Abstract
Atmospheric pollution poses varying degrees of health risks to the public health of local residents and ecological sustainability. As a typical basin-edge city, Xiangyang, one of the industrial center cities in Hubei Province, China, is facing challenges regarding air quality. However, previous research on the regional correlation, temporal potential sources, and dynamic changes in health risks related to air pollution in Xiangyang has been reported infrequently. The purpose is to investigate the spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang, their potential source regions, associated health risks, and spatial correlations. The health risks associated with air pollution in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 have showed downward trend from 2.252 in 2019 to 1.032 in 2023. The potential source regions of O3 in summer were concentrated in northeastern Hubei, southeastern Henan, western and northern Anhui, and central Shaanxi province. The weight of potential sources of O3 in summer demonstrated an increasing trend in central Shaanxi. The obvious potential sources regions of PM2.5 in winter extended to Hubei, northern Hunan, Henan, northern Anhui, western Shandong, and central Shaanxi. The weight of potential sources of PM2.5 in winter demonstrated an increasing trend in central Shaanxi.
1. Introduction
In the process of rapid urbanization and industrialization, anthropogenic activities inevitably discharge various pollutants into the atmosphere, resulting in the deterioration of air quality, which poses a certain threat to population health. As a consequence, the World Health Organization (WHO) has paid attention to this problem [1]. They found that long-term exposure to high concentrations of air pollutants increases the risk of cardiovascular, respiratory, and other related diseases, which could lead to a sharp increase in mortality among local residents exposed to air pollution, so assessments of regional health risk are necessary [2,3,4,5]. PM2.5 and other pollutants, upon entering the human bloodstream, exert toxicological effects on the body through different mechanisms [6]. The research conducted by BAULIG et al. confirms that the principle behind this phenomenon is the exposure to atmospheric pollutants, which increases the levels and concentrations of multiple inflammatory factors in animals or humans, subsequently presenting a dose–response relationship that leads to damage to lung tissue [7,8]. Considering the different particle sizes of aerosol particles and their toxicological aspects, the toxicity of dust increases as the dust size decreases, which is related to its penetrating ability and has been proven in studies on lung cell lines [9,10]. Therefore, the PM2.5 fraction was chosen for investigation according to the guidelines regulated by international organizations (WHO) [11]. Meanwhile, measuring the health risks of residents exposed to specific pollutants has become an effective approach [12]. It is important for us to note that the formation and impact of air pollution events are often influenced by meteorological and topographical factors, which can lead to their migration across different cities and regions, ultimately crossing administrative boundaries [13,14,15]. Biological aerosols can be transported over long distances through sandstorm events, influencing the concentration and distribution characteristics of microorganisms in different regions. The atmospheric pollution during different periods at the site of the Beijing Winter Olympics mainly originated from areas such as Mongolia and the northern part of Shanxi Province in China, which are rich in sources and exhibit temporal variations. This indicates that traditional atmospheric pollutants like PM2.5 possess the capability for long-distance transport, potentially disrupting existing ecological patterns in local environments [16,17]. This phenomenon is particularly evident in areas with relatively complex terrain, such as Xiangyang City, located at the southern edge of the Nanyang Basin in China [18]. Thus, it is extremely necessary to pay attention to the mutual migration of air pollutants between cities. To address this situation more effectively, a series of air pollution regulatory policies and special measures in China have moved the focus from regulation by a single city to collaborative regulation by multiple cities [19]. Research methods concerning spatial correlation analysis have been proven initially effective in analyzing the pollution correlation among regions [20,21]. Backward clustering trajectory analysis, potential source contribution function (PSCF), and concentration-weighted trajectory (CWT) methods can be applied to assess the source regions and transport pathways of the imported air pollutants [22,23,24].
Therefore, air pollution research is significant to the sustainable development of this city. Previous researchers have reported some research results on the temporal variation characteristics of single particulate matter and the influence of meteorological conditions on air pollution [25,26,27,28]. However, the correlation of air pollution between Xiangyang City and surrounding regions, the potential sources of air pollutants in multiple periods, and the dynamic changes in air pollution and health risks are still rarely reported based on the monitoring data in Xiangyang City. To address these academic gaps, this study undertakes the following: (1) It identifies the spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 using monitoring data from 2019 to 2023 and spatial clustering modes, including spatial autocorrelation and hot spot analysis, in Xiangyang City and its surrounding districts. (2) It then assesses the correlation through three main research methods, including backward clustering trajectory analysis, potential source contribution function (PSCF), and concentration-weighted trajectory (CWT), to determine the direction of air mass sources in relation to potential pollution sources in Xiangyang City, enabling the preliminary identification of significant source regions, and calculating the influence weights of these source regions mathematically. The purposes of this paper are to (1) explore the spatiotemporal characteristics of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City, (2) estimate the health risk for residents exposed to local pollutants, (3) further analyze the spatial correlation and cluster characteristics of air pollution in Xiangyang City with its surrounding districts, and (4) identify the potential source regions and transport pathways of atmospheric PM2.5 and O3. The results will provide scientific and technological support for future joint prevention and effective control of regional air pollution in Xiangyang City, as well as in its surrounding districts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Region
Xiangyang City, located in the northwest of Hubei Province, is a sub-regional city and the core city of the Automobile Industry Corridor in Hubei Province, making it a key development city of China’s automobile industry. Xiangyang City is located in the south of Nanyang Basin, the boundary between second- and third-order geomorphologic ladder of China, which is the transitional zone between Nanyang Basin and Jianghan Plain (Basin), while the Jingxiang Corridor connects the Nanyang Basin and the Jianghan–Dongtinghu Plain (Basin) to the south.
The natural and economic geographical environments of Xiangyang City are unique. Xiangyang City is located at the edge of southern Nanyang Basin. The altitude in the basin is mostly below 200 m, while it is surrounded by mountains with elevations above 1000 m. The relatively enclosed terrain results in low wind speeds and high atmospheric stability within the basin, which often results in the formation of temperature inversions that are unfavorable for the dispersion of atmospheric pollutants [29,30]. Additionally, the local industries encompass both agriculture and manufacturing, resulting in the potential for emissions of atmospheric pollutants from local pollution sources. Prevailing winds can transport these pollutants to downstream cities, while the upwind areas of Xiangyang City can similarly bring these pollutants from other industrial regions, due to the prevailing wind directions from the southeast and north.
The annual average wind velocity in Xiangyang City is 2.6 m/s, with the dominant wind direction being southeast by south (SSE). During the spring and summer seasons (March to July), the prevailing wind direction is southeast by south (SSE), whereas in the autumn and winter seasons (August to the following February), the prevailing wind direction shifts to the north. The average annual temperature in Xiangyang City is 16.0 °C, with the coldest month (in January) averaging 3.1 °C and the hottest month (in July) averaging 27.4 °C. The average annual precipitation of Xiangyang City is 827.9 mm, with the driest month (in January) averaging 19.5 mm and the wettest month (in July) averaging 148.7 mm. The topography and location of Xiangyang City and its surrounding regions are shown in Figure 1.
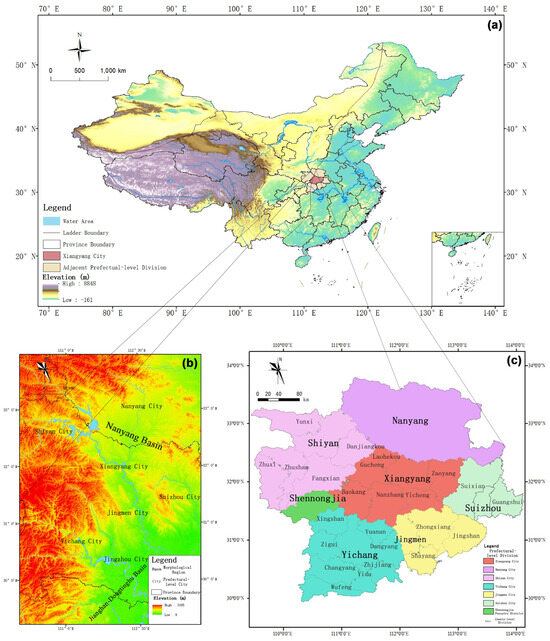
Figure 1.
Map of Xiangyang City and its surrounding regions. (a) Location of study region in China. (b) Location of study region corridor terrain. (c) Map of local study area.
2.2. Data Sources
The data for the concentration of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 were obtained from the national urban air quality real-time release platform of the China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (https://air.cnemc.cn:18007/, accessed on 22 March 2024) and the standard environmental monitoring station of Department of Ecology and Environment of Hubei Province (https://sthjt.hubei.gov.cn/, accessed on 31 March 2024), with 1 h temporal resolution. Such data have been widely utilized in research about the spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric pollution [31]. The meteorological factors needed for backward trajectory cluster analysis and potential source region research were derived from the historical time series data, with 6 h temporal resolution and 1° × 1° spatial resolution, of the Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) provided by the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) in the United States (ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives/gdas1/, accessed on 19 May 2024, and some of the missing data were statistically and scientifically processed. Zhao and other scholars have also utilized the data offered by this institution in the research of spatiotemporal characteristics of atmospheric pollution [30,31,32]. The datasets used in this study and their spatiotemporal resolution are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The datasets used in this study and their spatiotemporal resolution.
2.3. Methodologies
2.3.1. Aggregate Risk Index (ARI)
The Aggregate Risk Index (ARI), proposed by Cairncross [33], assesses the total health risk from exposure to multiple air pollutants based on the exposure–response relationship to air pollutants and relative risk (RR) between air pollutants and mortality [34]. Thus, ARI was used to evaluate the aggregate health risk caused by multiple air pollutants in Xiangyang City during 2019~2023 in this research. The formula for calculating ARI is as follows:
PSIi is the health risk of the pollutant i, n is the quantity of pollutant, ci is the time-averaged concentration of the pollutant i, and ai is the ratio coefficient of pollutant i to the risk value.
It has been found that the RR of PM10 is most significant when calculating the health risk due to pollutant exposure [12,35]. The formula for calculating ai is as follows:
aPM10 is a constant calculated by the WHO health risk study (aPM10 = 0.08), and the RRPM10 value is 1.014 [31]; RRi is the relative risk of death for every 10 μg·m−3 increase in pollutant i concentration, and the formula for calculating RRi is as follows:
βi is the exposure–response coefficient, which represents the additional health risk associated with the increasing concentration of pollutant i, ci is the time-averaged concentration of pollutant i, and c0 is the threshold concentration corresponding to pollutant i. When ci is higher than c0, the pollutant concentration has a significant effect on human health, and when ci is less than or equal to c0, the pollutant concentration has no significant effect on human health. The β values in this paper are based on a study in China by Shang et al. [36], which showed that the β values for PM2.5, SO2, NO2, O3, and CO are 0.032%, 0.081%, 0.13%, 0.048%, and 3.7%, respectively, for every increase of 1 μg·m−3 in pollutant concentration [36]. The corresponding threshold concentration c0 of pollutants is the national secondary standard in the “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China [37].
2.3.2. Moran’s Index
Moran’s index is often used to measure the spatial aggregation of data [22], which can be divided into global Moran’s index (IG) and local Moran’s index (IL). The global Moran’s index is used to analyze whether there is autocorrelation in the space on a whole, while the local Moran’s index reflects the spatial agglomeration near a certain unit i in multiple spatial units, which can be expressed by the formulas:
In these formulas, n represents the number of spatial units studied in the research. Wij represents the value of column j in row i, in the weight matrix N. xi and xj represent the attributive values of the spatial units i and j, respectively. is the averaged attributive value of all the spatial units [23].
The value range of the global Moran’s index is [−1, 1]. When the global Moran’s index is higher than 0, it indicates a positive spatial correlation, while if it is less than 0, it is a negative spatial correlation, and when the value is 0, it indicates a spatially random distribution. While there is no limit to the range of values of the local Moran’s index [38], the scatter plot is divided into four quadrants, the High–High cluster quadrant (HH) indicates a high-value area surrounded by high-value regions; the Low–High cluster quadrant (LH) indicates a low-value area surrounded by high-value regions; the Low–Low cluster quadrant (LL) indicates a low-value area surrounded by low-value regions; and the High–Low cluster quadrant (HL) indicates a high-value area surrounded by low-value regions [39].
The local Moran’s index includes an analysis of hot and cold spots, which can identify the spatial differentiation and extreme aggregation degree of hot spots and cold spots of specified indicators in the study area. Our study employed this analytical method to identify the spatial differences in hot spots and cold spots of ARI among county-level administrative units within the research area, as well as the degree of extreme value aggregation of ARI.
2.3.3. Potential Source Contribution Function (PSCF)
This research identified potential source regions by a Potential Source Contribution Function (PSCF) analysis. To use this effective method, the research divided the study region into several grids (i, j) with a certain resolution, and set a threshold for the elements under study. When the value of the corresponding elements of the trajectory is higher than this threshold, the trajectory is considered to be a pollution transport trajectory. Additionally, the number of endpoints of the pollution trajectory passing through the grid (i, j) is mij, and the number of endpoints of all trajectories falling in the grid (i, j) is nij. PSCF is calculated as follows:
The errors of PSCF increase with larger increases between the grid and the sample point. When nij is smaller, there is a lot of uncertainty. To reduce the influence of these special grids on the calculation results, the weight coefficient Wij is introduced, which is denoted as WPSCF (Weighted Potential Source Contribution Function). The formula is as follows [40]:
In the formula, nave is the average number of track endpoints for each grid.
2.3.4. Concentration-Weighted Trajectory (CWT)
The PSCF algorithm reflects the contribution of the grid to the pollution degree of the affected points, which cannot distinguish the contribution of the grid points with the same PSCF value from the pollution degree of the observation points. The CWT (concentration-weighted trajectory) analysis method can quantitatively determine the average weight concentration of each grid point by calculating the weight concentration of the trajectory, reflecting the contribution of different grid regions to the pollution degree in the study region. At the same time, the weight coefficient Wij is also introduced to reduce the uncertainty of CWT, which is denoted as WCWT (weighted-concentration-weighted trajectory), and the formula is as follows [40]
In the formula, WCWTij is the averaged weight concentration of the grid (i, j), l is the trajectory, M is the number of trajectories in the grid (i, j), Cl is the mass concentration of pollutants at the receiving point when the trajectory l passes through the grid (i, j), and τijl is the time that the trajectory l stays in the grid (i, j). The weight function Wij is the same as in PSCF [40].
The flowchart for the use of HYSPLIT is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Diagram of the HYSPLIT process.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Temporal Variation of PM2.5 and O3
3.1.1. Annual Variation of PM2.5 and O3
Figure 3 demonstrates the annual variation in the average concentration of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang from 2019 to 2023. The concentration of PM2.5 in Xiangyang City showed a marked decrease from 60 μg·m−3 in 2019 to 47 μg·m−3 in 2023. The total decrease was 21.67%, with the largest decrease of 13.33% from 2019 to 2020. The annual average concentration for five consecutive years was higher than the second-level standard of the national “Environmental Air Quality Standards”. The concentration of O3 in Xiangyang City decreased from 162 μg·m−3 to 153 μg·m−3, with the largest decrease of 12.35% from 2019 to 2020, and the largest increase in O3 from 2021 to 2022 of 12.59%. And O3 concentrations in 2020, 2021, and 2023 were 160 μg·m−3 below the secondary standard of the National Ambient Air Quality Standard. It can be seen that PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City decreased the most from 2019 to 2020, which may be related to the significant reduction in air pollutant emissions from human activities such as industrial production under the influence of the epidemic in 2020. From 2021 to 2022, the concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 increased to a certain extent, especially O3, which may be related to the gradual intensification of urban human activities.
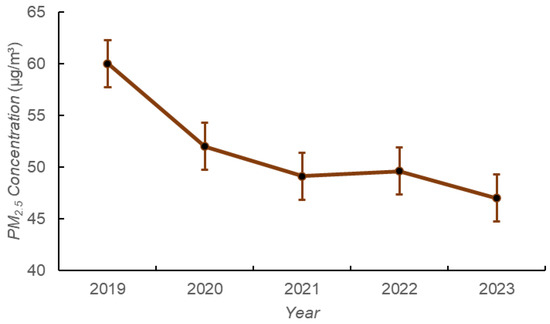
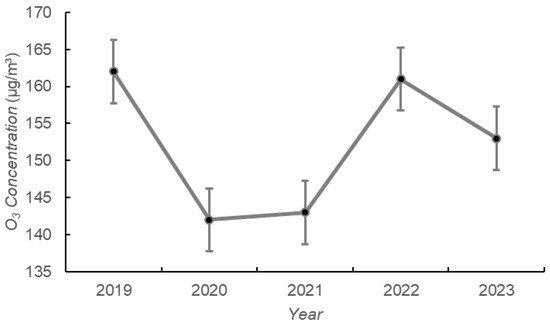
Figure 3.
Annual variation of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City.
3.1.2. Seasonal Variation of PM2.5 and O3
The results are presented based on the four seasons, namely, spring (March to May), summer (June to August), autumn (September to November), and winter (December to February of the following year) in this research. Table 2 shows the seasonal concentration changes of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023.

Table 2.
Seasonal average concentrations of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang from 2019 to 2023 (μg·m−3). (Accurate to two decimal places).
From 2019 to 2023, the seasonal concentrations of PM2.5 ranked in order from high to low were as follows: winter, autumn, spring, and summer. Except for summer, the average concentration of PM2.5 in the other three seasons was higher than the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China. The PM2.5 concentrations in the four seasons demonstrated an overall downward trend, with reduction rates of 12.77%, 17.65%, 19.59%, and 27.43%, respectively, and the largest decrease in winter, which was closely related to increased contributions from coal combustion and industry, as well as the effectiveness of urban air pollution control during the COVID-19 pandemic [41]. The highest PM2.5 concentrations in spring, summer, and winter occurred in 2019, and the highest PM2.5 concentrations in autumn (54.33 μg·m−3) occurred in 2020. Therefore, the PM2.5 pollution in Xiangyang City was heavy in winter, similar to many cities in China, which was probably related to the exogenous pollutants brought by local human activities and airflow activities.
From 2019 to 2023, the seasonal variation of O3 concentrations was as follows: summer > spring > autumn > winter. The average concentration of O3 in Xiangyang City in the spring from 2019 to 2023 was 140.87 μg·m−3. The O3 concentration (151 μg·m−3) in the spring of 2023 was the highest in five years, and the average concentration in the spring of each year was lower than the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China. The average O3 concentration in Xiangyang City in the summer from 2019 to 2023 was 165.13 μg·m−3, and the concentration (180.67 μg·m−3) in the summer of 2019 was the highest value in five years. Only the O3 concentration in 2020 was lower than the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China, and the other years were higher or close to the standard value. The average autumn concentration of O3 in Xiangyang City during the period 2019–2023 was 139.53 μg·m−3, with the O3 concentration (153.67 μg·m−3) in the autumn of 2022 being the highest value in five years. The average concentration in the autumn of each year was lower than the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China. The average winter concentration of O3 in Xiangyang City during the period 2019 to 2023 was 87.00 μg·m−3, and the O3 concentration (97 μg·m−3) in 2023 winter was the highest value in five years. The average concentration in each winter was lower than the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China. Consequently, summer was the main season for O3 pollution in Xiangyang City, similar to other cities in China, which was possibly related to the photochemical reaction of precursor pollutants to form O3.
3.1.3. Monthly Variation of PM2.5 and O3
The monthly variation of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 are shown in Figure 4a. It can be observed that the monthly variation curve of PM2.5 in Xiangyang City is “U”-shaped, while that of O3 exhibits an inverted “U” shape. Based on the five-year average, the concentration of PM2.5 was highest in January at 109.2 μg·m−3, which was 3.12 times the second-level standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standards” of China. This peak was followed by the concentrations in December, February, and November, in descending order. The concentration of O3 in June, was the highest with 177 μg·m−3, slightly exceeding the corresponding value of the secondary standard of the national “Ambient Air Quality Standard” of China, and was followed by the values for September, August, and May. In June 2022, the O3 concentration reached its highest value in five years at 196 μg·m−3. In December 2020, the O3 concentration reached its lowest value in five years at 70 μg·m−3. Overall, there were significant fluctuations in the monthly average values of both pollutants.
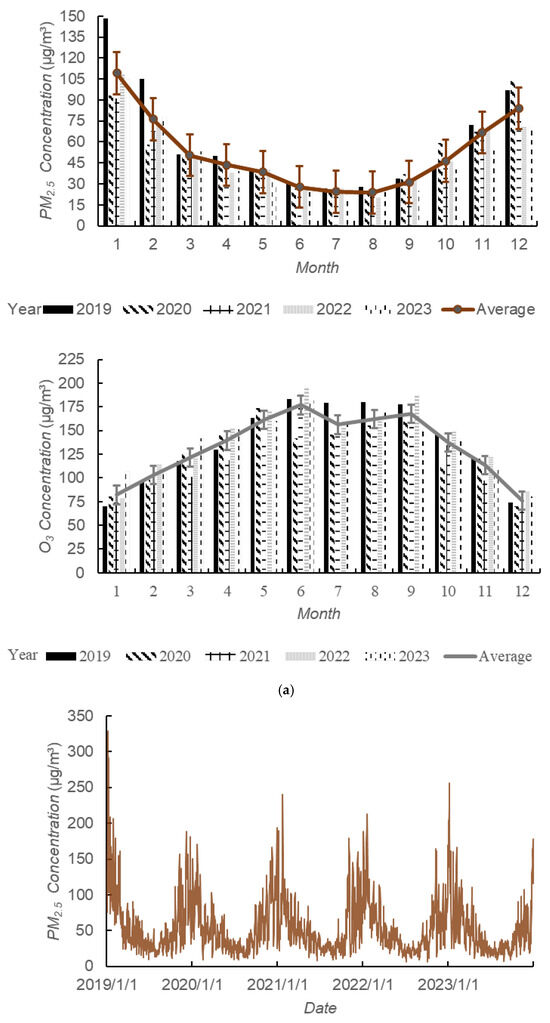
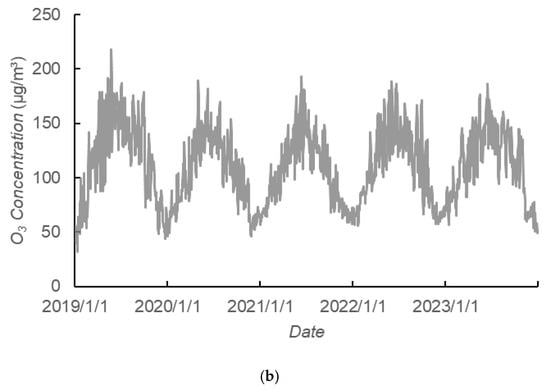
Figure 4.
Statistical chart of time variation of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City: (a) monthly variation of PM2.5 and O3; (b) daily variation of PM2.5 and O3.
3.1.4. Daily Variation of PM2.5 and O3
The daily variations of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 are shown in Figure 4b. PM2.5 concentration had a relatively longer peak time than O3 concentration. The peak time of PM2.5 concentration is from midnight to early in the morning (typically 00:00–04:00) and from morning to noon (typically 09:00–12:00), while the off-peak time of PM2.5 concentration is from noon to late in the afternoon (typically 13:00–19:00). Considering the difference between Beijing time and the local time in Xiangyang City, it has been observed that the periods of lower PM2.5 concentrations in Xiangyang during the day primarily occur in the afternoon before sunset. Generally, at this time, solar radiation is high, and convective activity is more pronounced compared to other times of the day, which facilitates the dispersion of atmospheric particulates. Additionally, since PM2.5 particles have a smaller diameter, they are more susceptible to being dispersed by air currents. Therefore, under relatively favorable dispersion conditions, it is natural for PM2.5 concentrations to be lower [42,43]. In Xiangyang City, the peak time of O3 concentration was from late in the afternoon to midnight (typically 19:00–00:00), while the off-peak time of O3 concentration was from after midnight to morning (typically 02:00–08:00). It can be inferred that the main reasons are likely the combined effects of precursor concentration, photochemical reaction intensity, and atmospheric diffusion capacity. After sunrise, human activities such as traffic contribute to an increase in NO, while O3 oxidizes NO into NO2, resulting in lower ozone concentrations. However, as solar radiation intensifies, atmospheric photochemical reactions become more pronounced. Additionally, the substantial emissions of NOx from vehicles result in a titration effect on ozone formation, leading to a gradual increase in ozone concentration. After noon, as solar radiation intensity gradually decreases, the photochemical reactions of precursors slow down, resulting in reduced ozone generation. Nevertheless, the peak traffic time causes an increase in NO, leading to ozone reaching its peak in the evening. Consequently, ozone is continuously consumed, causing the ozone concentration to reach its lowest point in the morning [44].
3.2. Spatial Aggregation Characteristics of PM2.5 and O3
Considering the major driving factors of air pollution such as topographical conditions, meteorological conditions, and socio-economic development conditions, this study selected Xiangyang City and its closely adjacent prefecture-level administrative divisions as the study region and used spatial autocorrelation analysis to further analyze the correlation of major air pollutants in Xiangyang City with those of neighboring regions. Nanyang City, Shiyan City, Yichang City, Jingzhou City, Suizhou City, and Shennongjia Forestry District are geographically adjacent to Xiangyang City and have potential inter-relations within their air environmental systems.
The study divided the objects of study into four time periods: three specific periods, namely, 2019, 2020–2022, and 2023, along with an overall period which encompasses the five-year period based on continuous data from 2019 to 2023. First, we conducted a global spatial autocorrelation analysis using ArcGIS 10.2 software, concluding that in each time period, the distributions of PM2.5 and O3 concentration levels exhibit significant spatial clustering characteristics relative to Xiangyang City and its closely connected regional administrative units in China, with a p-value < 0.01, demonstrating an ultra-high degree of reliability. The results of the global spatial autocorrelation analysis are illustrated in Table 3. Subsequently, we performed a local autocorrelation analysis based on a spatial weight matrix, in which the average adjacency distance of the counties, cities, and districts within the study area served as the distance threshold. The statistical significance of local spatial autocorrelation (LISA) was assessed through a permutation test in this study. We adopted p < 0.05 as the criterion for statistical significance, with significance evaluated using 999 permutations at α = 0.05 and FDR correction. Clusters reported in the results are deemed significant when the FDR-adjusted p-value is less than 0.05. The LISA agglomeration map is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of PM2.5 and O3 revealed the regional difference between presence and absence in Figure 5 and 6, respectively. In the research, absent regional classifications in spatial autocorrelation analysis of PM2.5 were High–Low outlier and Low–High outlier regions, while in spatial autocorrelation analysis of O3 was merely Low–High outlier regions.

Table 3.
Global spatial autocorrelation analysis results (accurate to three decimal places).
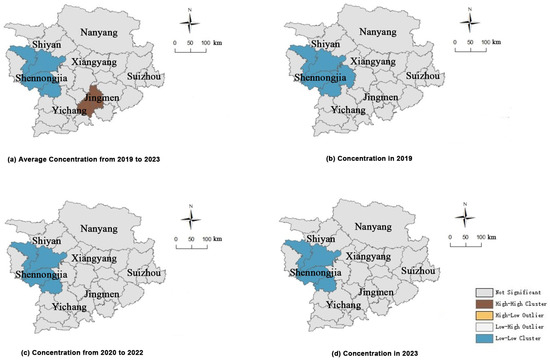
Figure 5.
LISA agglomeration map of PM2.5 concentrations in Xiangyang during (a) 2019–2023; (b) 2019; (c) 2020–2022; and (d) 2023.
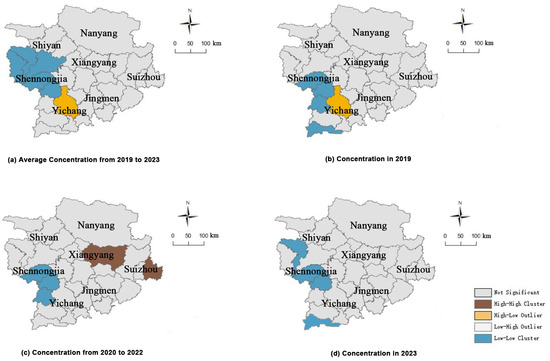
Figure 6.
LISA agglomeration map of O3 concentrations in Xiangyang during (a) 2019–2023; (b) 2019; (c) 2020–2022; and (d) 2023.
As seen in Figure 5, the regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 concentrations were southern Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forestry District, and northwestern mountainous region of Yichang City. The regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 concentrations expanded to the southwestern mountainous region of Xiangyang City in 2020–2022, while the overall change in the range of regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 concentrations was trivial. Significant High–High clusters of PM2.5 concentrations only appeared in the northeastern part of Yichang City and the western part of Jingmen City in 2019. The absence of significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 concentrations in later periods may be attributed to the strengthened enforcement of the Yangtze River ecological protection policies and rigorous restrictions controlling the spread of COVID-19 pandemic around 2020, as well as Yichang’s ongoing transition towards industrial greening, which involved shutting down several chemical enterprises and greatly reducing local pollution sources.
As can be seen from Figure 6, the regions with significant Low–Low clusters of O3 concentrations in 2019 were mainly distributed in southern Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forestry Region, and the northwestern mountainous region of Yichang City. The regions with significant of Low–Low clusters of O3 concentrations in 2020–2022 were primarily located in Shennongjia Forestry Region and the western mountainous region of Yichang. The significant Low–Low clusters of O3 concentrations were only found in the Shennongjia Forestry Region and the northwestern mountainous region of Yichang City in 2023. Distribution region changes indicated a continuous reduction in the distribution range of the regions with significant Low–Low clusters of O3 concentrations across the three research periods. The regions with significant High–Low cluster outliers of O3 concentrations occurred in 2019 and 2020–2022, both in the urban region of Yichang City. Yichang City is located at the junction of the upper and middle reaches of the Yangtze River, serving as a transitional area from the western Hubei mountainous region to the Jianghan Plain. As a sub-regional city in Hubei Province, Yichang is influenced by factors such as the obstruction of pollutant diffusion due to topography and a higher level of economic and industrial development. Consequently, there are significant differences and transitional characteristics between the urban area of Yichang and the mountainous region in the northwest. The regions with significant High–High clusters of O3 concentrations only appeared in 2023, and were distributed in the central and eastern parts of Xiangyang City and Suizhou City.
Figure 5d and Figure 6d show the results of data analysis based on the five-year average concentrations of PM2.5 and O3. The regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 concentration were primarily centered around Shennongjia Forest District in the Mount Daba region and the northern section of Mount Wu, particularly in the southern part of Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forest District, and northwestern region of Yichang City. These regions have a low population density and are predominantly natural reserves and vital water conservation regions in the Yangtze River basin. Human activities are relatively minimal, local pollution sources are few, and the terrain is relatively complex and enclosed, resulting in poor input conditions for pollutants. Therefore, this region also represented a concentrated zone of low PM2.5 concentrations surrounding Xiangyang City. There were no regions with significant High–High clusters of PM2.5 concentrations. The regions with significant Low–Low clusters of O3 concentration were primarily distributed in the southern region of Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forest District, and northwest Yichang City, and there were no regions with significant High–High clusters of O3 concentration. The regions with significant with Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 and O3 showed spatial consistency.
The changes observed in three periods indicated that the overlapping between regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 and O3 concentrations was larger in 2019. However, the area of overlapping regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 and O3 concentrations shrank significantly in 2020–2022 and 2023. In 2019, regions with significant Low–Low clusters of PM2.5 and O3 concentrations only overlapped in the Shennongjia Forestry District and Xingshan County, in Yichang City. The overlap in 2020–2022 added a new area including Wufeng Tujia Autonomous County and Zigui County, and in 2023, the overlapping region increased compared to 2019 by incorporating Zigui County. These observations suggest a certain spatial correlation between PM2.5 and O3, indicating that their sources may have some coupling.
3.3. Variation of ARI
3.3.1. Variation of ARI in Xiangyang
The annual averaged values of ARI and PSI in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 are shown in Table 4. The ARI values of Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 descended clearly, decreasing from 2.252 to 1.032. Compared to major urban agglomerations in China, the ARI in Xiangyang City still faced a slightly elevated health risk, which was similar to that of the cities in the Yangtze River Central Urban Group.

Table 4.
Variation of average ARI in Xiangyang City. (Accurate to three decimal places).
PSIPM2.5, a main contributor to ARI, was higher than 0 from 2019 to 2023, which indicated that Xiangyang City was confronted with higher health risks due to PM2.5 exposure. Moreover, annual PSIPM2.5 in Xiangyang City significantly declined, decreasing from 2.252 in 2019 to 1.032 in 2023, which signified that the health risks associated with PM2.5 exposure in Xiangyang City also reduced. PSIO3 values in Xiangyang City were all higher than 0 in 2019 and 2022, which indicated that Xiangyang City faced curtailed health risks due to O3 exposure. The annual PSIO3 from 2019 to 2023 demonstrated a distinct downward trend, decreasing from 0.102 in 2019 to 0 in 2023. This indicated that health risks from O3 exposure in Xiangyang City were also showing a distinct decline. Furthermore, annual PSISO2, PSINO2, and PSICO in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023 were all 0.
3.3.2. The Spatial Aggregation of ARI in Closely Adjacent Regions of Xiangyang
In conjunction with the previous conclusions of this research regarding the correlation of pollutants around Xiangyang City and its adjacent regions, this study selected Xiangyang City and its closely adjacent prefecture-level administrative divisions as the study region. We used an analysis of hot and cold spots to further assess the correlation of ARI in Xiangyang City with neighboring regions. Nanyang City, Shiyan City, Yichang City, Jingzhou City, Suizhou City, and Shennongjia Forestry District are geographically adjacent to Xiangyang City and have potential inter-related ARI. Thus, this study analyzed the spatial clustering of annual ARI values in Xiangyang City and its adjacent prefecture-level administrative divisions by using the hot and cold spot analysis method in the Moran index, and the results are shown in Figure 7. Among these, Hot and cold distribution analysis of ARI revealed the presence of regions, including not significant, hot spot (confidence > 90%, confidence > 95%) and cold spot (confidence > 90%, confidence > 95%), while hot spot (confidence > 99%) and cold spot (confidence > 99%) regions were found to be absent in Figure 7.
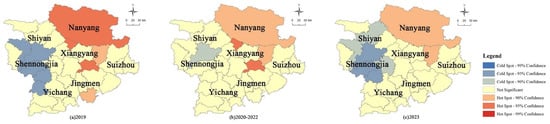
Figure 7.
Hot and cold spot distribution map of ARI during (a) 2019; (b) 2020–2022; and (c) 2023.
ArcGIS 10.2 software was used to analyze the hot spot distribution characteristics of ARI in closely adjacent regions of Xiangyang, and the ARI hot and cold spot distribution map at different stages is shown in Figure 7.
From 2019 to 2023, there was a significant trend of expansion in ARI cold spot regions. As seen in Figure 7, in 2019, the cold spot regions for ARI were southern Shiyan City, the Shennongjia Forestry District, and the northwestern mountainous region of Yichang City. The cold spot areas were primarily distributed in southern Shiyan and Shennongjia, where the confidence levels for cold spots were all higher than 95%. In 2020–2022, the cold spot regions of ARI shrank to the southern Shiyan City, with a confidence higher than 90%, so the range of cold spot regions for ARI was trivial. Meanwhile, the absence of significant cold spot regions (confidence > 95%) for ARI in these periods may be attributed to the strengthened enforcement of the Yangtze River ecological protection policies around 2020, as well as China’s scientific measures for COVID-19 prevention. In 2023, the cold spot regions of ARI expanded to the south central Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forestry District, the northwestern mountainous region of Yichang City and the southwestern mountainous region of Xiangyang City. Among these, the regions located in the southern Shiyan City, the Shennongjia Forestry District, and the northwestern mountainous areas of Yichang City were identified as cold spot areas with a confidence level higher than 95%, while the confidence levels of other cold spot areas were higher than 90%.
From 2019 to 2023, there was a significant trend of contraction in hot spot regions of ARI. This may be due to the environmental protection policies in China and the temporary and scientific control measures implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic to safeguard the health rights of the populace, which affected industrial development [41]. As seen in Figure 7, in 2019, the hot spot regions of ARI were the eastern and northwest regions of Xiangyang City, the southern part of Jingmen City, and Nanyang City, in Henan Province. The hot spot areas are primarily distributed in the southeastern part of Xiangyang City and its northwestern corner as well as Nanyang City, where the confidence levels for hot spots were all higher than 95%, while the confidence levels of other hot spot areas were higher than 90%. This may be related to the spatial distribution of the population and industry in the region. In 2020–2022, the hot spot regions of ARI shrank to the eastern and northwest regions of Xiangyang City, Nanyang City. The hot spot areas were primarily distributed in southeastern part of Xiangyang City and its northwestern corner, where the confidence levels for hot spots were all higher than 95%, while the confidence level of other hot spot areas is higher than 90%. In 2023, the hot spot regions of ARI further shrank to the eastern corner of Xiangyang City, Nanyang City, with a confidence level higher than 90%. This may be related to the need for further improvement in the coordination between provincial pollution control and industrial development [45].
3.4. Analysis of the Backward Trajectory Clustering of PM2.5 and O3
The research utilized the MeteoInfo 3.8.5 software developed by the Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences, taking Xiangyang City (112.12° E, 32.01° N) as the simulation receptor point to conduct post-HYSPLIT analysis, PSCF analysis, and CWT analysis.
Based on the backward trajectory clustering analysis model (Hybrid Single-Particle Lagrangian Integrated Trajectory, HYSPLIT), the trajectory simulation height was selected at 500 m. The O3 concentration in summer and the PM2.5 concentration in winter in 2019, 2020–2022, and 2023 serve as the basic data for analyzing the main sources of summer O3 and winter PM2.5 in Xiangyang City. In the trajectory clustering analysis results, longer trajectories indicate a greater distance traveled by the air mass during the study period, objectively reflecting the air flow field situation in Xiangyang City that determine the main source trajectories of input pollutants [24]. The results of the analysis are shown in Figure 8.
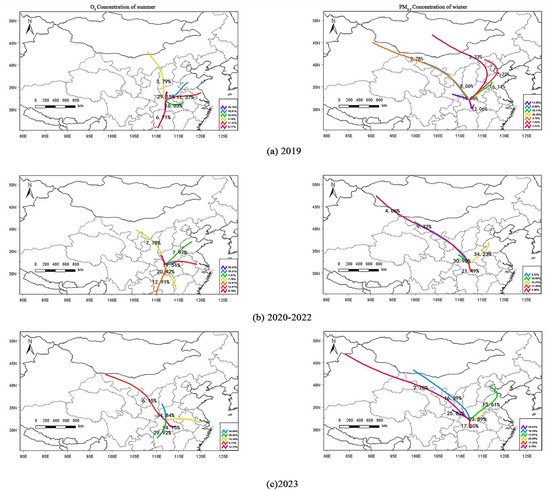
Figure 8.
Cluster analysis of backward trajectories in Xiangyang City during (a)2019; (b) 2020–2022; (c) 2023.
Compared to winter, the distance of airflow transport in summer was shorter, and the sources of air masses were more diverse in summer, and these were characterized by interannual differences. In 2019, the main transport trajectory (accounting for 29.15%) originated from the western mountainous regions of Henan Province, which had the shortest transport distance, passing through the southwestern part of Henan and northern Hubei to Xiangyang City. In 2020–2022, the primary airflow trajectory (accounting for 20.42%) came from the northern Dongtinghu Basin, passing through northern Hunan and the central Jianghan Basin of Hubei. In 2023, the highest proportion of airflow trajectory (accounting for 34.84%) and the shortest distance trajectory originated from the southwestern part of Shanxi Province, passing through western Henan and northern Hubei. The natural reasons that lead to the primary trajectory changes in the three research periods were the impacts of the evolution of El Niño and La Niña on the spatial and temporal distributions of the main summer rainfall band in China [46,47]. In 2019 and 2023, which were El Niño years, the quasi-stationary front was located in the southern part of the basin of the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, resulting in less precipitation in the northern regions. Airflows from the northwest, particularly in western Henan and southwestern Shanxi, were naturally able to move forward fluently with such meteorological and geographical factors. In contrast, during the years of 2021–2022, which were La Niña years, there was an increase in precipitation in northern China. The convergence of airflow in front of the front, along with multiple factors such as orographic uplift, contributed to the formation of extreme precipitation weather in certain regions [48].
In winter, compared to summer, the transport distance of air currents was longer, and the sources of air masses were relatively uniform but also exhibited interannual variation. In 2019, the main transport trajectory (accounting for 36.39%) originated from the eastern Henan Plain, with the shortest transport distance, passing through southern Henan and northern Hubei to reach Xiangyang City. The primary airflow trajectory (accounting for 34.23%) in 2020–2022, came from the northwestern Shandong Plain, passing through western Shandong, central and southern Henan, and northern Hubei. In 2023, the main airflow trajectory (accounting for 25.83%) originated from the Guanzhong Plain in Shaanxi, passing through southeastern Shaanxi and northwestern Hubei. From 2019 to 2022, the primary transport pathways for PM2.5 in winter were from the northeast of Xiangyang City, while in 2023, the main transport pathway was from the northwest of Xiangyang City, primarily influenced by changes in the high pressure system over the western Eurasian continent, which affected the pathway of cold air in East Asia during winter. The cold waves in northwest China gradually deepened due to the collapse of the blocking high over the Norwegian Sea, forming a ridge–trough–ridge wave pattern on the Eurasian continent, while the energy of the cold waves from the northern route propagated eastward from the Azores Islands to the Ural Mountains, triggering a blocking high [49]. During the years of 2019/2020 and 2020/2021, the blocking high was predominantly stronger than normal, and at this time, the cold waves affecting China were mainly from the northern route, so the primary airflow transport corridor for Xiangyang City came from the junction region of Shandong, Henan, and Anhui. In contrast, during the year 2022/2023, the blocking high was predominantly weaker than normal, and after entering 2023, the blocking high was persistently weaker than normal; therefore, the cold waves affecting China were mainly from the northern route, leading to the primary airflow transport corridor for Xiangyang City coming from the direction of Guanzhong plain in Shaanxi [50,51].
In summary, the airflow influencing O3 concentration in Xiangyang during the summer mainly originates from regions such as western Henan, southern Shanxi, and northern Hunan, where human activities are relatively frequent and intensive. Conversely, the airflow affecting PM2.5 concentration in winter primarily comes from the eastern Henan plain, the northwestern Shandong plain, and the Guanzhong plain, arriving at Xiangyang via topographical corridors. The concentration of atmospheric pollutants in adjacent regions contributes significantly to the variation of atmospheric pollutants in Xiangyang City. Moreover, provinces including Shanxi and Inner Mongolia, China, to the northwest, and Shandong, Anhui, Jiangsu, and Hunan to east and south, also exert a certain spatial transport effect on the summer O3 concentrations in Xiangyang. Other cities in Hubei, along with northwesterly and northeasterly airflows, also contribute to the winter PM2.5 pollution in Xiangyang.
3.5. Analysis of Potential Source Regions for PM2.5 and O3
This study analyzed the summer O3 concentrations, as well as the PM2.5 winter concentrations in 2019, 2020–2022 and 2023 using the PSCF (potential source contribution factor) analysis module in the TrajStat plugin of the MeteoInfo 3.8.5 software. The potential source regions for O3 concentrations of summer and PM2.5 concentrations of winter are detailed in Figure 9.
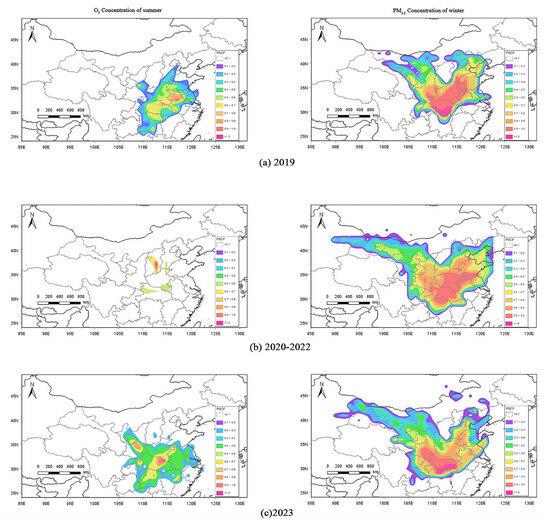
Figure 9.
Weighted potential source contribution function analysis in Xiangyang City during (a) 2019; (b) 2020–2022; and (c) 2023.
Based on the values and attributes used to analyze the studied regions with the weighted potential source contribution factor (WPSCF), and in conjunction with the characteristics of pollutant concentrations in Xiangyang City, the regions were categorized into extremely high-value regions (WPSCF > 1.00), very high-value regions (0.90 < WPSCF ≤ 1.00), high-value regions (0.70 < WPSCF ≤ 0.90), relatively high-value regions (0.50 < WPSCF ≤ 0.70), and other low-value regions (0.00 < WPSCF ≤ 0.50) [52].
In 2019, the high-value regions (WPSCF > 0.70) of summer O3 concentrations were located in the northeastern part of Hubei, the central-north part of Anhui, and the southwestern region of Anhui, while the relatively high-value regions were in central and northeastern Hubei, northern Hunan, southeastern Henan, and the western and central-northern parts of Anhui. There were no significant potential source regions for summer O3 concentrations in 2020–2022. In 2023, the high-value regions of summer O3 concentrations were mainly distributed over the northeastern part of Hubei, southeastern Henan, central Shaanxi, southeastern Gansu, and scattered regions in northern Yiyang, Hunan, and northern Chongqing. The relatively high-value regions (0.50 < WPSCF ≤ 0.70) were primarily distributed in central and northeastern Hubei, northern Hunan, southeastern Henan, and central and western Anhui. There were some overlapping potential summer O3 concentrations source regions between the high-value regions and relatively high-value regions in all three time periods, which were the main potential source regions for O3 concentrations in summer in Xiangyang City, and the research findings were generally consistent with the results from backward trajectory cluster analysis, indicating that Shanxi, Henan in the north, and Hunan in the south are the primary sources of summer O3 transport to Xiangyang City.
The distribution ranges of the high-value and relatively high-value regions for PM2.5 concentrations during the winters of 2019, 2020–2022 and 2023 exhibited considerable consistency. The high-value regions were primarily located in most of Hubei, northern Hunan, most of Henan, northern Anhui, northern Jiangsu, central and western Shandong, southeastern Hebei, southern Shanxi, northern Chongqing, central and southern Shaanxi, eastern Gansu, and other regions. The relatively high-value regions were mainly distributed in most of Hubei, northern Hunan, Henan, central and northern Anhui, central and northern Jiangsu, most of Shandong, Tianjin, southeastern Hebei, southern Shanxi, central and northern Chongqing, northeastern Sichuan, most of Shaanxi, eastern Gansu, eastern Ningxia, and southwestern Inner Mongolia, China. The extremely high-value regions during the three periods showed a certain degree of consistency in most of Hubei and northern Hunan, with the contribution rate from potential source regions exceeding 0.90. In 2019, southern Hubei and northern Hunan were identified as the extremely high-value regions for winter PM2.5 concentrations, with a contribution rate exceeding 1.00, which significantly overlapped with the distribution range of extremely high-value regions in 2023.
3.6. Weighted Trajectories of PM2.5 and O3
Based on summer O3 concentrations and winter PM2.5 concentrations during 2019, 2020–2022, and 2023, a CWT (concentration-weighted trajectory), the TrajStat plugin of the MeteoInfo 3.8.5 software was used to analyze the weighted concentrations of potential source regions for summer O3 concentrations and winter PM2.5 concentrations in Xiangyang City. The results are shown in Figure 10. According to the values and attributes of WCWT (weighted-concentration-weighted trajectory), combined with the pollutant concentrations in Xiangyang City, the regions were classified into ultra-high-value regions (cwt > 100 μg·m−3), high-value regions (70 μg·m−3 < cwt ≤ 100 μg·m−3), and other low-value regions (cwt ≤ 70 μg·m−3) [53,54].
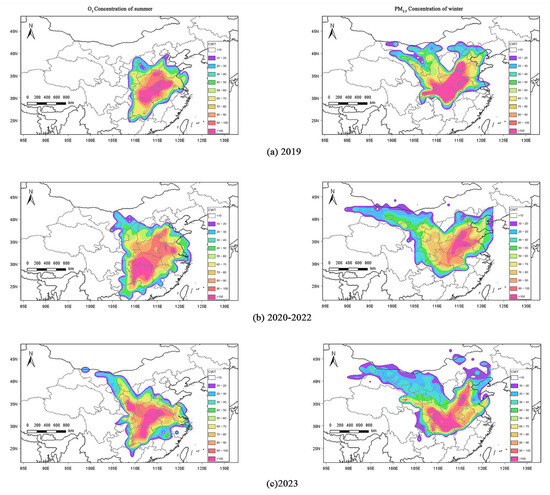
Figure 10.
Weighted-concentration-weighted trajectory analysis in Xiangyang City during (a) 2019; (b) 2020–2022; and (c) 2023.
The regions with ultra-high summer O3 concentrations in 2019 exhibited a zonal banded distribution from northeast to southwest, primarily located in eastern Hubei Province, northernmost Hunan Province, southeastern Henan Province, and northwestern Anhui Province. The ultra-high value regions of summer O3 concentrations in 2020–2022, formed a large cluster in southern Hubei Province and northern Hunan Province, with two smaller clusters located at the junction of Anhui, Shandong, and Henan and the border of Anhui and Jiangsu. In 2023, there were two patches of the ultra-high CWT value regions of summer O3 concentrations, with the larger patch roughly exhibiting a banded distribution orienting northeast–southwest, primarily involving the three provinces of Hunan, Hubei, and Henan, while the smaller patch was mainly located in the central part of the Guanzhong Plain in Shaanxi. The high-CWT regions of summer O3 concentrations extended outward from the center of the ultra-high value regions in these three research periods. In 2019, it primarily extended toward northwest along the zonal band. During 2020–2022, it mainly extended toward the larger northeastern cluster region. In 2023, it primarily connected from the large cluster region to the northwestern and northeastern small cluster region, merging into a new region.
The CWT values of winter PM2.5 concentrations in 2019 exhibited ultra-high value clusters, mainly distributed in most regions of Hubei, southeastern Henan, northwestern Anhui, and southeastern Hebei. During 2020–2022, the distribution of CWT values of winter PM2.5 concentrations showed smaller regional clusters than in 2019, located at the border of Henan, Anhui, and Shandong. The CWT values of winter PM2.5 concentrations in 2023 were mainly distributed in the western half of the clusters in 2019, extending toward the northwest from central Hubei to southern Shaanxi, and southward to northern Hunan, with smaller patches formed at the border of Henan and Shandong. In all three periods, the high-value regions of winter PM2.5 concentrations all expand outward from the ultra-high-value regions, with limited extension in 2019, a significant westward expansion during 2020–2022, and considerable extensions in both northwest and northeast directions in 2023.
The potential source regions contributing to summer O3 concentrations and winter PM2.5 concentrations in Xiangyang during the three research periods were comparable across the regions. However, the distribution ranges differ across different periods, with the surrounding provinces contributing to summer O3 concentrations and winter PM2.5 concentrations in Xiangyang.
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations and Prospects
Despite the valuable insights provided by this study into the spatiotemporal patterns, health risks, and potential sources of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City, several limitations should be acknowledged, and avenues for future research are suggested.
The limitations of this study include the following points:
(1) The research focus of this study is relatively conventional, with limited investigation of specific pollutants. This paper focuses on analyzing the atmospheric concentrations of conventional pollutants such as PM2.5 and O3 in the study of air pollutants. However, constrained by experimental conditions, our study lacks a specific analysis of the chemical characteristics and concentrations of these pollutants, resulting in a deficit in understanding their spatiotemporal distribution patterns regarding varying chemical components and their sources and contributions. This leads to an inadequate assessment of the harm to the health of local exposed populations from specific chemical pollutants. This limits the assessment of the impact of various harmful substances in the atmosphere on local communities, complicating more precise health risk assessments for populations exposed to air pollution. It is also important to note that different chemical components of pollutants have varying toxicological mechanisms and response times, with varying effects on the health of different populations. Due to practical constraints, this study does not differentiate between dynamic migrating populations and the static resident population, nor does it conduct detailed analysis of groups with varying age and occupational structures, and it fails to specifically analyze respiratory-sensitive populations.
(2) The research methods exhibit a certain degree of innovation but still have room for optimization. This study employs cold and hot spot analysis, spatial autocorrelation analysis, ARI, PSCF, and other cross-disciplinary research methods based on different data. ARI is a relatively simple exposure metric calculated using a formula that includes the relative risk (RR) value utilized by the authors. However, since it requires analysis of calculation results, which are not standardized values, there may be unavoidable subjectivity when determining the actual impact of these values. Therefore, compared to more rigorous methods and models such as GBD and GEMM, our methodology still has certain limitations. The PSCF method, on the other hand, cannot determine weight; therefore, we combined it with the CWT method to ascertain weight. However, the errors induced by its simulative evolution characteristics are difficult to avoid, and it only simulates the trajectory of input air masses, which does not fully and directly reflect the distribution of pollutant sources on a smaller scale.
(3) There are still constraints regarding the temporal aspect of the research data, and the data sources are somewhat sparse. Firstly, the number of air monitoring stations is limited, leading to relatively sparse sample sizes when analyzing spatiotemporal heterogeneity. Secondly, some monitoring stations have missing data or missing periods; higher time-resolution data could reveal more detailed diurnal variation patterns and short-term peak events, but we could only obtain hourly level data. This limitation may affect the precision of long-term trend analysis and source apportionment results. Furthermore, the meteorological data used for model simulation and analysis may lack sufficient spatial resolution or key variables, and not combining the data with lower-grade ground meteorological monitoring stations hinders capturing the complex interactions between meteorology and pollutant diffusion and formation in the unique plain–basin transition topography of Xiangyang, Hubei Province, China. Finally, the reliance solely on data published by official institutions, without any other scientific evidence for mutual support due to the lack of experimental and practical conditions, adversely affects the accuracy of the results analyzed based solely on these datasets.
The research future prospects are as follows:
(1) Future research will have a narrower focus to enhance specificity. Given the permissible experimental conditions, it is advisable to attempt a specific analysis of the chemical characteristics and concentrations of pollutants. This will enrich the understanding of the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of different chemical pollutants and the conditions influencing their sources and contributions. It will also involve examining the harm caused by specific chemical pollutants to the health of local exposed populations, in conjunction with the principles of toxicological effects of different harmful substances on various groups. This will help reveal the impact of different harmful substances in the atmosphere on local populations and enable more precise health risk assessments for those exposed to air pollution. Future research could also incorporate timely investigations based on actual circumstances, analyzing various populations differentiated by age and occupational structure, as well as those particularly sensitive to respiratory issues, including vulnerable social groups.
(2) Our future research aims to innovate research methods to reduce analytical simulation. Future research could employ more rigorous and less subjective methodologies and models, such as the GBD approach and GEMM model, for analyses. Although the PSCF method has inherent simulation characteristics that may lead to errors, we can utilize high-precision and high-resolution meteorological data, where experimental conditions permit, in conjunction with localized meteorological monitoring data for analysis and cross-validation. Enhancing cooperation among different regional institutions will also aid in accurately identifying pollution sources.
(3) Enriching the temporal aspects of data and its sources will also be a focus. Firstly, under permissible experimental conditions, we aim to increase the distribution density of both routine and specialized air monitoring sites to improve the sample size so that it better reflects spatiotemporal heterogeneity, thereby enhancing the quality and scientific rigor of the analysis. Secondly, we aim to improve the capacity to obtain high temporal resolution data, which will enhance the accuracy of long-term trend analysis and source apportionment results. Additionally, employing multiple data sources will improve the spatial resolution or critical variables of meteorological data used for model simulation and analysis.
4.2. Results Discussion
The conclusions presented in this study supplement the temporal and spatial distribution patterns, health risks, and potential sources of PM2.5 and O3 in Xiangyang City between 2019 and 2023, to a certain extent. This section discusses both the methodological application and regional comparison.
In terms of methodological application, the following aspects are explored:
The ARI index serves as a quantitative indicator to assess the cumulative health risks posed by various traditional pollutants using a comprehensive risk index model, which is the basis for analyzing the health risks of traditional air pollutants to residents in this study. The findings reveal that the ARI in Xiangyang City shows a significant declining trend (from 2.252 in 2019 to 1.032 in 2023), which aligns closely with the decreasing trend in PM2.5 concentrations. Additionally, the PSIPM2.5 data cross-verifies the correlation between ARI changes and PM2.5 air pollution concentrations. However, the ARI calculations depend on the selected relative risk values and threshold concentrations. Although effective for analyzing temporal trends in this research, comparisons with regions using different relative risk coefficients or thresholds may lead to biases, making such comparisons difficult. Future studies of this nature could improve the comparability and verifiability of health risk assessment indicators through sensitivity analysis of relative risk values or cross-supplementary health impact assessment models.
Regarding spatial autocorrelation analysis, the application of spatial autocorrelation analysis effectively reveals significant spatial clustering patterns of PM2.5 and O3, particularly in the Low–Low clustering areas that persist in the tightly connected prefecture-level administrative regions of Xiangyang City, Hubei Province, including Shiyan City, Shennongjia Forest District, and some mountainous areas in northwestern Yichang. This might reflect the impact of unique terrain and relatively limited human activities on air quality. The changes in spatial clustering areas over time, particularly the spatial consistency and shrinkage of Low–Low clustering areas for PM2.5 and O3, suggest the existence of potential common influencing factors. Therefore, future studies of this nature could further clarify specific emission sources or inter-regional atmospheric connectivity through backward trajectory simulation models and other methods.
In the context of HYSPLIT model analysis, the comprehensive application of HYSPLIT, PSCF, and CWT provides a multi-angle analysis of potential source regions. The HYSPLIT analysis reveals trajectory paths from western Henan, southern Shanxi, and northern Hunan in summer, and from the eastern plains of Henan, northwestern Shandong, and central Shaanxi in winter, highlighting consistency with the high WPSCF, WCWT regions, thus enhancing the credibility of the identified potential source regions in this research. The decreasing trend in the weights of traditional potential source regions—in summer dominated by O3 in Anhui, and in winter by PM2.5 in Shandong, Henan, and Anhui—along with the increasing trend in the potential area weights for O3 as the primary pollutant in central Shaanxi during summer and PM2.5 during winter, represents a significant finding. This underscores the dynamic nature of pollutant source propagation, potentially related to the industrial activities and energy structure of the Guanzhong urban agglomeration. The CWT analysis further refines the identification of core contributing areas by providing weighted concentration estimates. However, trajectory models still have limitations in accurately identifying local sources within the grid. Future studies could combine analytical models with local emission inventories to better parse the specific regional contributions within these source regions.
The comparison of regions was based on the following aspects:
In terms of urban temporal trends, from 2019 to 2023, the PM2.5 concentration in Xiangyang City, Hubei Province, China, significantly decreased, while the O3 concentration showed a fluctuating downward trend. Overall, this aligns with the national air quality improvement trend observed in China since the implementation of strict ecological and environmental protection policies in recent years. However, the notable decrease in PM2.5 concentration may reflect the impacts of regional environmental protection policies, dynamics in local industrial structures, as well as the unique effects of reduced activities during the pandemic control measures in 2020.
Regarding regional health risks, although there was a significant downward trend in the Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) rates in Xiangyang City from 2019 to 2023, the numerical levels still indicate a higher health risk compared to ecologically well-off areas in China. Combined with other relevant research findings, the level and trend of health risks associated with air pollution in Xiangyang City are more in line with the urban areas within the Yangtze River middle reaches in mainland China. Among these, PM2.5 is identified as a major driving factor for ARI, especially in winter, demonstrating its significant impact on the health risks posed by air pollution in Xiangyang City. The basin topology of cities within the Yangtze River middle reaches still holds practical research significance.
On the distribution of pollutant spatial aggregation and potential source regions, the observed Low–Low cluster phenomenon in mountainous regions is similar to that found in other ecologically well-preserved areas in complex terrain across China. The contraction of the Low–Low cluster over time may be related to regional policy impacts such as ecological protection in the Yangtze River basin. In contrast to research conducted in key areas such as the core cities of the North China Plain or the Fenwei Plain, the regions surrounding the Huanghuaihai Plain in China—including parts of northern Hubei, Henan, northern Anhui, Shandong, and Hebei—have been identified as major source regions for PM2.5 in winter. This aligns with numerous studies addressing haze formation in the central and eastern regions of China and highlights the uniqueness and significance of input transmission of traditional pollutants in Xiangyang City. The Guanzhong Plain in Shaanxi has emerged as a significant potential source region contributing to O3 as the primary pollutant in summer and particularly to PM2.5 in winter. This unique research finding is attributed to Xiangyang City’s geographical location, which is situated downwind of this developmental area. Furthermore, it indicates that air pollution control in Xiangyang City requires not only local measures but also coordination with neighboring regions to mitigate the adverse impact of input pollutants on local air quality.
5. Conclusions
The concentrations of PM2.5 in Xiangyang City decreased progressively from 2019 to 2023. The seasonal concentrations of PM2.5 were ranked in the following order: winter >autumn > spring > summer. The seasonal concentrations of O3 were ranked as follows: summer > spring > autumn > winter.
The ARI values of Xiangyang City dropped significantly, decreasing from 2.252 in 2019 to 1.032 in 2023. PSIPM2.5 was the main contributor in corresponding seasons. From 2019 to 2023, there was a significant trend of expansion in cold spot regions of ARI. And there was a significant trend of contraction in hot spot regions of ARI. This may be related to the coordination between pollution control and industrial development.
According to Spatial autocorrelation analysis based on Moran’s index, the spatiotemporal distribution of PM2.5 and O3 showed consistency in Xiangyang City and its adjacent districts, which implies significant spatial correlation between major pollutants. With the variation of the intensity of human activities in different years, the spatial aggregation regions of PM2.5 and O3 shrank gradually. The spatial correlation of PM2.5 and O3 indicated a significant possibility of common sources.
The results of backward trajectory clustering analysis, PSCF analysis and CWT analysis in Xiangyang City were basically consistent. The potential source regions of O3 in summer were concentrated in northeastern Hubei, southeastern Henan, western and northern Anhui and central Shaanxi. The weight of potential sources of O3 in summer showed a decreasing trend in Anhui and an increasing trend in central Shaanxi. The main potential pollution sources of PM2.5 in winter extended to Hubei, northern Hunan, Henan, northern Anhui, western Shandong, central Shaanxi province. The weight of potential sources of PM2.5 in winter showed a decreasing trend in Shandong, Henan and Anhui province, and an increasing trend in central Shaanxi. Thus, central Shaanxi was becoming a new major potential source region of atmospheric pollutants for Xiangyang City.
Author Contributions
Methodology, X.C.; Writing—original draft, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Program No. 2018JQ4038, 2021JQ-862).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Air quality data were published by the China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (https://air.cnemc.cn:18007/), and Ecology and Environment of Hubei Province (https://sthjt.hubei.gov.cn/). The historical time series meteorological data of the Global Data Assimilation System (GDAS) were provided by the National Center for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) in the United States (ftp://arlftp.arlhq.noaa.gov/pub/archives/gdas1/).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Program No. 2018JQ4038, 2021JQ-862).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The work described has not been submitted elsewhere for publication, in whole or in part, and all the authors listed have approved the manuscript that is enclosed.
References
- Motesaddi, S.; Hashempour, Y.; Nowrouz, P. Characterizing of air pollution in Tehran: Comparison of two air quality indices. Civ. Eng. J. 2017, 3, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Kan, H.D.; Chen, R.J.; Jiang, S.H.; Hong, C.J. Air pollution and health studies in China-policy implications. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2011, 61, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the air: A review of the effects of particulate matter air pollution on human health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.H.; Liu, H.; Liang, T.L.; Xiang, X.; Li, M.; Juan, J.; Song, J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, L.B.; et al. Ambient air pollution and daily hospital admissions: A nationwide study in 218 Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the global burden of diseases study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.J.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.H.; Wu, Y. Assessment of the Economic Loss of Health Damages Caused by Air Pollutants in Typical Chinese Cities from 2016 to 2023. Earth Environ. 2025, 53, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, M.; Mantecca, P.; Cetta, F.; Camatini, M. Organic compounds in tire particle induce reactive oxygen species and heatshock proteins in the human alveolar cell line A549. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.H.; Huang, Z.G.; Feng, C.; Li, B.; Li, T.S. Atmospheric Fine Particulate Pollutants Concentrations of PM2.5 and its Effects on Inflammatory Factors in Pulmonary Epithelial Cells. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 2015, 15, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, Z.X.; Shao, W.Q.; Sun, B.; Li, L.; Liu, J.G.; Li, G.; Lv, X.Q. Study on the Effects of Dust Particle Size and Respiratory Intensity on the Pattern of Respiratory Particle Deposition in Humans. Indoor Air 2024, 1, 5025616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.T.; Tang, A.; Cheng, Y.K.; Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, L.D.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.C. Study of dust deposition pattern in the respiratory tract of dust particles less than 10 μm in size. Powder Technol. 2024, 444, 120033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sicard, P.; Lesne, O.; Alexandre, N.; Mangin, A.; Collomp, R. Air quality trends and potential health effects-Development of an aggregate risk index. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Pan, X.L.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.T.; Lei, S.D.; Yao, W.J.; Liao, Q.; et al. Cross-boundary transport and source apportionment for PM2.5 in a typical industrial city in the Hebei Province, China: A modeling study. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 115, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Q.; Wei, W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Lv, Z.; Wang, C.D.; Niu, Y. Composition analysis and formation pathway comparison of PM1 between two pollution episodes during February 2017 in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 223, 117–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.W.; Hao, Y.P.; Zhu, X.D.; Wang, J.W.; Xue, P.; Liu, W.T. Variations in ozone pollution and their meteorological influences and transmission sources in Linfen City of China. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 42, 3626–3634. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.H.; Li, M.Z.; Gao, D.M.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, D.H. Impact of dust events on the concentration, property and distribution of atmospheric bioaerosols. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 568–577. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Pan, X.L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.S.; Ge, B.Z.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X.; Lei, S.D.; Yao, W.J.; et al. Transport Patterns and Potential Sources of Atmospheric Pollution during the XXIV Olympic Winter Games Period. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2022, 39, 1608–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.B.; Fu, F.; Wang, J.N.; Tang, G.Q.; Lei, Y.; Yang, J.T.; Wang, Y.S. Numerical study on the characteristics of regional transport of PM2.5 in China. China Environ. Sci. 2014, 34, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhong, Y.S.; Wang, R.P. Impacts of Anthropogenic Emission Reduction and Meteorological Conditions on PM2.5 Pollution in Typical Cities of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei in Winter. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 4095–4103. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, T.; Du, H.B.; Lin, Z.G.; Zuo, J. Spatial spillover effects of environmental regulations on air pollution: Evidence from urban agglomerations in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 110998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.H.; He, C.; Yang, L.; Ye, Z.X.; Tian, Y.; Ke, B.Q.; Mu, H.; Tu, P.Y.; Han, C.R.; Hong, S. Spatial Correlation between Changes in Global Temperature and Major Air Pollutants during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 740–749. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, Y.R.; Li, Q.F.; Liu, C.M.; Xiao, J.Y. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and potential source analysis of ozone in Shijiazhuang. Environ. Monit. China 2024, 40, 54–65. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Yu, Y.; He, J.J.; Zhao, S.P. Analysis of air pollutant transport in winter in Lanzhou. Res. Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 509–516. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; An, X.Q.; Fan, G.Z. Transport pathway and potential source region of atmospheric particulates in Beijing. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 39, 915–927. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.Y.; Yao, W.J. Emission prediction of major atmosphere pollutants in Xiangyang. J. Wuhan Polytech. Univ. 2020, 39, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F. Study on the Characteristics of Atmospheric PM2.5 Pollution Sources in Xiangyang During the 13th Five-Year Plan Period. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2023, 12, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Xu, H.H.; Qin, Q.G.; Peng, J.J.; Hu, C.J.; Xia, J.J.; Zhang, S.C. Analysis of Seasonal Characteristics and Potential Sources of Air Pollution in Xiangyang City. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2023, 32, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.C. Analysis of Influencing Factors of Meteorological Conditions on Air Quality: A Case Study of Xiangyang. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2021, 19, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.D. Temporal and spatial visibility trends in the Sichuan Basin, China, 1973 to 2010. Atmos. Res. 2012, 112, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Zhu, J.M. National environmental monitoring and local enforcement strategies. Nat Cities 2025, 2, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Guo, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, T.B.; Wang, G.X. Spatio-temporal Characteristics of Atmospheric Pollution and Cause Analysis of Haze Events in Sichuan Basin, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021, 31, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, X.M.; Shou, R.P.; Yang, L.X.; Wang, W.X. Semi-continuous analysis on the water-soluble inorganic ions of PM2.5 in spring in Jinan City. China Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cairncross, E.K.; John, J.; Zunckel, M. A novel air pollution index based on the relative risk of daily mortality associated with short term exposure to common air pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8442–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei Baghini, N.; Falahatkar, S.; Hassanvand, M.S. Time series analysis and spatial distribution map of aggregate risk index due to tropospheric NO2 and O3 based on satellite observation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyta, H. Classification of air quality based on factors of relative risk of mortality increase. Environ. Prot. Eng. 2008, 34, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y.; Sun, Z.W.; Cao, J.J.; Wang, X.M.; Zhong, L.J.; Bi, X.H.; Li, H.; Liu, W.X.; Zhu, T.; Huang, W. Systematic review of Chinese studies of short term exposure to air pollution and daily mortality. Environ. Int. 2013, 54, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095—2012; China National Standards. Ambient Air Quality Standards: GB 3095—2012. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Qi, K.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Li, Q.X. Metaphor representation of resource nodes in cyberspace based on local Moran index and PageRank algorithm. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2024, 26, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.J.; Zhou, W.Q.; Li, W.F.; Qian, Y.G. Urbanization strategy and environmental changes: An insight with relationship between population change and fine particulate pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.H.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, L.P.; Li, L.; Lou, S.R.; Yan, R.S.; Wang, H.L.; Tao, S.K.; Chen, C.H. Impact of the air mass trajectories on PM2.5 concentrations and distribution in the Yangtze River Delta in December 2015. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2016, 36, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.L.; Miao, Q.; Shen, L.J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Y.Z.; Wei, H. Air pollutant variations in Suzhou during the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) lockdown of 2020: High time-resolution measurements of aerosol chemical compositions and source apportionment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 271, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.Y.; Zhang, Y. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of air pollutant concentrations in Sichuan and Chongqing area. China Sci. 2018, 13, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.G.; Feng, X.Y.; Zeng, X.Q.; Ma, Y.X.; Shang, K.Z. A study on variations of concentrations of particulate matter with different sizes in Lanzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2823–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.Y.; Gou, X.H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Y.L. The Variety of Ozone and its Relationship with Meteorological Conditions in Typical Cities in China. Plateau Meteorol. 2020, 39, 416–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Shuai, C.Y.; Bian, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Shen, L.Y. Socioeconomic factors of PM2.5 concentrations in 152 Chinese cities: Decomposition analysis using LMDI. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.L.; Bao, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zhang, M. Recent progresses of studies on influence of ENSO on the East Asian summer monsoon and China summer rainfall. J. PLA Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2005, 4, 394–398. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Xing, C.; Wang, H. Different responses of East Asian summer rainfall to El Niño decays. Clim Dyn. 2019, 53, 1497–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.C.; Tian, J.H.; Chen, C.H.; Li, Z.F.; Fu, W.J.; Zhou, H.L.; Chen, H.X.; Wang, K.H. Causes Analysis of the 20 July, 2021 Extreme Rainstorm in Zhengzhou. Meteorol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 45, 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, B. Interdecadal Variations of Autumn Cold Surge Paths over North China and Its Possible Mechanism. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.G. Atmospheric circulation characteristics of northern hemisphere in winter of 2022/2023 and its impact on weather and climate of China. Meteorol. Mon. 2023, 49, 881–891. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.B.; Sun, S.Q.; Chen, B.M. Maintenance and Development of Ural Blocking High and its Relationship with Severe Cold Wave Activities in 2020/2021 Winter. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 47, 1421–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zhang, L.X.; Shan, M. Analysis of Potential Source Regions and Transport Pathways of PM2.5 and O3 in Tianjin by Season. Res. Environ. Sci. 2022, 35, 673–682. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.P.; Song, X.W.; Zhu, X.D.; Wang, J.W.; Cheng, P.; Kong, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Potential Source Regions of PM2.5 Pollution in Xianyang City, Guanzhong Basin. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 579–590. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.N.; Zhang, M.M.; Bian, S.P.; Yao, C.C.; Zhao, L.; Sun, T.B.; Cai, J.; Qiao, S.N. Characteristics and Sources Analysis of PM2.5 in Xiangyang in Autumn and Winter. Environ. Monit. China 2023, 39, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).