Evaluation of a BCC-CPSv3-S2Sv2 Model for the Monthly Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
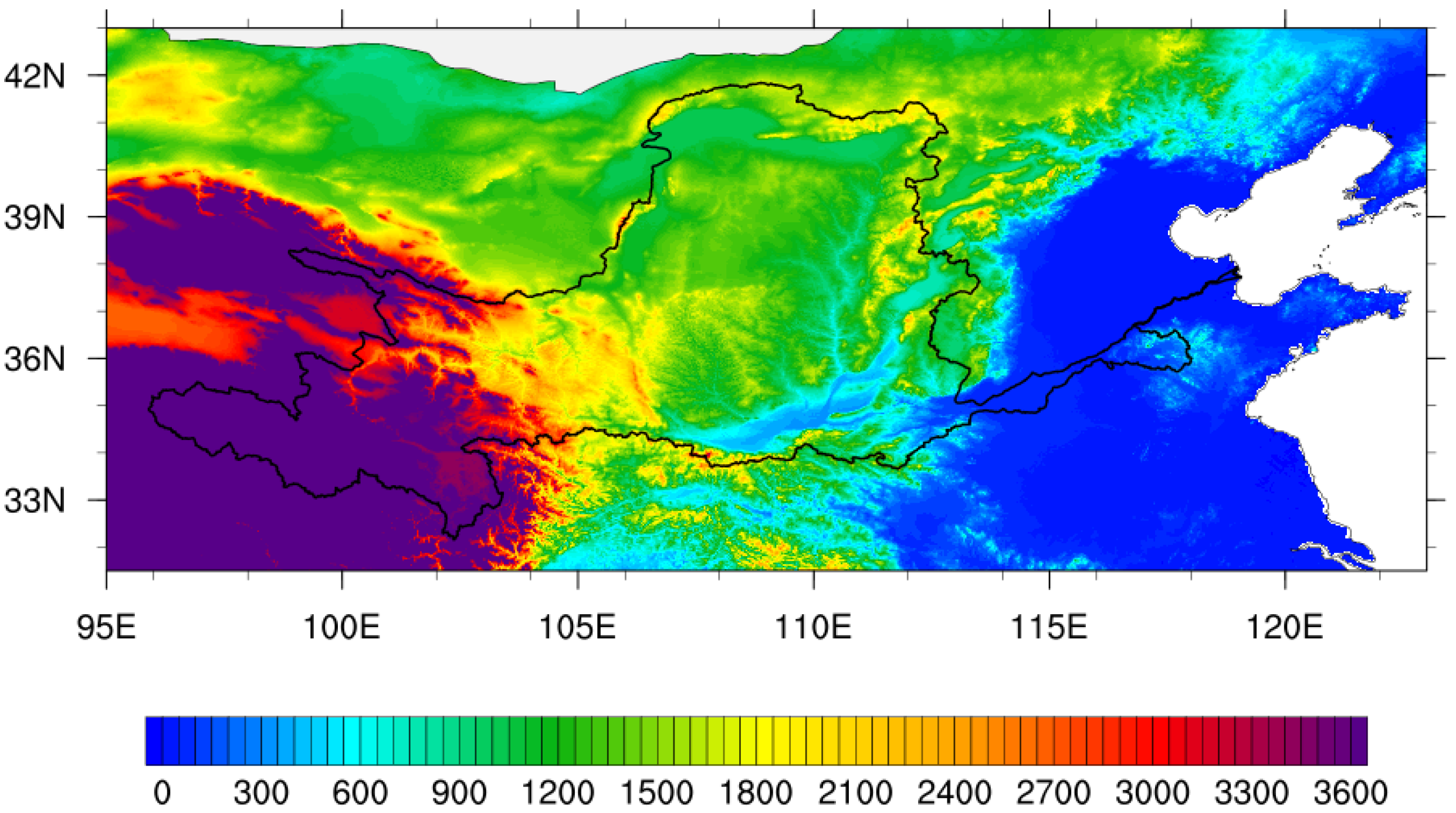
2. Model, Data and Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Overall Performance in Predicting Daily Precipitation Rate in JJA
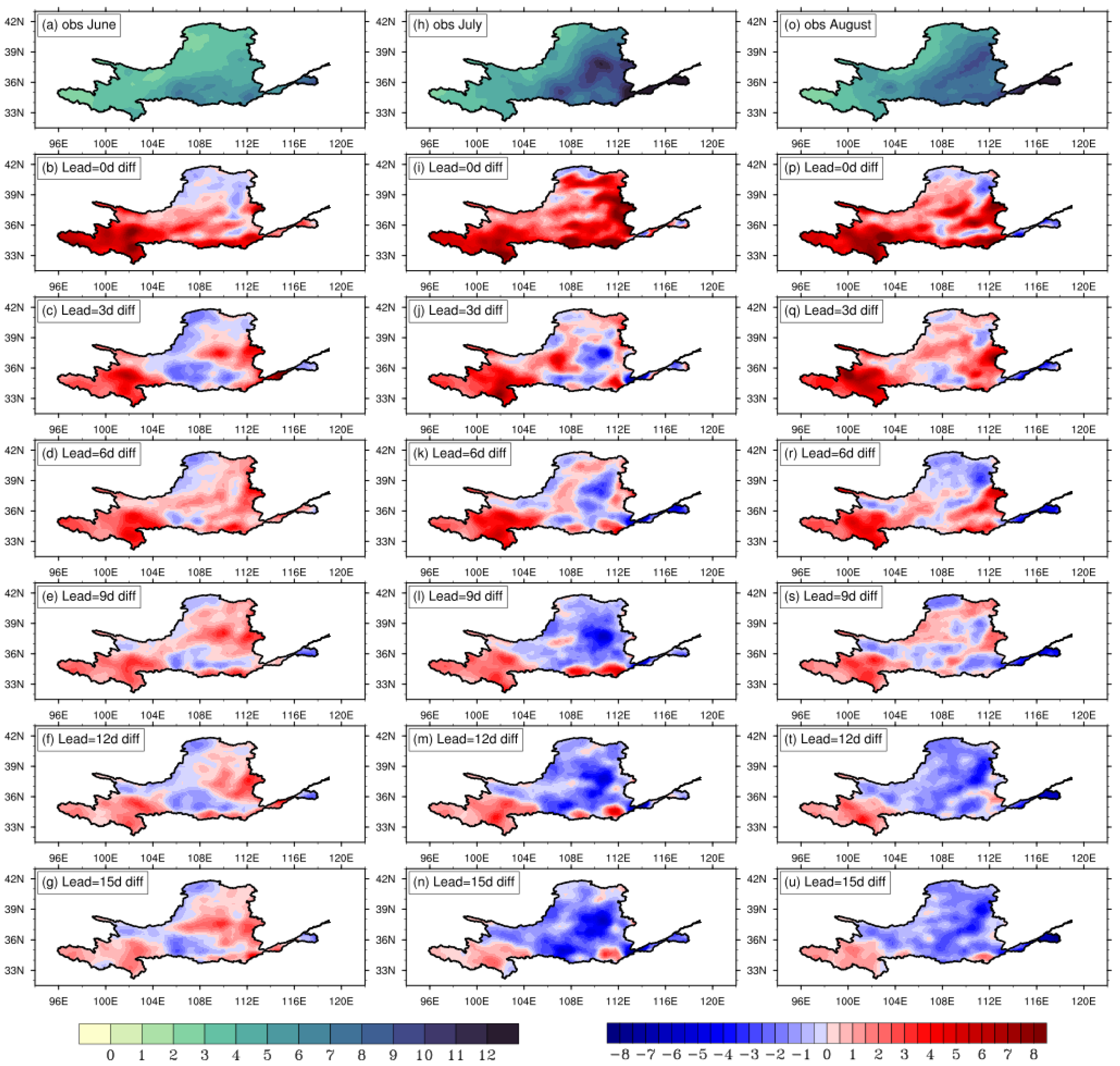
3.2. Representations of Monthly Prediction for Climatological Features
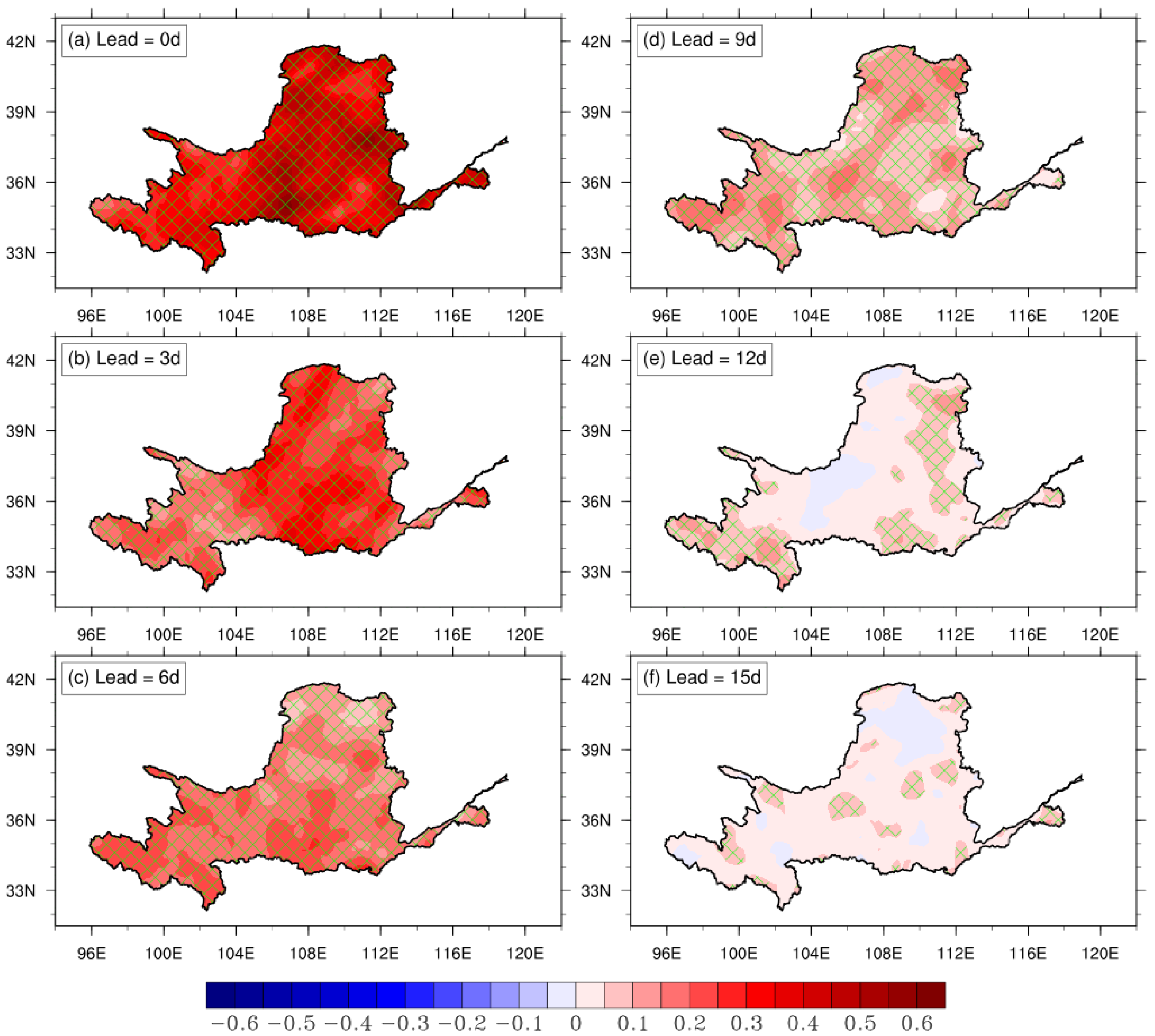
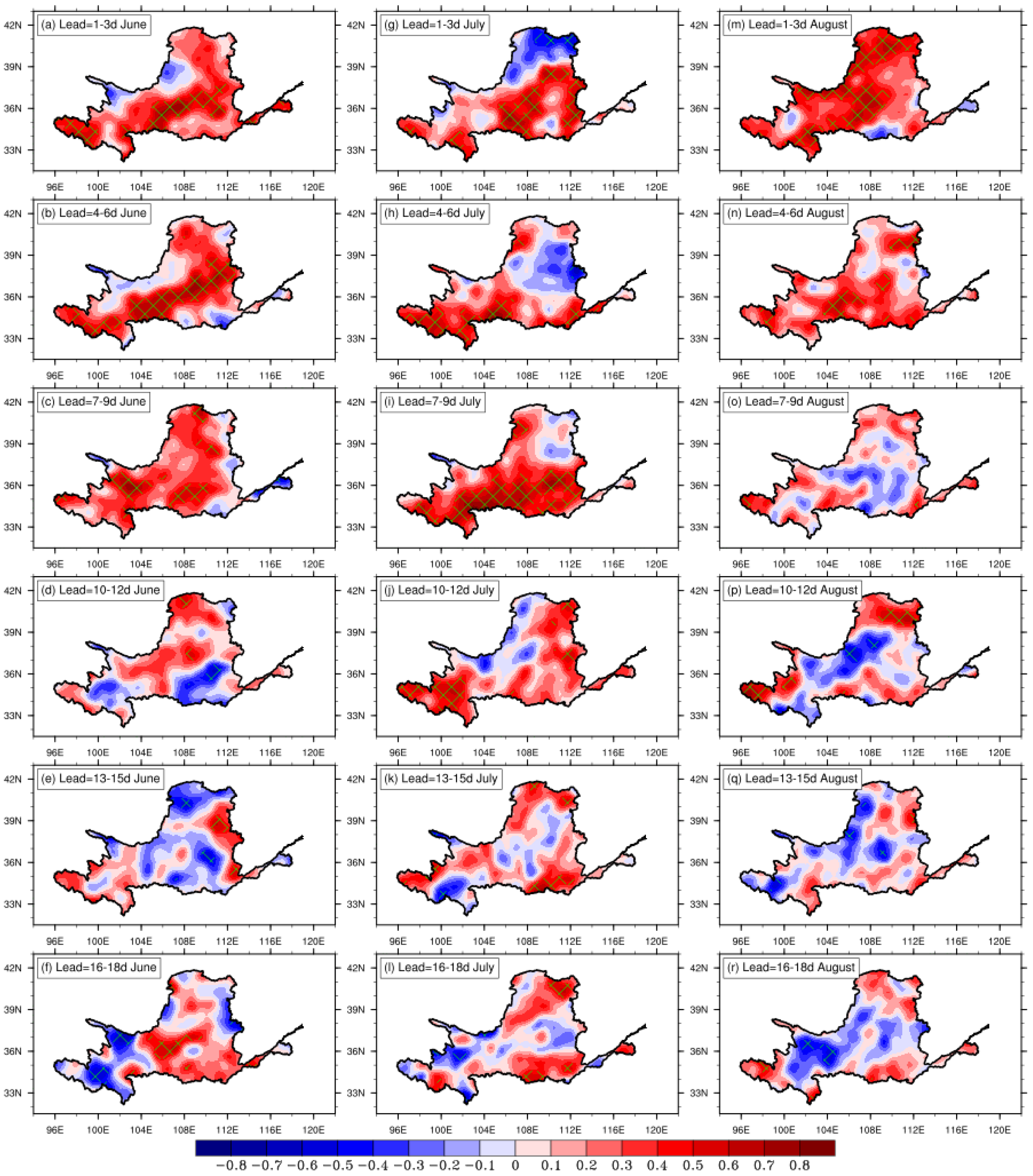
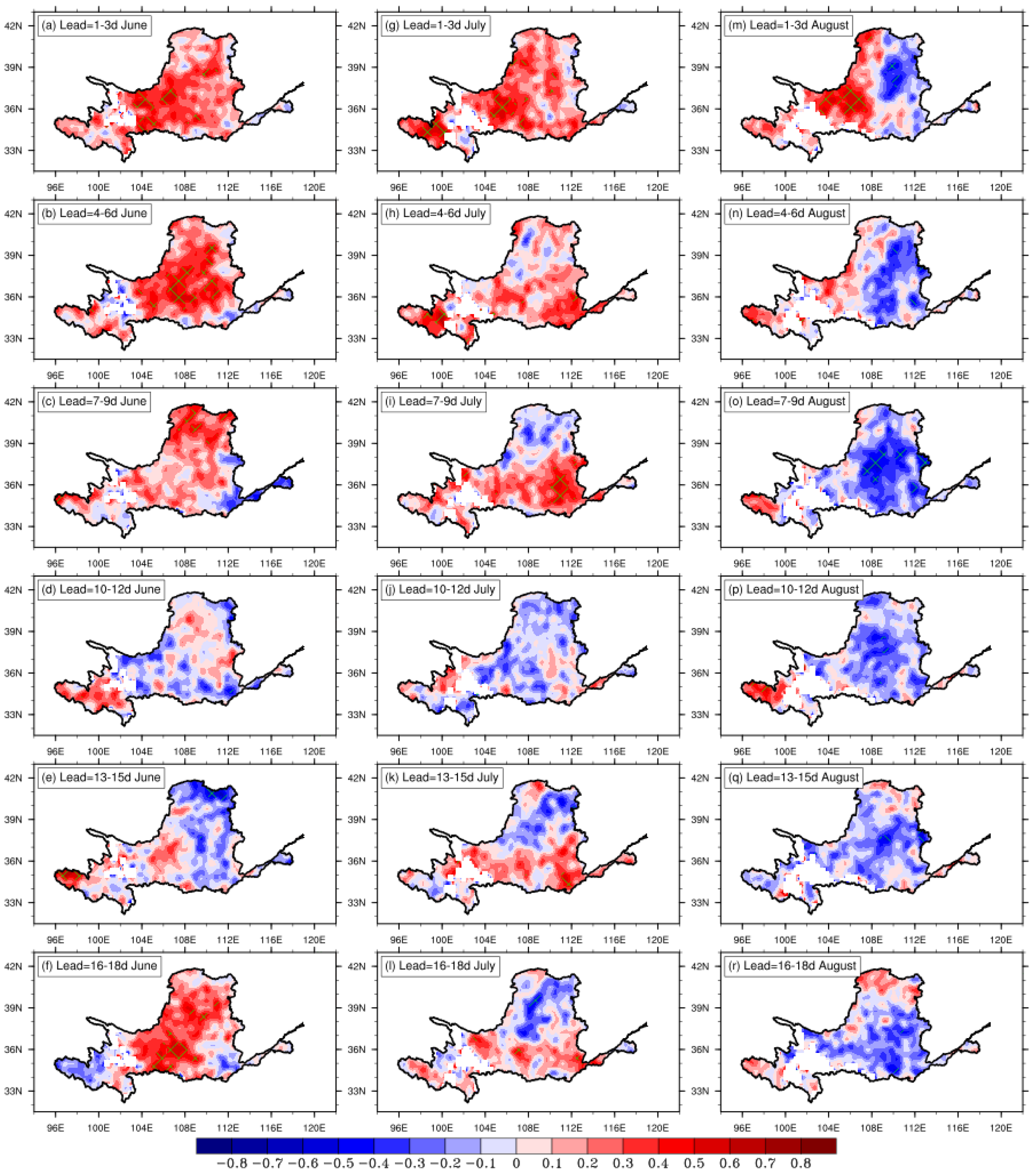
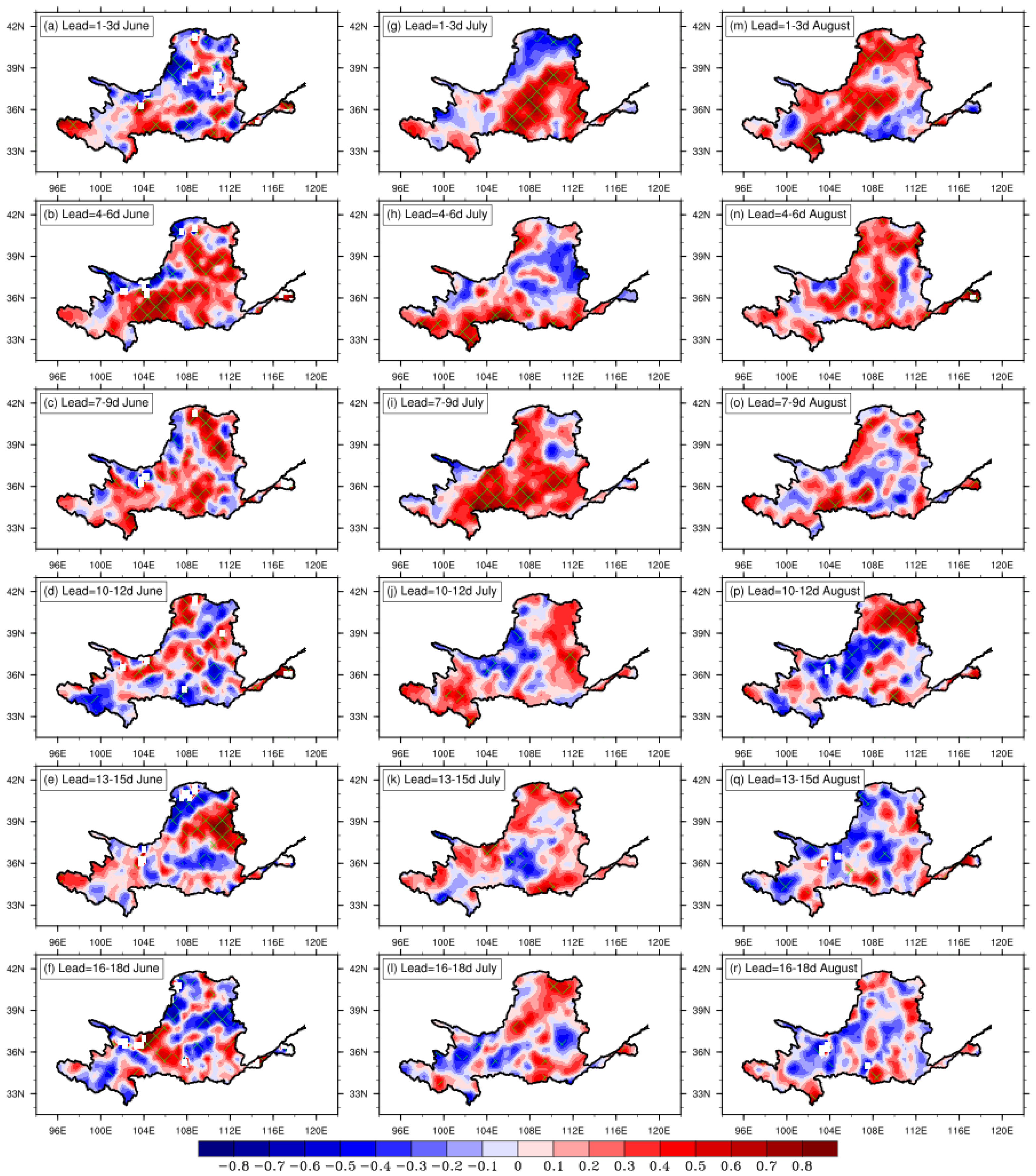
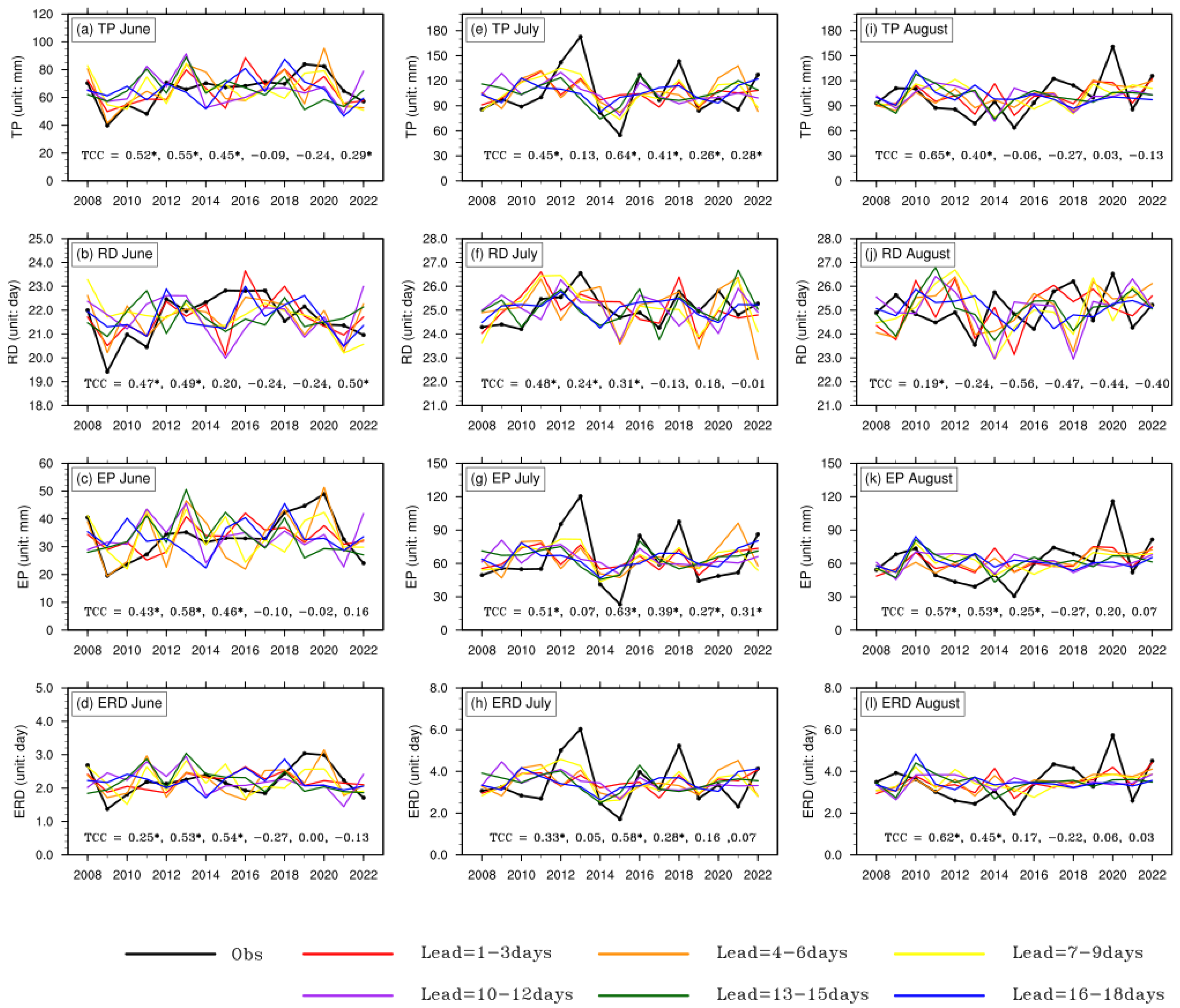
3.3. Monthly Prediction of Extreme Precipitation in the YRB
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez-Villalobos, C.; Neelin, J.D. Regionally High Risk Increase for Precipitation Extreme Events under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of Extreme Precipitation Increases Extensively with Event Rareness under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, B.; Dong, B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Extremely Persistent Precipitation Events during April–June 2022 in the Southern China: Projected Changes at Different Global Warming Levels and Associated Physical Processes. Clim. Dyn. 2025, 63, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, W.; Xiao, P.; Yao, W.; Liu, G. Driving Factors of Heavy Rainfall Causing Flash Floods in the Middle Reaches of the Yellow River: A Case Study in the Wuding River Basin, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Singh, V.P.; Wu, W.; Fan, K.; Shen, Z. Flood Disaster Risk and Socioeconomy in the Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Cui, B. Spatial and Temporal Variability of Annual Precipitation during 1961–2006 in Yellow River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xia, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Qin, F. Spatial–Temporal Variability of Hydrothermal Climate Conditions in the Yellow River Basin from 1957 to 2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Liu, S.; Bai, P.; Nie, R. The Yellow River Basin Becomes Wetter or Drier? The Case as Indicated by Mean Precipitation and Extremes during 1961–2012. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2015, 119, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Diao, Y.; Huang, P. Summer Precipitation Extremes over the Yellow River Loop Valley and Its Link to European Blocking. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Saito, Y.; Liu, J.P.; Sun, X. Interannual and Seasonal Variation of the Huanghe (Yellow River) Water Discharge over the Past 50 Years: Connections to Impacts from ENSO Events and Dams. Glob. Planet. Change 2006, 50, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Peng, M. Impacts of Climate Trends on the Heavy Precipitation Event Associated with Typhoon Doksuri in Northern China. Atmos. Res. 2025, 314, 107816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, J.; Tian, L.; Zhang, H.; Cui, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R. Characteristics of Atmospheric Rivers and the Impact of Urban Roof Roughness on Precipitation during the “23.7” Extreme Rainstorm against the Background of Climate Warming. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lv, X.; Men, B. Impact of Cumulus Parameterization Schemes on Summer Extreme Precipitation Simulation in the Yellow River Basin: The 2018 Case. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 2267–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, R.; Duan, Q. Evaluation of Tianji and ECMWF High-Resolution Precipitation Forecasts for Extreme Rainfall Event in Henan in July 2021. Water Sci. Eng. 2023, 16, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhu, X.; Dong, W. Historical Assessment and Future Projection of Extreme Precipitation in CMIP6 Models: Global and Continental. Intl. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 4119–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Xin, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, B. Simulation and Projection of Climate Extremes in China by Multiple Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 Models. Intl. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Jiang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Pang, K.; Zhang, X. Evaluation and Projection of Extreme Precipitation Using CMIP6 Model Simulations in the Yellow River Basin. J. Water Clim. Change 2024, 15, 2326–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, D.; Yu, X. Compound Successive Dry-Hot and Wet Extremes in China with Global Warming and Urbanization. J. Hydrol. 2024, 636, 131332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. The Predictability of a Flow Which Possesses Many Scales of Motion. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1969, 21, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Atmospheric Predictability Experiments with a Large Numerical Model. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1982, 34, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliser, D.E.; Jin, K.; Kang, I.-S.; Stern, W.F.; Schubert, S.D.; Wu, M.L.C.; Lau, K.-M.; Lee, M.-I.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Kitoh, A.; et al. AGCM Simulations of Intraseasonal Variability Associated with the Asian Summer Monsoon. Clim. Dyn. 2003, 21, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, F.; Ardilouze, C.; Bonet, A.; Brookshaw, A.; Chen, M.; Codorean, C.; Déqué, M.; Ferranti, L.; Fucile, E.; Fuentes, M.; et al. The Subseasonal to Seasonal (S2S) Prediction Project Database. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitar, F.; Robertson, A.W.; Anderson, D. Subseasonal to Seasonal Prediction Project: Bridging the Gap between Weather and Climate. Bull. World Meteorol. Organ. 2012, 61, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Vitart, F.; Robertson, A.W. The Sub-Seasonal to Seasonal Prediction Project (S2S) and the Prediction of Extreme Events. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2018, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.-L.; Bao, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wu, J.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Seamless Prediction in China: A Review. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 1501–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Xiao, C. Application of S2S Climate Model Products in Runoff Prediction in the Yellow River Basin. Meteor. Mon. 2023, 49, 1396–1404. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- White, C.J.; Carlsen, H.; Robertson, A.W.; Klein, R.J.T.; Lazo, J.K.; Kumar, A.; Vitart, F.; Coughlan De Perez, E.; Ray, A.J.; Murray, V.; et al. Potential Applications of Subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) Predictions. Meteorol. Appl. 2017, 24, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.J.; Domeisen, D.I.V.; Acharya, N.; Adefisan, E.A.; Anderson, M.L.; Aura, S.; Balogun, A.A.; Bertram, D.; Bluhm, S.; Brayshaw, D.J.; et al. Advances in the Application and Utility of Subseasonal-to-Seasonal Predictions. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1448–E1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, D.; Marshall, A.G.; Alves, O. Intraseasonal Forecasting of the 2009 Summer and Winter Australian Heat Waves Using POAMA. Wea. Forecast. 2011, 26, 257–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Lin, H. Sub-Seasonal Prediction over East Asia during Boreal Summer Using the ECCC Monthly Forecasting System. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 50, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Z.; Ma, L. Prediction Abilities of Subseasonal-to-seasonal Models for Regional Rainstorm Processes in South China. Intl J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 2896–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, W.; Duan, Q. Spatiotemporal Variations in Precipitation Forecasting Skill of Three Global Subseasonal Prediction Products over China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2023, 24, 2075–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.G.; Hendon, H.H. Subseasonal Prediction of Australian Summer Monsoon Anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 10913–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, W.; Vitart, F.; Wu, T.; Liu, X. Simulations of the Asian Summer Monsoon in the Sub-seasonal to Seasonal Prediction Project (S2S) Database. Quart. J. R. Meteoro Soc. 2017, 143, 2282–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, C. Subseasonal Predictability of South China Sea Summer Monsoon Onset with the ECMWF S2S Forecasting System. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, A.; La, M. Effects of the Madden–Julian Oscillation on 2-m Air Temperature Prediction over China during Boreal Winter in the S2S Database. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 52, 6671–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.; Jia, X.; Zhang, P. Climatological Diagnostics and Subseasonal-to-seasonal Predictions of Madden–Julian Oscillation Events. Intl. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 2449–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, X. Evaluation of the Subseasonal Forecast Skill of Surface Soil Moisture in the S2S Database. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2019, 12, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-Y.; Camargo, S.J.; Vitart, F.; Sobel, A.H.; Camp, J.; Wang, S.; Tippett, M.K.; Yang, Q. Subseasonal Predictions of Tropical Cyclone Occurrence and ACE in the S2S Dataset. Weather. Forecast. 2020, 35, 921–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.W.; Vitart, F.; Camargo, S.J. Subseasonal to Seasonal Prediction of Weather to Climate with Application to Tropical Cyclones. JGR Atmos. 2020, 125, e2018JD029375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.J.; Franks, S.W.; McEvoy, D. Using Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (S2S) Extreme Rainfall Forecasts for Extended-Range Flood Prediction in Australia. Proc. IAHS 2015, 370, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeisen, D.I.V.; White, C.J.; Afargan-Gerstman, H.; Muñoz, Á.G.; Janiga, M.A.; Vitart, F.; Wulff, C.O.; Antoine, S.; Ardilouze, C.; Batté, L.; et al. Advances in the Subseasonal Prediction of Extreme Events: Relevant Case Studies across the Globe. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1473–E1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Vitart, F.; Wu, T. Evaluation of Probabilistic Forecasts of Extreme Cold Events in S2S Models. Water 2023, 15, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoire, P.; Martius, O.; Naveau, P.; Tuel, A. Assessment of Subseasonal-to-Seasonal (S2S) Ensemble Extreme Precipitation Forecast Skill over Europe. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 23, 2857–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, J.; Garfinkel, C.I.; Chen, H.; White, I.P. The 2019 New Year Stratospheric Sudden Warming and Its Real-Time Predictions in Multiple S2S Models. JGR Atmos. 2019, 124, 11155–11174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Yao, S.; Huang, A.; Gong, K. Evaluation and Error Correction of the ECMWF Subseasonal Precipitation Forecast over Eastern China during Summer. Adv. Meteorol. 2020, 2020, 1920841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Skill Improvement of the Yearly Updated Reforecasts in ECMWF S2S Prediction from 2016 to 2022. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2023, 16, 100357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ren, H.-L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, Q. The Dynamical-Statistical Subseasonal Prediction of Precipitation over China Based on the BCC New-Generation Coupled Model. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 1213–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gao, X.-J. A Gridded Daily Observation Dataset over China Region and Comparison with the Other Datasets. Chin. J. Geophys. 2013, 56, 1102–1111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, D.; Wu, C.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, P. Changes in Extreme Precipitation in the Wei River Basin of China during 1957–2019 and Potential Driving Factors. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2022, 149, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Tian, Q.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.M.; Gui, J.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Q. Changes in Characteristics of Climate Extremes from 1961 to 2017 in Qilian Mountain Area, Northwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Asefa, T.; Erkyihun, S. Interannual Variabilities of the Summer and Winter Extreme Daily Precipitation in the Southeastern United States. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Index Name | Abbreviation | Definition | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total precipitation | TP | Accumulation of precipitation | mm |
| Rainy days | RD | Days with precipitation ≥ 1 mm | d |
| Extreme precipitation | EP | Precipitation above the 90th percentile | mm |
| Extreme rainy days | ERD | Days with precipitation ≥ the 90th percentile | d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Xia, Z.; Ke, J. Evaluation of a BCC-CPSv3-S2Sv2 Model for the Monthly Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070830
Li Z, Xia Z, Ke J. Evaluation of a BCC-CPSv3-S2Sv2 Model for the Monthly Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):830. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070830
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhe, Zhongyuan Xia, and Jiaying Ke. 2025. "Evaluation of a BCC-CPSv3-S2Sv2 Model for the Monthly Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070830
APA StyleLi, Z., Xia, Z., & Ke, J. (2025). Evaluation of a BCC-CPSv3-S2Sv2 Model for the Monthly Prediction of Summer Extreme Precipitation in the Yellow River Basin. Atmosphere, 16(7), 830. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070830




