Combined Exposure to High-Cholesterol Diet and PM2.5: Brain Injury and Regulatory Mechanism of HIF-1α in ApoE−/− Female Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
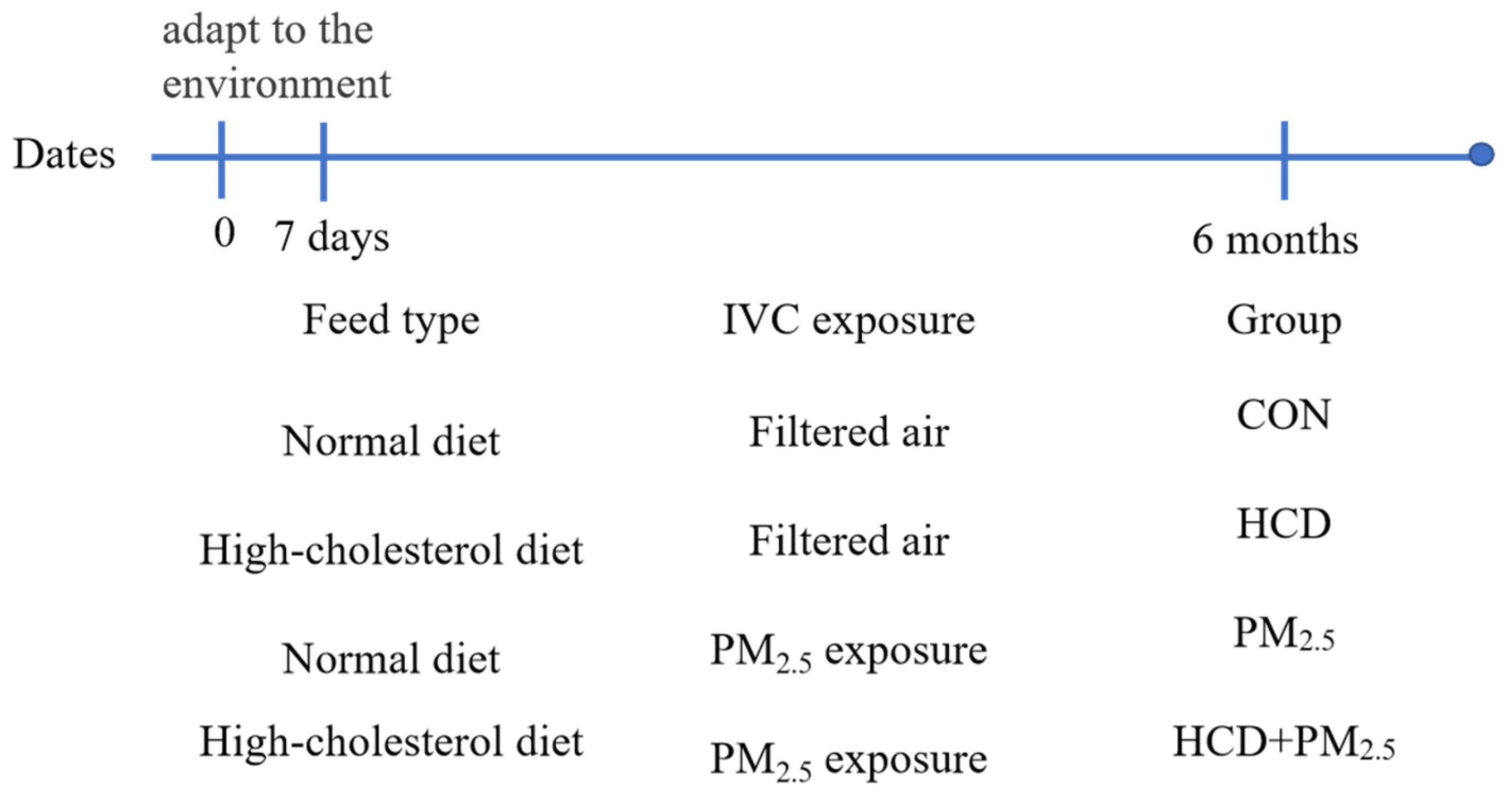
2.1. Animal
2.2. Behavioral Test
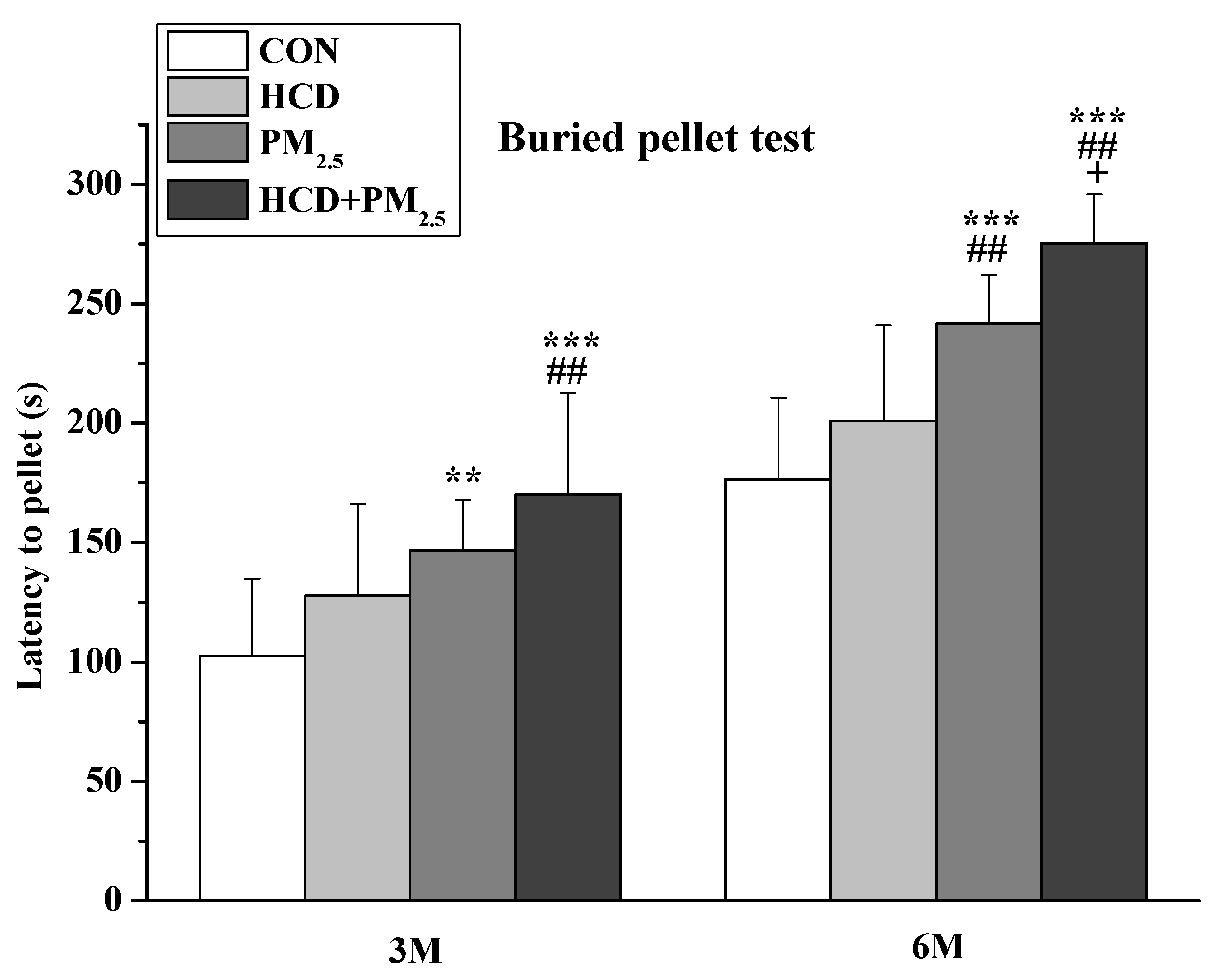
2.2.1. Buried Pellet Test
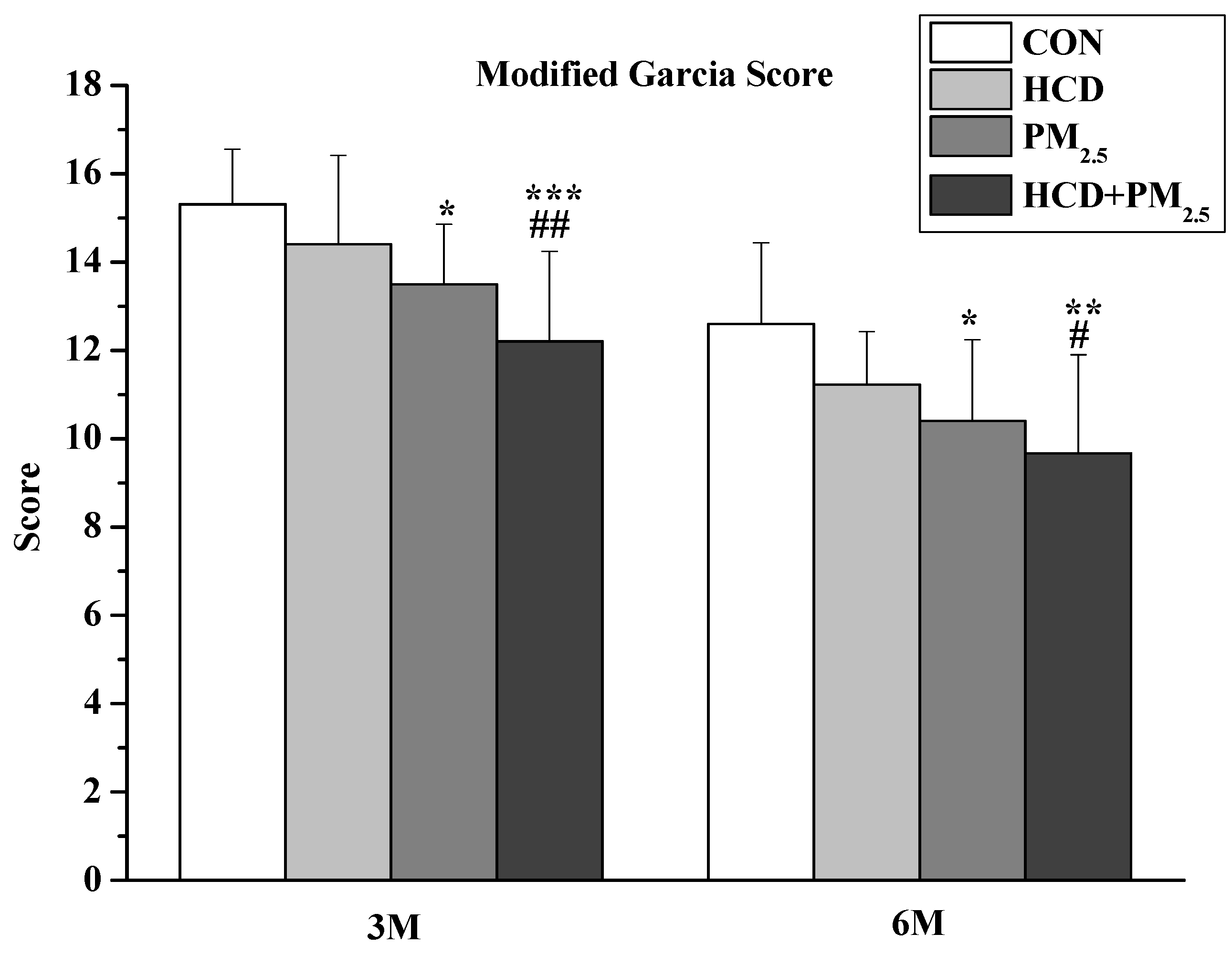
2.2.2. Neurological Score Evaluation
2.3. Tissue Collection
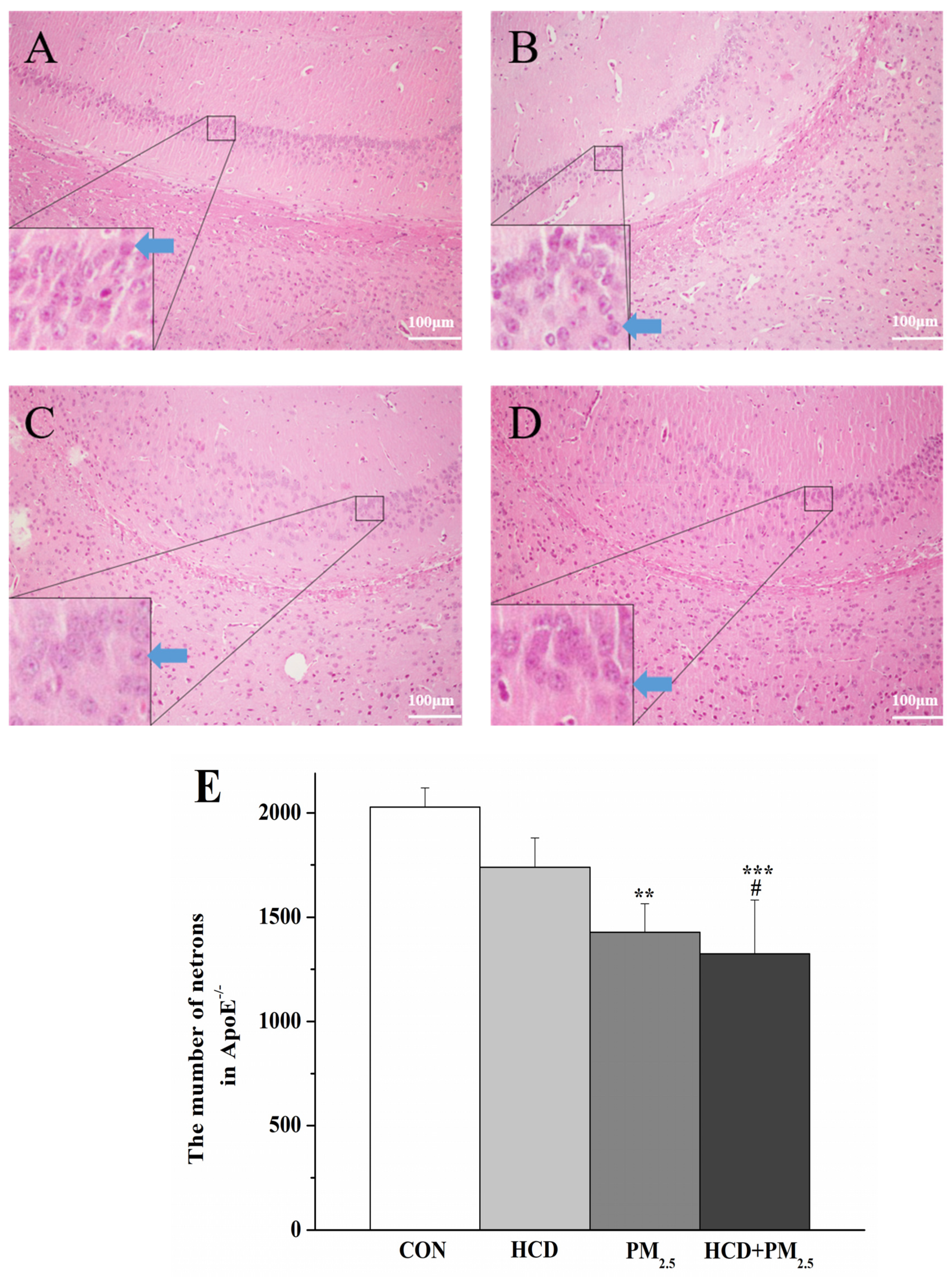
2.4. HE Staining Analysis
2.5. ELISA
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Organ Coefficients of Mice in Different Groups
3.2. Buried Pellet Test
3.3. Neurological Score Evaluation
3.4. HCD and PM2.5 Caused Pathological Changes
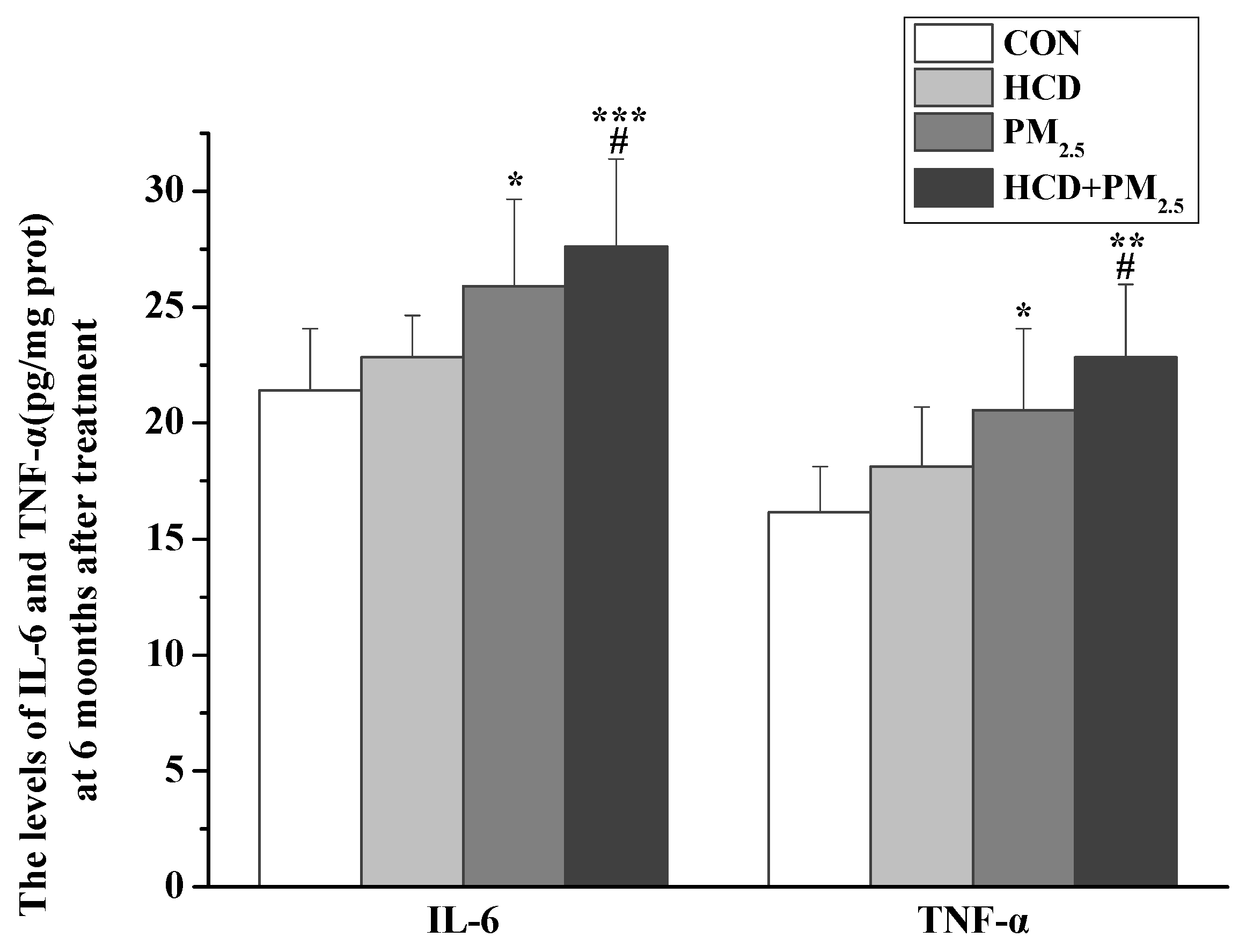
3.5. Effects of HCD and PM2.5 on the Expression of Inflammatory Markers
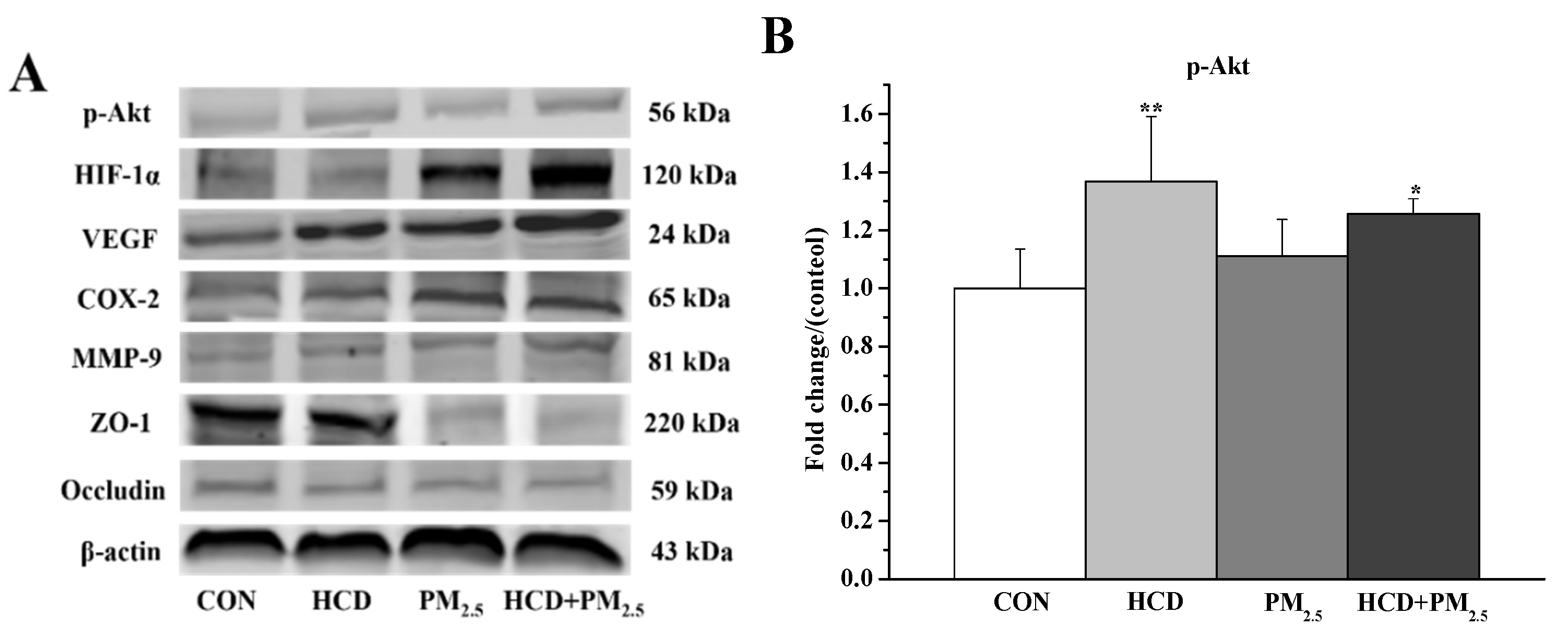
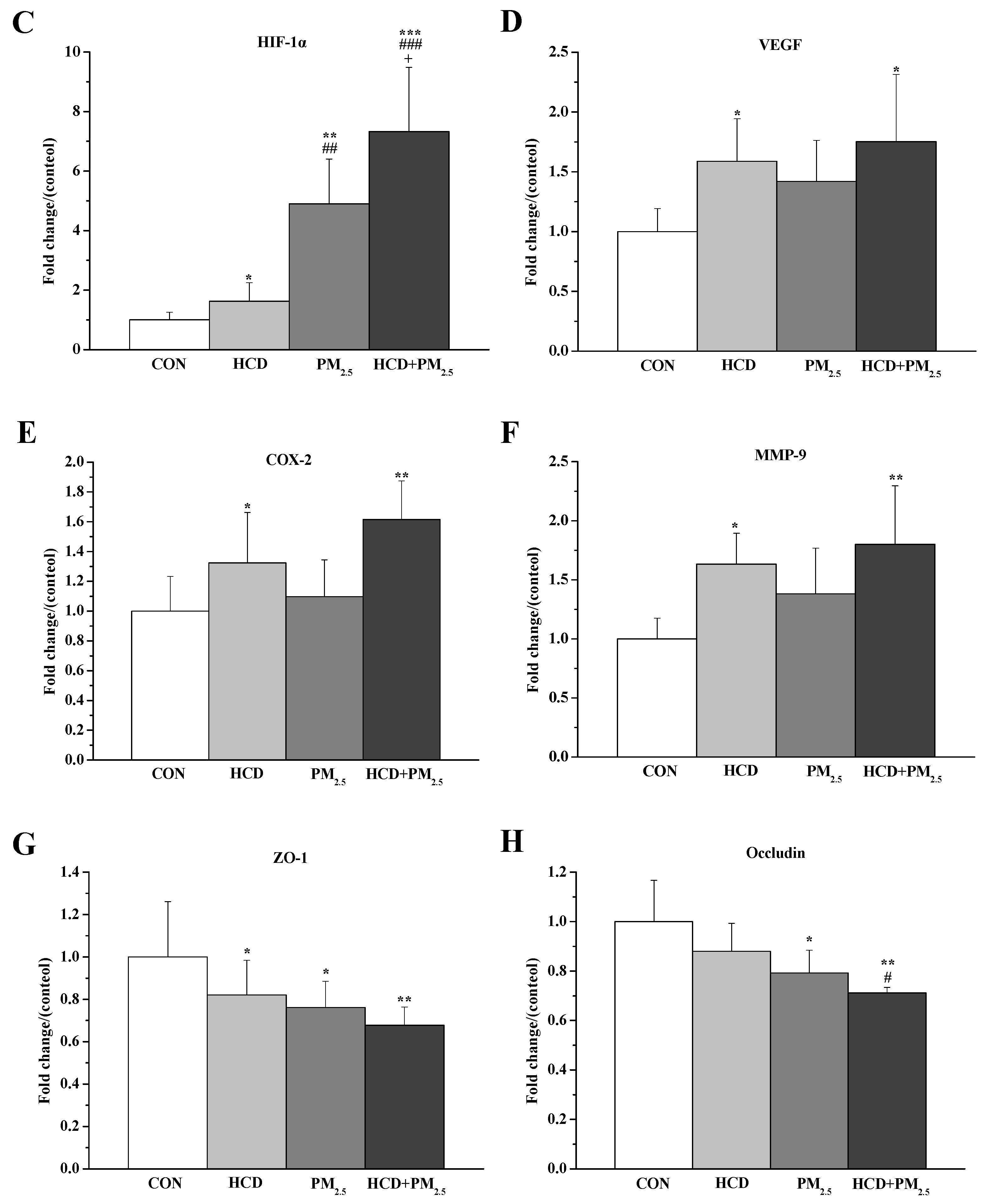
3.6. Effects of HCD and PM2.5 on the Protein Expressions of Stroke and BBB Basement Membrane Damage in the Brains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeffrey, D.S.; Ashkan, A.; Emmanuela, G.; Stephen, S.L.; Degu, A.; Kalkidan, H.A.; Cristiana, A.; Nooshin, A.; Hedayat, A.; Foad, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, N.; Olivieri, O.; Girelli, D. Air particulate matter and cardiovascular disease: A narrative review. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badyda, A.; Grellier, J.; Dabrowiecki, P. Ambient PM2.5 exposure and mortality due to lung cancer and cardiopulmonary diseases in Polish cities. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 944, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.F.; Guo, X.B.; Cheung, F.M.H.; Yung, K.K.L. The association between PM2.5 exposure and neurological disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levesque, S.; Surace, M.J.; McDonald, J.; Block, M.L. Air pollution & the brain: Subchronic diesel exhaust exposure causes neuroinflammation and elevates early markers of neurodegenerative disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 105. [Google Scholar]
- You, R.; Ho, Y.S.; Chang, R.C.C. The pathogenic effects of particulate matter on neurodegeneration: A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G.; Sharp, Z.; Atudorei, V.; Elder, A.; Gelein, R.; Kreyling, W.; Cox, C. Translocation of inhaled ultrafine particles to the brain. Inhal. Toxicol. 2004, 16, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proulx, S.T. Cerebrospinal fluid outflow: A review of the historical and contemporary evidence for arachnoid villi, perineural routes, and dural lymphatics. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 2429–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Luo, Q.; Chen, R.; Zhuansun, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; et al. Chemical multi-fingerprinting of exogenous ultrafine particles in human serum and pleural effusion. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Wei, S.; Xin, T.; Huang, C.; Pu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Lynch, I.; Liu, S. Passage of exogeneous fine particles from the lung into the brain in humans and animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117083119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.S.; Lee, K.K.; McAllister, D.A.; Hunter, A.; Nair, H.; Whiteley, W.; Langrish, J.P.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.L. Short term exposure to air pollution and stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2015, 350, h1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Sun, S.; Tsang, H.; Wong, C.M.; Lee, R.S.; Schooling, C.M.; Tian, L. Fine particulate matter exposure and incidence of stroke: A cohort study in Hong Kong. Neurology 2017, 88, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Qin, J.X.; Shi, J.Q.; Jiang, T.; Wang, F.; Xie, C.; Gao, Q.; Zhi, N.; Dong, Q.; Guan, Y.T. Fine particulate matter exposure aggravates ischemic injury via NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, H.A.; Lucero, J.; Guyot, A.; Herbert, L.M.; McDonald, J.D.; Mabondzo, A.; Lund, A.K. Exposure to vehicle emissions results in altered blood brain barrier permeability and expression of matrix metalloproteinases and tight junction proteins in mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Luo, Y.; Han, Z. Crosstalk between inflammation and the BBB in stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.G.; Prakash, R.; Chawla, D.; Du, W.T.; Didion, S.P.; Filosa, J.A.; Zhang, Q.G.; Brann, D.W.; Lima, V.V.; Tostes, R.C.; et al. Early effects of high-fat diet on neurovascular function and focal ischemic brain injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R1001–R1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Virtamo, J.; Wolk, A. Dietary fats and dietary cholesterol and risk of stroke in women. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colin-Castelan, D.; Zaina, S. Associations between atherosclerosis and neurological diseases, beyond ischemia-induced cerebral damage. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2019, 20, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.S.; Liu, T.W. Inflammatory cause of metabolic syndrome via brain stress and NF-kappa B. Aging 2012, 4, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diker, S.; Gelener, P.; Eker, A.; Kaymakamzade, B.; Mut, S.; Erem, A.; Balyemez, U. Association between cerebral microbleeds and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with ischemic stroke. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2022, 58, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.; Sohn, J.; Han, M.; Kang, D.R.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, H.C.; Suh, I.; Kim, C.; Shin, D.C. Long-term effects of cumulative average PM2.5 exposure on the risk of hemorrhagic stroke. Epidemiology 2019, 30 (Suppl. 1), S90–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkas, F.; Elisaf, M.; Milionis, H. Statins decrease the risk of stroke in individuals with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 2015, 243, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verghese, P.B.; Castellano, J.M.; Holtzman, D.M. Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.Y.; Shang, K.; Chu, Y.H.; Yu, H.H.; Chen, X.; Qin, C.; Pan, D.J.; Tian, D.S. Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 polymorphism as a risk factor for ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 1407183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Luo, X.L.; Chen, F.; Yuan, W.; Xiao, X.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Dong, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Y. LncRNA SNHG1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies as a competing endogenous RNA through HIF-1/VEGF signaling in ischemic stroke. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 5460–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, S.J.; Sun, Z.Y.; Poy, F.; Kung, A.L.; Livingston, D.M.; Wagner, G.; Eck, M.J. Structural basis for recruitment of CBP/p300 by hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 5367–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, S.N.; Metcalf, J.L.; Wang, Y.; Ohh, M. The updated biology of hypoxia-inducible factor. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 2448–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yang, Y.; DeMars, K.M.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 reduces blood-brain barrier damage in experimental ischemic stroke. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laughner, E.; Taghavi, P.; Chiles, K.; Mahon, P.C.; Semenza, G.L. HER2 (neu) signaling increases the rate of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) synthesis: Novel mechanism for HIF-1-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor expression. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pez, F.; Dayan, F.; Durivault, J.; Kaniewski, B.; Aimond, G.; Le Provost, G.S.; Deux, B.; Clezardin, P.; Sommer, P.; Pouyssegur, J.; et al. The HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1 via the Akt pathway in a positive regulation loop and synergizes with HIF-1 in promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1647–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ding, T.; Yu, L.; Zhong, Y.; Dai, H.; Yan, M. Dexmedetomidine protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced injury through the I2 imidazoline receptor-PI3K/Akt pathway in rat C6 glioma cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 64, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.; Zhang, Y.C.; Wang, L.; Wei, Y.L.; Lu, R.; Xia, J.J.; Chai, B.; Liang, X. Ambient fine particulate pollution and daily morbidity of stroke in Chengdu, China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Noh, J.; Noh, Y.; Oh, S.S.; Koh, S.B.; Kim, C. Gender difference in the effects of outdoor air pollution on cognitive function among elderly in Korea. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrea, R.E.; Beiser, A.S.; Seshadri, S.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Kase, C.S.; Wolf, P.A. Gender differences in stroke incidence and poststroke disability in the framingham heart study. Stroke 2009, 40, 1032–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnell, C.; McCullough, L.D.; Awad, I.A.; Chireau, M.V.; Fedder, W.N.; Furie, K.L.; Howard, V.J.; Lichtman, J.H.; Lisabeth, L.D.; Pina, I.L.; et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in women: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2014, 45, 1545–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xie, P.S.; Yong, T.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.J.; Wu, D.S.; Ji, F.F.; Li, M.; Zhang, D.D.; Li, R.J.; et al. Airborne fine particulate matter induces cognitive and emotional disorders in offspring mice exposed during pregnancy. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpetti, M.; Sala, A.; Vanoli, E.G.; Gianolli, L.; Luzi, L.; Perani, D. Unfavourable gender effect of high body mass index on brain metabolism and connectivity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.F.; Zhang, M.; Bai, L.R.; Zhao, Y.F.; Cai, Z.W.; Yung, K.K.L.; Dong, C.; Li, R.J. Real-world PM2.5 exposure induces pathological injury and DNA damage associated with miRNAs and DNA methylation alteration in rat lungs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 28788–28803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, W.; Zhu, X.; Chen, R.; Wang, X. Olfactory dysfunctions and decreased nitric oxide production in the brain of human P301L tau transgenic mice. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Enkhjargal, B.; Manaenko, A.; Tang, J.P.; Pearce, W.J.; Hartman, R.; Obenaus, A.; Chen, G.; et al. Recombinant osteopontin stabilizes smooth muscle cell phenotype via integrin receptor/integrin-linked kinase/rac-1 pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 2016, 47, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Manaenko, A.; Yang, P.; Tang, J.; Fu, W.; Zhang, J.H. Activation of dopamine D2 receptor suppresses neuroinflammation through alphaB-crystalline by inhibition of NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in experimental ICH mice model. Stroke 2015, 46, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, C.; Xie, P.; Huang, W.; Yong, T.; Cai, Z.W. Effects of PM2.5 exposure in utero on heart injury, histone acetylation and GATA4 expression in offspring mice. Chemosphere 2020, 256, 127133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zyl, P.J.; Dimatelis, J.J.; Russell, V.A. Behavioural and biochemical changes in maternally separated Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to restraint stress. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.C.; Kang, I.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Shin, N.; Kim, J.J.; Choi, S.W.; Kang, K.S. Human umbilical cord blood plasma alleviates age-related olfactory dysfunction by attenuating peripheral TNF-α expression. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.F.; Chuang, T.Y.; Lan, M.Y.; Chin, Y.C.; Wang, W.H.; Lin, Y.Y. Excessive expression of microglia/macrophage and proinflammatory mediators in olfactory bulb and olfactory dysfunction after stroke. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.C.; Yamauchi, H.; Fujioka, M.; Endres, M. Selective neuronal loss in ischemic stroke and cerebrovascular disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2014, 34, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.; Sarmah, D.; Kalia, K.; Borah, A.; Wang, X.; Dave, K.R.; Yavagal, D.R.; Bhattacharya, P. Advances in studies on stroke-induced secondary neurodegeneration (SND) and its treatment. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1154–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, Y.K.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhu, X.Z.; Liu, C.Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.H. A review of the possible associations between ambient PM2.5 exposures and the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2019, 174, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Guan, L.; Zhu, Y.; Geng, X. Filtered air intervention reduces inflammation and hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis activation in adult male and female rats after PM2.5 exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 35341–35348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; van, B.D.; Cassee, F.R.; Schins, R.P.F.; Wang, K.; Campbell, A. Effect of prolonged exposure to diesel engine exhaust on proinflammatory markers in different regions of the rat brain. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.X.; Bu, G.J. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane-Donovan, C.; Herz, J. The ApoE receptors Vldlr and Apoer2 in central nervous system function and disease. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evola, M.; Hall, A.; Wall, T.; Young, A.; Grammas, P. Oxidative stress impairs learning and memory in ApoE knockout mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getz, G.S.; Reardon, C.A. Animal models of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.G.; Schlage, W.K.; Boue, S.; Veljkovic, E.; Peitsch, M.C.; Hoeng, J. The Apoe−/− mouse model: A suitable model to study cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in the context of cigarette smoke exposure and harm reduction. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 146. [Google Scholar]
- Suwannasual, U.; Lucero, J.; McDonald, J.D.; Lund, A.K. Exposure to traffic-generated air pollutants mediates alterations in brain microvascular integrity in wildtype mice on a high-fat diet. Environ. Res. 2018, 160, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitsuji, K.; Hosono, T.; Nakamura, T.; Bu, G.J.; Michikawa, M. Apolipoprotein E regulates the integrity of tight junctions in an isoform-dependent manner in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17536–17542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Solt, A.C.; Henríquez-Roldán, C.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Nuse, B.; Herritt, L.; Villarreal-Calderon, R.; Osnaya, N.; Stone, I.; Garcia, R.; et al. Long-term air pollution exposure is associated with neuroinflammation, an altered innate immune response, disruption of the blood-brain barrier, ultrafine particulate deposition, and accumulation of amyloid beta-42 and alpha-synuclein in children and young adults. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 289–310. [Google Scholar]
- Fini, M.E.; Jeong, S.; Wilson, M.R. Therapeutic potential of the molecular chaperone and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor clusterin for dry eye. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Groups | Brain Weight | Body Weight | Brain–Body Weight Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 0.40 ± 0.04 | 10.33 ± 1.32 | 1.47 ± 0.18 |
| HCD | 0.39 ± 0.06 | 9.45 ± 3.47 | 1.52 ± 0.27 |
| PM2.5 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 9.59 ± 1.46 | 1.68 ± 0.13 * |
| HCD + PM2.5 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 10.80 ± 1.74 | 1.51 ± 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Bai, L.; Li, R. Combined Exposure to High-Cholesterol Diet and PM2.5: Brain Injury and Regulatory Mechanism of HIF-1α in ApoE−/− Female Mice. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080952
Chen W, Chen S, Bai L, Li R. Combined Exposure to High-Cholesterol Diet and PM2.5: Brain Injury and Regulatory Mechanism of HIF-1α in ApoE−/− Female Mice. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(8):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080952
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wenqi, Shanshan Chen, Lirong Bai, and Ruijin Li. 2024. "Combined Exposure to High-Cholesterol Diet and PM2.5: Brain Injury and Regulatory Mechanism of HIF-1α in ApoE−/− Female Mice" Atmosphere 15, no. 8: 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080952
APA StyleChen, W., Chen, S., Bai, L., & Li, R. (2024). Combined Exposure to High-Cholesterol Diet and PM2.5: Brain Injury and Regulatory Mechanism of HIF-1α in ApoE−/− Female Mice. Atmosphere, 15(8), 952. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15080952








