Precipitation Variation Characteristics in Gannan Prefecture, China: Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis and the BEAST (Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonality, and Trend) Ensemble Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Profile
2.2. Data Sources
3. Methods
3.1. Climate Change Trend Rate
3.2. Anomaly and Cumulative Anomaly
3.3. Innovation Trend Analysis (ITA)
3.4. ITA-Change Boxes (ITA-CB)
3.5. BEAST Ensemble Algorithm
4. Results
4.1. Precipitation Variability Analysis
4.1.1. Analysis of Interannual Precipitation Variability
4.1.2. Analysis of Interdecadal Precipitation Variation
4.1.3. Analysis of Precipitation Variability Within the Year
4.2. Spatial Distribution of the Annual Mean Precipitation
4.2.1. Spatial Distribution of the Annual Mean Precipitation Patterns
4.2.2. Seasonal Precipitation Spatial Patterns
4.3. Precipitation Abrupt Change
4.3.1. Analysis of Abrupt Changes in Annual Average Precipitation
4.3.2. Analysis of Abrupt Changes in Seasonal Average Precipitation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Lai, C.; Cheng, G.L.; Zhao, Y.Z.; Rui, D.Z.; Xiao, H.C.; Xiao, W.Z.; Ming, Y.W. Does drought in China show a significant decreasing trend from 1961 to 2009? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Q.; Hu, M.G.; Xu, C.D.; Zhou, L.; Nie, J. Exploring the spatial pattern of house collapse rates caused by extreme rainfall in central China: The role of natural and social factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, B.C.; Shi, Y.; Han, Z.Y.; Lu, B. Interpretation of the IPCC AR6 on the impacts and risks of climate change. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 18, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadnabizadeh, M. Critical findings of the sixth assessment report (AR6) of working Group I of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC) for global climate change policymaking a summary for policymakers (SPM) analysis. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2022, 15, 652–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Z. New physical science behind climate change: What does IPCC AR6 tell us? Innovation 2021, 2, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.X.; Chen, H.S.; Wang, G.J.; Xu, W.C.; Wang, S.M.; Yu, W.J. Characteristics of the precipitation concentration and their relationship with the precipitation structure: A case study in the Huai River basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 253, 105484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei Hassanlu, A.; Erfanian, M.; Javan, K.; Najafi, M.R. Daily precipitation concentration and Shannon’s entropy characteristics: Spatial and temporal variability in Iran, 1966–2018. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, S.S.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhou, Q.M.; Hu, Q. Spatiotemporal characteristics of seasonal precipitation and their relationships with ENSO in Central Asia during 1901–2013. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1341–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.D.; Wang, M.R.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, T. Spatial and Temporal Variability Characteristics and Driving Factors of Extreme Precipitation in the Wei River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, W. Spatial-temporal characteristics of precipitation and its relationship with land use/cover change on the qinghai-tibet plateau, China. Land 2021, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhang, P.C.; Tang, L.; Huang, Y.; Feng, N. Spatial and temporal variations of precipitation in Northwest China during 1973–2019. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2024, 155, 4347–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.P.; Fang, R.Y.; Deng, C.Y.; Zhao, H.J.; Shen, M.H.; Wang, Q. Slope aspect effects on plant community characteristics and soil properties of alpine meadows on Eastern Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, C.L. The contribution of common and rare species to species abundance patterns in alpine meadows: The effect of elevation gradients. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; Xue, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Driving mechanisms of ecosystem services and their trade-offs and synergies in the transition zone between the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and the Loess Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Wang, X.L.; Ji, Z.J.; Wang, S.P.; Fu, W.R. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of different intensity precipitation in flood season over the Gannan Plateau during 1976–2019. Desert Oasis Meteorol. 2022, 16, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Bai, B.; Chen, X.J.; Li, L.P. Variations and Distribution of precipitation of Gannan based on DEM during 1983–2012. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2016, 36, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.C.; Jiao, M.L.; Qin, T.; Guo, T. Variation characteristics and influencing factors of summer half-year precipitation in Hedong region of Gansu Province from 1973 to 2020. Arid Land Geogr. 2022, 4, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. An innovative trend analysis methodology. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Innovative trend significance test and applications. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadem, Z.; Tayfur, G. In-depth Exploration of Temperature Trends in Morocco: Combining Traditional Methods of Mann Kendall with Innovative ITA and IPTA Approaches. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2024, 181, 2717–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güçlü, Y.S. Improved Visualization for Trend Analysis by Comparing with Classical Mann-Kendall Test and ITA. J. Hydrol. 2020, 584, 124674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliengchuay, W.; Mingkhwan, R.; Kiangkoo, N.; Suwanmanee, S.; Sahanavin, N.; Kongpran, J.; Aung, H.W.; Tantrakarnapa, K. Analyzing temperature, humidity, and precipitation trends in six regions of Thailand using innovative trend analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshan, S. An improved version of innovative trend analyses. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.W.; Jin, L.; Li, W.; Wang, W.T. Assessing the Vulnerability of Grasslands in Gannan of China Under the Dual Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.P.; Gao, J.L.; Liang, T.G.; He, Z.B.; Feng, S.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, D.M. Comprehensive Ecological Risk Changes and Their Relationship with Ecosystem Services of Alpine Grassland in Gannan Prefecture from 2000-2020. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, F.J.; Dong, S.C.; Cheng, H. Research on the sustainable development mode of resource-oriented regions on plateaus—A case study for Gannan Tibetan autonomous prefecture. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 32, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozgatligil, C.; Aslan, S.; Iyigun, C.; Batmaz, I. Comparison of Missing Value Imputation Methods in Time Series: The Case of Turkish Meteorological Data. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Yuan, R.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, P.; Li, T.; Lin, Y.; Du, C.; et al. Characteristics of Potential Evapotranspiration Changes and Its Climatic Causes in Heilongjiang Province from 1960 to 2019. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, Y.F. Evolution of Dry/Wet Climate in Xichang from 1961 to 2016. Pearl River 2022, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tabari, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, S.; Hu, Z. Innovative Trend Analysis of Annual and Seasonal Rainfall in the Yangtze River Delta, Eastern China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Qian, H. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall and extreme values in Shaanxi, China, since the 1950s. Int. J. Climatol. 2017, 37, 2582–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Xue, H.R.; Liu, T. Change characteristics and trends of precipitation and average temperature changes in the Xilinhe River Basin from 1961 to 2016. Arid Land Geogr. 2021, 44, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wulder, M.A.; Hu, T.; Bright, R.; Wu, Q.; Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Toman, E.; Mallick, B.; Zhang, X.; et al. Detecting change-point, trend, and seasonality in satellite time series data to track abrupt changes and nonlinear dynamics: A Bayesian ensemble algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Adler, R.F. Interdecadal Variability/Long-Term Changes in Global Precipitation Patterns During the Past Three Decades: Global Warming and/or Pacific Decadal Variability? Clim. Dyn. 2013, 40, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Jia, X.; Chen, X.; Dong, W. Interdecadal changes in the interannual variations in spring precipitation over the Tarim Basin. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Jiao, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, Q. Spatial-Temporal Dynamics of Water Conservation in Gannan in the Upper Yellow River Basin of China. Land 2023, 12, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, P. Ecological Frangibility and Its Formation Cause of Important Water-supply Ecological Function Area of Yellow River in South Gansu Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 29, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Zhu, J.T.; Tian, T. Analysis of weather causes of summer precipitation events with different intensities in the eastern and western regions of Gansu Province. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.X.; Wang, B.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Huang, W.B. Spatiotemporal characteristics of summer rainstorm days in Gansu Province and their relationship with atmospheric circulation. Plateau Meteorol. 2017, 36, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Han, F.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.X.; Sun, Y.; Li, F.M. Analysis of spatial and seasonal variations in climate warming and humidification in northwest China. Arid Zone Res. 2023, 40, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caloiero, T.; Coscarelli, R.; Ferrari, E. Assessment of seasonal and annual rainfall trend in Calabria (southern Italy) with the ITA method. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 22, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzater, B.; Elouissi, A.; Fellah, S.; Hachemaoui, A. Spatio-temporal analysis of trends in annual maximum rainfall in the North-West of Algeria: Comparative analysis of recent and old non-parametric methods. Water Environ. J. 2024, 38, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ma, L.; Liu, T.; Huang, X.; Sun, G. Quantitative response relationships between annual precipitation in China from 1951 to 2018 and its influencing factors. Hydrol. Res. 2022, 53, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguglia, O.; Palazzi, E.; Arnone, E. Elevation dependent change in ERA5 precipitation and its extremes. Clim. Dyn. 2024, 62, 8137–8153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

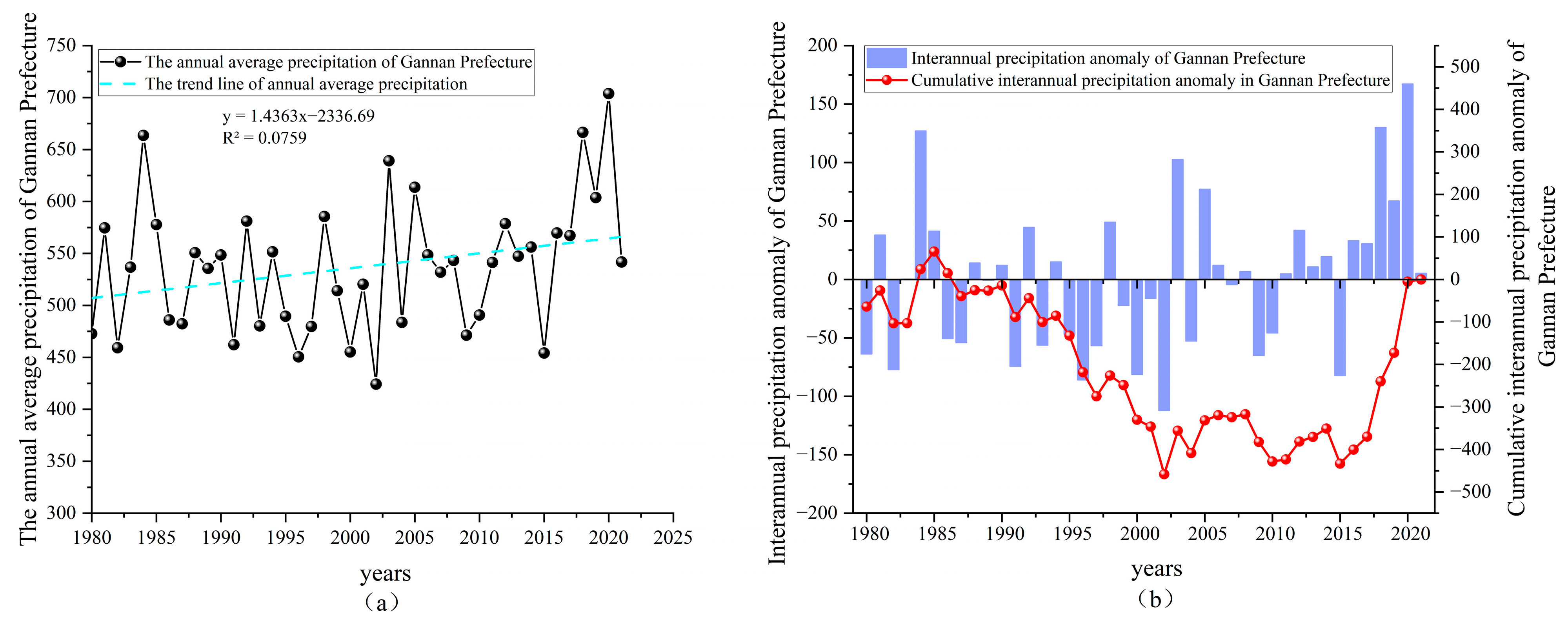


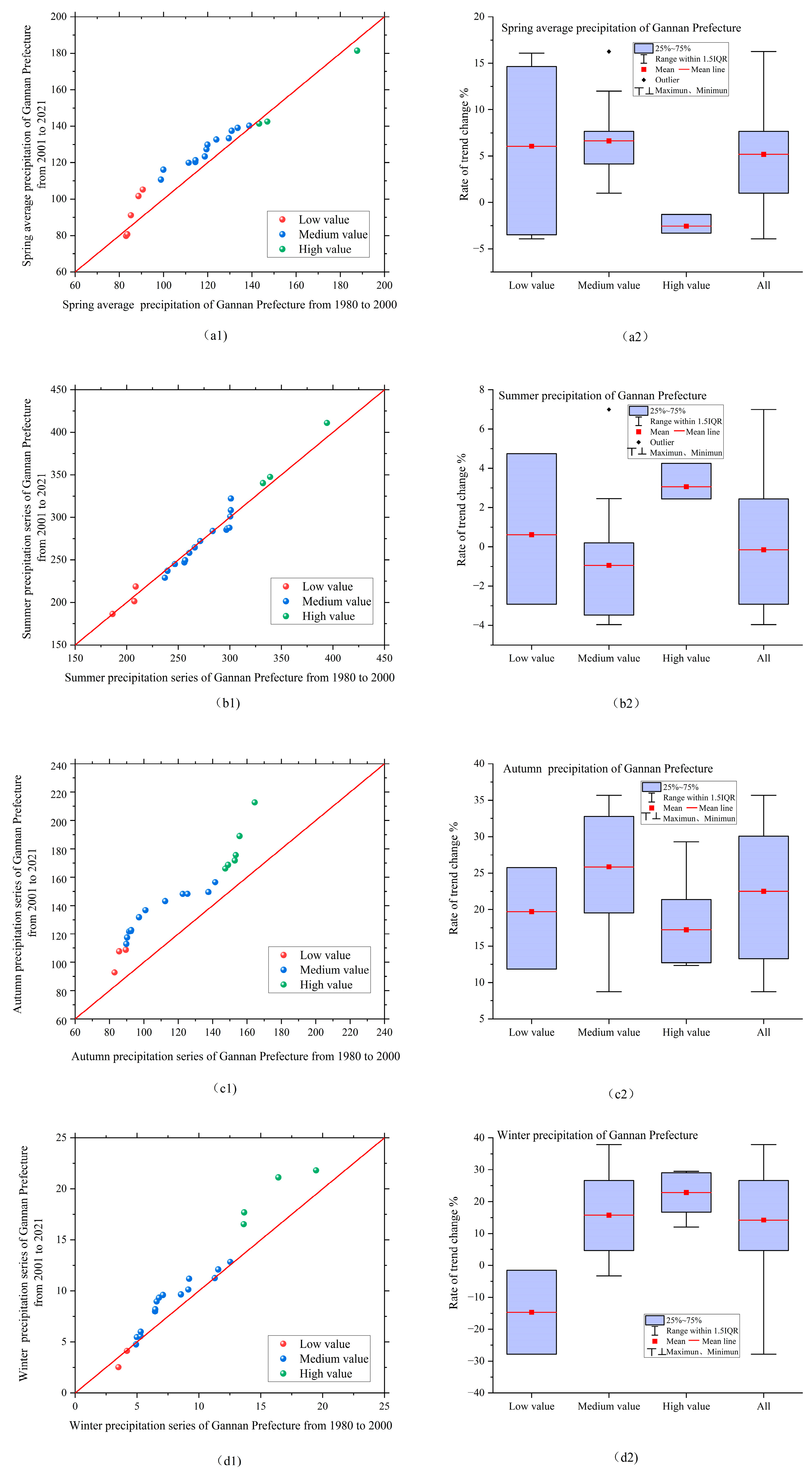
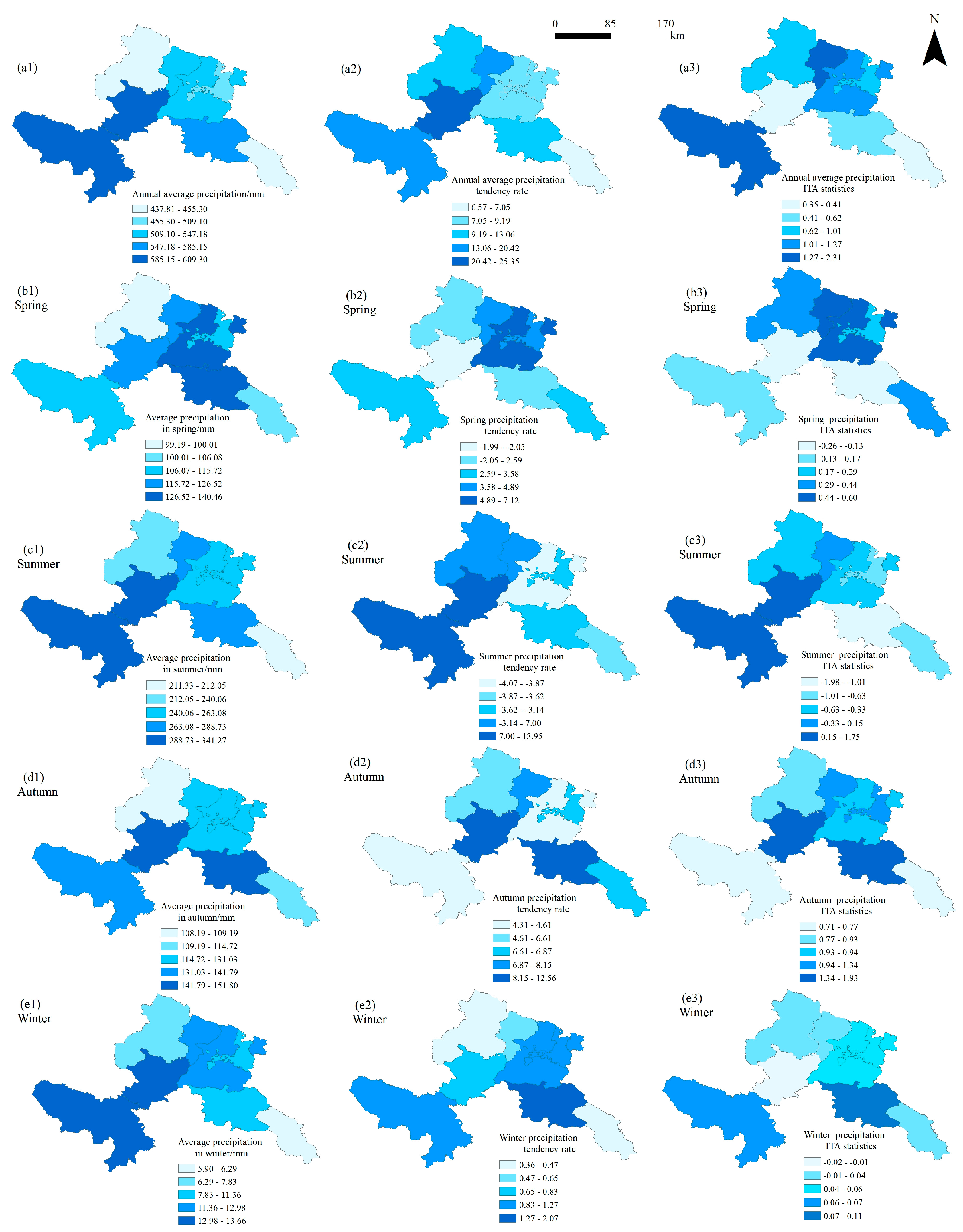

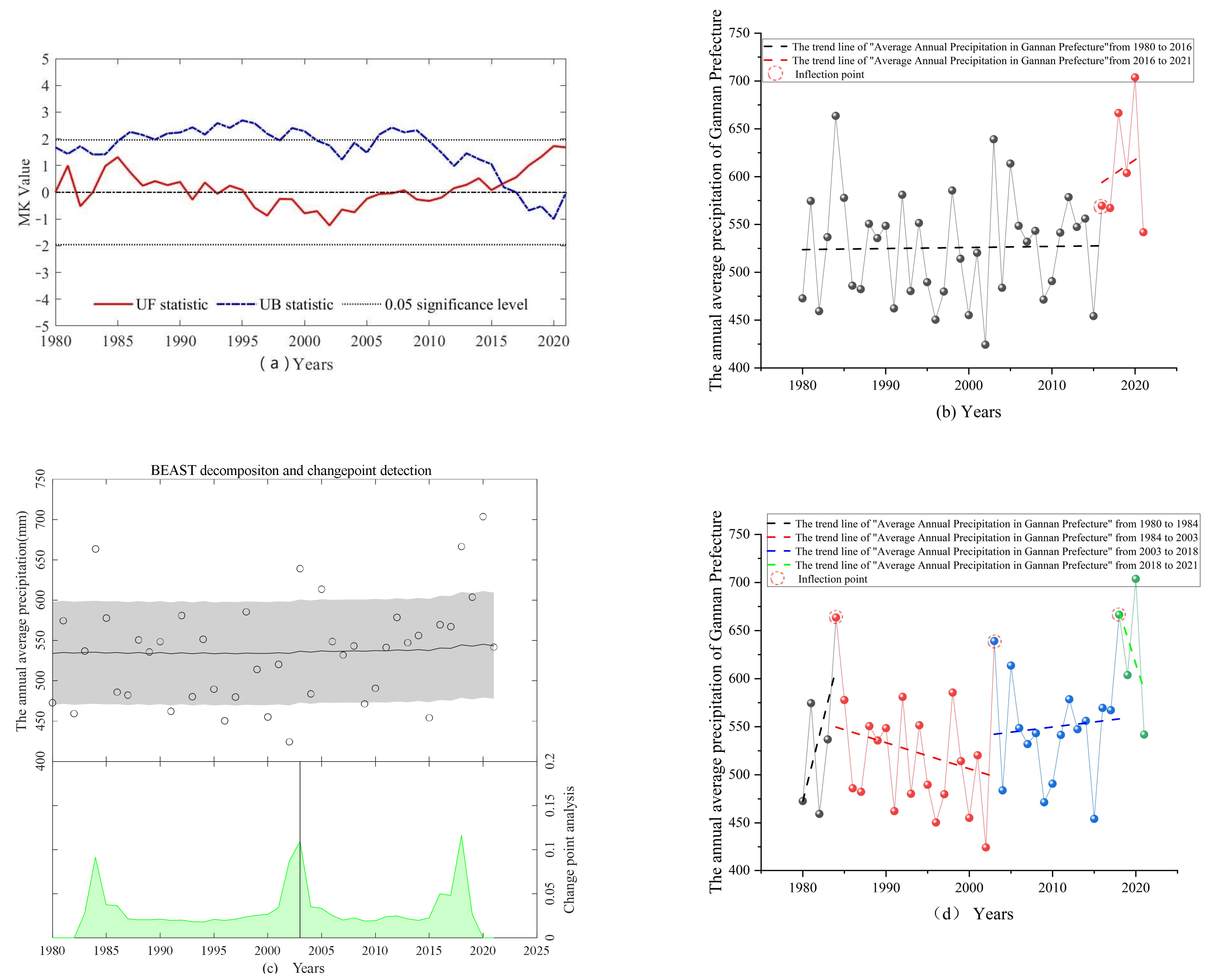
| Period | Annual Average Precipitation/mm | Average Precipitation in Spring/mm | Average Precipitation in Summer/mm | Average Precipitation in Autumn/mm | Average Precipitation in Winter/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980–1989 (1980s) | 533.92 | 120.65 | 274.59 | 129.67 | 8.00 |
| 1990–1999 (1990s) | 514.31 | 117.12 | 282.89 | 102.54 | 9.78 |
| 2000–2009 (2000s) | 523.15 | 110.76 | 261.60 | 141.12 | 7.87 |
| 2010–2019 (2010s) | 557.53 | 129.18 | 274.53 | 141.99 | 11.66 |
| 1980–2021 | 536.54 | 119.97 | 275.37 | 130.45 | 9.62 |
| Statistical Item | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December | January | February | |
| Precipitation/mm | 15.38 | 34.12 | 70.47 | 82.15 | 101.82 | 91.41 | 80.48 | 43.66 | 6.30 | 1.62 | 3.57 | 5.55 |
| Proportion of average annual precipitation % | 2.87 | 6.36 | 13.13 | 15.31 | 18.98 | 17.04 | 15.00 | 8.14 | 1.18 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 1.04 |
| 22.36 | 51.33 | 24.32 | 2.01 | |||||||||
| Season | Mann–Kendall Test for Change-Point Detection | BEAST Integrated Algorithm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year of Abrupt Changes | Trend Variability Before and After the Abrupt Change (mm/decade, p < 0.05) | Peak Year of Abrupt Changes | The Trend Variation Rate Before and After the Peak Year of Abrupt Changes (mm/decade, p < 0.05) | |
| Spring | 1981, 1991, 2012, 2015 | (1980–1981) +10.88 (1981–1991) +24.39 (1991–2012) −0.56 (2012–2015) −65.66 (2015–2021) +6.85 | 1995, 1999, 2004, 2008, 2018 | (1980–1995) −2.70 (1995–1999) +3.71 (1999–2004) +44.87 (2004–2008) −30.04 (2008–2018) +51.69 (2018–2021) −165.54 |
| Summer | 1981, 1984, 1990, 1998, 2003, 2018 | (1980–1981) +350.5 (1981–1984) +330.11 (1984–1990) −120.49 (1990–1998) +18.53 (1998–2003) −22.25 (2003–2018) −15.67 (2018–2021) −262.30 | 1984, 2003, 2015 | (1980–1984) +190.23 (1984–2003) −23.68 (2003–2015) −56.32 (2015–2021) +126.22 |
| Autumn | 2014, 2018 | (1980–2014) +5.01 (2014–2018) −26.04 (2018–2021) +158.69 | 2005 | (1980–2005) +0.931 (2005–2021) +2.94 |
| Winter | 1982, 1990, 1992, 2017 | (1980–1982) +19.25 (1982–1990) +9.04 (1990–1992) +123.75 (1992–2017) −0.50 (2017–2021) +8.96 | 1992, 2011, 2018 | (1980–1992) +6.66 (1992–2011) −1.65 (2011–2018) +5.17 (2018–2021) −1.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wei, L.; Cui, Y. Precipitation Variation Characteristics in Gannan Prefecture, China: Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis and the BEAST (Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonality, and Trend) Ensemble Algorithm. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111223
Zhou H, Wei L, Cui Y. Precipitation Variation Characteristics in Gannan Prefecture, China: Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis and the BEAST (Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonality, and Trend) Ensemble Algorithm. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111223
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Hui, Linjing Wei, and Yanqiang Cui. 2025. "Precipitation Variation Characteristics in Gannan Prefecture, China: Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis and the BEAST (Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonality, and Trend) Ensemble Algorithm" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111223
APA StyleZhou, H., Wei, L., & Cui, Y. (2025). Precipitation Variation Characteristics in Gannan Prefecture, China: Application of the Innovative Trend Analysis and the BEAST (Bayesian Estimator of Abrupt Change, Seasonality, and Trend) Ensemble Algorithm. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111223





