Wind Speed Forecasting in the Greek Seas Using Hybrid Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
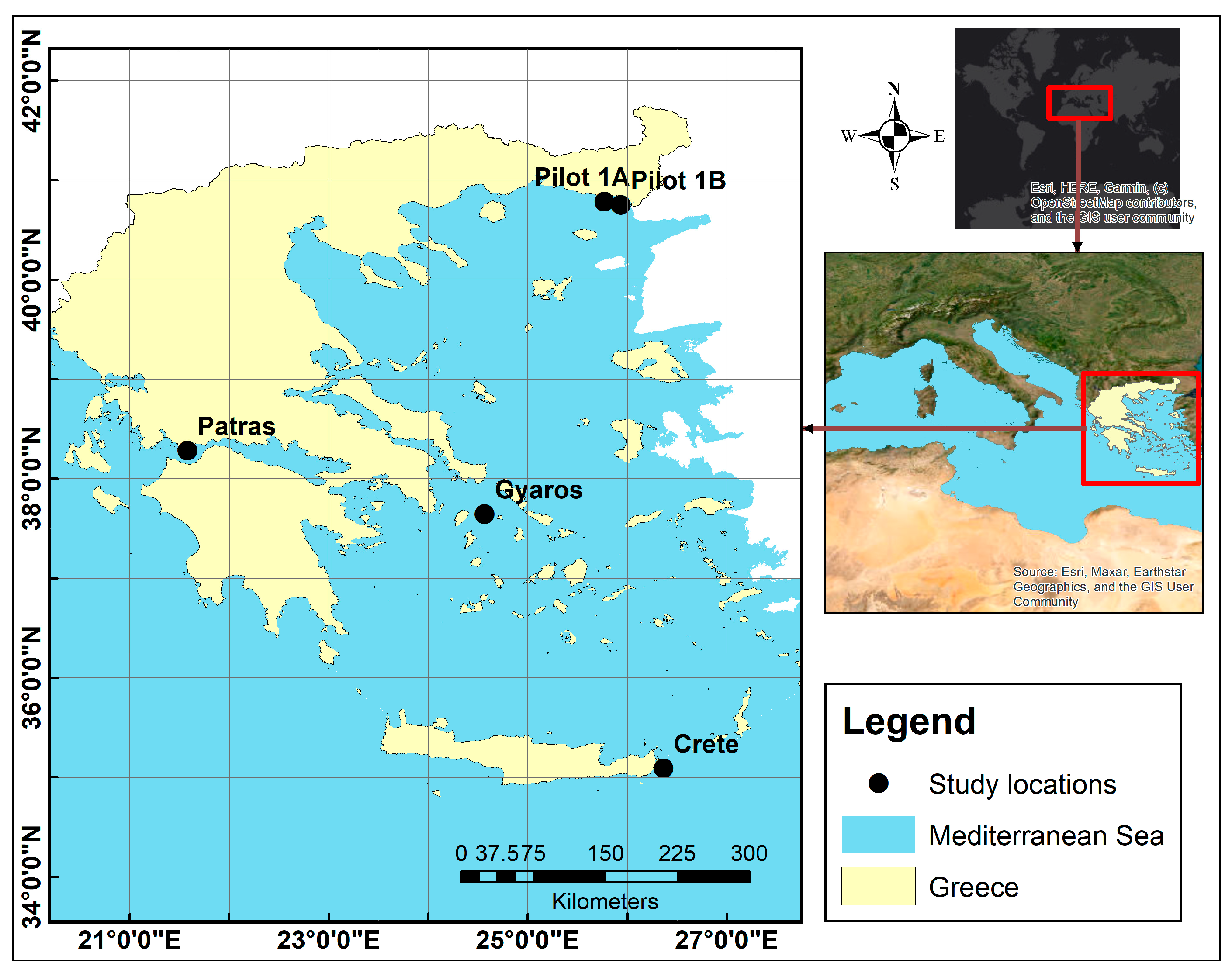
2.1. Study Area and Data Source
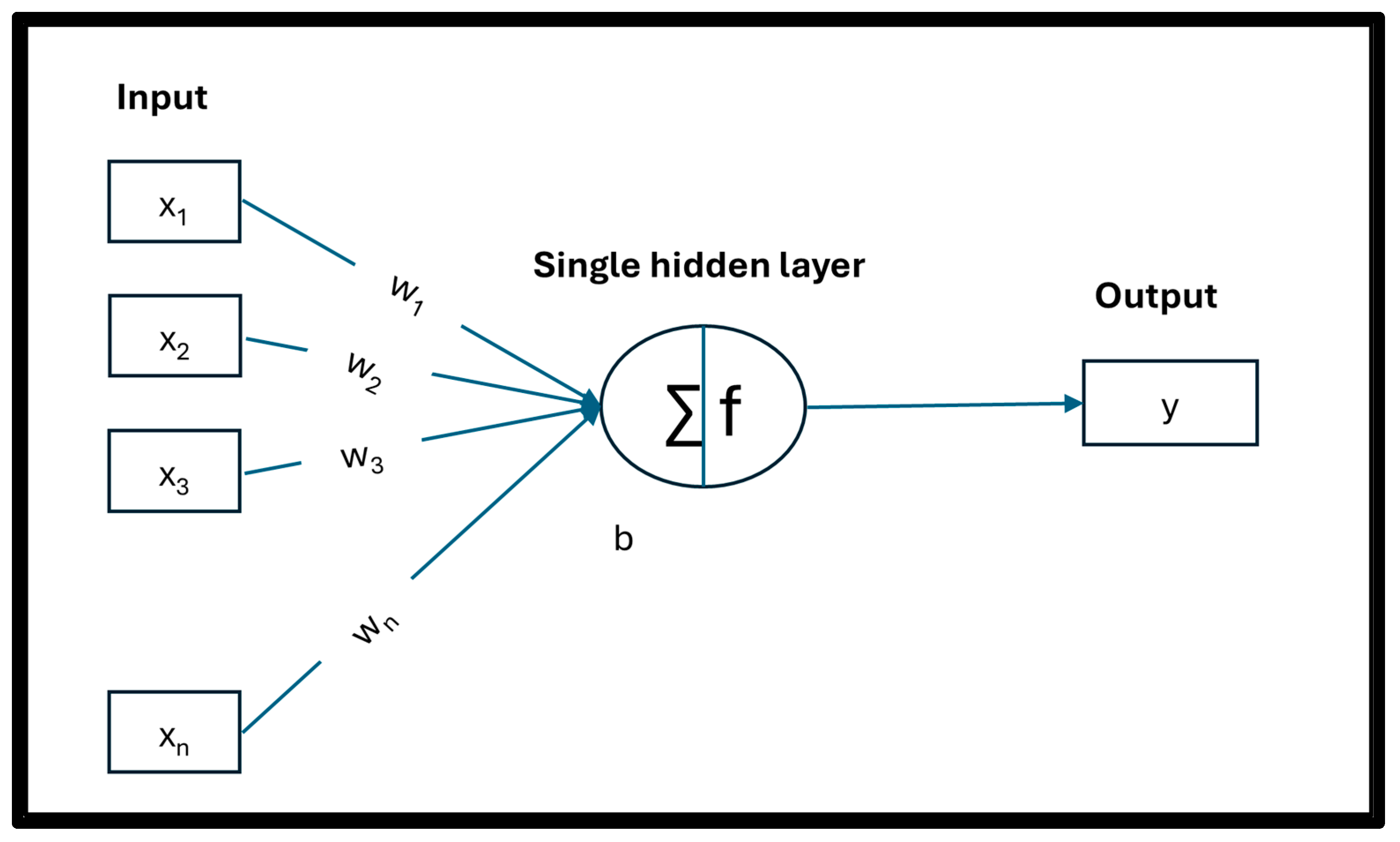
2.2. Feedforward Neural Network
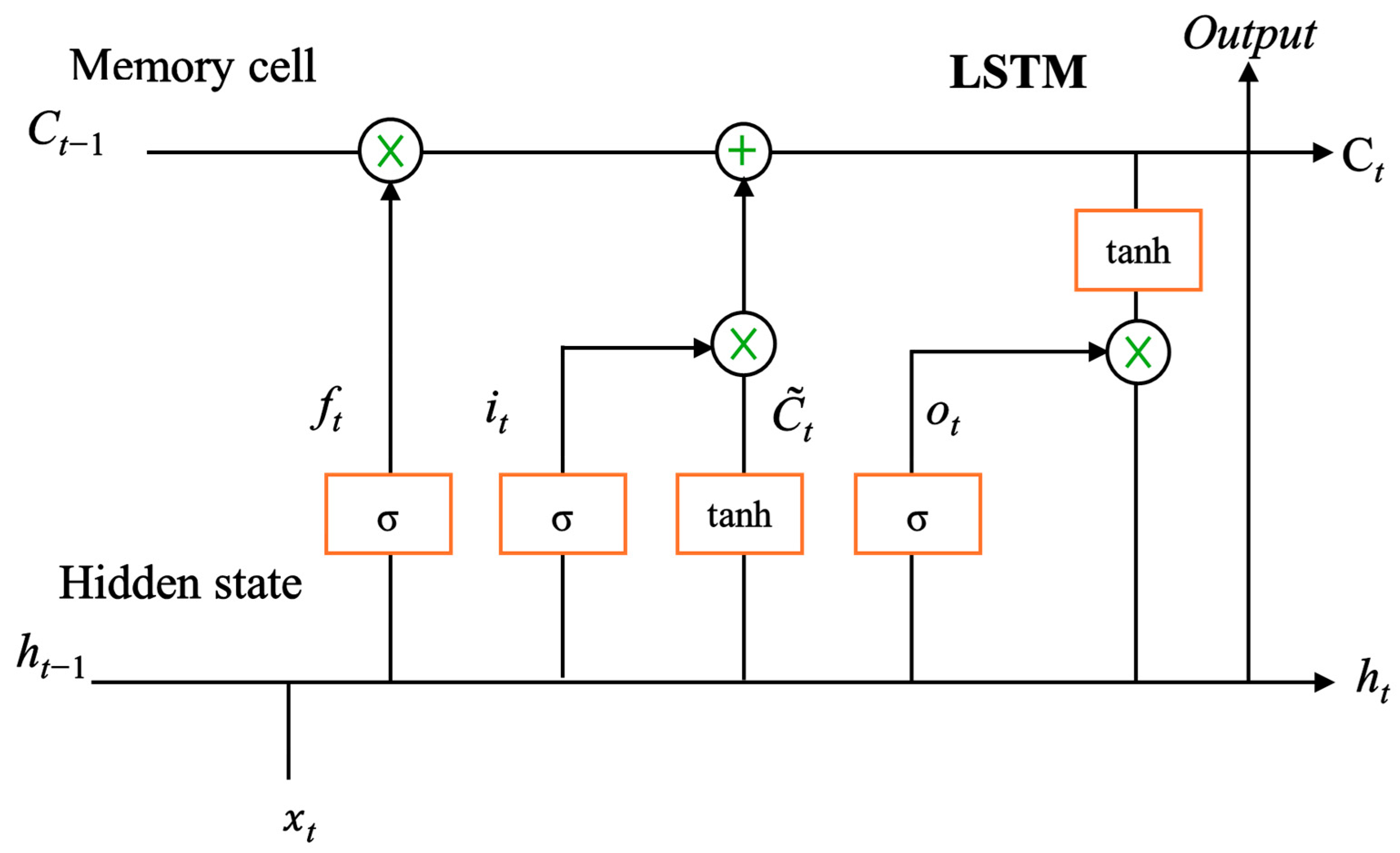
2.3. Long Short-Term Memory Network
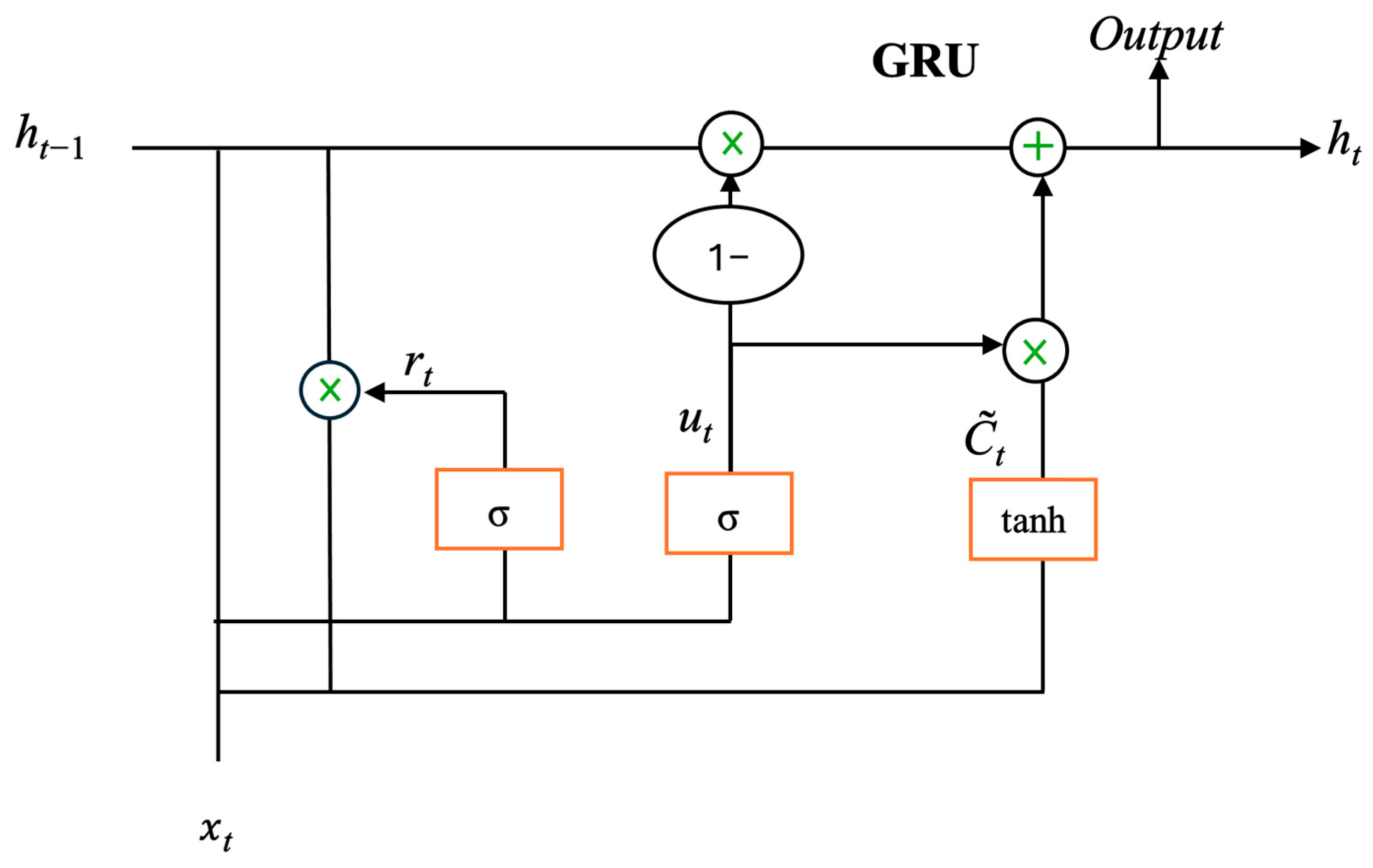
2.4. Gated Recurrent Unit Network
2.5. Experimental Approach
2.6. Network Performance
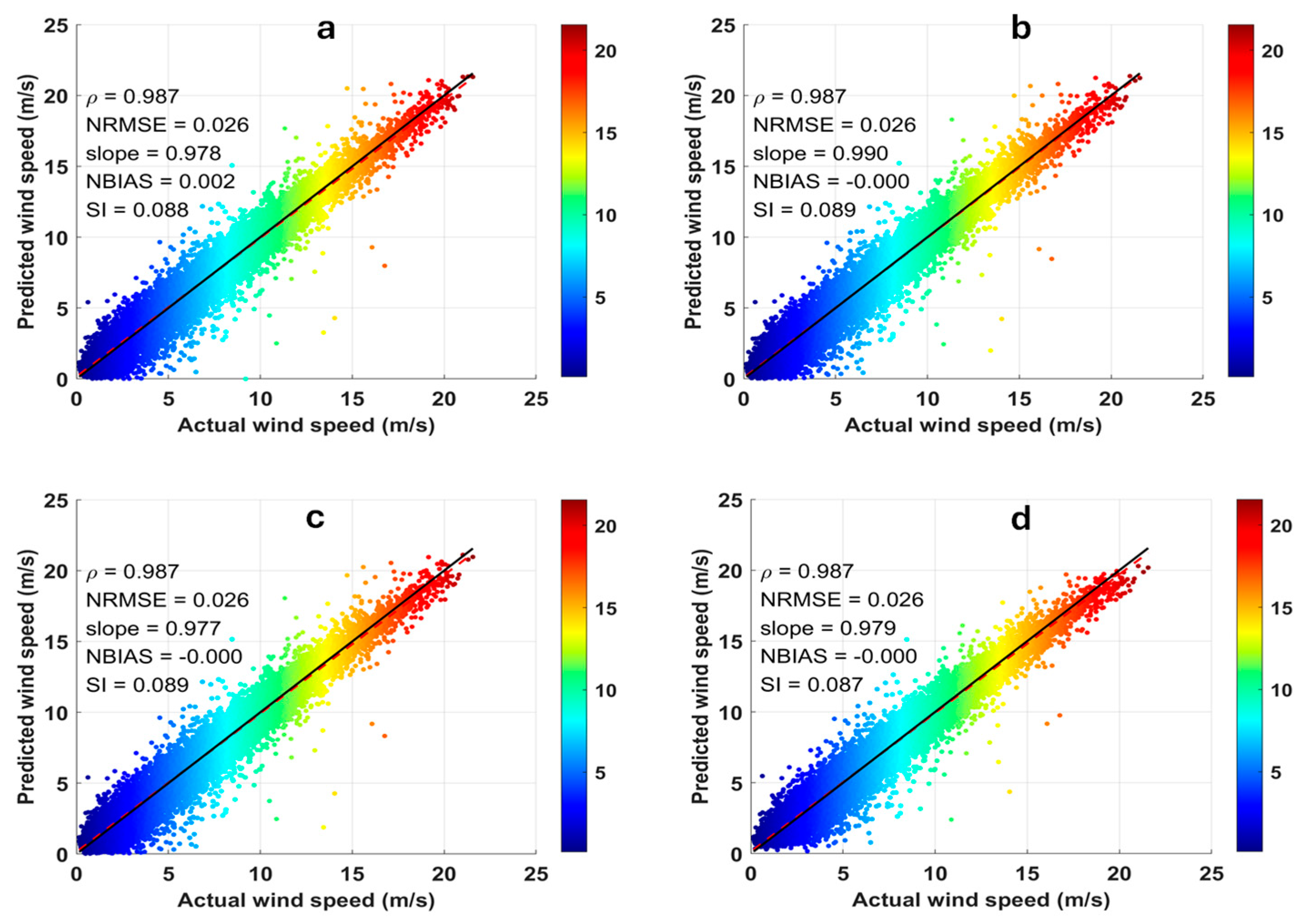
3. Results and Discussion
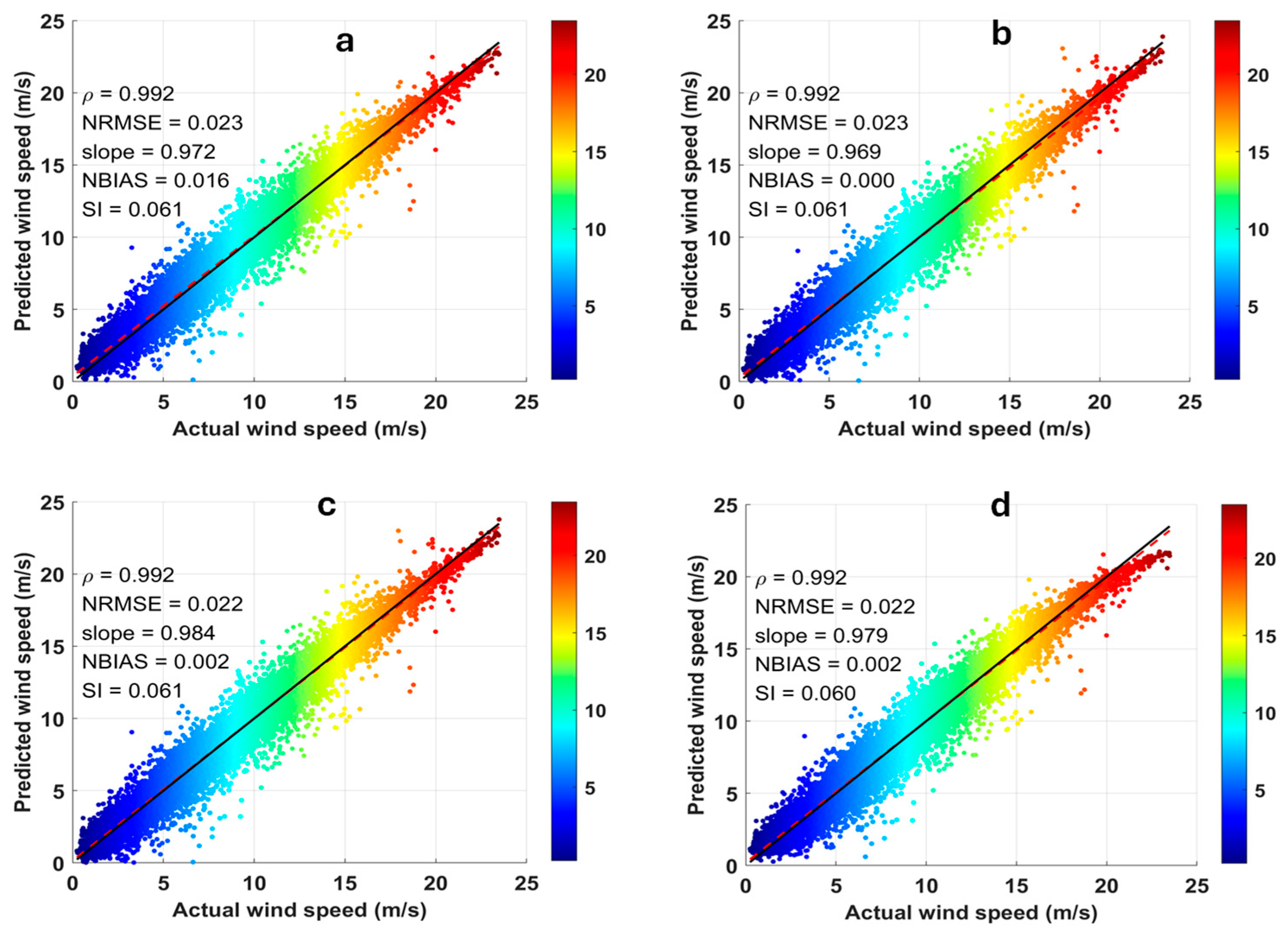
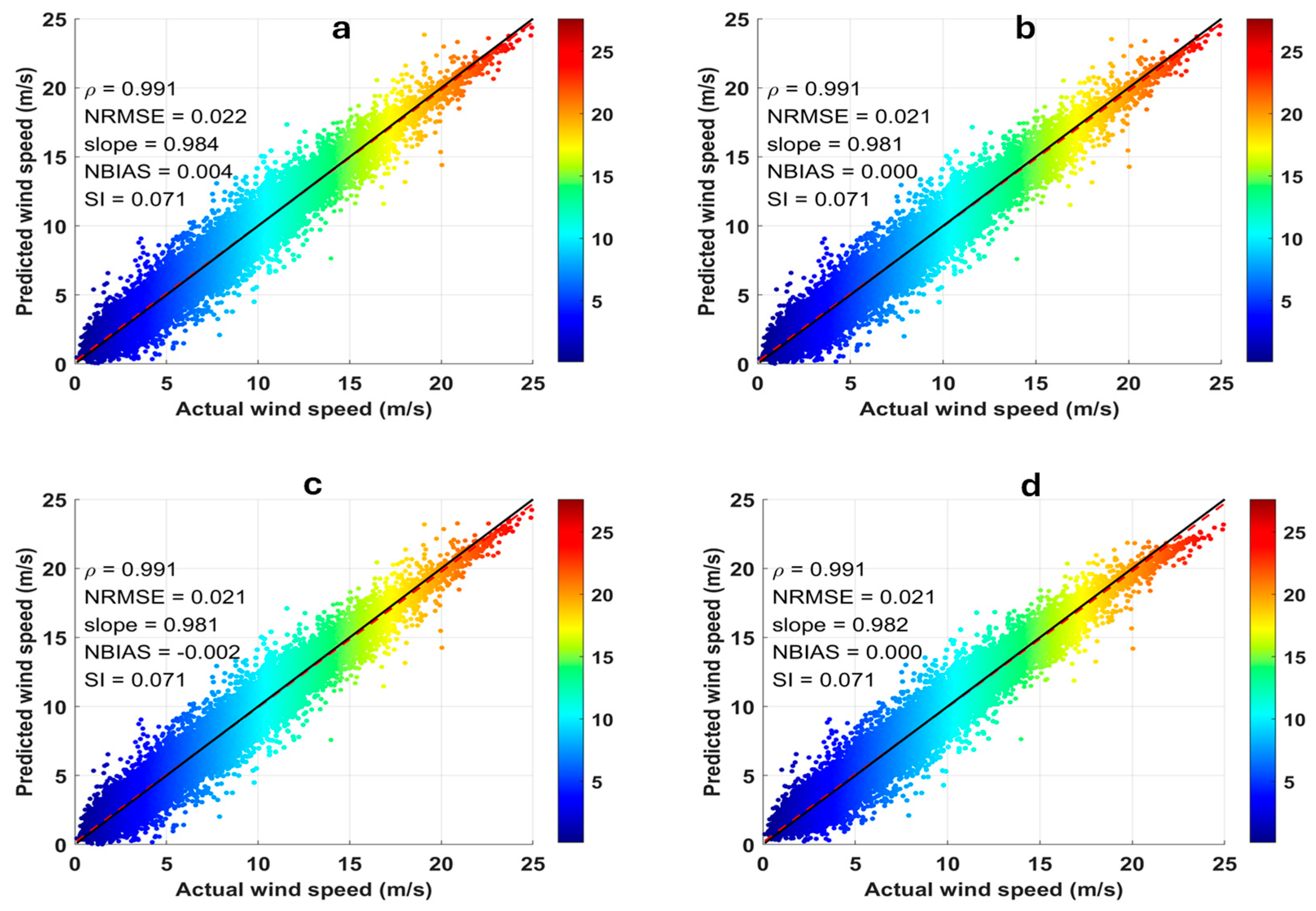
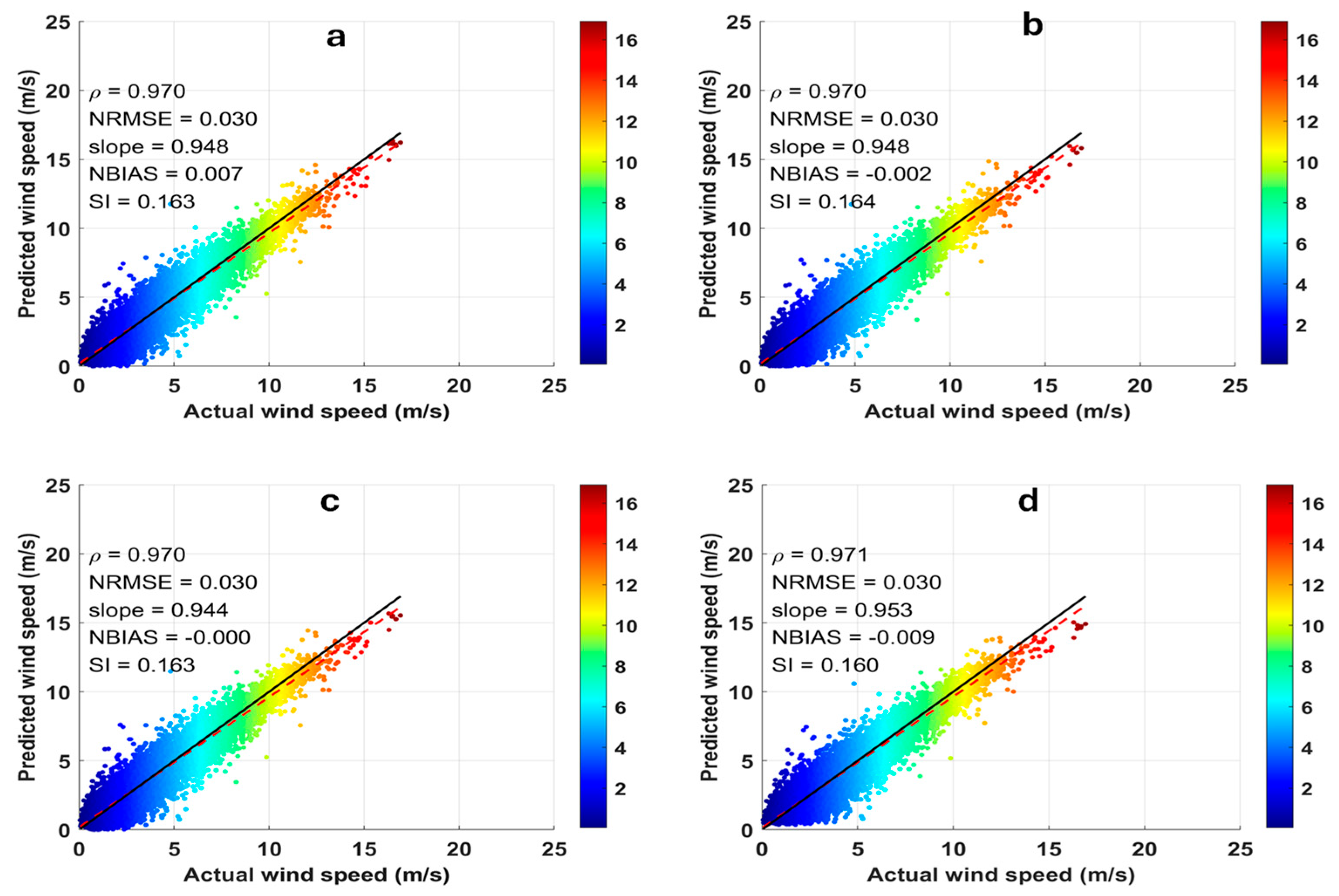
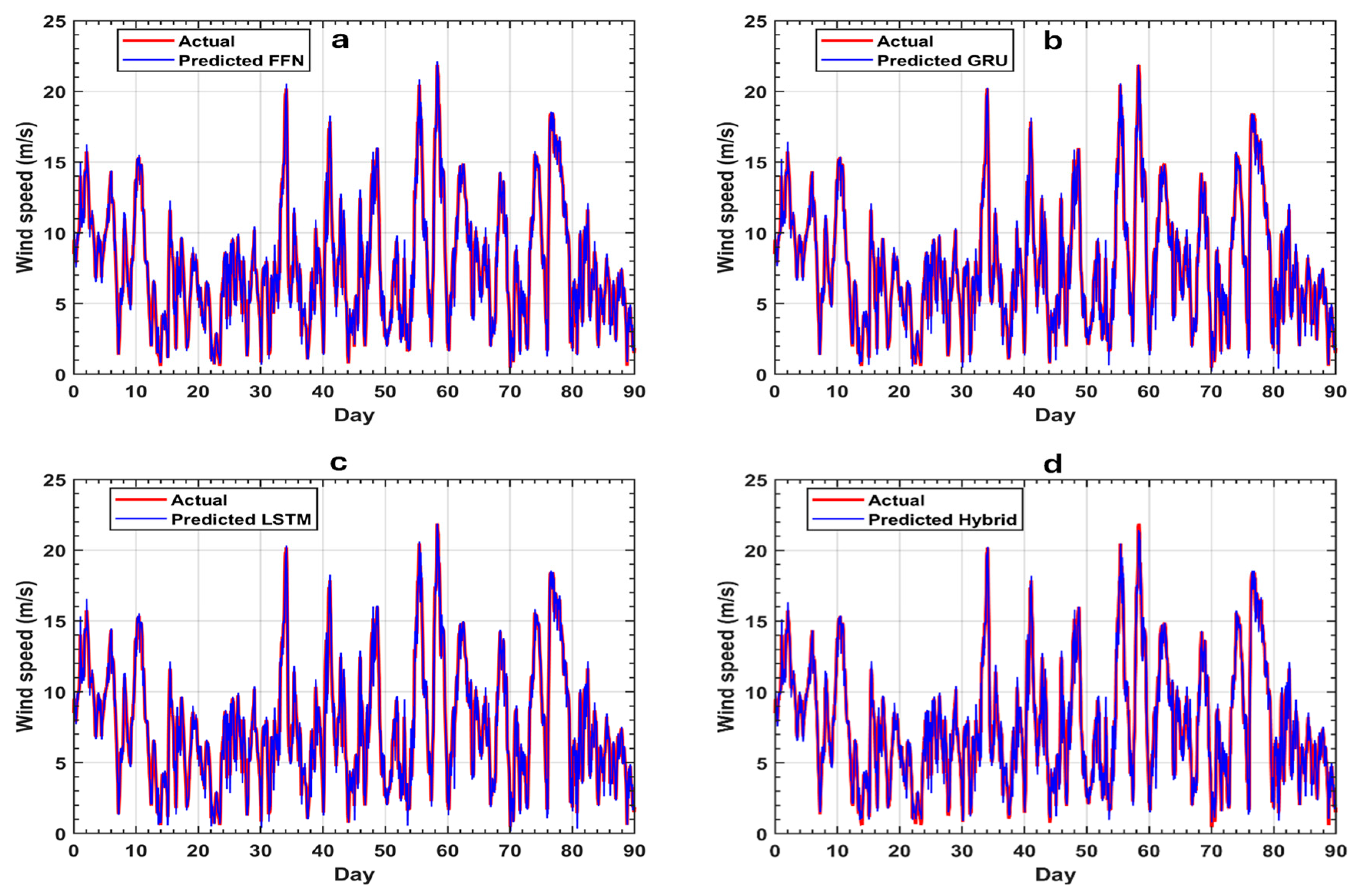
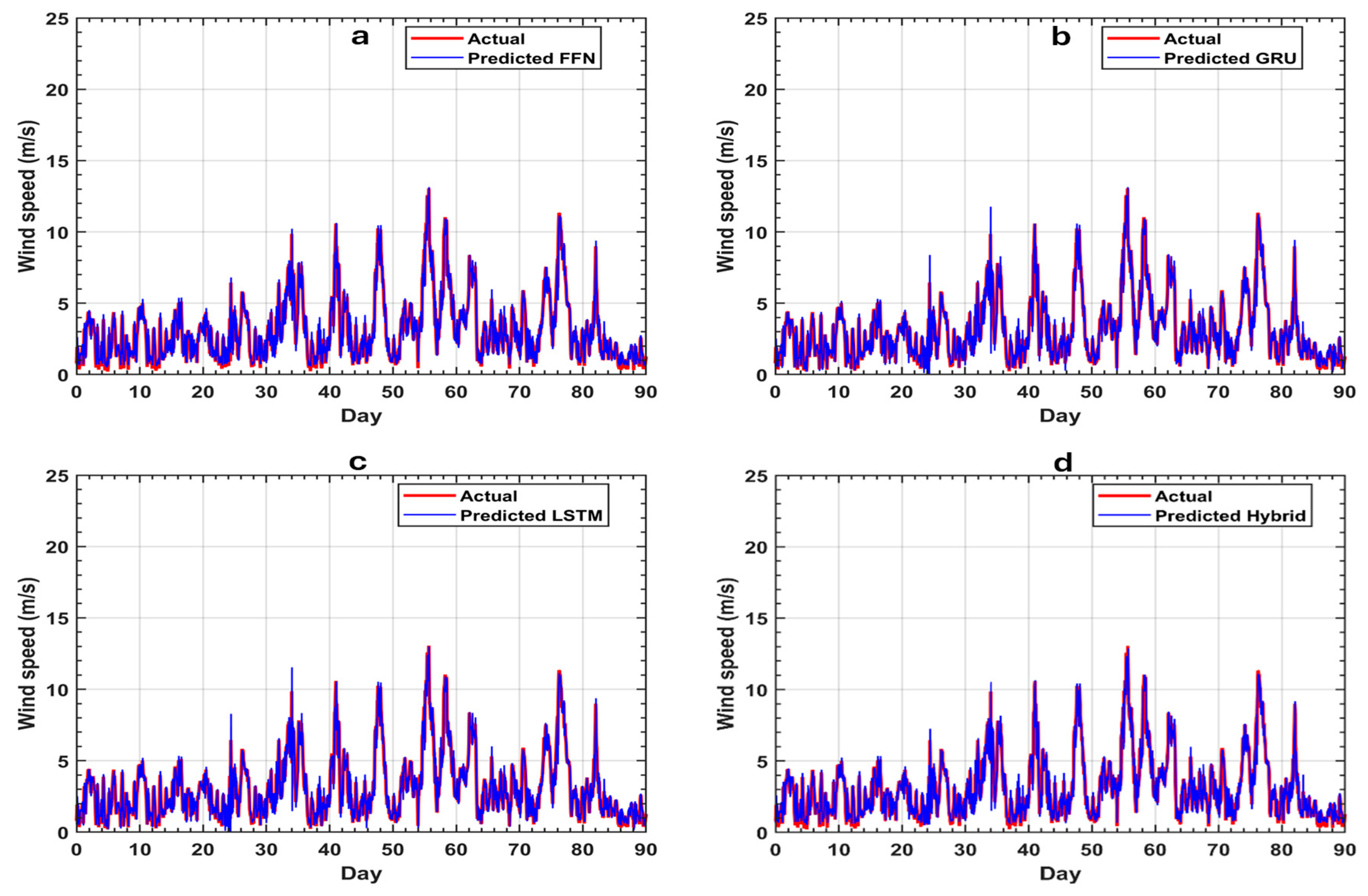
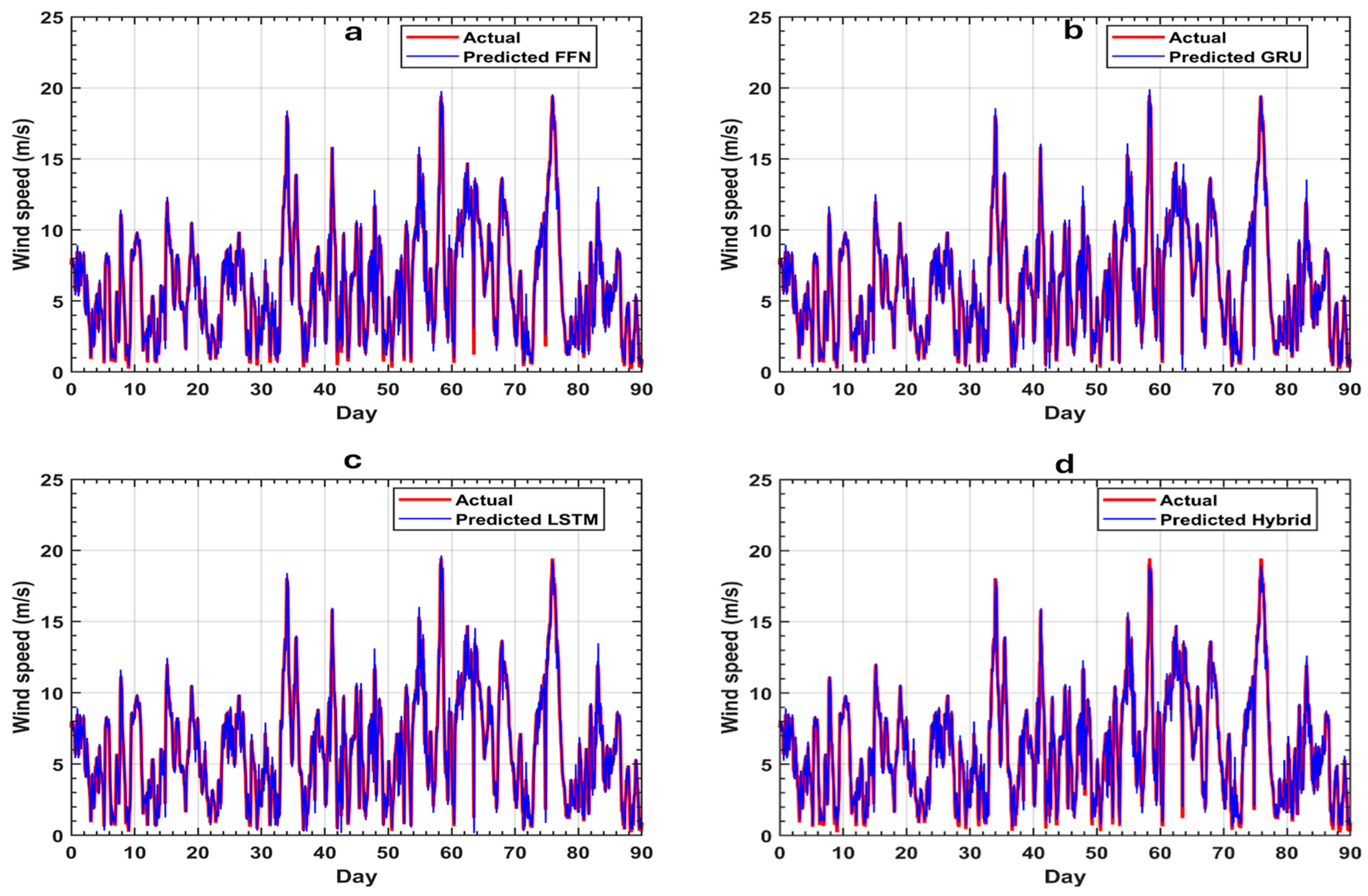
3.1. Network Prediction Results
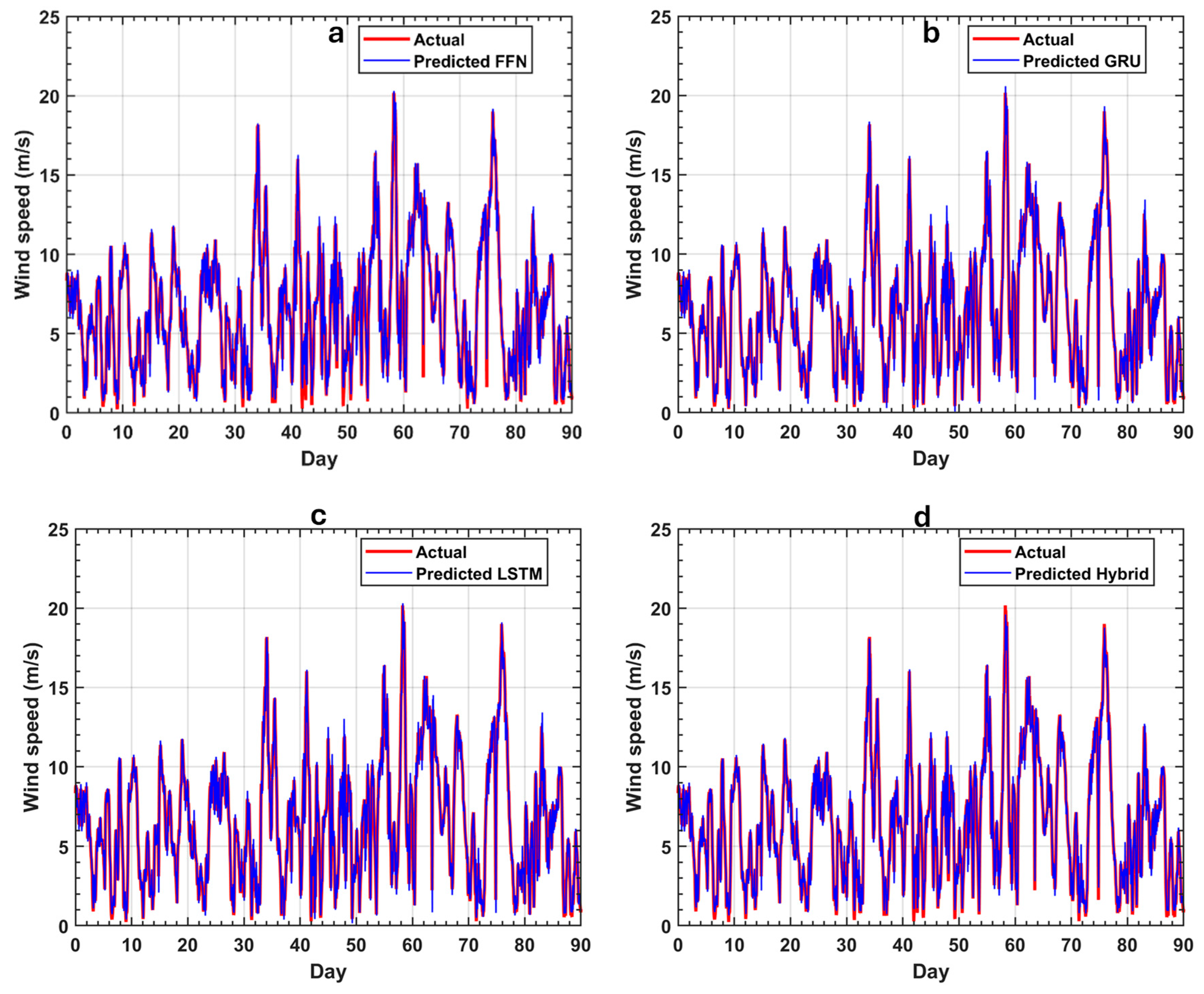
3.2. Network Prediction Results with Fresh Data
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Contestabile, P.; Di Lauro, E.; Galli, P.; Corselli, C.; Vicinanza, D. Offshore Wind and Wave Energy Assessment around Malè and Magoodhoo Island (Maldives). Sustainability 2017, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Khalid, M. A review on the selected applications of forecasting models in renewable power systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 100, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardakaris, K.; Boufidi, I.; Soukissian, T. Offshore Wind and Wave Energy Complementarity in the Greek Seas Based on ERA5 Data. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, E.; Xiang, Q.; Chan, J.C.L.; Dong, Y.; Tu, S.; Chan, P.-W.; Ni, Y.-Q. Increasing temporal stability of global tropical cyclone precipitation. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjady, N.; Keynia, F.; Zareipour, H. Short-term wind power forecasting using ridgelet neural network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 2099–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiadis, M.C.; Dokopoulos, P.; Sahsamanoglou, H.; Manousaridis, I. Short-term forecasting of wind speed and related electrical power. Sol. Energy 1998, 63, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landberg, L. Short-term prediction of the power production from wind farms. J. Wind. Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 1999, 80, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negnevitsky, M.; Potter, C.W. Innovative Short-Term Wind Generation Prediction Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–22 June 2006; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Dhiman, H.S.; Deb, D. A Review of Wind Speed and Wind Power Forecasting Techniques. 2020. Available online: http://arxiv.org/abs/2009.02279 (accessed on 13 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. A review of wind speed and wind power forecasting with deep neural networks. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadenas, E.; Rivera, W. Wind speed forecasting in three different regions of Mexico, using a hybrid ARIMA–ANN model. Renew. Energy 2010, 35, 2732–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Shiyan, L.; Chuanwen, J.; Hongling, L.; Yan, Z. A review on the forecasting of wind speed and generated power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lei, Z.; Jing, H.; Zhong, R. Short-Term Probabilistic Forecasting Method for Wind Speed Combining Long Short-Term Memory and Gaussian Mixture Model. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Gu, M. Characterizing Nonstationary Wind Speed Using the ARMA-GARCH Model. J. Struct. Eng. 2019, 145, 04018226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, S.-J. A Statistical Parameter Correction Technique for WRF Medium-Range Prediction of Near-Surface Temperature and Wind Speed Using Generalized Linear Model. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Karathanasi, F.E. On the use of robust regression methods in wind speed assessment. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouarda, B.M.J.; Charron, C. Non-stationary statistical modelling of wind speed: A case study in eastern Canada. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanis, G.; Kafatos, M.; Chu, P.C.; Hatzopoulos, N.; Papageorgiou, E.; Liakatas, A. Operational atmospheric and wave modelling in the California’s coastline and offshore area with applications to wave energy monitoring and assessment. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2017, 10, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, C.D.; Álvarez, M.A.; Giraldo, E. Short-term wind speed prediction based on robust Kalman filtering: An experimental comparison. Appl. Energy 2015, 156, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, S.S.; Zareipour, H.; Malik, O.; Mandal, P. A review of wind power and wind speed forecasting methods with different time horizons. In Proceedings of the North American Power Symposium 2010, Arlington, TX, USA, 26–28 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Camilo, D.; Huser, R.; Rue, H. A Spliced Gamma-Generalized Pareto Model for Short-Term Extreme Wind Speed Probabilistic Forecasting. J. Agric. Biol. Environ. Stat. 2019, 24, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masrur, H.; Nimol, M.; Faisal, M.; Mostafa, S.M.G. Short term wind speed forecasting using Artificial Neural Network: A case study. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Innovations in Science, Engineering and Technology (ICISET), Chittagong, Bangladesh, 28–29 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Noorollahi, Y.; Jokar, M.A.; Kalhor, A. Using artificial neural networks for temporal and spatial wind speed forecasting in Iran. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 115, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kırsal, Y.; Özbilge, E. Wind Speed Prediction Using Deep Recurrent Neural Networks and Farm Platform Features for One-Hour-Ahead Forecast. Cukurova Univ. J. Fac. Eng. 2024, 39, 287–300. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Zuo, H.; Bai, Y.; Duan, J.; Chang, M.; Chen, B. Short-term wind speed forecasting using recurrent neural networks with error correction. Energy 2021, 217, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbounis, T.G.; Theocharis, J.; Alexiadis, M.; Dokopoulos, P. Long-term wind speed and power forecasting using local recurrent neural network models. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z. Ultra-short-term wind speed forecasting using an optimized artificial intelligence algorithm. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1418–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Mao, W.; Ma, Y.; Fan, X. A combined model based on CEEMDAN and modified flower pollination algorithm for wind speed forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 136, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Song, W.; Song, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Multistep short-term wind speed prediction with rank pooling and fast Fourier transformation. Wind. Energy 2024, 27, 667–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Wang, X. A Novel Hybrid Model for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Based on Twice Decomposition, PSR, and IMVO-ELM. Complexity 2022, 2022, 4014048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yang, R.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L. A hybrid neural network model for short-term wind speed forecasting based on decomposition, multi-learner ensemble, and adaptive multiple error corrections. Renew. Energy 2021, 165, 573–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.R.; Vanitha, V.; Jisma, M. Forecasting of wind speed using ANN, ARIMA and Hybrid models. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Instrumentation and Control Technologies (ICICICT), Kannur, India, 6–7 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, Z.; Niu, X.; Zhang, L. A combined forecasting system based on statistical method, artificial neural networks, and deep learning methods for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energy 2021, 217, 119361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ren, T.; Yang, Y. A New Unified Deep Learning Approach with Decomposition-Reconstruction-Ensemble Framework for Time Series Forecasting. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.09695. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, R.; Suzuki, H.; Kitajima, T.; Kuwahara, A.; Yasuno, T. Wind Speed Prediction Model Using LSTM and 1D-CNN. J. Signal Process. 2018, 22, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhai, G. A novel framework for wind speed prediction based on recurrent neural networks and support vector machine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 178, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Nguyen, L.; Jin, F. A Multi-variable Stacked Long-Short Term Memory Network for Wind Speed Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Seattle, WA, USA, 10–13 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Hu, W.; Tang, M.; Yu, R.; Liu, B. Multi-step Ahead Wind Power Forecasting Based on Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference (APPEEC), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 7–10 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-D.; Ding, L.; Bai, Y.-L. Application of hybrid model based on empirical mode decomposition, novel recurrent neural networks and the ARIMA to wind speed prediction. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 233, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Zheng, Q.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittratorn, A.N.; Huang, C.-M.; Yang, H.-T. Very Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Using a Hybrid LSTMMarkov Model Based on Corrected Wind Speed. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2023, 21, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Valdivia-Bautista, S.M.; Domínguez-Navarro, J.A.; Pérez-Cisneros, M.; Vega-Gómez, C.J.; Castillo-Téllez, B. Artificial Intelligence in Wind Speed Forecasting: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyukarev, E. Comparison of Artificial Neural Network and Regression Models for Filling Temporal Gaps of Meteorological Variables Time Series. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kovadlo, P.G.; Kiselev, A.V.; Eselevich, M.V.; Lukin, V.P. Application of Neural Networks to Estimation and Prediction of Seeing at the Large Solar Telescope Site. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2023, 135, 014503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikhovtsev, A.Y.; Kiselev, A.V.; Kovadlo, P.G.; Kopylov, E.A.; Kirichenko, K.E.; Ehgamberdiev, S.A.; Tillayev, Y.A. Estimation of Astronomical Seeing with Neural Networks at the Maidanak Observatory. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yin, J.; Wang, M.; He, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Xie, Y. Evaluation of Five Reanalysis Products with Radiosonde Observations over the Central Taklimakan Desert During Summer. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2021EA001707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefabas, K.L.; Söder, L.; Mamo, M.; Olauson, J. Modeling of Ethiopian Wind Power Production Using ERA5 Reanalysis Data. Energies 2021, 14, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Karathanasi, F.; Axaopoulos, P.; Voukouvalas, E.; Kotroni, V. Offshore wind climate analysis and variability in the Mediterranean Sea. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 384–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.; Sotiriou, M.-A. Long-Term Variability of Wind Speed and Direction in the Mediterranean Basin. Wind 2022, 2, 513–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poupkou, A.; Zanis, P.; Nastos, P.; Papanastasiou, D.; Melas, D.; Tourpali, K.; Zerefos, C. Present climate trend analysis of the Etesian winds in the Aegean Sea. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2011, 106, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefatos, A.; Karathanasi, F.; Dimou, E.; Loukaidi, V.; Pashalinos, I.; Spinos, S.; Ninou, E.; Patra, S. National Development Program of offshore Wind Farms (in Greek); HEREMA: Athens, Greece, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Soukissian, H.T.; Koutri, N. The evaluation of offshore wind climate in Greece using the CERRA reanalysis dataset. In Innovations in Renewable Energies Offshore, Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Renewable Energies Offshore (RENEW 2024), Lisbon, Portugal, 19–21 November 2024; Soares, C.G., Wang, S., Eds.; CRC Press: Lisbon, Portugal, 2025; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Biavati, G.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Rozum, I.; et al. ERA5 Hourly Data on Single Levels from 1940 to Present; Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Climate Data Store (CDS): Reading, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Collet, F.; Di Luca, A. Evaluation of ERA5 precipitation and 10-m wind speed associated with extratropical cyclones using station data over North America. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 44, 729–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, Y.; Chappell, A.; Dong, L.; Xu, R.; Ekström, M.; Fu, T.-M.; Zeng, Z. Evaluation of Global Reanalysis Land Surface Wind Speed Trends to Support Wind Energy Development Using in Situ Observations. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2021, 60, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, G. Analysing the uncertainties of reanalysis data used for wind resource assessment: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukissian, T.H.; Karathanasi, F.E.; Zaragkas, D.K. Exploiting offshore wind and solar resources in the Mediterranean using ERA5 reanalysis data. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 237, 114092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olauson, J. ERA5: The new champion of wind power modelling? Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velo, R.; López, P.; Maseda, F. Wind speed estimation using multilayer perceptron. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shi, P.; Xing, H. Wave energy assessment based on reanalysis data calibrated by buoy observations in the southern South China Sea. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 5067–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londhe, S.N.; Shah, S.; Dixit, P.R.; Nair, T.M.B.; Sirisha, P.; Jain, R. A Coupled Numerical and Artificial Neural Network Model for Improving Location Specific Wave Forecast. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2016, 59, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Su, H.; Yang, X.; Yan, X.-H. Subsurface temperature estimation from remote sensing data using a clustering-neural network method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, S.; Chen, W.; Shi, P.; Liu, Y. Calibration Experiments of CFOSAT Wavelength in the Southern South China Sea by Artificial Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, L.A.; Russo, S.; Re, C.L.; Ludeno, G.; Nardone, G.; Vicinanza, D.; Contestabile, P. Underestimation of Wave Energy from ERA5 Datasets: Back Analysis and Calibration in the Central Tyrrhenian Sea. Energies 2025, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
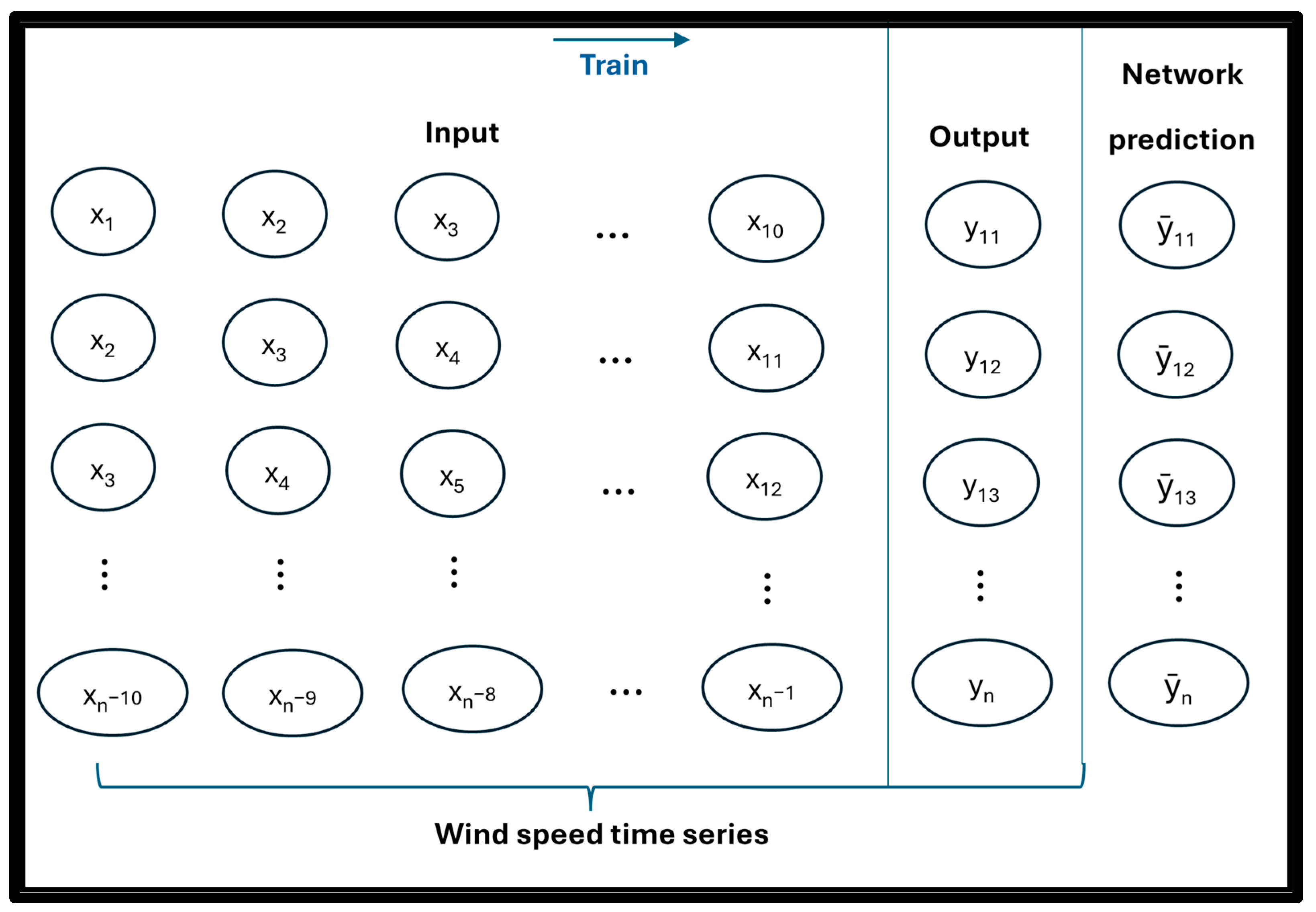


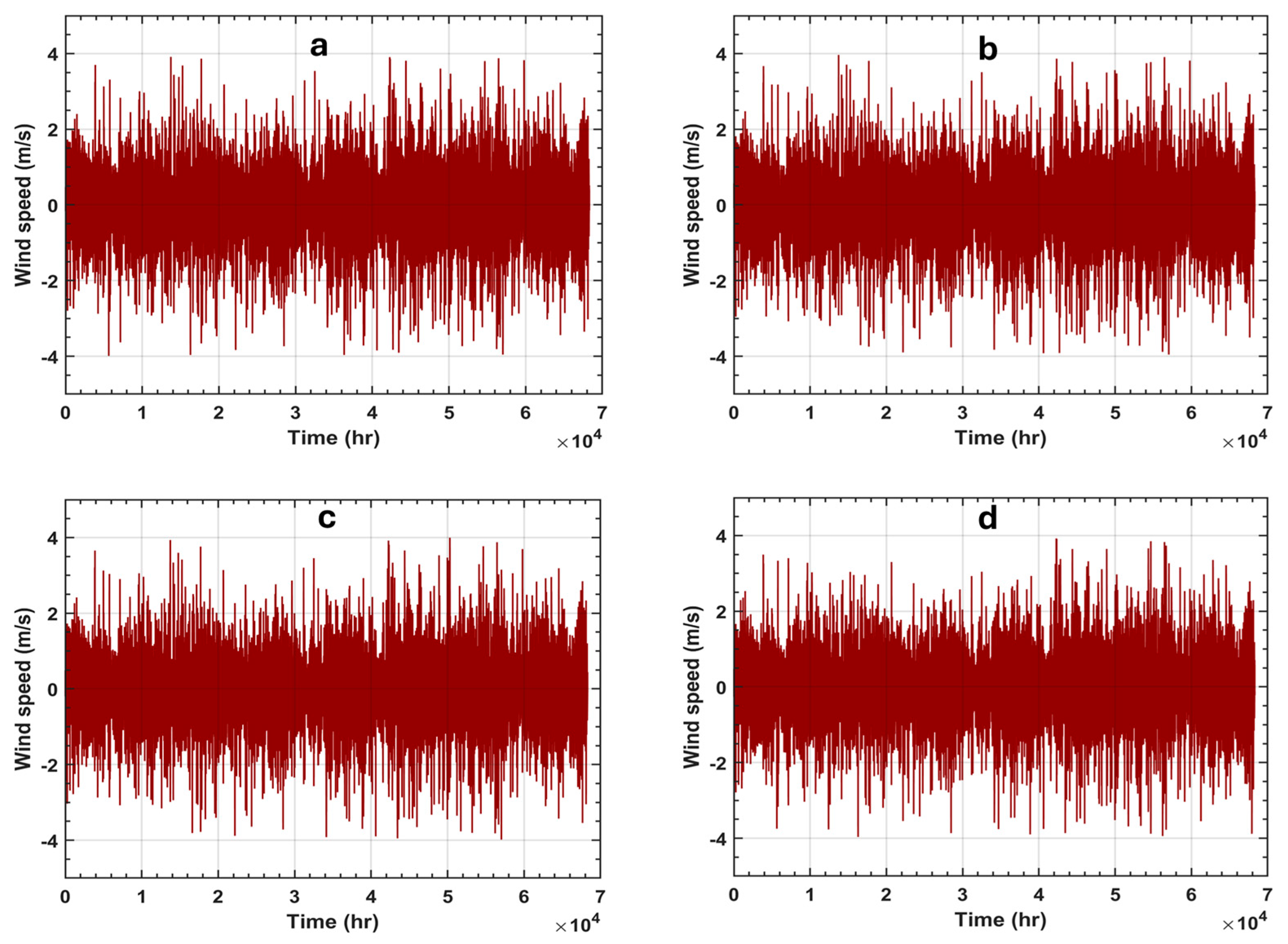

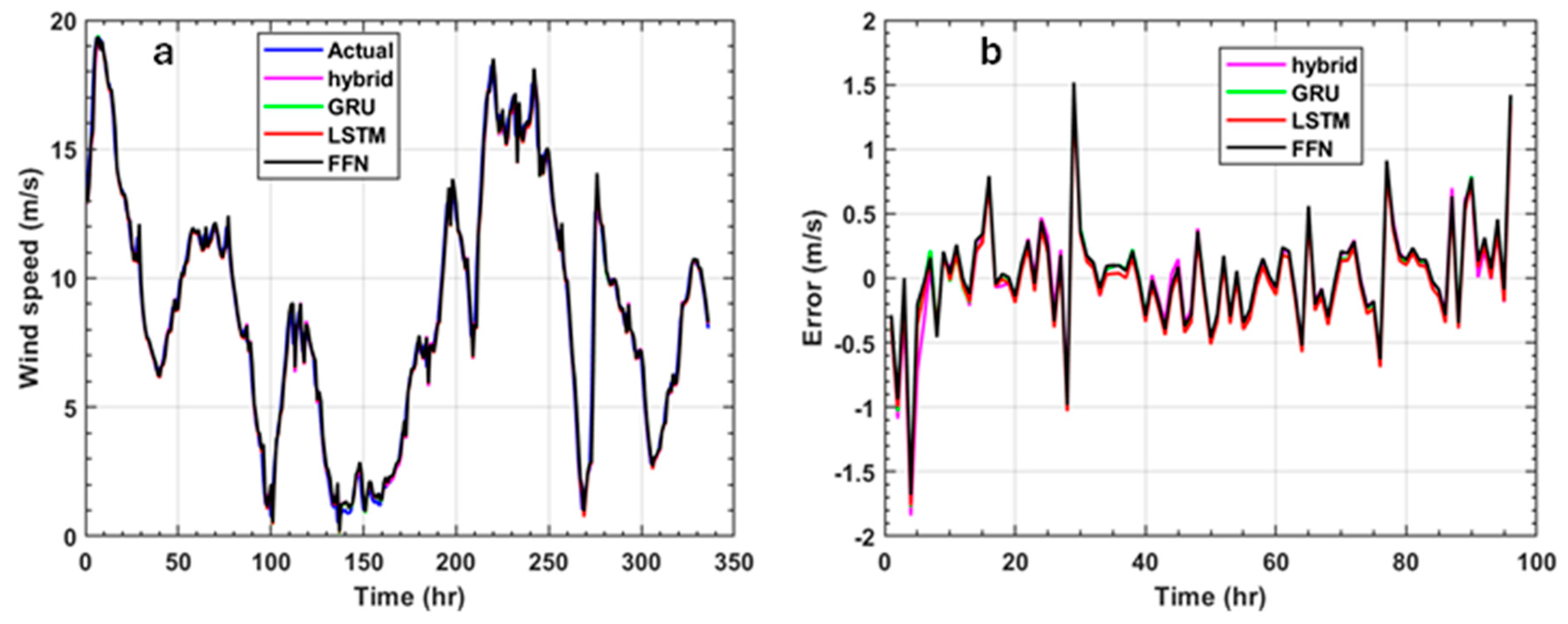

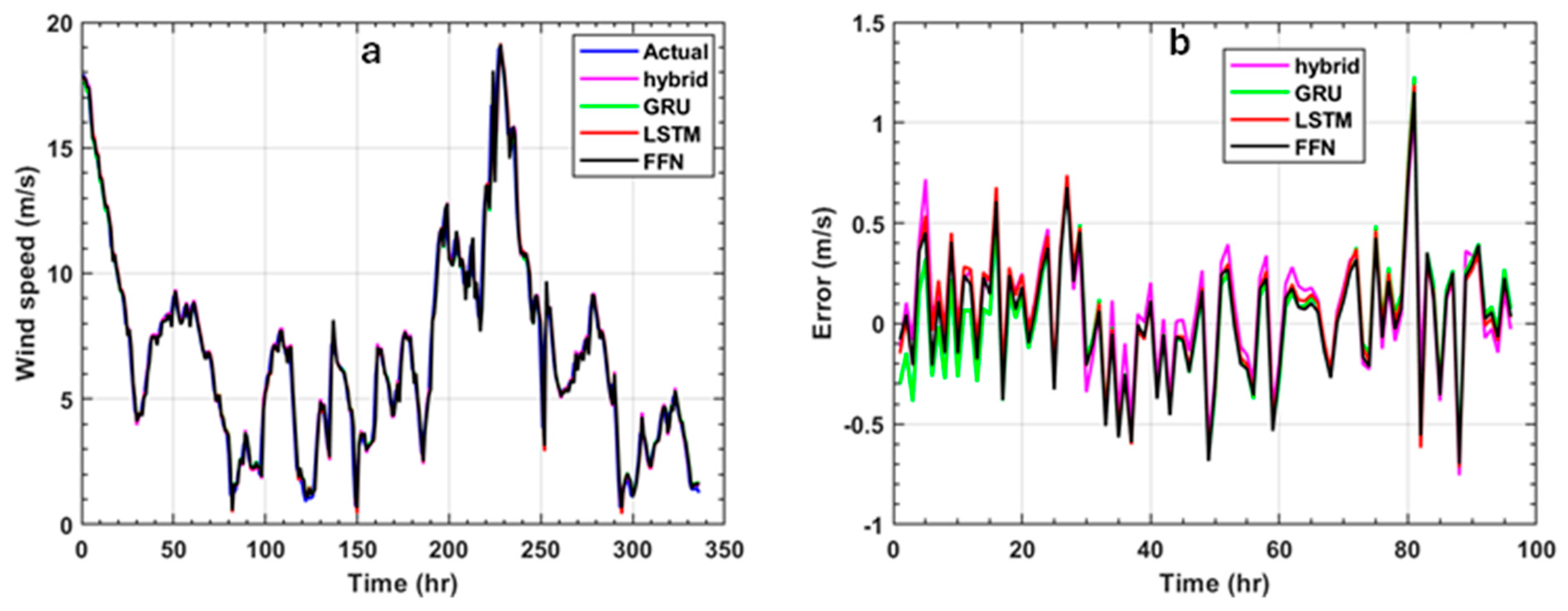
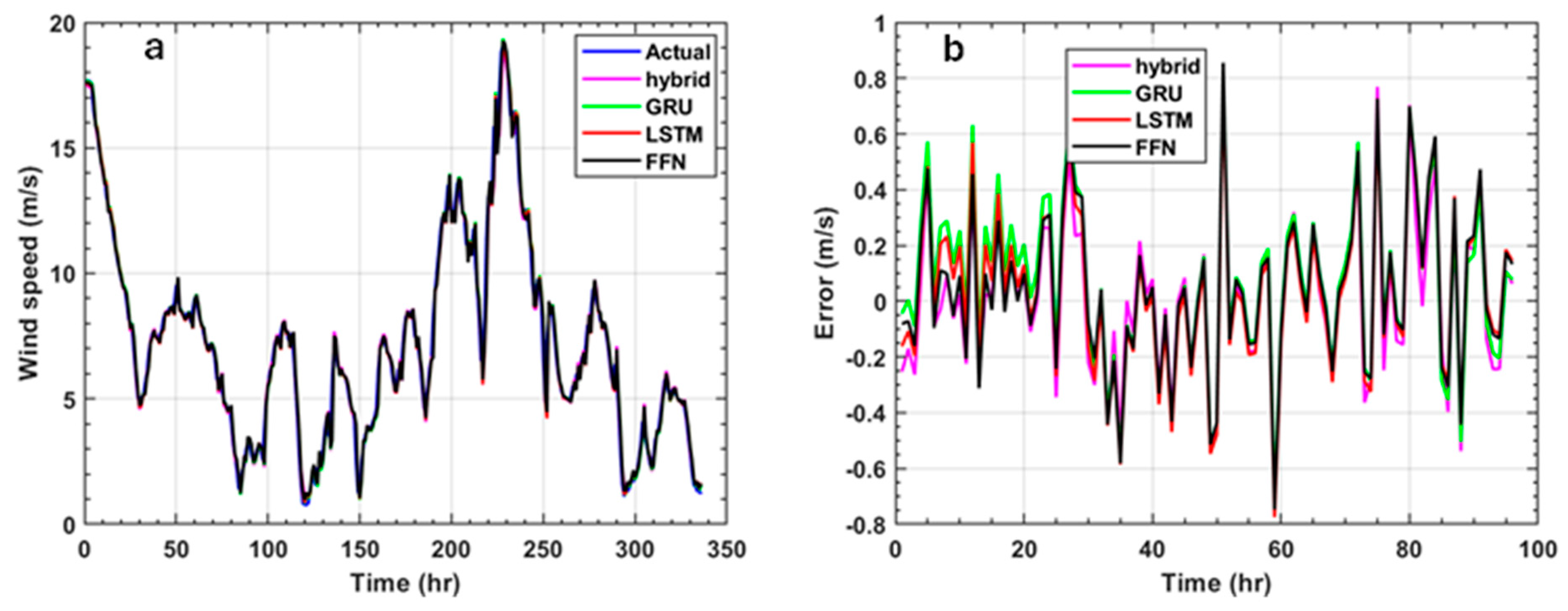

| FFN | LSTM | GRU | Hybrid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoch | 1000 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Learning rate | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Dropout | - | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| Minibatch | - | 512 | 512 | 512 |
| Optimizer | Bayesian | Adam (1) | Adam | Adam |
| Weight optimizer | - | Glorot | Glorot | Glorot |
| Networks | (m/s) | Bias (m/s) | (m/s) | (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crete | FFN | 0.5407 | 0.1342 | 0.3647 | 6.9700 | 0.9835 |
| GRU | 0.5272 | 0.0025 | 0.3482 | 6.3335 | 0.9843 | |
| LSTM | 0.5218 | 0.0158 | 0.3374 | 6.0118 | 0.9847 | |
| Hybrid | 0.5162 (2) | 0.0156 | 0.3364 | 6.1220 | 0.9850 | |
| Gyaros | FFN | 0.5922 | 0.0374 | 0.3892 | 7.5320 | 0.9815 |
| GRU | 0.5907 | 0.0010 | 0.3889 | 7.4216 | 0.9816 | |
| LSTM | 0.5904 | −0.0178 | 0.3890 | 7.3971 | 0.9816 | |
| Hybrid | 0.5890 | 0.0019 | 0.3860 | 7.3415 | 0.9817 | |
| Patras | FFN | 0.5059 | 0.0229 | 0.3594 | 18.6159 | 0.9414 |
| GRU | 0.5085 | −0.0074 | 0.3602 | 18.2314 | 0.9408 | |
| LSTM | 0.5061 | −0.0007 | 0.3597 | 18.3491 | 0.9413 | |
| Hybrid | 0.4983 | −0.0274 | 0.3508 | 17.4819 | 0.9431 | |
| Pilot 1A | FFN | 0.5894 | −0.0152 | 0.4027 | 11.6456 | 0.9714 |
| GRU | 0.5925 | −0.0147 | 0.4060 | 11.8742 | 0.9711 | |
| LSTM | 0.5918 | −0.0144 | 0.4023 | 11.6145 | 0.9712 | |
| Hybrid | 0.5766 | 0.0142 | 0.3964 | 11.7795 | 0.9727 | |
| Pilot 1B | FFN | 0.5627 | 0.0136 | 0.3838 | 9.8234 | 0.9736 |
| GRU | 0.5658 | −0.0001 | 0.3834 | 9.5777 | 0.9733 | |
| LSTM | 0.5636 | −0.0018 | 0.3839 | 9.8400 | 0.9735 | |
| Hybrid | 0.5529 | −0.0001 | 0.3795 | 9.7007 | 0.9745 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afolabi, L.A.; Soukissian, T.; Vicinanza, D.; Contestabile, P. Wind Speed Forecasting in the Greek Seas Using Hybrid Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070763
Afolabi LA, Soukissian T, Vicinanza D, Contestabile P. Wind Speed Forecasting in the Greek Seas Using Hybrid Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070763
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfolabi, Lateef Adesola, Takvor Soukissian, Diego Vicinanza, and Pasquale Contestabile. 2025. "Wind Speed Forecasting in the Greek Seas Using Hybrid Artificial Neural Networks" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070763
APA StyleAfolabi, L. A., Soukissian, T., Vicinanza, D., & Contestabile, P. (2025). Wind Speed Forecasting in the Greek Seas Using Hybrid Artificial Neural Networks. Atmosphere, 16(7), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070763









