Spatial Variability and Time Stability of Throughfall in a Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest in Jinyun Mountain, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
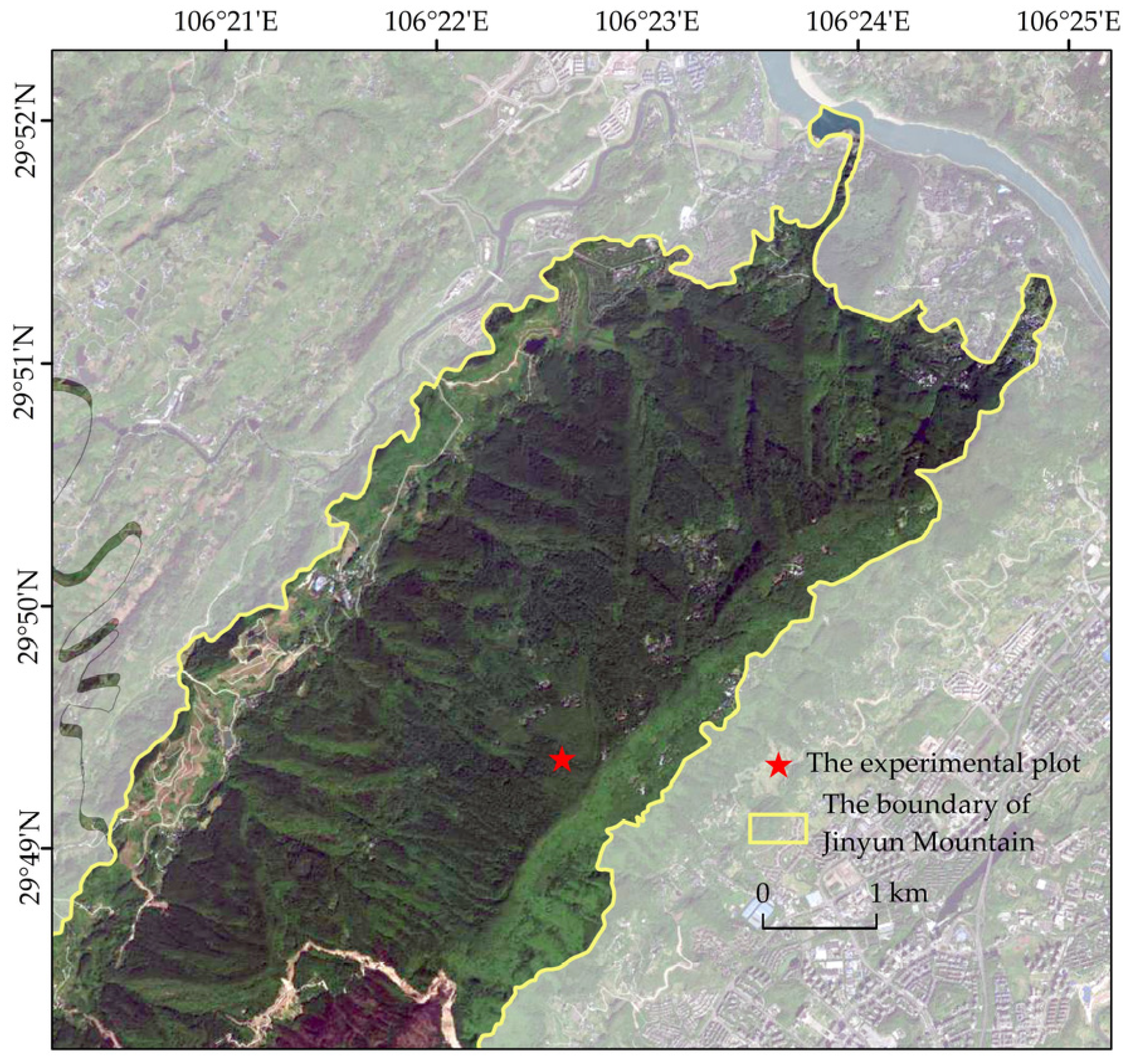
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Rainfall and Throughfall Measurement
2.3. Stand Structure Index Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.4.1. Spatial Variability of Throughfall Analysis
2.4.2. Temporal Stability of Throughfall Analysis
3. Results
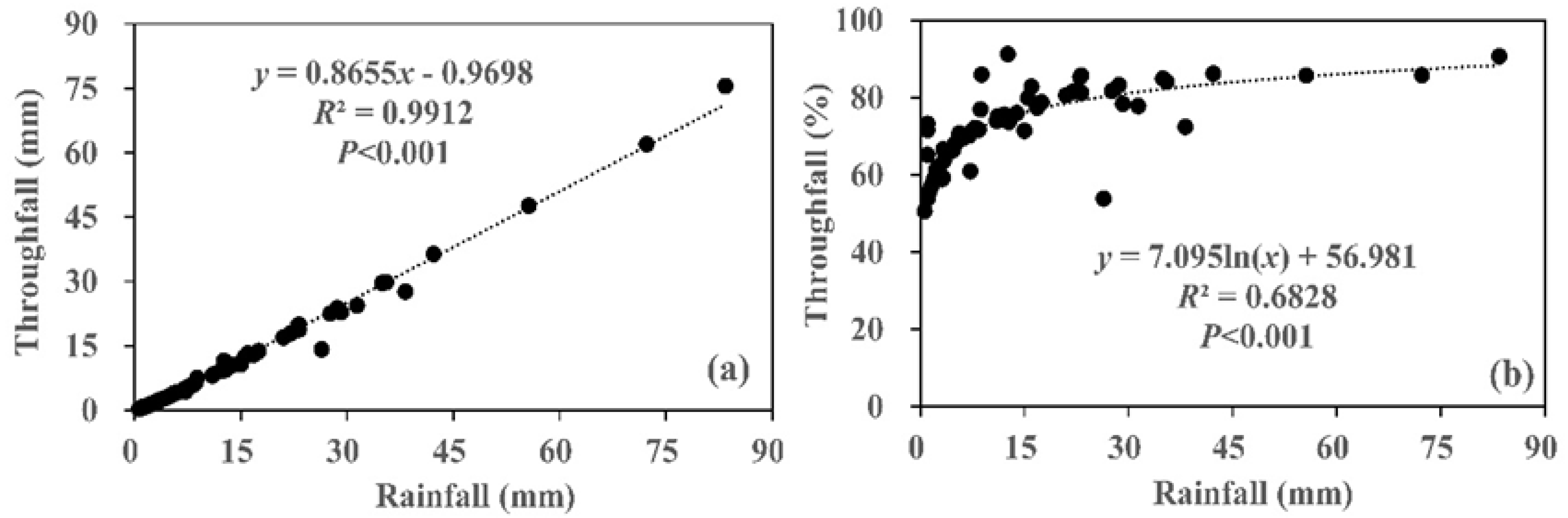
3.1. Characteristics of Rainfall and Throughfall During the Experimental Periods
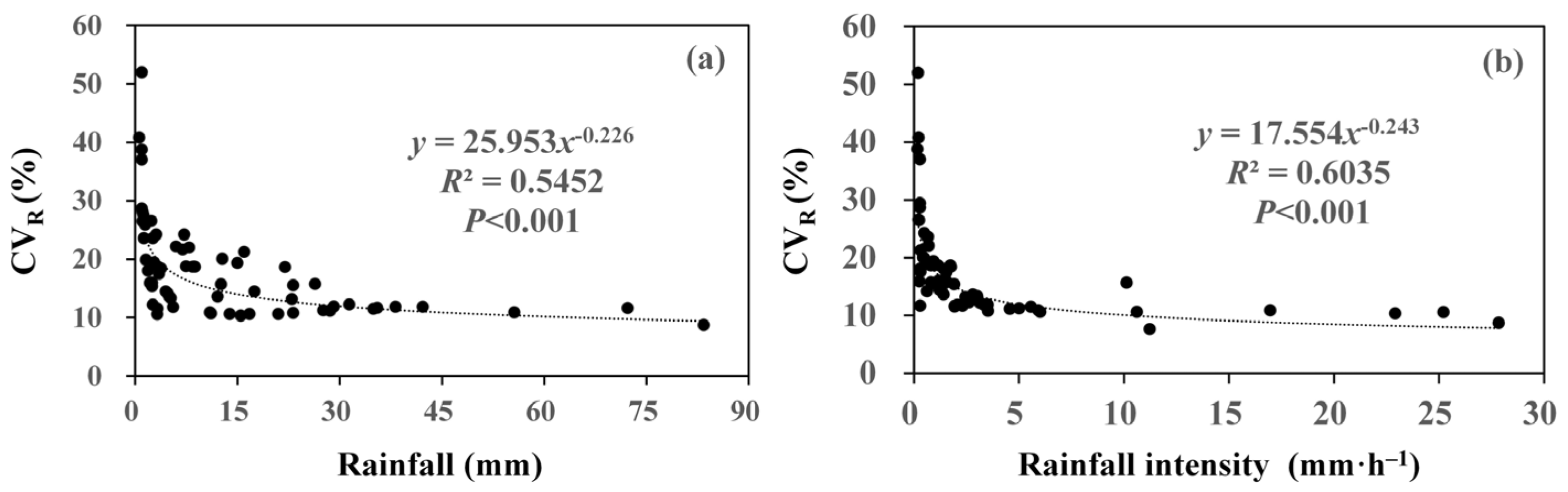
3.2. Spatial Variability of Throughfall in Relationship to Rainfall Characteristics
3.3. Spatial Variability of Throughfall in Relationship to Canopy Cover
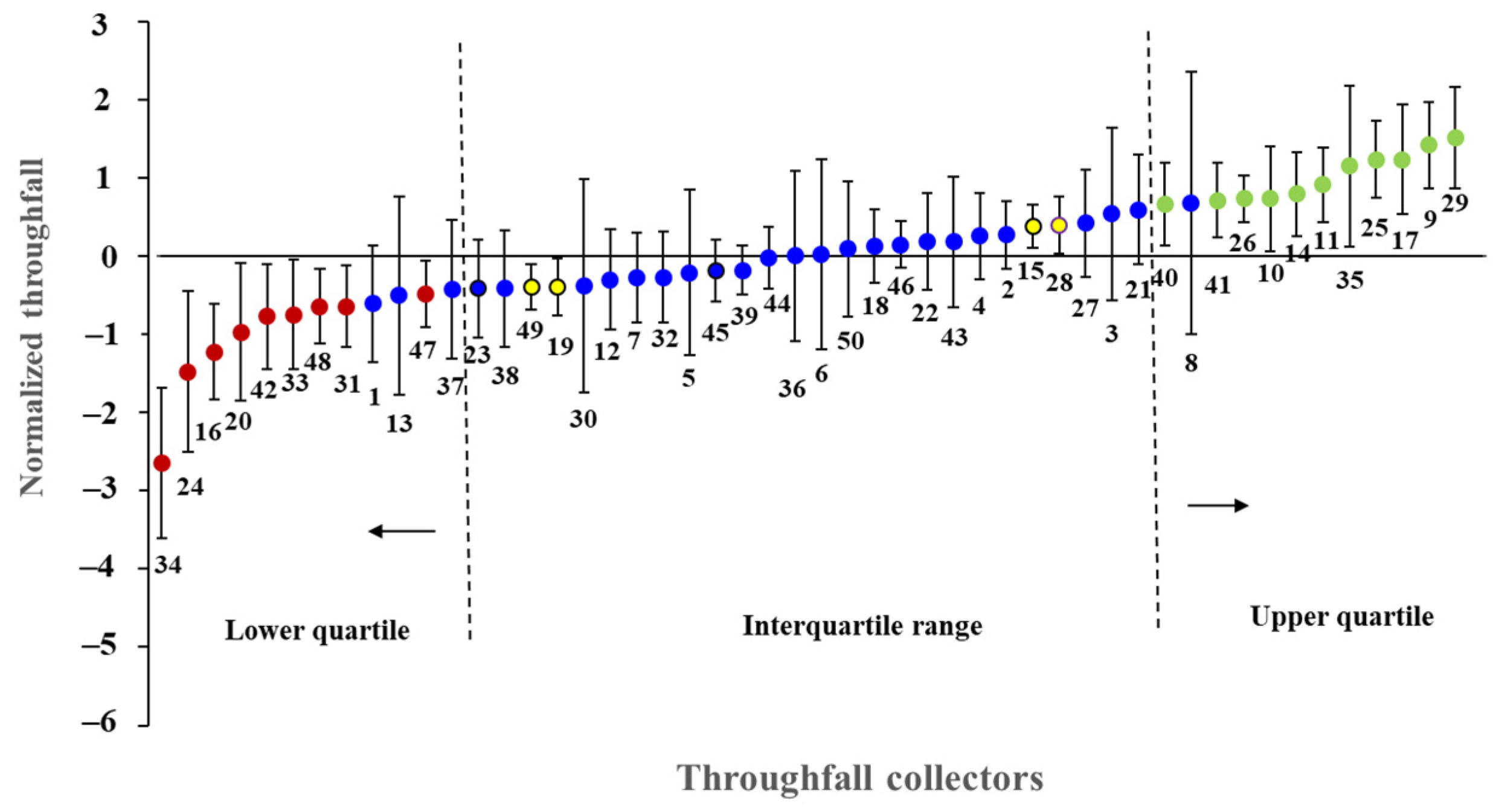
3.4. Characteristics of the Temporal Stability of Throughfall
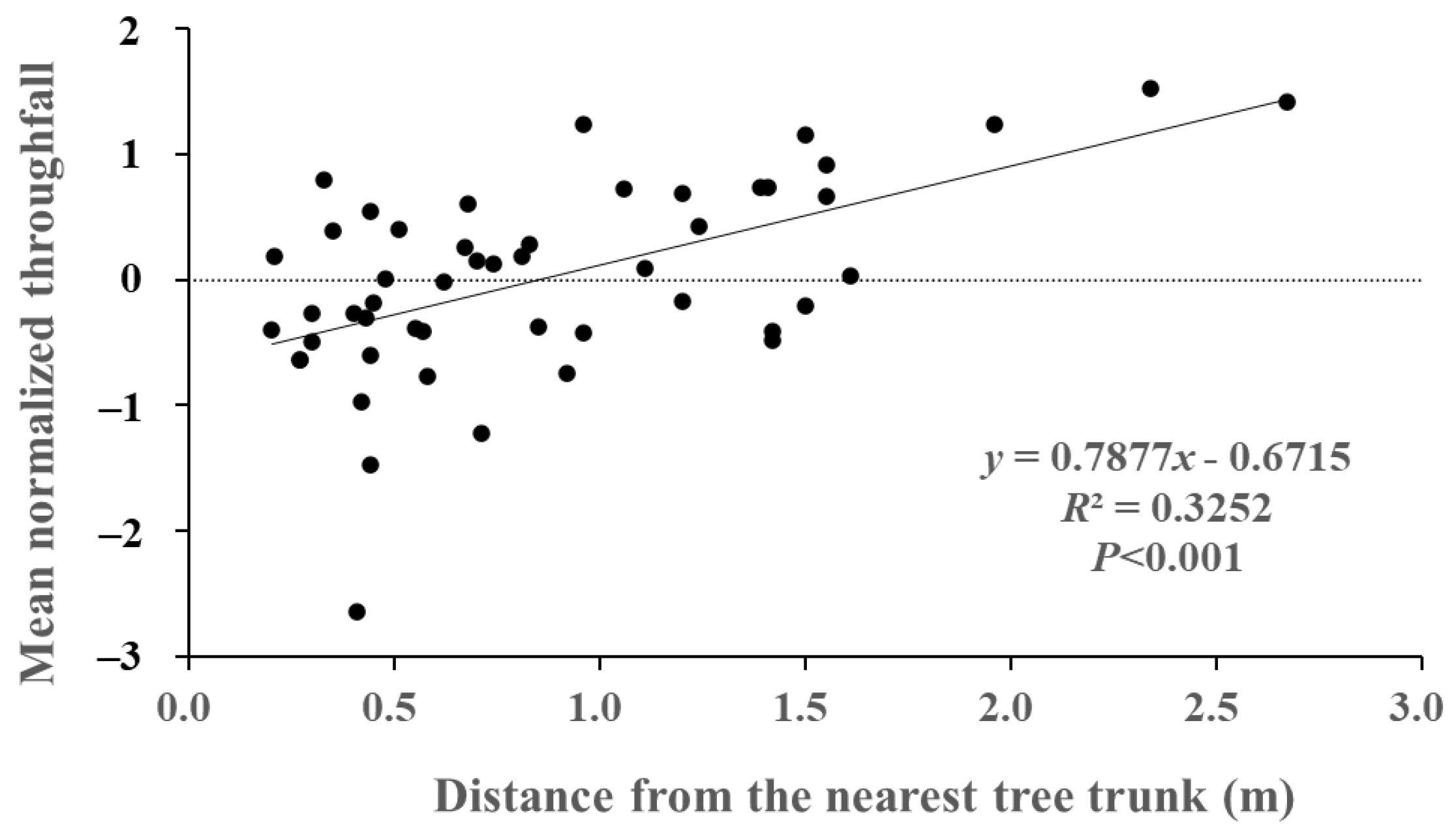
3.5. Spatial Variability of Throughfall in Relationship to the Distance from the Nearest Trunk
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Throughfall Amount and Its Spatial Variability
4.2. Controls of Spatial Throughfall Variability
4.3. Temporal Stability of Throughfall
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dunkerley, D. Measuring interception loss and canopy storage in dryland vegetation: A briefer view and evaluation of available research strategies. Hydrol. Process 2000, 14, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens, P.; Domingo, F. Rainfall partitioning by vegetation under Mediterranean conditions. A review of studies in Europe. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, X.P.; Hu, R.; Pan, Y.X.; Paradeloc, M. Rainfall partitioning into throughfall, stemflow and interception loss by two xerophytic shrubs within a rain-fed re-vegetated desert ecosystem, northwestern China. J. Hydrol. 2015, 527, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-S.; Yu, J.; Kun, H.; Jin, M. Impacts of Chinese Pine (Pinus Tabulae formis) plantations on rainfall redistribution processes: A case study for the mountainous area of North China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Janeau, J.L.; Grellier, S.; Podwojewski, P. Influence of rainfall interception by endemic plants versus short cycle crops on water infiltration in high altitude ecosystems of Ecuador. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, B.E.; Slatton, K.C.; Cohen, M.J. On the potential for high-resolution lidar to improve rainfall interception estimates in forest ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiko, C.T.; Makurira, H.; Gerrits, A.J.; Savenije, H.G. Measuring forest floor and canopy interception in a savannah ecosystem. Phys. Chem. Earth 2012, 47–48, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staelens, J.; De Schrijver, A.; Verheyen, K.; Verhoest, N.E. Spatial variability and temporal stability of throughfall water under a dominant beech ((Fagus sylvatica L.)) tree in relationship to canopy cover. J. Hydrol. 2006, 330, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Zimmermann, B.; Elsenbeer, H. Rainfall redistribution in a tropical forest: Spatial and temporal patterns. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, W11413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Zimmermann, B. Requirements for throughfall monitoring: The roles of temporal scale and canopy complexity. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2014, 189–190, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.T.; Wang, X.X.; Jiang, Y.; You, W. Spatial variations of throughfall through secondary succession of evergreen broad-leaved forests in eastern China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, H.; Cai, T. Spatial Variability of Throughfall in a Larch (Larix gmelinii) Forest in Great Kingan Mountain, Northeastern China. Forests 2021, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.X.; Wu, H.W.; Li, J.; He, B.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, N.; Duan, W.L.; Liao, A.M. Spatial-temporal variability of throughfall in a subtropical deciduous forest from the hilly regions of eastern China. J. Mt. Sci. 2019, 16, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, J.; Hölscher, D.; Leuschner, C.; Hendrayanto. Rainfall partitioning in relation to forest structure in differently managed montane forest stands in central sulawesi, indonesia. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 237, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teale, N.G.; Mahan, H.; Bleakney, S.; Berger, A.; Shibley, N.; Frauenfeld, O.W.; Quiring, S.M.; Rapp, A.D.; Roark, E.B.; Washington-Allen, R. Impacts of Vegetation and Precipitation on Throughfall Heterogeneity in a Tropical Pre-Montane Transitional Cloud Forest. Biotropica 2014, 46, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, X.P.; Hu, R. Throughfall and its spatial variability beneath xerophytic shrub canopies within water-limited arid desert ecosystems. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Zheng, H.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Su, Y. The spatial distribution characteristics of throughfall under Abies faxoniana forest in the Wolong Nature Reserve. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2004, 24, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Xiong, W.; Yu, P.T. The spatial heterogeneity of throughfall under the Larix principis-rupprechtii single tree’ s canopy. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Jian, S.Q. Spatial variability of throughfall in a Pinus tabulaeformis plantation forest in Loess Plateau, China. Scand. J. For. Res. 2016, 31, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, A.; Boczon’, A.; Hildebrand, R.; Polkowska, Ż. Spatial variability of throughfall in a stand of scots pine (pinus sylvestris L.) with deciduous admixture as influenced by canopy cover and stem distance. J. Hydrol. 2016, 538, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Onda, Y.; Chiara, S.; Kato, H.; Gomi, T. The effect of strip thinning on spatial and temporal variability of throughfall in a Japanese cypress plantation. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 5058–5070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, R.F.; Skaugset, A.E.; Weiler, M. Temporal persistence of spatial patterns in throughfall. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirlewagen, D.; von Wilpert, K. Modeling water and ion fluxes in a highly structured, mixed-species stand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2001, 143, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezhban, A.; Attarod, P.; Amiri, G.Z.; Pypker, T.G.; Nanko, K. Spatial and temporal variability of throughfall under a natural Fagusorientalis stand in the Hyrcanian forests, north of Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 1843–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Wullaert, H.; Pohlert, T.; Boy, J.; Valarezo, C.; Wilcke, W. Spatial throughfall heterogeneity in a montane rain forest in Ecuador: Extent, temporal stability and drivers. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germer, S.; Elsenbeer, H.; Moraes, J.M. Throughfall and temporal trends of rainfall redistribution in an open tropical rainforest, south-western Amazonia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 10, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Fu, M.; Xie, J.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. Ecological functions of bamboo forest: Research and Application. J. For. Res. 2005, 16, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.L.; Du, H.Q.; Han, N.; Xu, X. Mapping of Moso Bamboo Forest Using Object-Based Approach Based on the Optimal Features. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2016, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Booth, T.; He, X. Changes of carbon stocks in bamboo stands in China during 100 years. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Wilcke, W.; Elsenbeer, H. Spatial and temporal patterns of throughfall quantity and quality in a tropical montane forest in ecuador. J. Hydrol. 2007, 343, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hou, E.K.; Deng, J.w. Spatio-temporal differentiation characteristic and evolution process of meteorological drought in Northwest China from 1960 to 2018. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 857953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, A.; Germer, S.; Neill, C.; Krusche, A.V.; Elsenbeer, H. Spatio-temporal patterns of throughfall and solute deposition in an open tropical rain forest. J. Hydrol. 2008, 360, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, Q.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Hu, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; Cai, Z.Y. Global quantification of the spatial variability and temporal stability of throughfall. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Hu, H. Eco-hydrological Effects of Secondary Bamboo Forest (Phyllost achys edulis) Canopy and Its Influence Factors in North Subtropics. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 29, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Liu, N.; Liu, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, L. Simulation of Canopy Rainfall Interception of the Phyllostachys edulis Forest with the Revised Gash Model in the Jinyun Mountains of Chongqing. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2011, 47, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, Y. Hydrological Characteristics of the Canopy of Phyllostachy edulis Forest in Hilly Arears of Southern Jiangsu Province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Li, W.X.; Jiang, X.; Wu, J. Effects of rainfall on the spatial distribution of the throughfall kinetic energy on a small scale in a rubber plantation. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2018, 63, 1078–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegert, C.M.; Levia, D.F.; Hudson, S.A.; Dowtin, A.L.; Zhang, F.; Mitchell, M.J. Small-scale topographic variability influences tree species distribution and canopy throughfall partitioning in a temperate deciduous forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 359, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levia, D.F.; Frost, E.E. Variability of throughfall volume and solute inputs in wooded ecosytems. Progress. Phys. Geogr. 2006, 30, 605–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Xie, Z.Q.; Xu, W.T.; Zhao, C. Variability of throughfall quantity in a mixed evergreen-deciduous broadleaved forest in central China. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2019, 67, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyle-Moses, D.E.; Laureano, J.F.; Price, A. Throughfall and throughfall spatial variability in Madrean oak forest communities of northeastern Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2004, 297, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Q.; Liu, W.J.; Li, W.X.; Zeng, H. How does a rubber plantation affect the spatial variability and temporal stability of throughfall? Hydrol. Res. 2019, 50, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlyle-Moses, D.E.; Lishman, C.E. Temporal persistence of throughfall heterogeneity below and between the canopies of juvenile lodgepole pine (Pinus contorta). Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 4051–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Oestergaard, K.T.; Guyot, A.; Jensen, D.G.; Lockington, D.A. Spatial variability of throughfall and stemflow in an exotic pine plantation of subtropical coastal Australia. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.; Allen, S.T.; Keim, R.F. Fine-scale spatial variability of throughfall amount and isotopic composition under a hardwood forest canopy. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levia, D.F.; Keim, R.F.; Carlyle-Moses, D.E.; Frost, E.E. Throughfall and stemflow in wooded ecosystems. In Forest Hydrology and Biogeochemistry; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 425–443. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguer, A.F.; Terra, M.S.; Mantovani, V.A.; Cordeiro, N.G.; Ribeiro, J.P.; Guo, L.; Nehren, U.; Mello, J.M.; Mello, C.R. Throughfall spatial variability in a neotropical forest: Have we correctly accounted for time stability? J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanko, K.; Watanabe, A.; Hotta, N.; Suzuki, M. Physical interpretation of the difference in drop size distributions of leaf drips among tree species. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Age of Trees (Year) | Stand Density (n·ha−1) | DBH 1 (cm) | Height (m) | LAI (m2·m−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 4800 | 10.14 ± 1.62 | 14.4 ± 1.75 | 5.25 ± 1.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zong, Q.; Jin, K.; Qin, P.; Zhu, X.; Han, Y. Spatial Variability and Time Stability of Throughfall in a Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest in Jinyun Mountain, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070787
Liu C, Wang Y, Zong Q, Jin K, Qin P, Zhu X, Han Y. Spatial Variability and Time Stability of Throughfall in a Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest in Jinyun Mountain, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):787. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070787
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunxia, Yunqi Wang, Quanli Zong, Kai Jin, Peng Qin, Xiuzhi Zhu, and Yujie Han. 2025. "Spatial Variability and Time Stability of Throughfall in a Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest in Jinyun Mountain, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070787
APA StyleLiu, C., Wang, Y., Zong, Q., Jin, K., Qin, P., Zhu, X., & Han, Y. (2025). Spatial Variability and Time Stability of Throughfall in a Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) Forest in Jinyun Mountain, China. Atmosphere, 16(7), 787. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070787





