Spatiotemporal Variability of Road Transport Emissions Based on Vehicle Speed Profiles—Impacts on Urban Air Quality: A Case Study for Thessaloniki, Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
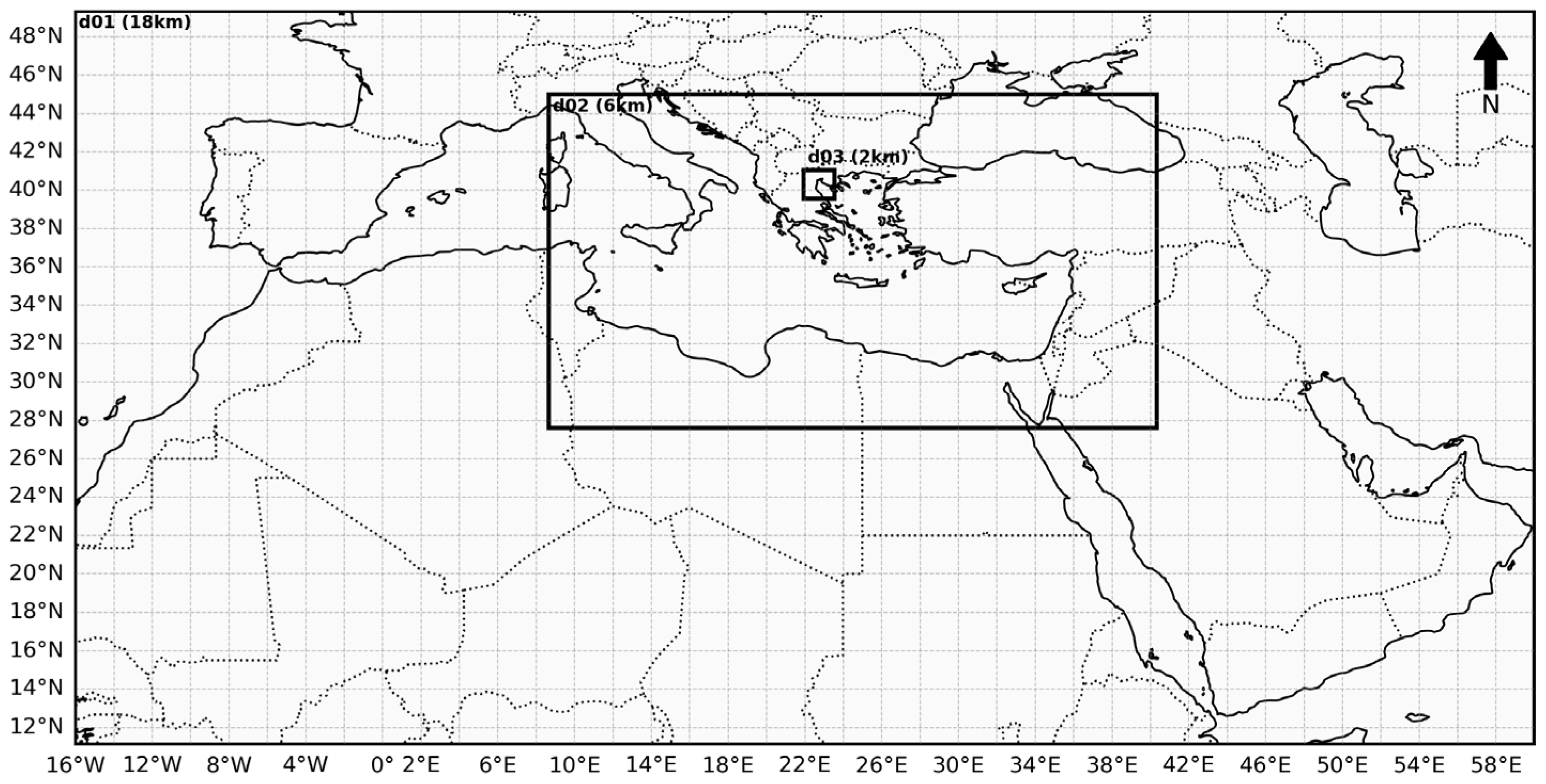
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Modeling System
2.2.1. Description of the Air Quality Modeling System
2.2.2. Simulation Scenarios—Base, Zero-Out and Dynamic Cases
- The Base Case Scenario (BSCN) represents the reference configuration, where all emission sources are included, and road transport emissions are temporally distributed using standard static profiles from the CAMS-REG inventory. These profiles are applied uniformly across the domains, assuming no spatial variability in traffic-related temporal patterns.
- The Zero-Out Scenario (ZeroSCN) excludes all road transport emissions (i.e., exhaust, non-exhaust, dust resuspension) entirely, enabling the quantification of their contribution to ambient pollutant concentrations. This scenario offers insight into the sensitivity of air pollution and particle levels to the temporal resolution and spatial allocation of transport emissions. The zero-out approach, also known as the Brute Force Method (BMF), has been widely applied by scientific community in air quality modeling in order to quantify the contribution of specific emissions sources on air quality levels [23,38,39,40,41]. For instance, these studies demonstrated its effectiveness in source apportionment by sequentially removing individual sectors from the model. Although computationally intensive, the method is straightforward to implement and provides intuitive results, making it a commonly used baseline approach despite its limitations in accounting for non-linear chemical interactions, as discussed by Thunis et al. [39].
- The Dynamic Scenario (DynSCN) incorporates the same total emissions and source categories as the BSCN but replaces the static road transport temporal profiles with the newly developed dynamic spatiotemporal profiles, which account for mean vehicle speeds and therefore traffic patterns within the Thessaloniki urban area (see Section 2.2.5). This scenario allows for a more realistic temporal and spatial distribution of road transport emissions in Thessaloniki.
2.2.3. Road Transport Emissions
2.2.4. Spatial Distribution
2.2.5. Temporal Distribution
Static Temporal Profiles
Dynamic Temporal Profiles
- Wi,t is the normalized inverse-speed weight, for link ID i at time step t,
- ui,t is the mean vehicle speed for link ID i and time step t and
- Pi,t is the spatiotemporal profile for link ID i and time step t
- Nt is the national static profile at time step t
3. Results and Discussion
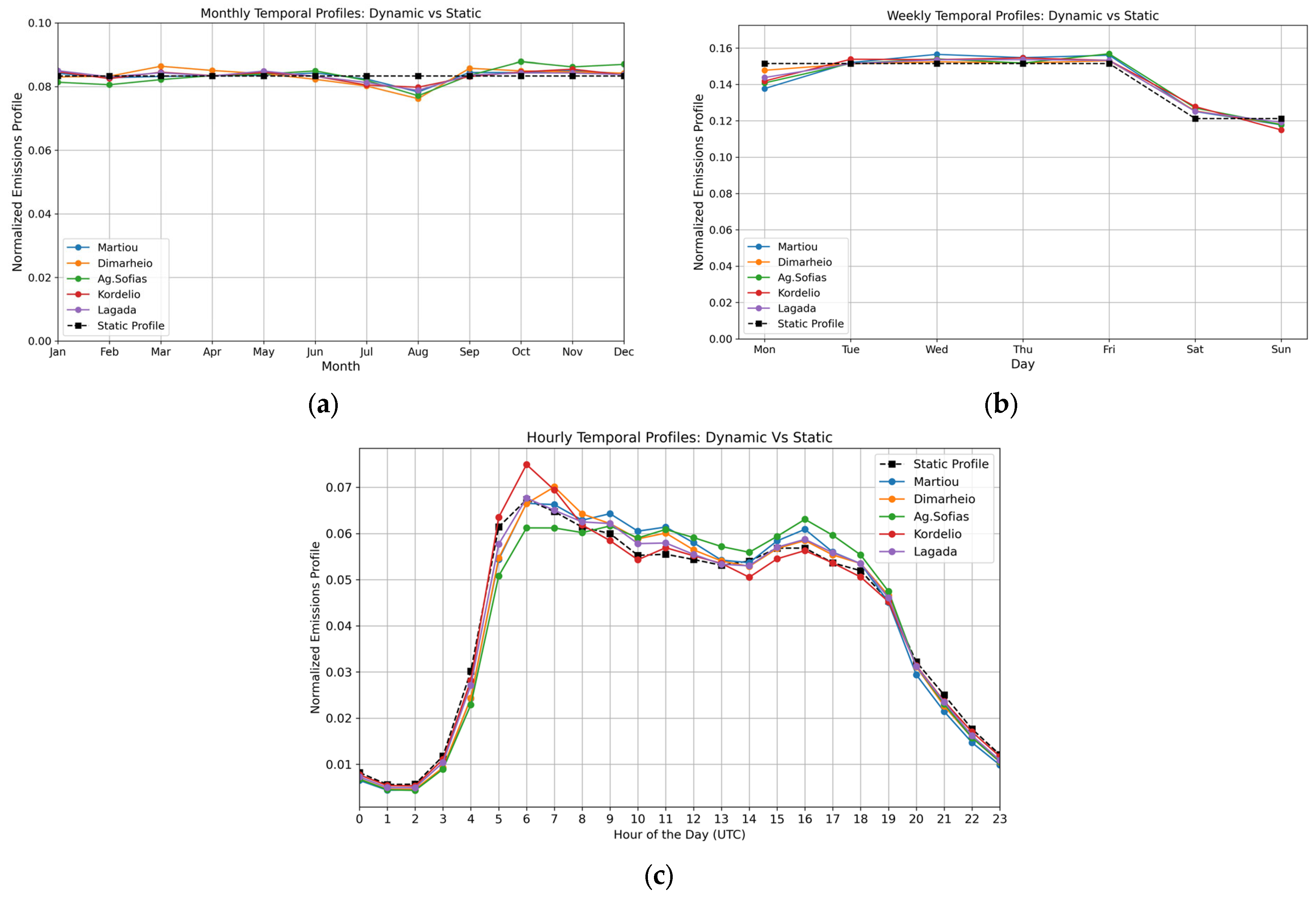
3.1. Dynamic Spatiotemporal Emissions Profiles
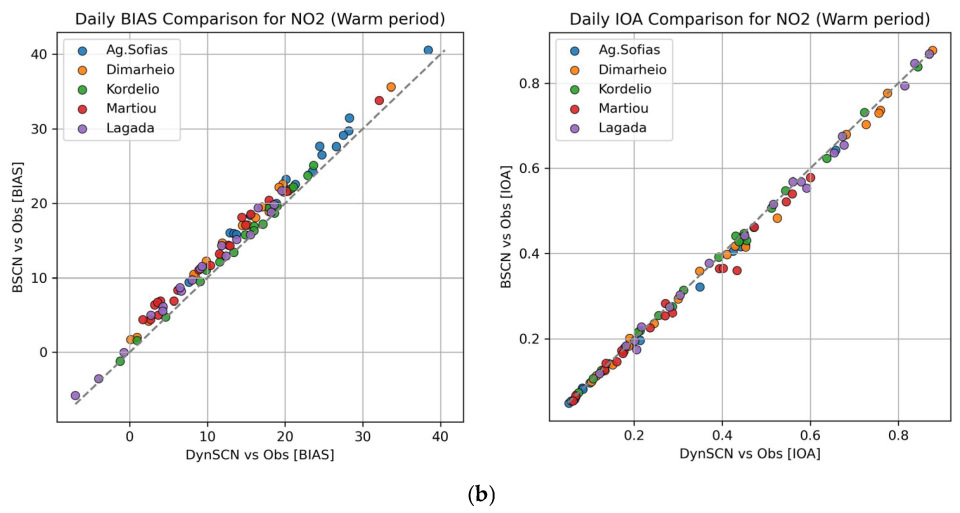
3.2. Modeling System Evaluation
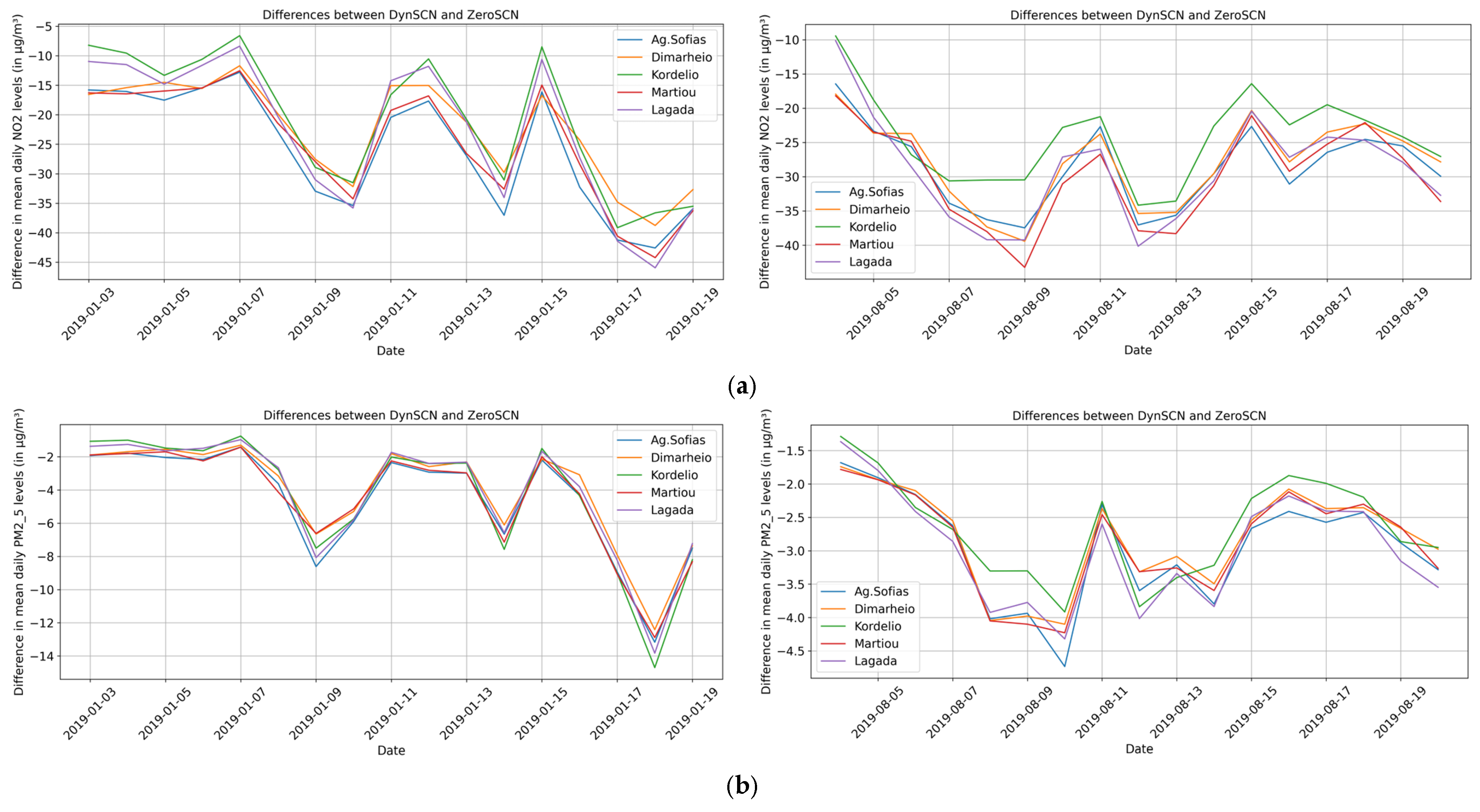
3.3. Contribution of Road Transport to Air Quality Levels
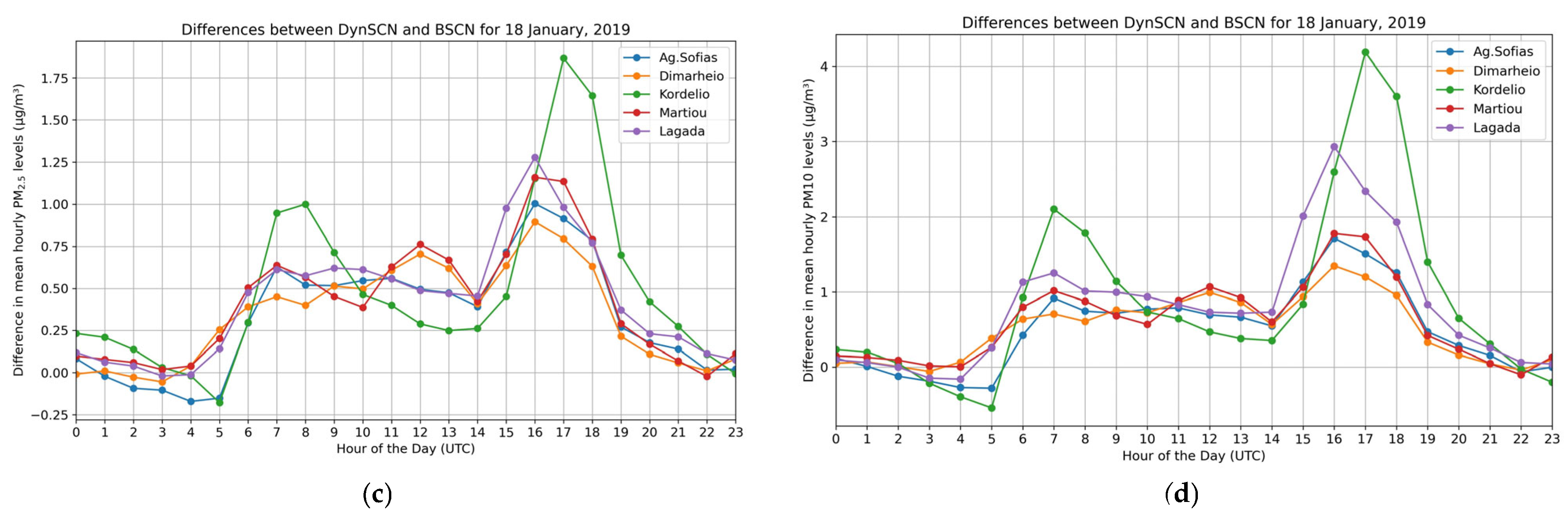
3.4. Impacts of Spatiotemporal Profiles of Road Transport Emissions on Air Quality Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liora, N.; Poupkou, A.; Kontos, S.; Meleti, C.; Chrysostomou, K.; Aifadopoulou, G.; Zountsa, S.; Kalogirou, C.; Chacartegui, R.; Liguori, F.; et al. Estimating Road Transport Pollutant Emissions Under Traffic-Congested Conditions with an Integrated Modelling Tool—Emissions Reduction Scenarios Analysis. Emiss. Control Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Managi, S. Contribution of On-Road Transportation to PM2.5. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liora, N.; Kontos, S.; Parliari, D.; Akritidis, D.; Poupkou, A.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Melas, D. “On-Line” Heating Emissions Based on WRF Meteorology—Application and Evaluation of a Modeling System over Greece. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiou, A.; Liora, N.; Sebos, I.; Chatzimichail, C.; Melas, D. Measures and Policies for Reducing PM Exceedances through the Use of Air Quality Modeling: The Case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Sustainability 2023, 15, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscitelli, P.; Valenzano, B.; Rizzo, E.; Maggiotto, G.; Rivezzi, M.; Esposito Corcione, F.; Miani, A. Air Pollution and Estimated Health Costs Related to Road Transportations of Goods in Italy: A First Healthcare Burden Assessment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progiou, A.G.; Ziomas, I.C. Road Traffic Emissions Impact on Air Quality of the Greater Athens Area Based on a 20year Emissions Inventory. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolsi, J.; Rehimi, F.; Kalboussi, A. Urban Traffic and Induced Air Quality Modeling and Simulation: Methodology and Illustrative Example. Urban Clim. 2017, 21, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Wu, Y.; Seigneur, C.; Roustan, Y. Multi-Scale Modeling of Urban Air Pollution: Development and Application of a Street-in-Grid Model (v1.0) by Coupling MUNICH (v1.0) and Polair3D (v1.8.1). Geosci. Model. Dev. 2018, 11, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fameli, K.-M.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. The New Open Flexible Emission Inventory for Greece and the Greater Athens Area (FEI-GREGAA): Account of Pollutant Sources and Their Importance from 2006 to 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, K.; Katragkou, E.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. MOSESS: A New Emission Model for the Compilation of Model-Ready Emission Inventories—Application in a Coal Mining Area in Northern Greece. Environ. Model. Assess. 2013, 18, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, F.; Fonseca, N.; Mera, Z.; López, J.-M. Assessing On-Road Emissions from Urban Buses in Different Traffic Congestion Scenarios by Integrating Real-World Driving, Traffic, and Emissions Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 161002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gately, C.K.; Hutyra, L.R.; Peterson, S.; Sue Wing, I. Urban Emissions Hotspots: Quantifying Vehicle Congestion and Air Pollution Using Mobile Phone GPS Data. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Villani, M.G.; D’Elia, I.; D’Isidoro, M.; Liberto, C.; Piersanti, A.; Tinarelli, G.; Valenti, G.; Ciancarella, L. A Study of Traffic Emissions Based on Floating Car Data for Urban Scale Air Quality Applications. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Mu, J.; Liu, S. A Systematic Review of Urban Road Traffic CO2 Emission Models. Carbon Footpr. 2025, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Int Panis, L.; Broekx, S.; Liu, R. Modelling Instantaneous Traffic Emission and the Influence of Traffic Speed Limits. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 371, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kühbacher, D.; Chen, J.; Aigner, P.; Ilic, M.; Super, I.; Van Der Gon, H.D. DRIVE v1.0: A Data-Driven Framework to Estimate Road Transport Emissions and Temporal Profiles. EGUsphere 2025, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiaousidis, D.T.; Liora, N.; Kontos, S.; Poupkou, A.; Akritidis, D.; Melas, D. Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Comission Air Quality: Commission Decides to Refer GREECE to the Court of Justice over Poor Air Quality. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/en/ip_20_2151 (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Chatzopoulou, A.; Mavroidis, I. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Air Pollutants in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulou, A.; Papargyri, E.; Boile, M. Innovative Scheme for Efficient Freight Movement and Sustainable Emissions Management. Transp. Telecommun. J. 2019, 20, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsilingiridis, G.; Zachariadis, T.; Samaras, Z. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Air Pollutant Emissions in Thessaloniki, Greece: Investigation of Emission Abatement Measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marécal, V.; Peuch, V.-H.; Andersson, C.; Andersson, S.; Arteta, J.; Beekmann, M.; Benedictow, A.; Bergström, R.; Bessagnet, B.; Cansado, A.; et al. A Regional Air Quality Forecasting System over Europe: The MACC-II Daily Ensemble Production. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 2777–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liora, N.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, T.M.; Kakosimos, K.E.; Stein, O.; Melas, D. Impacts of Natural Emission Sources on Particle Pollution Levels in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukouli, M.-E.; Pseftogkas, A.; Karagkiozidis, D.; Skoulidou, I.; Drosoglou, T.; Balis, D.; Bais, A.; Melas, D.; Hatzianastassiou, N. Air Quality in Two Northern Greek Cities Revealed by Their Tropospheric NO2 Levels. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocas, H.; Kelessis, A.; Helmis, C.; Petrakakis, M.; Zoumakis, M.; Pappas, K. Synoptic and Local Scale Atmospheric Circulation Associated with Air Pollution Episodes in an Urban Mediterranean Area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 95, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.A.; Kelessis, A.; Paschalidou, A.K.; Petrakakis, M. Identification of Sources and Processes Affecting Particulate Pollution in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 7293–7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussiopoulos, Ν.; Vlachokostas, C.; Tsilingiridis, G.; Douros, I.; Hourdakis, E.; Naneris, C.; Sidiropoulos, C. Air Quality Status in Greater Thessaloniki Area and the Emission Reductions Needed for Attaining the EU Air Quality Legislation. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M.; et al. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Model Version 4; UCAR/NCAR: Boulder, CO, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liora, N.; Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, T.M.; Melas, D. The Natural Emissions Model (NEMO): Description, Application and Model Evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, S.; Liora, N.; Giannaros, C.; Kakosimos, K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. Modeling Natural Dust Emissions in the Central Middle East: Parameterizations and Sensitivity. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENVIRON. User’s Guide CAMx Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions, 6.5th ed.; Ramboll US Corporation: Novato, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Soci, C.; Hersbach, H.; Simmons, A.; Poli, P.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis from 1940 to 2022. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 4014–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peuch, V.-H.; Engelen, R.; Rixen, M.; Dee, D.; Flemming, J.; Suttie, M.; Ades, M.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Ananasso, C.; Andersson, E.; et al. The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service: From Research to Operations. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E2650–E2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenen, J.; van der Gon, H.D.; Super, I.; Dellaert, S.; Visschedijk, A.; Guevara, M.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Majamäki, E.; Schindlbacher, S.; Matthews, B. Recent Developments in the CAMS European Regional Emissions Data (CAMS-REG); CAMS: Karachi, Pakistan, 2021; Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/sites/default/files/custom-uploads/CAMS-5thPUW/5.%20Kuenen_CAMS_emissions_PUW_Remote_20210629.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2024).
- Kuenen, J.; Dellaert, S.; Visschedijk, A.; Jalkanen, J.-P.; Super, I.; Van Der Gon, H.D. CAMS-REG-v4: A State-of-the-Art High-Resolution European Emission Inventory for Air Quality Modelling. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 491–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS). CAMS v6.2 Global and European Emission Inventories: Documentation of CAMS v6.2 Global and European Emission Inventories; Deliverable D6.1.2—202306, CAMS261_2021SC1; ECMWF: Reading, UK, 2023; Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/sites/default/files/publications/CAMS261_2021SC1_D6.1.2-2022_202306_Docu_v1_APPROVED_Ver1.pdf (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Schaap, Μ.; Manders, A.M.M.; Hendriks, E.C.J.; Cnossen, J.M.; Segers, A.J.S.; van der Gon, H.A.C.D.; Jozwicka, M. Regional Modelling of Particulate Matter for the Netherlands; Research Program on Particulate Matter; PBL: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Šedivá, T.; Štefánik, D. Combined Brute Force Method for Source Apportionment Purposes. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunis, P.; Clappier, A.; Tarrason, L.; Cuvelier, C.; Monteiro, A.; Pisoni, E.; Wesseling, J.; Belis, C.A.; Pirovano, G.; Janssen, S.; et al. Source Apportionment to Support Air Quality Planning: Strengths and Weaknesses of Existing Approaches. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nagashima, T.; Doan, Q.-V. Air Quality Modeling Study on the Controlling Factors of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in Hanoi: A Case Study in December 2010. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranishi, K.; Ikemori, F.; Nakatsubo, R.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A.; Kikutani, Y.; Asano, K.; Sugata, S. Identification of Biased Sectors in Emission Data Using a Combination of Chemical Transport Model and Receptor Model. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politis, I.; Georgiadis, G.; Papadopoulos, E.; Fyrogenis, I.; Nikolaidou, A.; Kopsacheilis, A.; Sdoukopoulos, A.; Verani, E. COVID-19 Lockdown Measures and Travel Behavior: The Case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2021, 10, 100345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA European Environment Agency. National Emission Reduction Commitments Directive (NECD)—National Emission Inventories: Greece Submission. 2023. Available online: https://cdr.eionet.europa.eu/gr/eu/nec_revised/inventories (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- EMISIA SA COPERT 5: Computer Programme to Calculate Emissions from Road Transport. Thessaloniki, Greece: EMISIA SA. 2023. Available online: https://www.emisia.com/utilities/copert/ (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- YPEN Greek Ministry of Environment and Energy. Greece’s Informative Inventory Report (IIR) 2024. Athens: Ministry of Environment and Energy. 2024. Available online: https://ypen.gov.gr/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/2024_IIR_gr_.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- NAP National Geospatial Data Infrastructure (Geoportal). Greek Road Network, OpenStreetMap Data in Layered GIS Format. 2022. Available online: http://data.nap.gov.gr/dataset/latest-open-street-map-objects-for-greece/resource/8de9d8dc-9d5d-4a59-af72-b8052b1ddc9b (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Eurostat Territorial Typologies Manual—Urban-Rural Typology. 2021. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=territorial_typologies_manual_-_urban-rural_typology (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- HELLASTRON Hellenic Association of Toll Road Network. Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://hellastronin.eu/statistics/statistics_show.php (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Ayfantopoulou, G.; Salanova Grau, J.M.; Tzenos, P.; Tolikas, A. Open Data from Taxis and Bluetooth Detectors to Extract Congestion and Mobility Patterns in Thessaloniki. Data Brief 2023, 47, 108899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TrafficThess Centre for Research and Technology Hellas—Hellenic Institute of Transport (CERTH/HIT). Traffic Monitoring System of Thessaloniki. Available online: https://www.trafficthess.imet.gr (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- International Tunnelling and Underground Space Association (ITA-AITES). Activity Report 2024; ITA-AITES: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://about.ita-aites.org/files/RapportNM/2024/Switzerland.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- European Commission. Stop Holding Your Breath: Thessaloniki Metro Is Open; Panorama Magazine, 12 November 2024. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/regional_policy/whats-new/panorama/2024/12/12-11-2024-stop-holding-your-breath-thessaloniki-metro-is-open_en (accessed on 1 September 2025).







| Site Name | Bias | R | IOA | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | W | C | W | C | W | C | W | |
| Kordelio | −0.15 | −1.32 | 0.81 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 2.32 | 1.82 |
| Dimarheio | −0.28 | −1.05 | 0.78 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 2.54 | 2.3 |
| Martiou | −0.22 | −0.47 | 0.80 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 2.35 | 1.24 |
| Site Name | BIAS | R | IOA | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | W | C | W | C | W | C | W | |
| Kordelio | −6.98 | 15.18 | 0.75 | 0.36 | 0.85 | 0.46 | 22.98 | 33.72 |
| Dimarheio | NA | 15.49 | NA | 0.55 | NA | 0.60 | NA | 30.23 |
| Martiou | −13.57 | 12.81 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 0.40 | 28.58 | 32.54 |
| Ag.Sofias | −22.11 | 22.74 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 32.75 | 38.83 |
| Lagada | −5.98 | 10.26 | 0.73 | 0.51 | 0.84 | 0.63 | 23.94 | 29.02 |
| Site Name | BIAS | R | IOA | RMSE | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | W | C | W | C | W | C | W | |
| Dimarheio | −3.15 | −5.91 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 22.37 | 9.74 |
| Martiou | 9.03 | −0.65 | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.60 | 19.29 | 5.46 |
| Ag.Sofias | −5.89 | −5.43 | 0.38 | 0.25 | 0.59 | 0.49 | 27.45 | 8.41 |
| Lagada | 1.05 | NA | 0.56 | NA | 0.73 | NA | 18.66 | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liora, N.; Kontos, S.; Tsiaousidis, D.; Salanova Grau, J.M.; Siomos, A.; Melas, D. Spatiotemporal Variability of Road Transport Emissions Based on Vehicle Speed Profiles—Impacts on Urban Air Quality: A Case Study for Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121337
Liora N, Kontos S, Tsiaousidis D, Salanova Grau JM, Siomos A, Melas D. Spatiotemporal Variability of Road Transport Emissions Based on Vehicle Speed Profiles—Impacts on Urban Air Quality: A Case Study for Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(12):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121337
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiora, Natalia, Serafim Kontos, Dimitrios Tsiaousidis, Josep Maria Salanova Grau, Alexandros Siomos, and Dimitrios Melas. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variability of Road Transport Emissions Based on Vehicle Speed Profiles—Impacts on Urban Air Quality: A Case Study for Thessaloniki, Greece" Atmosphere 16, no. 12: 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121337
APA StyleLiora, N., Kontos, S., Tsiaousidis, D., Salanova Grau, J. M., Siomos, A., & Melas, D. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variability of Road Transport Emissions Based on Vehicle Speed Profiles—Impacts on Urban Air Quality: A Case Study for Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmosphere, 16(12), 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121337








