Black Carbon in Urban and Suburban Hangzhou: Spatiotemporal Variation, Precipitation Scavenging, and Policy Impacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data
2.2. Data Preprocessing and Analysis Methods
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of BC Concentrations
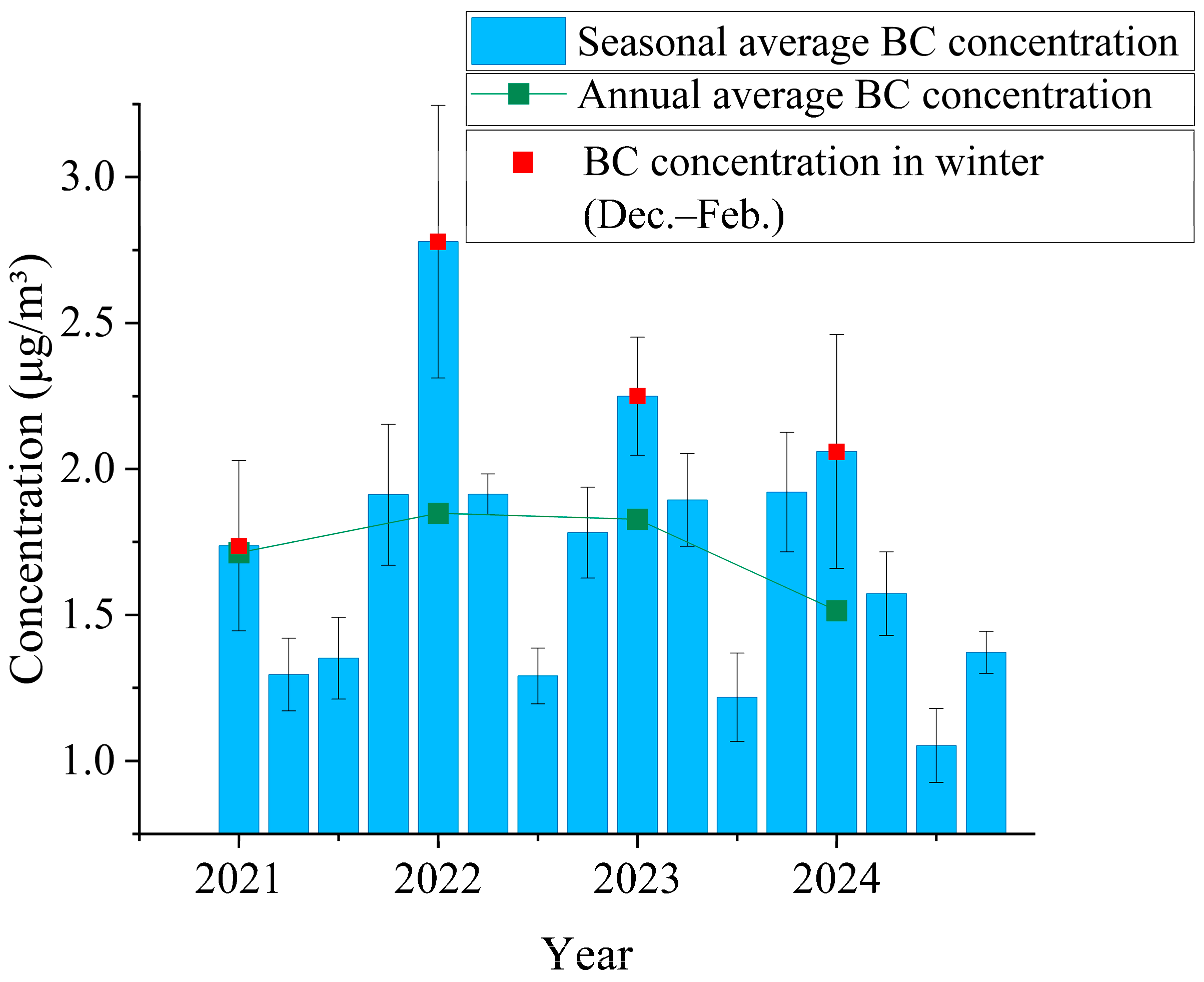
3.1.1. Interannual Variation Characteristics
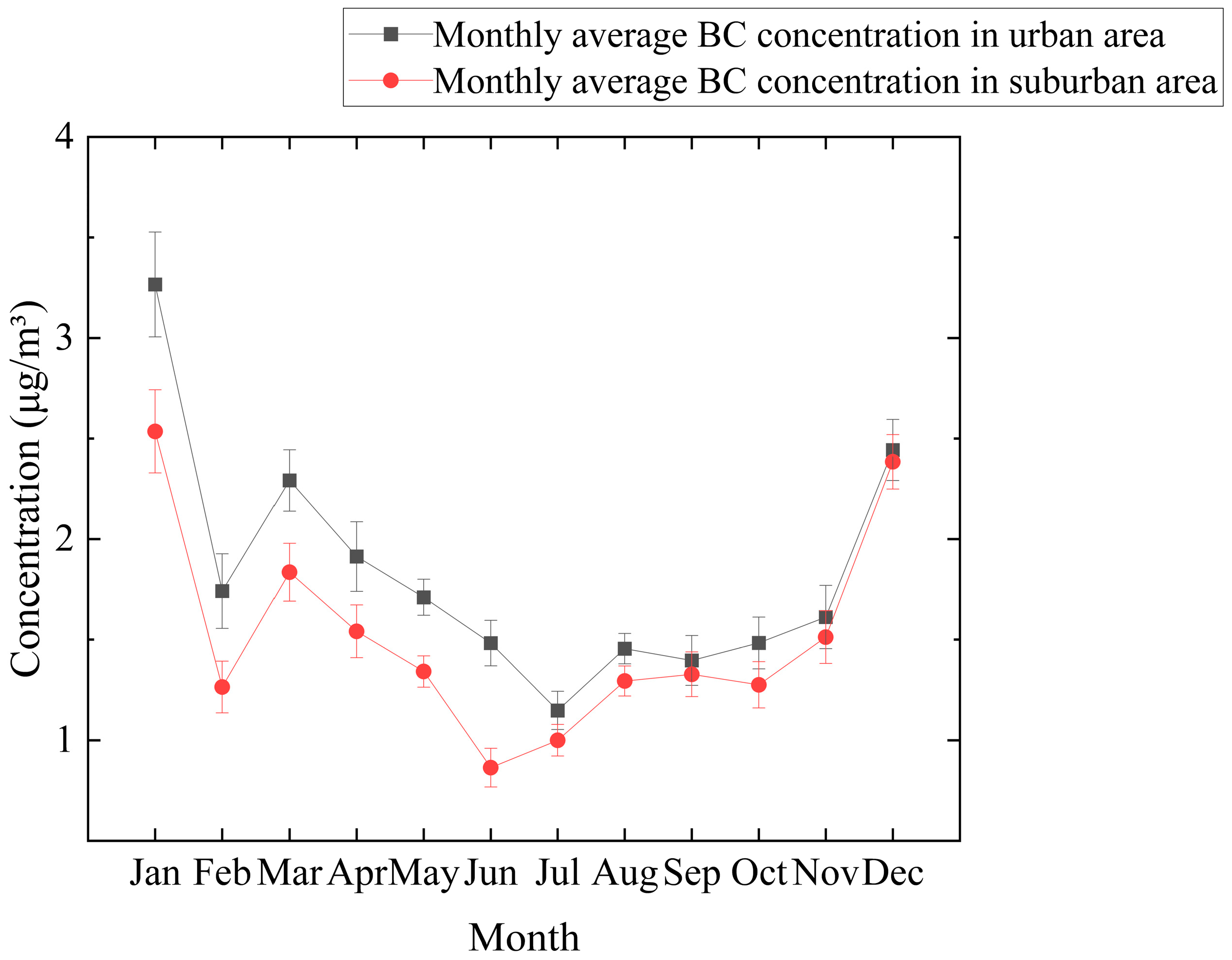
3.1.2. Seasonal Variation Characteristics
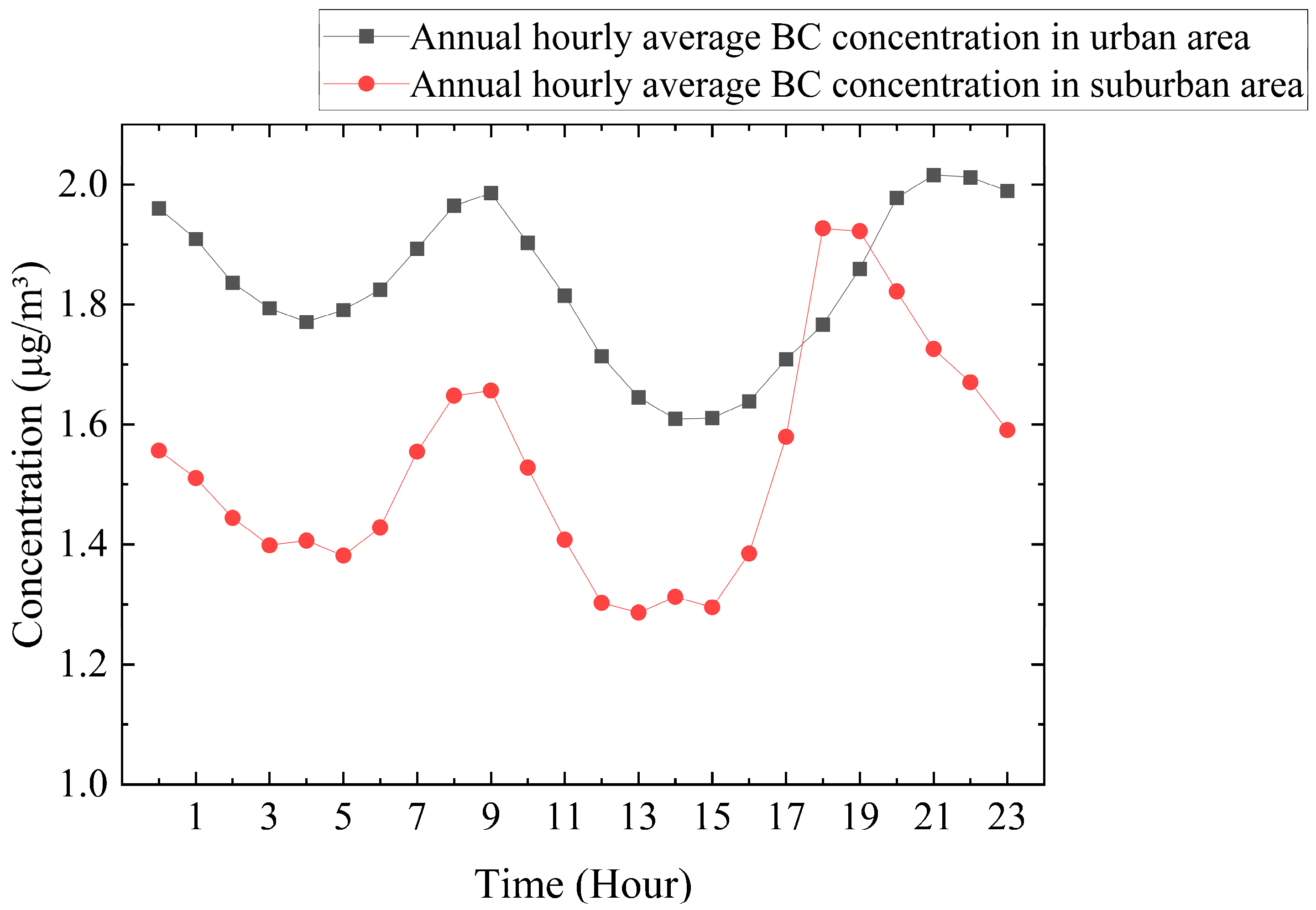
3.1.3. Diurnal Variation Characteristics
3.1.4. Spatial Differences Between the Urban and Suburban Areas
3.2. Analysis of Precipitation Scavenging Efficiency
3.2.1. Scavenging Efficiency Characteristics
3.2.2. Typical Event Analysis
3.3. Effect Evaluation of Emission Mitigation Policy
4. Conclusions and Prospects
4.1. Main Conclusions
4.2. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Black carbon |
| WMO | World Meteorological Organization |
| NOAA | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
References
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/345329 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Janssen, N.A.H.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; van Bree, L.; ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B.; et al. Black carbon as an additional indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Wang, W.T.; Liu, J.; Shen, H.; Shen, G.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Black carbon emissions in China from 1949 to 2050. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.T. Pollution Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Atmospheric Black Carbon Concentration in Urban Environments Based on Mobile Platform Monitoring. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J. Study on characteristics and source distribution of black carbon pollutants in Shanghai. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of the Chinese Meteorological Society—S9 Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment, Xiamen, China, 2 November 2011; Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, School of Physics, Peking University: Beijing, China, 2011. 150p. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Kong, S.F.; Zheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Qi, S. Black carbon aerosol concentration and sources in rural areas of southern North China Plain. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2363–2372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Cao, F.S.; Tian, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal characteristics of absorbing aerosols in the Yangtze River Delta region. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 3898–3907. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.J.; Xie, S.Y.; Meng, X.Y.; Qi, W.H.; Wang, S.; Pan, B.F. Characteristics of black carbon concentration in national atmospheric background regions of China. China Environ. Monit. 2018, 34, 32–40. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.C. Source Apportionment of Black Carbon Aerosols During Heavy Haze Episodes in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Rao, R.Z.; Huang, Y.B.; Mao, M.; Berg, M.J.; Sun, W.B. Black carbon aerosols in urban central China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 150, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.K. Pollution Characteristics and Source Analysis of Black Carbon in the Yangtze River Delta Region. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.Z.; Liu, P.F.; Geng, F.H.; Gao, W.; Zhen, C.; Zhao, C. Comparative observation of black carbon aerosols between urban and suburban areas in Shanghai. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2011, 22, 158–168. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A.; et al. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.L. Precipitation Scavenging, Source Apportionment and Carbon Sink Contribution of Aerosol Carbon in Nanchang Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanchang University, Nanchang, China, 2019. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.G.; Kong, W.L.; Zang, K.P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Yin, J.; Hong, H.; Qiu, X.; Fang, S.; Lin, Y. Volution characteristics and potential source analysis of atmospheric sulfur dioxide and aerosol concentrations in urban and suburban Hangzhou. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2024, 44, 287–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17626.2-2018; Electromagnetic Compatibility—Testing and Measurement Techniques-Electrostaic Discharge Immunity Test. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=88FC56474149E07039BCD95FB13B8360 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- GB/T 17626.4-2018; Electromagnetic Compatibility-Testing and Measurement Techniques-Electrical Fast Transient/Burst Immunity Test. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2018. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=877FD741E1D1BFFD7DC74AFCCE84E9FC (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- GB/T 17626.5-2019; Electromagnetic Compatibility—Testing and Measurement Techniques-Surge Immunity Test. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=534499018FB30E7FC5E646F89937B3A8 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Barnett, V.; Lewis, T. Outliers in Statistical Data; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, C.; Ley, C.; Klein, O.; Bernard, P.; Licata, L. Detecting outliers: Do not use standard deviation around the mean, use absolute deviation around the median. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2013, 49, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Development and Reform Commission. Notice on the Implementation Plan for Boosting the Operation of Industrial Economy and Promoting High Quality Industrial Development. 2021. Available online: https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xwdt/tzgg/202112/t20211214_1307767.html (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.N.; Hong, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Cui, H.; Man, H. Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of black carbon aerosols in Suzhou region. J. Mar. Meteorol. 2023, 43, 87–100. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudurexiati, A. Pollution Characteristics, Source Apportionment and Long-Term Trends of Black Carbon Aerosols in Northern Suburban Nanjing. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y. Variation of PM2.5 Pollution and the Role of Atmospheric Boundary Layer in Regional Transport Over the Two-Lake Basin. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2023. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.W. Spatiotemporal Variation, Sources and Interactions with East Asian Summer Monsoon of Black Carbon in East Asia. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, China, 2024. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.H.; Zeng, S.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Li, J.Z.; He, Y.L.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J.Y. Characteristics and source apportionment of black carbon concentration in the Sie Mountain region on the eastern slope of the Tibetan Plateau. China Environ. Monit. 2025, 41, 65–75. Available online: http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2861.x.20250523.1027.003.html (accessed on 14 May 2025). (In Chinese) [CrossRef]
- Perica, S.; Kane, D.; Dietz, S.; Maitaria, K.; Martin, D.; Pavlovic, S.; Roy, I.; Stuefer, S.; Tidwell, A.; Trypaluk, C.; et al. NOAA Atlas 14 Volume 7 Version 2.0, Precipitation-Frequency Atlas of the United States, Alaska. 2012. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/media/owp/oh/hdsc/docs/Atlas14_Volume7.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- WMO. Manual on Precipitation Measurement and Estimation (WMO-No. 587); WMO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Guo, W.; Gong, S.L. Carbonaceous aerosol composition over various regions of China during 2006. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronache, C. Estimated variability of below-cloud aerosol removal by rainfall for observed aerosol size distributions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2003, 3, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangzhou Municipal People’s Government. 14th Five-Year Plan for Air Quality Improvement in Hangzhou. 2022. Available online: https://epb.hangzhou.gov.cn/art/2022/1/7/art_1229354834_4008171.html (accessed on 14 May 2025).




| Precipitation Class | Intensity Range (mm/h) | Sample_Size | Mean_Efficiency (%) | Std_Efficiency | Min_Intensity | Max_Intensity | Mean_Duration (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Light rain | 0.1–2.5 | 77 | 27.117 | 27.338 | 0.3 | 2.4 | 4.8 |
| Moderate rain | 2.5–8.0 | 41 | 20.477 | 23.775 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 9.6 |
| Heavy rain | ≥8.0 | 20 | 22.612 | 32.267 | 8.1 | 27.6 | 8.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Shan, M.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Lei, Y. Black Carbon in Urban and Suburban Hangzhou: Spatiotemporal Variation, Precipitation Scavenging, and Policy Impacts. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101212
Zhu M, Xu H, Shan M, Chen H, Dong Y, Lei Y. Black Carbon in Urban and Suburban Hangzhou: Spatiotemporal Variation, Precipitation Scavenging, and Policy Impacts. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101212
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Mengjing, Honghui Xu, Meng Shan, Huansang Chen, Yilei Dong, and Yuyun Lei. 2025. "Black Carbon in Urban and Suburban Hangzhou: Spatiotemporal Variation, Precipitation Scavenging, and Policy Impacts" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101212
APA StyleZhu, M., Xu, H., Shan, M., Chen, H., Dong, Y., & Lei, Y. (2025). Black Carbon in Urban and Suburban Hangzhou: Spatiotemporal Variation, Precipitation Scavenging, and Policy Impacts. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101212






