The Effects of Nonplanar Cloud Top on Lightning Optical Observations from Space-Based Instruments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Simulation Process
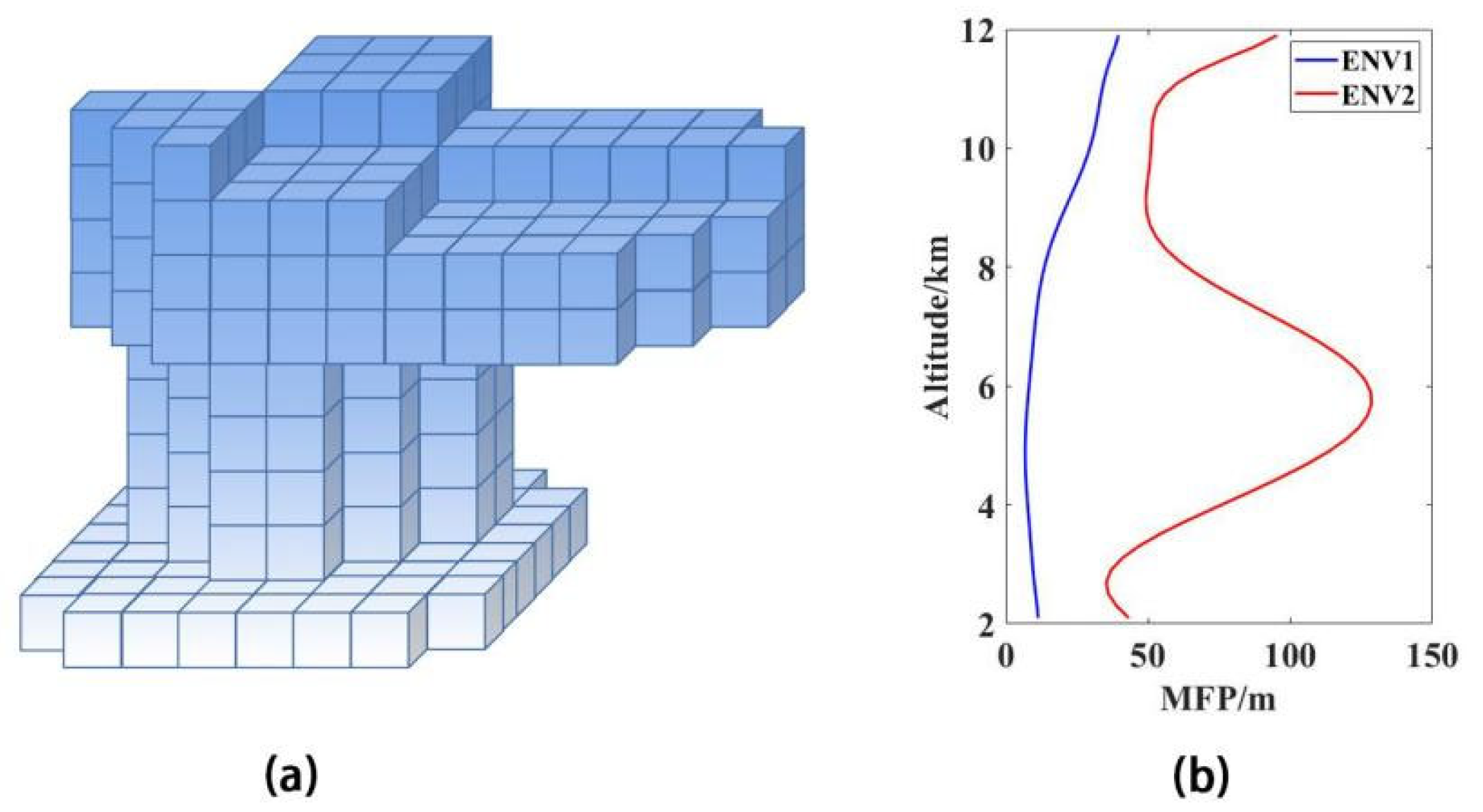
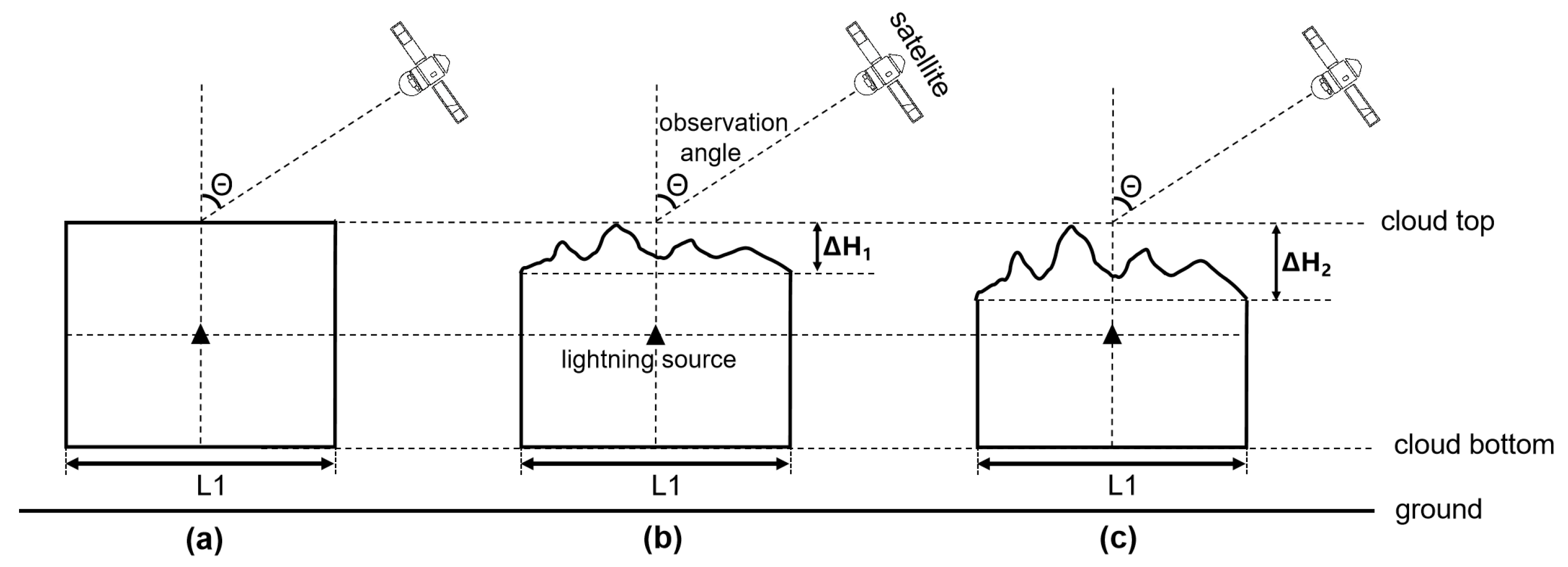
2.2. Cloud Settings
2.3. Lightning Source
2.4. Observation Angle
3. Results
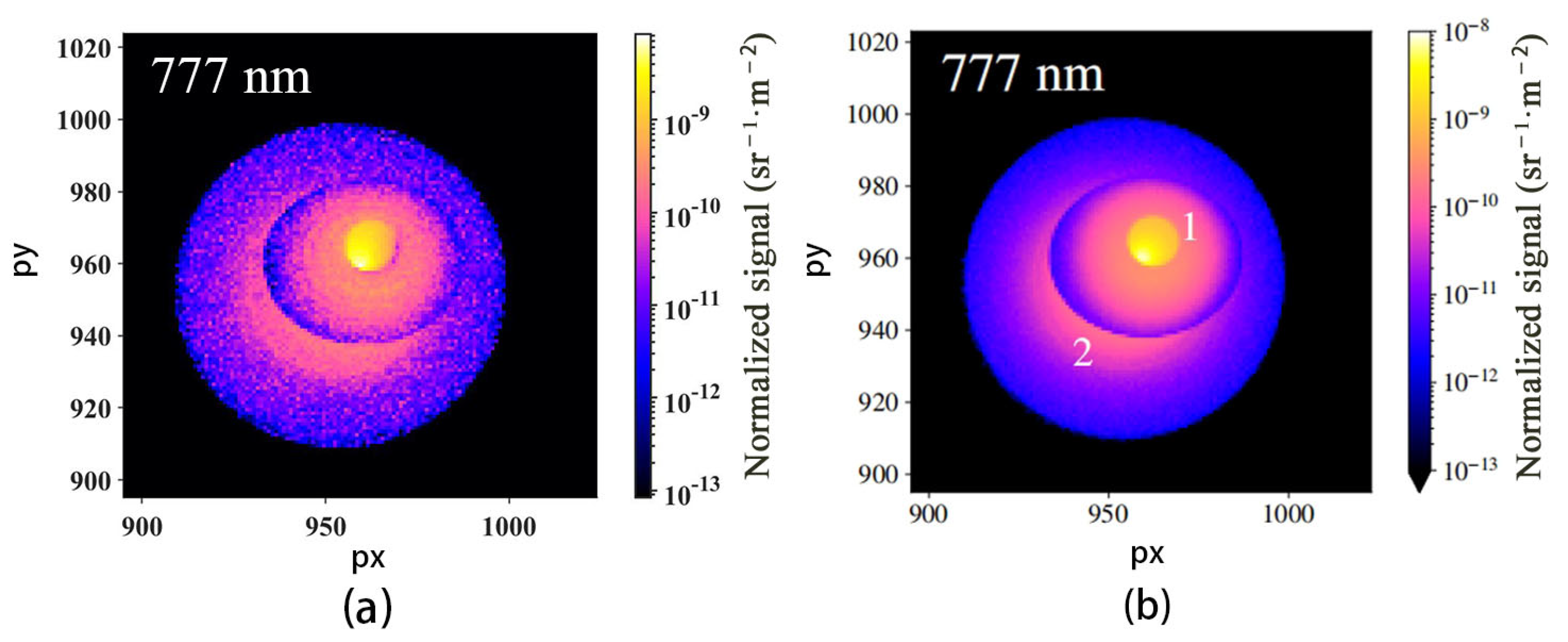
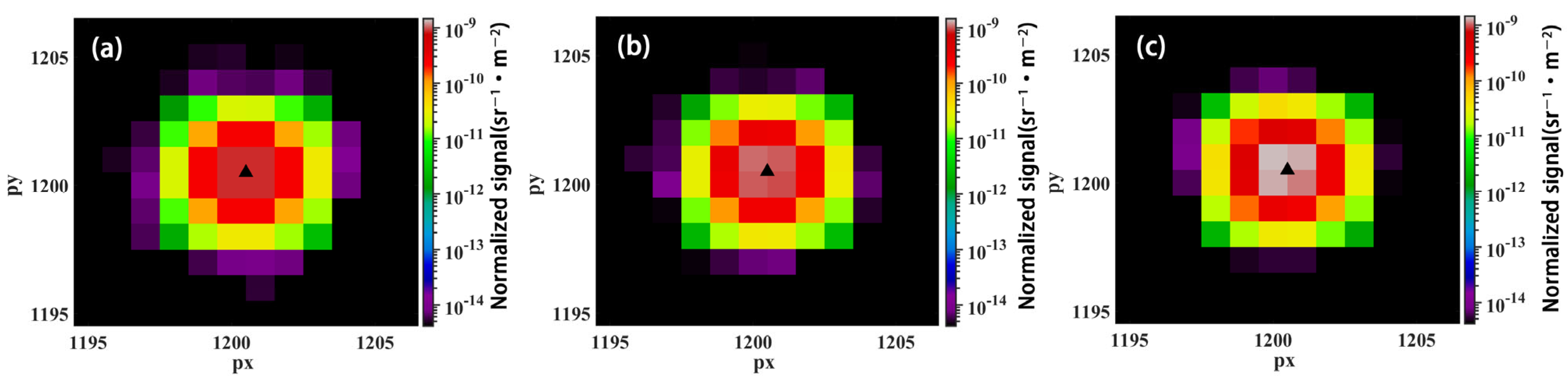
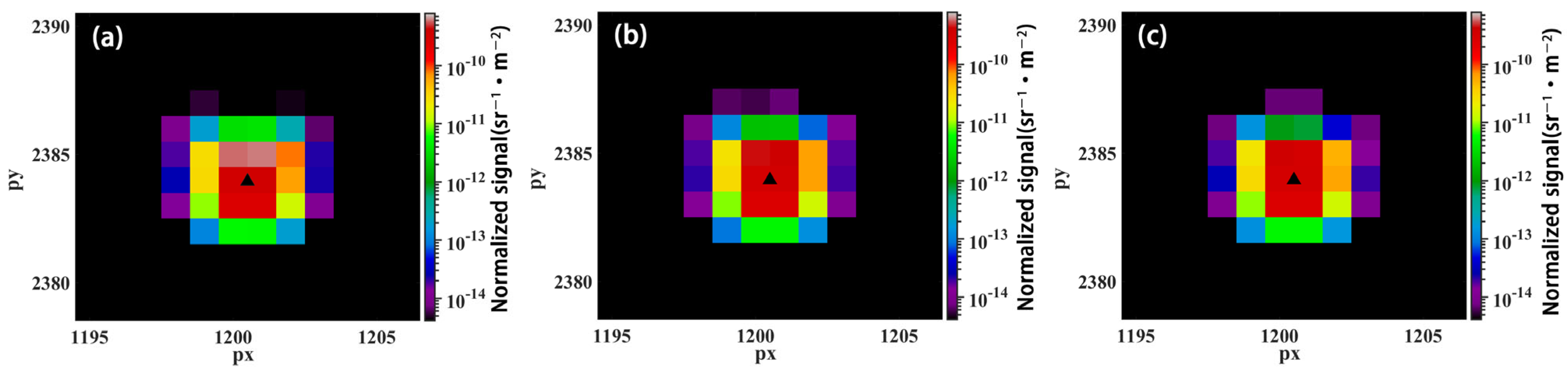
3.1. Model Verification
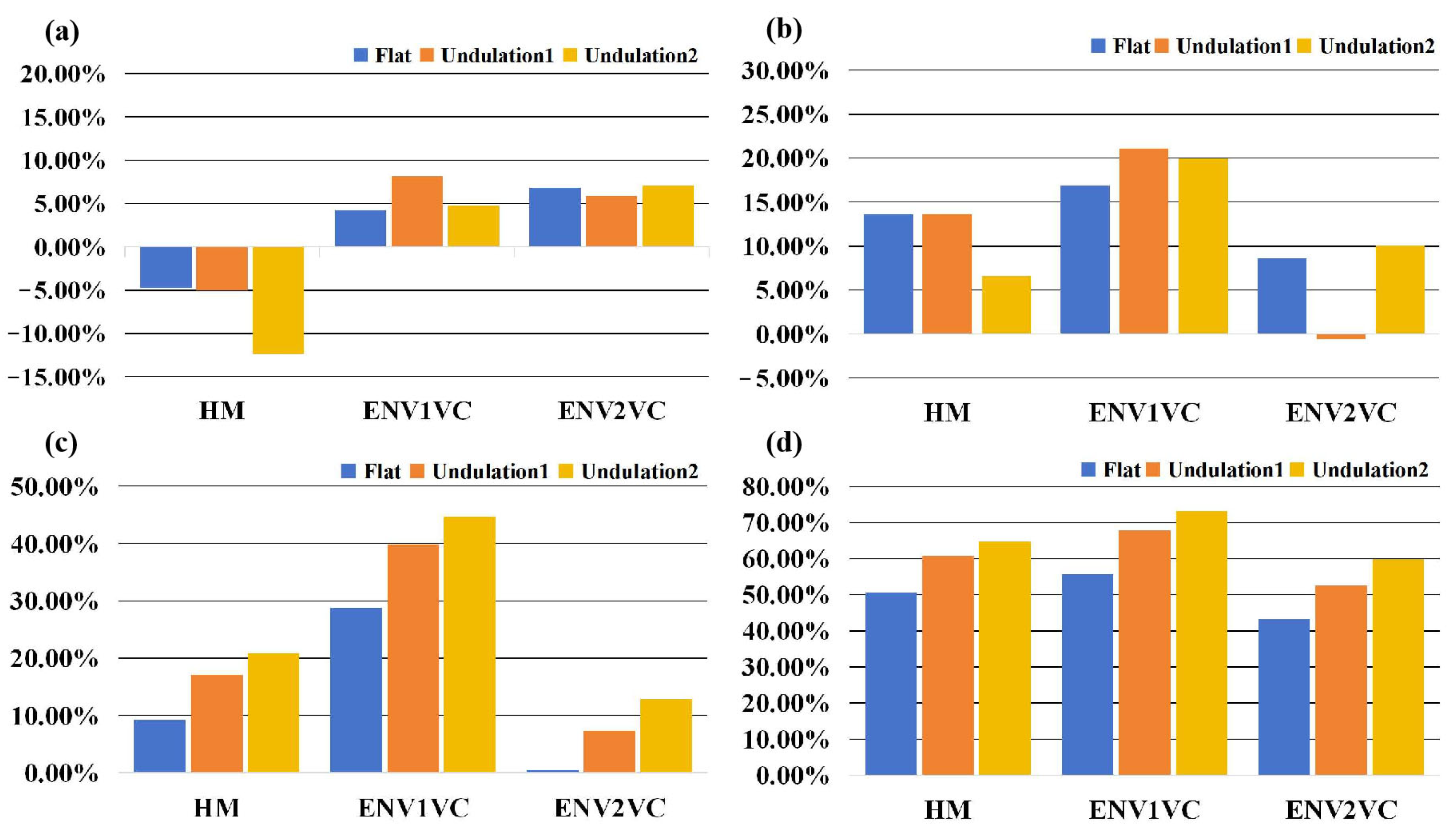
3.2. The Effect of Nonplanar Cloud Top
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLM | Geostationary Lightning Mapper |
| LIS | Lightning Imaging Sensor |
| LMI | Lightning Mapping Imager |
| MCARaTS | Monte Carlo Atmospheric Radiative Transfer Simulator |
| MFP | mean free path |
| OTD | Optical Transient Detector |
| WRF | Weather Research and Forecasting |
References
- Boccippio, D.J.; Koshak, W.; Blakeslee, R.; Driscoll, K.; Mach, D.; Buechler, D.; Boeck, W.; Christian, H.J.; Goodman, S.J. The Optical Transient Detector (OTD): Instrument characteristics and cross-sensor validation. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 441–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeslee, R.J.; Lang, T.J.; Koshak, W.J.; Buechler, D.; Gatlin, P.; Mach, D.M.; Stano, G.T.; Virts, K.S.; Walker, T.D.; Cecil, D.J.; et al. Three years of the lightning imaging sensor onboard the international space station: Expanded global coverage and enhanced applications. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD032918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, S.J.; Blakeslee, R.J.; Koshak, W.J.; Mach, D.; Bailey, J.; Buechler, D.; Carey, L.; Schultz, C.; Bateman, M.; McCaul, E.; et al. The GOES-R geostationary lightning mapper (GLM). Atmos. Res. 2013, 125, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudlosky, S.D.; Goodman, S.J.; Virts, K.S.; Bruning, E.C. Initial geostationary lightning mapper observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, C.; Lu, F.; Guo, Q. Introducing the new generation of Chinese geostationary weather satellites, Fengyun-4. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1637–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, L.W.; Krider, E.P. The effects of clouds on the light produced by lightning. J. Atmos. Sci. 1982, 39, 2051–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshak, W.J.; Solakiewicz, R.J.; Phanord, D.D.; Blakeslee, R.J. Diffusion model for lightning radiative transfer. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1994, 99, 14361–14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, T.E.; Suszcynsky, D.M.; Jacobson, A.R. Coincident radio frequency and optical emissions from lightning, observed with the FORTE satellite. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 28223–28231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, N.; Carey, L.D.; Schultz, C. An analysis of the lightning jump algorithm using geostationary lightning mapper flashes. In Proceedings of the International Lightning Detection Conference (ILDC 2018), Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 12–15 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, B.R.; Rutledge, S.A. Investigation of lightning flash locations in isolated convection using LMA observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 6158–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M. Using lightning flashes to image thunderclouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 10175–10185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, M.; Hilburn, K.; Miller, S.D. Geostationary Lightning Mapper and Earth Networks lightning detection over the contiguous United States and dependence on flash characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 11552–11567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M.; Liu, C. Characteristics of lightning flashes with exceptional illuminated areas, durations, and optical powers and surrounding storm properties in the tropics and inner subtropics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M. Holes in optical lightning flashes: Identifying poorly transmissive clouds in lightning imager data. Earth Space Sci. 2021, 8, e2020EA001294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, M. Modeling the transmission of optical lightning signals through complex 3-D cloud scenes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, K.N.; Bitzer, P.M. A first look at cloud inhomogeneity and its effect on lightning optical emission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, A.; Gordillo-Vázquez, F.J.; Li, D.; Malagón-Romero, A.; Pérez-Invernón, F.J.; Schmalzried, A.; Soler, S.; Chanrion, O.; Heumesser, M.; Neubert, T.; et al. Modeling lightning observations from space-based platforms (CloudScat. jl 1.0). Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 5549–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriedt, T. Mie theory: A review. In The Mie Theory: Basics and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Twersky, V. Rayleigh scattering. Appl. Opt. 1964, 3, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielson, R.E.; Moore, D.R.; Van de Hulst, H.C. The transfer of visible radiation through clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 1969, 26, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and scattering by a sphere. In Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1983; Volume 7, pp. 82–129. [Google Scholar]
- Iwabuchi, H. Efficient Monte Carlo methods for radiative transfer modeling. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 2324–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, B.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, X. The Effects of Nonplanar Cloud Top on Lightning Optical Observations from Space-Based Instruments. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060657
Dai B, Zhang Q, Pan X. The Effects of Nonplanar Cloud Top on Lightning Optical Observations from Space-Based Instruments. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(6):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060657
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Bingzhe, Qilin Zhang, and Xingke Pan. 2025. "The Effects of Nonplanar Cloud Top on Lightning Optical Observations from Space-Based Instruments" Atmosphere 16, no. 6: 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060657
APA StyleDai, B., Zhang, Q., & Pan, X. (2025). The Effects of Nonplanar Cloud Top on Lightning Optical Observations from Space-Based Instruments. Atmosphere, 16(6), 657. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16060657





