Abstract
The main goal of this study is to present future changes in various precipitation indices at a kilometer-scale resolution for Bulgaria on an annual and seasonal basis. Numerical simulations were conducted using the Non-Hydrostatic Regional Climate Model version 4 (RegCM4-NH) following the Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment Flagship Pilot Study protocol for three 10-year periods (1995–2004, 2041–2050, and 2090–2099), with horizontal grid resolutions of 15 km and 3 km, on the petascale supercomputer HPC Discoverer at Sofia Tech Park. Data from the Hadley Centre Global Environment Model version 2 (HadGEM2-ES), based on the Representative Concentration Pathway 8.5 (RCP8.5) scenario, were used as boundary conditions for the regional climate model (RCM) simulations, which were subsequently downscaled to the kilometer-scale (3 km) simulations using a one-way nesting approach. High-resolution model data were compared with high-resolution observational datasets as well as lower-resolution (15 km) data. Future changes in precipitation indices were analyzed on both annual and seasonal scales, including mean daily and hourly precipitation, the frequency and intensity of wet days (>1 mm/day) and wet hours (>0.1 mm/hour), extreme daily precipitation (99th percentile, p99), and extreme hourly precipitation (99.9th percentile, p99.9) for both future periods. Additionally, changes in near-surface (2 m) temperature and surface snow amount were also presented. There is no substantial difference in projected temperature change between the resolutions. A positive trend in annual mean precipitation is expected in the near future. Extreme precipitation (p99 and p99.9) is projected to increase in spring and winter, accompanied by a rise in daily and hourly precipitation intensity across both future periods. An increase in surface snow amount is observed in the central Danubian Plain, Thracian Lowland, and parts of the Rila and Pirin mountains for the near-future period. However, surface snow amount is expected to decrease by the end of the century.
1. Introduction
Global Climate Models (GCMs) are critical tools for projecting future climate scenarios. However, their coarse spatial resolution (typically 50–100 km) limits their ability to capture localized processes, such as convective precipitation and topographically driven weather patterns [1,2]. To address this limitation, Regional Climate Models (RCMs) dynamically downscale GCM outputs to finer resolutions (typically 10–50 km), thereby improving the representation of local climate variability, extreme weather events, and land–atmosphere interactions [3,4,5]. A significant advancement in climate modeling has been the development of convection-permitting models (CPMs), which operate at kilometer-scale resolutions (1–3 km). These models explicitly resolve convective processes, eliminating the need for parameterization schemes, and have significantly improved the simulation of extreme precipitation events, convective storms, and localized weather phenomena [6,7,8,9,10,11]. CPMs are increasingly used to assess future precipitation changes across Europe, where complex terrain and regional weather dynamics strongly influence precipitation intensity and frequency [9,11,12].
Recent advancements in computational resources have made kilometer-scale climate models feasible, though they require substantial computing power and extensive data storage capabilities [13]. Among these, the Regional Climate Model (RegCM) has been widely utilized at convection-permitting scales to enhance our understanding of precipitation dynamics and climate change impacts [3,5,14,15]. A major innovation in this field is the Non-Hydrostatic Regional Climate Model version 4 (RegCM4-NH [16]), which has demonstrated improved simulation of intense convective events [16]. International initiatives, such as the European Climate Prediction System (EUCP) and the Coordinated Regional Climate Downscaling Experiment Flagship Pilot Studies (CORDEX-FPS) on convection, have leveraged RegCM for high-resolution climate projections [4,17,18]. The CORDEX-FPS on convection focuses on producing ensembles of convection-permitting simulations over Europe and the Mediterranean, resulting in improved representations of convective processes and extreme precipitation events [11,18,19].
Over the past decade, advancements in computing power and numerical modeling techniques have driven a shift towards higher-resolution RCMs, reaching the convection-permitting (CP) scale of 1–3 km [7,11,20,21,22]. These high-resolution models enable the explicit simulation of deep convection, leading to more accurate predictions of extreme weather events such as heavy rainfall, thunderstorms, and tropical cyclones. The transition to CP scales relies on non-hydrostatic dynamical cores, which enhance the representation of small-scale atmospheric processes, alongside improved physical process parameterizations. Initial simulations with CPRCMs have shown substantial improvements in reproducing precipitation patterns and cloud dynamics compared to traditional hydrostatic RCMs [20,23]. Numerous CPRCM experiments across European domains have provided valuable insights into regional climate change impacts, including changes in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, heatwaves, and flooding [13,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. These high-resolution models have also enabled the investigation of local-scale processes that were previously unresolved in coarser models, such as land–atmosphere interactions, urban heat island effects, and convective feedback mechanisms. However, the increased resolution also brings challenges related to data storage, computational demands, and the feasibility of running long-term simulations over large domains.
As convection-permitting resolutions become the new standard for regional climate modeling, models like RegCM have been adapted to meet these challenges. Developed by research institutions worldwide, RegCM provides high-resolution climate simulations for applications such as impact assessments, adaptation strategies, and disaster risk reduction. The RegCM model has also been applied to Bulgaria, with recent studies evaluating the performance of RegCM4 for the region, specifically for the 2000–2010 period, using ERA-Interim data for initial and boundary conditions [29,30]. Additionally, research has focused on sensitivity studies [31,32], future climate change projections, and extreme meteorological events [33,34,35,36]. The main goal of this study is to present future changes in various precipitation indices at a kilometer-scale resolution for Bulgaria, on both an annual and seasonal basis, for near- and far-future periods, as well as changes in 2 m temperature and surface snow amount. The periods were selected in accordance with the CORDEX−FPS protocol [11].
2. Model Description and Experimental Design
The Regional Climate Model (RegCM) was originally developed at the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR) and has several versions through years, including RegCM1 [37,38], RegCM2 [39,40], and RegCM2.5 [41]. It was later improved at the Abdus Salam International Center for Theoretical Physics (ICTP), which resulted in RegCM3 [42] and RegCM4 [3]. RegCM4 introduces both hydrostatic [3] and non-hydrostatic (RegCM4-NH [16]) dynamical cores. This study uses the non-hydrostatic version, RegCM4-NH [16].
The integration domain focuses on Bulgaria with a grid spacing of 3 km and 41 vertical sigma levels (Figure 1). The domain consists of 260 × 200 grid points in the horizontal and meridional directions, respectively, with a lateral buffer zone of 30 grid points from each site. Numerical simulations were performed using the non-hydrostatic regional model RegCM4-NH for three 10-year periods (1995–2004, 2041–2050, and 2090–2099). These simulations were conducted at horizontal grid resolutions of 15 km and 3 km on the petascale supercomputer HPC Discoverer at Sofia Tech Park. The global climate model HadGEM2-ES [43], following the RCP8.5 emission scenario [44], provided boundary conditions for the regional climate model simulations, which were then downscaled to a finer resolution of 3 km. Each simulation performed a 1-year spin-up. A set of precipitation indices (Table 1) was applied to assess projected future changes. The indices are calculated annually (ANN) and on a seasonal basis, considering March–April–May for spring, June–July–August (JJA) for summer, September–October–November (SON) for autumn, and December–October–November for winter. All indices (seasonal and yearly) are computed with the Climate Data Operator tool (CDO) [45]. The simulations were performed on the Discoverer HPC with a time step of 6 s and a domain with 260 × 200 grid points at the 3 km horizontal resolution.
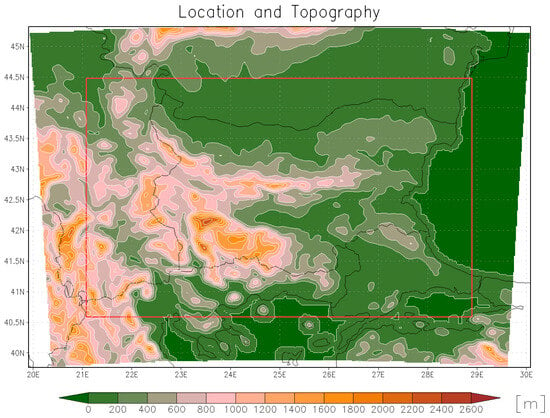
Figure 1.
Location and topography of the analysis region based on the high-resolution km scale simulation (3 km). The map displays terrain elevation (in meters above sea level) with 200 m contour intervals. The red bounding box indicates the location of the analysis region (Bulgaria and surrounding areas). Domain boundaries are 19.91° E–30.09° E; 39.76° N–45.32° N.

Table 1.
Statistical indices used in this study.
Bulgaria is located in Southeastern Europe, occupying a transitional zone between the continental climate of Central Europe and the Mediterranean climate to the south. Its diverse topography—including mountain ranges such as the Balkan Mountains, Rila, Rhodope, and Pirin, as well as lowland regions like the Danubian Plain and Thracian Valley—significantly influences regional climate patterns. Precipitation varies widely across the country, both spatially and seasonally, with higher amounts typically observed in mountainous areas due to orographic lifting, and lower totals in the plains and southeastern regions. The country is also affected by Mediterranean cyclones and convective summer storms, contributing to both seasonal rainfall and extreme precipitation events. This climatic complexity makes Bulgaria particularly sensitive to projected changes in precipitation patterns under future climate scenarios. Bulgaria’s geographical location and diverse terrain make it particularly vulnerable to climate variability and extreme weather events. Regional studies indicate increasing and intensifying heavy rainfall in the Balkans [29,33,34], consistent with broader trends observed across the Mediterranean. Therefore, high-resolution modeling is essential to accurately capture localized precipitation patterns and assess the potential impacts of climate change.
3. Data and Methods
The availability of high-resolution and high-quality datasets is essential to convection-permitting (CP) scale simulations. To assess daily precipitation metrics, we used the MESCAN-SURFEX reanalysis dataset at a 5.5 km resolution, covering the period from 1961 to 2019 [46], along with the Copernicus European Regional ReAnalysis Land (CERRA-Land) sub-daily regional reanalysis data, also at a 5.5 km resolution, covering the period from 1984 to 2021 [47]. For the evaluation of hourly precipitation, we employed the PERSIANN Dynamic Infrared–Rain Rate (PERSIANN-PDIR-Now) satellite data, which provides satellite-based precipitation estimates at a much finer resolution of 0.04° (~4 km), with hourly temporal resolution [48]. The hourly data is available starting from March 2000; therefore, the years 2001–2004 are considered in the analysis.
A set of well-known precipitation indices is applied to assess projected future changes. Table 1 provides an overview of the indices used. These indices include mean daily/hourly precipitation, wet day/hour intensity and wet day/hour frequency, and heavy daily and hourly precipitation, defined as the 99th percentile (p99) and the 99.9th percentile (p99.9), respectively. A wet day (hour) is defined as a day (hour) with precipitation exceeding 1 mm/day (>0.1 mm/hour). Percentiles are based on the values of all events, both wet and dry, over the entire 10-year period [49]. For the evaluation of the kilometer-scale simulation, observational data were interpolated onto a 3 km grid using the distance-weighted interpolation method. For the assessment of the coarse-resolution simulation, the data were interpolated onto a 15 km grid. The Climate Data Operator tool (CDO) [45] was used for this purpose. To assess annual and seasonal changes in precipitation, the indices are calculated annually (ANN) and seasonally, with March–April–May (MAM) used for spring, June–July–August (JJA) for summer, September–October–November (SON) for autumn, and December–January–February (DJF) for winter.
In this study, we employ the non-hydrostatic configuration of RegCM4, as described by Coppola et al. [16]. RegCM4-NH has been widely used in convection-permitting climate simulations within various research initiatives, such as European Climate Prediction System (EUCP) and the CORDEX Flagship Pilot Study on convection (CORDEX-FPS) [11]. Its effectiveness has been demonstrated through multiple-model experiments conducted across different regions [21,22].
4. Results
4.1. Annual Precipitation Indices Assessment
To evaluate the reliability and performance of the regional climate simulations in reproducing present-day precipitation characteristics, we compare model outputs with high-resolution observational and reanalysis datasets. This evaluation provides a baseline for assessing model skill and identifying potential biases before using the simulations for future climate projections. The assessment focuses on precipitation over Bulgaria and includes comparisons of annual mean indices at both daily and hourly resolutions, using datasets such as MESCAN-SURFEX, CERRA-Land, and the PERSIANN Dynamic Infrared–Rain Rate (PDIR-Now) satellite product. Spatial maps of mean values and model biases are presented for the historical period.
To further assess temporal characteristics, we analyze daily and hourly probability density functions (PDFs), the seasonal diurnal cycle of hourly precipitation, the monthly annual cycle of daily precipitation and monthly precipitation differences between simulations and observations. These metrics provide insight into the models’ ability to capture not only average precipitation but also its timing, intensity, and variability—factors that are crucial for hydrological modeling and climate impact assessments.
A comparison of annual mean daily precipitation indices from the MESCAN-SURFEX reanalysis dataset (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-uerra-europe-single-levels?tab=download, accessed on 30 May 2023), and simulations (15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM), along with mean biases for the historical period 1995–2004 is shown in Figure 2. The evaluated indices include mean daily precipitation, wet-day intensity and wet-day frequency, and heavy daily precipitation, defined as the 99th percentile (p99). A wet day is defined as a day with precipitation exceeding 1 mm/d. Percentile calculations are based on all recorded events, including both wet and dry days, over the entire period. The annual mean biases (Table 2) indicate that the RCM underestimates all precipitation indices, except for frequency, by ~10–15%. In contrast, the CPRCM overestimates all indices, with intensity increasing by ~30%, mean precipitation by ~57%, and heavy precipitation (p99) by ~80%. Specifically, the RCM underestimates mean precipitation by ~10%, intensity by ~15%, and heavy precipitation by ~10%. A more detailed validation by Valcheva [29,33], focusing on seasonal and hourly precipitation metrics, showed that despite these biases, CP simulations demonstrate improvements, particularly in representing hourly intensity and extreme precipitation.
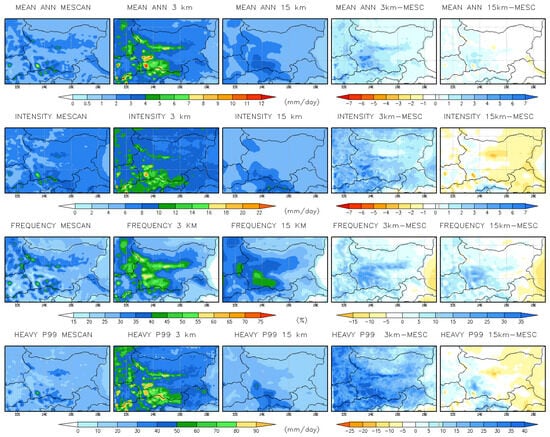
Figure 2.
Comparison of annual mean daily precipitation indices from MESCAN-SURFEX datasets and simulations (15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM), along with mean biases for the historical period 1995–2004. Units: mm/d for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.

Table 2.
Annual mean daily precipitation indices, including means (MESCAN-SURFEX, 3 km CPRCM, 15 km RCM) and biases, area-averaged over Bulgaria (21.08° E–28.9° E; 40.59° N–44.48° N), for the historical period 1995–2004. Units: mm/d for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.
A comparison of annual mean daily precipitation indices from CERRA reanalysis datasets (https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-cerra-land?tab=overview, accessed on 25 April 2025), and simulations (15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM), along with mean biases for the historical period 1995–2004 are shown in Figure 3. The annual mean biases (Table 3) indicate that the RCM underestimates all precipitation indices, except for frequency, by approximately 12–17%. In contrast, the CPRCM overestimates all indices, with intensity increasing by ~31%, mean precipitation by ~54%, and heavy precipitation (p99) by ~74%. Specifically, the RCM underestimates mean precipitation by ~12%, intensity by ~17%, and heavy precipitation by ~15%. Overall, these results suggest that while the convection-permitting model (CPRCM) more effectively captures precipitation frequency and extremes, it tends to overestimate precipitation amounts and intensities, whereas the coarser RCM underestimates most metrics.
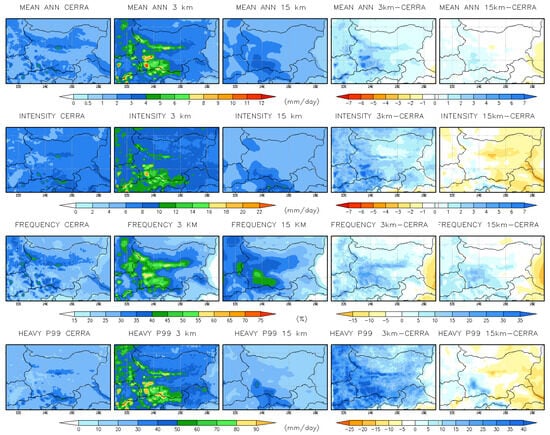
Figure 3.
Comparison of annual mean daily precipitation indices from CERRA datasets and simulations (15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM), along with mean biases for the historical period 1995–2004. Units: mm/d for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.

Table 3.
Annual mean daily precipitation indices, including means (CERRA, 3 km CPRCM, 15 km RCM) and biases, area-averaged over Bulgaria, for the historical period 1995–2004. Units: mm/d for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.
To further assess temporal characteristics of precipitation, we analyze the monthly annual cycle of daily precipitation (Figure 4) and monthly precipitation differences between simulations and observations (Figure 5).
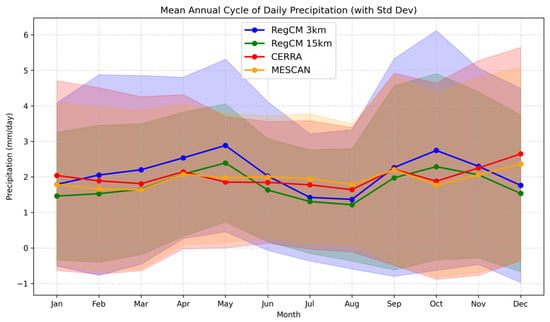
Figure 4.
Mean annual cycle of daily precipitation over Bulgaria for the period 1995–2004, with standard deviation shading (mean ± standard deviation). The comparison includes two model simulations—RegCM at 3 km (blue line) and 15 km (green line)—and two observational datasets—MESCAN (yellow line) and CERRA (red line).
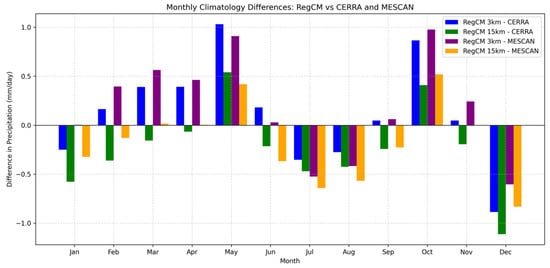
Figure 5.
Monthly precipitation differences between the two RegCM model simulations and two reference datasets (CERRA and MESCAN).
Figure 4 illustrates the comparison of the monthly annual precipitation cycle from simulations (RegCM 3 km and 15 km) and observational datasets (MESCAN and CERRA), including standard deviation shading to represent variability (mean ± standard deviation). Both models exhibit similar seasonal patterns, though the 3 km simulation tends to overestimate precipitation in spring and autumn. The wider shading in May and October for the 3 km simulation, compared to observations, suggests greater uncertainty or variability in the model. Both simulations underestimate precipitation during the summer months. In general, the two observational datasets show consistent annual cycles, providing a reliable reference for model evaluation. The inclusion of multiple datasets helps illustrate model uncertainty and performance across seasons.
Figure 5 illustrates the monthly precipitation differences between the model simulations and observational datasets. Compared to CERRA, the kilometer-scale simulation (blue line) exhibits a greater overestimation of precipitation in May and October than the 15 km simulation (green line). However, the 3 km model demonstrates improved performance in representing winter and summer precipitation compared to the coarser-resolution model (Figure 5).
An important aspect of precipitation characteristics is the distribution of precipitation intensity, which can be assessed using probability density functions (PDFs). PDFs of daily simulated and observed precipitation over the study region are presented in Figure 6. All datasets are shown on their native grids. The highest observed daily precipitation values in the tails of the PDFs range from approximately 120–260 mm/day for MESCAN and 140–260 mm/day for CERRA (Figure 6, gray and black markers, respectively). The kilometer-scale simulation exhibits more frequent and more intense precipitation events (Figure 6), but fewer occurrences of moderate precipitation below 20 mm/day. The most intense events, exceeding 260 mm/day, are produced by the RegCM 3 km simulation, which also shows a generally higher frequency of events exceeding ~40 mm/day compared to MESCAN and CERRA.
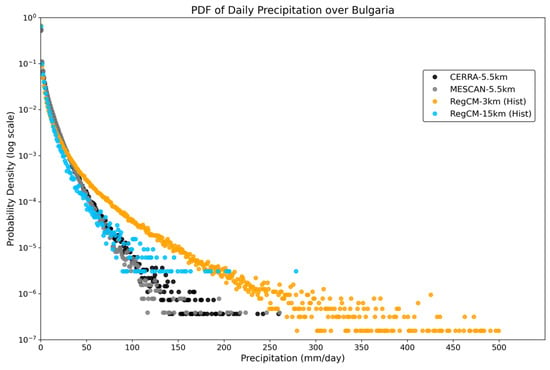
Figure 6.
Daily probability density functions (PDFs) from simulations (3 km and 15 km) and observations (CERRA, MESCAN). The datasets are in their original grid.
In summary, Figure 6 demonstrates that model resolution has a strong influence on the intensity distribution of precipitation. The increased resolution of the convection-permitting (CP) RegCM configuration provides significant added value in simulating extreme precipitation events.
A comparison of hourly mean precipitation indices from PERSIANN Dynamic Infrared–Rain Rate (PDIR-Now)—a near-real-time, quasi-global satellite precipitation dataset [48]—and simulations, along with mean biases for the historical period 2001–2004, are shown in Figure 7. Area average values of all indices over the territory of Bulgaria are summarized in Table 4. The evaluated indices include mean hourly precipitation, wet-hour intensity and wet-hour frequency, and heavy hourly precipitation, defined as the 99.9th percentile (p99.9). A wet hour is defined as an hour with precipitation exceeding 0.1 mm/hour. Percentile calculations are based on all recorded events, including both wet and dry hours, over the entire period. Overall, both models underestimate mean precipitation, intensity, and frequency, except in mountainous regions. In contrast, the CPRCM overestimates extreme precipitation, with p99.9 values exceeding those of the PDIR-Now dataset by more than 69%.
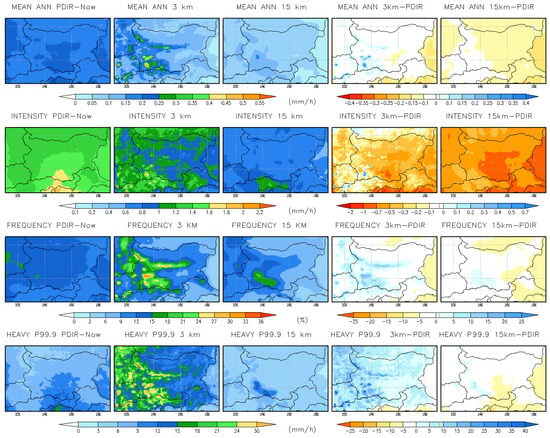
Figure 7.
Comparison of annual mean hourly precipitation indices from PDIR-Now datasets and simulations (15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM), along with mean biases for the historical period 2001–2004. Units: mm/hour for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.

Table 4.
Annual mean hourly precipitation indices, including means (PDIR-Now, 3 km CPRCM, 15 km RCM) and biases, area-averaged over Bulgaria for the historical period 2001–2004. Units: mm/hour for all indices except frequency, which is expressed in %.
The evaluation of daily and hourly precipitation indices across different reanalysis and satellite datasets reveals systematic biases in both RCM and CPRCM simulations. While the RCM consistently underestimates most precipitation metrics, the CPRCM tends to overestimate them, especially for extreme events. Despite these biases, CPRCM simulations demonstrate improved representation of hourly precipitation metrics compared with RCM simulation, especially in mean hourly precipitation, wet-hour intensity, and frequency (Table 4). These results highlight the added value of convection-permitting simulations in capturing sub-daily precipitation characteristics more realistically.
Another feature that is generally better captured by convection-permitting regional climate models (CPRCMs) is the diurnal cycle of precipitation during spring and summer [20], as also illustrated in Figure 8. The 3 km CPRCM simulates the timing of precipitation more accurately than the coarse-resolution model. Both models tend to underestimate seasonal hourly precipitation, except during midday hours in JJA, when simulated values align more closely with observations. The kilometer-scale model more realistically represents the peak of spring and summer precipitation compared to the coarse-resolution model. This improvement is consistent with findings from previous studies [6,7,9,12,20]. For example, in the diurnal cycle, RegCM 3 km simulates the peak precipitation around 15 UTC during both MAM and JJA, which is a notable improvement over the RegCM 15 km simulation that places the peak too early, at around 13 UTC. Overall, the kilometer-scale model demonstrates clear added value by more accurately reproducing the late-afternoon maximum in the diurnal cycle and showing better agreement with observational datasets.
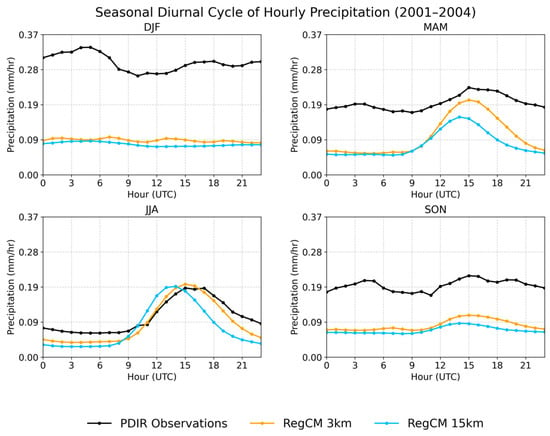
Figure 8.
2001–2004 seasonal diurnal cycle of hourly precipitation.
Figure 9 presents the hourly precipitation probability density functions (PDFs) from simulations and observations. All datasets are shown on their native grids. Both models tend to underestimate precipitation compared to the observational datasets. The regional climate model (RCM) overestimates the frequency of light precipitation but underestimates precipitation events exceeding 20 mm/hour relative to CPRCM (Figure 9). The convection-permitting regional climate model (CPRCM) captures the most extreme precipitation events above 110 mm/hour. The highest observed hourly precipitation values in the PDF tails range from approximately 70 to 110 mm/hour in the PDIR dataset (Figure 9, black dots). The strongest extremes, exceeding 120 mm/hour, are simulated by the RegCM 3 km model, which generally produces higher frequencies of intense precipitation than the coarse-resolution model at intensities above ~5 mm/hour.
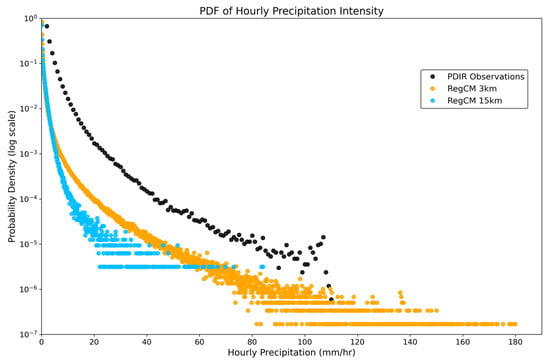
Figure 9.
Hourly probability density functions (PDFs) from simulations (CPRCM and RCM, in yellow and blue color, respectively) and observation (black dots).
4.2. Precipitation Indices Change
4.2.1. Near-Future Precipitation Indices Changes 2041–2050 vs. 1995–2004
This section assesses projected changes in precipitation indices for the near-future period (2041–2050) relative to the historical baseline (1995–2004). The analysis examines spatial patterns of change as well as variations in total precipitation, intensity, frequency, and extremes. Beyond traditional indices, changes in the probability density functions (PDFs) of daily precipitation are evaluated to provide a detailed perspective on how the full distribution—encompassing light, moderate, and extreme events—may evolve under future climate conditions. These insights are critical for understanding potential hydrological impacts and informing effective adaptation strategies for climate-sensitive sectors in Bulgaria.
Annual and seasonal changes (%) in daily precipitation indices at a 3 km resolution for the near-future period (2041–2050) are presented in Figure 10. The annual precipitation indices indicate an overall increase, except for frequency (Figure 10, last column), especially over the northern parts of Bulgaria, with an increase of about 20–25%. Annual mean precipitation is projected to rise, particularly in the northern regions of Bulgaria, with wet-day intensity increasing by approximately 20%. Heavy precipitation is also expected to increase in the northernmost and southernmost parts of the country. In winter, all indices are anticipated to rise: mean precipitation by 25%, intensity by 15%, frequency by 3%, and heavy precipitation by 22%, but in some places above 30%. A similar trend is observed in spring, especially in Eastern Bulgaria, although with slightly lower values. During the March–April–May (MAM) period, heavy precipitation is expected to increase by 30% in northeastern and southeastern Bulgaria. In contrast, wet day-frequency is projected to decrease during summer (June–July–August, JJA) and autumn (September–October–November, SON). In summer, mean precipitation is expected to decline, except in the northernmost and westernmost regions. However, precipitation intensity and extreme events (p99) are projected to increase by 12.42% and 8.35%, respectively, particularly in northern Bulgaria, the westernmost regions, and some areas along the Black Sea coast. In autumn, extreme precipitation (p99) will rise in central and northwestern Bulgaria. These changes indicate a more intense and irregular precipitation pattern, with a higher likelihood of extreme weather events, particularly in the northern and coastal regions.
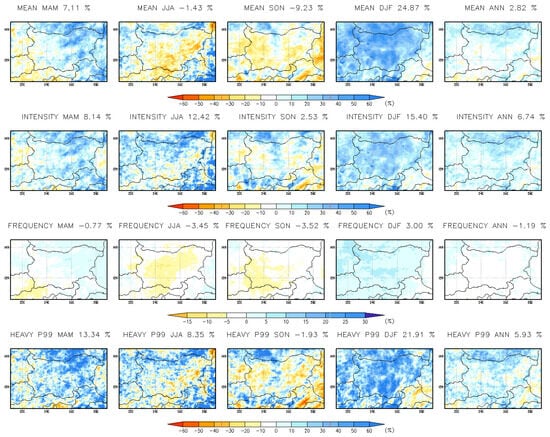
Figure 10.
Annual and seasonal changes (%) in daily precipitation indices at 3 km resolution for the near-future period 2041–2050 vs. 1995–2004.
The annual changes in RCM simulations (Table 5, Figure 11) closely resemble those in CPRCM, with mean precipitation increasing by 2.37%, intensity by 5.84%, frequency decreasing by 0.92%, and extreme precipitation (p99) rising by 5.11%. However, CPRCM projects a more pronounced increase in heavy precipitation along the Black Sea coast. Compared to CPRCM, RCM underestimates heavy precipitation changes across all seasons. Notably, in autumn (SON), RCM fails to capture the increase in extreme precipitation (p99) in northwestern Bulgaria. Both RCM and CPRCM simulations are strongly influenced by the GCM boundary conditions (Figure 12). The GCM results indicate an increase in all precipitation indices during winter, spring, and annually, except for frequency. Additionally, GCM projections show a 10–20% increase in extreme precipitation across all seasons. Annually, the GCM predicts increases in all indices: mean precipitation by 7.87%, intensity by 11.63%, with frequency decreasing by 1.1%, and extreme precipitation (p99) rising by 12.76%.

Table 5.
Percentage changes (%) in the analyzed indices for the two simulations (3 km CPRCM and 15 km RCM) for spring (MAM), summer (JJA), autumn (SON), winter (DJF), and annual (ANN) means, area-averaged for Bulgaria (21.08° E–28.9° E; 40.59° N–44.48° N). Comparisons are made for near-future (NF, 2041–2050) and far-future (FF, 2090–2099) periods relative to reference period (RF, 1995–2004).
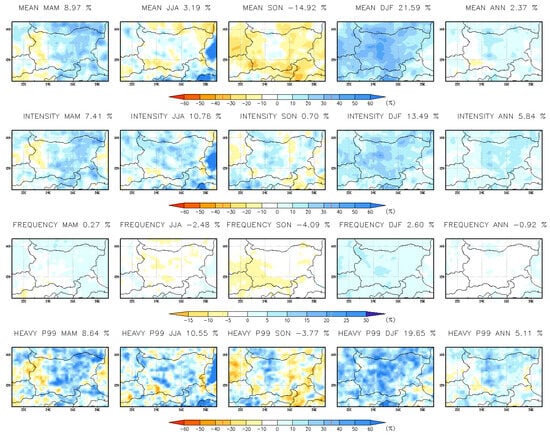
Figure 11.
Annual and seasonal changes (%) in daily precipitation indices at 15 km resolution for the near-future period 2041–2050 vs. 1995–2004.
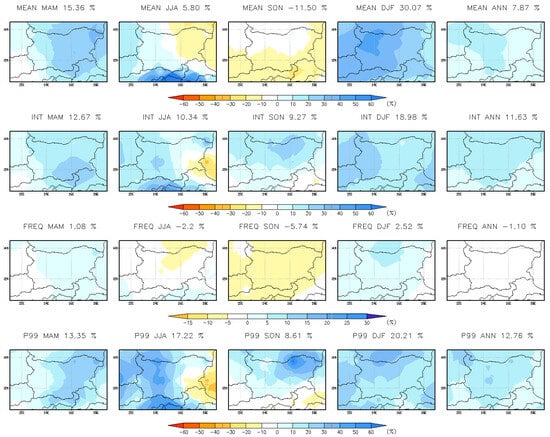
Figure 12.
Annual and seasonal changes (%) in daily precipitation indices from GCM simulation for the near-future period 2041–2050 Vs. 1995–2004.
Future projections of annual and seasonal hourly precipitation indices at a 3 km resolution for the near-future period (2041–2050) are shown in Figure 13. Annual precipitation is expected to increase by approximately 3%, particularly in northern Bulgaria. Precipitation intensity is projected to rise by about 4%, while extreme precipitation (p99.9) is expected to increase, especially in northern Bulgaria, along the Black Sea coast, and in some southern regions up to 20%. Mean hourly precipitation is anticipated to increase during March–May (MAM) and December–February (DJF) but decrease in June–August (JJA) and September–November (SON), except in the northernmost and westernmost parts of Bulgaria during JJA. Both precipitation intensity (~10%) and extreme precipitation (~20%) are projected to increase in MAM, DJF, and JJA across the entire country. Meanwhile, precipitation frequency is expected to decrease, except in winter. The biggest changes are shown in the winter and spring seasons, where mean and extreme precipitation are expected to increase above 30%.
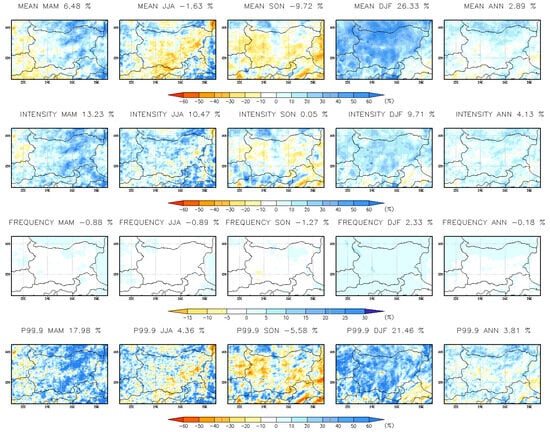
Figure 13.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in hourly precipitation indices at 3 km resolution for the near-future period 2041–2050.
The RCM precipitation projections (Figure 14, Table 5) generally align with these findings, with one key exception: the change in extreme precipitation (p99.9). The CPRCM suggests a stronger increase in p99.9 during MAM and DJF, as well as a greater rise in precipitation intensity during summer.
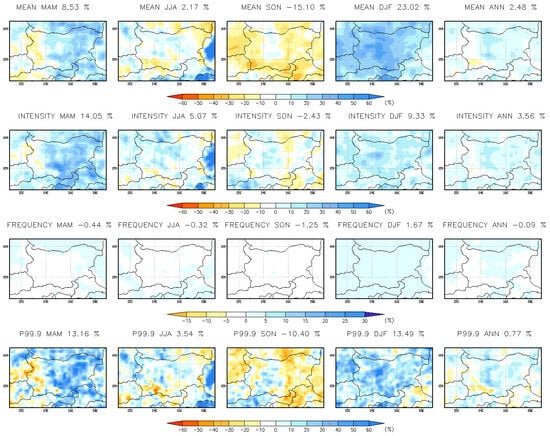
Figure 14.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in hourly precipitation indices at 15 km resolution for the near-future period 2041–2050.
4.2.2. Far-Future Precipitation Indices Changes 2090–2099 vs. 1995–2004
Annual and seasonal changes (%) in daily precipitation indices at a 3 km resolution for the far-future period (2090–2099) are presented in Figure 15. The projected annual changes in daily indices are as follows: mean precipitation is expected to decrease by 10.34%, precipitation intensity to increase by 7.56%, frequency to decline by 5.25%, and heavy precipitation (p99) to rise by 0.73%. Precipitation frequency is projected to decrease across the entire territory of Bulgaria, while mean precipitation is also expected to decline, except in the south-easternmost and northernmost regions. Wet-day intensity and extreme precipitation are anticipated to increase over the Danubian Plain and Thracian Lowlands. The most significant changes are observed during the winter season. The CPRCM projects a ~20% increase in mean winter precipitation across the entire region, with extreme precipitation rising by over 35% and precipitation intensity increasing by more than 20%. These findings align with previous research [33], which also reported an increase in extreme winter precipitation simulated by the CPRCM. There is also a notable increase in wet-day intensity and extreme precipitation in MAM and SON, and especially in north-westernmost parts of the country in autumn, where p99 is projected to rise above 30% and in eastern parts in MAM. The RCM projections (Figure 16, Table 5) show similar trends; however, RCM underestimates all winter indices except wet-day frequency. Additionally, in autumn, RCM underestimates mean precipitation, intensity, and extreme precipitation (p99) in northwestern Bulgaria. This chapter complements and expands upon the findings of [33].
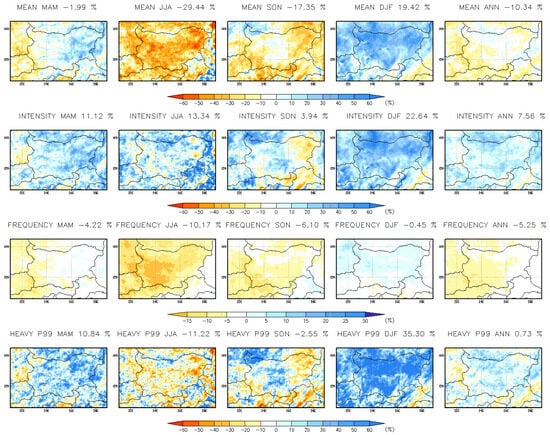
Figure 15.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in daily precipitation indices at 3 km resolution for the far-future period 2090–2099.
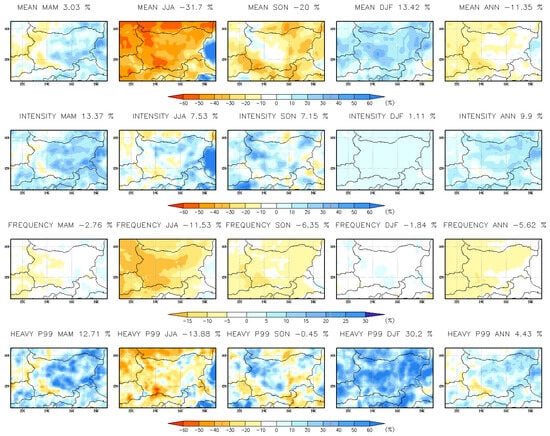
Figure 16.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in daily precipitation indices at 15 km resolution for the far-future period 2090–2099.
Figure 17 shows the daily precipitation probability density functions (PDFs) for the historical period (yellow and blue lines for CPRCM and RCM, respectively) and for the two future periods: 2041–2050 (purple and red lines for CPRCM and RCM, respectively) and 2090–2099 (pink and green lines for CPRCM and RCM, respectively). The changes in the PDFs suggest that the convection-permitting regional climate model (CPRCM) projects more frequent and intense precipitation events in both future periods.
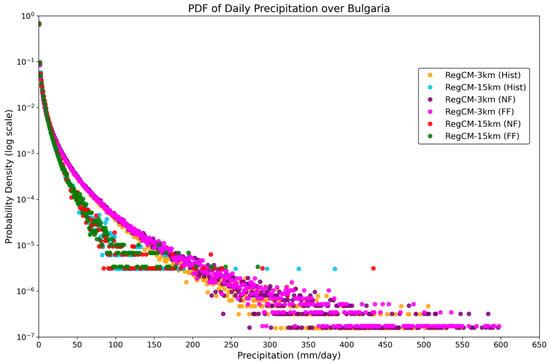
Figure 17.
Daily probability density functions (PDFs) of precipitation for the historical period (1995–2004, shown by blue and orange lines) and future periods (2041–2050 and 2090–2099).
Figure 18 presents the seasonal and annual mean changes (%) in hourly precipitation indices at a 3 km resolution for the far-future period (2090–2099). The projected annual changes in hourly precipitation indices are as follows: mean precipitation is expected to decrease by 10.28%, except in the south-easternmost and northernmost regions; wet-hour intensity is projected to increase by 4.15%; wet-hour frequency to decline by 1.62%; and heavy precipitation (p99.9) to rise by 3.17%, particularly in southern and eastern Bulgaria. In winter, all precipitation indices show an increase across Bulgaria, with mean precipitation rising by approximately 20%, heavy precipitation (p99.9) increasing by around 30%, and wet-hour intensity growing by about 18%. During autumn (SON), intensity and heavy precipitation increase by more than 30% in the northwestern and central regions, while decreases are observed in eastern Bulgaria. In spring (MAM), mean precipitation, intensity, and extreme precipitation (p99.9) increase by more than 30% all over the country. In summer (JJA), mean precipitation decreases, but wet-hour intensity rises, and heavy precipitation (p99.9) increases in some southeastern regions of Bulgaria. The area-averaged percentage changes are summarized in Table 5. The RCM simulation results (Figure 19, Table 5) show similar trends but underestimate heavy precipitation (p99.9) in spring, wet-hour intensity in summer, extreme precipitation (p99.9) in autumn over northwestern Bulgaria, and heavy precipitation in winter. Heavy precipitation intensifies at both hourly and daily timescales, confirming findings from previous studies in other European regions [22,33,50]. The differences between models stem not only from resolution but also from how deep convection processes are represented. In RCM simulation, these processes are parameterized using cumulus convection schemes, whereas in CPRCM simulations, they are explicitly resolved [7].
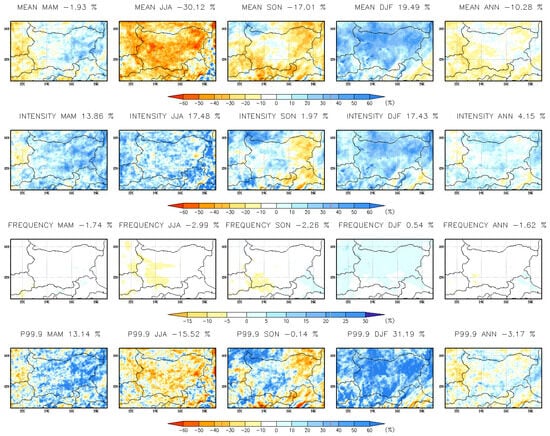
Figure 18.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in hourly precipitation indices at 3 km resolution for the far-future period 2090–2099.
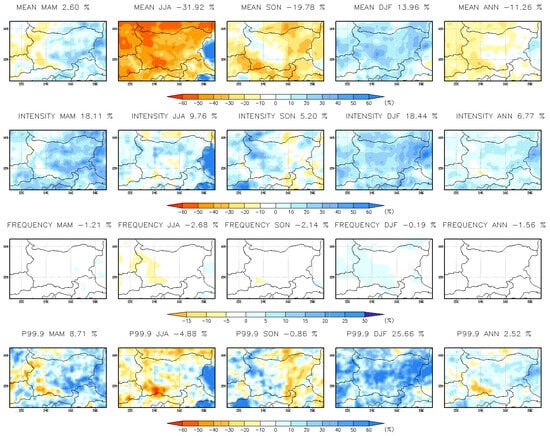
Figure 19.
Seasonal and annual mean change (%) in hourly precipitation indices at 15 km resolution for the far-future period 2090–2099.
4.3. Temperature Change
This section presents the projected changes in near-surface air temperature over Bulgaria, based on annual and seasonal averages for the near-future (2041–2050) and far-future (2090–2099) periods, relative to the historical baseline (1995–2004). The analysis includes spatial maps illustrating the geographic distribution and magnitude of temperature changes across the country. Understanding these temperature shifts is crucial for assessing broader climate change impacts, especially those affecting snow cover, growing seasons, and heat-related extremes, which depend on both long-term warming trends and seasonal variations. Figure 20 shows the seasonal and annual mean 2 m temperature changes for the period 2041–2050 using both the 3 km CPRCM and 15 km RCM, while Figure 21 presents the results for the period 2090–2099. The temperature changes are similar between the two resolutions. Area-averaged values are provided in Table 6. For the near-future period, projected temperature changes are approximately 1.6 °C in DJF, 2.2 °C in JJA, 1.9 °C in SON, 1.7 °C in DJF, and 1.9 °C annually. For the far-future period, projected changes are approximately 3.4 °C in DJF, 4.3 °C in MAM and SON, and 4.5 °C annually.
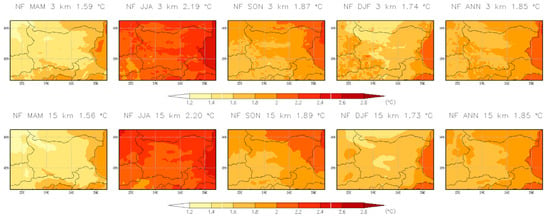
Figure 20.
Seasonal and annual mean 2 m temperature change for the period 2041–2050 with 3 km CPRCM and 15 km RCM. Units are in °C.
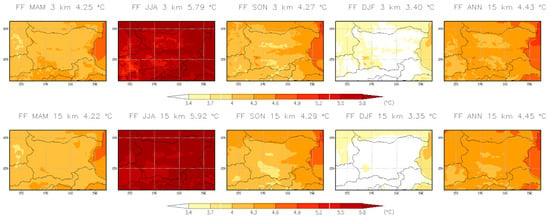
Figure 21.
Seasonal and annual mean 2 m temperature change for the period 2090–2099 with 3 km CPRCM and 15 km RCM. Units are in °C.

Table 6.
Two-meter temperature change (°C) from the 15 km RCM and 3 km CPRCM for both future periods. Units are in °C.
4.4. Surface Snow Amount Change
This section analyzes projected changes in surface snow amount over Bulgaria, focusing on the cold season months from November to April (NDJFMA). Additionally, monthly mean snow amounts for December, January, February, and March are shown to provide a detailed view of intra-seasonal variations in snowpack under warming conditions. These results are essential for understanding the future dynamics of snow accumulation and melt, which directly impact water resources, winter tourism, and ecosystem functioning in both mountainous and lowland regions.
The annual mean historical surface snow amount (kg/m2) and projected percentage changes for the near-future (2041–2050) and far-future (2090–2099) periods, considering the months November through April (NDJFMA), are presented in Figure 22. For the near-future period, an increase in surface snow is observed in the central Danubian Plain, Thracia Lowland, and parts of the Rila and Pirin mountains. However, for the far-future period, surface snow is expected to decrease significantly in lowland areas by the end of the century. Figure 23 and Table 7 display the monthly mean surface snow amounts for the historical period (first row), as well as projected changes for the near-future (2041–2050, second row) and far-future (2090–2099, third row) in December, January, February, and March. The units are in kg/m2. Overall, a decline in snow is projected across all months.
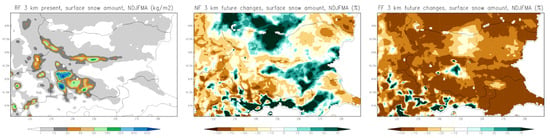
Figure 22.
Annual mean historical surface snow amount (kg/m2) and projected changes (%) for the near-future 2041–2050 and far-future 2090–2099 periods. Considering months NDJFMA (November–December–January–February–March–April).
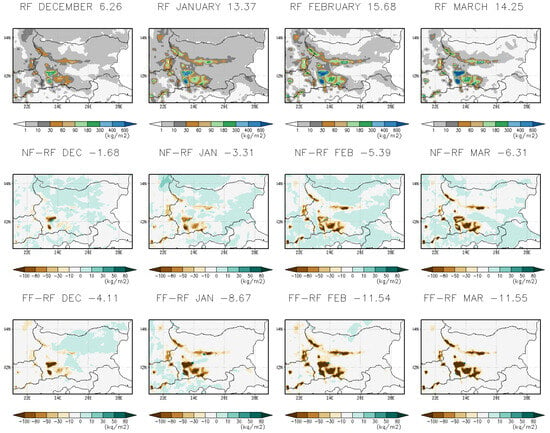
Figure 23.
Monthly mean surface snow amount for the historical period (first row) and projected changes for near-future 2041–2050 (second row) and far-future 2090–2099 (third row) in December, January, February, and March. Units are in kg/m2.

Table 7.
Monthly mean surface snow amount for the historical period (1995–2004) and future periods (2041–2050 and 2090–2099). Units: kg/m2.
5. Discussion
The results from the simulations suggest notable changes in precipitation patterns in Bulgaria, with both near- and far-future periods showing significant shifts. For the near-future (2041–2050), the projected increase in annual and seasonal precipitation across Bulgaria, particularly in the northern regions, highlights a trend of intensified precipitation events. This is especially pronounced during the winter and spring months, where mean precipitation, intensity, frequency, and heavy precipitation indices all show increases. The results are consistent with previous studies [22,33]. The most striking change is in the March–April–May (MAM) period, where heavy precipitation is expected to rise by 30% in northeastern and southeastern Bulgaria, signaling a higher risk of extreme weather events, especially in these regions. In contrast, the summer (JJA) and autumn (SON) months show a general decline in precipitation frequency, with a noticeable decrease in mean precipitation. However, extreme precipitation events (p99) are expected to intensify in both summer and autumn, particularly in the northern and coastal areas. These shifts in precipitation patterns indicate a more irregular distribution of rainfall, with increased occurrences of extreme events, such as heavy rainfall, in certain regions. The results are in line with previous works [12].
The RCMs and CPRCMs present generally consistent findings, with minor differences in projections. The CPRCM simulation predicts a stronger increase in heavy precipitation along the Black Sea coast compared to the RCM, which tends to underestimate these increases. Additionally, the RCM fails to capture the rise in extreme precipitation (p99) in northwestern Bulgaria during the autumn months, while the CPRCM shows a more accurate representation of these changes. The temperature projections for the near-future period (2041–2050) also indicate a warming trend. Both the 3 km CPRCM and 15 km RCM simulations show similar results, with temperature increases of approximately 1.6 °C in winter, 2.2 °C in summer, and 1.9 °C annually. These changes are more pronounced in the far-future (2090–2099), where temperatures are projected to rise by up to 4.5 °C annually. This warming trend is consistent across all seasons, with particularly large increases expected in the summer months (JJA). The temperature rise further supports the projections of intensified extreme weather events, including heavier precipitation and more frequent extreme events. The results are in line with previous works [4,51].
6. Conclusions
This paper presents climate simulations for three 10-year periods: historical (1995–2004), near-future (2041–2050), and far-future (2090–2099) at a convection-permitting scale (3 km) for Bulgaria. The main goal of the study is to summarize future changes in various precipitation indices under the RCP8.5 emission scenario and to examine projected changes in 2 m temperature and surface snow amount at high-resolution grid spacing. The methodology involves downscaling the global climate model HadGEM2-ES to a 15 km grid, followed by further downscaling to 3 km using a convection-permitting model. A key difference between the two models is the treatment of deep convective processes, which are explicitly resolved in the convection-permitting model (CPRCM) but parameterized using a cumulus convective scheme in the RCM.
The projected changes in precipitation in Bulgaria for the near and far future suggest a shift towards more extreme and irregular weather patterns. The near-future period (2041–2050) is expected to experience increased precipitation, particularly in the northern and coastal regions, with more frequent heavy rainfall events and a decline in summer precipitation. Temperature increases will likely exacerbate these changes, further contributing to the frequency of extreme precipitation events. Higher temperatures increase atmospheric moisture capacity, leading to more intense precipitation. Warming also shifts precipitation from snow to rain, reducing snow accumulation. These results underscore the need for adaptive strategies to manage water resources, protect infrastructure, and mitigate the impacts of extreme precipitation events, especially in vulnerable regions such as the northern and coastal areas of Bulgaria. For the near-future period, an increase in surface snow is observed in the central Danubian Plain, Thracia Lowland, and parts of the Rila and Pirin mountains. However, for the far-future period, surface snow is expected to decrease by the end of the century. The near-future increase may result from enhanced winter precipitation, while the far-future decrease is likely due to warming-induced shifts from snow to rain and faster snowmelt. Projections for the near-future period (2041–2050) suggest a moderate increase in annual precipitation (around 3%), particularly in northern Bulgaria. While mean precipitation is expected to rise in winter (DJF) and spring (MAM), it is projected to decline in summer (JJA) and autumn (SON), except for localized increases in northernmost and westernmost regions during JJA. Both precipitation intensity and extreme precipitation (p99.9) are anticipated to increase across the country, with the most pronounced changes occurring in winter and spring, where increases exceed 30%. Extreme precipitation is projected to rise by up to 20%, especially in northern Bulgaria, along the Black Sea coast, and in some southern regions. Meanwhile, precipitation frequency is expected to decline in most seasons, except in winter, suggesting a shift toward less frequent but more intense rainfall events. Comparisons with RCM simulations show generally consistent trends, though the convection-permitting model (CPRCM) indicates a stronger increase in extreme precipitation (p99.9) during winter and spring, as well as greater intensification of precipitation during summer.
The analysis of future precipitation projections at a convection-permitting scale (3 km) for Bulgaria reveals notable seasonal changes in precipitation patterns by the end of the 21st century (2090–2099). While the annual mean precipitation is expected to decline by approximately 10.28%, wet-hour intensity and extreme precipitation (p99.9) show localized increases, particularly in southern and eastern Bulgaria. Seasonal trends reveal a general increase in precipitation indices during winter and spring, with heavy precipitation rising by around 30% in both seasons. Autumn exhibits a mixed pattern, with considerable increases in intensity and extreme precipitation in northwestern and central regions, but declines in eastern Bulgaria. Summer, on the other hand, is characterized by an overall decrease in mean precipitation, though wet-hour intensity and localized heavy precipitation events increase in some southeastern areas. Comparison with RCM simulations shows that while both models exhibit similar trends, RCM tends to underestimate heavy precipitation in spring and winter, as well as wet-hour intensity in summer and autumn. This discrepancy highlights the importance of using convection-permitting models, which explicitly resolve deep convection processes rather than relying on parameterization schemes. Overall, the findings confirm that heavy precipitation will intensify at both hourly and daily timescales in the future, in line with previous studies in other European regions. These results emphasize the need for high-resolution climate modeling to capture localized precipitation extremes, which have critical implications for hydrological risks and climate adaptation strategies in Bulgaria.
One of the main drawbacks of the non-hydrostatic RegCM4-NH model is its high computational cost. The model utilizes the MM5 dynamical core, which employs a split-explicit scheme requiring short time steps to ensure stability [52]. In the future, we plan to compare the results and evaluate the performance of the latest RegCM5 model [53], maintained at ICTP, on the HPC Discoverer. This updated version is much more computationally efficient [54], operating four to five times faster than its predecessor [52,53,54].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.V. and I.P.; methodology, R.V.; software, R.V. and I.P.; validation, R.V.; formal analysis, R.V.; investigation, R.V. and I.P.; resources, R.V. and I.P.; data curation, I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, R.V.; writing—review and editing, R.V.; visualization, R.V.; project administration, R.V.; funding acquisition, R.V. and I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by the Bulgarian National Science Fund, grant number KP−06−M57/3.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
We used publicly archived high-resolution datasets available at Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS) https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-uerra-europe-single-levels?tab=download, accessed on 30 May 2023 and https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-cerra-land?tab=overview, assessed on 25 April 2025. We used publicly archived data available at https://chrsdata.eng.uci.edu/, accessed on 16 May 2023.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Discoverer PetaSC and EuroHPC JU for granting this project access to the Discoverer supercomputer resources. The authors express their gratitude to the Copernicus Climate Change Service and the Climate Data Store. We acknowledge the Center for Hydrometeorology & Remote Sensing (CHRS, https://chrs.web.uci.edu, accessed on 16 May 2023). The simulations were performed using the non-hydrostatic RegCM4-NH model. We also extend our appreciation to the Earth System Physics group at the ICTP for providing the RegCM software free of charge. Finally, we sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments, suggestions, and efforts, which have greatly contributed to improving the quality of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Giorgi, F.; Gutowski, W.J. Regional dynamical downscaling and the CORDEX initiative. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2015, 40, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Wetterhall, F.; Ireson, A.M.; Chandler, R.E.; Kendon, E.J.; Widmann, M.; Brienen, S.; Rust, H.W.; Sauter, T.; Themel, M.; et al. Precipitation downscaling under climate change: Recent developments to bridge the gap between dynamical models and the end user. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E.; Solmon, F.; Mariotti, L.; Sylla, M.B.; Bi, X.; Elguindi, N.; Diro, G.T.; Nair, V.; Giuliani, G.; et al. RegCM4: Model description and preliminary tests over multiple CORDEX domains. Clim. Res. 2012, 52, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Change 2014, 14, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, C.; Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E. Added value of regional climate modeling over areas characterized by complex terrain—Precipitation over the Alps. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 3957–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.; Schmidli, J.; Schär, C. Evaluation of the convection-resolving regional climate modeling approach in decade-long simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 7889–7907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prein, A.F.; Langhans, W.; Fosser, G.; Ferrone, A.; Ban, N.; Goergen, K.; Keller, M.; Tölle, M.; Gutjahr, O.; Feser, F.; et al. A review on regional convection-permitting climate modeling: Demonstrations, prospects, and challenges. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 323–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prein, A.F.; Liu, C.; Ikeda, K.; Trier, S.B.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Holland, G.J.; Clark, M.P. Increased rainfall volume from future convective storms in the US. Nat. Clim. Change 2017, 7, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, E.J.; Ban, N.; Roberts, N.M.; Fowler, H.J.; Roberts, M.J.; Chan, S.C.; Evans, J.P.; Fosser, G.; Wilkinson, J.M. Do convection--permitting regional climate models improve projections of future precipitation change? Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendon, E.J.; Prein, A.F.; Senior, C.A.; Stirling, A. Challenges and outlook for convection-permitting climate modelling. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2021, 379, 20190547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Sobolowski, S.; Pichelli, E.; Raffaele, F.; Ahrens, B.; Anders, I.; Ban, N.; Bastin, S.; Belda, M.; Belusic, D.; et al. A first-of-its-kind multi-model convection permitting ensemble for investigating convective phenomena over Europe and the Mediterranean. Clim. Dyn. 2020, 55, 3–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthou, S.; Kendon, E.J.; Chan, S.C.; Ban, N.; Leutwyler, D.; Schär, C.; Fosser, G. Pan-European climate at convection-permitting scale: A model intercomparison study. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 55, 35–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schär, C.; Fuhrer, O.; Arteaga, A.; Ban, N.; Charpilloz, C.; Di Girolamo, S.; Osterried, K. Kilometer-scale climate models: Prospects and challenges. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 101, E567–E587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Raffaele, F.; Giorgi, F. Impact of climate change on snow melt driven runoff timing over the Alpine region. Clim. Dyn. 2018, 51, 1259–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sante, F.; Coppola, E.; Giorgi, F. Projections of river floods in Europe using EURO--CORDEX, CMIP5 and CMIP6 simulations. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3203–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Stocchi, P.; Pichelli, E.; Torres Alavez, J.A.; Glazer, R.; Giuliani, G.; Di Sante, F.; Nogherotto, R.; Giorgi, F. Non-Hydrostatic RegCM4 (RegCM4-NH): Model description and case studies over multiple domains. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 7705–7723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Jones, C.; Asrar, G. Addressing climate information needs at the regional level: The CORDEX framework. WMO Bull. 2009, 58, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, F.; Raffaele, F.; Coppola, E. The response of precipitation characteristics to global warming from climate projections. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2019, 10, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlarski, S.; Keuler, K.; Christensen, O.B.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Gobiet, A.; Goergen, K.; Jacob, D.; Lüthi, D.; Van Meijgaard, E.; et al. Regional climate modeling on European scales: A joint standard evaluation of the EURO-CORDEX RCM ensemble. Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 1297–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Picher, P.; Brisson, E.; Caillaud, C.; Alias, A.; Nabat, P.; Lemonsu, A.; Poncet, N.; Hernandez, V.E.C.; Michau, Y.; Doury, A.; et al. Evaluation of the convection-permitting regional climate model CNRM-AROME41t1 over Northwestern Europe. Clim. Dyn. 2023, 62, 4587–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.; Caillaud, C.; Coppola, E.; Pichelli, E.; Sobolowski, S.; Adinolfi, M.; Ahrens, B.; Alias, A.; Anders, I.; Bastin, S.; et al. The first multi-model ensemble of regional climate simulations at kilometer-scale resolution part 1: Evaluation of precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichelli, E.; Coppola, E.; Sobolowski, S.; Ban, N.; Giorgi, F.; Stocchi, P.; Alias, A.; Belušić, D.; Berthou, S.; Caillaud, C.; et al. The first multi-model ensemble of regional climate simulations at kilometer-scale resolution part 2: Historical and future simulations of precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 56, 3581–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocchi, P.; Pichelli, E.; Alavez, J.A.T.; Coppola, E.; Giuliani, G.; Giorgi, F. Non-Hydrostatic Regcm4 (Regcm4-NH): Evaluation of Precipitation Statistics at the Convection-Permitting Scale over Different Domains. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Raffaele, F.; Giorgi, F.; Giuliani, G.; Xuejie, G.; Ciarlo, J.M.; Sines, T.R.; Torres-Alavez, J.A.; Das, S.; di Sante, F.; et al. Climate hazard indices projections based on CORDEX-CORE, CMIP5 and CMIP6 ensemble. Clim. Dyn. 2021, 57, 1293–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estermann, R.; Rajczak, J.; Velasquez, P.; Lorenz, R.; Schär, C. Projections of heavy precipitation characteristics over the Greater Alpine Region using a kilometer–scale climate model ensemble. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2025, 130, e2024JD040901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosser, G.; Gaetani, M.; Kendon, E.J.; Adinolfi, M.; Ban, N.; Belušić, D.; Caillaud, C.; Careto, J.A.M.; Coppola, E.; Demory, M.-E.; et al. Convection–permitting climate models offer more certain extreme rainfall projections. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosser, G.; Kendon, E.J.; Stephenson, D.; Tucker, S. Convection–permitting models offer promise of more certain extreme rainfall projections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosser, G.; Khodayar, S.; Berg, P. Benefit of convection permitting climate model simulations in the representation of convective precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcheva, R.; Popov, I.; Gerganov, N. Convection-Permitting Regional Climate Simulation over Bulgaria: Assessment of Precipitation Statistics. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcheva, R.; Popov, I.; Gerganov, N. Assessment of precipitation statistics with non-hydrostatic regional climate model RegCM4.7.1 at regional and convection-permitting scale over Bulgaria. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly 2023, Vienna, Austria, 24–28 April 2023. EGU23-9768. [Google Scholar]
- Valcheva, R.; Popov, I.; Gerganov, N. A Sensitivity Study of the Non-Hydrostatic Regional Climate Model REGCM-4.7.1 to Physical Parametrization Schemes over the Balkan Peninsula and Bulgaria. SGEM 2022, 22, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Valcheva, R.; Peneva, E. Sensitivity to the parametrization of cumulus convection in the RegCM4.3 simulations focused on Balkan Peninsula and Bulgaria. Annu. Sofia Univ. “St. Kliment Ohridski” Fac. Phys. 2014, 107, 113–131. [Google Scholar]
- Valcheva, R.; Popov, I.; Gerganov, N. Convection-Permitting Future Climate Simulations for Bulgaria under the RCP8.5 Scenario. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcheva, R.; Spiridonov, V. Regional climate projections of heavy precipitation over the Balkan Peninsula. IDŐJÁRÁS 2023, 127, 77–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcheva, R. Climate Change Projections According to RCP45 Scenario until 2099 for Bulgaria. In Air Pollution Modeling and its Application XXVII 27; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume XXVII, pp. 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Valcheva, R.; Spiridonov, V. Climate change projections of infrastructure-hazardous phenomena (heavy rainfall and wind) in Bulgaria. Bulg. J. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2021, 25, 24–44. [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson, R.E.; Errico, R.M.; Giorgi, F.; Bates, G.T. A regional climate model for the western United States. Clim. Change 1989, 15, 383–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Bates, G.T. The climatological skill of a regional model over complex terrain. Mon. Weather Rev. 1989, 117, 2325–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Marinucci, M.R.; Bates, G.T. Development of a second generation regional climate model (RegCM2). Part I: Boundary layer and radiative transfer processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2794–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Marinucci, M.R.; Bates, G.T.; De Canio, G. Development of a second-generation regional climate model (RegCM2). Part II: Convective processes and assimilation of lateral boundary conditions. Mon. Weather Rev. 1993, 121, 2814–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Mearns, L.O. Introduction to special section: Regional climate modeling revisited. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 6335–6352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, J.S.; Giorgi, F.; Bi, X.; Elguindi, N.; Solmon, F.; Gao, X.; Ashfaq, M.; Francisco, R.; Bell, J.; Diffenbaugh, N.; et al. The ICTP RegCM3 and RegCNET: Regional climate modeling for the developing World. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 1395–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, W.J.; Bellouin, N.; Doutriaux-Boucher, M.; Gedney, N.; Halloran, P.; Hinton, T.; Hughes, J.; Jones, C.D.; Joshi, M.; Liddicoat, S.; et al. Development and evaluation of an Earth-System model—HadGEM2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2011, 4, 1051–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.H.; Edmonds, J.A.; Hibbard, K.A.; Manning, M.R.; Rose, S.K.; Van Vuuren, D.P.; Carter, T.R.; Emori, S.; Kainuma, M.; Kram, T.; et al. The next generation of scenarios for climate change research and assessment. Nature 2010, 463, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulzweida, U. CDO User Guide (2.1.0); Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Climate Change Service, Climate Data Store. UERRA Regional Reanalysis for Europe on Single Levels from 1961 to 2019. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). Climate Data Store (CDS). 2019. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-uerra-europe-single-levels?tab=overview (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Verrelle, A.; Glinton, M.; Bazile, E.; Le Moigne, P.; Randriamampianina, R.; Ridal, M.; Berggren, L.; Undén, P.; Schimanke, S.; Mladek, R.; et al. CERRA-Land Sub-Daily Regional Reanalysis Data for Europe from 1984 to Present. Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). Climate Data Store (CDS). 2022. Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/datasets/reanalysis-cerra-land?tab=overview (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Nguyen, P.; Ombadi, M.; Gorooh, V.A.; Shearer, E.J.; Sadeghi, M.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; Bolvin, D.; Ralph, M.F. PERSIANN Dynamic Infrared-Rain Rate (PDIR-Now): A Near-real time, Quasi-Global Satellite Precipitation Dataset. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 2893–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schär, C.; Ban, N.; Fischer, E.M.; Rajczak, J.; Schmidli, J.; Frei, C.; Giorgi, F.; Karl, T.R.; Kendon, E.J.; Tank, A.M.K.; et al. Percentile indices for assessing changes in heavy precipitation events. Clim. Change 2016, 137, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinolfi, M.; Raffa, M.; Reder, A.; Mercogliano, P. Evaluation and Expected Changes of Summer Precipitation at Convection Permitting Scale with COSMO-CLM over Alpine Space. Atmosphere 2020, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, N.; Schmidli, J.; Schär, C. Heavy precipitation in a changing climate: Does short-term summer precipitatio increase faster? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, E.; Giorgi, F.; Giuliani, G.; Pichelli, E.; Ciarlo, J.M.; Raffaele, F.; Nogherotto, R.; Reboita, M.S.; Lu, C.; Zazulie, N.; et al. The Fifth Generation Regional Climate Modeling System, RegCM5: The first CP European wide simulation and validation over the CORDEX-CORE domains. Preprint 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Coppola, E.; Giuliani, G.; Ciarlò, J.M.; Pichelli, E.; Nogherotto, R.; Raffaele, F.; Malguzzi, P.; Davolio, S.; Stocchi, P.; et al. The fifth generation regional climate modeling system, RegCM5: Description and illustrative examples at parameterized convection and convection-permitting resolutions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2023, 128, e2022JD038199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, C.Z.; Giorgi, F. Convection Permitting Regional Climate Modelling Over the Carpathian Region. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 9, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).