Lake-Effect Snowfall Climatology over Lake Champlain: A Comparative Analysis of the 2015–2024 and 1997–2006 Periods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radar and Event Classification
- Transitional events (NorthTRAN and SouthTRAN): evolved from broader synoptic systems into narrow bands with distinct LE features;
- Synoptic events (NorthSYNOP and SouthSYNOP): maintained mesoscale structure while embedded within transient synoptic environments;
- North–South events: rare cases in which band orientation transitioned from northward to southward or vice versa due to shifting wind regimes.
2.2. Surface Observations
2.3. Lake Temperature and Ice Cover
2.4. Event Filtering Criteria
- Wind direction (WDF2) was within 22.5–337.5° (excluding easterly winds);
- Wind speed (WSF2) was less than or equal to 11.5 m/s;
- Minimum Temperature (TMIN) satisfied: −34 °C ≤ TMIN ≤ −5 °C;
- Dew point (ADPT) satisfied: −34 °C ≤ ADPT ≤ −4 °C;
- Mean sea-level pressure (ASLP) satisfied: 1010 hPa ≤ ASLP ≤ 1044 hPa.
2.5. Visualization and Statistical Tools
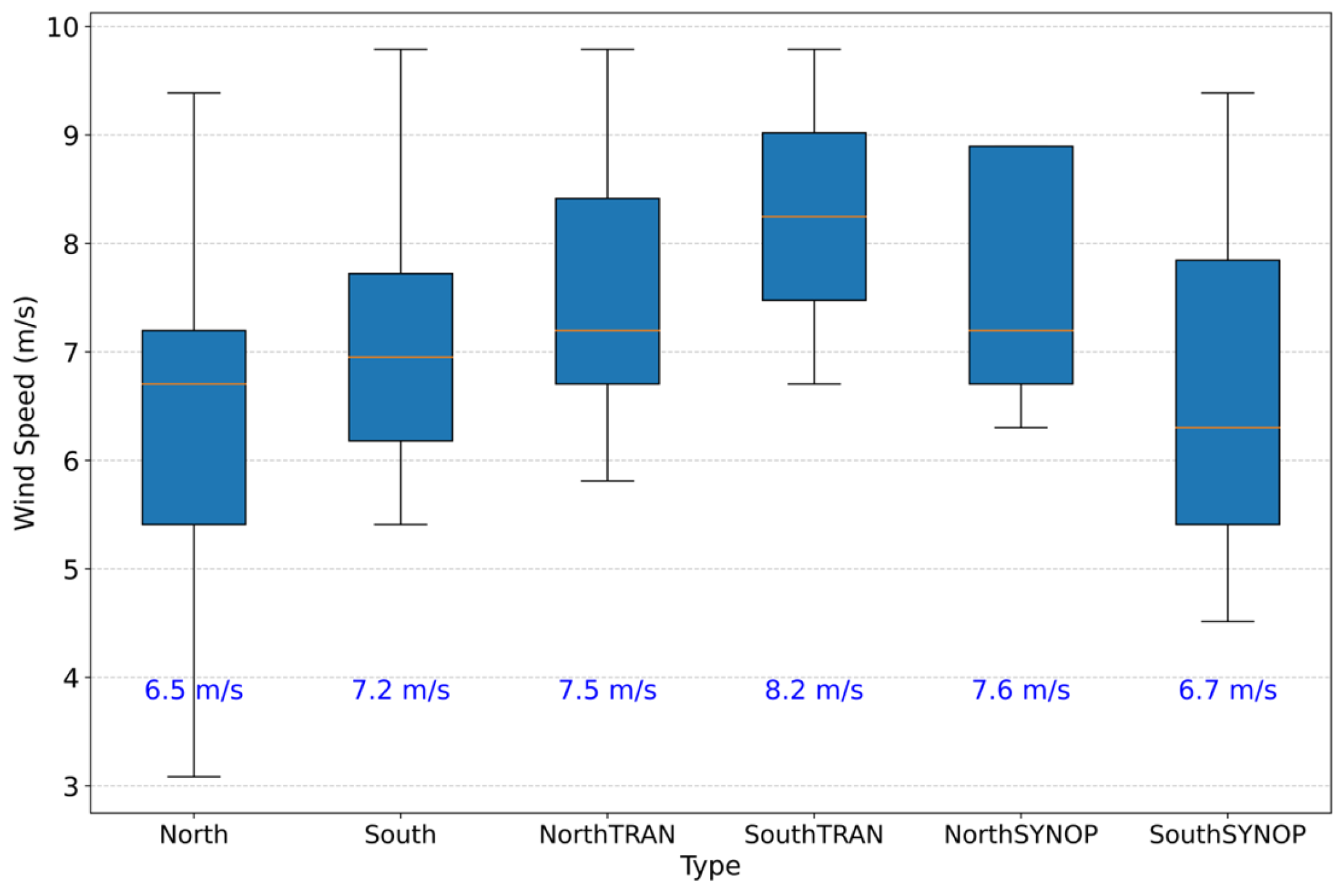
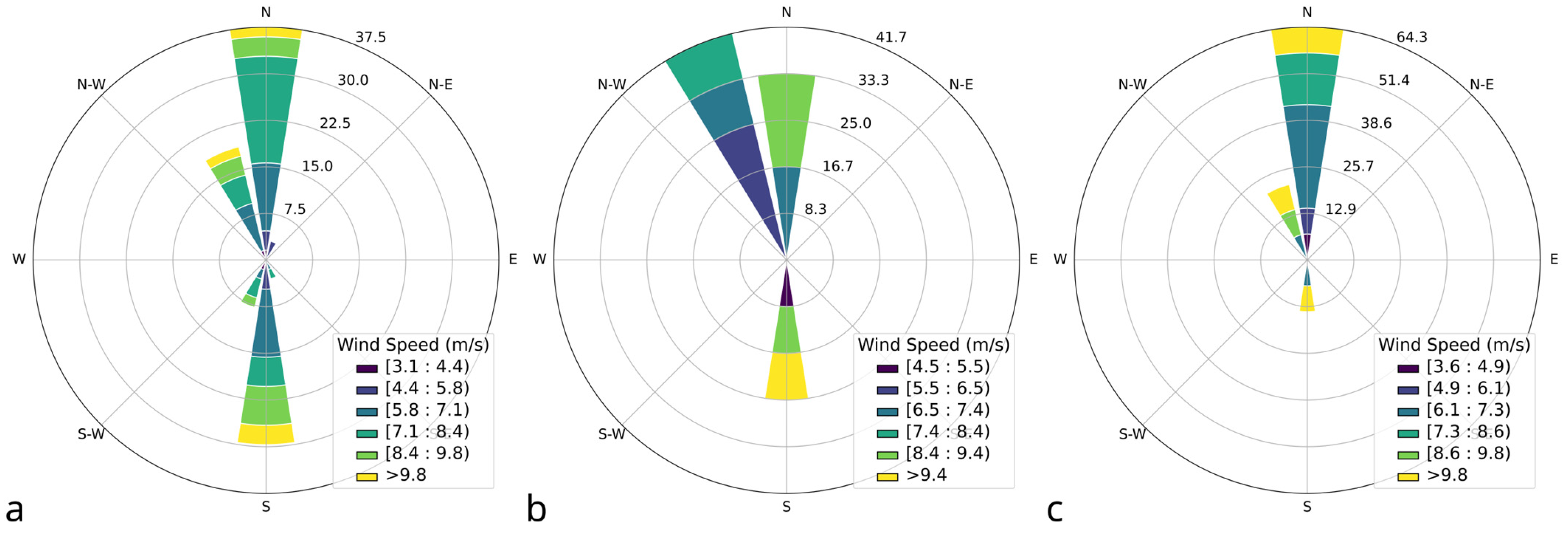
- Wind roses based on the highest daily 2 min sustained wind, with a maximum wind speed value of 9.8 m/s;
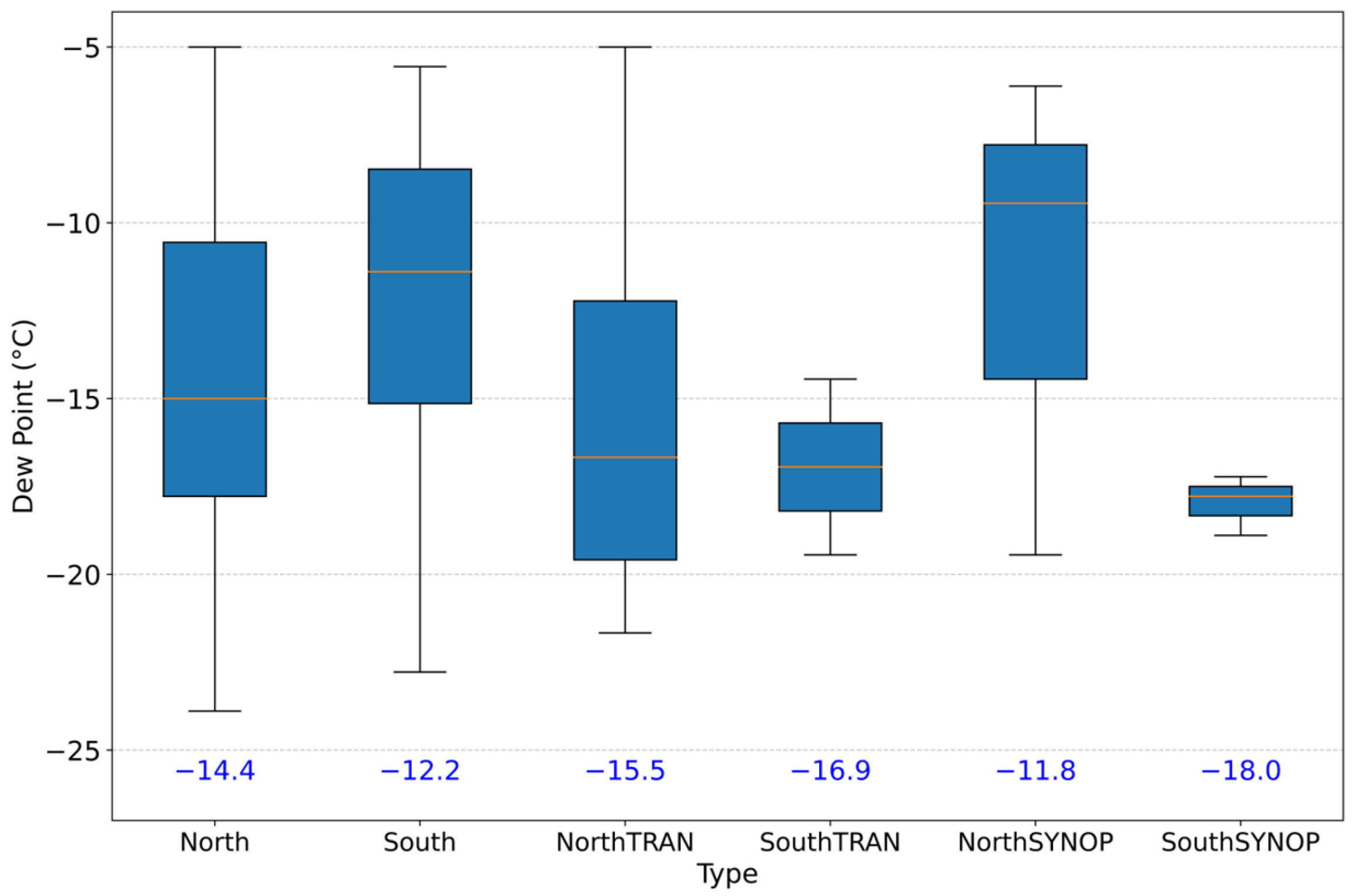
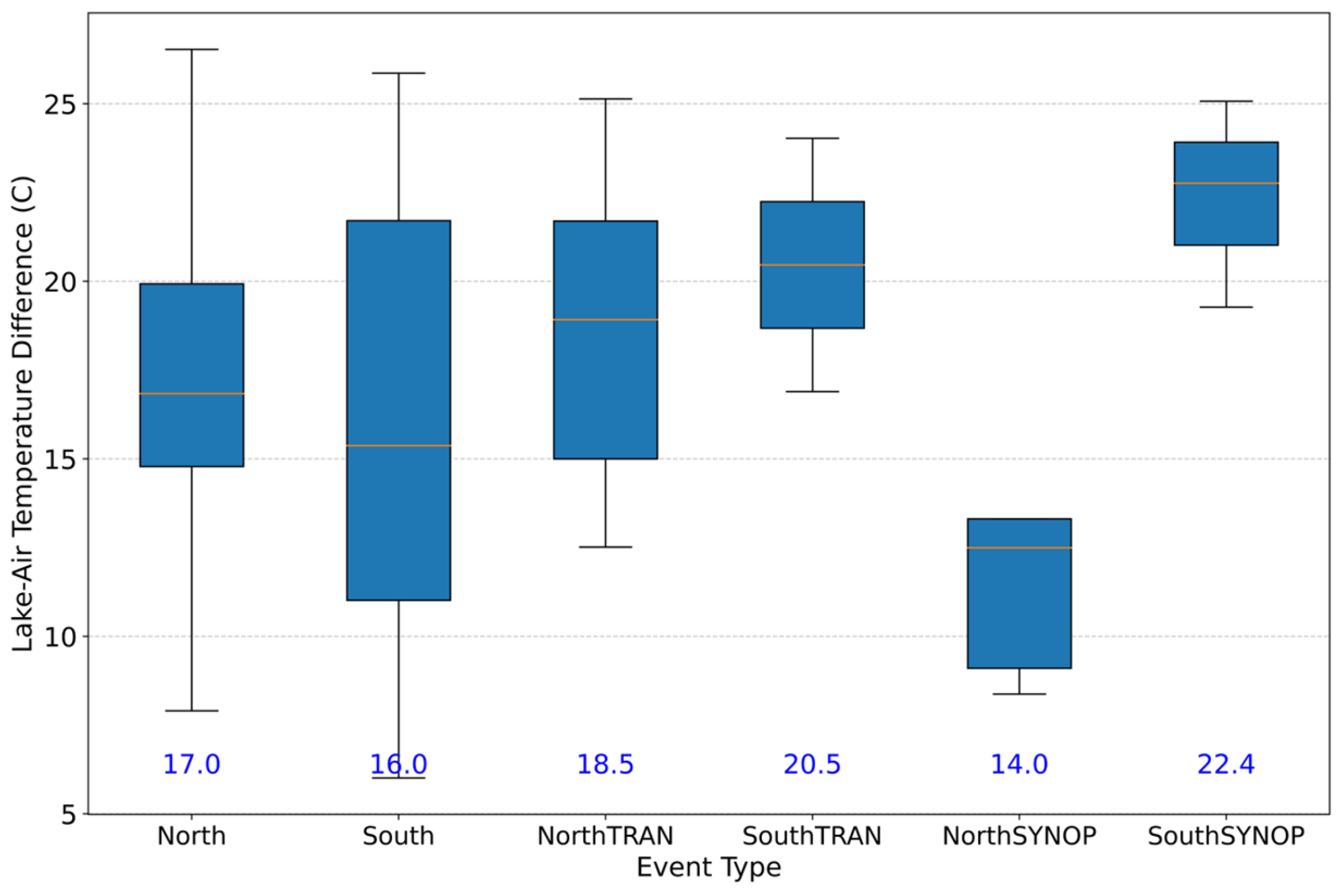
- Box-and-whisker plots showing distributions of key variables, including minimum temperature, dew point, and pressure. These plots display the mean (orange line), interquartile range (box), whiskers (1.5× IQR), and outliers (open circles);
- Event timelines indicating the seasonal distribution and interannual frequency of LE events.
3. Results
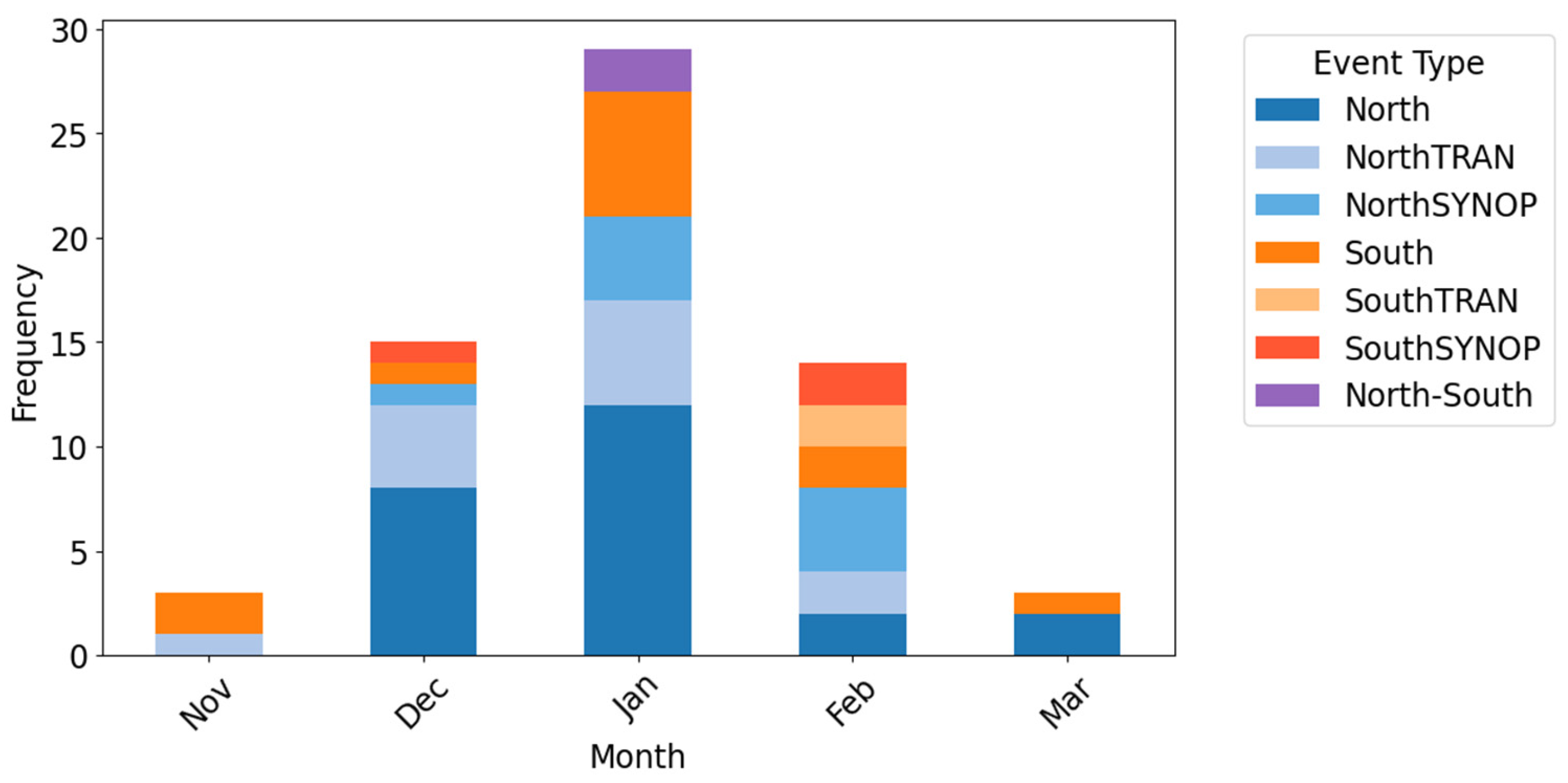
3.1. Event Classification and Frequency
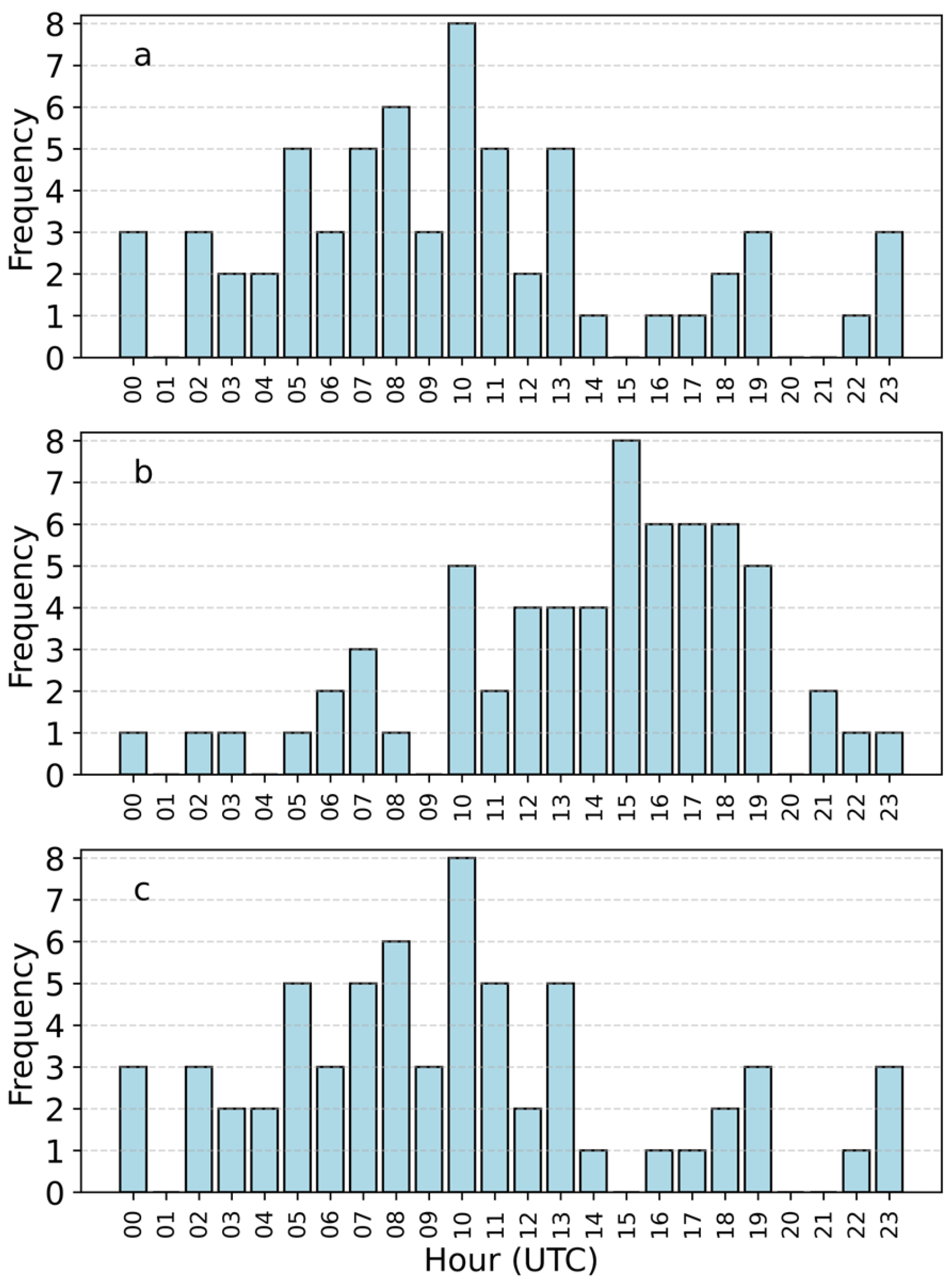
3.2. Event Duration and Timing
3.3. Seasonal Timing and Lake Ice Effects
3.4. Thermal Characteristics
3.5. Dew Point Temperature
3.6. Sea-Level Pressure
3.7. Wind Speed and Direction
3.8. Lake–Air Temperature Difference
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NEXRAD | Next Generation Weather Radar |
| WSR-88D | Weather Surveillance Doppler Radar—88D |
| KCXX | Doppler Radar at Burlington, Vermont |
| LE | Lake-effect |
| NCDC | National Climatic Data Center |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
| NorthTRAN | North transitional |
| SouthTRAN | South transitional |
| NorthSYNOP | North synoptic |
| SouthSYNOP | South synoptic |
| KBTV | Patrick Leahy Burlington International Airport |
| WSF2 | Magnitude of the Fastest 2 min Wind |
| WDF2 | Direction of the Fastest 2 min Wind |
| ASLP | Mean Sea-level Pressure |
| ADPT | Dew Point Temperature |
| TMIN | Minimum Temperature |
| USGS | The United States Geological Survey |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
References
- Peace, R.L.; Sykes, R.B. Mesoscale study of a lake effect snow storm. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1966, 94, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niziol, T.A.; Snyder, W.R.; Waldstreicher, J.S. Winter weather forecasting throughout the eastern United States. Part IV: Lake effect snow. Wea. Forecast. 1995, 10, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, Y.; Kristovich, D.A.R.; Hjelmfelt, M.R. Lake-to-lake cloud bands: Frequencies and locations. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2007, 135, 4202–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eipper, D.T.; Young, G.S.; Greybush, S.J.; Saslo, S.; Sikora, T.D.; Clark, R.D. Predicting the inland penetration of long-lake-axis-parallel snowbands. Wea. Forecast. 2018, 33, 1435–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayastha, M.B.; Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chakraborty, T.; Pringle, W.J.; Hetland, R.D.; Xue, P. How could future climate conditions reshape a devastating lake-effect snow storm? Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, N.F.; Miller, L.J.; Kristovich, D.A.R. Synthetic dual-Doppler analysis of a winter mesoscale vortex. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 312–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kristovich, D.A.R.; Spinar, M.L. Diurnal variations in lake-effect precipitation near the western Great Lakes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, N.F.; Desrochers, J.; Payer, M. Climatology of Lake-Effect Precipitation Events over Lake Champlain. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Yao, T.; Li, X.; Ping, F. The impact of lake effects on the temporal and spatial distribution of precipitation in the Nam Co basin, Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2018, 475, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirtaş, M. A lake-effect snowstorm over southern Europe with upstream blocking in early January 2017. Weather 2023, 78, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.M. The lake effect of the Great Salt Lake. Overview and forecast problems. Wea. Forecast. 1993, 8, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.S.; Steenburgh, W.J.; Veals, P.G.; Letcher, T.W.; Minder, J.R. Lake-Effect Mode and Precipitation Enhancement over the Tug Hill Plateau during OWLeS IOP2b. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2016, 144, 1729–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filazzola, A.; Blagrave, K.; Imrit, M.A.; Sharma, S. Climate change drives increases in extreme events for lake ice in the Northern Hemisphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL089608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, W.M.; Minder, J.R. Evaluating stochastic parameter perturbations in convection-permitting ensemble forecasts of lake-effect snow. Wea. Forecast. 2025, 7, 1181–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewey, K.F. The prediction of Lake Huron lake-effect snowfall systems. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1975, 14, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braham, R.R., Jr.; Dungey, M.J. Quantitative estimates of the effect of Lake Michigan on snowfall. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 1984, 23, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenburgh, W.J.; Halvorson, S.F.; Onton, D.J. Climatology of lake-effect snowstorms of the Great Salt Lake. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2000, 128, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmaier, P.T.; Geerts, B. LLAP band structure and intense lake-effect snowfall downwind of Lake Ontario: Insights from the OWLeS 7–9 January 2014 event. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2020, 59, 1691–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greybush, S.J.; Sikora, T.D.; Young, G.S.; Mulhern, Q.; Clark, R.D.; Jurewicz, M.L., Sr. Elevated mixed layers during Great Lake lake-effect events: An investigation and case study from OWLeS. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2023, 152, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeira, J.M.; Laird, N.F. The Influence of Ice Cover on Two Lake-Effect Snow Events over Lake Erie. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, K.E.; Westcott, N.E.; Kristovich, D.A.R. Assessment of potential effects of climate change on heavy lake-effect snowstorms near Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2002, 28, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.W.; Kirby, M.E.; Mullins, H.T.; Patterson, W.P. Increasing Great Lake–Effect Snowfall during the Twentieth Century: A Regional Response to Global Warming? J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenburgh, W.J.; Onton, D.J. Multiscale analysis of the 7 December 1998 Great Salt Lake–effect snowstorm. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 1296–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onton, D.J.; Steenburgh, W.J. Diagnostic and sensitivity studies of the 7 December 1998 Great Salt Lake–effect snowstorm. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 1318–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcott, T.I.; Steenburgh, W.J. Orographic Influences on a Great Salt Lake-Effect Snowstorm. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2013, 144, 2432–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, B.A.; Colucci, S.J.; Ballentine, R.J.; Waldstreicher, J.S. Lake Effect Snow in the Finger Lakes Region. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting, Norfolk, VA, USA, 19–23 August 1996; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 573–576. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, J.S.; Jurewicz, M.L.; Ballentine, R.J.; Colucci, S.J.; Waldstreicher, J.S. High Resolution Numerical Simulations of Finger Lakes Snow Bands. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference on Weather Analysis and Forecasting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–16 January 1998; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 308–310. [Google Scholar]
- Laird, N.; Sobash, R.; Hodas, N. Climatological Conditions of Lake-Effect Precipitation Events Associated with the New York State Finger Lakes. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmaier, P.T.; Geerts, B. Airborne Radar Observations of Lake-Effect Snow Bands over the New York Finger Lakes. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2016, 144, 3895–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, N.; Bentley, A.M.; Ganetis, S.A.; Steineke, A.; Tushaus, S.A. Climatology of Lake-Effect Precipitation Events over Lake Tahoe and Pyramid Lake. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilken, G.R. A lake-effect snow in Arkansas. NWS/NOAA Tech. Attach. SR/SSD 1997, 97, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Guilbert, J.; Beckage, B.; Winter, J.M.; Horton, R.M.; Perkins, T.; Bomblies, A. Impacts of Projected Climate Change over the Lake Champlain Basin in Vermont. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2014, 53, 1861–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, T.O.; Hunkins, K.L.; Saylor, J.H.; Miller, G.S.; Manley, P.L. Aspects of summertime and wintertime hydrodynamics of Lake Champlain. Lake Champlain Transit. Res. Towar. Restor. 1999, 1, 67–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenburgh, W.J.; Cunningham, J.A.; Bergmaier, P.T.; Geerts, B.; Veals, P. Characteristics of lake-effect precipitation over the Black River Valley and Western Adirondack Mountains. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2023, 9, 1347–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, A. Lake-Effect and Lake-Enhanced Snow in the Champlain Valley of Vermont; United States National Weather Service, Eastern Region: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020; p. 27.
- Payer, M.; Desrochers, J.; Laird, N.F. A lake-effect snow band over Lake Champlain. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2007, 135, 3895–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosiba, K.A.; Wurman, J.; Knupp, K.; Pennington, K.; Robinson, P. Ontario winter lake-effect system (OWLeS): Bulk characteristics and kinematic evolution of mesovortices in long-lake-axis-parallel snowbands. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2019, 1, 131–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guan, Y.; Wu, L.; Guan, X.; Cai, W.; Huang, J.; Dong, W.; Zhang, B. Changing lengths of the four seasons by global warming. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhimireddy, S.R.; Kristovich, D.A.R. Identification of convective boundary layer depth over the Great Lakes region using aircraft observations: A comparison of various methods. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2024, 3, 401–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
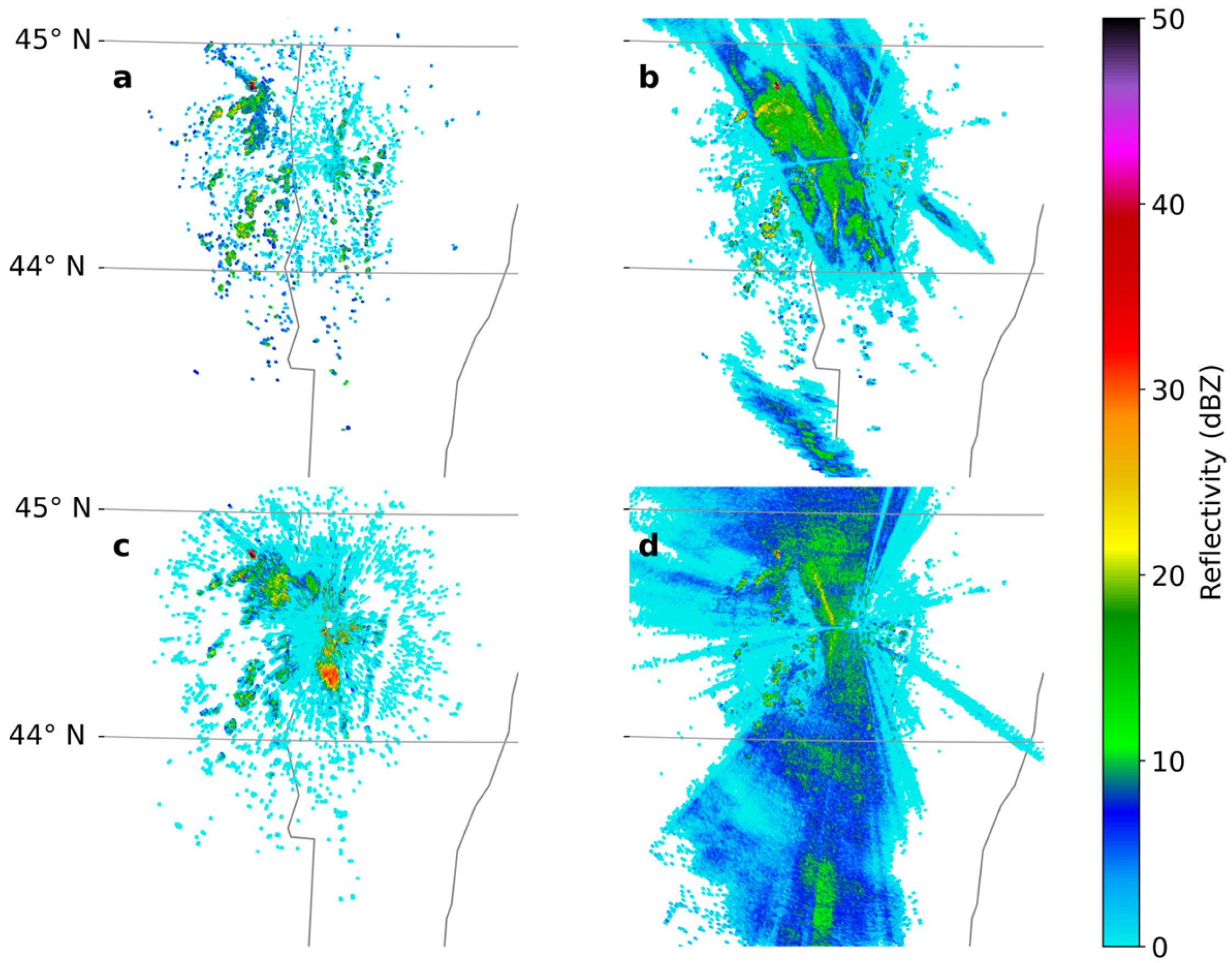




| No. | Start Date | Start Time (UTC) | End Date | End Time (UTC) | Duration (h) | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 Jan 2016 | 0843 | 4 Jan 2016 | 0000 | 15.28 | NorthTRAN |
| 2 | 7 Jan 2016 | 0237 | 7 Jan 2016 | 1145 | 9.13 | South |
| 3 | 23 Jan 2016 | 1021 | 23 Jan 2016 | 1822 | 8.02 | North |
| 4 | 24 Jan 2016 | 0232 | 24 Jan 2016 | 1556 | 13.4 | SouthTRAN |
| 5 | 15 Feb 2016 | 0708 | 15 Feb 2016 | 1945 | 12.62 | NorthSYNOP |
| 6 | 22 Feb 2016 | 0652 | 22 Feb 2016 | 1559 | 9.12 | North |
| 7 | 3 Mar 2016 | 0444 | 3 Mar 2016 | 1211 | 7.45 | North |
| 8 | 19 Dec 2016 | 0817 | 19 Dec 2016 | 1222 | 4.08 | North |
| 9 | 7 Jan 2017 | 1007 | 7 Jan 2017 | 1656 | 6.82 | North |
| 10 | 31 Jan 2017 | 1056 | 31 Jan 2017 | 1459 | 4.05 | South |
| 11 | 11 Dec 2017 | 1702 | 11 Dec 2017 | 2134 | 4.53 | North |
| 12 | 21 Dec 2017 | 0341 | 21 Dec 2017 | 1709 | 13.47 | North |
| 13 | 29 Dec 2017 | 0000 | 29 Dec 2017 | 1305 | 13.08 | NorthTRAN |
| 14 | 30 Dec 2017 | 1114 | 31 Dec 2017 | 2223 | 11.15 | SouthSYNOP |
| 15 | 2 Jan 2018 | 0735 | 2 Jan 2018 | 1219 | 4.73 | NorthSYNOP |
| 16 | 13 Jan 2018 | 1927 | 14 Jan 2018 | 0353 | 8.43 | NorthTRAN |
| 17 | 15 Jan 2018 | 2233 | 16 Jan 2018 | 0718 | 8.75 | North |
| 18 | 18 Jan 2018 | 0318 | 18 Jan 2018 | 0655 | 3.62 | South |
| 19 | 25 Jan 2018 | 0507 | 15 Jan 2018 | 1039 | 5.53 | North |
| 20 | 3 Feb 2018 | 1100 | 3 Feb 2018 | 1404 | 3.07 | North |
| 21 | 23 Nov 2018 | 1217 | 23 Nov 2018 | 1619 | 4.03 | South |
| 22 | 8 Dec 2018 | 0641 | 8 Dec 2018 | 1754 | 11.22 | North |
| 23 | 12 Dec 2018 | 1625 | 12 Dec 2018 | 1957 | 3.53 | NorthTRAN |
| 24 | 20 Dec 2018 | 0415 | 20 Dec 2018 | 1556 | 11.68 | South |
| 25 | 30 Dec 2018 | 0500 | 30 Dec 2018 | 1000 | 5 | North |
| 26 | 2 Jan 2019 | 0504 | 2 Jan 2019 | 1811 | 13.12 | North |
| 27 | 6 Feb 2019 | 0732 | 6 Feb 2019 | 1030 | 2.97 | North |
| 28 | 11 Nov 2019 | 1309 | 11 Nov 2019 | 1427 | 1.3 | NorthTRAN |
| 29 | 20 Dec 2019 | 1010 | 21 Dec 2019 | 1813 | 3.05 | North |
| 30 | 18 Jan 2020 | 0235 | 18 Jan 2020 | 1839 | 16.07 | North-South |
| 31 | 20 Jan 2020 | 0600 | 20 Jan 2020 | 1051 | 4.85 | NorthTRAN |
| 32 | 23 Jan 2020 | 0840 | 23 Jan 2020 | 1728 | 8.8 | South |
| 33 | 31 Jan 2020 | 0519 | 31 Jan 2020 | 1523 | 10.07 | South |
| 34 | 9 Feb 2020 | 1045 | 9 Feb 2020 | 1555 | 5.17 | South |
| 35 | 14 Feb 2020 | 1136 | 14 Feb 2020 | 1633 | 4.95 | NorthTRAN |
| 36 | 20 Feb 2020 | 1313 | 20 Feb 2020 | 1926 | 6.22 | North |
| 37 | 21 Feb 2020 | 1125 | 21 Feb 2020 | 1338 | 2.22 | South |
| 38 | 17 Dec 2020 | 1950 | 17 Dec 2020 | 2355 | 4.08 | NorthTRAN |
| 39 | 18 Dec 2020 | 0539 | 18 Dec 2020 | 1739 | 12 | North |
| 40 | 6 Jan 2021 | 0821 | 6 Jan 2021 | 1904 | 10.72 | NorthSYNOP |
| 41 | 8 Jan 2021 | 0817 | 8 Jan 2021 | 1622 | 8.08 | North |
| 42 | 30 Jan 2021 | 1332 | 30 Jan 2021 | 1817 | 4.75 | NorthSYNOP |
| 43 | 11 Feb 2021 | 1206 | 11 Feb 2021 | 1336 | 1.5 | NorthTRAN |
| 44 | 17 Mar 2021 | 0031 | 17 Mar 2021 | 0524 | 4.88 | South |
| 45 | 30 Nov 2021 | 1822 | 30 Nov 2021 | 2158 | 3.6 | South |
| 46 | 19 Dec 2021 | 1908 | 20 Dec 2021 | 0750 | 11.7 | NorthSYNOP |
| 47 | 3 Jan 2022 | 0929 | 4 Jan 2022 | 1503 | 29.56 | North-South |
| 48 | 8 Jan 2022 | 0954 | 8 Jan 2022 | 1142 | 1.8 | North |
| 49 | 16 Jan 2022 | 0703 | 16 Jan 2022 | 1731 | 10.45 | South |
| 50 | 21 Jan 2022 | 0913 | 21 Jan 2022 | 1656 | 7.72 | North |
| 51 | 26 Jan 2022 | 1155 | 26 Jan 2022 | 1717 | 5.37 | North |
| 52 | 4 Feb 2022 | 0755 | 5 Feb 2022 | 0859 | 25.07 | NorthSYNOP |
| 53 | 26 Feb 2022 | 1023 | 26 Feb 2022 | 1416 | 3.83 | SouthTRAN |
| 54 | 12 Dec 2022 | 1351 | 12 Dec 2022 | 1531 | 1.67 | North |
| 55 | 14 Dec 2022 | 1024 | 14 Dec 2022 | 1532 | 5.13 | NorthTRAN |
| 56 | 10 Jan 2023 | 2308 | 11 Jan 2023 | 1052 | 11.73 | North |
| 57 | 13 Jan 2023 | 2329 | 15 Jan 2023 | 0202 | 26.52 | NorthSYNOP |
| 58 | 15 Jan 2023 | 0814 | 15 Jan 2023 | 1800 | 9.77 | NorthTRAN |
| 59 | 21 Jan 2023 | 1012 | 21 Jan 2023 | 1249 | 2.62 | North |
| 60 | 23 Feb 2023 | 1313 | 23 Feb 2023 | 1628 | 3.25 | NorthSYNOP |
| 61 | 25 Feb 2023 | 1857 | 26 Feb 2023 | 0659 | 12.03 | SouthSYNOP |
| 62 | 19 Jan 2024 | 1447 | 19 Jan 2029 | 1939 | 4.87 | NorthTRAN |
| 63 | 2 Feb 2024 | 2356 | 3 Feb 2024 | 1352 | 13.93 | NorthSYNOP |
| 64 | 24 Mar 2024 | 0055 | 29 Mar 2024 | 0708 | 6.22 | North |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nyzio, K.D.; Liu, P. Lake-Effect Snowfall Climatology over Lake Champlain: A Comparative Analysis of the 2015–2024 and 1997–2006 Periods. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091011
Nyzio KD, Liu P. Lake-Effect Snowfall Climatology over Lake Champlain: A Comparative Analysis of the 2015–2024 and 1997–2006 Periods. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(9):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091011
Chicago/Turabian StyleNyzio, Kazimir D., and Ping Liu. 2025. "Lake-Effect Snowfall Climatology over Lake Champlain: A Comparative Analysis of the 2015–2024 and 1997–2006 Periods" Atmosphere 16, no. 9: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091011
APA StyleNyzio, K. D., & Liu, P. (2025). Lake-Effect Snowfall Climatology over Lake Champlain: A Comparative Analysis of the 2015–2024 and 1997–2006 Periods. Atmosphere, 16(9), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091011






