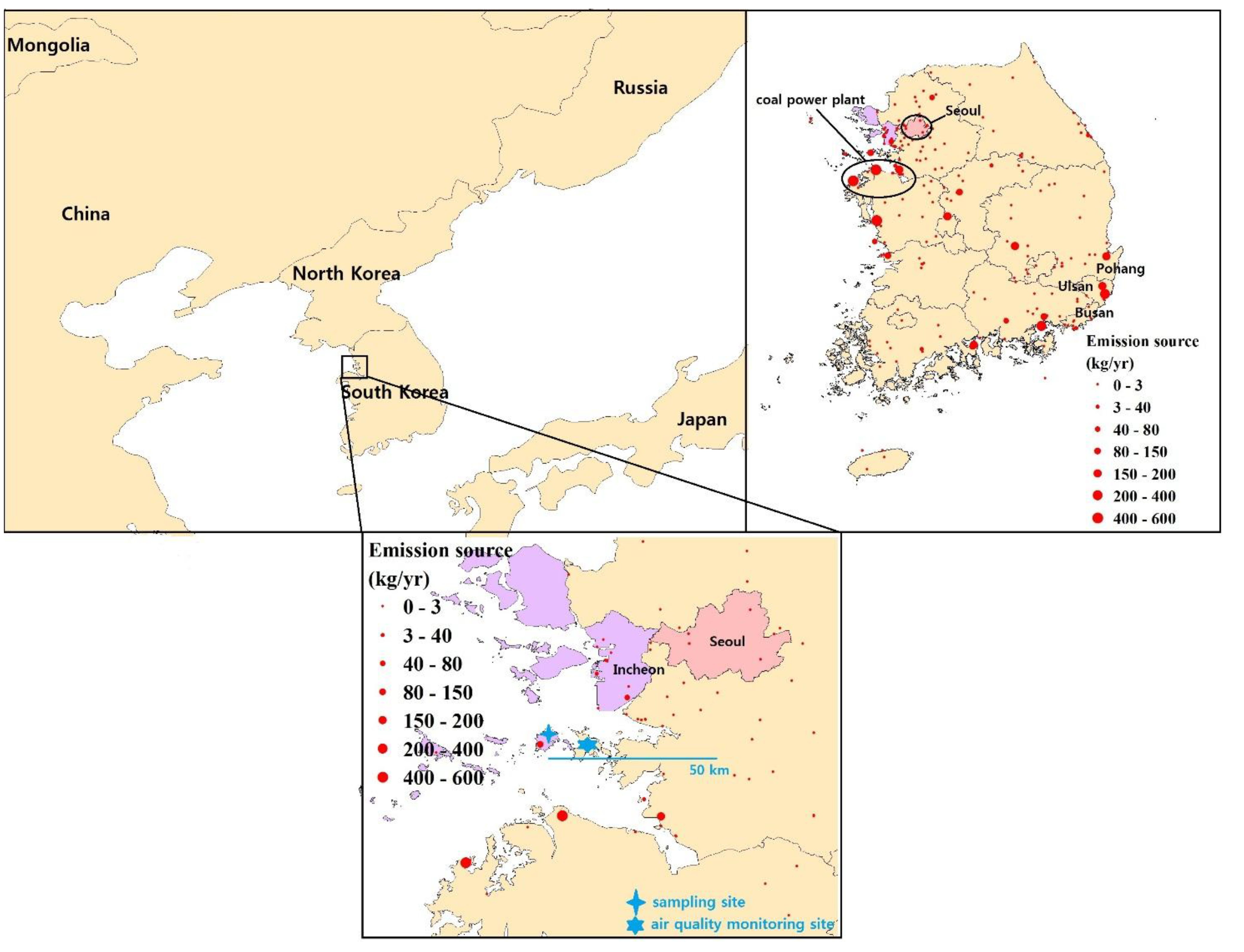
2.1. Sampling Description
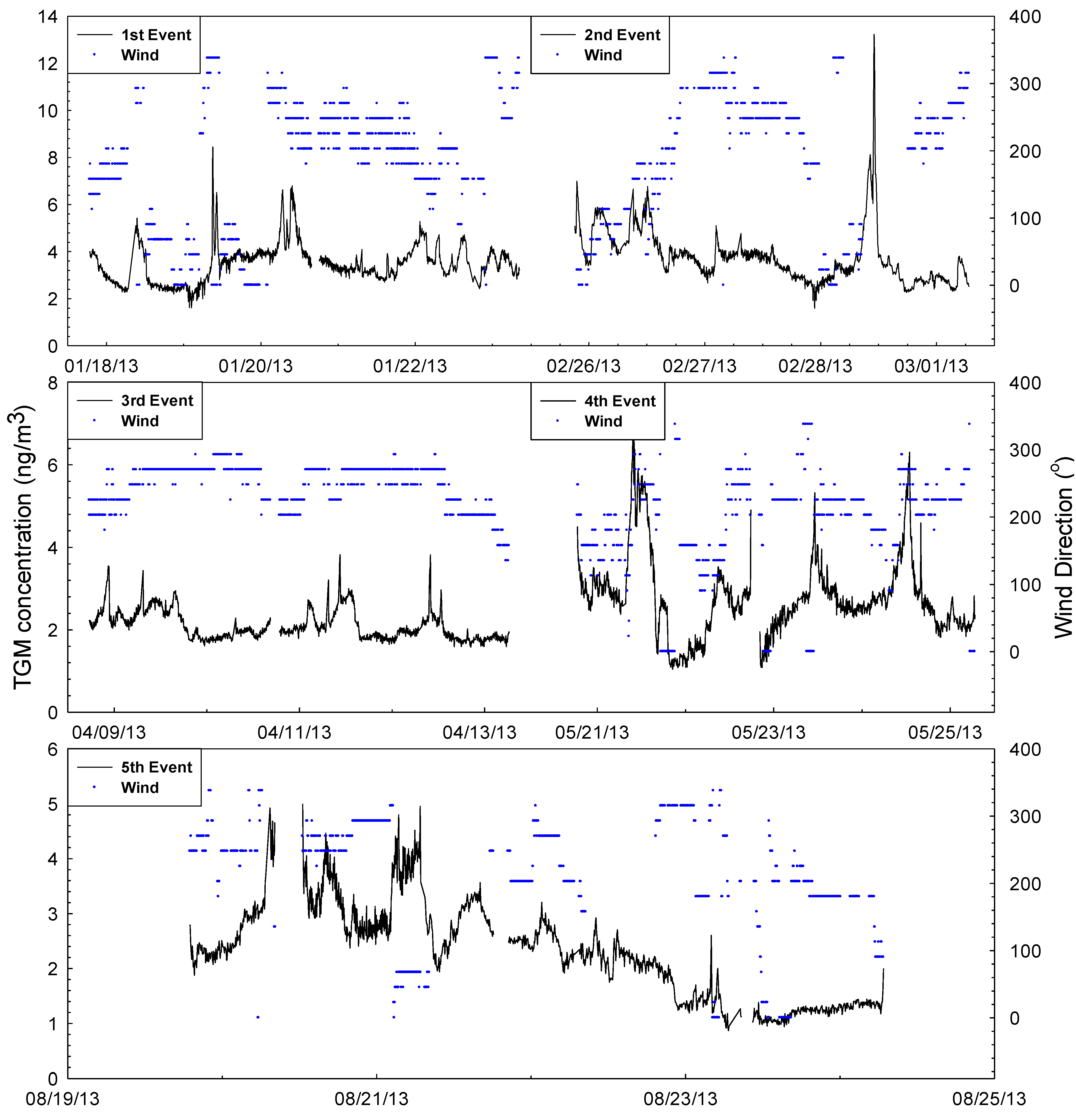
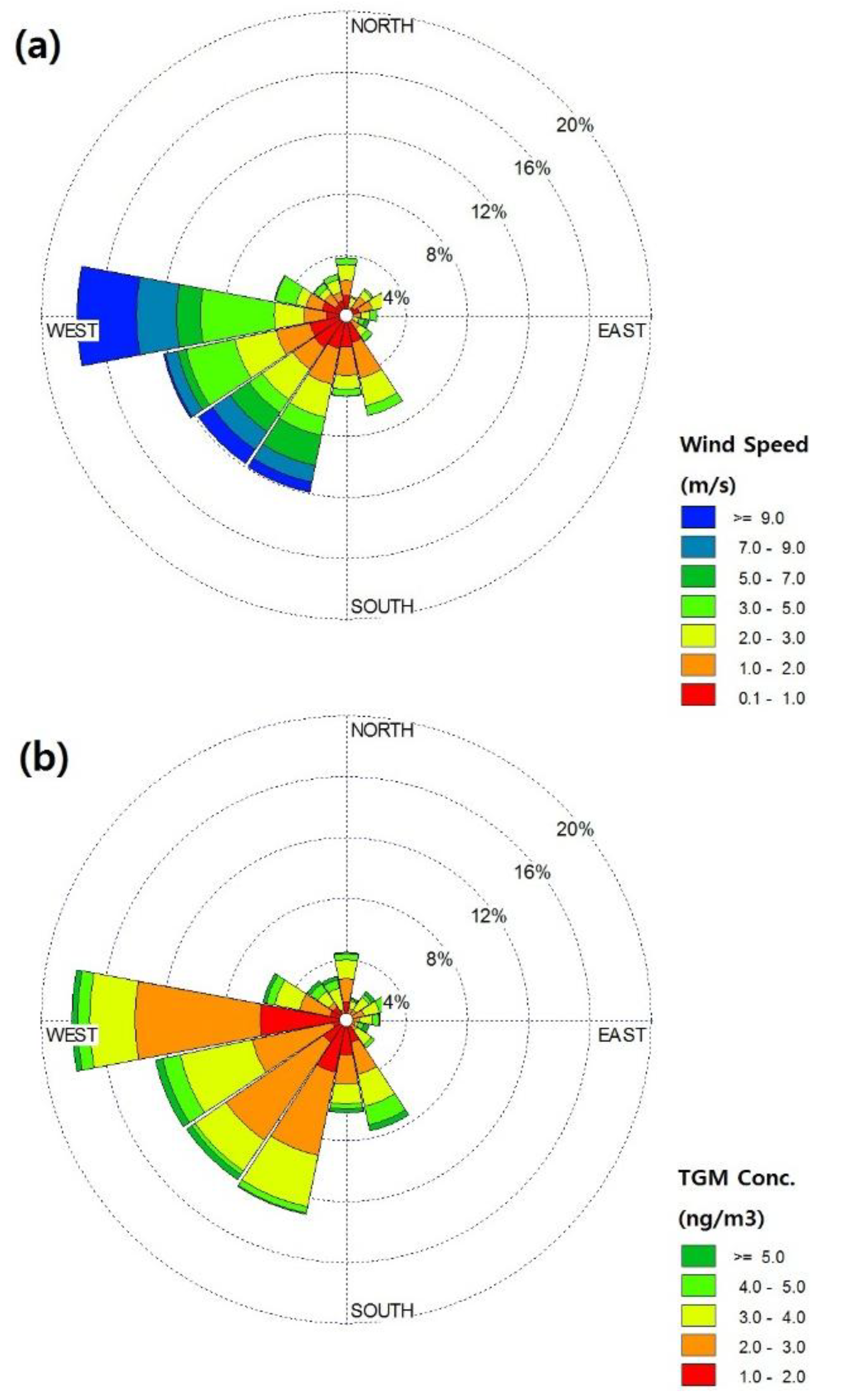
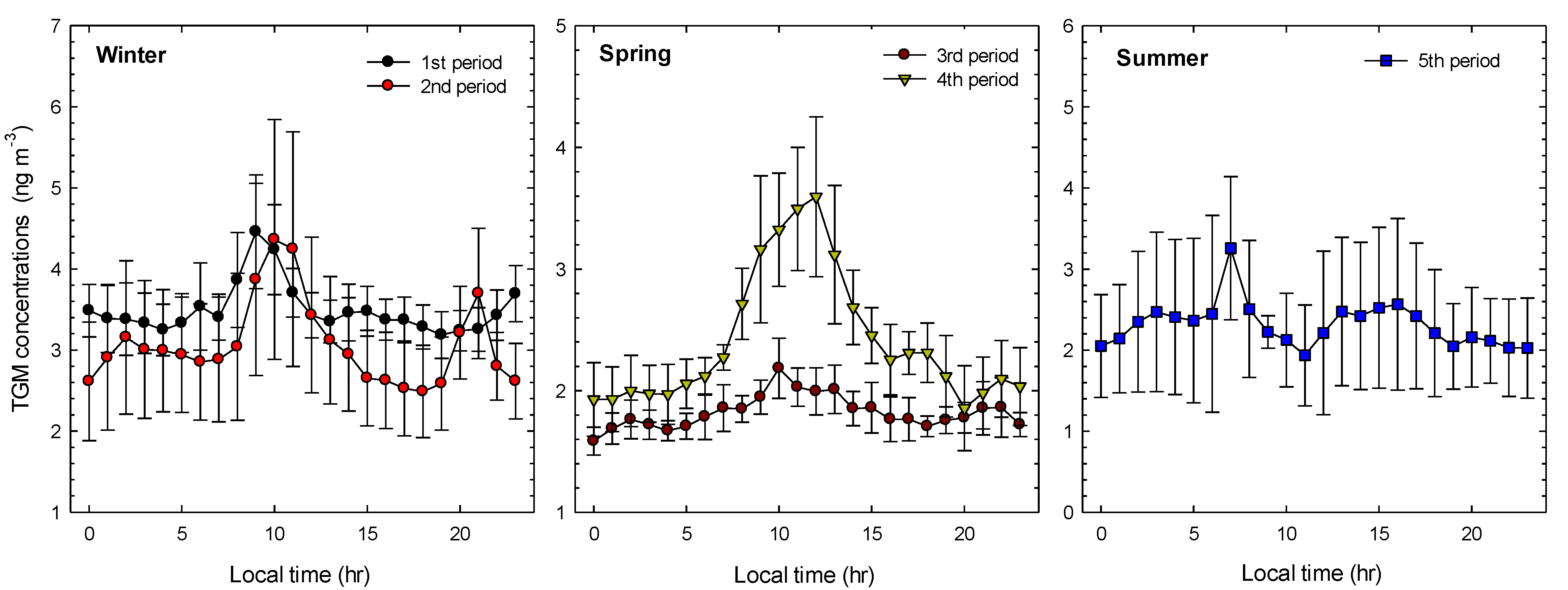
2.2. General TGM Patterns
| Sampling | Date | Season | TGM (ng∙m−3) | Wind Speed (m∙s−1) | Temperature (°C) | Solar Radiation (W m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Period | 2013.01.17–2013.01.21 | Winter | 3.49 ± 0.81 | 1.45 ± 1.05 | 1.00 ± 2.71 | 68.94 ± 136.49 |
| 2nd Period | 2013.02.25–2013.03.01 | 3.67 ± 0.91 | 1.55 ± 1.41 | 2.59 ± 2.33 | 40.55 ± 81.21 | |
| 3rd Period | 2013.04.08–2013.04.13 | Spring | 2.09 ± 0.40 | 6.98 ± 2.56 | 5.58 ± 1.01 | 238.99 ± 324.75 |
| 4th Period | 2013.05.20–2013.05.25 | 2.80 ± 1.00 | 1.56 ± 1.08 | 13.60 ± 2.93 | 252.30 ± 318.84 | |
| 5th Period | 2013.08.19–2013.08.24 | Summer | 2.29 ± 0.85 | 1.03 ± 1.15 | 25.74 ± 1.91 | 180.55 ±274.40 |
| Country | Site | Year | Remarks | TGM (ng∙m−3) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korea | Seoul | 2005–2006 | Urban | 3.4 ± 2.1 | 33 |
| Seoul | 2005–2006 | Urban | 3.2 ± 2.1 | 23 | |
| Jeju* | 2006–2007 | Island | 3.9 ± 1.7 | 18 | |
| Chuncheon | 2006–2009 | Rural | 2.1 ± 1.5 | 25 | |
| This study | 2013 | Island | 2.9 ± 1.1 | ||
| China | Pearl River | 2008 | Background | 2.9 | 34 |
| Guiyang | 2009 | Urban | 9.7 ± 10.2 | 35 | |
| Beijing | 1998 | Urban | 7.9 ± 34.9 | 36 | |
| Taiwan | Central Taiwan | 2010–2011 | Urban | 6.1 ± 3.7 | 37 |
| U.S.A. | Reno, Nevada | 2007–2009 | Suburban | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 38 |
| Great Smoky Mt. | 2007 | Background | 1.65 | 22 | |
| Detroit | 2002 | Urban | 3.1 | 39 | |
| Canada | Nova Scotia | 2010–2011 | Rural | 1.4 ± 0.2 | 24 |
| Wind speed | Temp | RH | Solar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Period | 0.065* (0.012) | 0.178* (<0.001) | 0.153* (<0.001) | 0.106* (<0.001) |
| 2nd Period | −0.189* (<0.001) | 0.067 (0.053) | −0.544* (<0.001) | 0.209* (<0.001) |
| 3rd Period | 0.307* (<0.001) | 0.367* (<0.001) | 0.254* (<0.001) | 0.368* (<0.001) |
| 4th Period | 0.137* (<0.001) | −0.153* (<0.001) | 0.377* (<0.001) | 0.680* (<0.001) |
| 5th Period | 0.032 (0.275) | 0.011 (0.716) | 0.035 (0.255) | 0.325* (<0.001) |
| Total | −0.242* (<0.001) | −0.345* (<0.001) | 0.148* (<0.001) | 0.103* (<0.001) |
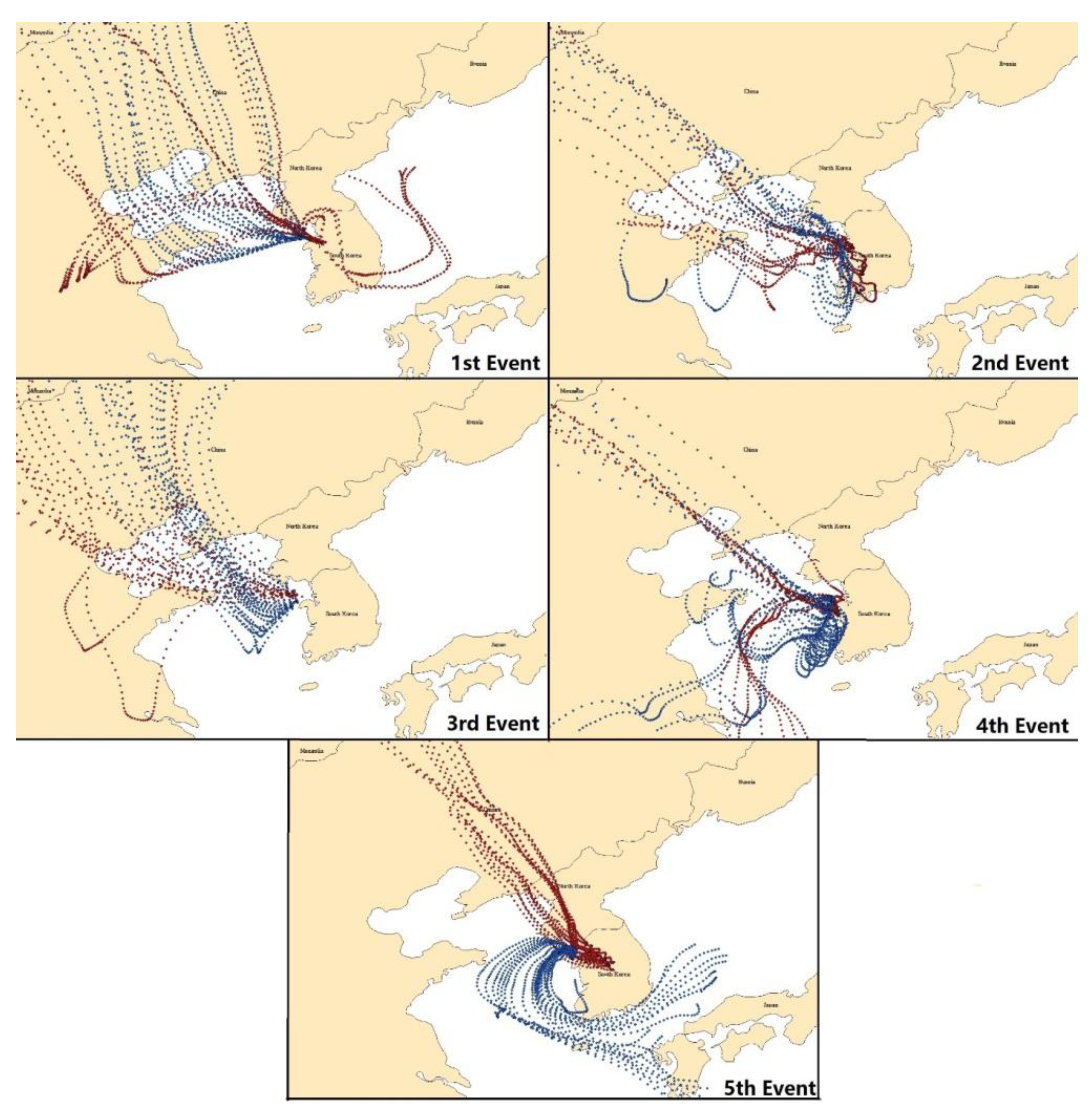
2.3. Impact of Local vs. Regional Sources
2.3.1. First Sampling Period
| SO2 | NO2 | CO | O3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (p-value) | Conc. (ppb) | R (p-value) | Conc. (ppb) | R (p-value) | Conc. (ppm) | R (p-value) | Conc. (ppb) | |
| 1st Period | 0.474* (<0.001) | 5.76 ± 4.24 | 0.155 (0.078) | 26.71 ± 12.38 | 0.465* (<0.001) | 0.52 ± 0.17 | −0.135 (0.129) | 21.71 ± 13.54 |
| 2nd Period | 0.552* (<0.001) | 7.31 ± 3.02 | 0.558* (<0.001) | 28.84 ± 19.10 | 0.362* (0.001) | 0.65 ± 0.19 | −0.532* (<0.001) | 28.33 ± 14.67 |
| 3rd Period | 0.402* (<0.001) | 4.83 ± 1.68 | 0.304* (0.001) | 8.61 ± 3.33 | 0.543* (<0.001) | 0.35 ± 0.08 | −0.136 (0.162) | 46.76 ± 6.04 |
| 4th Period | 0.286* (0.003) | 5.67 ± 2.48 | 0.040 (0.684) | 17.18 ± 5.91 | 0.438* (<0.001) | 0.48 ± 0.11 | 0.224* (0.020) | 36.15 ± 19.40 |
| 5th Period | 0.161 (0.103) | 4.65 ± 1.59 | 0.254* (0.009) | 10.20 ± 3.76 | 0.484* (<0.001) | 0.50 ± 0.12 | 0.241* (0.014) | 40.93 ± 29.58 |
| Total | 0.441* (<0.001) | 5.58 ± 2.98 | 0.560* (<0.001) | 18.22 ± 13.11 | 0.560* (<0.001) | 0.50 ± 0.16 | −0.242* (<0.001) | 34.53 ± 20.40 |
2.3.2. Second Sampling Period
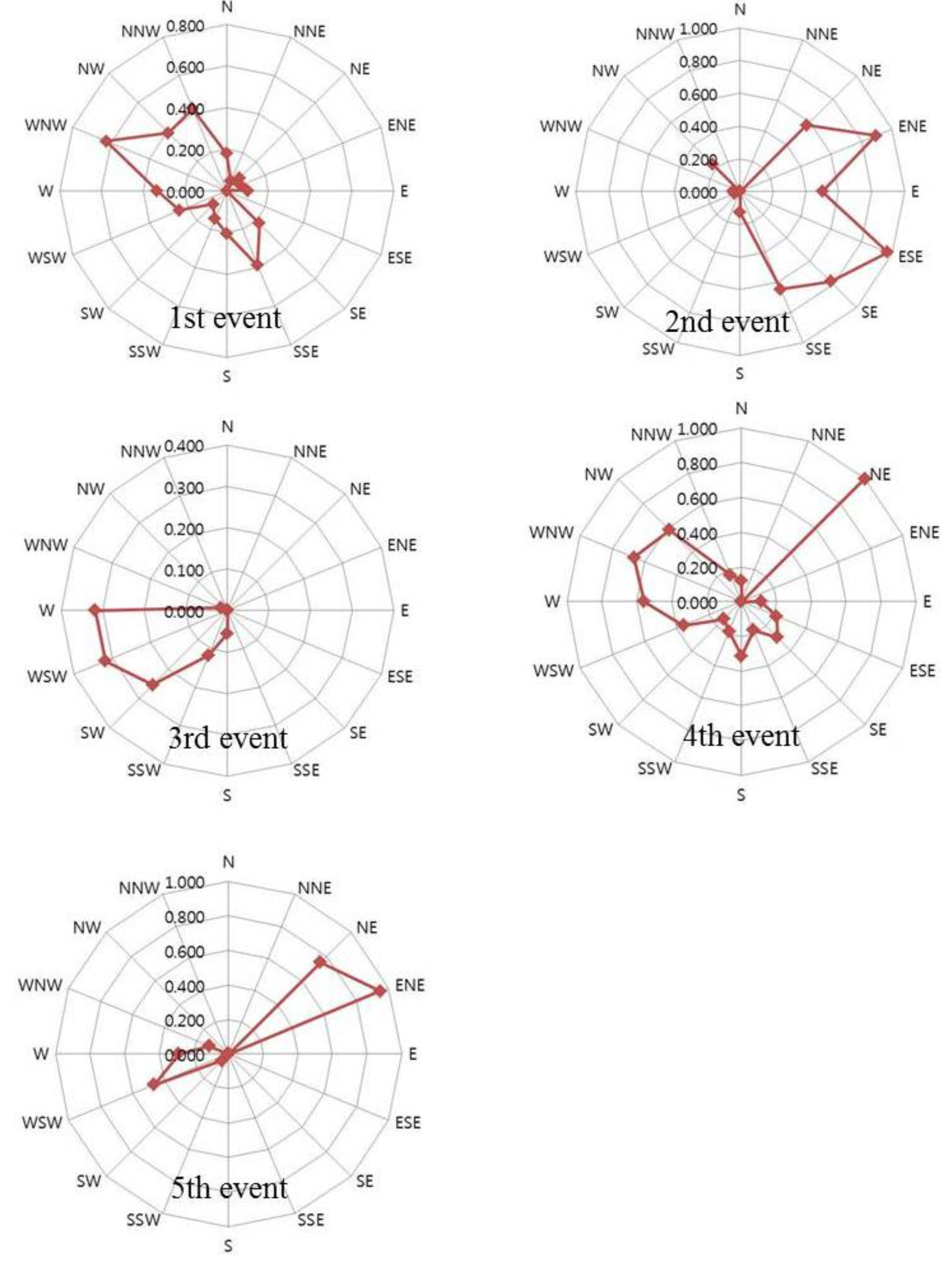
2.3.3. Third Sampling Period
2.3.4. Fourth Sampling Period
2.3.5. Fifth Sampling Period
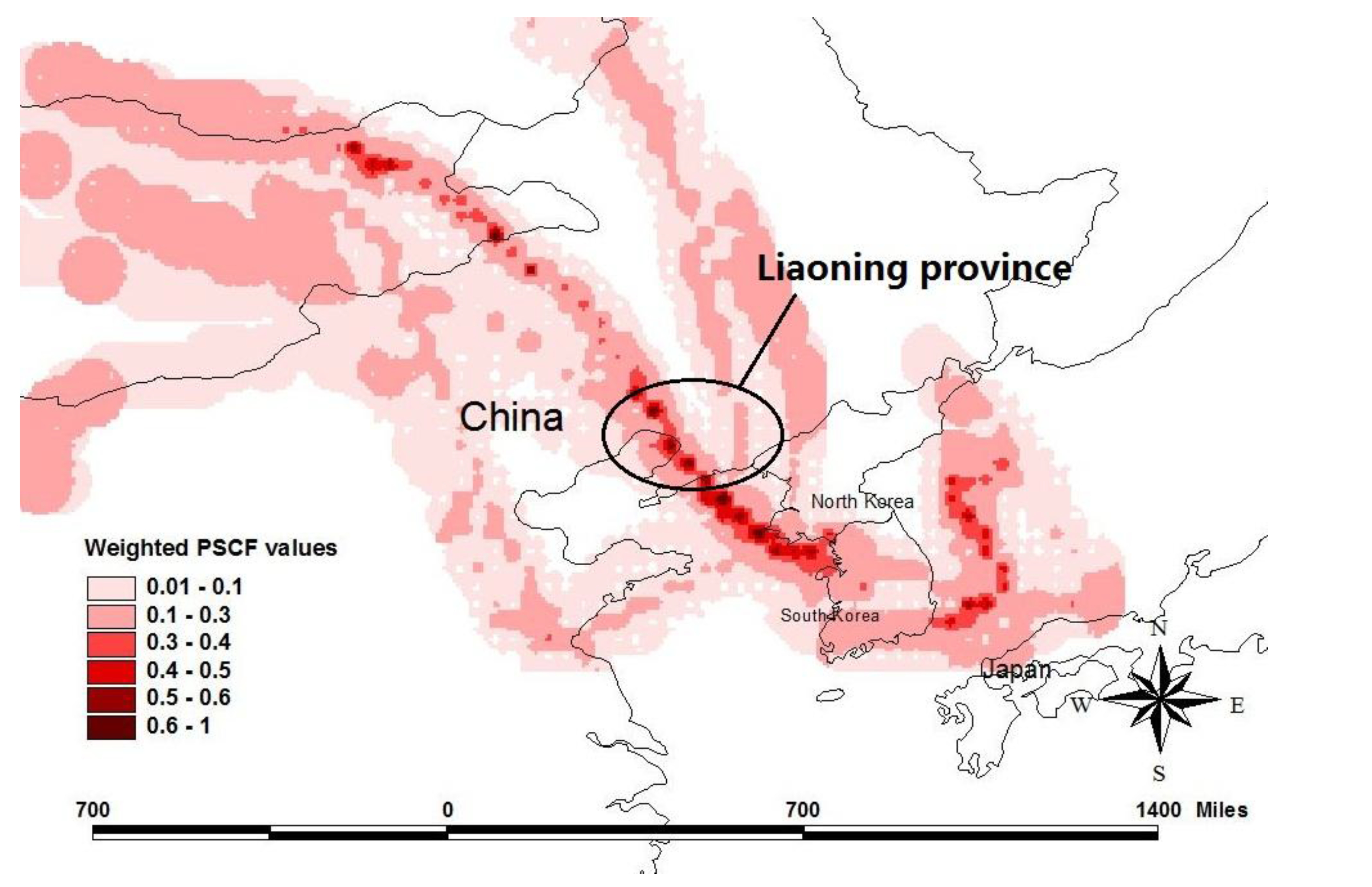
2.4. Potential Source Contribution Function

3. Experimental Section
3.1. Sampling and Analysis
3.2. Other Atmospheric Pollutants
3.3. Backward Trajectory
3.4. Conditional Probability Function

3.5. Potential Source Contribution Function
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Driscoll, C.T.; Han, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Evers, D.C.; Lambert, K.F.; Holsen, T.M.; Kamman, N.C.; Munson, R.K. Mercury contamination in forest and freshwater ecosystems in the Northeastern United States. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 57, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Buehler, S.S.; Hites, R.A. The Great Lakes integrated atmospheric deposition network. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 354A–359A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, M.; Vette, A.F.; Keeler, G.J. Atmospheric mercury in the Lake Michigan Basin: Influence of the Chicago/Gary Urban Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4508–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munthe, J. Recovery of mercury-contaminated fisheries. Ambio 2007, 36, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.N.; Gustin, M.S.; Prestbo, E.M.; Kilner, P.I.; Edgerton, E.; Hartsell, B. Testing and application of surrogate surfaces for understanding potential gaseous oxidized mercury dry deposition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6235–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. The Global Atmospheric Mercury Assessment; UNEP Chemicals Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, W.H.; Munthe, J. Atmospheric mercury—An overview. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 809–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, S.; Padro, J.; Barrie, L. A size-segregated particle dry deposition scheme for and atmospheric aerosol module. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, C.S. Measurement of size-fractionated concentration and bulk dry deposition of atmospheric particulate bound mercury. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slemr, F.; Schuster, G.; Seiler, W. Distribution, speciation and budget of atmospheric mercury. J. Atmos. Chem. 1985, 3, 407–434. [Google Scholar]
- Seigneur, C; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Lohman, K.; Karamchandani, P.; Scott, C. Global source attribution for mercury deposition in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.; Prestbo, E.; Swartzendruder, P.; Weiss-Penzias, P.; Kato, S.; Takami, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Kaiji, Y. Export of atmospheric mercury from Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrist, D.; Gannet, H.A.; McCubbin, I.; Stephens, B.B.; Rahn, T. Atmospheric mercury concentrations at Storm Peak Laboratory in the Rocky Mountains: Evidence for long-range transport from Asia, boundary layer contributions, and plant mercury uptake. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7579–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.Y. The effects of anthropogenic sources on temporal distribution characteristics of total gaseous mercury in Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3337–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, G.W. The concentrations and fluxes of total gaseous mercury in a western coastal area of Korea during late March 2001. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 34, 3413–3427. [Google Scholar]
- Shon, Z.H.; Kim, K.H.; Song, S.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.S. Environmental fate of gaseous elemental mercury at an urban monitoring site based on long-term measurements in Korea (1997–2005). Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.Y.; Choi, E.M.; Seo, Y.S.; Yi, S.M.; Han, Y.J. Characteristic of atmospheric speciated mercury measured in Seoul, Chuncheon and Ganghwado. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 5, 213–214. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, K.H. The influence of long-range transport on atmospheric mercury on Jeju Island, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Shon, Z.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Jung, K.; Park, C.G.; Bae, G.N. The effect of man made source processes on the behavior of total gaseous mercury in air: A comparison between four urban monitoring sites in Seoul Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3801–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.C. Personal Communication. Yonsei University: Seoul, Korea, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- AMAP/UNEP Technical Background Report on the Global Anthropogenic Mercury Assessment; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme/UNEP Chemicals Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; p. 159.
- Kim, S.H.; Han, Y.J.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.M. Characteristic of atmospheric speciated mercury concentrations (TGM, Hg(II) and Hg(p)) in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3267–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, I.; Zhang, L.; Mao, H.; Blanchard, P.; Tordon, R.; John, D. Seasonal and diurnal patterns of speciated atmospheric mercury at a coastal-rural and coastal-urban site. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, R.; Shea, C.; Lynn, H.K.; Tanner, R. Atmospheric mercury in the Great Smoky Mountains compared to regional and global levels. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, P.R.; Kim, W.J.; Yi, S.M.; Seo, Y.S.; Kim, S.H. General trends of Atmospheric mercury concentrations in urban and rural areas in Korea and characteristics of high-concentration events. Atmos. Environ. 2014. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Yoon, H.O.; Richard, J.C.B.; Jeon, E.C.; Sohn, J.R.; Jung, K.; Park, C.C.; Kim, I.S. Simultaneous monitoring of total gaseous mercury at four urban monitoring stations in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Res. 2013, 132–133, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Yan, H.; Wang, S.; Qiu, G.; Tang, S.; Shang, L.; Dai, Q.; Hou, Y. Seasonal variation of gaseous mercury exchange rate between air and water surface over Baihua reservoir, Guizhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 4721–4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poissant, L.; Pilote, M.; Beauvais, C.; Constant, P.; Zhang, H.H. A year of continuous measurements of three atmospheric mercury species (GEM, RGM and Hgp) in southern Quebec, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Atmospheric mercury in the Adirondacks: Concentrations and sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5644–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amyot, M.; Auclair, J.C.; Poissant, L. In situ high temporal resolution analysis of elemental mercury in natural waters. Anal. Chimica Acta 2001, 447, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, N.J.; Siciliano, S.D.; Lean, D.R.S. Continuous analysis of dissolved gaseous mercury in freshwater lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 304, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.D.; Holsen, T.M. Gaseous mercury emission from the forest floor of the Adirondacks. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.M.; Kim, S.H.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.M. Total gaseous concentration in mercury in Seoul, Korea: Local sources compared to long-range transport from China and Japan. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xia, C; Wang, X.; Xiang, Y.; Xie, Z. Total gaseous mercury in Pearl River Delta region, China during 2008 winter period. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Qiu, G.; Shang, L.; Zhang, H. Speciated atmospheric mercury and its potential source in Guiyang, China. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Nadim, F.; Perkins, C.; Carley, R.J.; Hoag, G.E.; Lin, Y.; Chen, L. Atmospheric mercury monitoring survey in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, C.K.; Huang, C.S.; Fang, G.C. Atmospheric mercury pollution at an urban site in central Taiwan: Mercury emission sources at ground level. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, S.N.; Gustin, M.S. Determinants of atmospheric mercury concentrations in Reno, Nevada, U.S.A. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, M.M.; Keeler, G.J. Source-receptor relationships for atmospheric mercury in urban Detroit, Michigan. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3144–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidy, G.M. Atmospheric Sulfur and Nitrogen Oxides: Eastern North America Source-Receptor Relationships; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; p. 447. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.H.; Chung, S.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Kim, M.Y.; Shon, Z.H. Long term study of NOx behavior at urban roadside and background locations in Seoul, Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Dollard, G.J.; Pepler, S. Gas-phase mercury in the atmosphere of the United Kingdom. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-J.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K.; Cheong, J.-P.; Kim, H.; Yi, S.-M. Identification of source locations for atmospheric dry deposition of heavy metals during yellow-sand events in Seoul, Korea in 1998 using hybrid receptor models. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5353–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Fan, R.; Ma, S.; Xu, Z.; Ren, M.; He, Q. Mercury speciation and emission from municipal solid waste incinerators in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 447, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Shon, Z.H. Nationwide shift in CO concentration levels in urban areas of Korea after 2000. J. Hazard Mater. 2011, 188, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Estimation of source location of total gaseous mercury measured in New York State using trajectory-based models. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 6033–6047. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lindberg, S.E. Sunlight and iron (III)-induced photochemical production of dissolved gaseous mercury in freshwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 5, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, S.D.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Lean, D.R.S. Microbial reduction and oxidation of mercury in freshwater lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 3064–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.C.; Kim, B.C.; Holsen, T.M.; Yi, S.M.; Han, Y.J. Factor influencing concentrations of dissolved gaseous mercury (DGM) and total mercury (TM) in an artificial reservoir. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.J.; Holsen, T.M.; Lai, S.O.; Hopke, P.K.; Yi, S.M.; Liu, W.; Pangano, J.; Falanga, L.; Milligan, M.; Andolina, C. Atmospheric gaseous mercury concentration in New York State: relationships with meteorological data and other pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 6431–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Fan, R.; Tao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, D.; Xie, D.; Sun, J. Variation trends and influencing factors of total gaseous mercury in the Pearl River Delta-A highly industrialised region in South China influenced by seasonal monsoons. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Wan, Q.; Meng, B.; Yan, H.; Guo, Y. Probing Hg evasion from surface waters of two Chinese hyper/meso-eutrophic reservoirs. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5887–5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Harris, J.M. Source regions for atmospheric aerosol measured at Barrow, Alaska. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4214–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissar, A.V.; Hopke, P.K.; Poirot, R.L. Atmospheric aerosol over Vermont: Chemical composition and sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 4604–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, X.; Sommar, J.; Wang, S. A review of studies on atmospheric mercury in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashbaugh, L.L.; Malm, W.C.; Sadeh, W.D. A residence time probability analysis of sulfur concentrations at Grand Canyon National Park. Atmos. Environ. 1985, 19, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar]
- Malm, W.C.; Johnson, C.E.; Bresch, J.F. Application of principal component analysis for purposes of identifying source-receptor relationships in receptor methods for source apportionment. In Receptor Methods for Source Apportionment; Air Pollution Control Association: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1986; pp. 127–148. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.J. Mercury in New York State: Concentrations and Source Identification Using Hybrid Receptor Modeling. Ph.D. Thesis, Clarkson University, Potsdam, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, G.S.; Kim, P.R.; Han, Y.J.; Holsen, T.M.; Lee, S.H. Tracing Sources of Total Gaseous Mercury to Yongheung Island off the Coast of Korea. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 273-291. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5020273
Lee GS, Kim PR, Han YJ, Holsen TM, Lee SH. Tracing Sources of Total Gaseous Mercury to Yongheung Island off the Coast of Korea. Atmosphere. 2014; 5(2):273-291. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5020273
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Gang S., Pyung R. Kim, Young J. Han, Thomas M. Holsen, and Seung H. Lee. 2014. "Tracing Sources of Total Gaseous Mercury to Yongheung Island off the Coast of Korea" Atmosphere 5, no. 2: 273-291. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5020273
APA StyleLee, G. S., Kim, P. R., Han, Y. J., Holsen, T. M., & Lee, S. H. (2014). Tracing Sources of Total Gaseous Mercury to Yongheung Island off the Coast of Korea. Atmosphere, 5(2), 273-291. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5020273





