Study on the Interaction Effect of Negative Air Ions and Nitrogen Oxide Concentrations in Urban Forest Ecosystems Driven by Meteorological Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
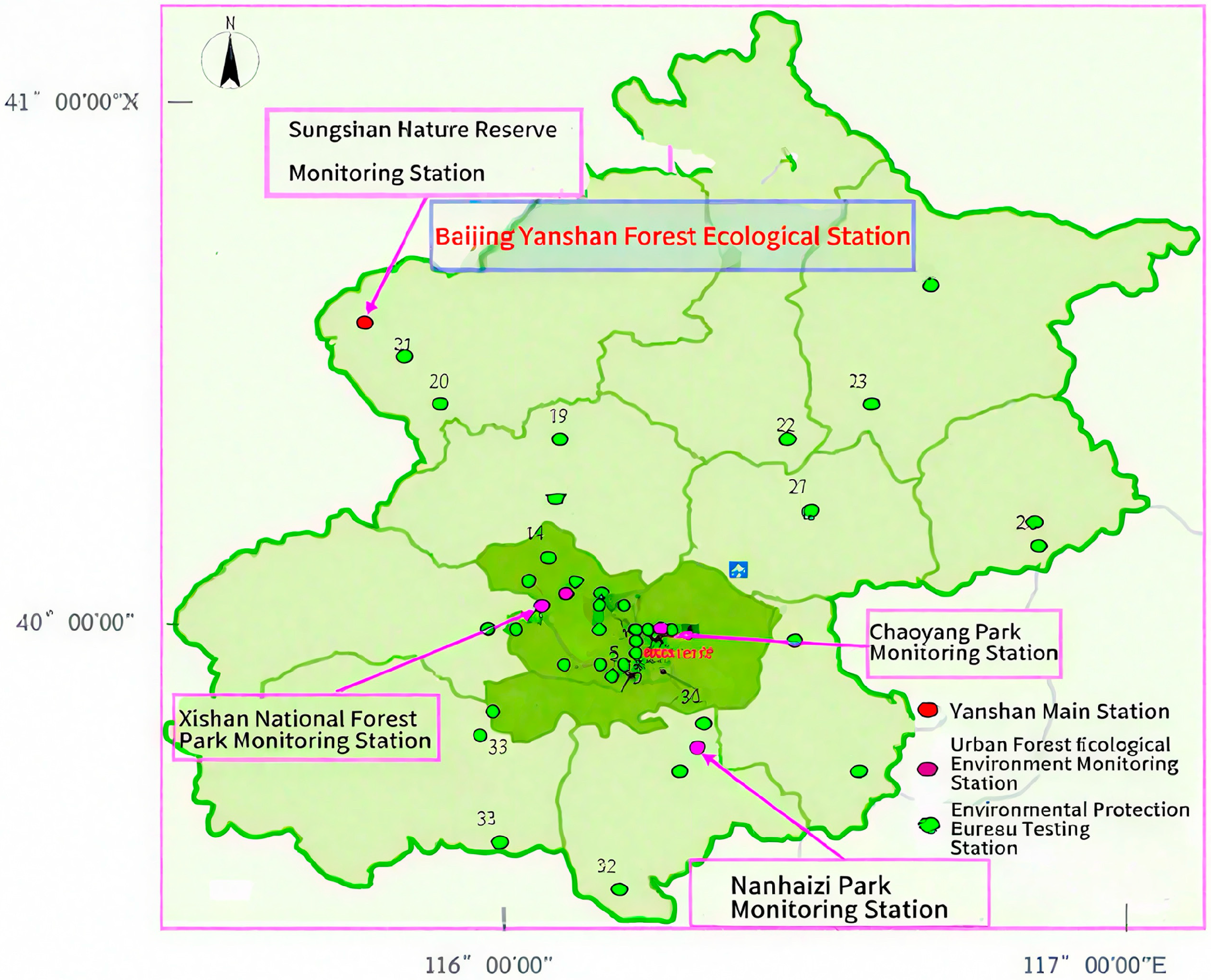
2.1. Overview of Urban Forest Ecological Environment Monitoring Station
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
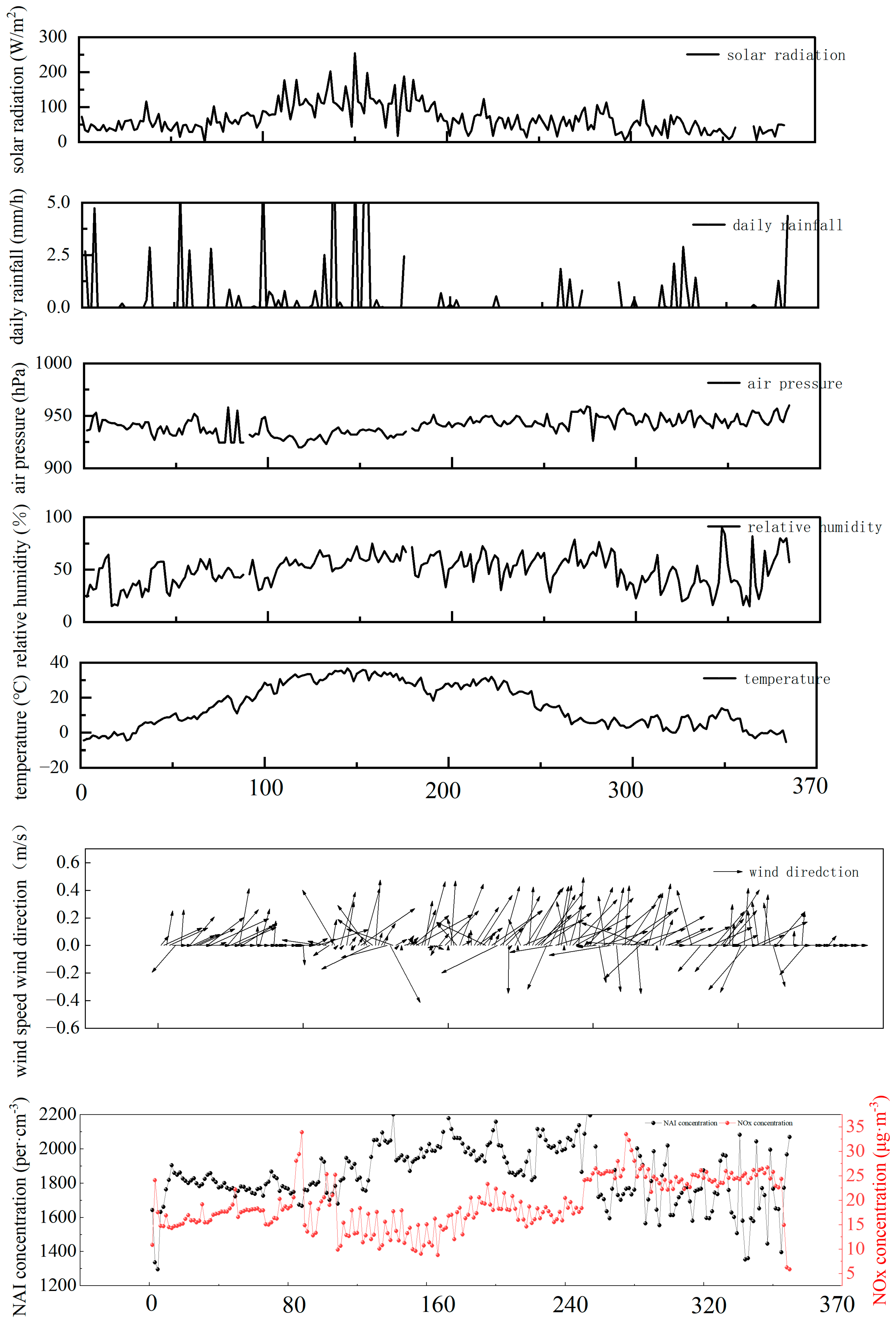
3.1. Characteristics of Meteorological Factors
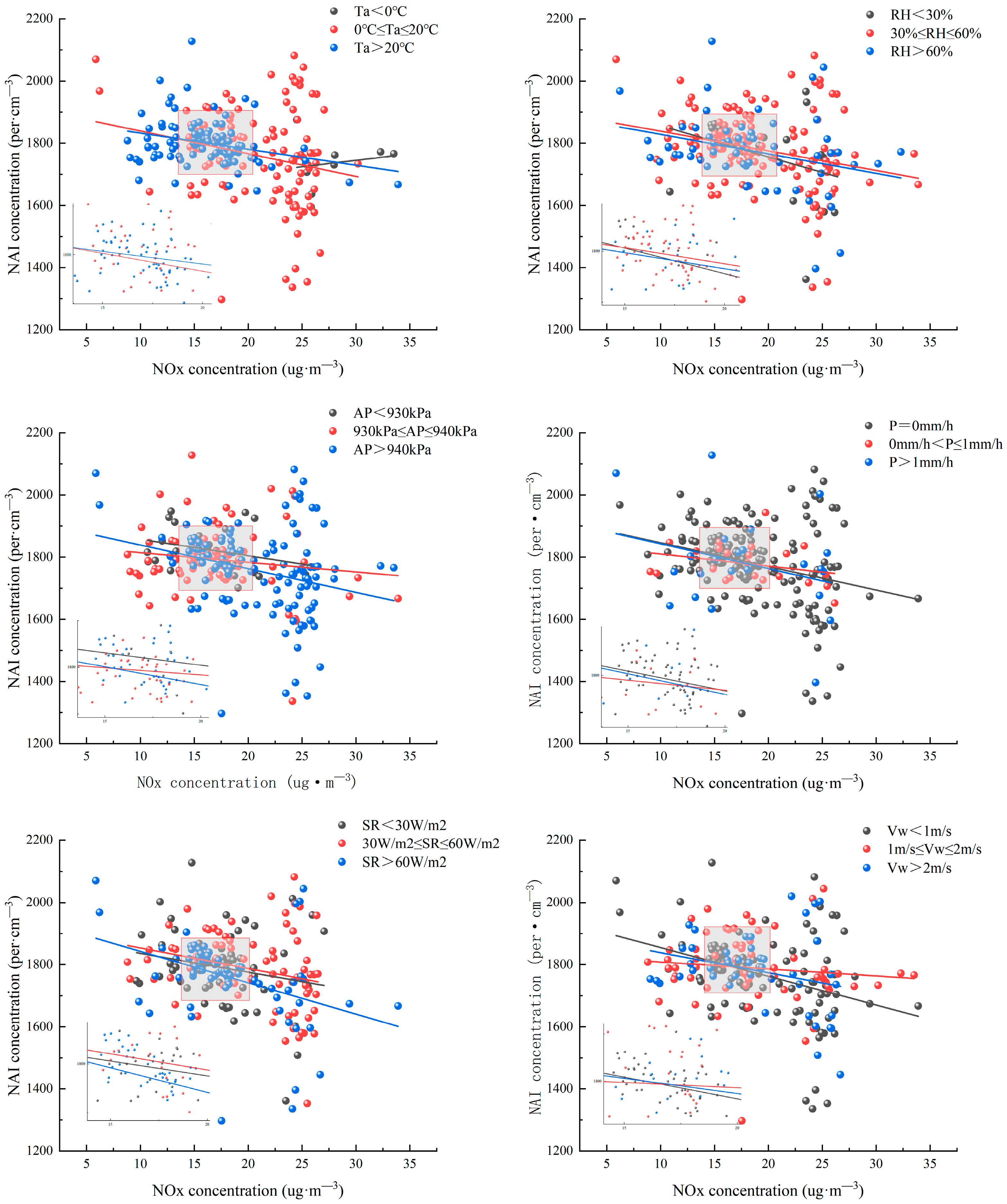
3.2. Correlation Between Atmospheric Negative Ions and Nitrogen Oxides Under Different Meteorological Conditions
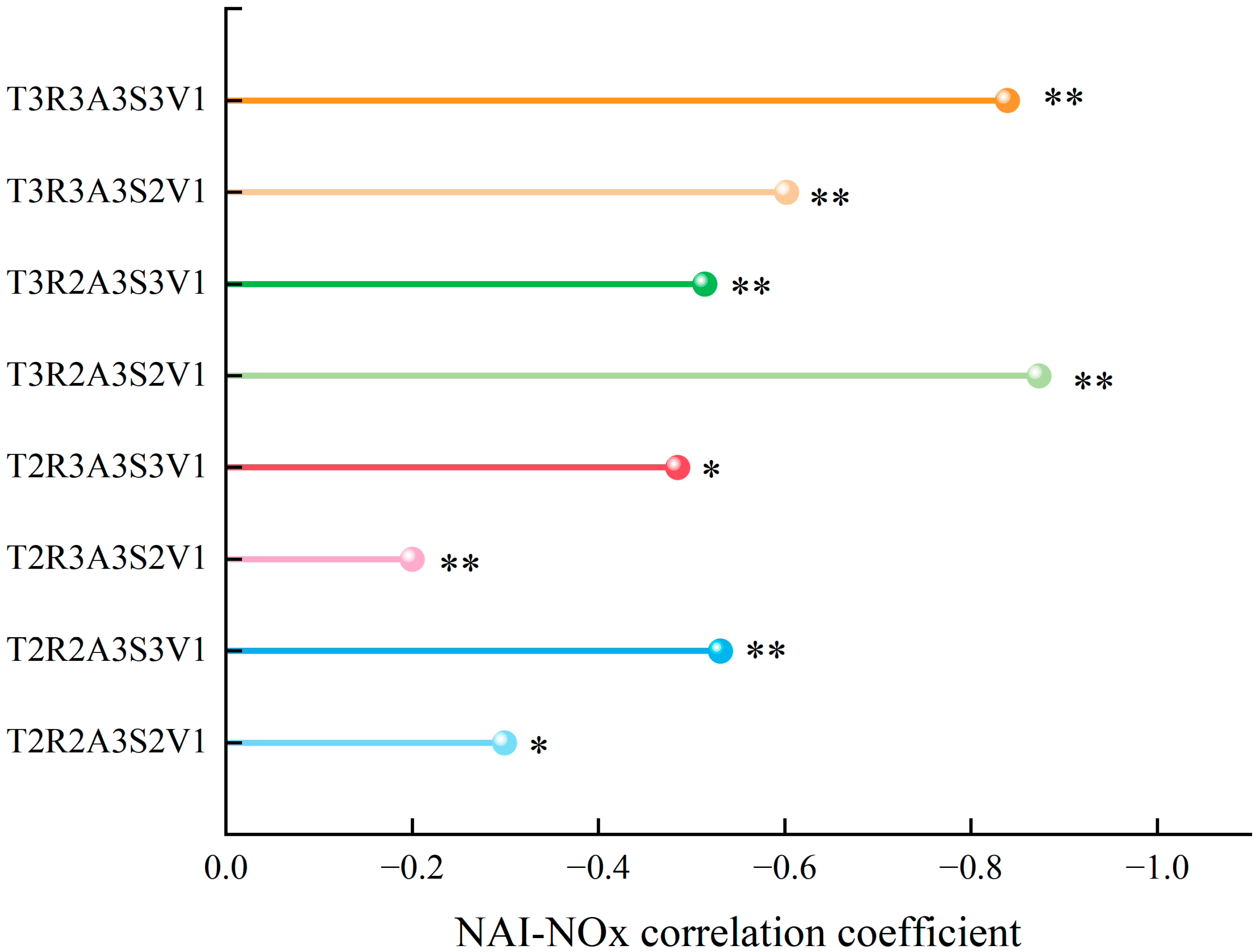
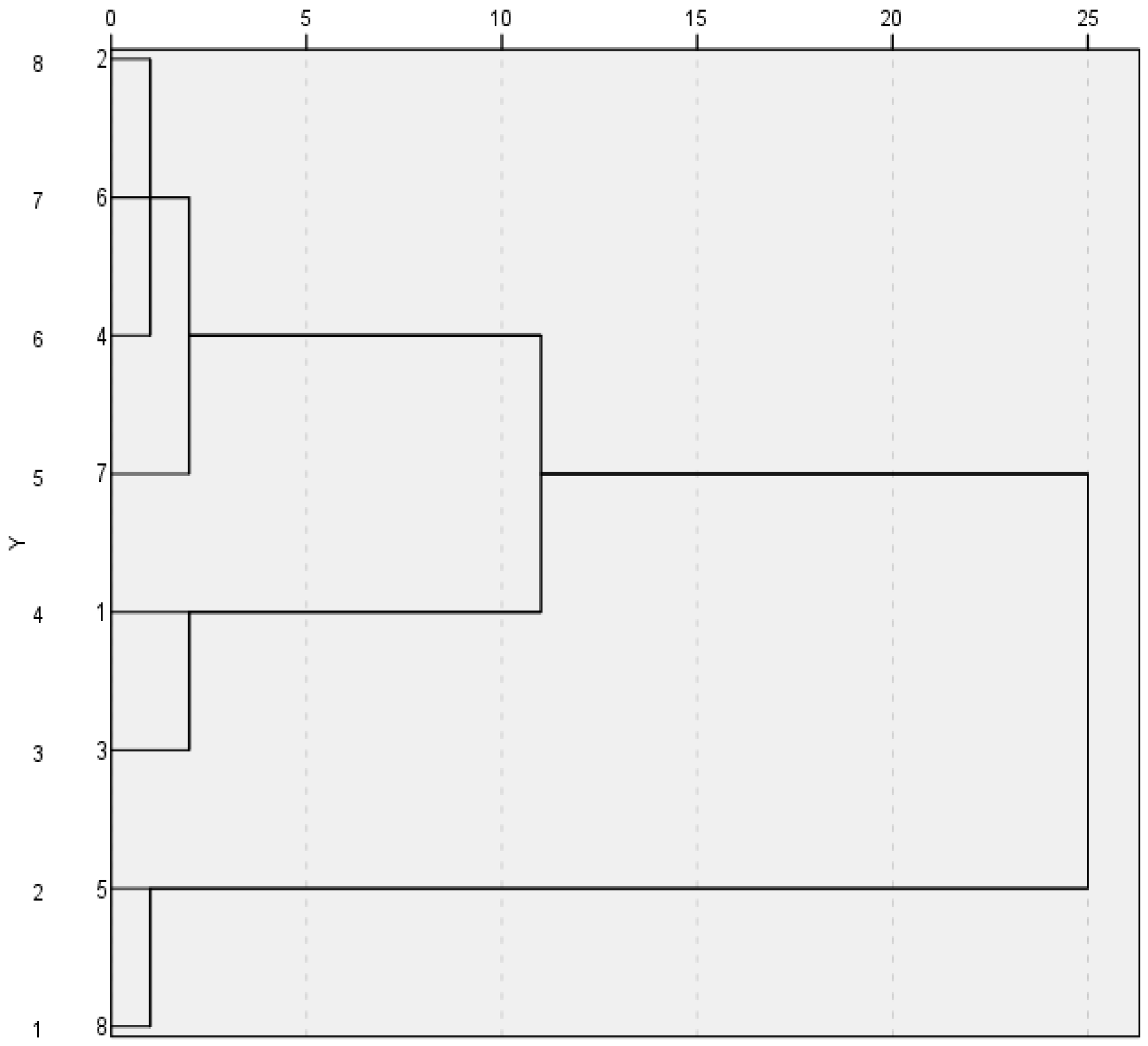
3.3. Correlation Analysis Between Air Negative Ions and Nitrogen Oxides in Hierarchical Coordinated Control of Meteorological Factors
3.4. The Moderating Effect of Main Meteorological Factors on the Relationship Between Air Negative Ions and Nitrogen Oxides
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Temperature on the Correlation Between NAI and NOx
4.2. Impact of Humidity on the Correlation Between NAI and NOx
4.3. Impact of Air Pressure on the Correlation Between NAI and NOx
4.4. Impact of Solar Radiation on the Correlation Between NAI and NOx
4.5. Impact of Wind Speed on the Correlation Between NAI and NOx
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, A.; Li, Q.; Zhou, B.; Ge, X.; Cao, Y. Temporal dynamics of negative air ion concentration and its relationship with environmental factors: Results from long-term on-site monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Zhang, X.; Han, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, C.; Yin, S. Random Forest Algorithm for the Relationship between Negative Air Ions and Environmental Factors in an Urban Park. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, D. Review on research of the negative air ion concentration distribution and its correlation with meteorological elements in mountain tourist areas. Earth Sci. 2019, 8, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Li, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; He, Z. The lagging effect of precipitation on NAIs concentrations on rainy days in Wuyi Mountain National Park, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Tan, Y.M.; Wu, Z.W. Study on the relationship between negative air ion concentration and air temperature and humidity. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2011, 31, 114–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.B.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Z.T. Negative air ions on the surface of remaining mountain bodies in cities of different sizes in karst areas and their influencing factors—A case study of Guiyang City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6257–6277. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.G.; Xu, W.J.; Cui, H.P.; Mei, Y.Y.; Cai, B.F. Variation of negative air ion concentration in Quzhou Daju Hai Forest Park. J. Zhejiang A&F Univ. 2016, 33, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, G.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Sang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.S.; Meng, P.; Cai, L.L.; Pei, S.Y.; Wang, Y. Analysis of the influence of meteorological factors on negative air ions based on random forest method. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2021, 42, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W. Adaptive Study on Evaluating Urban Residential Ventilation Based on Negative Air Ion Concentration. Ph.D Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.F.; Liu, C.M.; Ding, X.Y.; Li, S.; Cao, R.J.; Gu, J.F.; Wang, Y. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of NO2 in Shijiazhuang City. Environ. Monit. China 2022, 38, 62–73. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, K.; Tan, G.; Lu, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Lv, R.; Jing, D.; Luo, P.; Dong, G. The temperature-controlled optimization of g-C3N4 structure significantly enhances the efficiency of photothermal catalytic NO removal. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.C.; Chen, W.H.; Wu, Y.K.; Wu, L.M.; Wang, X.M. Temporal and spatial characteristics of ozone suppression events under high temperatures in China and their influencing factors. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 6586–6597. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.M.; Zou, Q.; Zhou, G.B. Influence of precipitation intensity on air pollutants in winter and spring in the main urban area of Chongqing. J. Southwest China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 38, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y. Study on Temporal and Spatial Variation of Nitrogen Oxides and Sulfur Dioxide Concentrations in the Eastern Suburbs of Xi’an in Spring. Master’s Thesis, Shaanxi Normal University, Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Nie, S.S.; Feng, Y.P.; Cui, J.S.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.X.; Shi, W.Y. Temporal and spatial succession characteristics and source analysis of ozone and nitrogen dioxide in Shijiazhuang City. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 2679–2690. [Google Scholar]
- GB 3095-2012/XG1-2018; Ambient Air Quality Standards. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Luo, L.T.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lin, Y.Q.; Mozaffar, A.; Cao, M.Y. Photochemical characteristics and sensitivity analysis of atmospheric ozone in Nanjing in summer. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 1382–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.X.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Cui, G.F.; Li, J.Y. Study on negative air ion concentration and its influencing factors in urban forests in different geographical spaces. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 66–77. [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov, B.M. Cluster Ions and Van der Waals Molecules; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Luo, J.L.; Zhang, Z.Q. Seasonal dynamics of atmospheric PM2.5 and its influencing factors in centralized heating areas—A case study of Baoji City, Shaanxi Province. J. Baoji Univ. Arts Sci. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2013, 33, 40–43, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, G.; Zhang, J.; Rahman, Z.U.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Vujanović, M.; Mikuli, H.; Manic, N.; Magdziarz, A.; Tan, H. Multi-pollutant formation and control in pressurized oxy-combustion: SOx, NOx, particulate matter, and mercury. Engineering 2024, 39, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.Y.; Ma, A.; Ramachandran, S. Negative air ions and their effects on human health and air quality improvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.R.; He, Q.T.; Yan, H.P.; Hou, Z.; Li, T. Study on temporal and spatial variation characteristics of negative air ion concentration in Beijing area. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2005, 3, 35–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.F.; Du, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Gong, D.C.; Li, L. Estimation of near-surface NO2 concentration in Guangdong Province based on Catboost model. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 6276–6285. [Google Scholar]

| Meteorological Factor | Subregion | Rhand Over | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | Sig | Model Equation | ||
| Temperature (°C) | <0 | 0.163 | 0.652 | Not significantly relevant |
| 0–20 | −0.212 * | 0.022 | y = 1912.20 − 7.30x | |
| >20 | −0.284 ** | 0.004 | y = 1844.25 − 5.17x | |
| Humidity (%) | <30 | −0.332 | 0.131 | Not significantly relevant |
| 30–60 | −0.254 ** | 0.002 | y = 1844.25 − 5.17x | |
| >60 | −0.300 * | 0.021 | y = 1890.93 − 6.26x | |
| atmospheric pressure (kPa) | <930 | −0.316 | 0.108 | Not significantly relevant |
| 930–940 | −0.139 | 0.22 | Not significantly relevant | |
| >940 | −0.267 ** | 0.003 | y = 1915.36 − 7.62x | |
| Rainfall (mm·h−1) | 0 | −0.274 | 0.001 | Not significantly relevant |
| 0–1 | −0.294 | 0.173 | Not significantly relevant | |
| >1 | −0.295 | 0.171 | Not significantly relevant | |
| Radiation (w·m−2) | <30 | −0.195 | 0.131 | Not significantly relevant |
| 30–60 | −0.261 * | 0.02 | y = 1919.88 − 6.61x | |
| >60 | −0.382 ** | 0.001 | y = 1943.60 − 10.09x | |
| wind speed (m·s−1) | <1 | −0.365 ** | 0.001 | y = 1947.16 − 9.23x |
| 1–2 | −0.11 | 0.385 | Not significantly relevant | |
| >2 | −0.275 | 0.07 | Not significantly relevant | |
| Interaction | Synergistic Regulation of Meteorological Factors |
|---|---|
| pole-strength | T3R2A3S2V1 (temperature > 20 °C, relative humidity 30–60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation 30–60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) T3R3A3S3V1 (temperature > 20 °C, relative humidity > 60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation > 60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) |
| strength | T3R2A3S3V1 (temperature > 20 °C, relative humidity 30–60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation > 60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) T3R3A3S2V1 (temperature > 20 °C, relative humidity > 60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation 30–60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) |
| weak | T2R2A3S3V1 (temperature 0–20 °C, relative humidity 30–60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation > 60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) T2R3A3S3V1 (temperature 0–20 °C, relative humidity > 60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation > 60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) |
| pole-weak | T2R2A3S2V1 (temperature 0–20 °C, relative humidity 30–60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation 30–60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) T2R3A3S2V1 (temperature 0–20 °C, relative humidity > 60%, air pressure > 940 kPa, solar radiation 30–60 W·m−2, wind speed < 1 m·s−1) |
| Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | Pattern 3 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | t | p | β | B | Standard Error | t | p | β | B | Standard Error | t | p | β | |
| constant | 1771.85 | 15.96 | 111.05 | 0.00 ** | - | 1771.85 | 16.10 | 110.07 | 0.00 ** | - | 1774.71 | 14.97 | 118.55 | 0.00 ** | - |
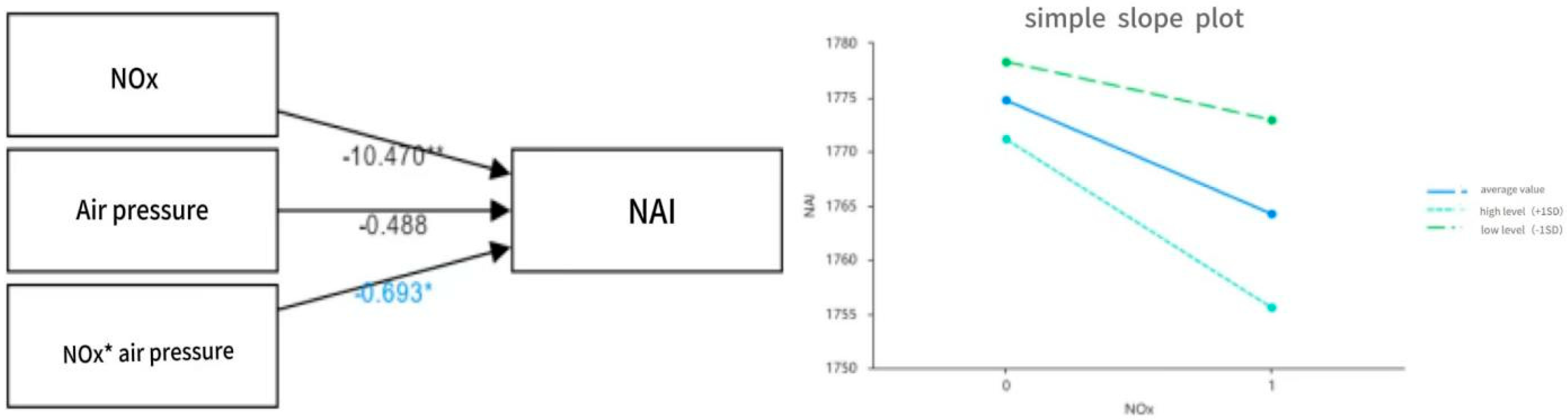
| NOx | −13.91 | 1.65 | −8.46 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −13.85 | 1.66 | −8.33 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −10.47 | 2.04 | −5.13 | 0.00 ** | −0.62 |
| atmospheric pressure | −1.40 | 2.23 | −0.63 | 0.53 | −0.06 | −0.49 | 2.09 | −0.23 | 0.82 | −0.02 | |||||
| NOx * atmospheric pressure | −0.69 | 0.27 | −2.53 | 0.02 * | −0.31 | ||||||||||
| R2 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.74 | ||||||||||||
| Adjust R2 | F = 71.55, p = 0.00 | F = 35.34, p = 0.00 | F = 29.53, p = 0.00 | ||||||||||||
| F value | 0.68 | 0.01 | 0.05 | ||||||||||||
| △R2 | F = 71.55, p = 0.00 | F = 0.40, p = 0.53 | F = 6.38, p = 0.02 | ||||||||||||
| Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | Pattern 3 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | t | p | β | B | Standard Error | t | p | β | B | Standard Error | t | p | β | |
| constant | 1771.85 | 15.96 | 111.06 | 0.00 ** | - | 1771.85 | 16.02 | 110.59 | 0.00 ** | - | 1774.55 | 14.34 | 123.72 | 0.00 ** | - |
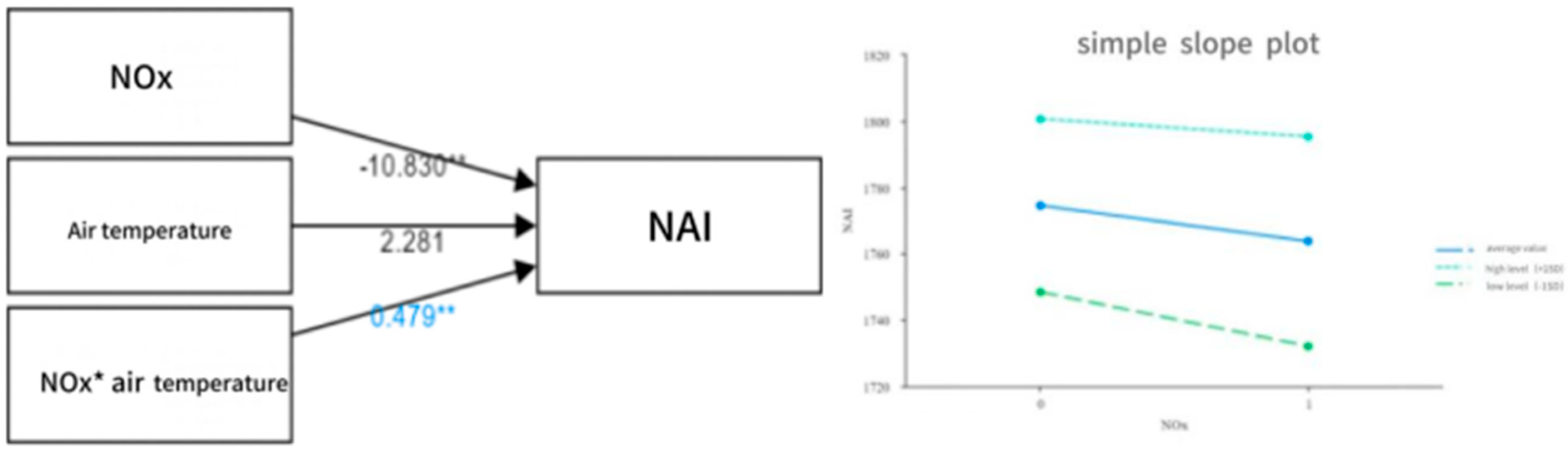
| NOx | −13.92 | 1.64 | −8.46 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −13.84 | 1.65 | −8.37 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −10.83 | 1.78 | −6.10 | 0.00 ** | −0.64 |
| atmospheric pressure | 1.20 | 1.42 | 0.85 | 0.40 | 0.08 | 2.28 | 1.32 | 1.73 | 0.09 | 0.16 | |||||
| NOx * atmospheric pressure | 0.48 | 0.16 | 3.06 | 0.01 ** | 0.33 | ||||||||||
| R2 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.76 | ||||||||||||
| Adjust R2 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.73 | ||||||||||||
| F value | F = 71.55, p = 0.00 | F = 35.83, p = 0.00 | F = 33.04, p = 0.00 | ||||||||||||
| △R2 | 0.68 | 0.01 | 0.07 | ||||||||||||
| Adjust F value | F = 71.55, p = 0.00 | F = 0.72, p = 0.40 | F = 9.34, p = 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| Pattern 1 | Pattern 2 | Pattern 3 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | t | B | Standard Error | t | B | Standard Error | t | B | Standard Error | t | B | Standard Error | t | |
| constant | 1771.85 | 15.96 | 111.04 | 0.00 ** | - | 1771.85 | 16.19 | 109.41 | 0.00 ** | - | 1764.57 | 15.88 | 111.12 | 0.00 ** | - |
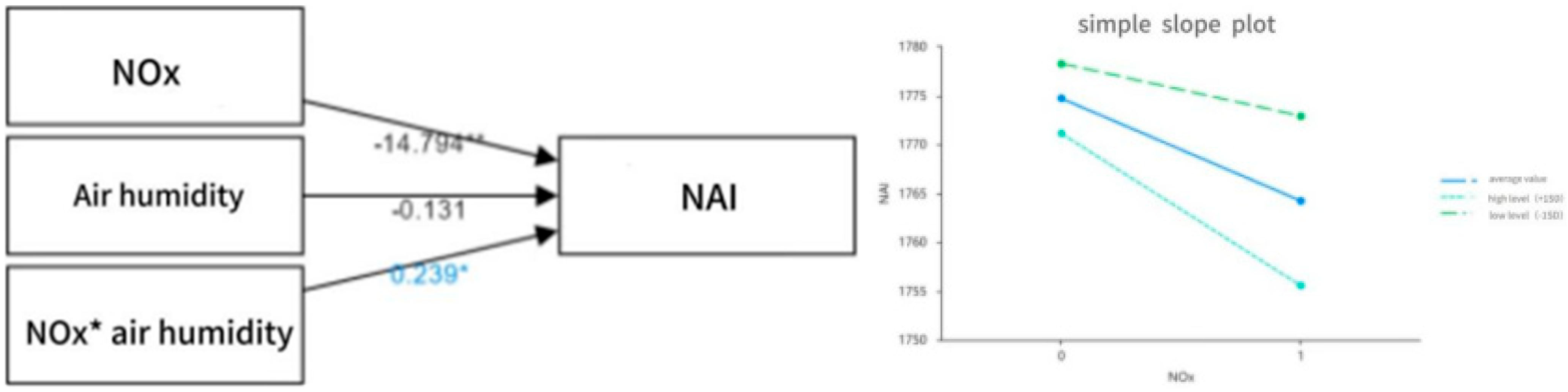
| NOx | −13.91 | 1.65 | −8.46 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −13.93 | 1.72 | −8.11 | 0.00 ** | −0.82 | −14.79 | 1.70 | −8.73 | 0.00 ** | −0.88 |
| air humidity | 0.06 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 0.96 | 0.01 | −0.13 | 1.20 | −0.11 | 0.91 | −0.01 | |||||
| NOx * air humidity | 0.24 | 0.12 | 2.04 | 0.05 * | 0.20 | ||||||||||
| R2 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.71 | ||||||||||||
| Adjust R2 | 0.67 | 0.66 | 0.69 | ||||||||||||
| F value | F = 71.55, p = 0.000 | F = 34.73, p = 0.00 | F = 26.75, p = 0.00 | ||||||||||||
| △R2 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.04 | ||||||||||||
| △F value | F = 71.55, p = 0.00 | F = 0.002, p = 0.96 | F = 4.15, p = 0.05 | ||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Xu, X.; Yu, D.; Zhang, W.; Wu, S.; Zhao, N.; Li, B.; Lu, S. Study on the Interaction Effect of Negative Air Ions and Nitrogen Oxide Concentrations in Urban Forest Ecosystems Driven by Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101186
Li S, Xu X, Yu D, Zhang W, Wu S, Zhao N, Li B, Lu S. Study on the Interaction Effect of Negative Air Ions and Nitrogen Oxide Concentrations in Urban Forest Ecosystems Driven by Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(10):1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101186
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shaoning, Xiaotian Xu, Di Yu, Weikang Zhang, Siqi Wu, Na Zhao, Bin Li, and Shaowei Lu. 2025. "Study on the Interaction Effect of Negative Air Ions and Nitrogen Oxide Concentrations in Urban Forest Ecosystems Driven by Meteorological Factors" Atmosphere 16, no. 10: 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101186
APA StyleLi, S., Xu, X., Yu, D., Zhang, W., Wu, S., Zhao, N., Li, B., & Lu, S. (2025). Study on the Interaction Effect of Negative Air Ions and Nitrogen Oxide Concentrations in Urban Forest Ecosystems Driven by Meteorological Factors. Atmosphere, 16(10), 1186. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16101186






