Threefold Threshold: Synergistic Air Pollution in Greater Athens Area, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
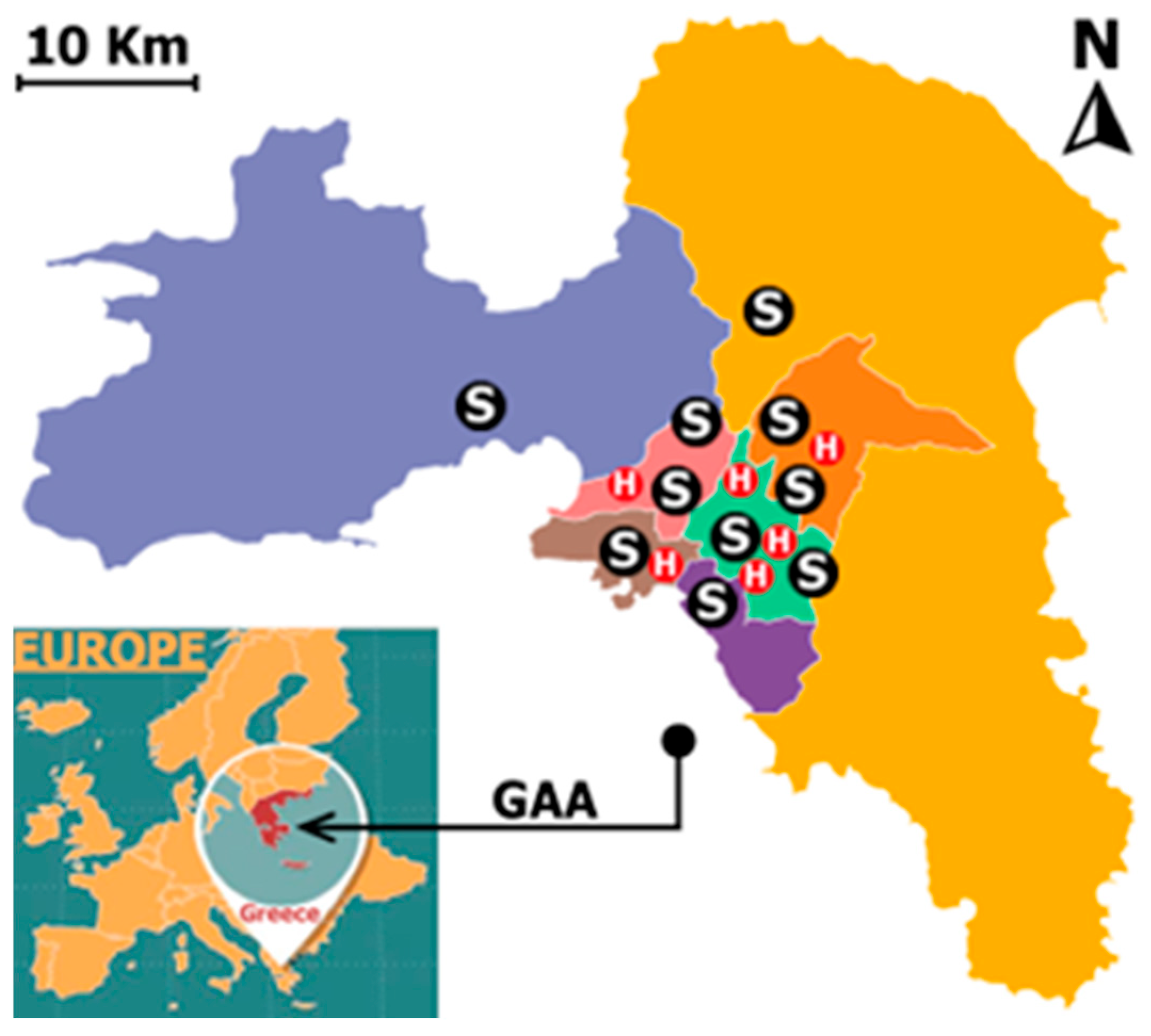
2.1. Data Collected and Study Area
- PM10 ≥ 20 μg/m3
- NO2 ≥ 40 μg/m3
- O3 ≥ 50 μg/m3
2.2. Distributed Lag Non-Linear Model (DLNM)
- ns(time, df = df_time × 5) to control for long-term trends;
- year as a categorical factor to capture inter-annual variability;
- ns(doy, df = 6) to adjust for seasonality.
3. Results and Discussion
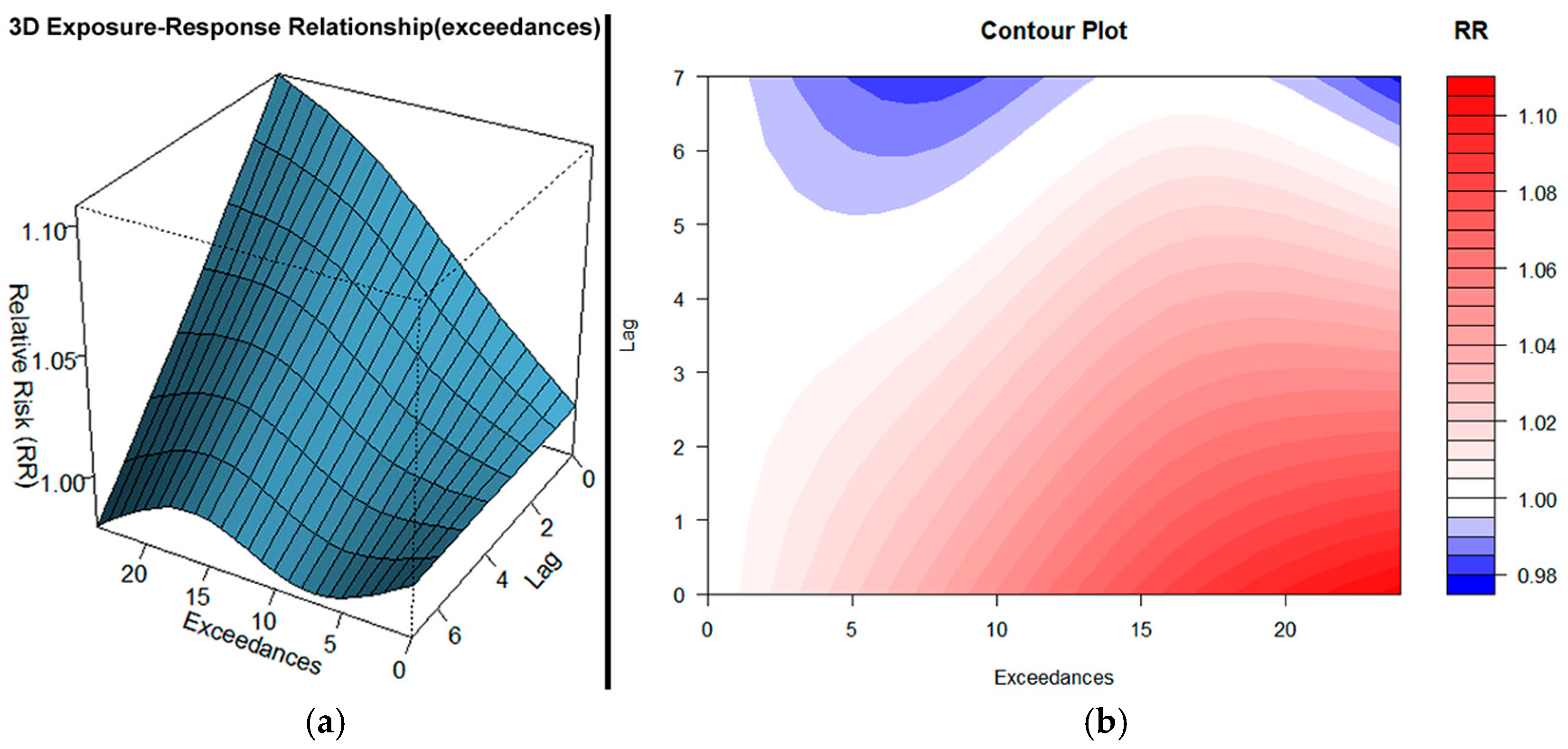
3.1. PM10 Exceedances
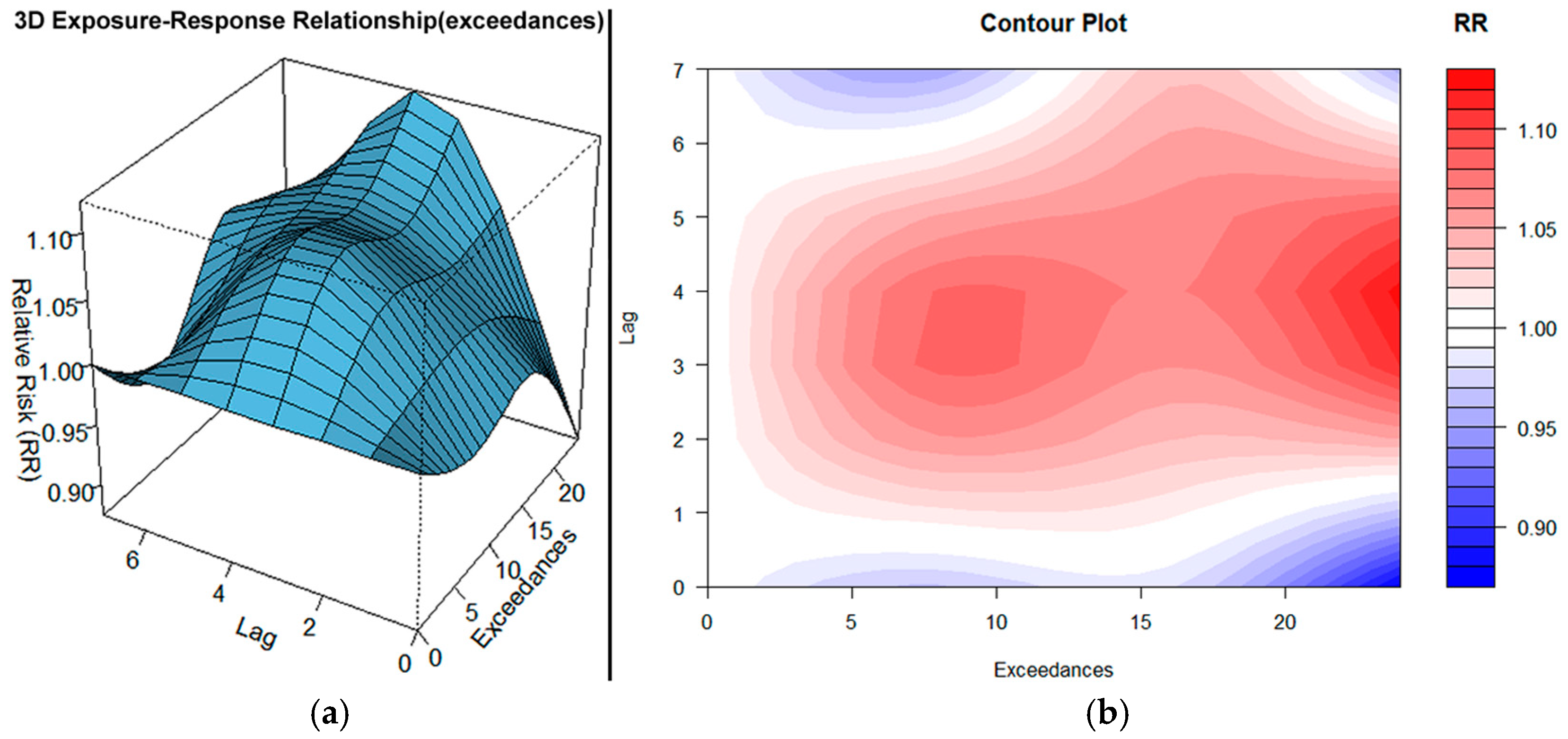
3.2. O3 Exceedances
3.3. NO2 Exceedances
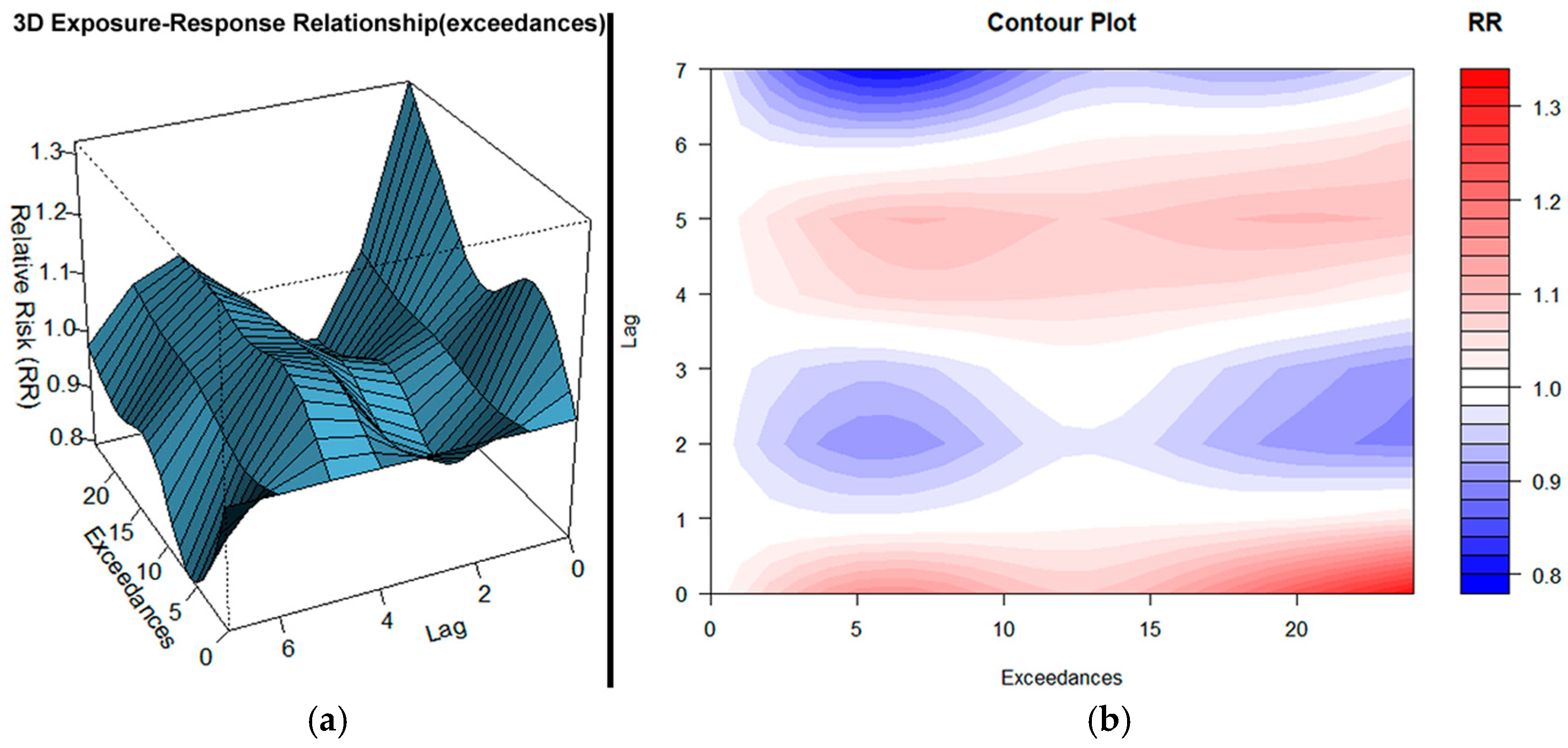
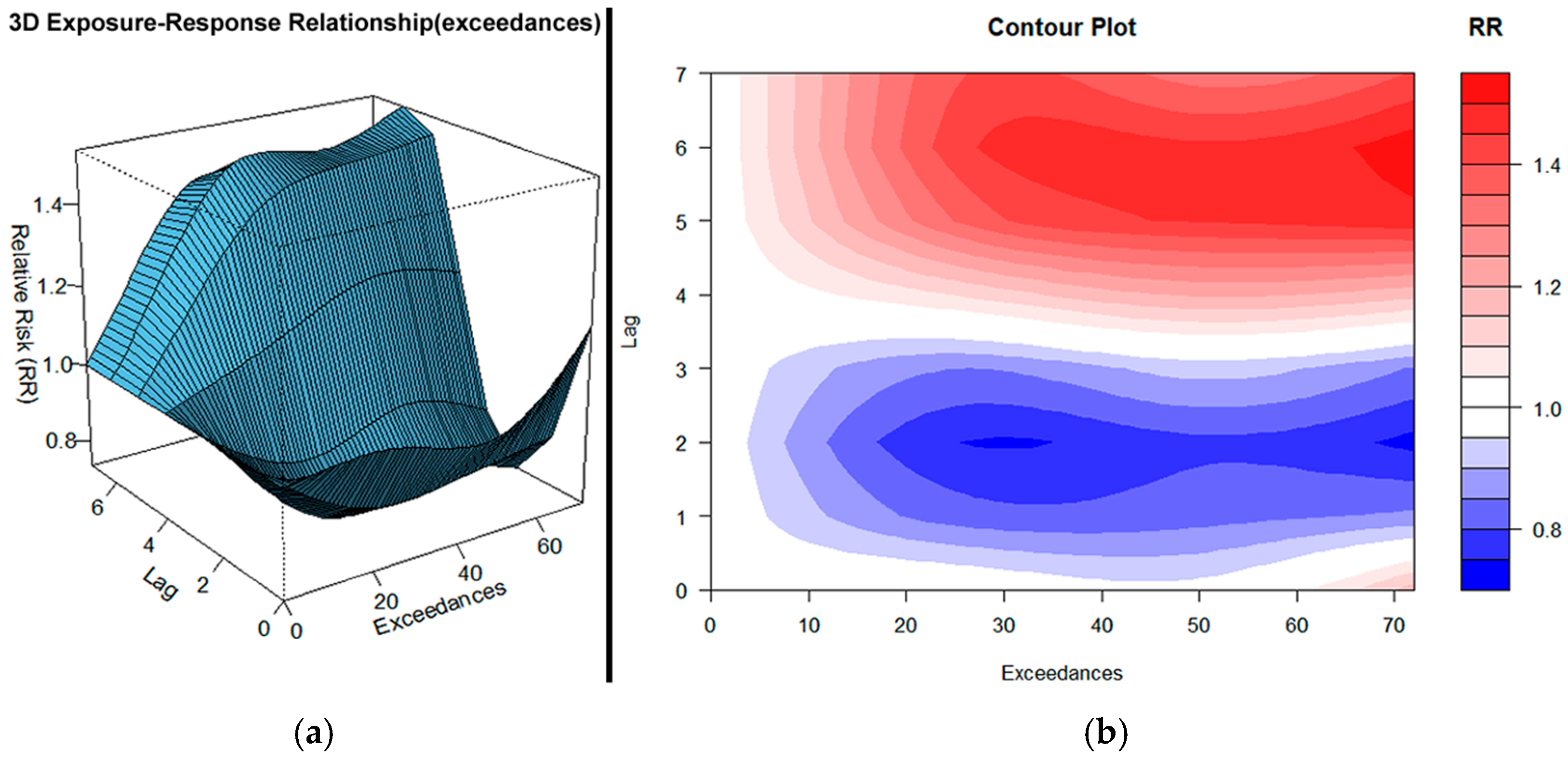
3.4. Combined PM10, O3, and NO2 Exceedances
4. Conclusions
- ❖
- PM10 exerts strong immediate and sustained health effects, with the highest risk on the day of exposure (lag 0), and continuing up to a week. Apparently, these findings highlight the acute inflammatory and cardiopulmonary stress caused by particulate matter.
- ❖
- Ozone impacts are delayed and cumulative, with risk beginning mainly at lag 1 and peaking around lag 3–4. This pattern suggests that the health burden from ozone builds progressively over several days of exposure, even when initial levels are modest.
- ❖
- NO2 shows a biphasic response, with the most substantial impact at lag 0 and a secondary rise around lag 4. Notably, even small exceedances of NO2 levels can lead to significant health burdens, indicating its high toxicity and rapid biological effects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAA | Greater Athens Area |
| RR | Relative Risk |
| HA | Hospital Admissions |
| RD | Respiratory Diseases |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Diseases |
| CE | Co-Exposure |
| DLNM | Distributed Lag Non-linear Model |
| ER | Exposure-Response |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| EU AQI | European Union Air Quality Index |
References
- Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F.; Curriero, F.C.; Coursac, I.; Zeger, S.L. Fine particulate air pollution and mortality in 20 U.S. cities, 1987–1994. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Dockery, D.W.; Muller, J.E.; Mittleman, M.A. Increased particulate air pollution and the triggering of myocardial infarction. Circulation 2001, 103, 2810–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.D. Airborne particulates and hospital admissions for cardiovascular disease: A quantitative review of the evidence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Metzger, K.B.; Tolbert, P.E.; Klein, M.; Peel, J.L.; Flanders, W.D.; Todd, K.; Mulholland, J.A.; Ryan, P.B.; Frumkin, H. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular emergency department visits. Epidemiology 2004, 15, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Barr, C.D.; Bell, M.L. Protecting human health from air pollution: Shifting from a single-pollutant to a multipollutant approach. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.W.; Williams, G.; Petroeschevsky, A.; Morgan, G.; Rutherford, S. Associations between outdoor air pollution and daily mortality in Brisbane, Australia. Arch. Environ. Health 1997, 52, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunyer, J.; Basagaña, X. Particles, and not gases, are associated with the risk of death in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 30, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pönkä, A.; Savela, M.; Virtanen, M. Mortality and air pollution in Helsinki. Arch. Environ. Health 1998, 53, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.W.; Lau, T.S.; Yu, T.S.; Neller, A.; Wong, S.L.; Tam, W.; Pang, S.W. Air pollution and hospital admissions for respiratory and cardiovascular diseases in Hong Kong. Occup. Environ. Med. 1999, 56, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.C.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, H.; Ha, E.H.; Schwartz, J.; Christiani, D.C. Effects of air pollutants on acute stroke mortality. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, H.R.; Atkinson, R.W.; Bremner, S.A.; Carrington, J.; Peacock, J. Quantitative Systematic Review of Short Term Associations Between Ambient Air Pollution (Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulphur Dioxide And Carbon Monoxide), and Mortality and Morbidity. Department of Health. Available online: http://www.dh.gov.uk/en/Publicationsandstatistics/Publications/PublicationsPolicyAndGuidance/DH_121200 (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Burnett, R.T.; Cakmak, S.; Brook, J.R. The effect of the urban ambient air pollution mix on daily mortality rates in 11 Canadian cities. Can. J. Public Health Rev. Can. Sante Publique 1998, 89, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touloumi, G.; Katsouyanni, K.; Zmirou, D.; Schwartz, J.; Spix, C.; de Leon, A.P.; Tobias, A.; Quennel, P.; Rabczenko, D.; Bacharova, L.; et al. Short-term effects of ambient oxidant exposure on mortality: A combined analysis within the APHEA project. Air Pollution and Health: A European Approach. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 146, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoli, E.; Aga, E.; Touloumi, G.; Nisiotis, K.; Forsberg, B.; Lefranc, A.; Pekkanen, J.; Wojtyniak, B.; Schindler, C.; Niciu, E.; et al. Short-term effects of nitrogen dioxide on mortality: An analysis within the APHEA project. Eur. Respir. J. 2006, 27, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.; Williams, G.; Petroeschevsky, A.; Best, T.; Morgan, G.; Denison, L.; Hinwood, A.; Neville, G.; Neller, A. The short-term effects of air pollution on daily mortality in four Australian cities. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2005, 29, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryparis, A.; Forsberg, B.; Katsouyanni, K.; Analitis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Schwartz, J.; Samoli, E.; Medina, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Niciu, E.M.; et al. Acute effects of ozone on mortality from the “air pollution and health: A European approach” project. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HEI Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia Program. Public Health and Air Pollution in Asia (PAPA): Coordinated Studies of Short-Term Exposure to Air Pollution and Daily Mortality in Four Cities; HEI Research Report 154; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chardon, B.; Host, S.; Lefranc, A.; Millard, F.; Gremy, I. What exposure indicator should be used to study the short-term respiratory health effect of photochemical air pollution? A case study in the Paris metropolitan area (2000–2003). Environ. Risques Santé 2007, 6, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25- year trends of the global burden of disease attributable to ambient air pollution: An analysis of data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellano, P.; Reynoso, J.; Quaranta, N.; Bardach, A.; Ciapponi, A. Short-term exposure to particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and ozone (O3) and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Lu, K.; Liu, W.; Xiao, D. Efficiency and marginal abatement cost of PM2.5 in China: A parametric approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revich, B.; Shaposhnikov, D. The effects of particulate and ozone pollution on mortality in Moscow, Russia. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liang, L.; Lyu, B.; Cai, Y.S.; Zuo, Y.; Su, J.; Tong, Z. Double trouble: The interaction of PM2.5 and O3 on respiratory hospital admissions. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fameli, K.-M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. The new open Flexible Emission Inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area (FEI-GREGAA): Account of pollutant sources and their importance from 2006 to 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallos, G.; Kassomenos, P.; Pielke, R.A. Synoptic and mesoscale weather conditions during air pollution episodes in Athens, Greece. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1993, 62, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaziris, A.; Yannis, G. A critical assessment of Athens Traffic Restrictions using multiple data sources. Traportation Res. Procedia 2022, 72, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health. Hospital Admissions and Hospital Beds. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.gr/articles/bihealth/stoixeia-noshleytikhs-kinhshs/10431-klines-noshleythentes-hmeres-noshleias-2021 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Singh, N.; Area, A.; Breitner, S.; Zhang, S.; Agewall, S.; Schikowski, T.; Schneider, A. Heat and Cardiovascular Mortality: An Epidemiological Perspective. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparrini, A. Modeling exposure-lag-response associations with distributed lag non-linear models. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 881–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparrini, A.; Armstrong, B.; Kenward, M.G. Distributed lag non-linear models. Stat. Med. 2010, 29, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparrini, A.; Armstrong, B.; Kenward, M.G. Reducing and meta-analyzing estimates from distributed lag non-linear models. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparrini, A. Distributed lag linear and non-linear models in R: The package dlnm. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hong, Y.; Liu, N. Association of ambient Particulate matter 2.5 with intensive care unit admission due to pneumonia: A distributed lag non-linear model. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Xu, J.; Ning, L.; Feng, T.; Cao, P.; Gao, S.; Shang, P.; Yu, X. Ambient air pollution, temperature and hospital admissions due to respiratory diseases in a cold, industrial city. J. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 04085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Peel, J.L.; Hannigan, M.P.; Dutton, S.J.; Sheppard, L.; Clark, M.L.; Vedal, S. The temporal lag structure of short-term associations of fine particulate matter chemical constituents and cardiovascular and respiratory hospitalizations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.D.; Chang, H.H.; Bell, M.L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Coarse particulate matter air pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases among medicare patients. JAMA 2008, 299, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Li, H.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Effects of particulate matter on hospital admissions for respiratory diseases: An ecological study based on 12.5 years of time series data in Shanghai. Environ. Health 2022, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Ramón, M.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J. The effect of ozone and PM10 on hospital admissions for pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A national multicity study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, C.W.; Hsu, P.C. Association between Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Hospital Emergency Room Visits for Pneumonia with Septicemia: A Retrospective Analysis. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Ban, J.; Lu, F.; Guo, M.; Zhong, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, C.; Li, T.; Shi, X. Risk of Cardiovascular Hospital Admission After Exposure to Fine Particulate Pollution. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassomenos, P.; Papaloukas, C.; Petrakis, M.; Karakitsios, S. Assessment and prediction of short term hospital admissions: The case of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7078–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, P.S.; Rahman, I.; Donaldson, K.; MacNee, W. Histone acetylation regulates epithelial IL-8 release mediated by oxidative stress from environmental particles. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2003, 284, L533–L540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.T. Short-term exposure to PM10 and cardiovascular hospitalization in persons with and without disabilities: Invisible population in air pollution epidemiology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagawa, E.; Bai, N.; Morimoto, K.; Gray, C.; Mui, T.; Yatera, K.; Zhang, X.; Xing, L.; Li, Y.; Laher, I.; et al. Particulate matter exposure induces persistent lung inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L79–L85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; He, G.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The unexpected high frequency of nocturnal surface ozone enhancement events over China: Characteristics and mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15243–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladakis, A.; Retalis, A.; Giannaros, C.; Vafeiadis, V.; Fameli, K.-M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Moustris, K.; Nastos, P.T. Evaluating the Health Risks of Air Quality and Human Thermal Comfort–Discomfort in Relation to Hospital Admissions in the Greater Athens Area, Greece. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirowsky, J.E.; Carraway, M.S.; Dhingra, R.; Tong, H.; Neas, L.; Diaz-Sanchez, D.; Cascio, W.; Case, M.; Crooks, J.; Hauser, E.R.; et al. Ozone exposure is associated with acute changes in inflammation, fibrinolysis, and endothelial cell function in coronary artery disease patients. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shi, Y.; Burnett, R.T.; McGrail, K.M.; Krewski, D. Association between ozone and respiratory admissions among children and the elderly in Vancouver, Canada. Inhal. Toxicol. 2003, 15, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Guo, T.; Si, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Deng, F.; Chen, L.; Wei, C.; Lin, S.; Guo, X.; et al. Association Between Ambient Air Pollution and Daily Hospital Admissions for Depression in 75 Chinese Cities. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroeschevsky, A.; Simpson, R.W.; Thalib, L.; Rutherford, S. Associations between outdoor air pollution and hospital admissions in Brisbane, Australia. Arch. Environ. Health 2001, 56, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.H.; Chen, B.Y.; Kim, H.; Honda, Y.; Guo, Y.L. Significant Effects of Exposure to Relatively Low Level Ozone on Daily Mortality in 17 cities from three Eastern Asian Countries. Environ. Res. 2018, 168, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987–2000. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 292, 2372–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.B.; Huang, W.; Huang, X.L.; Zhong, L.J.; Lu, S.E.; Li, Y.; Dai, L.Z.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhul, T. Estimated acute effects of ambient ozone and nitrogen dioxide on mortality in the Pearl River Delta of Southern China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.E.; Zu, K.; Loftus, C.T.; Tao, G.; Liu, X.; Lange, S. Ambient ozone and asthma hospital admissions in Texas: A time-series analysis. Asthma Res. Pract. 2017, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Lu, K.; Fu, J. A Time-Series Study for Effects of Ozone on Respiratory Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, China. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 864537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Liao, H.L.; Tian, X.J. Sepsis-related hospital admissions and ambient air pollution: A time series analysis in 6 Chinese cities. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.; Strak, M.; Velders, G.J.M.; Zorn, J.; Hogerwerf, L.; Simões, M.; Mijnen-Visser, S.; Wesseling, J.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.; Smit, L.; et al. Short-term exposure to ambient air pollution and severe COVID-19: Mortality and hospital admission to COVID-19 in the Netherlands from February to December 2020. Environ. Adv. 2024, 17, 100592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Gong, H.; Hu, X.; Xie, Y.; Rui, D. The Impact of Air Pollutant Exposure on Diabetes Hospital Admissions in a City in Xinjiang. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stosic, L.T.; Dragic, N.; Stojanovic, D.; Lazarevic, K.; Bijelovic, S.; Apostolovic, M. Air Pollution and Hospital Admissions for Respiratory Diseases in Nis, Serbia. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4677–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bont, J.; Jaganathan, S.; Dahlquist, M.; Persson, Å.; Stafoggia, M.; Ljungman, P. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 291, 779–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd Rahim, N.N.; Ahmad Zaki, R.; Yahya, A.; Wan Mahiyuddin, W.R. Acute effects of air pollution on cardiovascular hospital admissions in the port district of Klang, Malaysia: A time-series analysis. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 333, 120629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Barnes, A.J.; He, D.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Ambient Nitrogen Dioxide and Respiratory Disease in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collart, P.; Dubourg, D.; Levêque, A.; Sierra, N.B.; Coppieters, Y. Short-term effects of nitrogen dioxide on hospital admissions for cardiovascular disease in Wallonia, Belgium. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 255, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, F.; Ma, Q. Association and interaction of O3 and NO2 with emergency room visits for respiratory diseases in Beijing, China: A time-series study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, P.C.; Fine, D.H.; Vásquez, G.B.; Gamero, L.; Slaughter, M.S.; Dasse, K.A. The Pathophysiology of Nitrogen Dioxide During Inhaled Nitric Oxide Therapy. ASAIO J. 2017, 63, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostro, B.D.; Feng, W.Y.; Broadwin, R.; Malig, B.J.; Green, R.S.; Lipsett, M.J. The impact of components of fine particulate matter on cardiovascular mortality in susceptible subpopulations. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 65, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, I.T.; Qiu, H.; Wang, X.; Tian, L.; Tse, L.A. Synergy between particles and nitrogen dioxide on emergency hospital admissions for cardiac diseases in Hong Kong. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 2831–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustini, A.; Stafoggia, M.; Williams, M.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F. The effect of short-term exposure to O3, NO2, and their combined oxidative potential on mortality in Rome. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.A.; van der Vliet, A.; Eiserich, J.P.; Last, J.A.; Halliwell, B.; Cross, C.E. Oxidative damage by ozone and nitrogen dioxide: Synergistic toxicity in vivo but no evidence of synergistic oxidative damage in an extracellular fluid. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1995, 61, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.L.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Kelly, F.J. Associations between daily mortality in London and combined oxidant capacity, ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2014, 7, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Sera, F.; Vicedo-Cabrera, A.M.; Guo, Y.; Tong, S.; Lavigne, E.; Correa, P.M.; Ortega, N.V.; Achilleos, S.; et al. Interactive effects of ambient fine particulate matter and ozone on daily mortality in 372 cities: Two stage time series analysis. BMJ 2023, 383, e075203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurai, J.; Onuma, K.; Sano, H.; Okada, F.; Watanabe, M. Ozone augments interleukin-8 production induced by ambient particulate matter. Genes Environ. 2018, 40, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glencross, D.A.; Ho, T.R.; Camina, N.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; Pfeffer, P.E. Air pollution and its effects on the immune system. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Chen, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Jiang, J.; Wu, W.; Cai, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; Kan, H. Ozone exposure leads to changes in airway permeability, microbiota and metabolome: A randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2000165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamon, L.F.; White, J.M.; Wille, U. Oxidative damage of aromatic dipeptides by the environmental oxidants NO2 and O3. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 8280–8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathanael, J.G.; Wille, U. Phenylalanine Residues Are Very Rapidly Damaged by Nitrate Radicals (NO3 ⋅) in an Aqueous Environment. Chembiochem A Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2023, 24, e202200731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Year | PM10 | O3 | NO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 127 | 124 | 14 |
| 2006 | 166 | 98 | 7 |
| 2007 | 186 | 91 | 7 |
| 2008 | 150 | 143 | 5 |
| 2009 | 88 | 100 | 5 |
| 2010 | 70 | 116 | 2 |
| 2011 | 86 | 108 | 0 |
| 2012 | 42 | 74 | 0 |
| 2013 | 73 | 84 | 0 |
| 2014 | 29 | 46 | 0 |
| 2015 | 94 | 93 | 1 |
| 2016 | 72 | 77 | 0 |
| 2017 | 74 | 89 | 1 |
| 2018 | 62 | 92 | 0 |
| 2019 | 58 | 68 | 0 |
| 2020 | 27 | 38 | 0 |
| 2021 | 59 | 97 | 6 |
| 2022 | 64 | 61 | 0 |
| Variable | df_var | df_lag | df_time | Max_Lag (Days) | AIC | BIC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 15,417.62 | 15,593.81 |
| O3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 15,419.94 | 15,612.65 |
| NO2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 15,375.68 | 15,606.94 |
| Interaction | 2 | 4 | 3 | 7 | 15,399.24 | 155,608.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kladakis, A.; Fameli, K.-M.; Moustris, K.; Assimakopoulos, V.D.; Nastos, P.T. Threefold Threshold: Synergistic Air Pollution in Greater Athens Area, Greece. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070888
Kladakis A, Fameli K-M, Moustris K, Assimakopoulos VD, Nastos PT. Threefold Threshold: Synergistic Air Pollution in Greater Athens Area, Greece. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070888
Chicago/Turabian StyleKladakis, Aggelos, Kyriaki-Maria Fameli, Konstantinos Moustris, Vasiliki D. Assimakopoulos, and Panagiotis T. Nastos. 2025. "Threefold Threshold: Synergistic Air Pollution in Greater Athens Area, Greece" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070888
APA StyleKladakis, A., Fameli, K.-M., Moustris, K., Assimakopoulos, V. D., & Nastos, P. T. (2025). Threefold Threshold: Synergistic Air Pollution in Greater Athens Area, Greece. Atmosphere, 16(7), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070888










