Variability in Summer Rainfall and Rain Days over the Southern Kalahari: Influences of ENSO and the Botswana High
Abstract
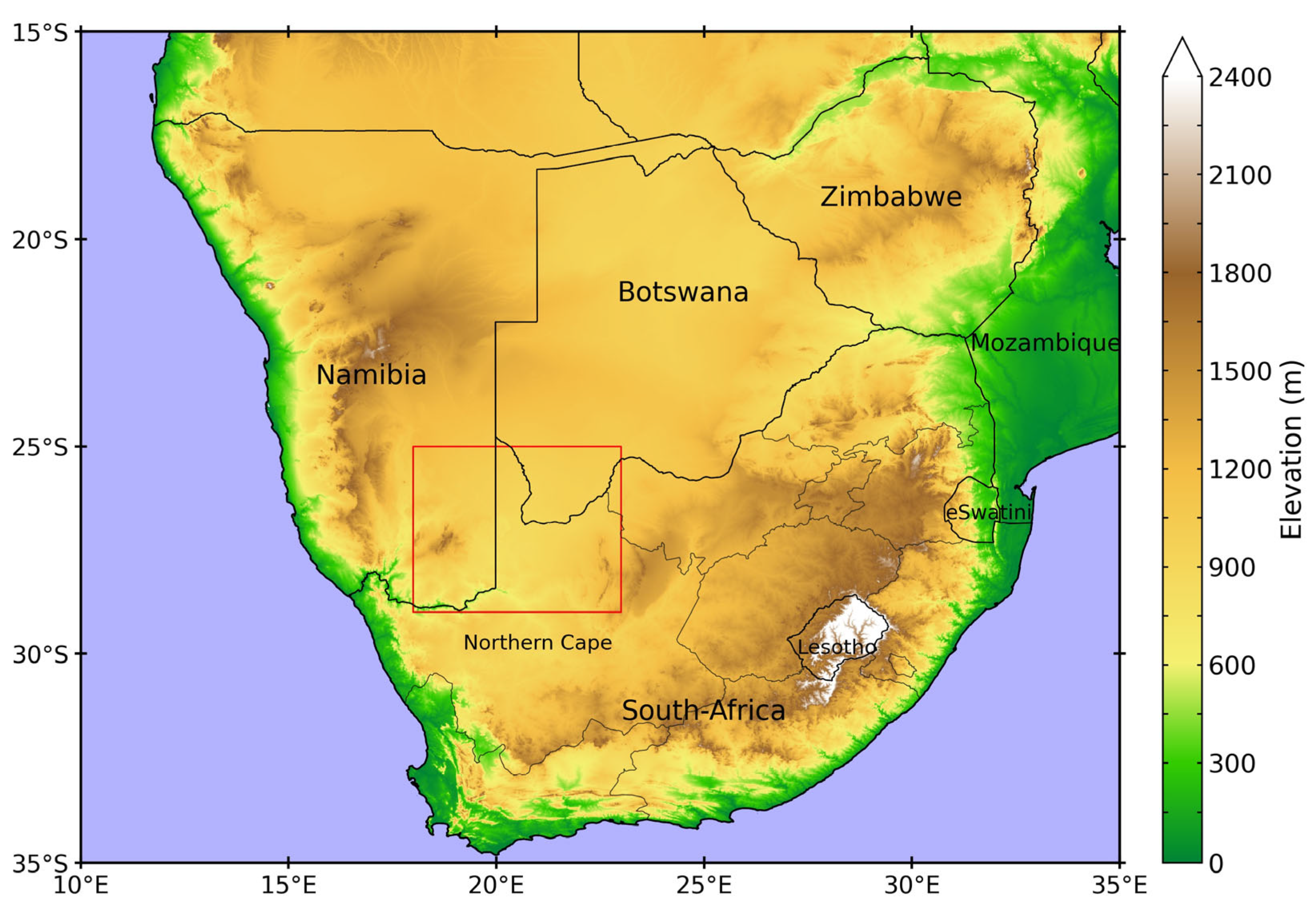
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
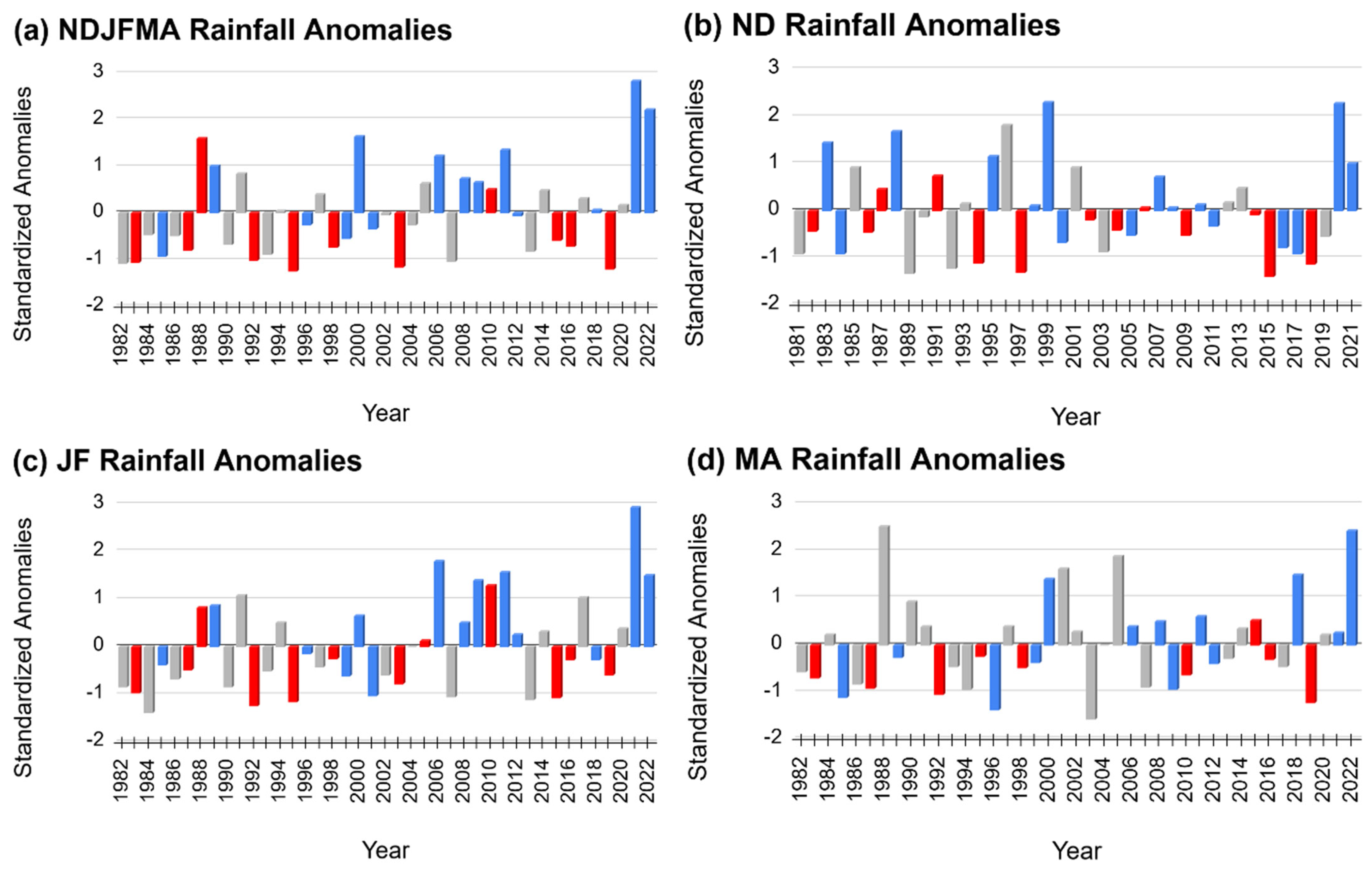
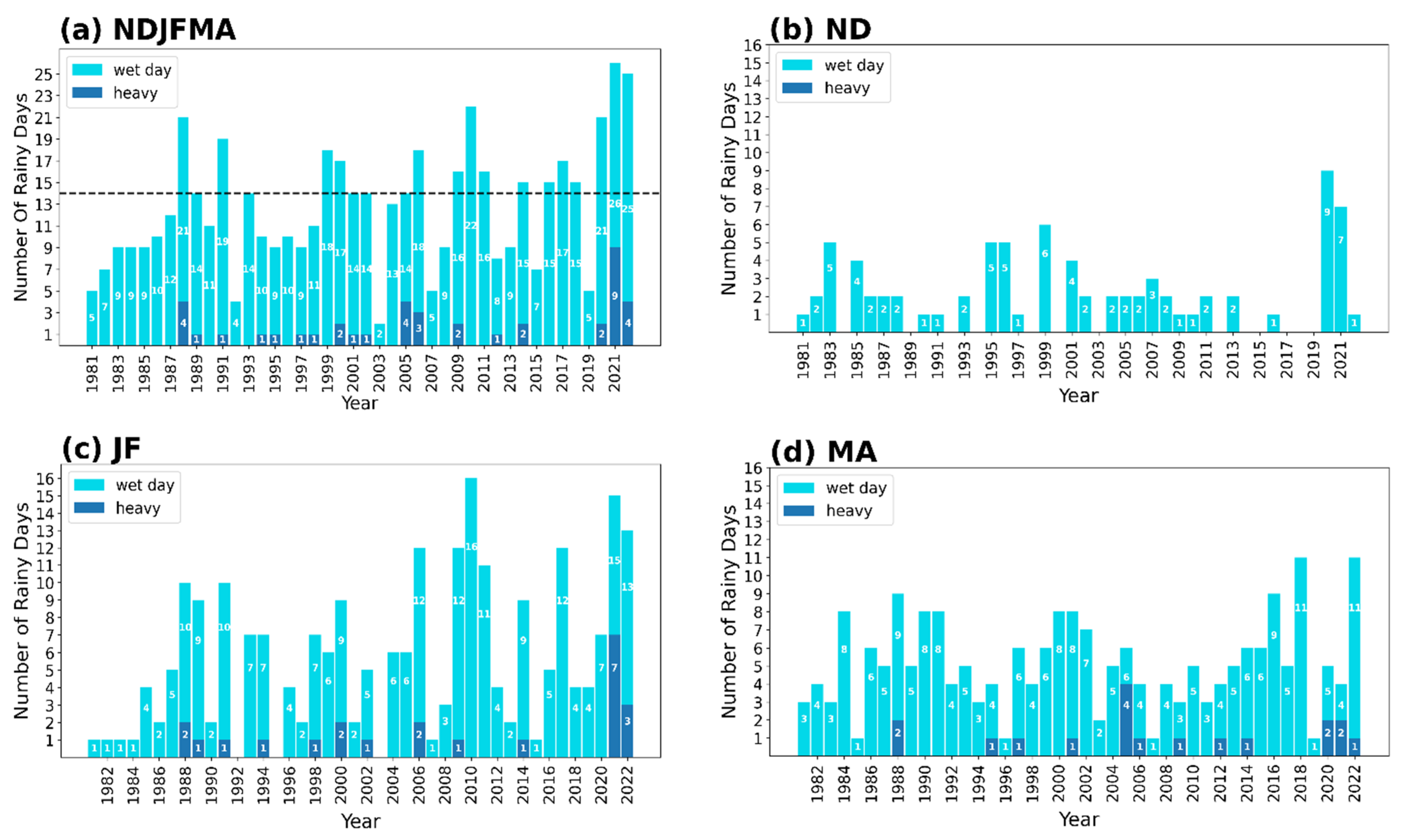
3.1. Rainfall Variations
3.2. Rainfall Relationships with the Main Modes of Variability
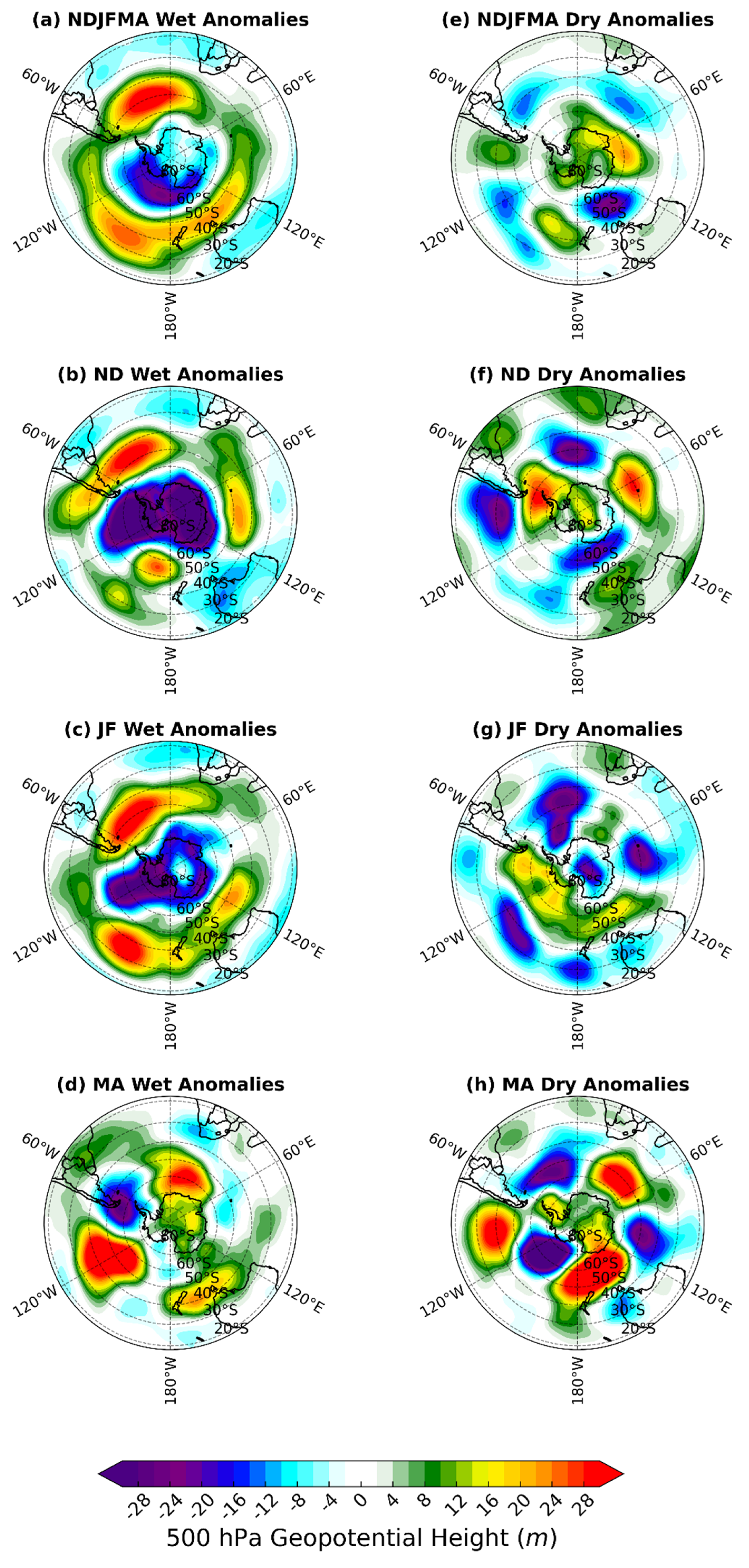
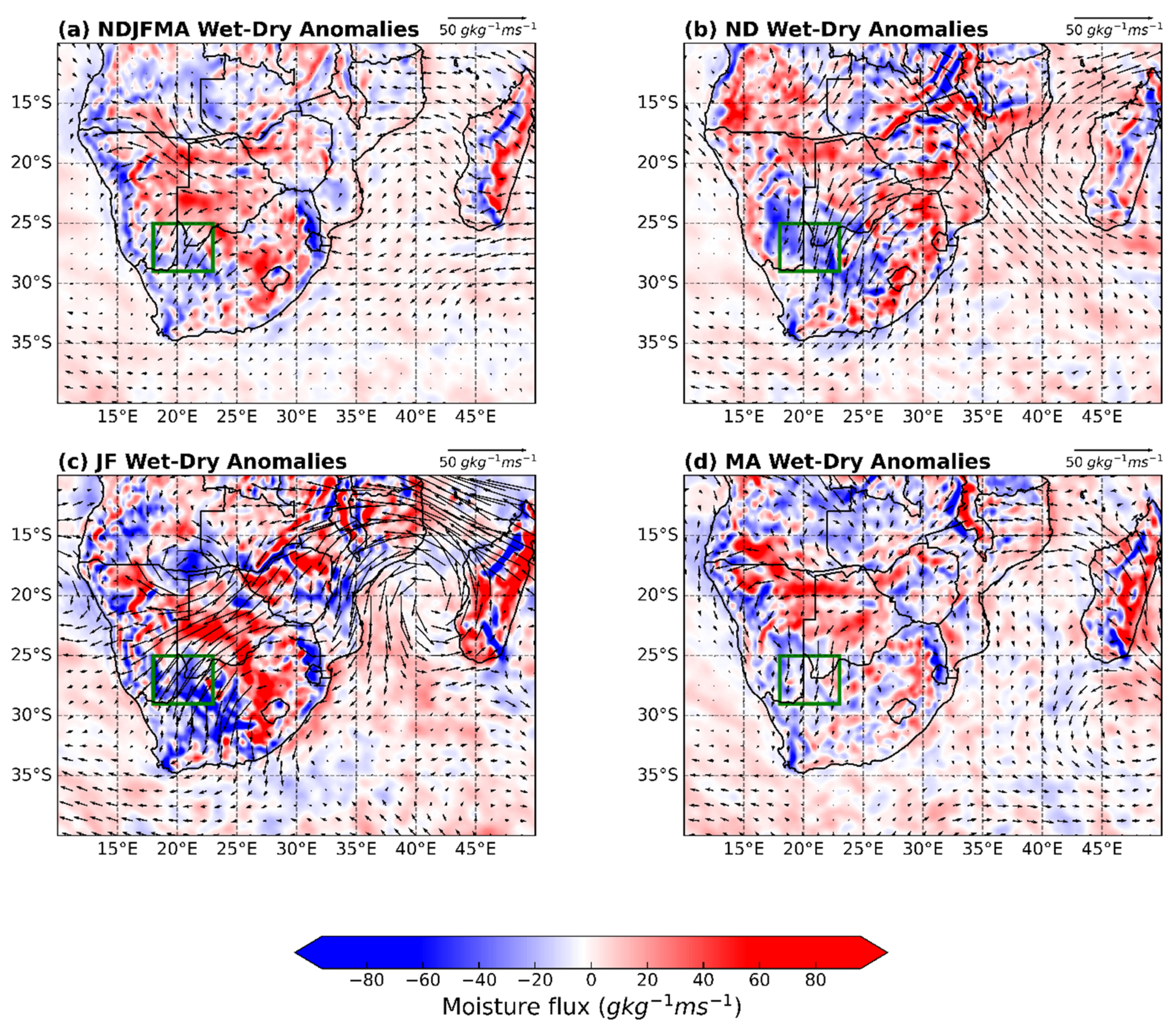
3.3. Circulation Patterns Linked to Wet and Dry Summers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weldon, D.; Reason, C.J.C. Variability of rainfall characteristics over the South Coast region of South Africa. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2014, 115, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, B.M.; Meadows, M.E. Late Quaternary dynamics of southern Africa’s winter rainfall zone. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2007, 84, 103–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, C.J.; Landman, W.A.; Engelbrecht, F.A.; Malherbe, J. A synoptic decomposition of rainfall over the Cape south coast of South Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 44, 2589–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Van Garderen, E.A.; Deryng, D.; Dorling, S.; Krueger, T.; Landman, W.; Lankford, B.; Lebek, K.; Osborn, T.; Ringler, C.; et al. Climate and southern Africa’s water–energy–food nexus. Nat. Clim. Change 2015, 5, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Richard, Y. Intensity and spatial extension of drought in South Africa at different time scales. Water SA 2003, 29, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, O.; Blamey, R.C.; Reason, C.J.C. Drought metrics and temperature extremes over the Okavango River basin, southern Africa, and links with the Botswana high. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 6463–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramblay, Y.; Villarini, G.; Zhang, W. Observed changes in flood hazard in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1040b5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, D.; Haimbili, E.; Angula, M.; Baudoin, M.A.; Hegga, S.; Zaroug, M.; Okeyo, A. Vulnerability and Adaptation to Climate Change in the Semi-Arid Regions of Southern Africa; ASSAR Working Paper; University of Cape Town: Rondebosch, South Africa, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Thoithi, W.; Blamey, R.C.; Reason, C.J.C. Dry spells, wet days, and their trends across Southern Africa during the summer rainy season. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, E.; Steele, J.; Keys, E.; Muyengwa, S.; Child, B.; Southworth, J. Local perception of risk to livelihoods in the semi-arid landscape of Southern Africa. Land 2013, 2, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphengst, T.; Ward, D. Effects of habitat structure and shrub encroachment on bird species diversity in arid savanna in Northern Cape province, South Africa. J. Afr. Ornithol. 2008, 79, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, J.S. ‘Only connect’: Restoring resilience in the Kalahari ecosystem. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoithi, W.; Blamey, R.; Reason, C.J.C. Floods over east coast South Africa: Interactions between a Mesoscale Convective System and a Coastal Meso-Low. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, L.L.; Van Heerden, J. The heavy rainfall and floods over the northeastern interior of South Africa during February 2000. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2001, 97, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, A.; Reason, C.J.; Fauchereau, N. Extreme rainfall in the Namib Desert during late summer 2006 and influences of regional ocean variability. Int. J. Climatol. 2008, 28, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesay, J.A. South African rainfall, the Southern Oscillation and a Southern Hemisphere semi-annual cycle. J. Climatol. 1988, 8, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.; Simmonds, I. Interannual variability of south-eastern African summer rainfall. Part 1: Relationships with air–sea interaction processes. Int. J. Climatol. 1997, 17, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, S.J. El Niño, climate change, and Southern African climate. Environmetrics Off. J. Int. Environmetrics Soc. 2001, 12, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C.; Allan, R.J.; Lindesay, J.A.; Ansell, T.J. ENSO and climatic signals across the Indian Ocean basin in the global context: Part I, Interannual composite patterns. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1285–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, K.H. A Southern Hemisphere wave response to ENSO with implications for southern Africa precipitation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2001, 58, 2146–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.; Jagadheesha, D. A model investigation of recent ENSO impacts over southern Africa. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 181–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, R.C.; Kolusu, S.R.; Mahlalela, P.; Todd, M.C.; Reason, C.J.C. The role of regional circulation features in regulating El Niño climate impacts over southern Africa: A comparison of the 2015/2016 drought with previous events. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 4276–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philander, S.G.H. A review of tropical ocean–atmosphere interactions. Tellus B 1999, 51, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlalela, P.T.; Blamey, R.C.; Reason, C.J.C. Mechanisms behind early winter rainfall variability in the southwestern Cape, South Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2019, 53, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillett, N.P.; Kell, T.D.; Jones, P.D. Regional climate impacts of the Southern Annular Mode. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.K.; Yamagata, T. Subtropical SST dipole events in the southern Indian Ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C. Subtropical Indian Ocean SST dipole events and southern African rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2225–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, M.S.J. A generalized classification of South African summer rain-bearing synoptic systems. J. Climatol. 1984, 4, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, M.; Washington, R. Circulation anomalies associated with tropical-temperate troughs in southern Africa and the south west Indian Ocean. Clim. Dyn. 1999, 15, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.C.; Reason, C.J.C.; Fauchereau, N. Cloud bands over southern Africa: Seasonality, contribution to rainfall variability and modulation by the MJO. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 1199–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macron, C.; Pohl, B.; Richard, Y. How do Tropical Temperate Troughs Form and Develop over Southern Africa? J. Clim. 2014, 27, 1633–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C. The Bolivian, Botswana, And Bilybara Highs And Southern Hemisphere Drought/Floods. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unganai, L.S.; Mason, S.J. Long-range predictability of Zimbabwe summer rainfall. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulenga, H.M. Southern African Climate Anomalies, Summer Rainfall and the Angola Low. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 1999. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11427/19649 (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Munday, C.; Washington, R. Circulation controls on southern African precipitation in coupled models: The role of the Angola Low. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault, M.; Florenchie, P.; Fauchereau, N.; Reason, C.J. South East tropical Atlantic warm events and southern African rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.; Reason, C.J.C.; Hewitson, B.C. Wet and dry spells within particularly wet and dry summers in the South African. Clim. Res. 2004, 26, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, N.C.G.; Reason, C.J.C.; Fauchereau, N. Tropical–extratropical interactions over southern Africa: Three cases of heavy summer season rainfall. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 138, 2608–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The climate hazards infrared precipitation with stations—A new environmental record for monitoring extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeidizand, R.; Sabetghadam, S.; Tarnavsky, E.; Pierleoni, A. Evaluation of CHIRPS rainfall estimates over Iran. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, W.V.; Bailey, A.K. Can CHIRPS fill the gap left by the decline in the availability of rainfall stations in Southern Africa? Water SA 2021, 47, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.F.; Huffman, G.J.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Arkin, P.A. Global precipititation: A 17-year monthly analysis based on gauge observations, satellite estimates, and numerical model outputs. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2539–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, J.A.; Kibii, J.K. Applicability of CHIRPS-based satellite rainfall estimates for South Africa. J. S. Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2021, 63, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novella, N.S.; Thiaw, W.M. African rainfall climatology version 2 for famine early warning systems. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2013, 52, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidment, R.I.; Grimes, D.; Allan, R.P. The 30 year TAMSAT African rainfall climatology and time series (TARCAT) data set. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphugwi, M.; Blamey, R.C.; Reason, C.J.C. Rainfall characteristics over the Congo Air Boundary region in southern Africa: A comparison of station and gridded rainfall products. Atmos. Res. 2024, 311, 107718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E. The definition of El Niño. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1997, 78, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, G.J. Trends in the Southern Annular Mode from observations and reanalyses. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 4134–4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Ambrizzi, T. Opposite phases of the Antarctic oscillation and relationships with intraseasonal to interannual activity in the tropics during the austral summer. J. Clim. 2005, 18, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, K.R.; Fogt, R.L. Varying roles of ENSO and SAM on the Antarctic Peninsula climate in austral spring. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11481–11492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, B.; Fauchereau, N.; Richard, Y.; Rouault, M.; Reason, C.J.C. Interactions between synoptic, intraseasonal and interannual convective variability over Southern Africa. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 33, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauchereau, N.; Pohl, B.; Reason, C.J.C.; Rouault, M.; Richard, Y. Rouault Recurrent daily OLR patterns in the Southern Africa/Southwest Indian Ocean region, implications for South African rainfall and teleconnections. Clim. Dyn. 2009, 32, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, A.T.; Reason, C.J.C. Variability in the characteristics of cut-off low pressure systems over subtropical southern Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, A.; Hewitson, B.; Lennard, C.; Cerezo-Mota, R.; Tadross, M. Cut-off lows in the South Africa region and their contribution to precipitation. Clim. Dyn. 2013, 41, 2331–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spavins-Hicks, Z.D.; Washington, R.; Munday, C. The Limpopo Low-Level Jet: Mean climatology and role in water vapor transport. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, C.; Washington, R.; Hart, N. African low-level jets and their importance for water vapor transport and rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barimalala, R.; Blamey, R.C.; Desbiolles, F.; Reason, C.J. Variability in the Mozambique Channel Trough and Impacts on Southeast African Rainfall. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, P.D.; Dyer, T.G.; Mametse, M.N. Secular changes in South African rainfall: 1880 to 1972. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1975, 101, 817–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyson, P.D.; Preston-Whyte, R. The Weather and Climate of Southern Africa; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; 396p. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, R.J.; Reason, C.J.C.; Lindesay, J.A.; Ansell, T.J. Protracted ENSO episodes and their impacts in the Indian Ocean region. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2003, 50, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reason, C.J.C.; Rouault, M. ENSO-like decadal patterns and South African rainfall. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 16-1–16-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, J.; Dieppois, B.; Maluleke, P.; Van Staden, M.; Pillay, D.L. South African droughts and decadal variability. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 657–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillitt, C.G.; Nieuwoudt, W.L.; Backeberg, G.R. Water markets in the lower Orange River catchment of South Africa. Agrekon 2005, 44, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
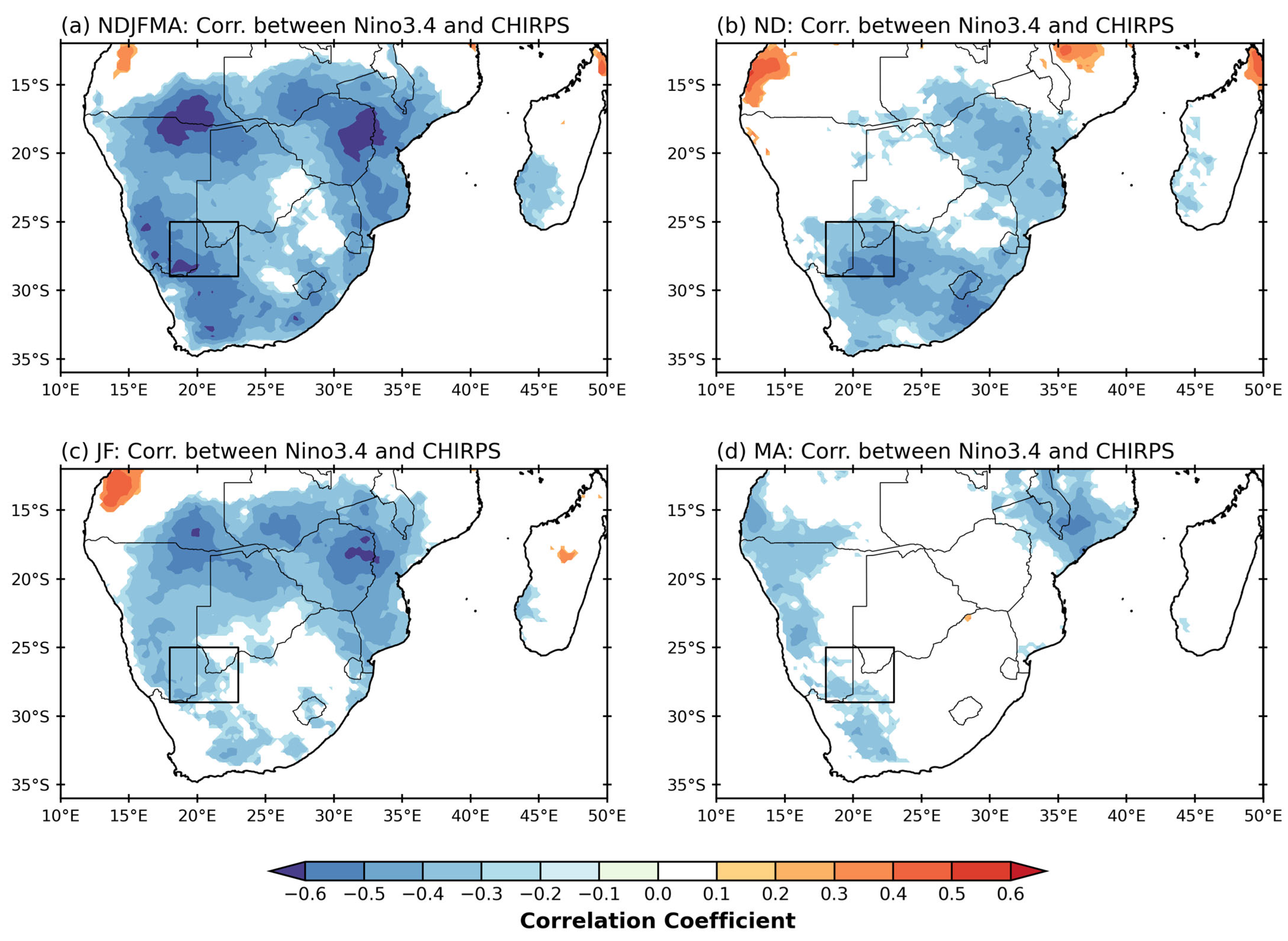
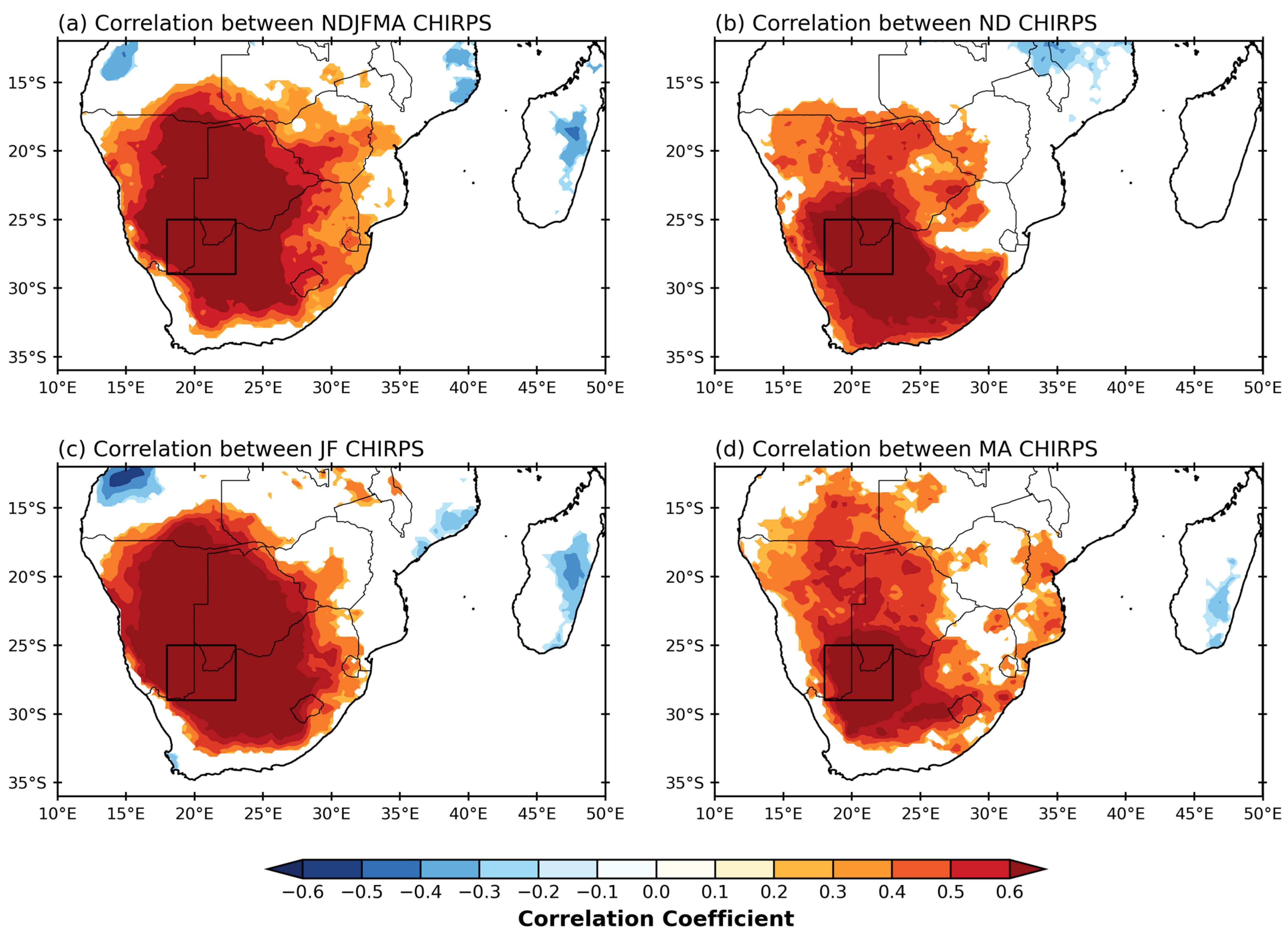

| SAM | ENSO | SIOD | BH Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDJFMA | 0.3 | −0.5 | −0.1 | −0.5 |
| ND | 0.4 | −0.5 | −0.1 | −0.4 |
| JF | 0.04 | −0.3 | 0.2 | −0.5 |
| MA | 0.1 | −0.3 | −0.05 | −0.3 |
| Months | Wet | Dry | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Rain Total (mm) | Std. Anom | ENSO | SAM | Year | Rain Total (mm) | Std. Anom | ENSO | SAM | |
| NDJFMA | 2020/21 | 301.9 | 2.8 | La Niña | Pos | 1981/82 | 58.9 | −2.0 | Neutral | Pos |
| NDJFMA | 2021/22 | 271.3 | 2.2 | La Niña | Pos | 1994/95 | 98.2 | −1.2 | El Niño | Pos |
| NDJFMA | 1999/2000 | 242.9 | 1.6 | La Niña | Neg | 2019/20 | 100.5 | −1.2 | Neutral | Neg |
| NDJFMA | 1987/88 | 240.4 | 1.6 | La Niña | Pos | 2002/03 | 102.0 | −1.2 | El Niño | Neg |
| NDJFMA | 2010/11 | 227.8 | 1.3 | La Niña | Pos | 1982/83 | 106.4 | −1.1 | El Niño | Neg |
| ND | 1999 | 71.0 | 2.3 | La Niña | Pos | 2015 | 15.1 | −1.4 | El Niño | Pos |
| ND | 2020 | 70.8 | 2.3 | La Niña | Pos | 1989 | 16.0 | −1.4 | Neutral | Pos |
| ND | 1996 | 63.8 | 1.8 | Neutral | Neg | 1997 | 16.4 | −1.3 | El Niño | Neg |
| ND | 1988 | 61.6 | 1.7 | La Niña | Pos | 1992 | 17.8 | −1.2 | Neutral | Pos |
| ND | 1983 | 58.0 | 1.4 | La Niña | Pos | 2018 | 18.9 | −1.2 | El Niño | Pos |
| JF | 2021 | 170.6 | 3.0 | La Niña | Pos | 1984 | 19.0 | −1.4 | Neutral | Neg |
| JF | 2006 | 130.3 | 1.8 | La Niña | Neg | 1992 | 24.4 | −1.2 | El Niño | Neg |
| JF | 2011 | 122.5 | 1.6 | La Niña | Pos | 1995 | 27.1 | −1.1 | El Niño | Pos |
| JF | 2022 | 120.4 | 1.5 | La Niña | Pos | 2013 | 28.8 | −1.1 | Neutral | Pos |
| JF | 2009 | 116.5 | 1.4 | La Niña | Pos | 2015 | 30.3 | −1.1 | El Niño | Pos |
| MA | 1988 | 100.8 | 2.5 | Neutral | Pos | 2003 | 27.8 | −1.5 | Neutral | Pos |
| MA | 2022 | 99.5 | 2.4 | La Niña | Pos | 1996 | 31.5 | −1.3 | La Niña | Pos |
| MA | 2005 | 89.6 | 1.9 | Neutral | Pos | 1981 | 33.0 | −1.3 | Neutral | Neg |
| MA | 2001 | 84.9 | 1.6 | Neutral | Pos | 2019 | 34.2 | −1.2 | El Niño | Pos |
| MA | 2018 | 82.6 | 1.5 | La Niña | Neg | 1985 | 35.9 | −1.1 | La Niña | Pos |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kekana, B.; Blamey, R.; Reason, C. Variability in Summer Rainfall and Rain Days over the Southern Kalahari: Influences of ENSO and the Botswana High. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060747
Kekana B, Blamey R, Reason C. Variability in Summer Rainfall and Rain Days over the Southern Kalahari: Influences of ENSO and the Botswana High. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(6):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060747
Chicago/Turabian StyleKekana, Bohlale, Ross Blamey, and Chris Reason. 2025. "Variability in Summer Rainfall and Rain Days over the Southern Kalahari: Influences of ENSO and the Botswana High" Atmosphere 16, no. 6: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060747
APA StyleKekana, B., Blamey, R., & Reason, C. (2025). Variability in Summer Rainfall and Rain Days over the Southern Kalahari: Influences of ENSO and the Botswana High. Atmosphere, 16(6), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060747






