Surface Ozone Variability in Two Contrasting Megacities, Cairo and Paris, and Its Observation from Satellites
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The variability in the surface ozone concentration in the two megacities will be analyzed to understand how it is modulated by the emission of precursors and possibly by the subsidence of higher-level air masses.
- The performance of the sounding methods will be evaluated by comparison of their products with the direct measurements of the surface ozone concentration. If necessary, a way to adjust the satellite retrievals to provide near-surface ozone abundances will be sought.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Available Data
2.1.1. Surface Measurements
2.1.2. Remote Sensing of the Tropospheric Ozone by Satellite-Borne Sounders
2.2. Analysis of the Temporal Variability in the Surface Ozone
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Ozone Concentration
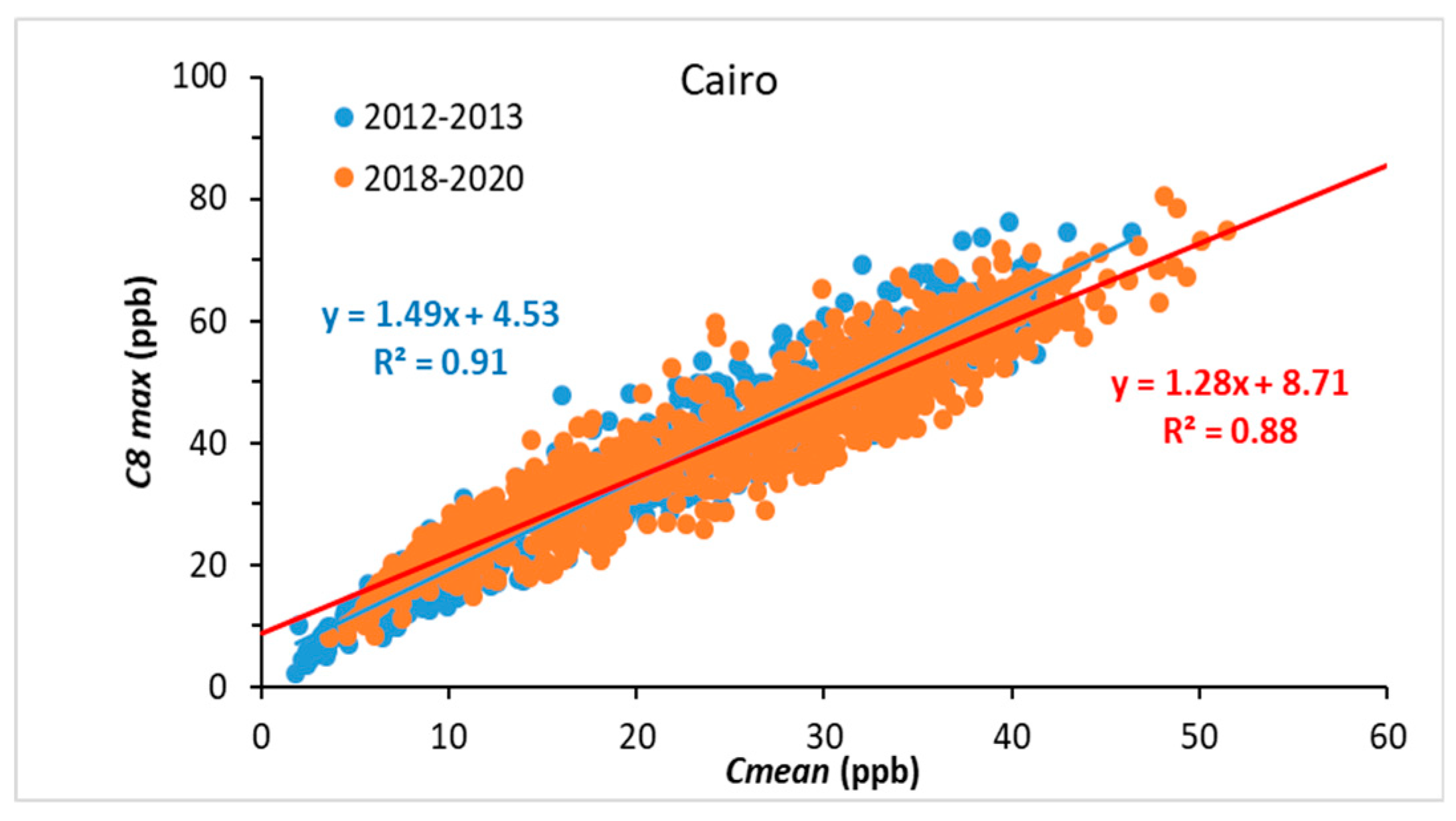
3.1.1. Cairo
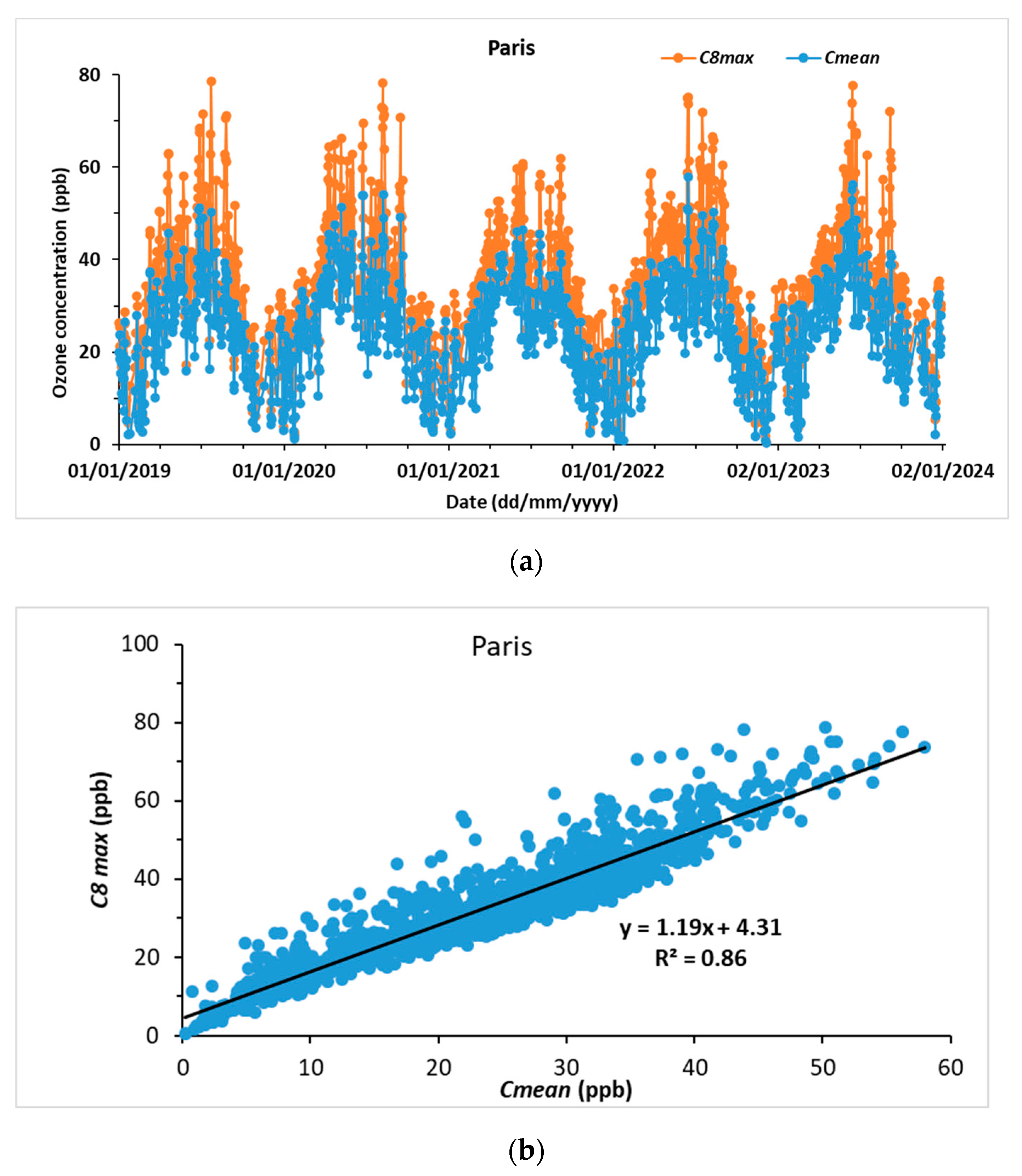
3.1.2. Paris
- The 5th, 50th, and 95th percentiles of the BAU years in Paris (11, 38, and 59 ppb, respectively) are all smaller than in Cairo (19, 44, and 65 ppb, respectively). Logically, the rate of exceedance of the 35 ppb WHO recommendation (42 to 46%) is also smaller than in Cairo (67%).
- Despite the severe lockdown imposed in Paris, the statistical indicators of 2020 do not differ significantly from those of the preceding and 3 following years, which were not affected by circulation restrictions.
3.2. Remote Sensing of the Tropospheric Concentration
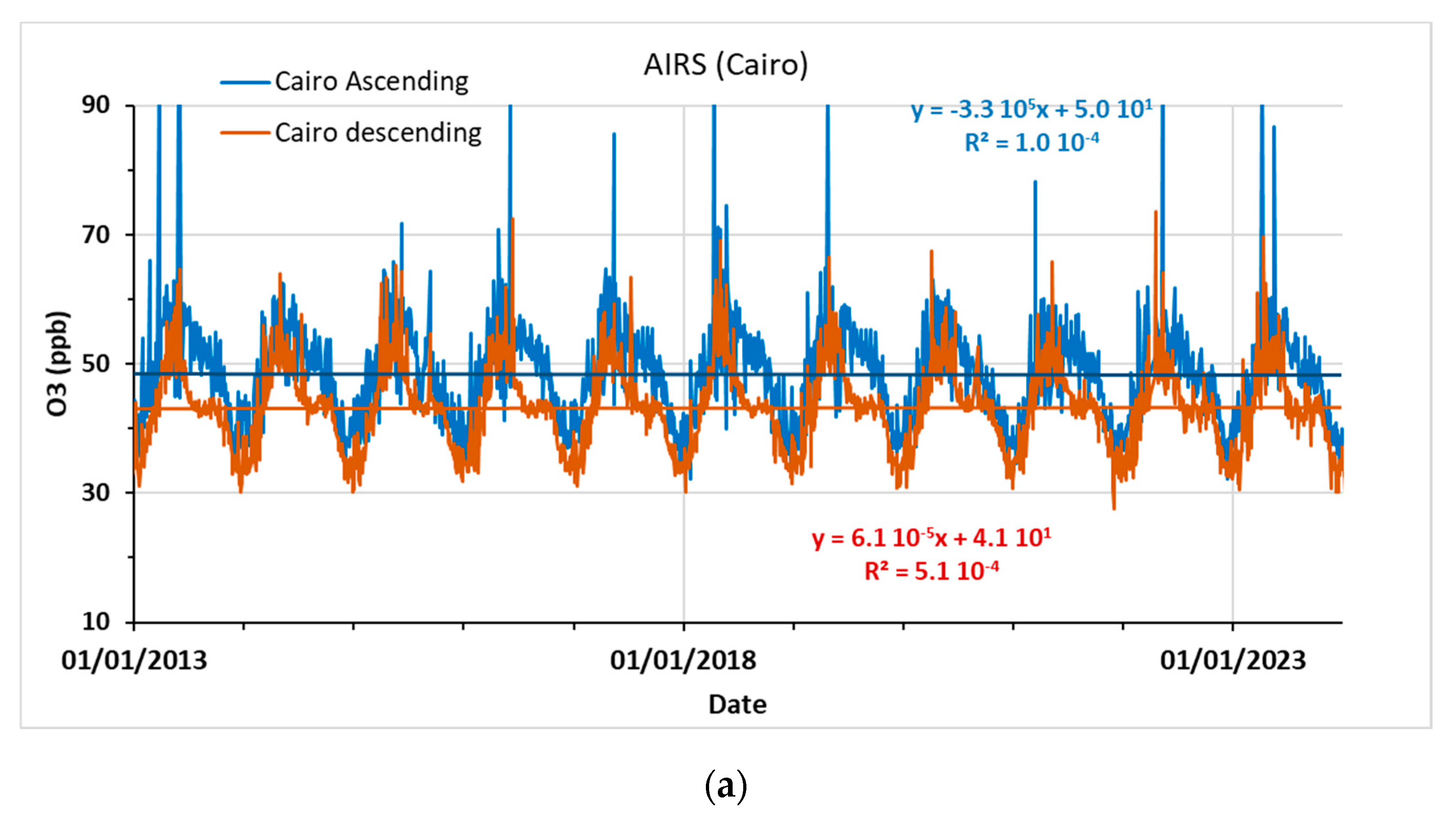
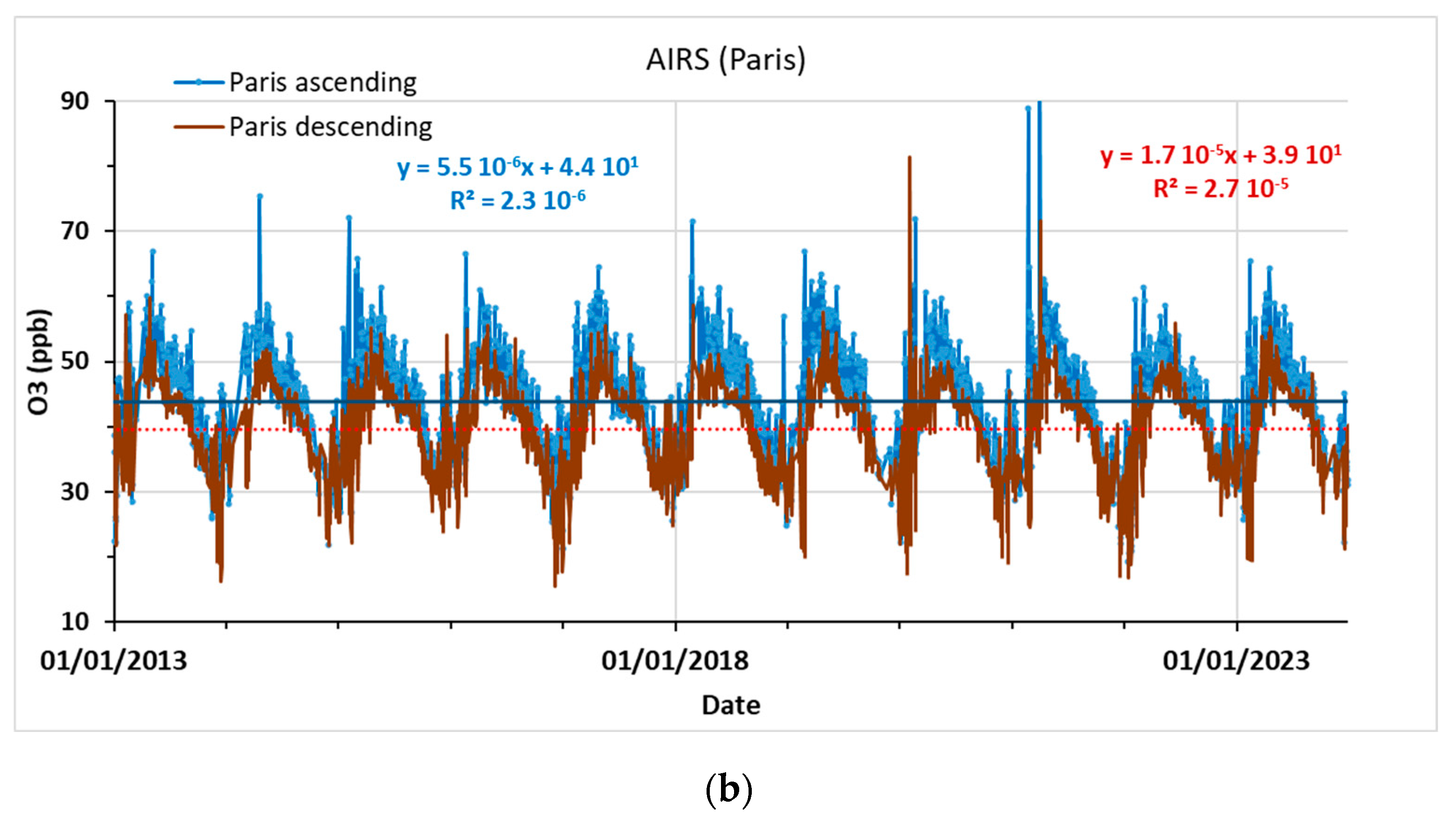
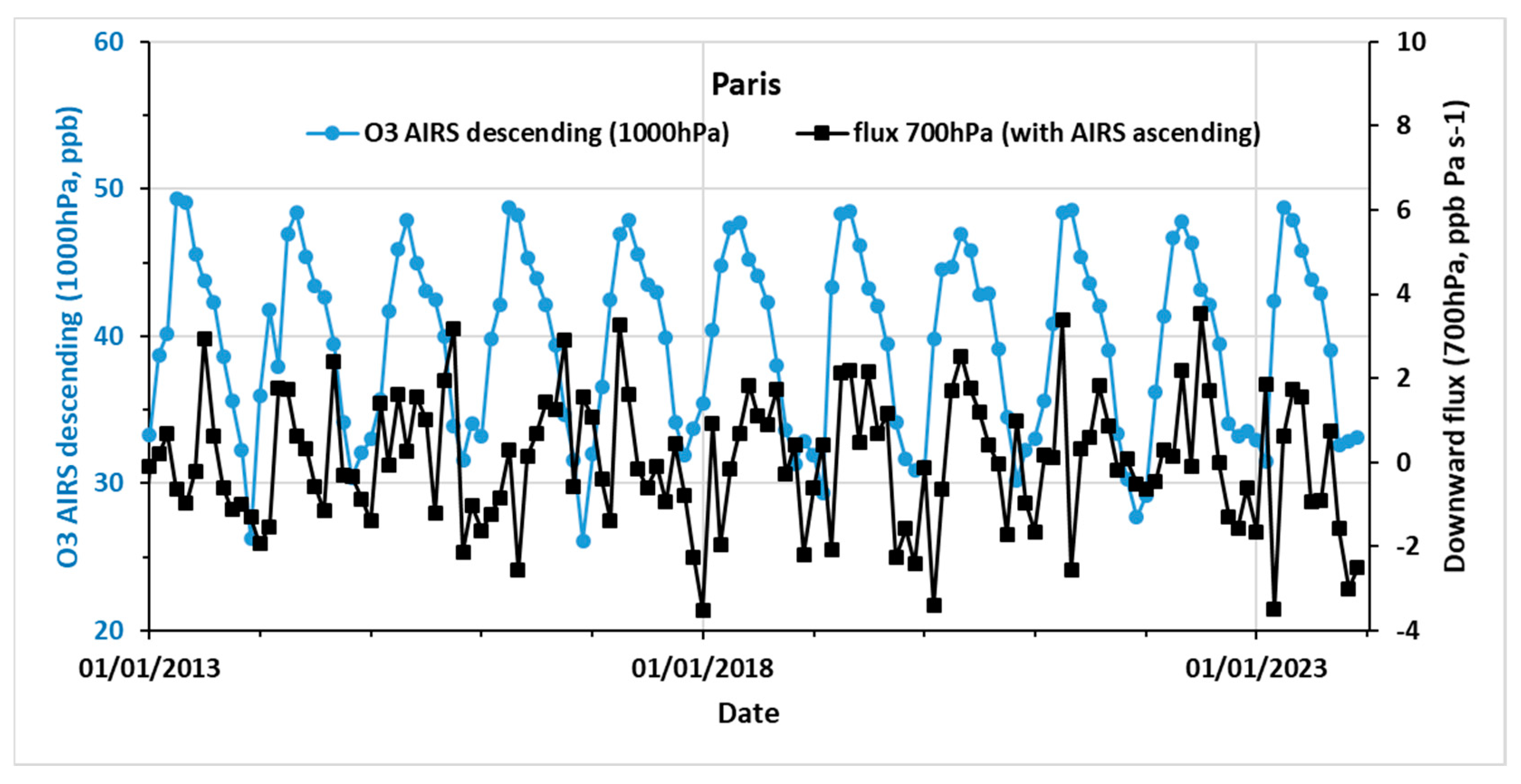
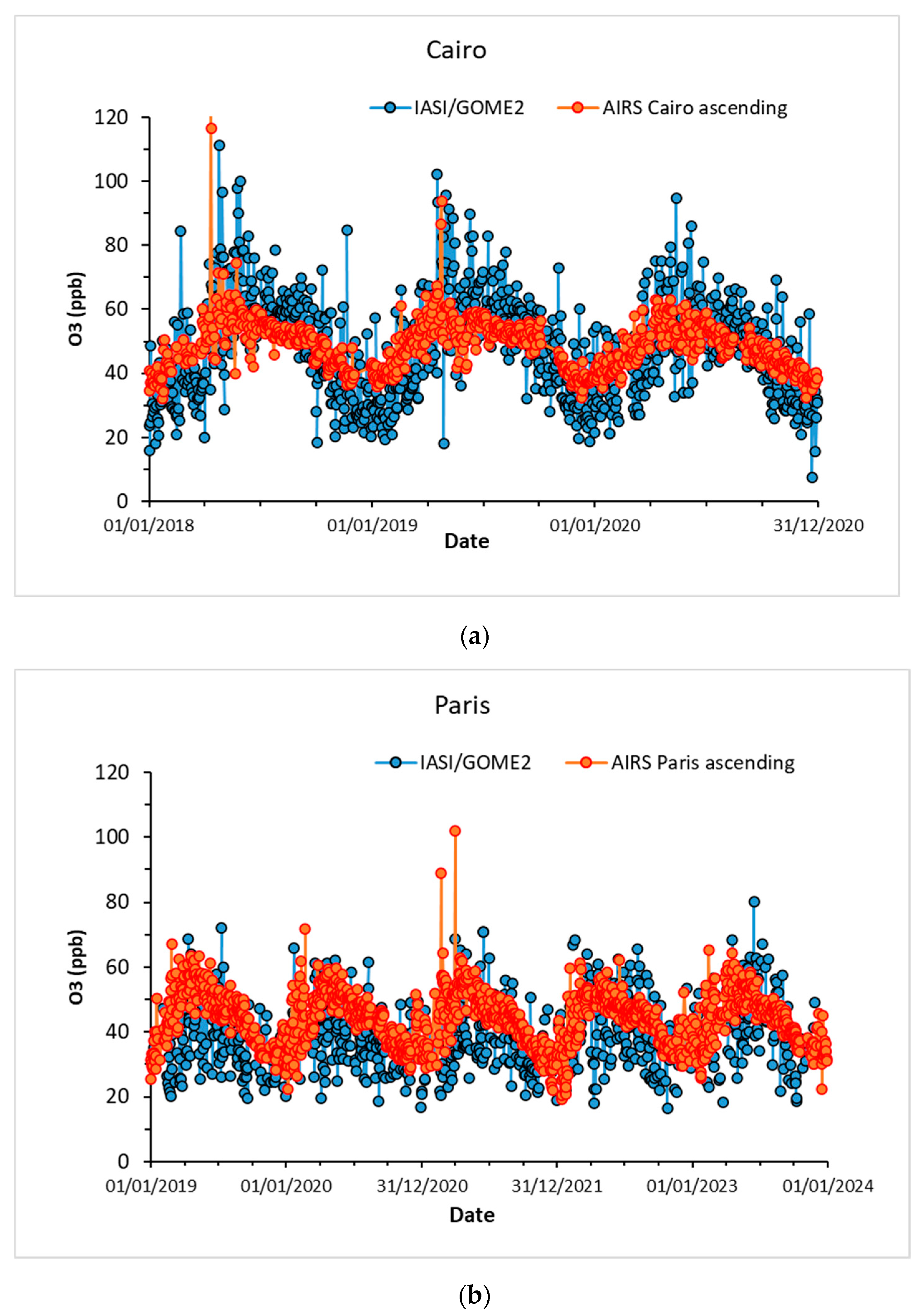
3.2.1. AIRS
3.2.2. IASI+GOME2
3.3. Comparison with the Surface Observations
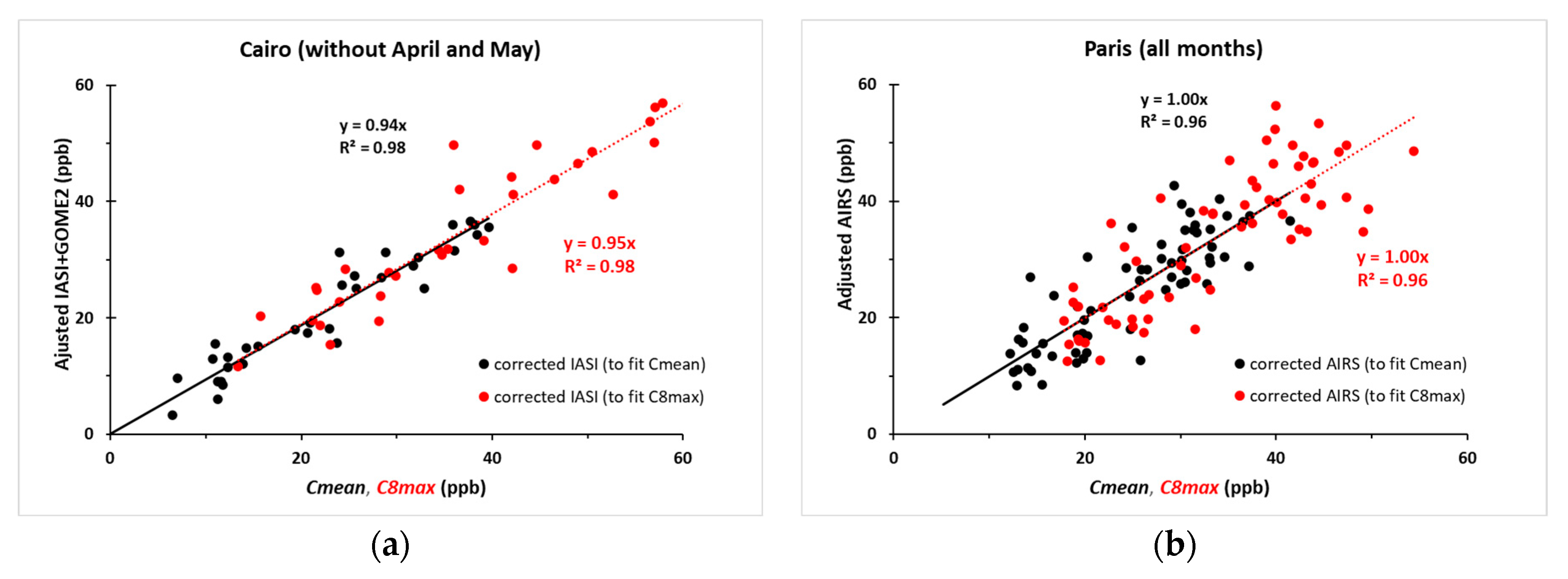
3.3.1. Correlation Between the Sounders’ Retrievals and the Surface Observations
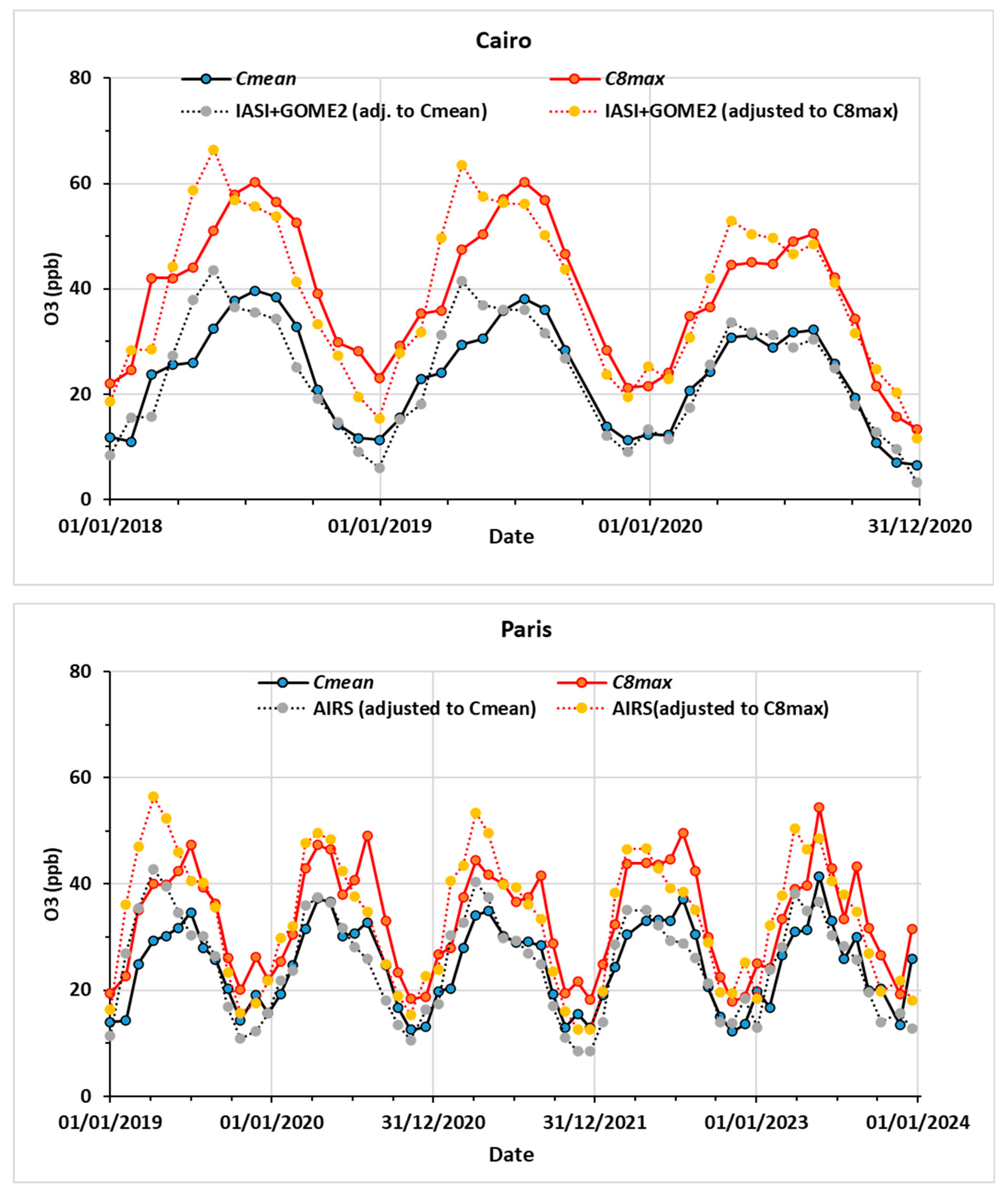
3.3.2. A Proxy of Surface Concentrations by Linear Adjustment of Satellite Retrievals
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Surface Observations
3.4.2. Observations of the Satellite Sounders
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Royal Society. Ground-Level Ozone in the 21st Century: Future Trends, Impacts and Policy Implications Science Policy; The Royal Society: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Oksanen, E.; Sicard, P.; Wang, Q.; Saitanis, C.J.; Araminiene, V.; Blande, J.D.; Hayes, F.; Calatayud, V.; et al. Ozone affects plant, insect, and soil microbial communities: A threat to terrestrial ecosystems and biodiversity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhre, G.; Samset, B.H.; Schulz, M.; Balkanski, Y.; Bauer, S.; Berntsen, T.K.; Bian, H.; Bellouin, N.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; et al. Radiative Forcing of the Direct Aerosol Effect from AeroCom Phase II Simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 1853–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA Ground-Level Ozone Basics. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ground-level-ozone-pollution/ground-level-ozone-basics (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- NASA Ozone. Available online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/Ozone/ozone_2.php (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Checa-Garcia, R.; Hegglin, M.I.; Kinnison, D.; Plummer, D.A.; Shine, K.P. Historical Tropospheric and Stratospheric Ozone Radiative Forcing Using the CMIP6 Database. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 3264–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kavassalis, S.C.; Murphy, J.G. Understanding Ozone-Meteorology Correlations: A Role for Dry Deposition. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hess, P.; Liu, C. The Impact of Meteorological Persistence on the Distribution and Extremes of Ozone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, N.; Sillmann, J.; Schnell, J.L.; Rust, H.W.; Butler, T. Synoptic and Meteorological Drivers of Extreme Ozone Concentrations over Europe. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 024005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, D.S.; Dentener, F.J.; Schultz, M.G.; Ellingsen, K.; van Noije, T.P.C.; Wild, O.; Zeng, G.; Amann, M.; Atherton, C.S.; Bell, N.; et al. Multimodel Ensemble Simulations of Present-Day and near-Future Tropospheric Ozone. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCAC Tropospheric Ozone. Available online: https://www.ccacoalition.org/short-lived-climate-pollutants/tropospheric-ozone#resources (accessed on 8 September 2024).
- Stordal, F.; Bekki, S.; Hauglustaine, D.; Millan, M.; Sausen, R.; Schuepbach, E.; Stevenson, D.; van Dorland, R.; Volz-Thomas, A. Climate impact of tropospheric ozone changes. In Air Pollution Report N°81: Ozone-Climate Interactions; Isaksen, I.S., Ed.; EU 20623, Chapter 4; European Communities; 2003; pp. 73–95. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-03327712/document (accessed on 21 March 2025).
- Garatachea, R.; Pay, M.T.; Achebak, H.; Jorba, O.; Bowdalo, D.; Guevara, M.; Petetin, H.; Ballester, J.; Pérez García-Pando, C. National and Transboundary Contributions to Surface Ozone Concentration across European Countries. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wang, T.; Kasoar, M.; Wells, C.; Yuan, C.; Varma, S.; Mansfield, L. A Study of the Effect of Aerosols on Surface Ozone through Meteorology Feedbacks over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5705–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, F.; Sauvage, S.; Hamonou, E. Atmospheric Chemistry in the Mediterranean Region Volume 1-Background Information and Pollutant Distribution; Springer International Publishing AG: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jaidan, N.; El Amraoui, L.; Attiè, J.L.; Ricaud, P.; Dulac, F. Future Changes in Surface Ozone over the Mediterranean Basin in the Framework of the Chemistry-Aerosol Mediterranean Experiment (ChArMEx). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9351–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanelli, P.; Bonasoni, P. Background Ozone in the Southern Europe and Mediterranean Area: Influence of the Transport Processes. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasopoulos, E.; Kouvarakis, G.; Vrekoussis, M.; Kanakidou, M.; Mihalopoulos, N. Ozone Variability in the Marine Boundary Layer of the Eastern Mediterranean Based on 7-Year Observations. J. Geophys. Res. D Atmos. 2005, 110, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Dentener, F.J. What Controls Tropospheric Ozone? J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 3531–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Berresheim, H.; Borrmann, S.; Crutzen, P.J.; Dentener, F.J.; Fischer, H.; Feichter, J.; Flatau, P.J.; Heland, J.; Holzinger, R.; et al. Global Air Pollution Crossroads over the Mediterranean. Science 2002, 298, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingarzan, R. A Review of Surface Ozone Background Levels and Trends. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, P.S. A Review of the Observations and Origins of the Spring Ozone Maximum. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 3545–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabokas, P.D.; Cammas, J.P.; Thouret, V.; Volz-Thomas, A.; Boulanger, D.; Repapis, C.C. Examination of the Atmospheric Conditions Associated with High and Low Summer Ozone Levels in the Lower Troposphere over the Eastern Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10339–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, M.; Segers, A.; Kranenburg, R.; Querol, X.; Alastuey, A.; Borge, R.; De La Paz, D.; Gangoiti, G.; Schaap, M. Analysis of Summer O3 in the Madrid Air Basin with the LOTOS-EUROS Chemical Transport Model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14211–14232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalabokas, P.; Repapis, C. A Review of Surface and Lower Troposphere Ozone Concentration Characteristics Around the Urban Area of Athens, the Aegean Sea and at the Central and Eastern Mediterranean, in Perspectives on Atmospheric Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Massagué, J.; Torre-Pascual, E.; Carnerero, C.; Escudero, M.; Alastuey, A.; Pandolfi, M.; Querol, X.; Gangoiti, G. Extreme Ozone Episodes in a Major Mediterranean Urban Area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 4827–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pay, M.T.; Gangoiti, G.; Guevara, M.; Napelenok, S.; Querol, X.; Jorba, O.; García-Pando, C.P. Ozone Source Apportionment during Peak Summer Events over Southwestern Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5467–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, W.C.; Heald, C.L. The Mechanisms and Meteorological Drivers of the Summertime Ozone-Temperature Relationship. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 13367–13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunier, A.; Ormeño, E.; Piga, D.; Armengaud, A.; Boissard, C.; Lathière, J.; Szopa, S.; Genard-Zielinski, A.C.; Fernandez, C. Isoprene Contribution to Ozone Production under Climate Change Conditions in the French Mediterranean Area. Reg. Environ. Change 2020, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.N.; Zakey, A.S.; Monem, A.S.; Abdel Wahab, M.M. Analysis of the Surface Air Quality Measurements in The Greater Cairo (Egypt) Metropolitan. Glob. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 5, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cuesta, J.; Costantino, L.; Beekmann, M.; Siour, G.; Menut, L.; Bessagnet, B.; Landi, T.C.; Dufour, G.; Eremenko, M. Ozone Pollution during the COVID-19 Lockdown in the Spring of 2020 over Europe, Analysed from Satellite Observations, in Situ Measurements, and Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 4471–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; De Marco, A.; Agathokleous, E.; Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Paoletti, E.; Rodriguez, J.J.D.; Calatayud, V. Amplified Ozone Pollution in Cities during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Toshniwal, D. Impact of Lockdown on Air Quality over Major Cities across the Globe during COVID-19 Pandemic. Urban. Clim. 2020, 34, 100719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Stavrakou, T.; Elguindi, N.; Doumbia, T.; Granier, C.; Bouarar, I.; Gaubert, B.; Brasseur, G.P. Diverse Response of Surface Ozone to COVID-19 Lockdown in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, H.H.; Chahine, M.T.; Gautier, C.; Goldberg, M.D.; Kalnay, E.; McMillin, L.M.; Revercomb, H.; Rosenkranz, P.W.; Smith, W.L.; Staelin, D.H.; et al. AIRS/AMSU/HSB on the Aqua Mission: Design, Science Objectives, Data Products, and Processing Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, J.; Eremenko, M.; Liu, X.; Dufour, G.; Cai, Z.; Höpfner, M.; Von Clarmann, T.; Sellitto, P.; Foret, G.; Gaubert, B.; et al. Satellite Observation of Lowermost Tropospheric Ozone by Multispectral Synergism of IASI Thermal Infrared and GOME-2 Ultraviolet Measurements over Europe. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 9675–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, S.; Cuesta, J.; Beekmann, M.; Dufour, G.; Eremenko, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Boonne, C.; Tanimoto, H.; Akimoto, H. Impact of Different Sources of Precursors on an Ozone Pollution Outbreak over Europe Analysed with IASI+GOME2 Multispectral Satellite Observations and Model Simulations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 7399–7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuesta, J.; Kanaya, Y.; Takigawa, M.; Dufour, G.; Eremenko, M.; Foret, G.; Miyazaki, K.; Beekmann, M. Transboundary Ozone Pollution across East Asia: Daily Evolution and Photochemical Production Analysed by IASI + GOME2 Multispectral Satellite Observations and Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 9499–9525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudel, A.; Bourgeois, I.; Li, M.; Chang, K.-L.; Ziemke, J.; Sauvage, B.; Stauffer, R.M.; Thompson, A.M.; Kollonige, D.E.; Smith, N.; et al. Tropical Tropospheric Ozone Distribution and Trends from in Situ and Satellite Data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 9975–10000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasick, D.; Galbally, I.E.; Cooper, O.R.; Schultz, M.G.; Ancellet, G.; Leblanc, T.; Wallington, T.J.; Ziemke, J.; Liu, X.; Steinbacher, M.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Tropospheric Ozone from 1877 to 2016, Observed Levels, Trends and Uncertainties. Elementa 2019, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmazzahi, D.; Shawkat, Y. (Re)Defining the Greater Cairo Region. Available online: https://marsadomran.info/en/2024/04/3265/ (accessed on 22 December 2024).
- Wheida, A.; Nasser, A.; El Nazer, M.; Borbon, A.; Abo El Ata, G.A.; Abdel Wahab, M.; Alfaro, S.C. Tackling the Mortality from Long-Term Exposure to Outdoor Air Pollution in Megacities: Lessons from the Greater Cairo Case Study. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divakarla, M.G.; Barnet, C.D.; Goldberg, M.D.; McMillin, L.M.; Maddy, E.; Wolf, W.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X. Validation of Atmospheric Infrared Sounder Temperature and Water Vapor Retrievals with Matched Radiosonde Measurements and Forecasts. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerbaux, C.; Boynard, A.; Clarisse, L.; George, M.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Herbin, H.; Hurtmans, D.; Pommier, M.; Razavi, A.; Turquety, S.; et al. Monitoring of Atmospheric Composition Using the Thermal Infrared IASI/MetOp Sounder. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6041–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.N.; Zakey, A.S.; Alfaro, S.C.; Wheida, A.A.; Monem, S.A.; Abdul Wahab, M.M. Validation of RegCM-CHEM4 Model by Comparison with Surface Measurements in the Greater Cairo (Egypt) Megacity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23524–23541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.E.; Dupont, J.C.; Favez, O.; Gros, V.; Zhang, Y.; Sciare, J.; Simon, L.; Truong, F.; Bonnaire, N.; Amodeo, T.; et al. Response of Atmospheric Composition to COVID-19 Lockdown Measures during Spring in the Paris Region (France). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 17167–17183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroubaix, A.; Brasseur, G.; Gaubert, B.; Labuhn, I.; Menut, L.; Siour, G.; Tuccella, P. Response of Surface Ozone Concentration to Emission Reduction and Meteorology during the COVID-19 Lockdown in Europe. Meteorol. Appl. 2021, 28, e1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favez, O.; Cachier, H.; Sciare, J.; Alfaro, S.C.; El-Araby, T.M.; Harhash, M.A.; Abdelwahab, M.M. Seasonality of Major Aerosol Species and Their Transformations in Cairo Megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, A.; Bezantakos, S.; Bourtsoukidis, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Pikridas, M.; Oikonomou, K.; Iakovides, M.; Hassan, S.K.; Boraiy, M.; El-Nazer, M.; et al. Submicron Aerosol Pollution in Greater Cairo (Egypt): A New Type of Urban Haze? Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentener, F.J.; Carmichael, G.R.; Zhang, Y.; Lelieveld, J.; Crutzen, P.J. Role of Mineral Aerosol as a Reactive Surface in the Global Troposphere. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 22869–22889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasne, J.; Romanias, M.N.; Thevenet, F. Ozone Uptake by Clay Dusts under Environmental Conditions. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2018, 2, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| BAU Years | Singular Years | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentile (ppb) | 2002–2005 | 2018–2019 | 2013 | 2020 |
| 5th | 12 | 20 | 9 | 16 |
| 50th | 40 | 44 | 33 | 37 |
| 95th | 66 | 65 | 53 | 55 |
| SD | 17 | 17 | 15 | 13 |
| % > 35 ppb | 58% | 67% | 44% | 54% |
| BAU Years | COVID-19 Year | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentile (ppb) | 2019 | 2021–2023 | 2020 |
| 5th | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 50th | 33 | 34 | 33 |
| 95th | 62 | 59 | 62 |
| SD | 15 | 14 | 15 |
| % > 35 ppb | 42% | 46% | 45% |
| Paris | Cairo | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IASI+G | AIRS | IASI+G | AIRS | ||||||||||
| a | b | R2 | a | b | R2 | a | b | R2 | a | b | R2 | ||
| Cmean | daily | 0.40 | 28.5 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 32.9 | 0.34 | 0.85 | 28.0 | 0.34 | 0.45 | 38.9 | 0.35 |
| weekly | 0.48 | 26.4 | 0.43 | 0.60 | 28.8 | 0.51 | 0.97 | 25.3 | 0.64 | 0.49 | 38.2 | 0.51 | |
| monthly | 0.59 | 23.6 | 0.66 | 0.73 | 25.5 | 0.69 | 1.08 | 22.3 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 37.22 | 0.63 | |
| C8max | daily | 0.30 | 27.9 | 0.16 | 0.35 | 32.3 | 0.34 | 0.63 | 23.9 | 0.33 | 0.30 | 37.7 | 0.32 |
| weekly | 0.35 | 26.5 | 0.36 | 0.46 | 28.1 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 20.58 | 0.61 | 0.32 | 37.1 | 0.46 | |
| monthly | 0.47 | 22.4 | 0.62 | 0.57 | 24.1 | 0.68 | 0.79 | 16.9 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 35.7 | 0.58 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafa, A.N.; Alfaro, S.; Cuesta, J.; Hassan, I.A.; Abdel Wahab, M.M. Surface Ozone Variability in Two Contrasting Megacities, Cairo and Paris, and Its Observation from Satellites. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040475
Mostafa AN, Alfaro S, Cuesta J, Hassan IA, Abdel Wahab MM. Surface Ozone Variability in Two Contrasting Megacities, Cairo and Paris, and Its Observation from Satellites. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(4):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040475
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafa, Amira N., Stephane Alfaro, Juan Cuesta, Ibrahim A. Hassan, and M. M. Abdel Wahab. 2025. "Surface Ozone Variability in Two Contrasting Megacities, Cairo and Paris, and Its Observation from Satellites" Atmosphere 16, no. 4: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040475
APA StyleMostafa, A. N., Alfaro, S., Cuesta, J., Hassan, I. A., & Abdel Wahab, M. M. (2025). Surface Ozone Variability in Two Contrasting Megacities, Cairo and Paris, and Its Observation from Satellites. Atmosphere, 16(4), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16040475






