Ozone Pollution Impairs Athletic Performance in Female Football Players: A Gender-Specific Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Setting
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Correlation Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Impact of Ambient Air Pollutants on the Athletic Performance
3.2. Comparisons Between the Fixed Effects
3.3. Lag Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
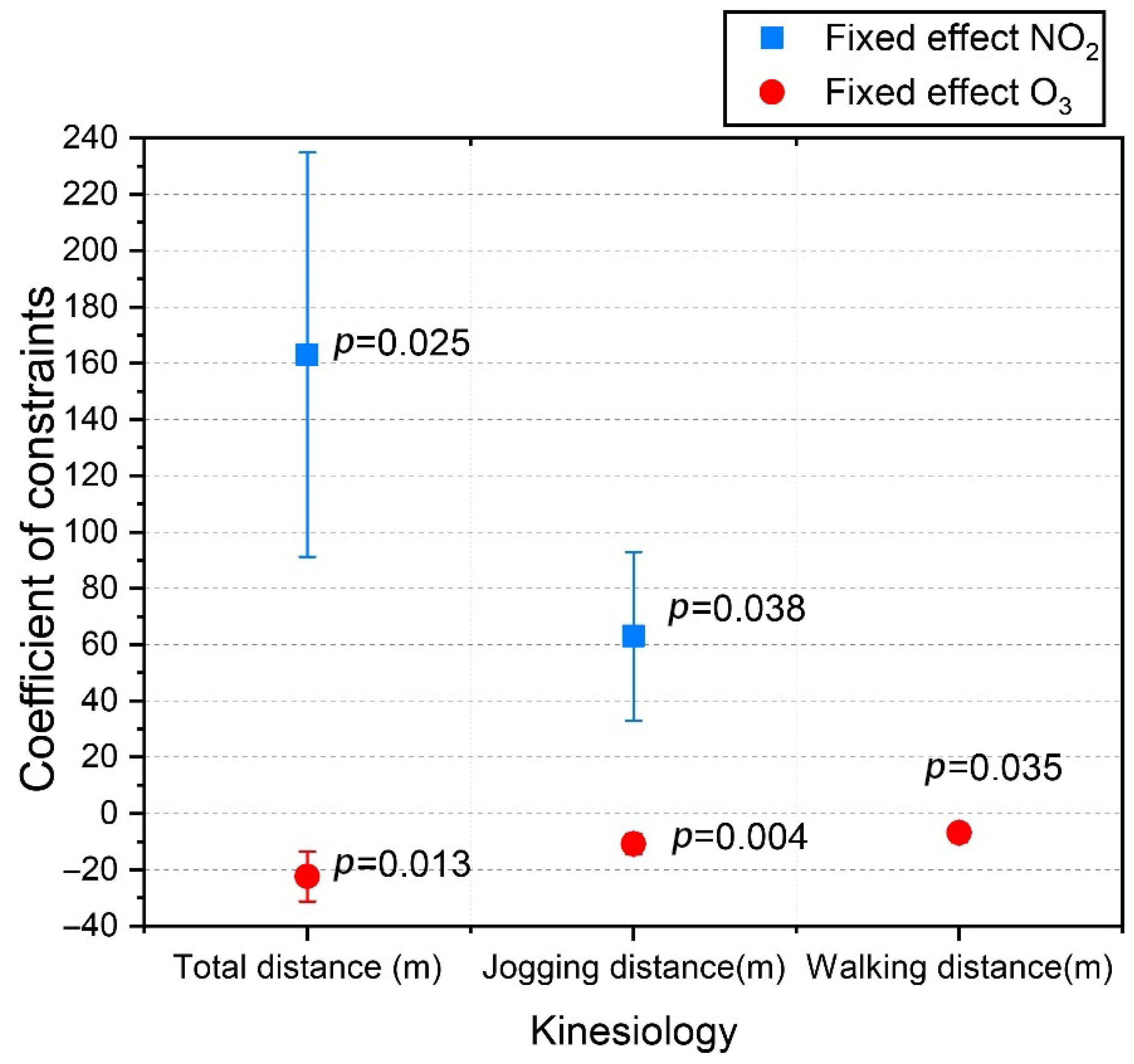
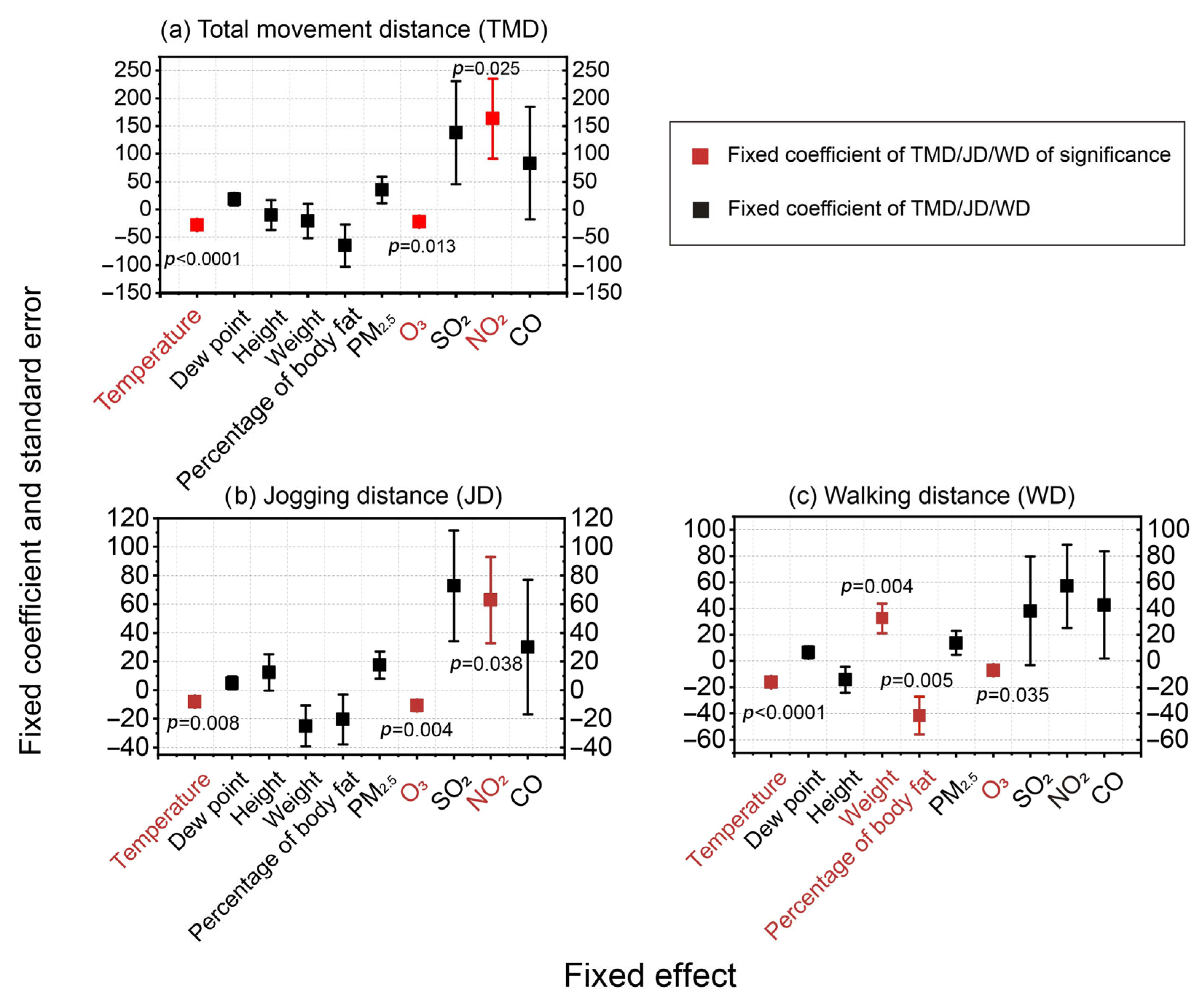
- A strong negative association was observed between the O3 concentration and long-term endurance. The fixed effect coefficients for O3 on total movement distance, jogging distance, and walking distance were −22.426 ± 8.889, −10.817 ± 3.697, and −6.943 ± 3.265, respectively;
- (2)
- No significant correlation was found between the PM2.5, SO2, and CO concentrations and athletic performance. This may be attributed to the relatively low levels of these pollutants compared with the threshold value for air quality during the match period, which likely had a limited impact on the athletes;
- (3)
- No lag effect was observed in the impact of air pollutants on athletic performance;
- (4)
- During the monitored match period, the temperature was negatively correlated with athletic performance.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter with aerodynamic diameter less than 2.5 μm |
| O3 | Ozone |
| SO2 | Sulfur dioxide |
| NO | Nitrogen dioxide |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
| TMD | Total movement distance |
| JD | Jogging distance |
| WD | Walking distance |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| RTI | Respiratory Tract Infections |
| FIFA | Fédération Internationale de Football Association |
| CNEMC | China National Environmental Monitoring Center |
| GLMM | Generalized Linear Mixed Model |
| GLM | Generalized Linear Model |
References
- Song, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, Y.; He, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Jin, T.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; et al. Air pollution in China: Status and spatiotemporal variations. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 227, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Kong, S.; Hu, W.; Xiong, J.; Liu, L.; Zheng, H.; Meng, K. Aggravation effect of regional transport on wintertime PM2.5 over the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under China’s air pollutant emission reduction process. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101111. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone pollution in China: A review of concentrations, meteorological influences, chemical precursors, and effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Guan, P.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, W.; Dai, W. A review of the technology and applications of methods for evaluating the transport of air pollutants. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Ucheje, O.O.; Ikebude, C.F. An Evaluation of Environmental Contamination on Public Health: A Review of Air Pollution in Nigeria. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 2024, 26, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.B.; Kendrick, P.J.; Paulson, K.R.; Gupta, V.; Abrams, E.M.; Adedoyin, R.A.; Adhikari, T.B.; Advani, S.M.; Agrawal, A.; Ahmadian, E.; et al. Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Apte, J.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M. Addressing Global Mortality from Ambient PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8057–8066. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Braun, D.; Schwartz, J.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Dominici, F. Evaluating the impact of long-term exposure to fine particulate matter on mortality among the elderly. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba5692. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, O.D.; Goncalves, P.E.O.; Hung, A.; Stothers, B.; Bougault, V.; Sheel, A.W.; Koehle, M.S. Ozone exposure limits cardiorespiratory function during maximal cycling exercise in endurance athletes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2024, 136, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, W.C. Comparison of Chamber 6.6-h Exposures to 0.04–0.08 PPM Ozone via Square-wave and Triangular Profiles on Pulmonary Responses. Inhal. Toxicol. 2008, 18, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.S.; Alexis, N.E.; Rappold, A.G.; Kehrl, H.; Hazucha, M.J.; Lay, J.C.; Schmitt, M.T.; Case, M.; Devlin, R.B.; Peden, D.B.; et al. Lung Function and Inflammatory Responses in Healthy Young Adults Exposed to 0.06 ppm Ozone for 6.6 Hours. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schelegle, E.S.; Morales, C.A.; Walby, W.F.; Marion, S.; Allen, R.P. 6.6-Hour Inhalation of Ozone Concentrations from 60 to 87 Parts per Billion in Healthy Humans. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.L.; Peng, R.D.; Dominici, F. The Exposure–Response Curve for Ozone and Risk of Mortality and the Adequacy of Current Ozone Regulations. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gryparis, A.; Forsberg, B.; Katsouyanni, K.; Analitis, A.; Touloumi, G.; Schwartz, J.; Samoli, E.; Medina, S.; Anderson, H.R.; Niciu, E.M.; et al. Acute Effects of Ozone on Mortality from the “Air Pollution and Health A European Approach” Project. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Aaron, C.P.; Madrigano, J.; Hoffman, E.A.; Angelini, E.; Yang, J.; Laine, A.; Vetterli, T.M.; Kinney, P.L.; Sampson, P.D.; et al. Association Between Long-term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution and Change in Quantitatively Assessed Emphysema and Lung Function. JAMA 2019, 322, 546–556. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GB 3095–2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Beavan, A.; Hartel, S.; Spielmann, J.; Koehle, M. Air pollution and elite adolescent soccer players’ performance and well-being; an observational study. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107943. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharko, M.; Cichowicz, R.; Andrzejewski, M.; Chmura, P.; Kowalczuk, E.; Chmura, J.; Konefal, M. Air Pollutants Reduce the Physical Activity of Professional Soccer Players. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12928. [Google Scholar]
- Cakmak, S.; Dales, R.; Leech, J.; Liu, L. The influence of air pollution on cardiovascular and pulmonary function and exercise capacity: Canadian Health Measures Survey (CHMS). Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, W.C. Effects of Ozone Exposure at Ambient Air Pollution Episode Levels on Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 1987, 4, 395–424. [Google Scholar]
- Rundell, W.K.; Caviston, R. Ultrafine and fine particulate matter inhalation decreases exercise performance in healthy subjects. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Carlisle, A.J.; Sharp, N.C.C. Exercise and outdoor ambient air pollution. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elliott, L.; Loomis, D. Respiratory effects of road pollution in recreational cyclists: A pilot study. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2020, 76, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thaller, E.I.; Petronella, S.A.; Hochman, D.; Howard, S.; Chhikara, R.S.; Brooks, E.G. Moderate increases in ambient PM2.5 and ozone are associated with lung function decreases in beach lifeguards. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2008, 50, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beavan, A.; Härtel, S.; Spielmann, J.; Koehle, M. Air pollution, a worthy opponent? How pollution levels impair athlete performance across physical, technical, and cognitive domains. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165707. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, C. Distribution characteristics of inhalable particulate pollutants and their effects on cardiopulmonary respiratory system of outdoor football players in a smart healthcare system. Soft Comput. 2024, 28, 2683–2700. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Sun, S.; Ho, M.S. Immediate Impacts of Air Pollution on the Performance of Football Players. J. Sports Econ. 2024, 25, 753–776. [Google Scholar]
- Kubayi, A. Evaluation of match-running distances covered by soccer players during the UEFA EURO 2016. S. Afr. J. Sports Med. 2019, 31, v31i31a6127. [Google Scholar]
- Cusick, M.; Rowland, S.T.; DeFelice, N. Impact of air pollution on running performance. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1832. [Google Scholar]
- Mazic, S.; Lazovic, B.; Djelic, M.; Suzic-Lazic, J.; Djordjevic-Saranovic, S.; Durmic, T.; Soldatovic, I.; Zikic, D.; Gluvic, Z.; Zugic, V. Respiratory parameters in elite athletes—Does sport have an influence? Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2015, 21, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Bezuglov, E.; Ahmetov, I.I.; Lazarev, A.; Mskhalaya, G.; Talibov, O.; Ustinov, V.; Shoshorina, M.; Bogachko, E.; Azimi, V.; Morgans, R.; et al. The relationship of testosterone levels with sprint performance in young professional track and field athletes. Physiol. Behav. 2023, 271, 114344. [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger, V.; Villagrossi, L.; Taus, F.; Gottin, L.; Bonora, E.; Anderloni, M.; Varrassi, G.; Polati, L.; Nizzero, M.; Martini, A.; et al. Acetyl-L-Carnitine as an Add-On Treatment in Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Retrospective Analysis on 183 Patients, According to the Generalized Linear Mixed Model for Longitudinal Data. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 820. [Google Scholar]
- Oluwadare, J.R.; Adesina, O.S.; Adedotun, A.F.; Odetunmibi, O.A. Estimation Techniques for Generalized Linear Mixed Models with Binary Outcomes: Application in Medicine. Int. J. Comput. Methods Exp. Meas. 2024, 12, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bolker, B.M.; Brooks, M.E.; Clark, C.J.; Geange, S.W.; Poulsen, J.R.; Stevens, M.H.; White, J.S. Generalized linear mixed models: A practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Sun, G.; Qiu, C.; Mao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fan, J.; Jin, Y.; Liu, K.; Sun, P.; et al. Beyond addiction: Exploring the factors behind suicidal thoughts among methamphetamine users in Guangdong, China. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 1631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; London, S.J.; Song, G.; Chen, G.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, N.; Chen, B.; Kan, H. Ozone and daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, L.C.; Ely, M.R. Effect of air pollution on marathon running performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Hogstrom, G.M.; Pietila, T.; Nordstrom, P.; Nordstrom, A. Body composition and performance: Influence of sport and gender among adolescents. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 1799–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Urdampilleta Otegui, A.; Roche Collado, E. Intermittent hypoxia in sport nutrition, performance, health status and body composition. Nutr. Hosp. 2024, 41, 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Haiyan, J.; Simei, Z.; Xuecheng, Y.; Lin, M.; Yaoyao, L.; Fanjia, G.; Dandan, Y.; Mingjuan, J.; Jianbing, W.; Mengling, T.; et al. Does physical activity attenuate the association between ambient PM2.5 and physical function? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 162501. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, D.R.; Brandley, D.C. Exercise in Thermal Inversions: PM 2.5 Air Pollution Effects on Pulmonary Function and Aerobic Performance. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2020, 31, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Zou, J.; Yang, W.; Li, C.-Q. A Review of Recent Advances in Research on PM2.5 in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 438. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Total Movement Distance (TMD) | Jogging Distance (JD) | Walking Distance (WD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimated Value (EV) | Standard Error (SE) | EV | SE | EV | SE | ||
| Fixed effect parameters | Intercept | 12,926.1 | 3982.8 | 2466.7 | 1865.3 | 6191.6 | 1525.6 |
| Ambient temperature | −28.1 *** | 6.7 | −8.1 ** | 3.0 | −16.1 *** | 2.6 | |
| Dew point | 18.2 | 10.8 | 5.035 | 4.6 | 6.6 | 4.7 | |
| Height | −9.8 | 27.0 | 12.490 | 12.7 | −14.4 | 9.9 | |
| Weight | −20.8 | 31.0 | −25.049 | 14.2 | 32.4 ** | 11.2 | |
| Percentage of body fat | −64.9 | 38.0 | −20.373 | 17.4 | −41.4 ** | 14.4 | |
| PM2.5 | 35.3 | 23.8 | 17.592 | 9.5 | 13.8 | 9.2 | |
| O3 | −22.4 * | 8.9 | −10.817 ** | 3.7 | −6.9 * | 3.3 | |
| SO2 | 138.0 | 92.9 | 72.912 | 38.6 | 38.1 | 41.4 | |
| NO2 | 163.1 * | 72.0 | 62.922 * | 30.1 | 56.9 | 31.8 | |
| CO | 83.199 | 101.312 | 30.096 | 47.060 | 42.627 | 40.8 | |
| Air Pollutant | Mean Value (μg/m3) | Standard Deviation (μg/m3) | 2021 WHO Guideline (μg/m3) [16] | Classification | 2012 China Air Quality Threshold Value (μg/m3) [17] | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | 17.7 | 15.7 | 15 (24 h) | Below Interim target 4 | 75 (24 h) | Excellent |
| O3 | 81.0 | 39.5 | 100 (8 h) | Below AQG levels | 200 (1 h) | Excellent |
| SO2 | 7.4 | 2.5 | 40 (24 h) | Below AQG levels | 500 (1 h) | Excellent |
| NO2 | 7.1 | 2.3 | 25 (24 h) | Below AQG levels | 200 (1 h) | Excellent |
| CO | 794.0 | 1273.0 | 4000 (24 h) | Below AQG levels | 10,000 (1 h) | Excellent |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, W. Ozone Pollution Impairs Athletic Performance in Female Football Players: A Gender-Specific Analysis. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070834
Xing W, Wang Y, Xie Y, Zheng W. Ozone Pollution Impairs Athletic Performance in Female Football Players: A Gender-Specific Analysis. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070834
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Wei, Yuxin Wang, Yangyang Xie, and Wenbo Zheng. 2025. "Ozone Pollution Impairs Athletic Performance in Female Football Players: A Gender-Specific Analysis" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070834
APA StyleXing, W., Wang, Y., Xie, Y., & Zheng, W. (2025). Ozone Pollution Impairs Athletic Performance in Female Football Players: A Gender-Specific Analysis. Atmosphere, 16(7), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070834






