Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Isohyets on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
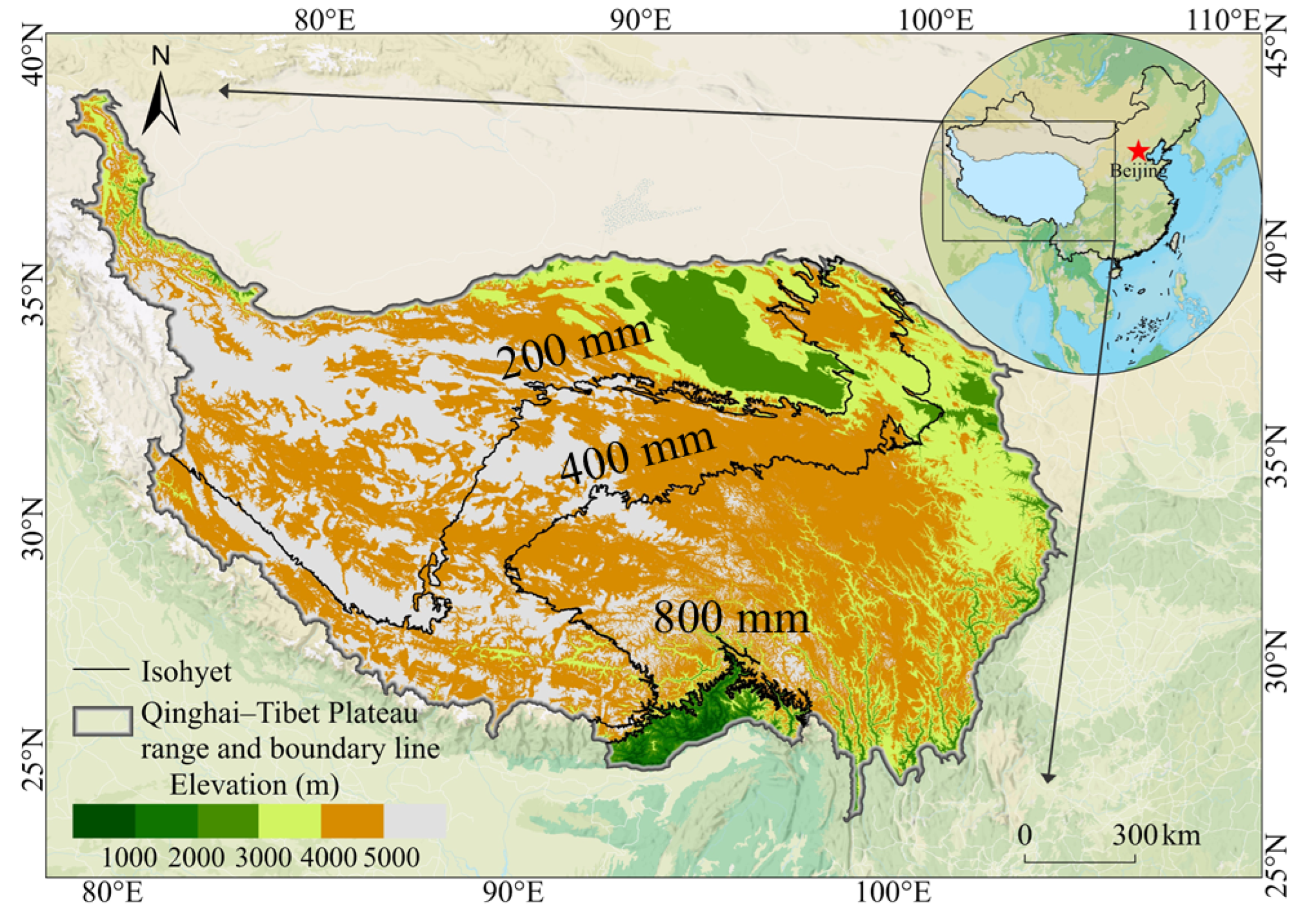
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Sources, Accuracy Validation, and Preprocessing
2.2.1. DEM Data
2.2.2. Multi-Year Average Precipitation Data
2.2.3. Accuracy Validation of the Data
2.2.4. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Research Methodology
2.3.1. Contour Line Extraction
2.3.2. Climate Trend Rate Method
2.3.3. Mann–Kendall Abrupt Change Test
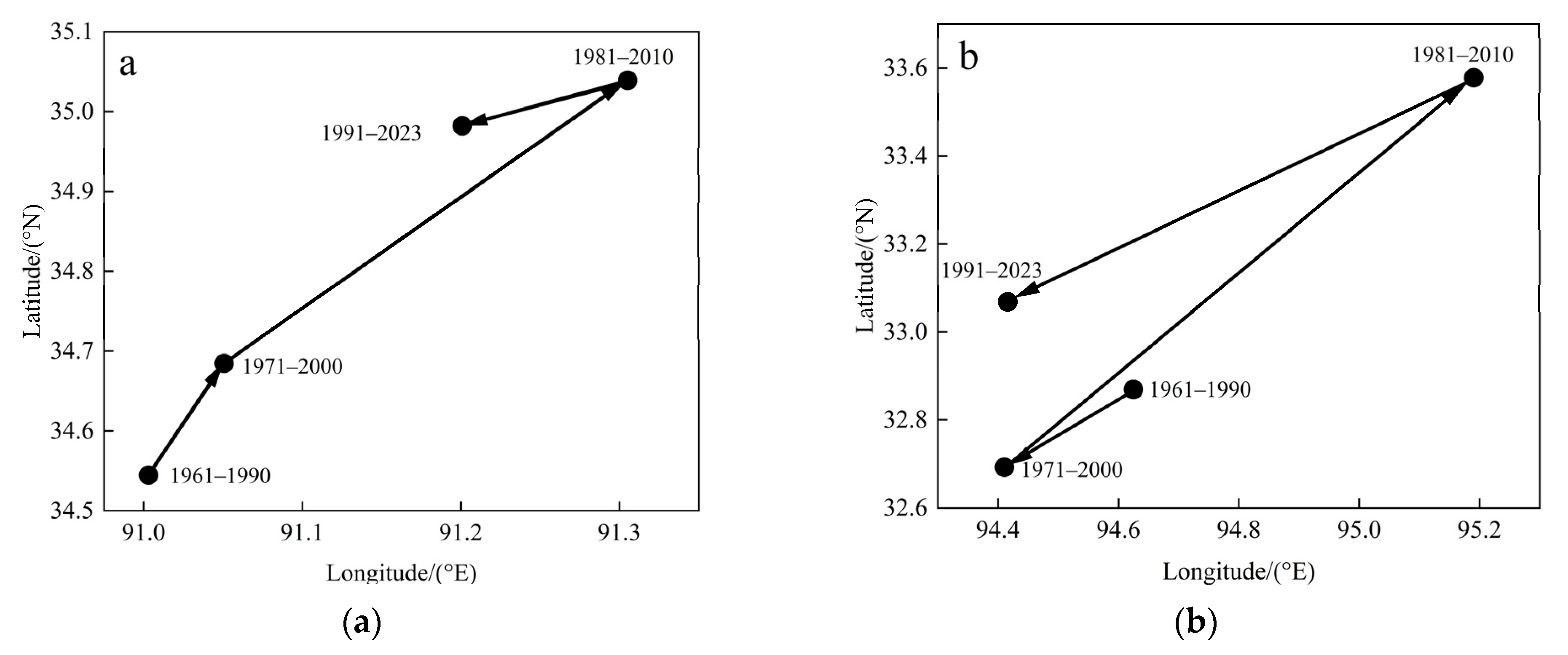
2.3.4. Centroid Tracking Method
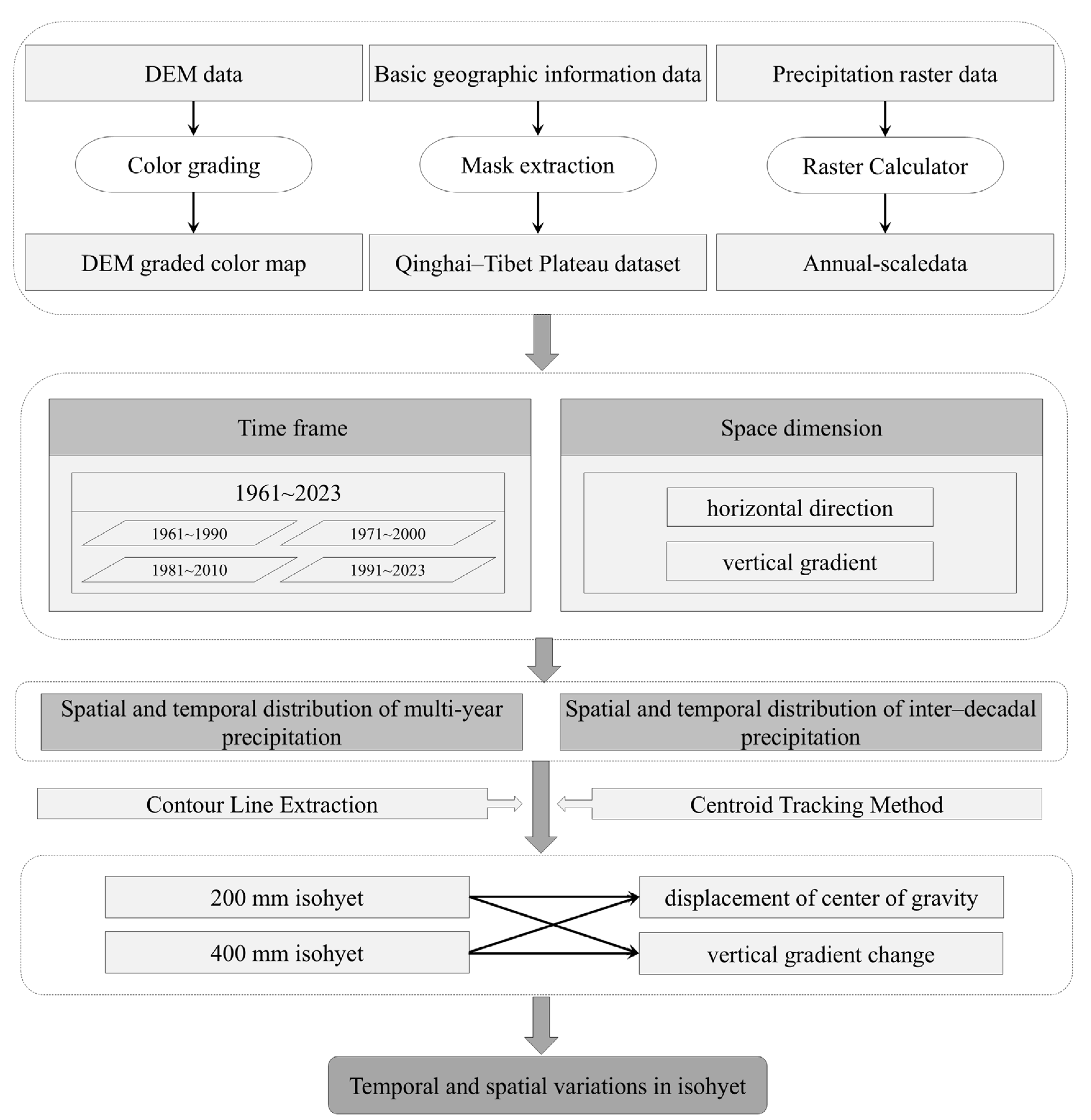
2.4. Technology Roadmap
3. Results
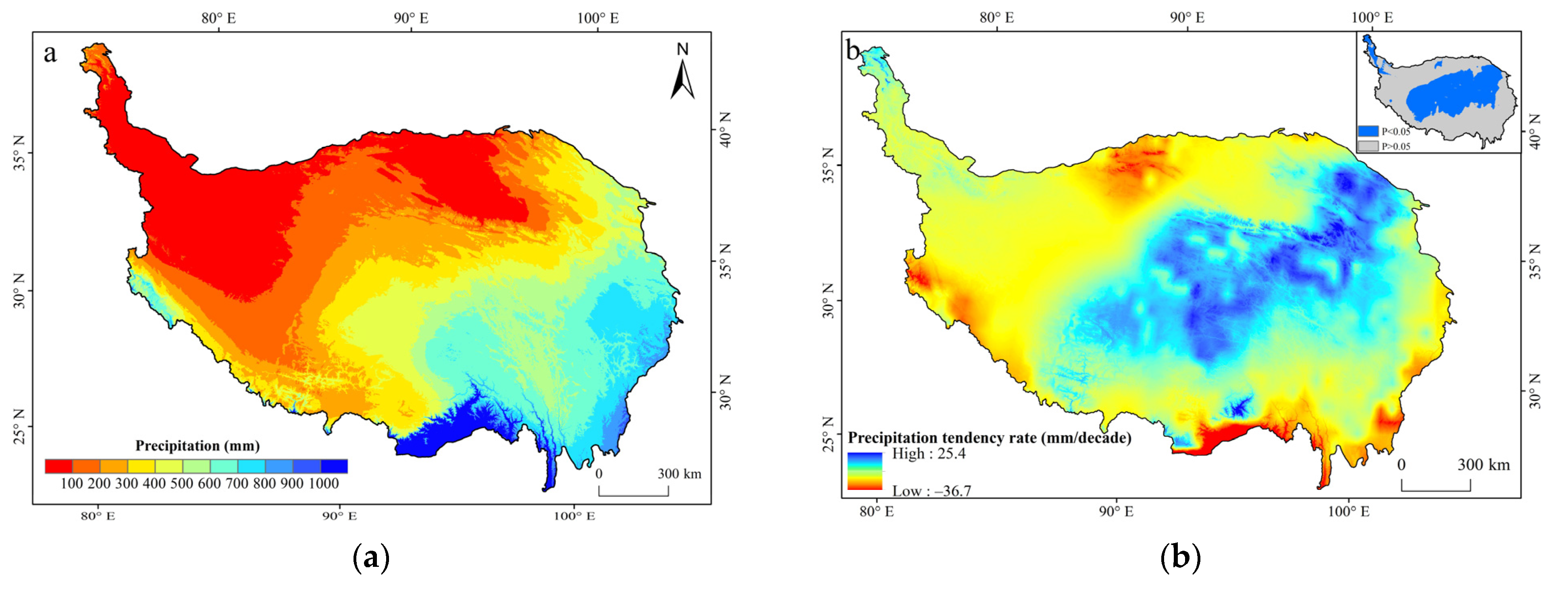
3.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Precipitation over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau (1961–2023)
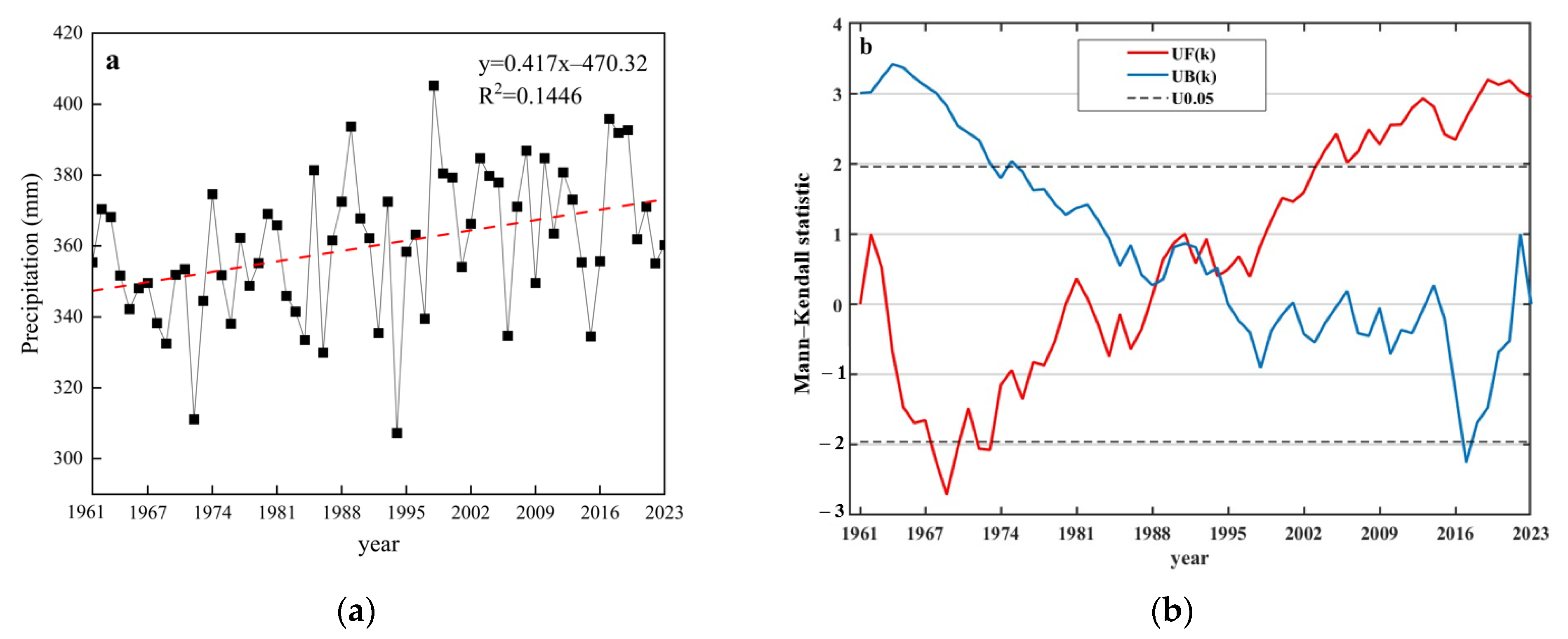
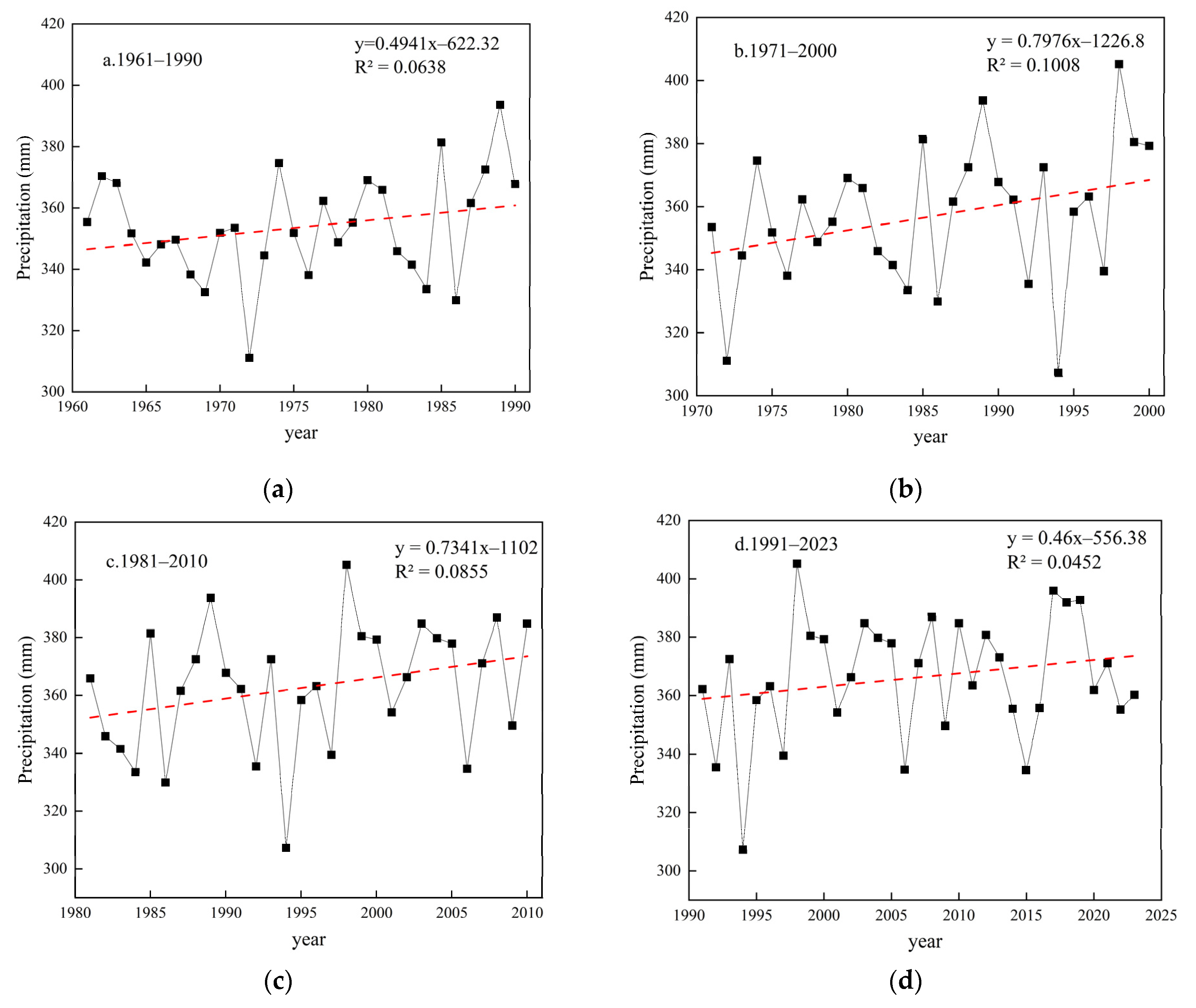
3.1.1. Long-Term Mean Precipitation and Interannual Variability
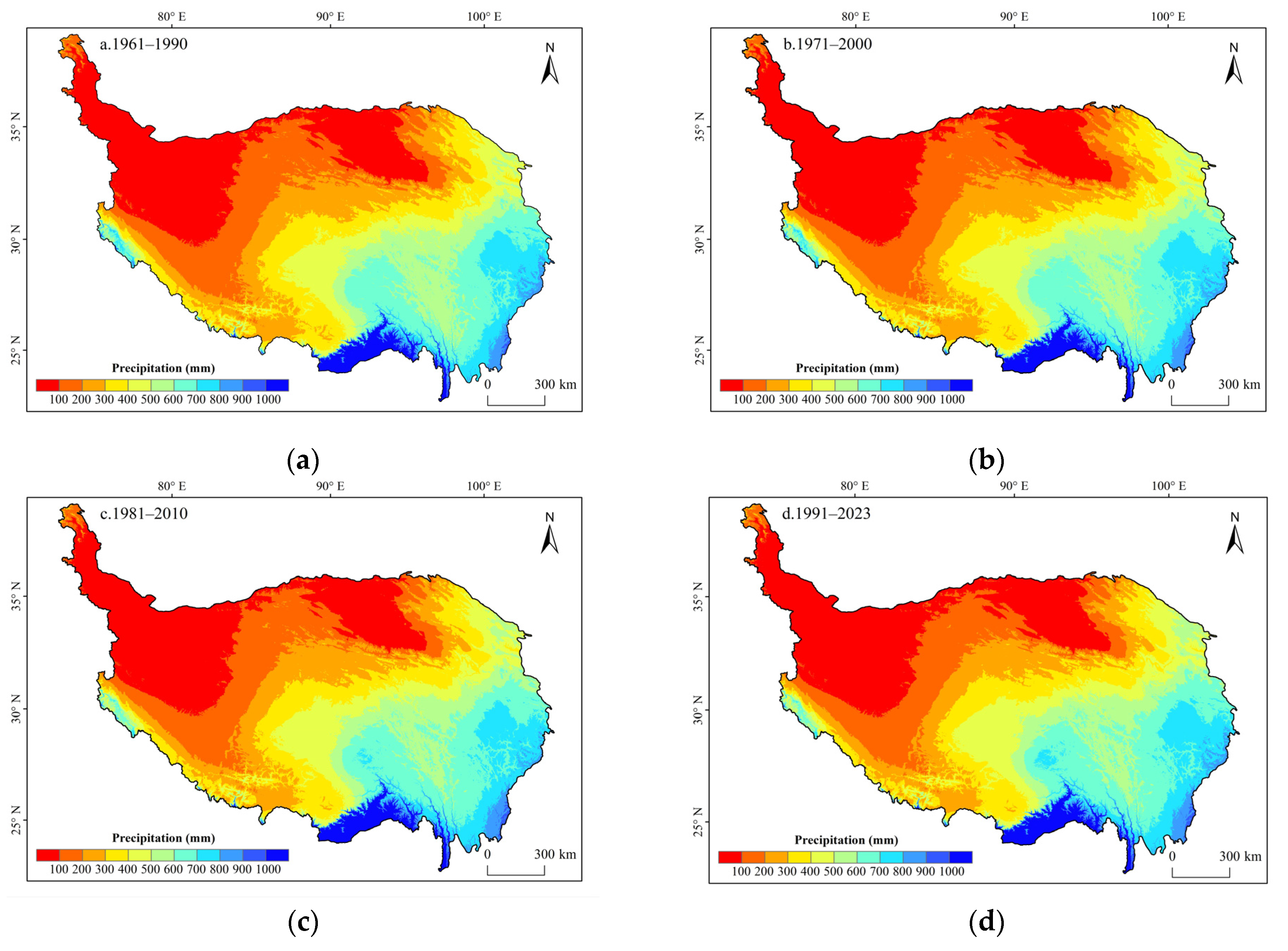
3.1.2. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Multi-Decadal Average Precipitation for Four Periods
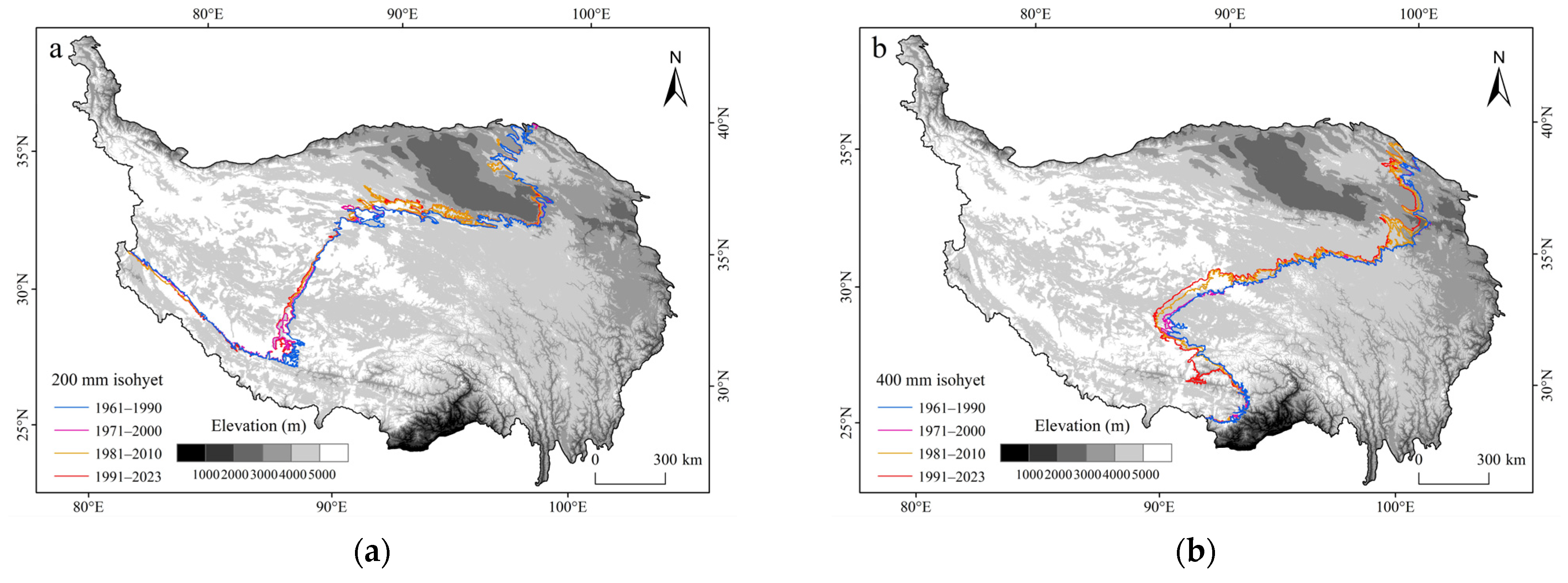
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Iso-Precipitation Line and Its Centroid over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023
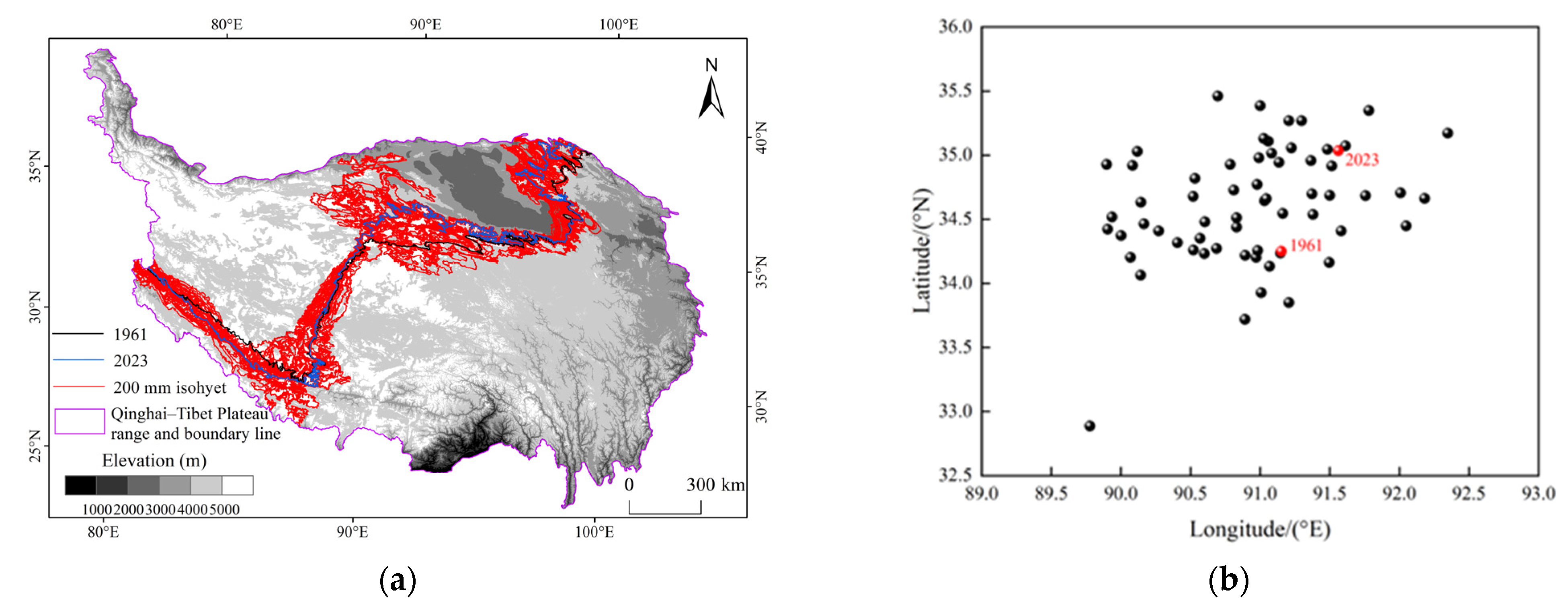
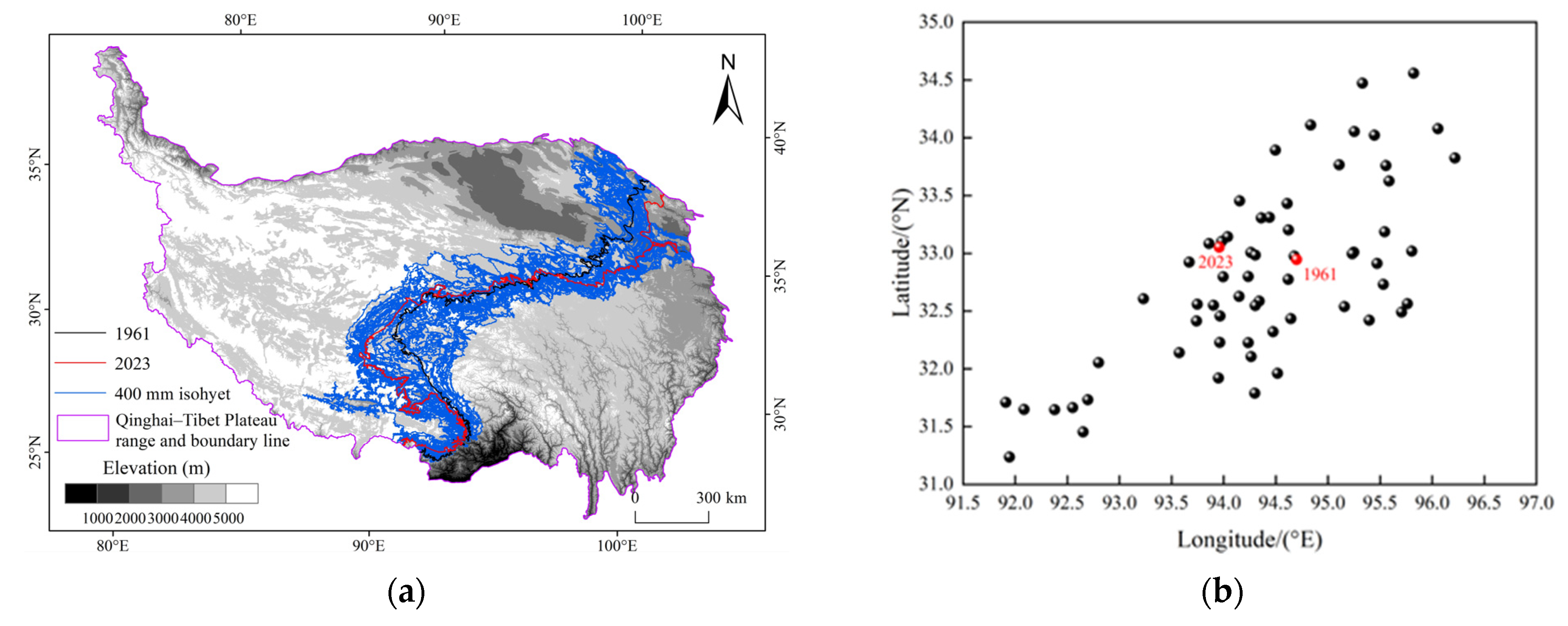
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Isohyets and Their Centroids over Multiple Years
3.2.2. Temporal and Spatial Distribution of Isohyets During Four Periods
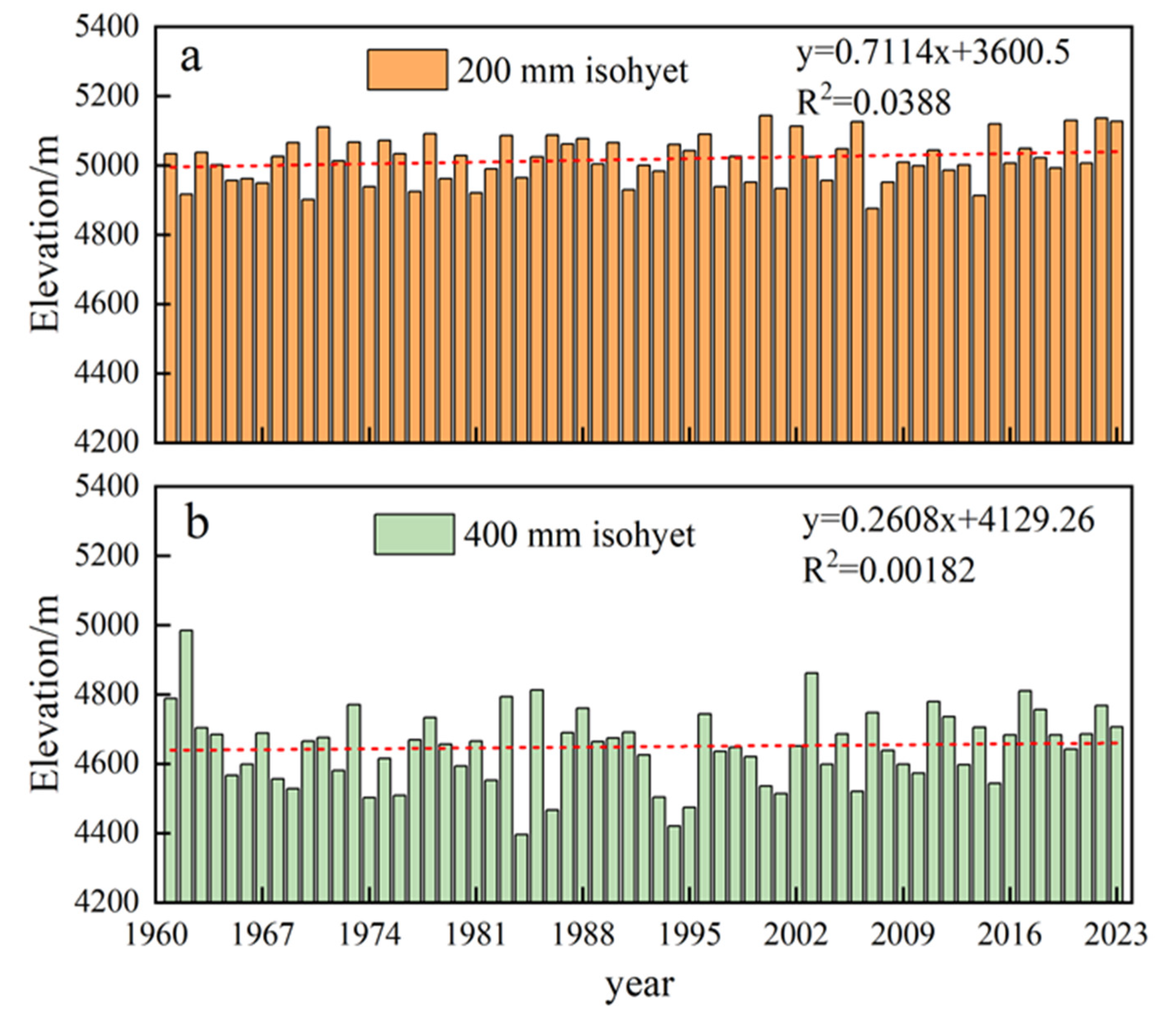
3.3. The Variation of Precipitation Lines, Such as 200 mm and 400 mm, in the Vertical Gradient
4. Discussion
4.1. The Impact of Climate Warming on Moisture Transport over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
4.2. The Influence of Changes in the Precipitation Patterns on the Plateau’s Water Cycle and Ecosystem Evolution
4.3. The Impact of Shifts in Isopluvial Lines on Agricultural Production
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ye, B.; Yao, S. Spatiotemporal variations in temperature and precipitation in Northwest China over the past 50 years. Plateau Meteorol. 2011, 30, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Qin, Y.; Gao, X. Interpretation of the Main Conclusions and Suggestions of IPCC AR6 Working Group I Report. Environ. Prot. 2021, 49, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The changing character of precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.; Yao, T.; Wang, N.; Tian, L.; Xu, B. The difference in precipitation variability between the north and south Qinghai-Tibet Plateaus. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 726–732. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.; Kong, F. Research on Related Factors to Decadal Accumulated Heavy Rainfall Spatio-temporal Patterns Change in China During 1951–2010. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, A.Y.; Kakar, R.K.; Neeck, S.; Azarbarzin, A.A.; Kummerow, C.D.; Kojima, M.; Iguchi, T. The global precipitation measurement mission. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 95, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blacutt, L.A.; Herdies, D.L.; de Gonçalves, L.G.G.; Vila, D.A.; Andrade, M. Precipitation comparison for the CFSR, MERRA, TRMM3B42 and Combined Scheme datasets in Bolivia. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, T.; Guo, Z.; Cui, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.; Fan, J.; et al. Assessment of past, present and future environmental changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3025–3035. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Thompson, L.; Yang, W. Different glacier status with atmospheric circulations in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and surroundings. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 663–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T. A comprehensive study of Water-Ecosystem-Human activities reveals unbalancing Asian Water Tower and accompanying potential risks. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2761–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, T.; Wu, W.; Zhang, K.; Feng, A.; Shen, Z. Water circulation and water resources of Asia’s water tower. The past and future. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 4982–4994. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Bolch, T.; Chen, D.; Gao, J.; Immerzeel, W.; Piao, S.; Wu, F.; Thompson, L.; Wada, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. The imbalance of the Asian water tower. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouregaa, T.; Fenni, M. Assessment of inter-seasonal temperature and precipitation changes under global warming over Setif high plains region, vulnerability and adaptation. World J. Sci. Technol. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 11, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdiguer-Lopez, R.; Berne, V.J.L.; Garrido-Villen, N. GNSS-retrieved precipitable water vapour in the Atlantic coast of France and Spain with GPT3 model. Acta Geod. Et Geophys. 2023, 58, 575–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasamak, W.; Soisuvarn, S.; Rangsanseri, Y. Empirical Model for Total Precipitable Water Retrieval from Ground-based GNSS Observations in Thailand. J. Mob. Multimed. 2020, 16, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Inatsu, M. Stochastic Precipitation Model Using Large Ensemble Data: Regular Papers. J. Disaster Res. 2023, 18, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, B.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, S. TRMM-data- based spatial and seasonal patterns of precipitation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 999–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Temporo-spatial distribution of summer precipitation over Qinghai-Tibet plateau during the Last 44 year. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 945–958. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Interpretation Skills of Isotherm Maps and Isoprecipitation Maps. Questions and Research. 2014, pp. 60–63. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=ygxn0A4FGUHRccwi0vFPuu40l7PiXa-nFeVTeS2z-UuMChOQ5mefjhoO9pNeIsa3kTvs8tCt2s6CNnrQ8X7X2HnTukequwCdVDNJ4ZKyMebR0DflzhYL4DQpXLOHJS6CcBTv-3VwCB1ce-30-pF3hmgCUIKsBJGJ9uPlifqP5YZNvoHMf2HKtg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Che, Y.; Guan, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, R. Spatial analysis of annual precipitation lines of 800 mm in the eastern monsoon of China. Plateau Meteorl. 2020, 39, 997–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, M. Migration and its in ducements of 400 mm precipitation contour in the mainland China from 1951 to 2012 year. J. Henan Polytech Nic Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2016, 35, 520–525. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, F. Advances in the study of the 400 mm isohyet migrations and wetness and dryness changes on the Chinese mainland. Adv. Earth Sci. 2020, 35, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Study on Spatial and Temporal Variation of the Bound Ary and Area of the Semi-Arid Region in Northern China over the Past 60 Years. Master’s Thesis, Northwest University, Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Yao, T. Research progress on formation and evolution of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its environmental and resource effects. Chin. Basic Sci. 2004, 6, 15–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhen, X.; Song, J. The environmental impacts and response strategies in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under the global changes. China Tibetol. 2021, 4, 21–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liao, Y.; Duan, J.; Song, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, S. The progresses of dry-wet climate divisional research in China. Clim. Change Res. 2016, 12, 261–267. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Qin, D.; Wang, J. A study of the spatial shift of 400 mm-rainfall contours in the yellow river ba sin during recent 50 years. Adv. Earth Sci. 2005, 20, 649–655. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Zheng, D. A discussion on the boundary and area of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. Geogr. Res. 2002, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Dong, X.; Wei, C.; Ouyang, X.; Wu, H. Precipitation Division of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1978 to 2018 and Spatio-temporal Evolution Characteristics of Each Zone. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2022, 33, 96–108. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y. Temporal-Spatial Characteristics of Precipitation over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Dong, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Effect of the Asian Water Tower over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the characteristics of atmospheric water circulation. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2830–2841. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Yao, T.; Delmotte, V.M.; Steen-Larsen, H.C.; Wang, W. Collapsing glaciers threaten Asia’s water supplies. Nature 2019, 565, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Tang, Z. Effects of changed Asian water tower on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau ecosystem: A review. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H. Advances in research on wetlands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Ma, Y. The impact of “Asian Water Tower” change on the geopolitical environment around China. World Reg. Stud. 2020, 29, 223–231. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, Z. 1 km monthly temperature and precipitation dataset for China from 1901 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F. Modern Climate Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction Techniques; Meteorological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J. Quantitative Geography, 2nd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Yan, D.; Yang, Z.; Yin, J.; Yuan, Y. Research on temporal and spatial change of 400 mm and 800 mm rainfall contours of China in 1961–2000. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 494–502. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y. Characteristics of extreme precipitation over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2017. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 3039–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Guo, Z. Discriminating the law of geographical differentiation based on the idea of scale. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Geogr. 2015, 16, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Sun, Y.; Qiao, W. Analysis of the temporal and spatial variation patterns of precipitation in Lanxi Bridge Reservoir from 1963 to 2021. Water Resour. Sci. Cold Reg. Eng. 2024, 7, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Yao, J.; He, Q.; Chen, J. Elevation-Dependent Trends in Precipitation Observed over and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau from 1971 to 2017. Water 2021, 13, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, H. Comprehensive analysis of the precipitation changes over the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during 1961–2015. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2018, 40, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Li, J. Quickly calculate the distance between two points and measurement error based on latitude and longitude. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2013, 36, 235–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y. Water vapor sources and their contributions to precipitation change in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Adv. Water Sci. 2024, 35, 890–899. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Xie, T.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, J. Discussion of the “warming and wetting” trend and its future variation in the drylands of Northwest China under global warming. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 66, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, D.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhou, A. Holocene summer monsoon varation and environmental reponse in the drainage basin of lake Bande in the inner Tibetan Plateau. Quatemary Sci. 2022, 42, 1328–1348. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, F.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, D. Research progress on moisture source change of precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding areas. Trans. Atmos. Sci. 2020, 43, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. Study on the Correlation Between Drought and Snow Disaster and Monsoon Circulation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Master’s Thesis, Qinghai Normal University, Xining, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Lu, F.; Cai, Y.; Yu, H.; Guo, H.; Fu, C.; Fan, W.; Wu, D. Progress of recent 60 years climate change and its environmental impacts on the Qinghai-Xizang plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2022, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Duan, K.; Shang, W.; Shi, P.; Meng, Y. Characteristics of Precipitation Change over the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau from 1961 to 2099 based on CMIP6 Models. Plateau Meteorol. 2023, 42, 294–304. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Ran, J. Global semi-arid climate change over last 60 years. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 46, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Sha, T.; Zhang, C. A dataset of boundaries data of the lakes (≥1.0 km2) in Qinghai Province in 2020. Sci. Data Bank 2023, 8, 315–327. [Google Scholar]
- Qinghai Provincial Water Resources Department. 2023 Qinghai Provincial Water Resources Bulletin; Qinghai Provincial Water Resources Department: Xining, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Bai, W.; Ding, M.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Xu, E.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. Spatial and temporal characteristics of land use and cover changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2019, 64, 2865–2875. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W. Evaluation of impact of climate change on Highland barley cultivation in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ph.D. Thesis, Qinghai Normal University, Xining, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, H.; Qiao, B.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H. Research progress on the impact of climate change on vegetation ecosystem in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Arid. Meteorol. 2022, 40, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Wang, J. Changes in the altitude of barley cultivation in the context of climate change—A case study of Menyuan County. Qinghai Environ. 2024, 34, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Song, W. Integrating potential ecosystem services losses into ecological risk assessment of land use changes: A case study on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 318, 115607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zhi, Z.; Liu, R.; Ma, W. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Isohyets on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060698
Liu X, Zhou Q, Ma Y, Zhi Z, Liu R, Ma W. Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Isohyets on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(6):698. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060698
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xuan, Qiang Zhou, Yonggui Ma, Zemin Zhi, Rui Liu, and Weidong Ma. 2025. "Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Isohyets on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023" Atmosphere 16, no. 6: 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060698
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhou, Q., Ma, Y., Zhi, Z., Liu, R., & Ma, W. (2025). Temporal and Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation Isohyets on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau from 1961 to 2023. Atmosphere, 16(6), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060698





