Spatiotemporal Analysis of NH3 Emission Sources and Their Relation to Land Use Types in the Eastern German Lowlands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
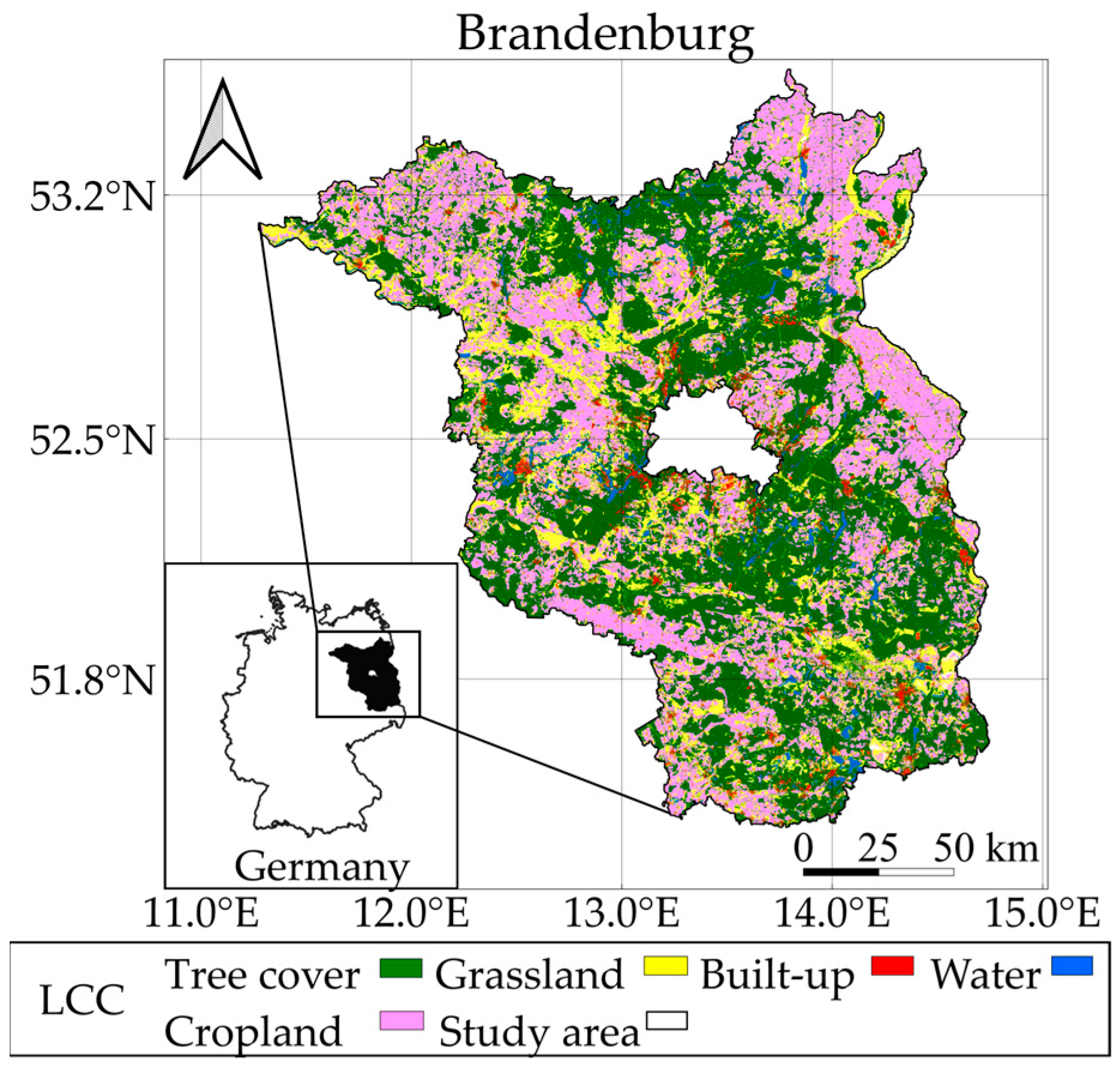
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite-Based NH3 Observation
2.3. CAMS Global Reanalysis (EAC4) Meteorological Conditions
2.4. K-Means Clustering of NH3 Emission
2.5. Back-Trajectories Analysis
3. Results
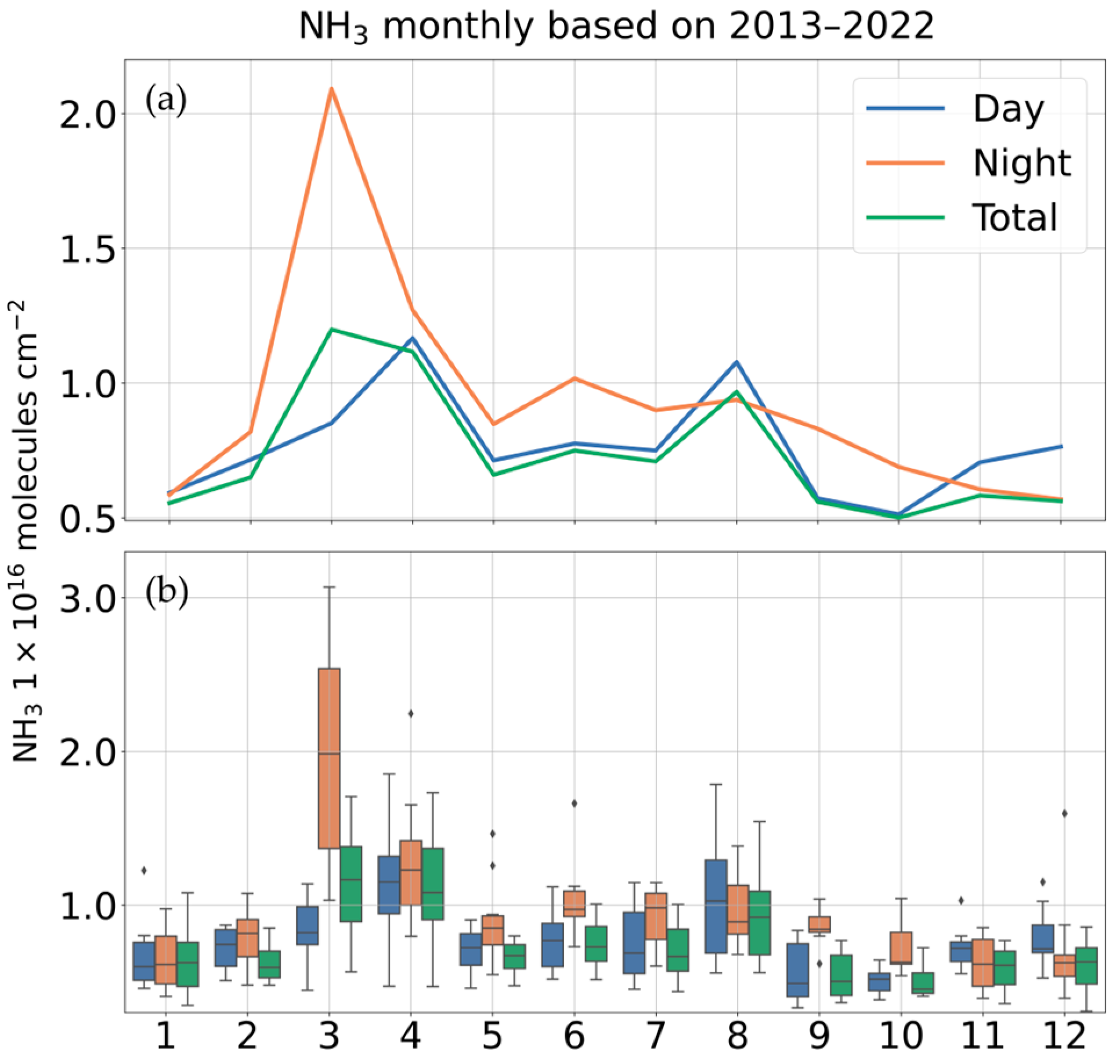
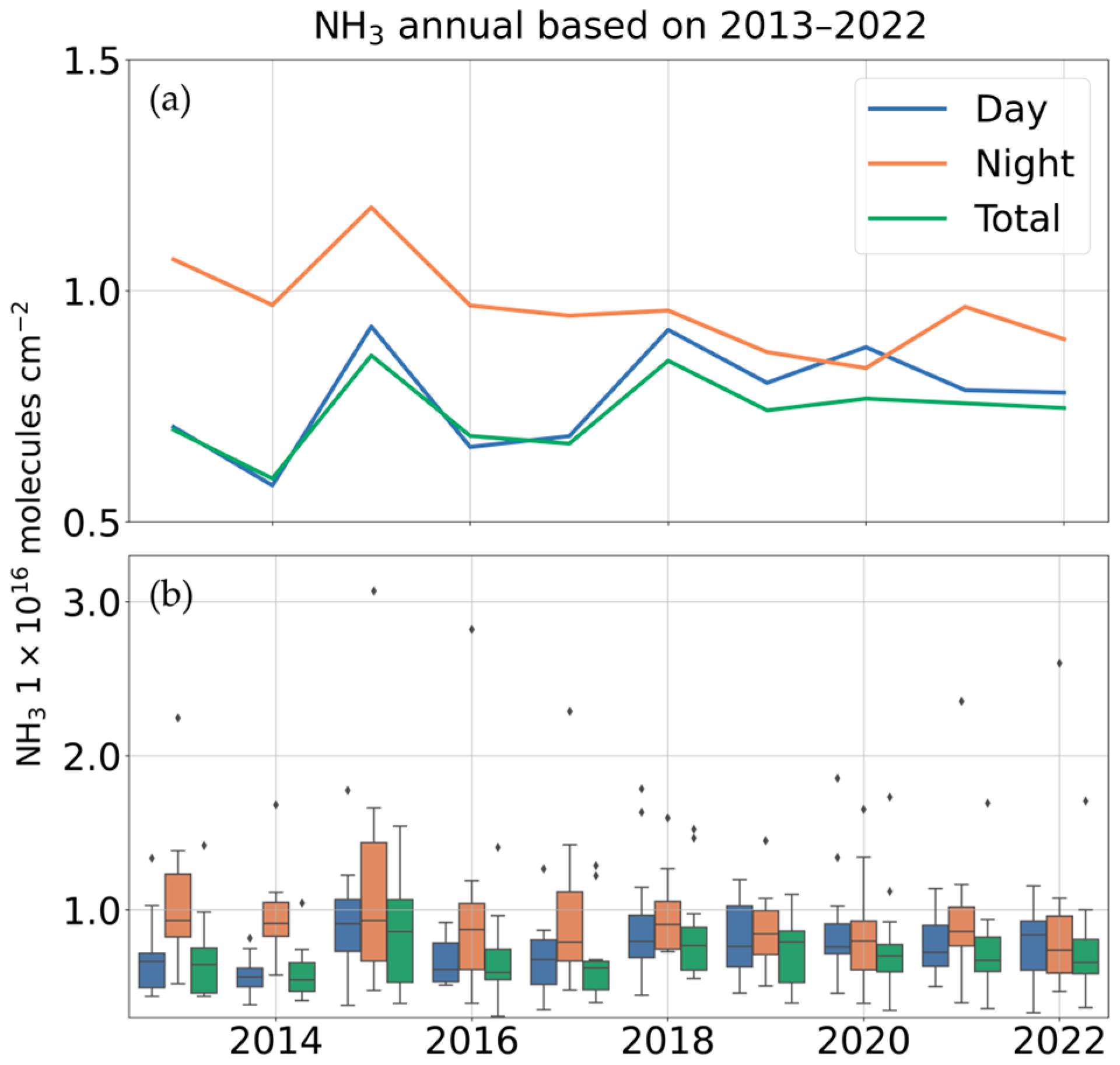
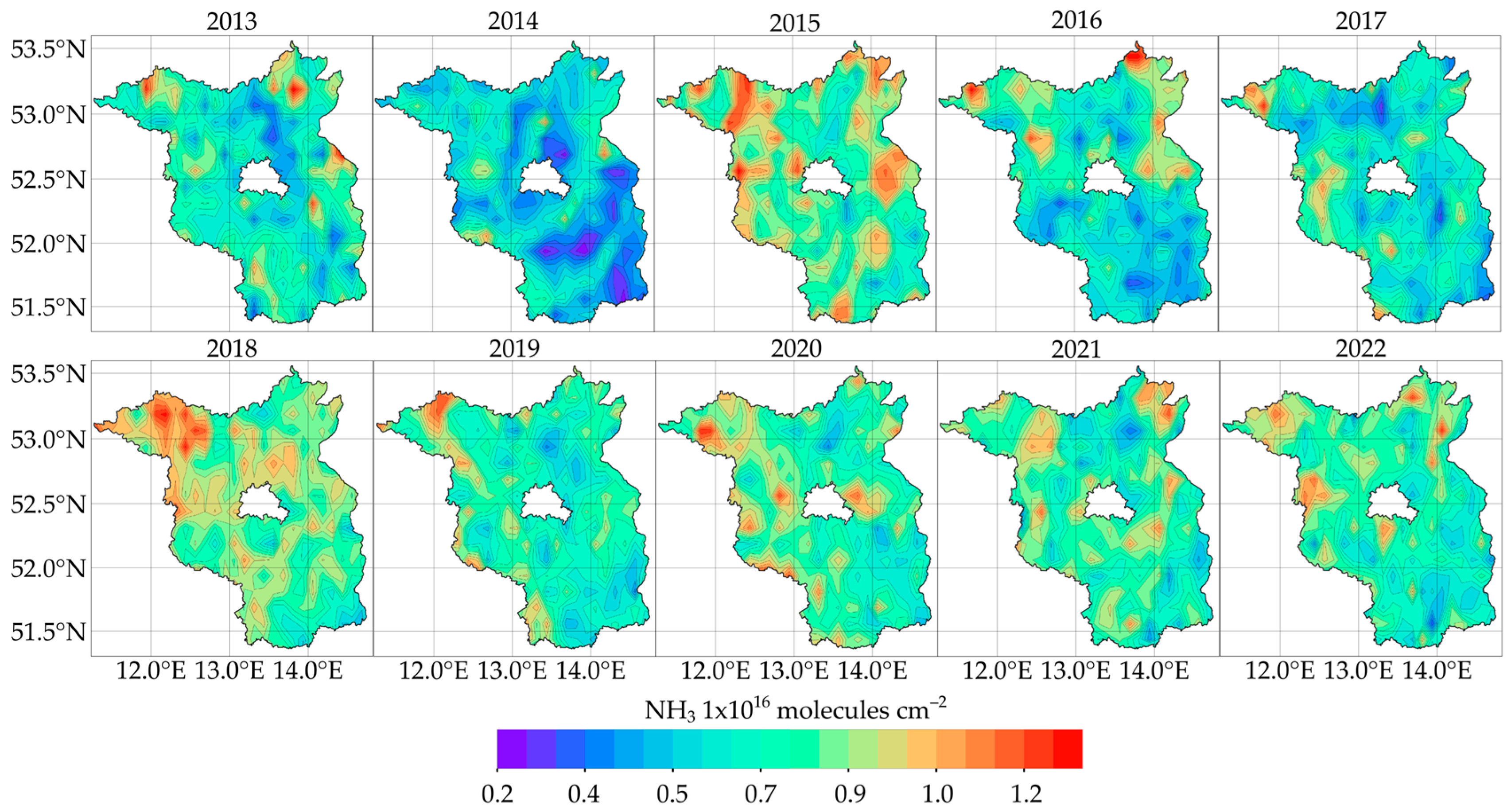
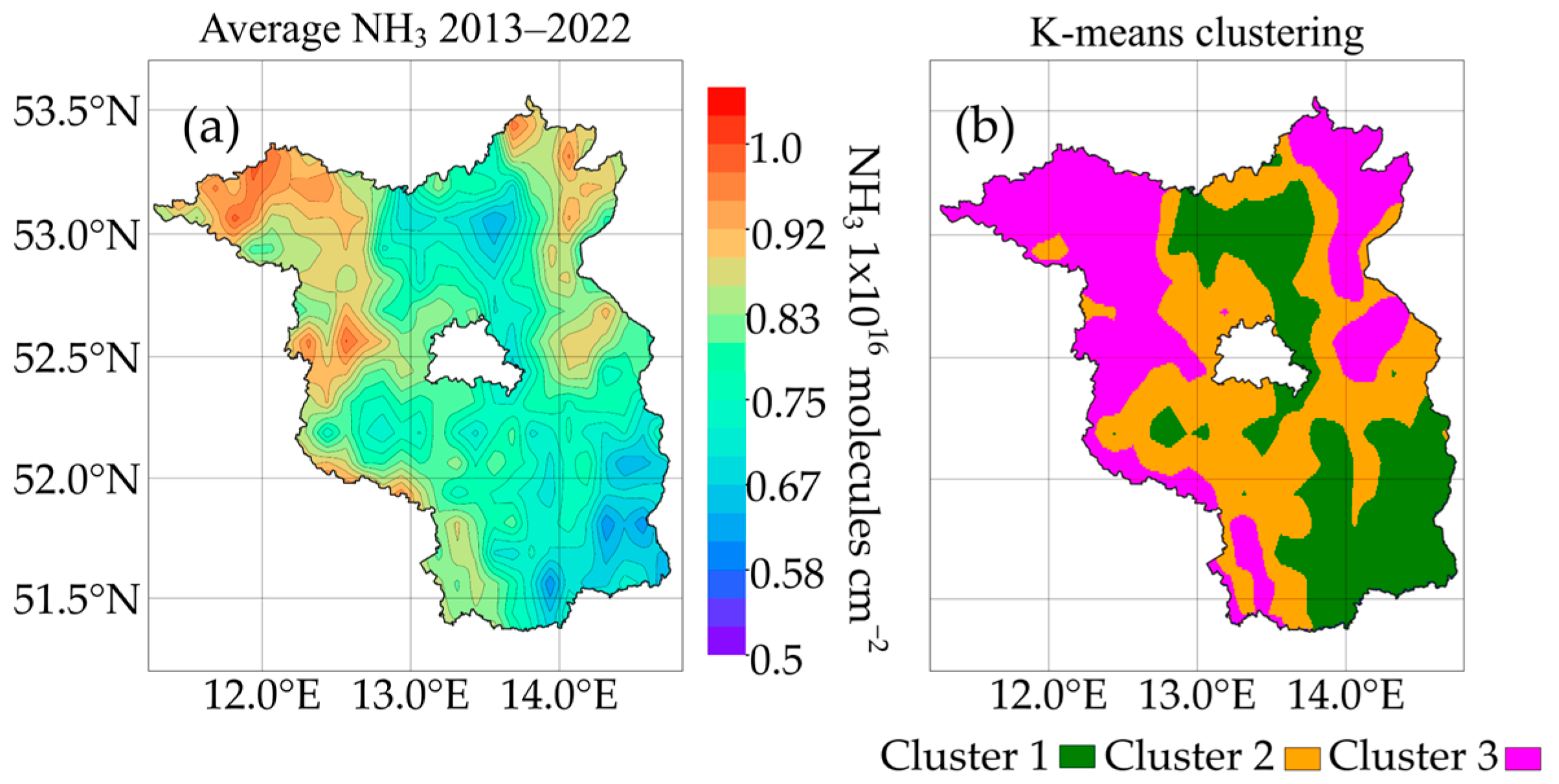
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations of Ammonia Emissions
3.2. Meteorological Parameters and NH3
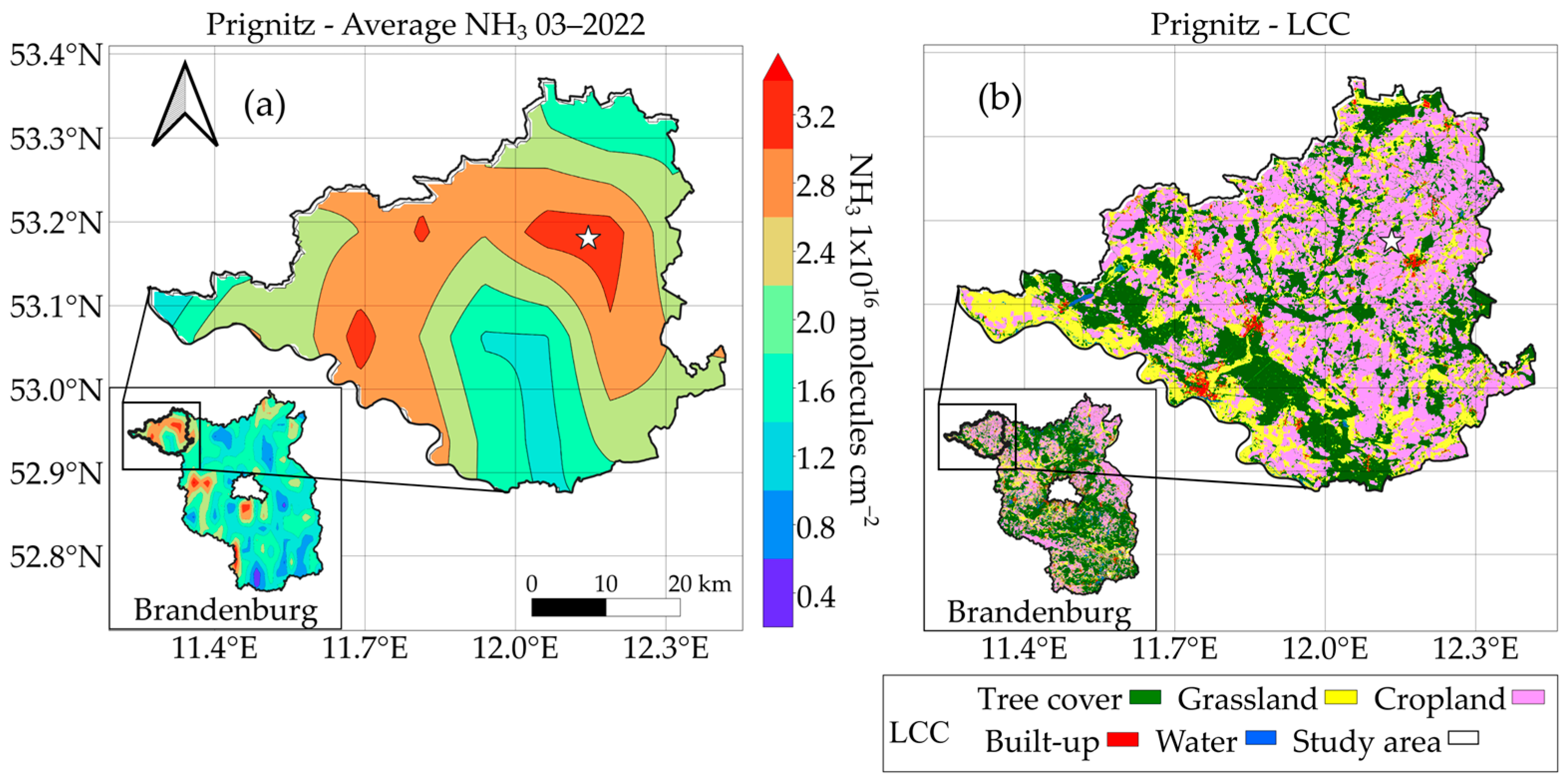
3.3. Land-Use-Related NH3 Emissions
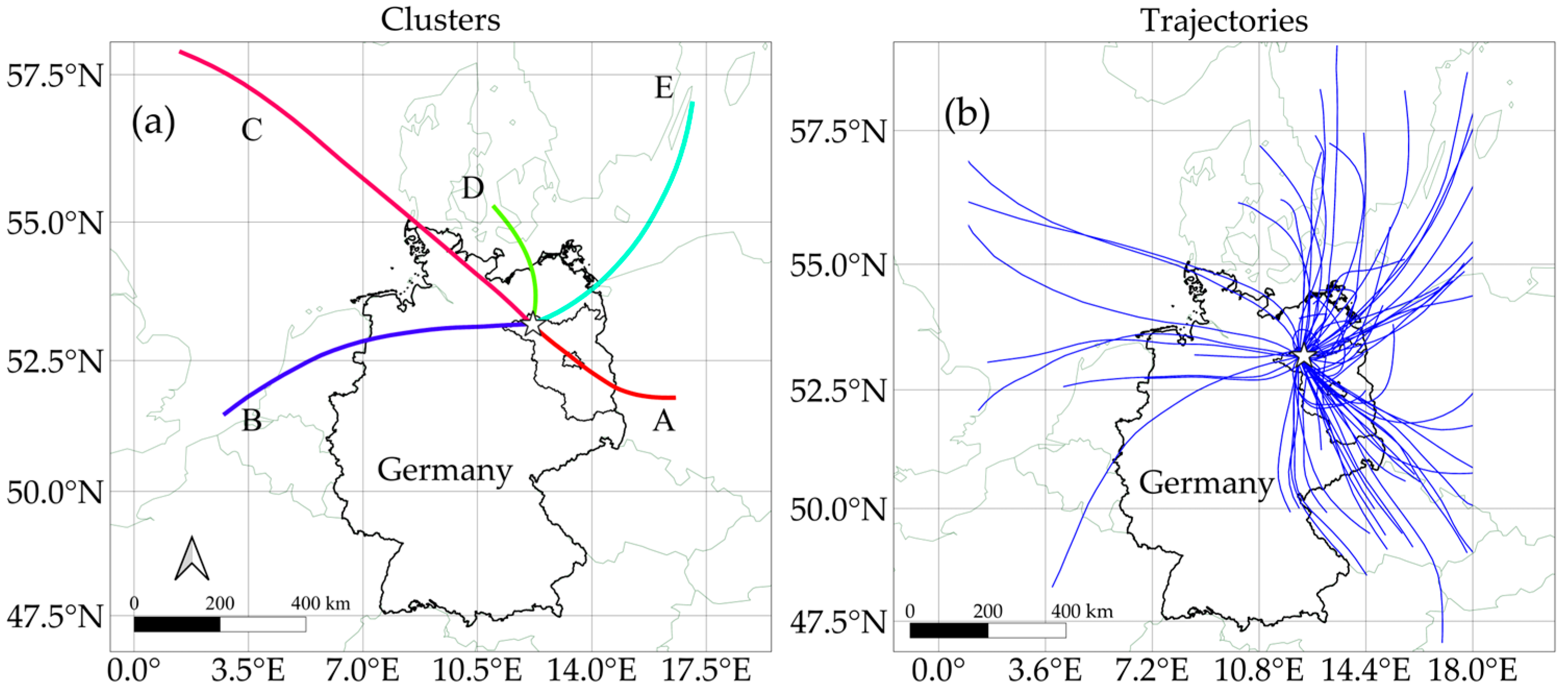
3.4. Case Study of NH3 Emission Using HYSPLIT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Zhou, H.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K.; Edgerton, E.S.; Schwab, J.J. Ambient Ammonia Concentrations Across New York State. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 8287–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharja, P.; Ali, K.; Ghude, S.D.; Sinha, V.; Sinha, B.; Kulkarni, R.; Gultepe, I.; Rajeevan, M.N. Enhanced Secondary Aerosol Formation Driven by Excess Ammonia during Fog Episodes in Delhi, India. Chemosphere 2022, 289, 133155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farren, N.J.; Davison, J.; Rose, R.A.; Wagner, R.L.; Carslaw, D.C. Underestimated Ammonia Emissions from Road Vehicles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 15689–15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Nan, J.; Shi, C.; Fu, Q.; Gao, S.; Wang, D.; Cui, H.; Saiz-Lopez, A.; Zhou, B. Atmospheric Ammonia and Its Impacts on Regional Air Quality over the Megacity of Shanghai, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Franco, B.; Sutton, M.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Wichink Kruit, R.; van Zanten, M.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; et al. Global, Regional and National Trends of Atmospheric Ammonia Derived from a Decadal (2008–2018) Satellite Record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.; Karbakhsh, M.; Momeni, M.; Taheri, M.; Amini, S.; Mansourian, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Long-Term Exposure to PM2.5 and Cardiovascular Disease Incidence and Mortality in an Eastern Mediterranean Country: Findings Based on a 15-Year Cohort Study. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Erisman, J.W.; Clarisse, L.; Dammers, E.; Whitburn, S.; Clerbaux, C.; Dolman, A.J.; Coheur, P.-F. Worldwide Spatiotemporal Atmospheric Ammonia (NH3) Columns Variability Revealed by Satellite. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 8660–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Reis, S.; Riddick, S.N.; Dragosits, U.; Nemitz, E.; Theobald, M.R.; Tang, Y.S.; Braban, C.F.; Vieno, M.; Dore, A.J.; et al. Towards a Climate-Dependent Paradigm of Ammonia Emission and Deposition. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20130166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammers, E.; Palm, M.; Van Damme, M.; Vigouroux, C.; Smale, D.; Conway, S.; Toon, G.C.; Jones, N.; Nussbaumer, E.; Warneke, T.; et al. An Evaluation of IASI-NH3 with Ground-Based Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10351–10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, B.; Bezanilla, A.; Blumenstock, T.; Dammers, E.; Hase, F.; Clarisse, L.; Magaldi, A.; Rivera, C.; Stremme, W.; Strong, K.; et al. Measurement Report: Evolution and Distribution of NH3 over Mexico City from Ground-Based and Satellite Infrared Spectroscopic Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 14119–14132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, M.A.; Nemitz, E.; Erisman, J.W.; Beier, C.; Bahl, K.B.; Cellier, P.; de Vries, W.; Cotrufo, F.; Skiba, U.; Di Marco, C.; et al. Challenges in Quantifying Biosphere–Atmosphere Exchange of Nitrogen Species. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 150, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Sutton, M.A.; Chang, S.X.; Ge, Y.; Chang, J. Agricultural Ammonia Emissions Contribute to China’s Urban Air Pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014, 12, 265–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.B.; Neuman, J.A.; Bahreini, R.; Brock, C.A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Wollny, A.G.; Holloway, J.S.; Peischl, J.; Ryerson, T.B.; Fehsenfeld, F.C. Airborne Observations of Ammonia and Ammonium Nitrate Formation over Houston, Texas. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D22304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Rieder, H.E.; Schmidt, C.; Mayer, M.; Guo, Y.; Winiwarter, W.; Zhang, L. Optimal Reactive Nitrogen Control Pathways Identified for Cost-Effective PM2.5 Mitigation in Europe. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, G.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Xue, T.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Peng, Y.; et al. Tracking Air Pollution in China: Near Real-Time PM5 Retrievals from Multisource Data Fusion. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12106–12115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, B.; Li, P.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Deng, J. Spatio-Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of Synergizing the Reduction of Pollution and Carbon Emissions—Utilizing Multi-Source Remote Sensing Data and GTWR Model. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F.; Lee, D.S.; Asman, W.A.; Dentener, F.J.; Van Der Hoek, K.W.; Olivier, J.G.J. A Global High-resolution Emission Inventory for Ammonia. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 561–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, R.; Pan, D.; Zondlo, M.A.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Whitburn, S.; Coheur, P.; Clerbaux, C.; Franco, B.; et al. Validation of IASI Satellite Ammonia Observations at the Pixel Scale Using In Situ Vertical Profiles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD033475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Henze, D.K.; Bash, J.O.; Cady-Pereira, K.E.; Shephard, M.W.; Luo, M.; Capps, S.L. Sources and Impacts of Atmospheric NH3: Current Understanding and Frontiers for Modeling, Measurements, and Remote Sensing in North America. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 95–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.J.; Turner, A.J.; Maasakkers, J.D.; Sheng, J.; Sun, K.; Liu, X.; Chance, K.; Aben, I.; McKeever, J.; Frankenberg, C. Satellite Observations of Atmospheric Methane and Their Value for Quantifying Methane Emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14371–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coheur, P.-F.; Clarisse, L.; Turquety, S.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C. IASI Measurements of Reactive Trace Species in Biomass Burning Plumes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5655–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Dentener, F.; Hurtmans, D.; Coheur, P.-F. Global Ammonia Distribution Derived from Infrared Satellite Observations. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F. Industrial and Agricultural Ammonia Point Sources Exposed. Nature 2018, 564, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, S.; Angenendt, E.; Beletskaya, O.; Zeddies, J. Assessing Ammonia Emission Abatement Measures in Agriculture: Farmers’ Costs and Society’s Benefits—A Case Study for Lower Saxony, Germany. Agric. Syst. 2017, 157, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, B.H.; Latacz-Lohmann, U.; Luesink, H.; Michels, R.; Ståhl, L. Costs of Regulating Ammonia Emissions from Livestock Farms near Natura 2000 Areas—Analyses of Case Farms from Germany, Netherlands and Denmark. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeed, R.; Viatte, C.; Porter, W.C.; Evangeliou, N.; Clerbaux, C.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Coheur, P.-F.; Safieddine, S. Estimating Agricultural Ammonia Volatilization over Europe Using Satellite Observations and Simulation Data. EGUsphere 2022, 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, V.; Gilmer, A.; Hellebust, S.; McGovern, E.; Cassidy, J.; Byers, V.; McGillicuddy, E.J.; Neeson, F.; O’Connor, D.J. Ammonia Cycling and Emerging Secondary Aerosols from Arable Agriculture: A European and Irish Perspective. Air 2022, 1, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Adalibieke, W.; Cui, X.; Winiwarter, W.; Reis, S.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Huang, W.; Zhou, F. Improved Estimates of Ammonia Emissions from Global Croplands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R’Honi, Y.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Hurtmans, D.; Duflot, V.; Turquety, S.; Ngadi, Y.; Coheur, P.-F. Exceptional Emissions of NH3 and HCOOH in the 2010 Russian Wildfires. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitburn, S.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F. IASI-Derived NH3 Enhancement Ratios Relative to CO for the Tropical Biomass Burning Regions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12239–12252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malherbe, L.; German, R.; Couvidat, F.; Zanatta, L.; Blannin, L.; James, A.; Lètinois, L.; Schucht, S.; Berthelot, B.; Raoult, J. Emissions of Ammonia and Methane from the Agricultural Sector Emissions from Livestock Farming; ETC HE: Jülich, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-82-93970-25-5. [Google Scholar]
- European Union DIRECTIVE (EU) 2016/2284 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL—Of 14 December 2016—On the Reduction of National Emissions of Certain Atmospheric Pollutants, Amending Directive 2003/35/EC and Repealing Directive 2001/81/EC. 2016. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:32016L2284 (accessed on 5 June 2024).
- UmweltBundesamt Ammoniak-Emissionen. 2016. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/daten/luft/luftschadstoff-emissionen-in-deutschland/ammoniak-emissionen#entwicklung-seit-1990 (accessed on 27 June 2024).
- Umweltbundesamt Background March 2023: Air Quality 2022 (Preliminary Evaluation). 2023. Available online: https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/sites/default/files/medien/479/publikationen/2023_uba_hgp_luftqualitaet_engl_bf.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2024).
- Kleemola-Juntunen, P.; Kirchner, S. Gothenburg Protocol and Convention on Long-Range Transboundary Air Pollutions. In Global Encyclopedia of Territorial Rights; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Stavrakou, T.; Wichink Kruit, R.; Sellekaerts, L.; Viatte, C.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.F. On the Weekly Cycle of Atmospheric Ammonia over European Agricultural Hotspots. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clerbaux, C.; Boynard, A.; Clarisse, L.; George, M.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Herbin, H.; Hurtmans, D.; Pommier, M.; Razavi, A.; Turquety, S.; et al. Monitoring of Atmospheric Composition Using the Thermal Infrared IASI/MetOp Sounder. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 6041–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Franco, B.; Van Damme, M.; Gioacchino, T.D.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Whitburn, S.; Noppen, L.; Hurtmans, D.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P. The IASI NH 3 Version 4 Product: Averaging Kernels and Improved Consistency. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2023, 2023, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, M.; Lakes, T. Land Use Conflicts and Synergies on Agricultural Land in Brandenburg, Germany. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistisches Jahrbuch 2020—Brandenburg Amt Für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg; Amt Für Statistik Berlin-Brandenburg: Potsdam, Germany, 2020.
- Reyer, C.; Bachinger, J.; Bloch, R.; Hattermann, F.F.; Ibisch, P.L.; Kreft, S.; Lasch, P.; Lucht, W.; Nowicki, C.; Spathelf, P.; et al. Climate Change Adaptation and Sustainable Regional Development: A Case Study for the Federal State of Brandenburg, Germany. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2012, 12, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzler, C.; Helming, K.; Balla, D.; Dannowski, R.; Deumlich, D.; Glemnitz, M.; Knierim, A.; Mirschel, W.; Nendel, C.; Paul, C.; et al. Agricultural Land Use Changes—A Scenario-Based Sustainability Impact Assessment for Brandenburg, Germany. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirschel, W.; Wieland, R.; Luzi, K.; Groth, K. Model-Based Estimation of Irrigation Water Demand for Different Agricultural Crops Under Climate Change, Presented for the Federal State of Brandenburg, Germany; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 311–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ihinegbu, C.; Ogunwumi, T. Multi-Criteria Modelling of Drought: A Study of Brandenburg Federal State, Germany. Model Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 2035–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.; Fröhlich, K.; Saha, S. A Case Study on the Perceptions of Forest Owners on Restoring the Forests after a Wildfire in the Treuenbrietzen Forest of Brandenburg, Germany. Preprints 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaga, D.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Daems, D.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Brockmann, C.; Kirches, G.; Wevers, J.; Cartus, O. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2021 V200 (Version 200); Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitburn, S.; Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Bauduin, S.; Heald, C.L.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; Zondlo, M.A.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P. -F A Flexible and Robust Neural Network IASI-NH3 Retrieval Algorithm. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 6581–6599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, B.; Clarisse, L.; Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.-F.; Van Damme, M.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; Taraborrelli, D.; Clerbaux, C.; et al. A General Framework for Global Retrievals of Trace Gases From IASI: Application to Methanol, Formic Acid, and PAN. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 13963–13984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Whitburn, S.; Clarisse, L.; Clerbaux, C.; Hurtmans, D.; Coheur, P.-F. Version 2 of the IASI NH3 Neural Network Retrieval Algorithm: Near-Real-Time and Reanalysed Datasets. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4905–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Fang, L.; Li, B.; Liao, H.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Li, K.; Pang, M.; Wu, X.; Xiang Lin, H. 4DEnVar-Based Inversion System for Ammonia Emission Estimation in China through Assimilating IASI Ammonia Retrievals. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeed, R.; Clerbaux, C.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Coheur, P.-F.; Safieddine, S. A Space View of Agricultural and Industrial Changes during the Syrian Civil War. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2021, 9, 000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viatte, C.; Petit, J.-E.; Yamanouchi, S.; Van Damme, M.; Doucerain, C.; Germain-Piaulenne, E.; Gros, V.; Favez, O.; Clarisse, L.; Coheur, P.-F.; et al. Ammonia and PM2.5 Air Pollution in Paris during the 2020 COVID Lockdown. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ding, J.; Ji, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Xiao, B.; Jin, H.; Zhong, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Satellite Support to Estimate Livestock Ammonia Emissions: A Case Study in Hebei, China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Pan, D.; Guo, X.; Sun, K.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; ois Coheur, P.-F.; Clerbaux, C.; Puchalski, M.; Zondlo, M.A. Bridging the Spatial Gaps of the Ammonia Monitoring Network Using Satellite Ammonia Measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 13217–13234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Shephard, M.W.; Dentener, F.; Hurtmans, D.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Karagulian, F.; Van Damme, M.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P. Satellite Monitoring of Ammonia: A Case Study of the San Joaquin Valley. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Clerbaux, C.; Coheur, P.-F. Tracking down Global NH3 Point Sources with Wind-Adjusted Super Resolution. Atmos. Meas. Technol. 2019, 12, 5457–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammers, E.; Schaap, M.; Haaima, M.; Palm, M.; Wichink Kruit, R.J.; Volten, H.; Hensen, A.; Swart, D.; Erisman, J.W. Measuring Atmospheric Ammonia with Remote Sensing Campaign: Part 1—Characterisation of Vertical Ammonia Concentration Profile in the Centre of The Netherlands. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inness, A.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Barré, J.; Benedictow, A.; Blechschmidt, A.-M.; Dominguez, J.J.; Engelen, R.; Eskes, H.; Flemming, J.; et al. The CAMS Reanalysis of Atmospheric Composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 3515–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, D.C.; Ropkins, K. Openair—An R Package for Air Quality Data Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 27–28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Dimov, S.S.; Nguyen, C.D. Selection of K in K-Means Clustering. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2005, 219, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Dey, L. A K-Mean Clustering Algorithm for Mixed Numeric and Categorical Data. Data Knowl. Eng. 2007, 63, 503–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparović, M.; Zrinjski, M.; Gudelj, M. Automatic Cost-Effective Method for Land Cover Classification (ALCC). Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahata, K.; Das, R.; Das, S.; Sarkar, A. Land Use Land Cover Map Segmentation Using Remote Sensing: A Case Study of Ajoy River Watershed, India. J. Intell. Syst. 2020, 30, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, N.H. Squared Euclidean Distances. In Essentials of Multivariate Data Analysis; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; p. 95. ISBN 9781466584792. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hendricks, J.; Righi, M.; Beer, C.G. An Aerosol Classification Scheme for Global Simulations Using the K-Means Machine Learning Method. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2022, 15, 509–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouilloux Annefou, A. annefou/metos_python: Working with Spatio-Temporal Data in Python (V2018.0.0); Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Duchesnay, É. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Umargono, E.; Suseno, J.E.; Vincensius, G. K-Means Clustering Optimization Using the Elbow Method and Early Centroid Determination Based-on Mean and Median. In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology; SCITEPRESS—Science and Technology Publications: Setúbal, Portugal, 2019; pp. 234–240. [Google Scholar]
- Naghizadeh, A.; Metaxas, D.N. Condensed Silhouette: An Optimized Filtering Process for Cluster Selection in K-Means. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 176, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Franco-Penya, H.; Kelleher, J.D.; Pugh, J.; Ross, R. Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition; Perner, P., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10358, ISBN 978-3-319-62415-0. [Google Scholar]
- Suraya, S.; Sholeh, M.; Lestari, U. Evaluation of Data Clustering Accuracy Using K-Means Algorithm. Int. J. Multidiscip. Approach Res. Sci. 2023, 2, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahapure, K.R.; Nicholas, C. Cluster Quality Analysis Using Silhouette Score. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Sydney, Australia, 6–9 October 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 747–748. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An Overview of the HYSPLIT_4 Modelling System for Trajectories, Dispersion, and Deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. Description of the HYSPLIT_4 Modeling System. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Draxler, R.R.; Stunder, B.; Rolph, G.; Stein, A.; Taylor, A. HYSPLIT4 User’s Guide Version 4-Last Revision 2016; HYSPLIT Air Resources Laboratory: College Park, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rolph, G.D.; Draxler, R.R.; Stein, A.F.; Taylor, A.; Ruminski, M.G.; Kondragunta, S.; Zeng, J.; Huang, H.-C.; Manikin, G.; McQueen, J.T.; et al. Description and Verification of the NOAA Smoke Forecasting System: The 2007 Fire Season. Weather Forecast 2009, 24, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Ginoux, P.; Stein, A.F. An Empirically Derived Emission Algorithm for Wind-blown Dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunder, B.J.B.; Heffter, J.L.; Draxler, R.R. Airborne Volcanic Ash Forecast Area Reliability. Weather. Forecast. 2007, 22, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassò, A.; Rodeschini, J.; Fusta Moro, A.; Shaboviq, Q.; Maranzano, P.; Cameletti, M.; Finazzi, F.; Golini, N.; Ignaccolo, R.; Otto, P. Agrimonia: A Dataset on Livestock, Meteorology and Air Quality in the Lombardy Region, Italy. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kułek, B.; Weidinger, T. The Influence of Meteorological Factors and the Time of Day on the Concentration of Ammonia in the Atmosphere Measured Using the Photoacoustic Method near a Cattle Farm—A Case Study. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Heald, C.L.; Hurtmans, D.; Ngadi, Y.; Clerbaux, C.; Dolman, A.J.; Erisman, J.W.; Coheur, P.F. Global Distributions, Time Series and Error Characterization of Atmospheric Ammonia (NH3) from IASI Satellite Observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, T. The Revision of the German Fertiliser Ordinance in 2017. Food Resour. Econ. Discuss. Pap. 2017, 2, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnilke, A.; Sanders, T. Forest Fires and the Role of Military Contaminated Sites on Forest and Succession Areas in Brandenburg; Thünen Institute of Forest Ecosystems: Braunschweig, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, C.; Kreutzer, K. Three Years of Continuous Measurements of Atmospheric Ammonia Concentrations over a Forest Stand at the Höglwald Site in Southern Bavaria. Plant Soil. 2002, 240, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quakernack, R.; Pacholski, A.; Techow, A.; Herrmann, A.; Taube, F.; Kage, H. Ammonia Volatilization and Yield Response of Energy Crops after Fertilization with Biogas Residues in a Coastal Marsh of Northern Germany. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 160, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Q.; Groot, J.C.J.; Zhang, K.; Schulte, R.P.O. Effects of Housing System, Measurement Methods and Environmental Factors on Estimating Ammonia and Methane Emission Rates in Dairy Barns: A Meta-Analysis. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 205, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qi, J.; Shi, J.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Identification of Major Sources of Atmospheric NH3 in an Urban Environment in Northern China During Wintertime. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6839–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Wang, W.; Tan, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, L. Roles of Historical Land Use/Cover and Nitrogen Fertilizer Application Changes on Ammonia Emissions in Farmland Ecosystem from 1990 to 2020 in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, D.S.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, J.B.; Li, M.J.; Ren, Z.H. Identification of Regional Atmospheric PM10 Transport Pathways Using HYSPLIT, MM5-CMAQ and Synoptic Pressure Pattern Analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2010, 25, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalmogith, S.S.; Harrison, R.M. The Use of Trajectory Cluster Analysis to Examine the Long-Range Transport of Secondary Inorganic Aerosol in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6686–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





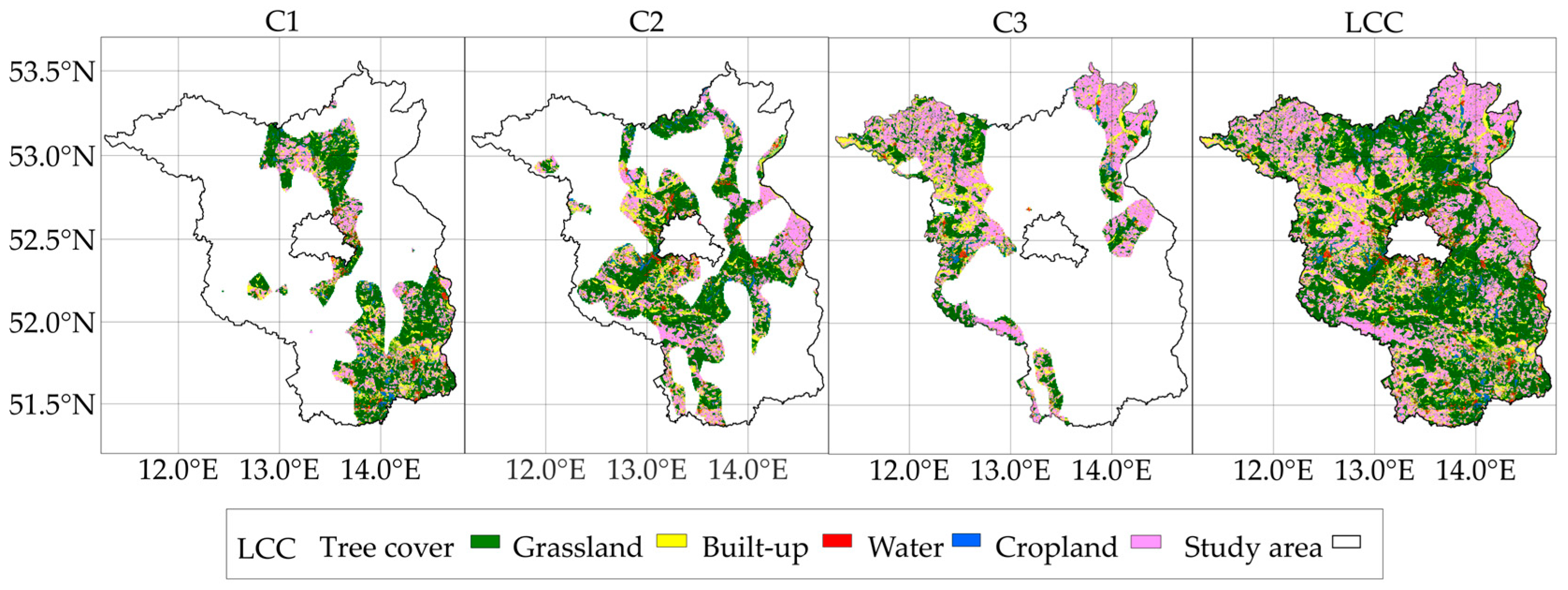
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCC | Percentage % | Area km2 | Percentage % | Area km2 | Percentage % | Area km2 |
| Tree Cover | 13.11 | 4531.837 | 22.55 | 5544.947 | 5.86 | 3060.388 |
| Grassland | 4.71 | 1631 | 10.17 | 2237.918 | 3.93 | 2047.746 |
| Cropland | 5.1 | 1760.729 | 15.55 | 3050.081 | 8.02 | 4172.607 |
| Built-up | 0.81 | 282.08 | 1.44 | 357.85 | 0.38 | 197.77 |
| Water | 0.77 | 265.98 | 1.34 | 317.758 | 0.36 | 187.211 |
| LCC | % | km2 |
|---|---|---|
| Tree Cover | 14.62 | 621.47235 |
| Grassland | 11.34 | 481.81842 |
| Cropland | 22.11 | 938.78178 |
| Built-up | 0.8 | 34.07092 |
| Water | 0.33 | 13.84679 |
| Cluster | Frequency | Direction |
|---|---|---|
| A | 20 | SE |
| B | 5 | W |
| C | 18 | NW |
| D | 32 | N |
| E | 25 | NEN |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saravia, C.; Trachte, K. Spatiotemporal Analysis of NH3 Emission Sources and Their Relation to Land Use Types in the Eastern German Lowlands. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030346
Saravia C, Trachte K. Spatiotemporal Analysis of NH3 Emission Sources and Their Relation to Land Use Types in the Eastern German Lowlands. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaravia, Christian, and Katja Trachte. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Analysis of NH3 Emission Sources and Their Relation to Land Use Types in the Eastern German Lowlands" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030346
APA StyleSaravia, C., & Trachte, K. (2025). Spatiotemporal Analysis of NH3 Emission Sources and Their Relation to Land Use Types in the Eastern German Lowlands. Atmosphere, 16(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030346







