Children’s Allergic Sensitization to Pets: The Role of Air Pollution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol and Questionnaire
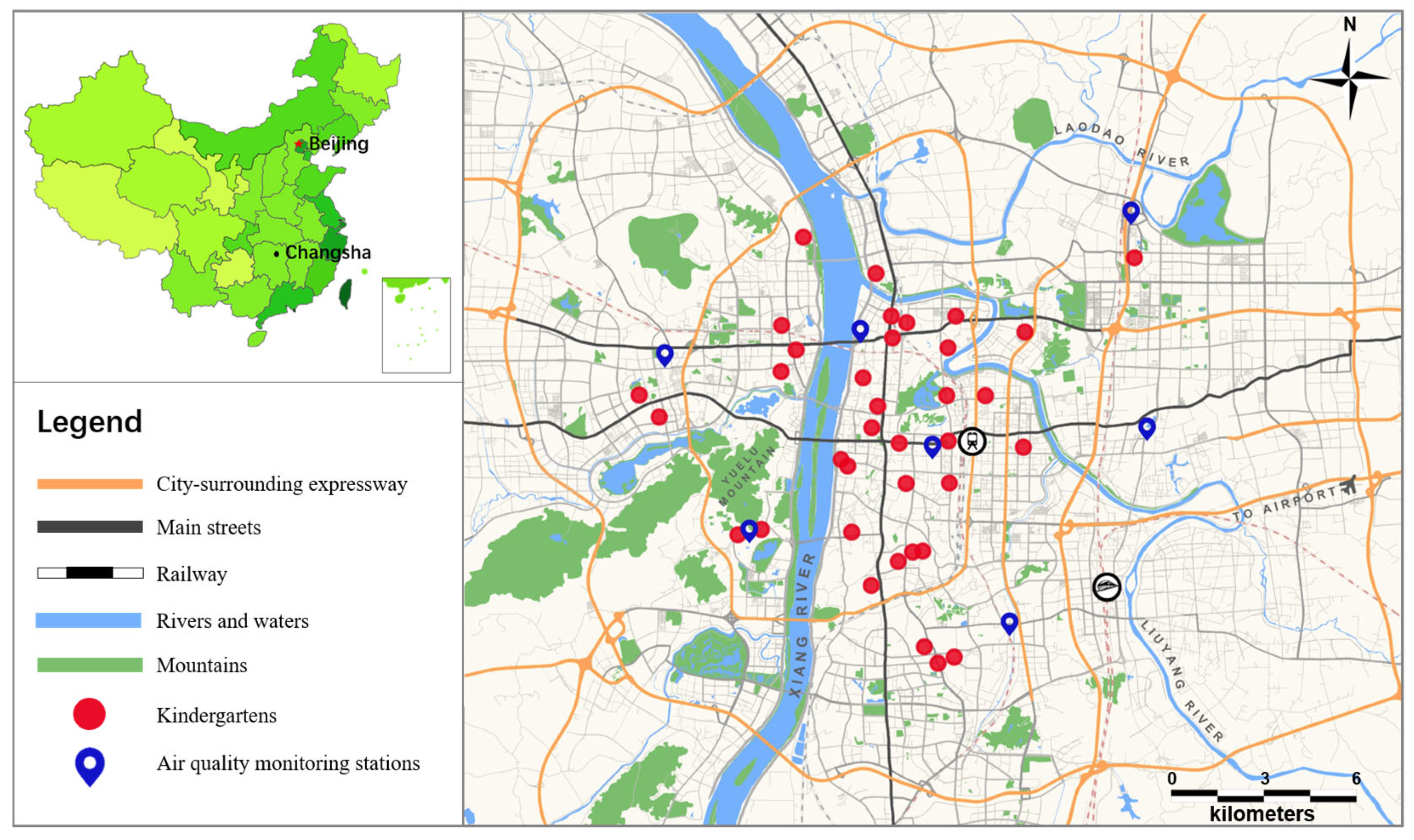
2.2. Exposure Windows
2.3. Exposure to Animals or Pets
2.4. Exposure to Air Pollution
2.5. Health Outcome
2.6. Confounding Covariates
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Allergic sensitization |
| CCHH | China–Children–Homes–Health |
| ETS | Environmental tobacco smoke |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Ádám, M. The Science of a Friendship. Sci. Am. Mind 2015, 26, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, M.; Mitsui, S.; En, S.; Ohtani, N.; Ohta, M.; Sakuma, Y.; Onaka, T.; Mogi, K.; Kikusui, T.J.S. Oxytocin-gaze positive loop and the coevolution of human-dog bonds. Science 2015, 348, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall-Pescini, S.; Schaebs, F.S.; Gaugg, A.; Meinert, A.; Deschner, T.; Range, F.J.A. The role of oxytocin in the dog–owner relationship. Animals 2019, 9, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.X.; Tan, J.S.Q.; Syn, N.L.; Tan, B.S.W.; Low, J.Y.; Foo, Y.H.; Fung, W.; Hoong, B.Y.D.; Pang, J.; Phase IV CHP 2020 Group 8. Association between pet ownership and physical activity levels, atopic conditions, and mental health in Singapore: A propensity score-matched analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reider, L.B.; Kim, E.; Mahaffey, E.; LoBue, V. The impact of household pets on children’s daily lives: Differences in parent–child conversations and implications for children’s emotional development. Dev. Psychol. 2023, 59, 2148–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ein, N.; Li, L.; Vickers, K. The effect of pet therapy on the physiological and subjective stress response: A meta-analysis. Stress Health 2018, 34, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Haire, M. Companion animals and human health: Benefits, challenges, and the road ahead. J. Vet. Behav. 2010, 5, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, O.E. No longer the lonely species: A post-mead perspective on animals and sociology. Int. J. Sociol. Soc. Policy 2003, 23, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, E.R. Dogs and Practices of Community and Neighboring. Anthrozoös 2013, 26, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virués-Ortega, J.; Buela-Casal, G. Psychophysiological Effects of Human-Animal Interaction. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2006, 194, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, S.; Loc, M.D.; Howell, T.J. Social Support and Wellbeing in Cat and Dog Owners, and the Moderating Influence of Pet–Owner Relationship Quality. Anthrozoös 2023, 36, 891–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalongo, M.R. The World’s Children and Their Companion Animals: Developmental and Educational Significance of the Child/Pet Bond; Association for Childhood Education International: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Burr, M.L.; Limb, E.S.; Andrae, S.; Barry, D.M.J.; Nagel, F. Childhood Asthma in Four Countries: A Comparative Survey. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1994, 23, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, D.; Keil, T.; Grabenhenrich, L.; Dubakiene, R.; Drasutiene, G.; Fiocchi, A.; Dahdah, L.; Sprikkelman, A.B.; Schoemaker, A.A.; Roberts, G.; et al. The EuroPrevall birth cohort study on food allergy: Baseline characteristics of 12,000 newborns and their families from nine European countries. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 23, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C. Pooch Protection and Profit: South Korea to Overhaul Pet Sector [Internet]; Reuters: London, UK, 6 July 2016; Available online: http://www.reuters.com/article/us-southkoreaeconomy-pets-idUSKCN0ZN05V (accessed on 10 October 2017).
- Newman, A.; Smith, D.; Ghai, R.R.; Wallace, R.M.; Torchetti, M.K.; Loiacono, C.; Murrell, L.S.; Carpenter, A.; Moroff, S.; Rooney, J.A.J.M.; et al. First reported cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in companion animals—New York, March–April 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 710. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, Y. Pet Food Market in Japan; JA2021-0015; ATO: Osaka, Japan, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyoncu, A.; Demir, A.; Ozcakar, B.; Bozkurt, B.; Artvinli, M. Asthma and allergy in Turkish university students: Two cross-sectional surveys 5 years apart. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2001, 29, 264–271. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, M.I.; Montefort, S.; Björkstén, B.; Lai, C.K.; Strachan, D.P.; Weiland, S.K.; Williams, H.; Group, I.P.T.S. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet 2006, 368, 733–743. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, M.; Kim, H.-H.; Sohn, M.H.; Kim, K.-E.; Kim, C.; Shin, D.C. Prevalence of allergic diseases among Korean school-age children: A nationwide cross-sectional questionnaire study. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 332–338. [Google Scholar]
- Salo, P.M.; Arbes Jr, S.J.; Jaramillo, R.; Calatroni, A.; Weir, C.H.; Sever, M.L.; Hoppin, J.A.; Rose, K.M.; Liu, A.H.; Gergen, P.J. Prevalence of allergic sensitization in the United States: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2005–2006. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lombardi, C.; Savi, E.; Ridolo, E.; Passalacqua, G.; Canonica, G.W. Is allergic sensitization relevant in severe asthma? Which allergens may be culprit? World Allergy Organ. J. 2017, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Rzehak, P.; Zutavern, A.; Fahlbusch, B.; Bischof, W.; Herbarth, O.; Borte, M.; Lehmann, I.; Behrendt, H.; Kramer, U.; et al. Longitudinal study on cat allergen exposure and the development of allergy in young children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Tischer, C.; Schnappinger, M.; Heinrich, J. The role of cats and dogs in asthma and allergy—A systematic review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2010, 213, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, C.J.; Allen, K.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Hill, D.J.; Hosking, C.S.; Abramson, M.J.; Dharmage, S.C.J.C.; Immunology, D. Perinatal cat and dog exposure and the risk of asthma and allergy in the urban environment: A systematic review of longitudinal studies. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 176484. [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood, J.; Ownby, D. Exposure to dog allergens and subsequent allergic sensitization: An updated review. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2012, 12, 424–428. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, O.B.; van Hage, M.; Gronlund, H. Mammalian-derived respiratory allergens–implications for diagnosis and therapy of individuals allergic to furry animals. Methods 2014, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celedón, J.C.; Litonjua, A.A.; Ryan, L.; Platts-Mills, T.; Weiss, S.T.; Gold, D.R. Exposure to cat allergen, maternal history of asthma, and wheezing in first 5 years of life. Lancet 2002, 360, 781–782. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hesselmar, B.; Aberg, N.; Aberg, B.; Eriksson, B.; Björkstén, B.J.C. Does early exposure to cat or dog protect against later allergy development? Clin. Exp. Allergy J. Br. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 29, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, S.; Illi, S.; Sommerfeld, C.; Niggemann, B.; Bergmann, R.; von Mutius, E.; Wahn, U.; the Multicentre Allergy Study Group. Early exposure to house-dust mite and cat allergens and development of childhood asthma: A cohort study. Lancet 2000, 356, 1392–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Lindfors, A.; van Hage-Hamsten, M.; Rietz, H.; Wickman, M.; Nordvall, S.L. Influence of interaction of environmental risk factors and sensitization in young asthmatic children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 755–762. [Google Scholar]
- Mandhane, P.J.; Sears, M.R.; Poulton, R.; Greene, J.M.; Lou, W.Y.W.; Taylor, D.R.; Hancox, R.J. Cats and dogs and the risk of atopy in childhood and adulthood. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 745–750.e744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ownby, D.R.; Johnson, C.C.; Peterson, E.L.J.J. Exposure to dogs and cats in the first year of life and risk of allergic sensitization at 6 to 7 years of age. JAMA 2002, 288, 963–972. [Google Scholar]
- Remes, S.T.; Castro-Rodriguez, J.A.; Holberg, C.J.; Martinez, F.D.; Wright, A.L. Dog exposure in infancy decreases the subsequent risk of frequent wheeze but not of atopy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Moira, A.P.; Strandberg-Larsen, K.; Van Meel, E.; Mensink-Bout, R.; Popovic, M.; Cadman, T.; Yang, T.; Thorbjørnsrud Nader, J.; Foong, R.; Jankowska, A.; et al. Pet ownership and allergic sensitisation and asthma in childhood: Findings from the EU Child Cohort Network. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rönmark, E.; Bunne, J.; Bjerg, A.; Perzanowski, M.; Winberg, A.; Andersson, M.; Platts-Mills, T.; Hedman, L. Prevalence and risk factors for allergic sensitization: 3 cross-sectional studies among schoolchildren from 1996 to 2017. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2023, 2, 100150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyokuni, K.; Yamamoto-Hanada, K.; Yang, L.; Hagino, K.; Harama, D.; Omori, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Suzuki, D.; Umezawa, K.; Takada, K.; et al. Influence of household pet ownership and filaggrin loss-of-function mutations on eczema prevalence in children: A birth cohort study. Allergol. Int. 2024, 73, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegienka, G.; Johnson, C.C.; Havstad, S.; Ownby, D.R.; Zoratti, E.M. Indoor pet exposure and the outcomes of total IgE and sensitization at age 18 years. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 274–279.e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, C.J.; Lowe, A.J.; Gurrin, L.C.; Matheson, M.; Balloch, A.; Axelrad, C.; Hill, D.J.; Hosking, C.S.; Rodrigues, S.; Svanes, C.J.C.; et al. Pets at birth do not increase allergic disease in at-risk children. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wypych-Ślusarska, A.; Krupa-Kotara, K.; Oleksiuk, K.; Głogowska-Ligus, J.; Słowiński, J. Respiratory Status in Children and Exposure to Animal Allergens—The Problem of Reverse Causality in Cross-Sectional Studies. Children 2024, 11, 941. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelsen, R.J.; Lødrup Carlsen, K.C.; Carlsen, K.H.; Granum, B.; Doekes, G.; Håland, G.; Mowinckel, P.; Løvik, M. Childhood asthma and early life exposure to indoor allergens, endotoxin and β(1,3)-glucans. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downes, M.J.; Roy, A.; McGinn, T.G.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Factors Associated with Furry Pet Ownership Among Patients with Asthma. J. Asthma 2010, 47, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ownby, D.; Johnson, C.C. Recent Understandings of Pet Allergies. F1000Res 2016, 5, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, R. Clearing the Air: Asthma and Indoor Air Exposures; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Oh, S.Y.; Zheng, T.; Kim, Y.-K. Immunomodulating effects of endotoxin in mouse models of allergic asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinn, S.; Heinrich, J.; Anto, J.M.; Janson, C.; Norback, D.; Olivieri, M.; Svanes, C.; Sunyer, J.; Verlato, G.; Wjst, M.; et al. Bronchial responsiveness in atopic adults increases with EXDOsure to cat alleraen. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsollahi, H.R.; Ghoochani, M.; Jaafari, J.; Moosavi, A.; Sillanpää, M.; Alimohammadi, M. Environmental exposure to endotoxin and its health outcomes: A systematic review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, Q.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Sundell, J.; Norbäck, D. Exposure to outdoor air pollution during trimesters of pregnancy and childhood asthma, allergic rhinitis, and eczema. Environ. Res. 2016, 150, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakerkhatibi, M.; Benis, K.Z.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Sadeghi-Bazarghani, H.; Allahverdipour, H.; Oskouei, D.S.; Fatehifar, E.; Farajzadeh, M.; Yadeghari, A.; Ansarin, K.; et al. Air pollution-related asthma profiles among children/adolescents: A multi-group latent class analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 219, 112344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isa, K.N.M.; Jalaludin, J.; Elias, S.M.; Than, L.T.L.; Jabbar, M.A.; Saudi, A.S.M.; Norbäck, D.; Hashim, J.H.; Hashim, Z. Metagenomic characterization of indoor dust fungal associated with allergy and lung inflammation among school children. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 221, 112430. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.; Dong, G.-H.; Ren, W.-H.; Simckes, M.; Wang, J.; Zelicoff, A.; Trevathan, E. Effect of pet ownership on respiratory responses to air pollution in Chinese children: The Seven Northeastern Cities (SNEC) study. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 87, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölscher, B.; Frye, C.; Wichmann, H.E.; Heinrich, J. Exposure to pets and allergies in children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2002, 13, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Roost, H.-P.; Künzli, N.; Schindler, C.; Jarvis, D.; Chinn, S.; Perruchoud, A.P.; Ackermann-Liebrich, U.; Burney, P.; Wüthrich, B. Role of current and childhood exposure to cat and atopic sensitization. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 104, 941–947. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.-B.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, E.J.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, J.T.; Lim, D.H.; Kim, W.K.; Song, D.J.; Yoo, Y.; Suh, D.I.; et al. Pet Ownership Increases the Exhaled Nitric Oxide and Asthma Severity in Children With Atopic Asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2025, 17, 394–404. [Google Scholar]
- El Sharif, N.; Douwes, J.; Hoet, P.; Doekes, G.; Nemery, B.J.A. Concentrations of domestic mite and pet allergens and endotoxin in Palestine. Allergy 2004, 59, 623–631. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Feng, W.; Wei, W.; Yang, B.; Wang, L. Prevalence of food-allergen and aeroallergen sensitization among people in Sichuan, Western China: An 8-year observational study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22723. [Google Scholar]
- Hassen, H.Y.; Govarts, E.; Remy, S.; Cox, B.; Iszatt, N.; Portengen, L.; Covaci, A.; Schoeters, G.; Den Hond, E.; Henauw, S.; et al. Association of environmental pollutants with asthma and allergy, and the mediating role of oxidative stress and immune markers in adolescents. Environ. Res. 2025, 265, 120445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, H.; Xing, W.; Li, X.; Han, Z.; Ji, R.; Deng, Z.; Jung, M.; Sun, S.; Chung, B.I.; et al. Air pollution mixture associated with oxidative stress exacerbation and symptoms deterioration in allergic rhinitis patients: Evidence from a panel study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, B. Relationship between indoor and outdoor NO2: A review. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 106909. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Yang, X.; Qian, H.; Deng, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Li, A.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. Ten cities cross-sectional questionnaire survey of children asthma and other allergies in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar]
- Bornehag, C.-G.; Sundell, J.; Sigsgaard, T.J.I.A. Dampness in buildings and health (DBH): Report from an ongoing epidemiological investigation on the association between indoor environmental factors and health effects among children in Sweden. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Liu, Z.; Liao, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q.; Deng, Q. Interaction of exposure to outdoor air pollution and temperature during pregnancy on childhood asthma: Identifying specific windows of susceptibility. Build. Environ. 2022, 225, 109676. [Google Scholar]
- Westgate, S.; Ng, N.L. Using in-situ CO2, PM1, PM2.5, and PM10 measurements to assess air change rates and indoor aerosol dynamics. Build. Environ. 2022, 224, 109559. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Lu, C.; Norbäck, D.; Bornehag, C.-G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, H.; Sundell, J. Early life exposure to ambient air pollution and childhood asthma in China. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, C.; Li, Y.; Norbäck, D.; Murthy, P.; Sram, R.J.; Deng, Q. Early-life exposure to air pollution associated with food allergy in children: Implications for ‘one allergy’concept. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114713. [Google Scholar]
- Norbäck, D.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, X.; Qian, H.; Sun, Y. Asthma and rhinitis among Chinese children—Indoor and outdoor air pollution and indicators of socioeconomic status (SES). Environ. Int. 2018, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, M.; Tang, Y.; Liu, K.; Huang, K.; Yan, S.; Ding, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; et al. Prenatal low-dose antibiotic exposure and children allergic diseases at 4 years of age: A prospective birth cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 225, 112736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Miao, Y.; Zeng, J.; Jiang, W.; Shen, Y.-M.; Deng, Q. Prenatal exposure to ambient temperature variation increases the risk of common cold in children. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 154, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.; Li, B.; Yu, W.; Wang, L.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y. Damp indicators in different areas of residence in different periods are strongly associated with childhood asthma and wheeze. Build. Environ. 2020, 182, 107131. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Liao, H.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q.; Li, Q. Association between early life exposure to indoor environmental factors and childhood asthma. Build. Environ. 2022, 226, 109740. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Deng, G.; Wang, Z. Exposure level and influential factors of HCHO, BTX and TVOC from the interior redecoration of residences. Build. Environ. 2020, 168, 106494. [Google Scholar]
- Konradsen, J.R.; Fujisawa, T.; van Hage, M.; Hedlin, G.; Hilger, C.; Kleine-Tebbe, J.; Matsui, E.C.; Roberts, G.; Ronmark, E.; Platts-Mills, T.A. Allergy to furry animals: New insights, diagnostic approaches, and challenges. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Gehring, U.; Wickman, M.; Hoek, G.; Giovannangelo, M.; Nordling, E.; Wijga, A.; de Jongste, J.; Pershagen, G.; Almqvist, C.; et al. Domestic cat allergen and allergic sensitisation in young children. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2008, 211, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, J.Y.; Kwon, J.-W.; Hong, S.-N.; Lee, W.H. Age differences in pet sensitization by pet ownership. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 14, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, W.; Elsheikha, H.M.; Zhou, N.; Peng, P.; Qin, S.-Y.; Meng, Q.-F.; Qian, A.-D. Prevalence of antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii in pets and their owners in Shandong province, Eastern China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 430. [Google Scholar]
- Kääriö, H. The Allergy and Asthma Protective Effects of Farm Environment and Pet Animals: The Role of Immunomodulation. Ph.D. Thesis, Itä-Suomen Yliopisto, Joensuu, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzarella, G.; Esposito, V.; Bianco, A.; Ferraraccio, F.; Prati, M.V.; Lucariello, A.; Manente, L.; Mezzogiorno, A.; De Luca, A. Inflammatory effects on human lung epithelial cells after exposure to diesel exhaust micron sub particles (PM1.0) and pollen allergens. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, H.; Ichinose, T.; Miyabara, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Sagai, M. Diesel exhaust particles enhance airway responsiveness following allergen exposure in mice. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1998, 20, 329–336. [Google Scholar]
| n (Case)/N (Number) | Prevalence (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 48/2598 | 1.8 | — |
| Sex | |||
| Boys | 32/1399 | 2.3 | 0.071 |
| Girls | 16/1199 | 1.3 | |
| Age (years) | |||
| 3 | 10/665 | 1.5 | 0.182 |
| 4 | 14/952 | 1.5 | |
| 5 | 22/815 | 2.7 | |
| 6 | 2/166 | 1.2 | |
| Birth season | |||
| Warm (May–September) | 21/1152 | 1.8 | 0.928 |
| Cold (October–April) | 27/1446 | 1.9 | |
| Breastfeeding | |||
| No | 7/222 | 3.2 | 0.124 |
| Yes | 41/2376 | 1.7 | |
| Antibiotics use | |||
| No | 7/432 | 1.6 | 0.650 |
| Yes | 41/2115 | 1.9 | |
| Parental atopy | |||
| No | 372214 | 1.7 | 0.046 |
| Yes | 11/340 | 3.2 | |
| House size (m2) | |||
| ≤75 | 19/836 | 2.3 | 0.306 |
| >75 | 29/1732 | 1.7 | |
| Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) at home | |||
| No | 16/864 | 1.9 | 0.997 |
| Yes | 32/1734 | 1.8 | |
| Indoor new furniture | |||
| No | 16/1248 | 1.3 | 0.036 |
| Yes | 28/1156 | 2.4 | |
| House redecoration | |||
| No | 26/1689 | 1.5 | 0.356 |
| Yes | 13/620 | 2.1 | |
| Visible mold/damp stains at home | |||
| No | 32/1985 | 1.6 | 0.101 |
| Yes | 16/606 | 2.6 | |
| Window condensation in winter | |||
| No | 18/1175 | 1.5 | 0.217 |
| Yes | 30/1369 | 2.2 | |
| n with AS/total N | (%) | Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Perinatal animal or pet ownership | ||||
| No (Ref = no pet exposure) | 44/2341 | (1.9) | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 4/238 | (1.7) | 0.89 (0.32–2.51) | 1.09 (0.38–3.15) |
| Current animal or pet ownership | ||||
| No (Ref = no pet exposure) | 36/2216 | (1.6) | 1 | 1 |
| Yes | 12/369 | (3.3) | 2.02 (1.04–3.93) * | 2.40 (1.17–4.93) * |
| Crude OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI) # | |
|---|---|---|
| Outdoor air pollution | ||
| Prenatal | ||
| PM10 | 1.09 (0.80–1.48) | 0.84 (0.50–1.42) |
| SO2 | 1.12 (0.77–1.65) | 0.92 (0.55–1.53) |
| NO2 | 0.74 (0.47–1.16) | 0.62 (0.33–1.14) |
| Current | ||
| PM10 | 0.83 (0.46–1.48) | 0.64 (0.32–1.28) |
| SO2 | 0.99 (0.61–1.61) | 0.90 (0.52–1.57) |
| NO2 | 0.94 (0.50–1.75) | 0.74 (0.36–1.55) |
| Exposure Level | Number | OR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoor air pollution | |||
| PM10 | Low | 1277 | 2.97 (1.21–7.27) * |
| High | (1321 | 1.60 (0.43–5.91) | |
| SO2 | Low | 1288 | 2.22 (0.84–5.89) |
| High | 1310 | 2.80 (0.93–8.46) | |
| NO2 | Low | 1283 | 3.01 (1.23–7.37) * |
| High | 1315 | 1.59 (0.43–5.86) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Xue, Y.; Liu, L.; Deng, Q. Children’s Allergic Sensitization to Pets: The Role of Air Pollution. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070833
Miao Y, Liu Y, Huang R, Xue Y, Liu L, Deng Q. Children’s Allergic Sensitization to Pets: The Role of Air Pollution. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070833
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Yufeng, Yingjie Liu, Ruixue Huang, Yuan Xue, Le Liu, and Qihong Deng. 2025. "Children’s Allergic Sensitization to Pets: The Role of Air Pollution" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070833
APA StyleMiao, Y., Liu, Y., Huang, R., Xue, Y., Liu, L., & Deng, Q. (2025). Children’s Allergic Sensitization to Pets: The Role of Air Pollution. Atmosphere, 16(7), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070833







