Comparison of the Chemical Composition of the Middle Atmosphere During Energetic Particle Precipitation in January 2005 and 2012
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EPP During Solar Proton Events and Geomagnetic Disturbances in January of 2005 and 2012
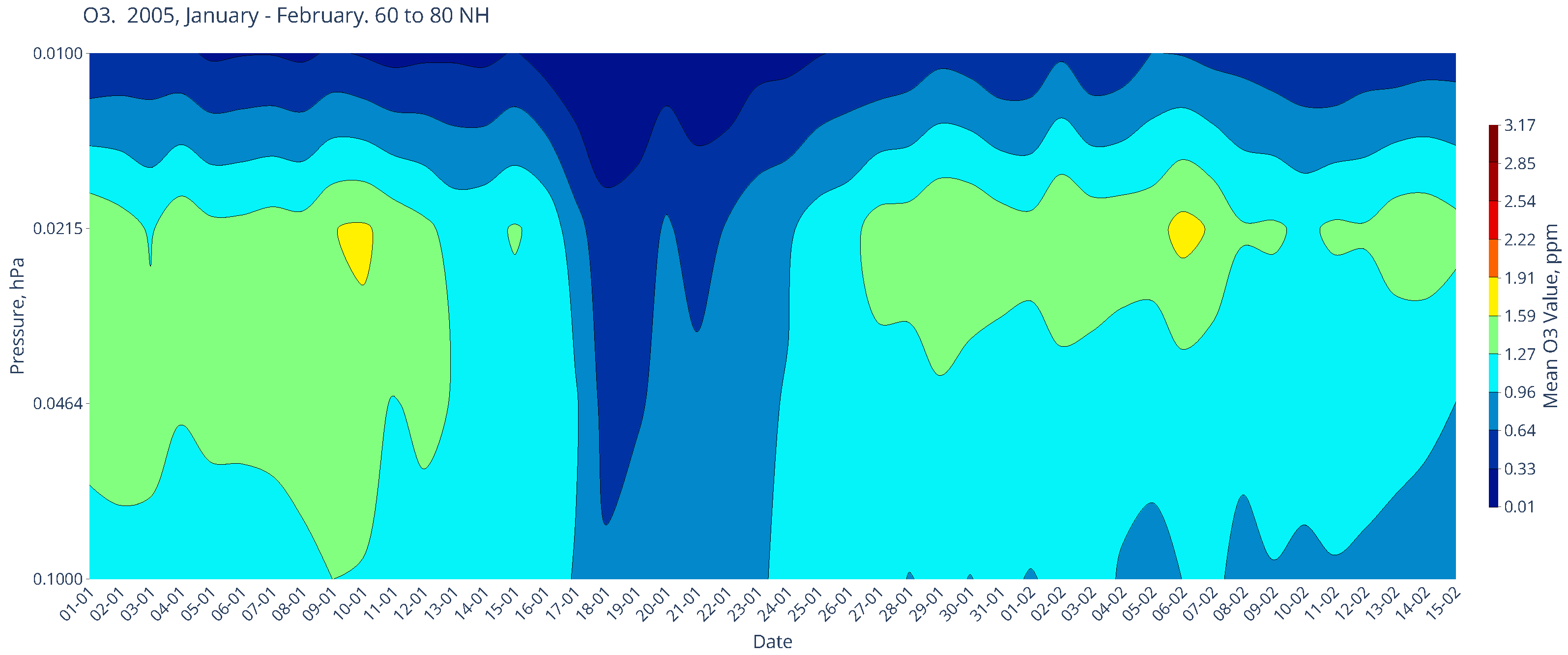
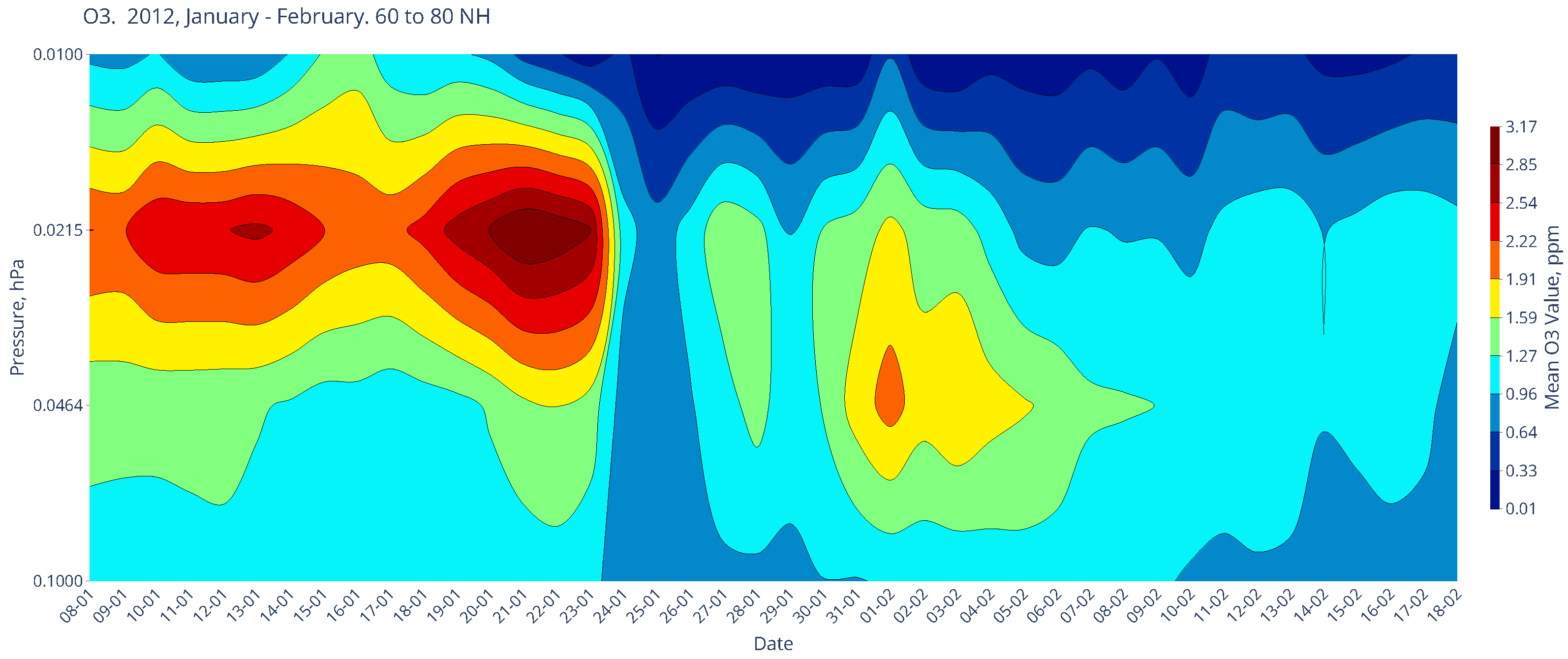
Chemical Composition in January of the Boreal Winters of 2005 and 2012
3. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Randall, C.E.; Harvey, V.L.; Manney, G.L.; Orsolini, Y.; Codrescu, M.; Sioris, C.; Brohede, S.; Haley, C.S.; Gordley, L.L.; Zawodny, J.M.; et al. Stratospheric effects of energetic particle precipitation in 2003–2004. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L05802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, E.; Calisto, M.; Egorova, T.; Peter, T.; Schmutz, W. Influence of the Precipitating Energetic Particles on Atmospheric Chemistry and Climate. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, I.A.; Aplin, K.L.; Arnold, F.; Bazilevskaya, G.A.; Harrison, R.G.; Krivolutsky, A.A.; Nicoll, K.A.; Rozanov, E.V.; Turunen, E.; Usoskin, I.G. Energetic Particle Influence on the Earth’s Atmosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 194, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, K.; Funke, B.; Andersson, M.E.; Barnard, L.; Beer, J.; Charbonneau, P.; Clilverd, M.A.; Dudok de Wit, T.; Haberreiter, M.; Hendry, A.; et al. Solar forcing for CMIP6 (v3.2). Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 2247–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnhuber, M.; Berger, U.; Funke, B.; Nieder, H.; Reddmann, T.; Stiller, G.; Versick, S.; von Clarmann, T.; Maik Wissing, J. NOy production, ozone loss and changes in net radiative heating due to energetic particle precipitation in 2002–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1115–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, C.; Harvey, L.; Pedatella, N.; Bailey, S.; Maruyama, N.; Chen, T. Sun-Earth Coupling via Energetic Particle Precipitation. Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 2023, 55, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Kovaltsov, G.A.; Mironova, I.A. Cosmic ray induced ionization model CRAC:CRII: An extension to the upper atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D10302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Randall, C.E.; Lummerzheim, D.; Wang, W.; Lu, G.; Solomon, S.C.; Frahm, R.A. Parameterization of monoenergetic electron impact ionization. Geoph. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L22106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonov, A.A.; Mishev, A.L.; Usoskin, I.G. Atmospheric ionization induced by precipitating electrons: Comparison of CRAC:EPII model with a parametrization model. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2016, 149, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Marshall, R.A.; Tyssøy, H.N.; Fang, X. A Generalized Method for Calculating Atmospheric Ionization by Energetic Electron Precipitation. J. Geophys. Res. 2020, 125, e28482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, I.; Kovaltsov, G.; Mishev, A.; Artamonov, A. Ionization in the Earth’s Atmosphere Due to Isotropic Energetic Electron Precipitation: Ion Production and Primary Electron Spectra. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Kovaltsov, G.A.; Mishev, A.L. Updated model of cosmic-ray-induced ionization in the atmosphere (CRAC:CRII_v3): Improved yield function and lookup tables. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2024, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycroft, M.J.; Nicoll, K.A.; Aplin, K.L.; Giles Harrison, R. Recent advances in global electric circuit coupling between the space environment and the troposphere. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2012, 90, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozóki, T.; Sátori, G.; Williams, E.; Mironova, I.; Steinbach, P.; Bland, E.C.; Koloskov, A.; Yampolski, Y.M.; Budanov, O.V.; Neska, M.; et al. Solar cycle-modulated deformation of the Earth-ionosphere cavity. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.S. Calculation of rate coefficients of electron energy transfer processes for molecular nitrogen and molecular oxygen. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 33, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, C.H.; Marsh, D.R.; Vitt, F.M.; Garcia, R.R.; Fleming, E.L.; Labow, G.J.; Randall, C.E.; López-Puertas, M.; Funke, B.; von Clarmann, T.; et al. Short and medium term atmospheric constituent effects of very large solar proton events. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 765–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacza, J.; Raulin, J.P.; Mendonca, R.R.S.; Makhmutov, V.S.; Marun, A.; Fernandez, G. Solar Effects on the Atmospheric Electric Field During 2010–2015 at Low Latitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 11970–11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraner, K.; Schmidt, H. Climate impact of idealized winter polar mesospheric and stratospheric ozone losses as caused by energetic particle precipitation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishev, A.L. Application of the global neutron monitor network for assessment of spectra and anisotropy and the related terrestrial effects of strong SEPs. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2023, 243, 106021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, K.; Veretenenko, S. Solar influences on the Earth’s atmosphere: Solved and unsolved questions. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2023, 10, 1244402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chum, J.; Langer, R.; Kolmašová, I.; Lhotka, O.; Rusz, J.; Strhárský, I. Solar cycle signatures in lightning activity. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 9119–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siingh, D.; Singh, R.; Victor, N.J.; Kamra, A. The DC and AC global electric circuits and climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 244, 104542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winant, A.; Pierrard, V.; Botek, E.; Herbst, K. The Atmospheric Influence on Cosmic-Ray-Induced Ionization and Absorbed Dose Rates. Universe 2023, 9, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, B.; Baumgaertner, A.; Calisto, M.; Egorova, T.; Jackman, C.H.; Kieser, J.; Krivolutsky, A.; López-Puertas, M.; Marsh, D.R.; Reddmann, T.; et al. Composition changes after the “Halloween” solar proton event: The High Energy Particle Precipitation in the Atmosphere (HEPPA) model versus MIPAS data intercomparison study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9089–9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.E.; Verronen, P.T.; Marsh, D.R.; Seppälä, A.; Päivärinta, S.M.; Rodger, C.J.; Clilverd, M.A.; Kalakoski, N.; van de Kamp, M. Polar Ozone Response to Energetic Particle Precipitation Over Decadal Time Scales: The Role of Medium-Energy Electrons. J. Geophys. Res. 2018, 123, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, I.; Karagodin-Doyennel, A.; Rozanov, E. The effect of Forbush decreases on the polar-night HOx concentration affecting stratospheric ozone. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 8, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grankin, D.; Mironova, I.; Bazilevskaya, G.; Rozanov, E.; Egorova, T. Atmospheric Response to EEP during Geomagnetic Disturbances. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doronin, G.; Mironova, I.; Bobrov, N.; Rozanov, E. Mesospheric Ozone Depletion during 2004–2024 as a Function of Solar Proton Events Intensity. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rusch, D.W.; Gerard, J.C.; Reid, G.C.; Crutzen, P.J. The effect of particle precipitation events on the neutral and ion chemistry of the middle atmosphere: II. Odd hydrogen. Planet. Space Sci. 1981, 29, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, H.S.; Jackman, C.H.; Green, A.E.S. Efficiencies for production of atomic nitrogen and oxygen by relativistic proton impact in air. J. Chem. Phys. 1976, 65, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mironova, I.; Grankin, D.; Rozanov, E. Mesospheric Ozone Depletion Depending on Different Levels of Geomagnetic Disturbances and Seasons. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, C.H.; Deland, M.T.; Labow, G.J.; Fleming, E.L.; Weisenstein, D.K.; Ko, M.K.W.; Sinnhuber, M.; Russell, J.M. Neutral atmospheric influences of the solar proton events in October-November 2003. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, A09S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, C.H.; Marsh, D.R.; Vitt, F.M.; Roble, R.G.; Randall, C.E.; Bernath, P.F.; Funke, B.; López-Puertas, M.; Versick, S.; Stiller, G.P.; et al. Northern Hemisphere atmospheric influence of the solar proton events and ground level enhancement in January 2005. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6153–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Clarmann, T.; Funke, B.; López-Puertas, M.; Kellmann, S.; Linden, A.; Stiller, G.P.; Jackman, C.H.; Harvey, V.L. The solar proton events in 2012 as observed by MIPAS. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2339–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Kovaltsov, G.A.; Mironova, I.A.; Tylka, A.J.; Dietrich, W.F. Ionization effect of solar particle GLE events in low and middle atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, C.H.; Randall, C.E.; Harvey, V.L.; Wang, S.; Fleming, E.L.; López-Puertas, M.; Funke, B.; Bernath, P.F. Middle atmospheric changes caused by the January and March 2012 solar proton events. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, N.J.; Tang, A.J.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Stachnik, R.A.; Jarnot, R.; Kooi, J.W.; Millan, L.; Santee, M.L.; Chang, M.C.; Huang, R. A Continuity Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) instrument to augment the record from Aura MLS. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting, Online, 1–20 December 2020; Volume 2020, p. A197-09. [Google Scholar]
- Turunen, E.; Verronen, P.T.; Seppälä, A.; Rodger, C.J.; Clilverd, M.A.; Tamminen, J.; Enell, C.F.; Ulich, T. Impact of different energies of precipitating particles on NOx generation in the middle and upper atmosphere during geomagnetic storms. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2009, 71, 1176–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonov, A.; Mironova, I.; Kovaltsov, G.; Mishev, A.; Plotnikov, E.; Konstantinova, N. Calculation of atmospheric ionization induced by electrons with non-vertical precipitation: Updated model CRAC-EPII. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnhuber, M.; Nieder, H.; Wieters, N. Energetic Particle Precipitation and the Chemistry of the Mesosphere/Lower Thermosphere. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 1281–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, Y.J.; Urban, J.; Murtagh, D.P. Nitric acid in the stratosphere based on Odin observations from 2001 to 2009–Part 2: High-altitude polar enhancements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 7045–7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verronen, P.T.; Santee, M.L.; Manney, G.L.; Lehmann, R.; Salmi, S.M.; Seppälä, A. Nitric acid enhancements in the mesosphere during the January 2005 and December 2006 solar proton events. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
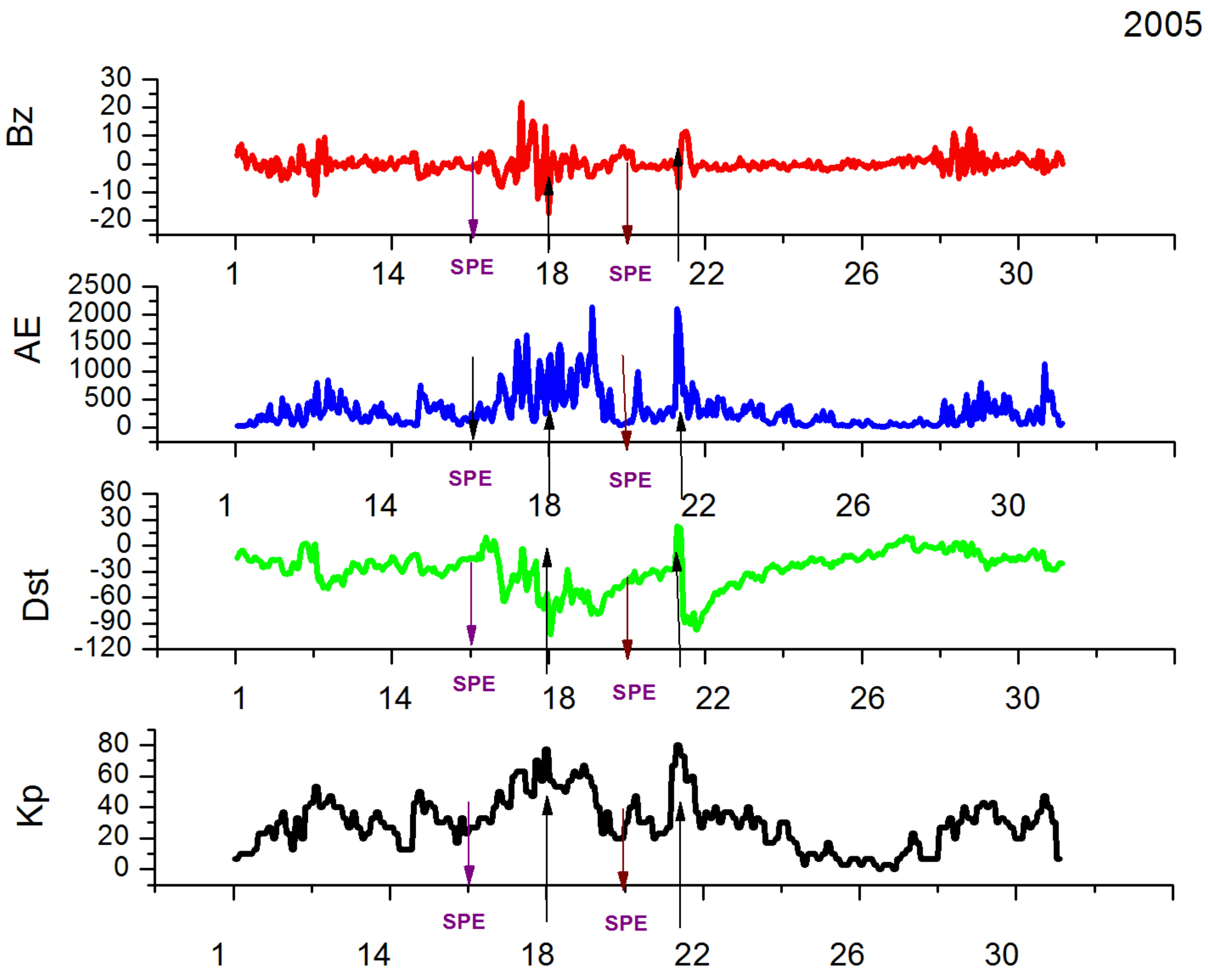

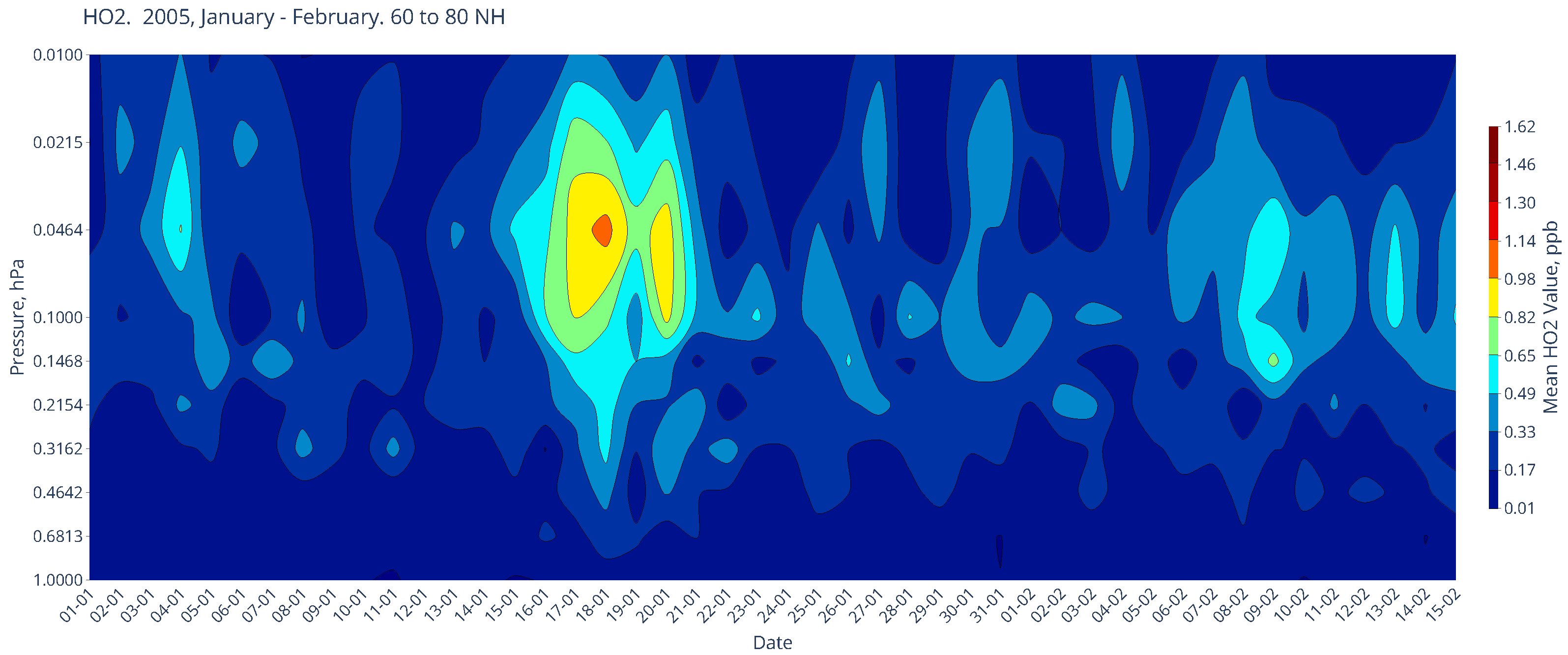
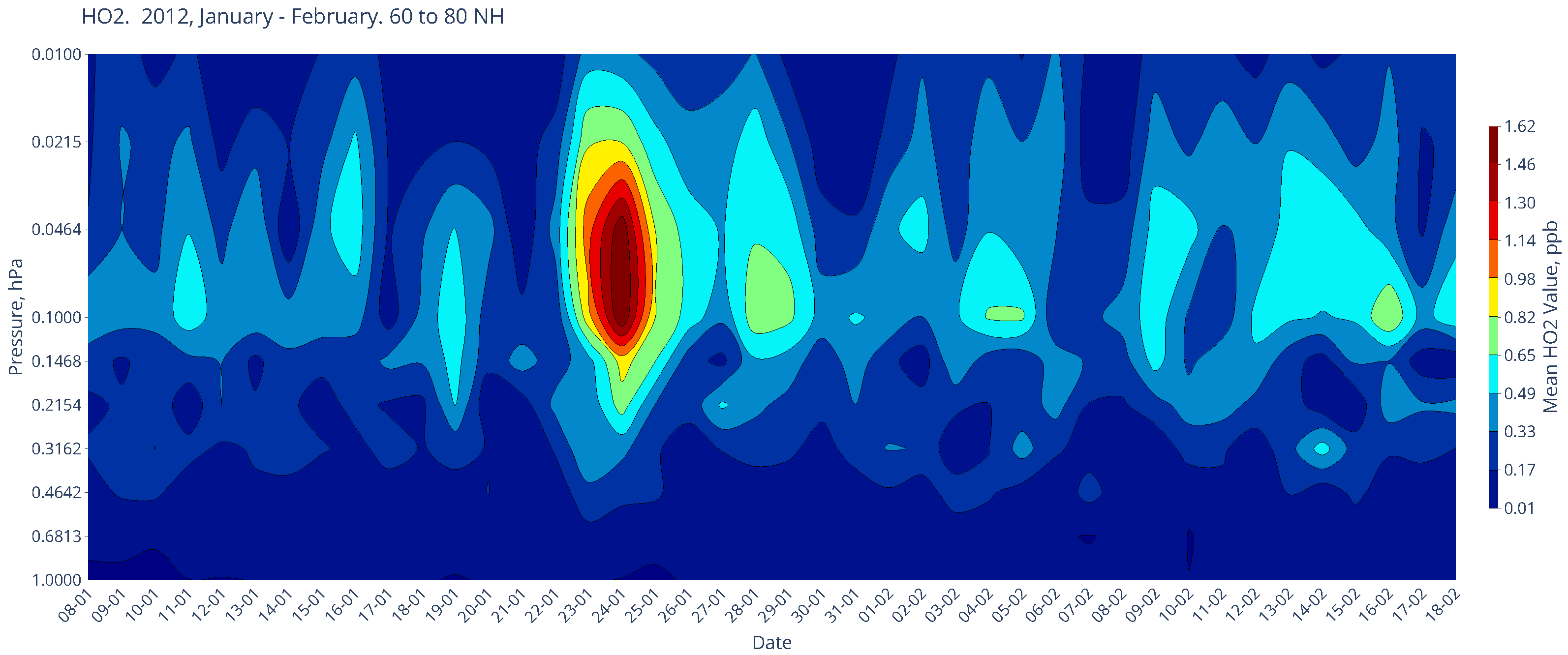
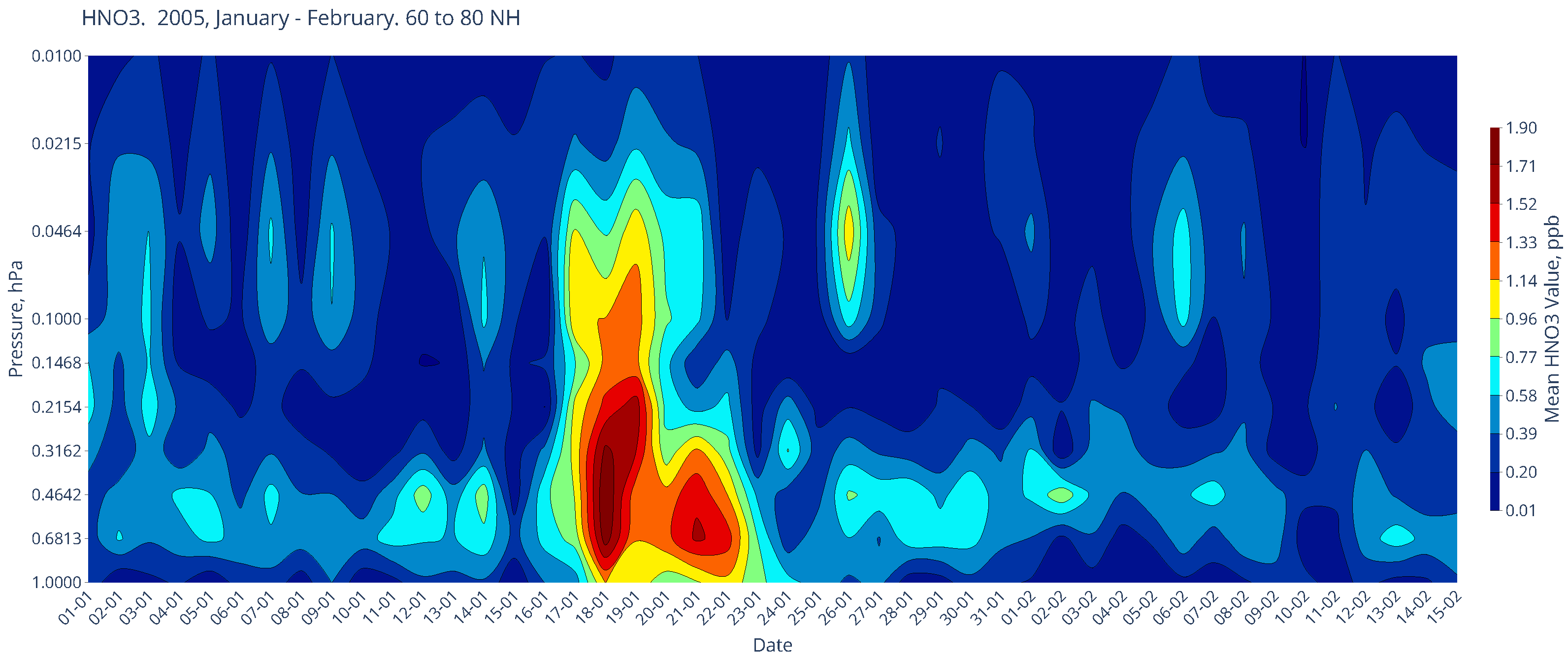

| SPE Start Date | SPE Maximum Date | >10 MeV Maximum (pfu) |
|---|---|---|
| D M Yr (UTC) | Yr M/D (UTC) | |
| 16 January 2005 (02:10) | 17 January 2005 (17:50) | 5040 |
| 20 January 2005 (—) | 20 January 2005 (08:10) | 1860 |
| 23 January 2012 (05:30) | 24 January 2012 (15:30) | 6310 |
| 27 January 2012 (19:05) | 28 January 2012 (02:05) | 796 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doronin, G.; Mironova, I.; Rozanov, E. Comparison of the Chemical Composition of the Middle Atmosphere During Energetic Particle Precipitation in January 2005 and 2012. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050506
Doronin G, Mironova I, Rozanov E. Comparison of the Chemical Composition of the Middle Atmosphere During Energetic Particle Precipitation in January 2005 and 2012. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(5):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050506
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoronin, Grigoriy, Irina Mironova, and Eugene Rozanov. 2025. "Comparison of the Chemical Composition of the Middle Atmosphere During Energetic Particle Precipitation in January 2005 and 2012" Atmosphere 16, no. 5: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050506
APA StyleDoronin, G., Mironova, I., & Rozanov, E. (2025). Comparison of the Chemical Composition of the Middle Atmosphere During Energetic Particle Precipitation in January 2005 and 2012. Atmosphere, 16(5), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050506







