Exploring the Effects of Elevated Ozone Concentration on Physiological Processes in Summer Maize in North China Based on Exposure–Response Relationships
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
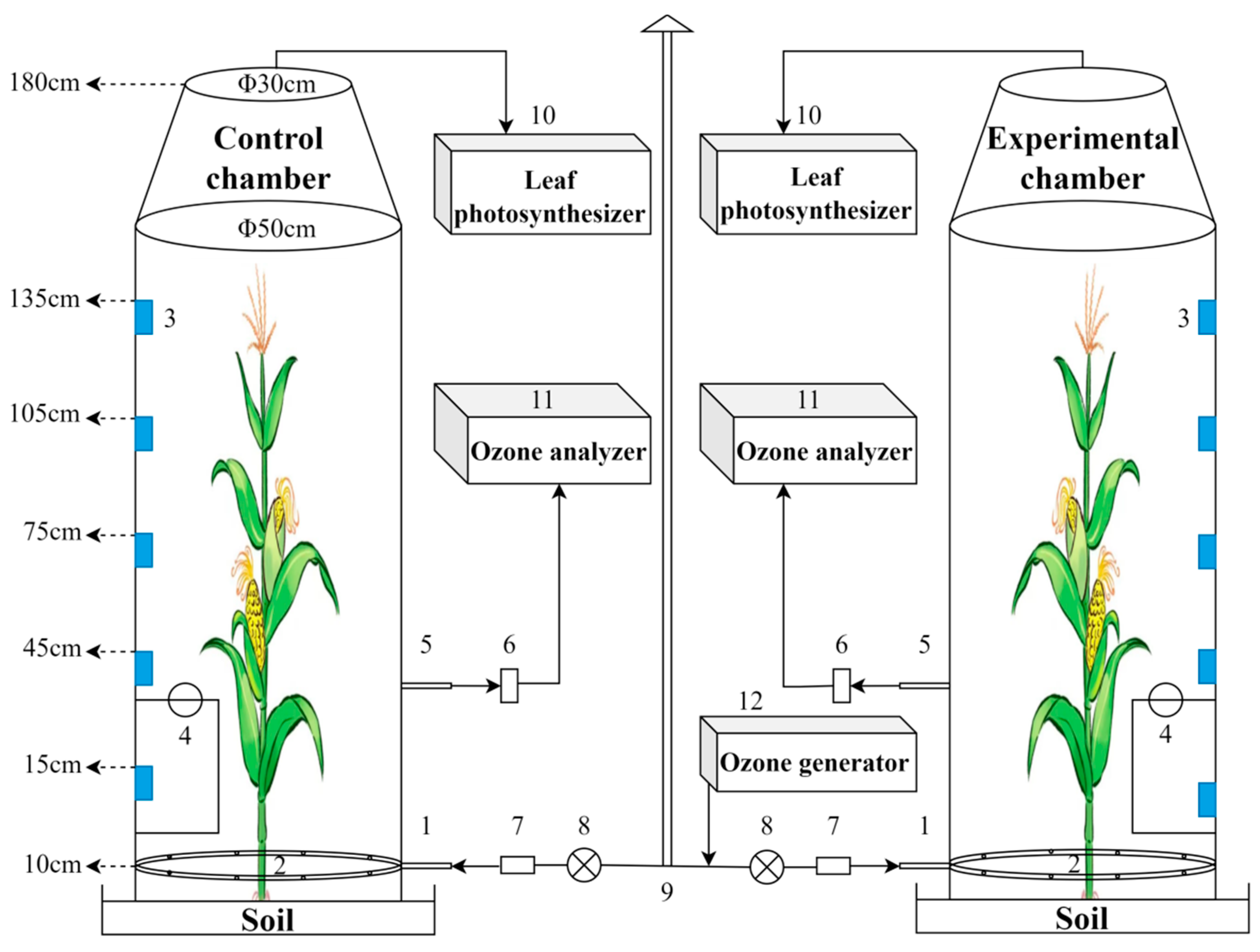
2.2. Ozone Treatment
2.3. Parameter Measurements
2.3.1. Visible Leaf Damage
2.3.2. Physiological Parameter
2.3.3. Photosynthetic Parameters
2.3.4. Data Quality Assurance
3. Results
3.1. Ozone Concentration and AOT40
3.2. Visible Leaf Damage
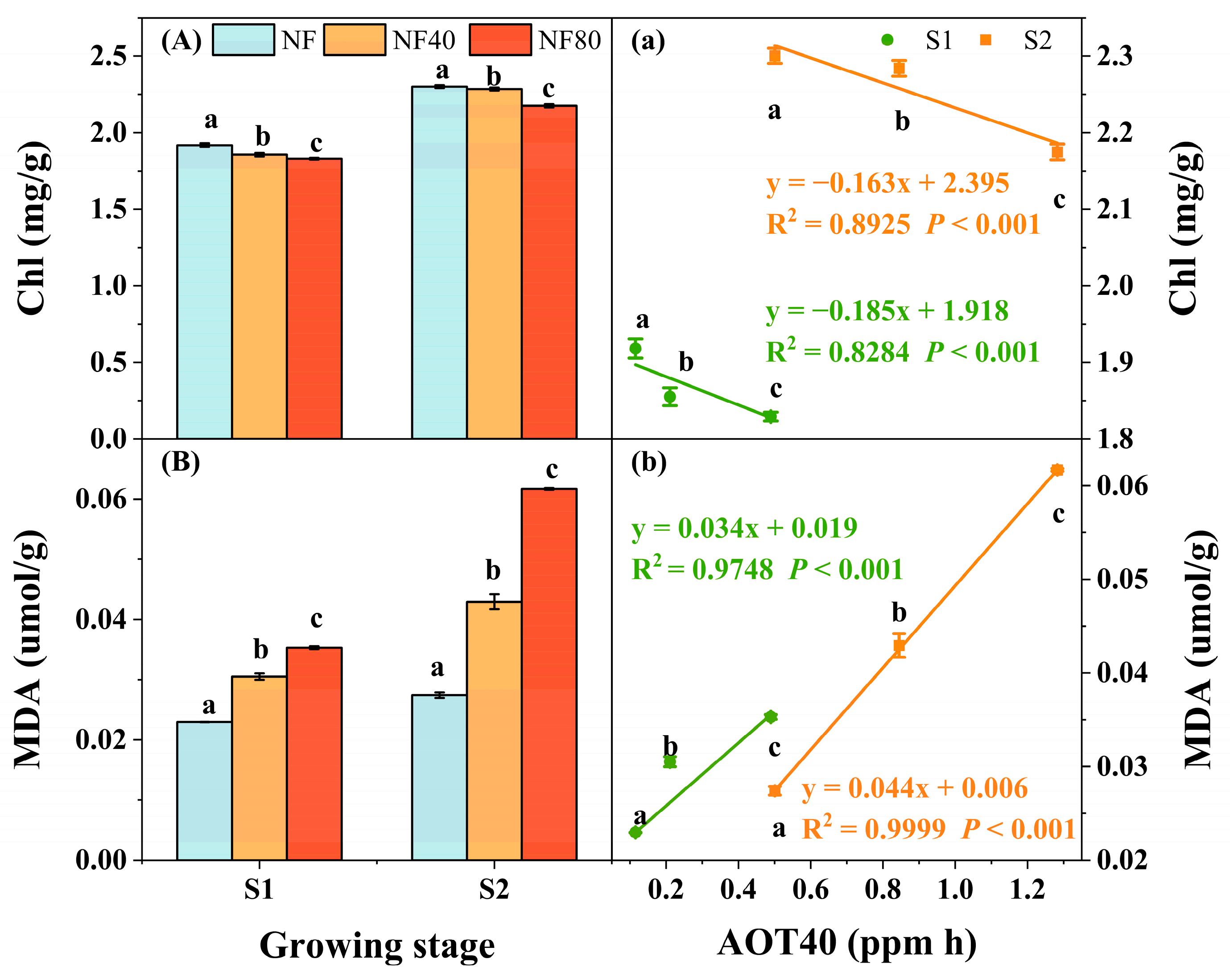
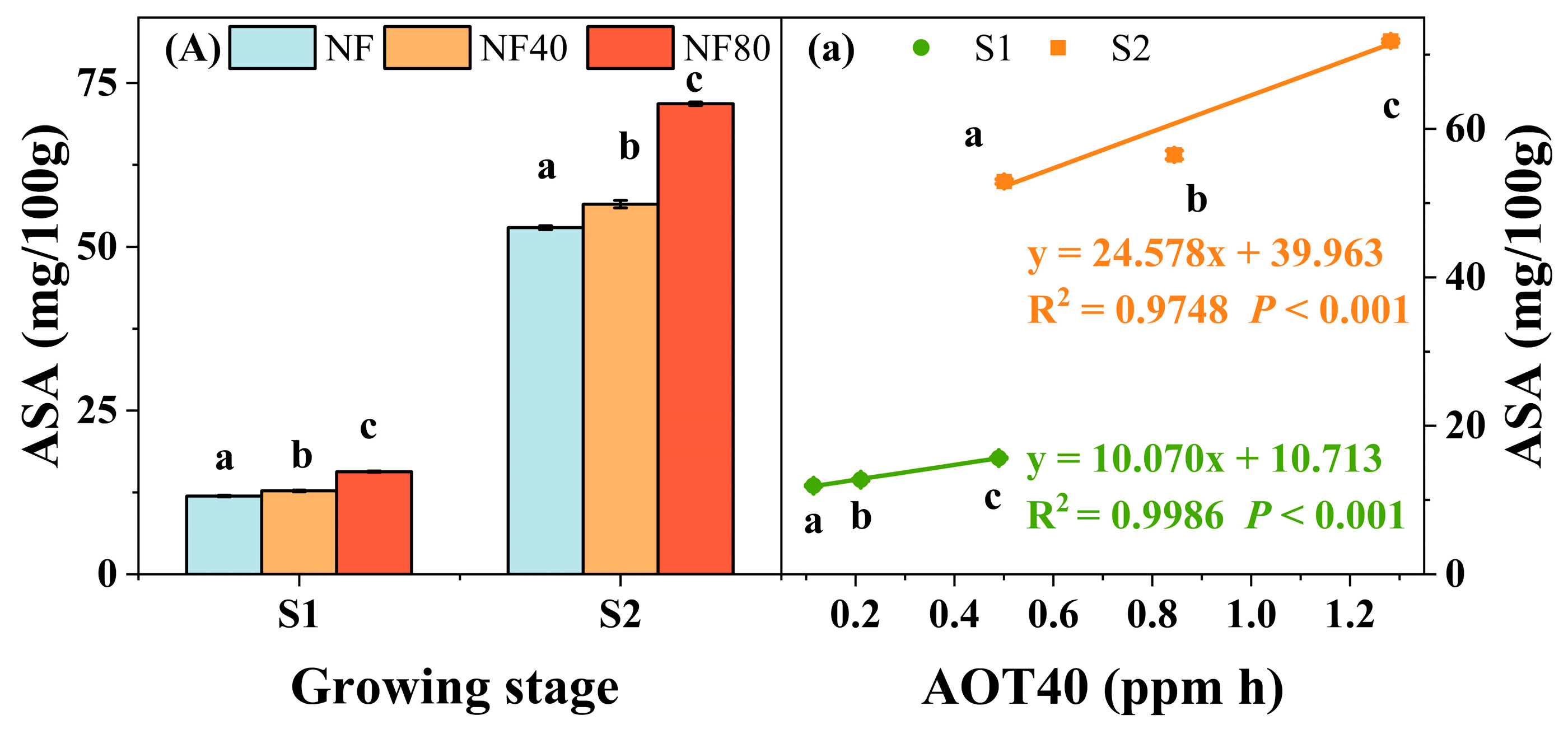
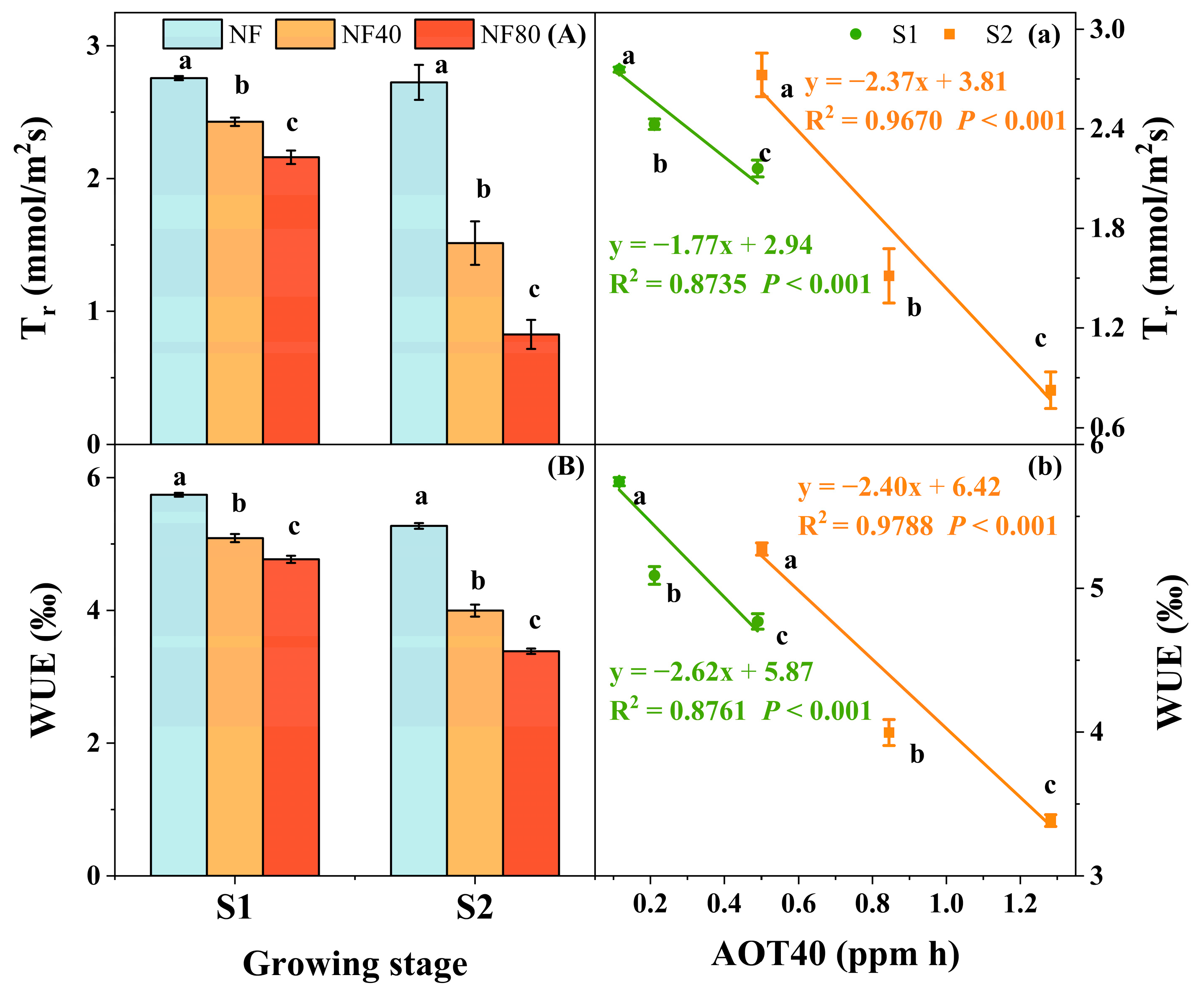
3.3. Physiological Responses of Maize to Elevated O3 Concentrations at Different Growth Stages
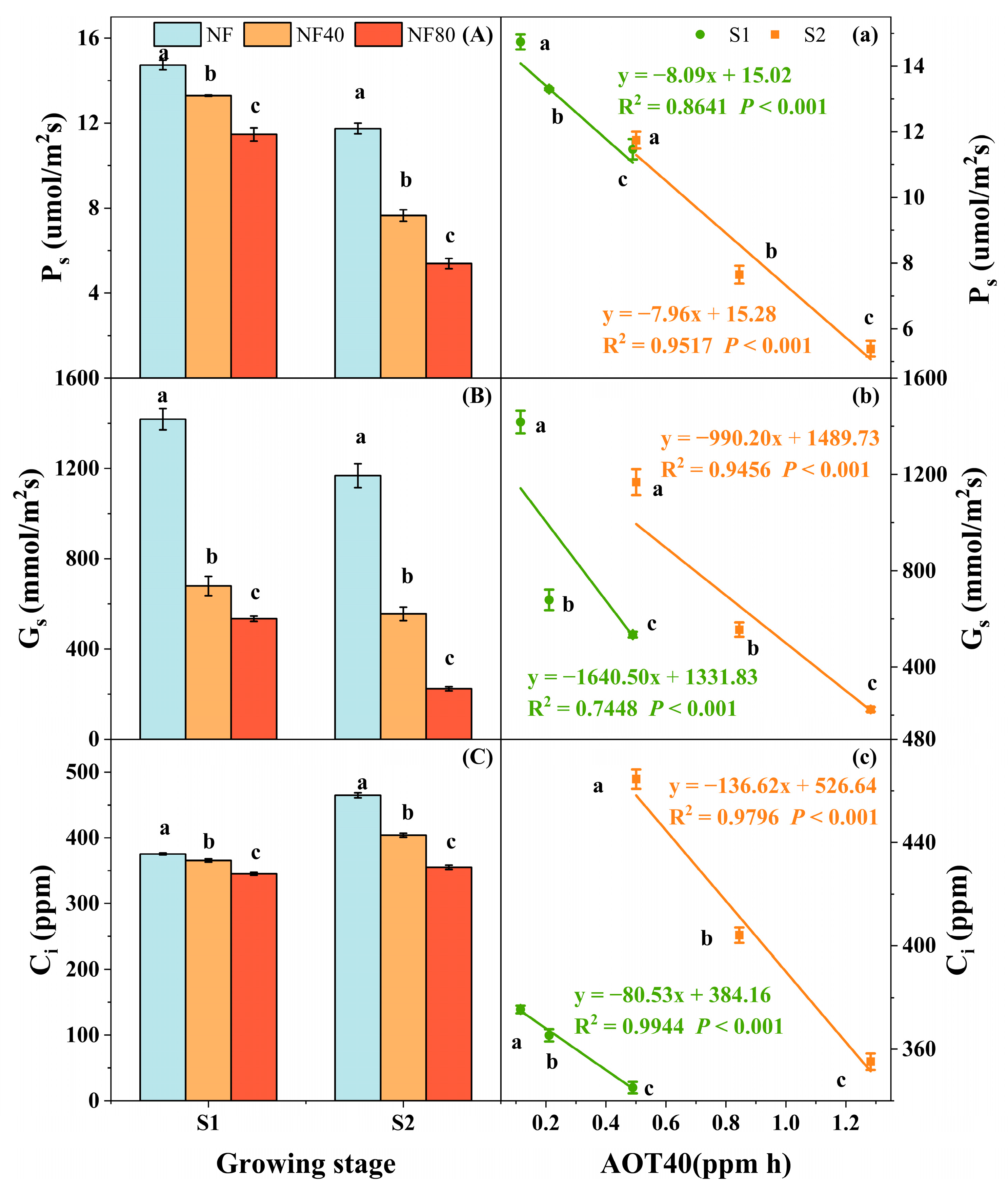
3.4. Photosynthetic Response of Maize to Elevated O3 Concentration at Different Growth Stages
4. Discussion
4.1. Physiological Response of Maize to O3 Exposure
4.2. Photosynthetic Response of Maize to O3 Exposure
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, K.; Inn, E.C.Y.; Zelikoff, M. Absorption coefficients of oxygen in the vacuum ultraviolet. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calfapietra, C.; Fares, S.; Manes, F.; Morani, A.; Sgrigna, G.; Loreto, F. Role of Biogenic Volatile Organic Compounds (BVOC) emitted by urban trees on ozone concentration in cites: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Manning, W.; Feng, Z.; Zhu, Y. Ground-level ozone in China: Distribution and effects on crop yields. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 147, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.Z.; Kobayashi, K.; Ainsworth, E.A. Impact of elevated ozone concentration on growth, physiology, and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serengil, Y.; Augustaitis, A.; Bytnerowicz, A.; Grulke, N.; Kozovitz, A.R.; Matyssek, R.; Müller-Starck, G.; Schaub, M.; Wieser, G.; Aydin Coskun, A.; et al. Adaptation of forest ecosystems to air pollution and climate change: A global assessment on research priorities. iForest-Biogeosciences For. 2011, 4, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, I.A.; Bell, N.B.; Ashmore, M.R.; Cotrozzi, L.; Haiba, N.S.; Basahi, J.M. Cultivar-Specific Response to O3: Patterns of Biochemical and Plant Growth Characteristics. Clean Soil Air Water 2018, 46, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Takigawa, M.; Liu, G.; Zhu, J.; Kobayashi, K. A projection of ozone induced wheat production loss in China and India for the years 2000 and 2020 with exposure-based and flux based approaches. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2739–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingarzan, R. A review of surface ozone background levels and trends. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Anav, A.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E. Projected global ground level ozone impacts on vegetation under different emission and climate scenarios. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 12177–12196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrer, J.; Skarby, L.; Ashmore, M.R. Critical levels for ozone effects on vegetation in Europe. Environ. Pollut. 1997, 97, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleijel, H.; Danielsson, H.; Ojanpera, K.; De Temmerman, L.; Hogy, P.; Badiani, M.; Karlsson, P.E. Relationships between ozone exposure and yield loss in European wheat and potato—A comparison of concentration-and flux-based exposure indices. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, G.; Hayes, F.; Simpson, D.; Emberson, L.; Norris, D.; Harmens, H.; Buker, P. Evidence of widespread effects of ozone on crops and (semi-)natural vegetation in Europe (1990–2006) in relation to AOT40-and flux-based risk maps. Glob. Change Biol. 2011, 17, 592–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.L.; Shang, B.; Xu, Y.S.; Feng, Z.Z.; Pleijel, H.; Calatayud, V. Ozone exposure- and flux-yield response relationships for maize. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Sun, J.; Wan, W.; Hu, E.; Calatayud, V. Evidence of widespread ozone-induced visible injury on plants in Beijing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Hu, E.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X. Ground-level O3 pollution and its impacts on food crops in China: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 199, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.X.; Kiang, C.S.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Chameides, W.L. Surface ozone: A likely threat to crops in Yangtze delta of China. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3843–3850. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhang, Y. Rapid increases in warm-season surface ozone and resulting health impact in China since 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 7, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Shao, L.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Dong, X. Impact of different cropping systems and irrigation schedules on evapotranspiration, grain yield and groundwater level in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 211, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Z.; Peng, J.L. Relationship between Relative Crop Yield/Woody Plant Biomass and Groud-level Ozone Pollution in China. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3084–3090. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, L.; Zhang, T.; Agathokleous, E.; Calatayud, V.; Paoletti, E.; Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M.; et al. Ozone pollution threatens the production of major staple crops in East Asia. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Shang, B.; Chen, X.L.; Feng, Z.Z. Effects of elevated ozone and nitrogen deposition on photosynthetic characteristics and biomass of Populus cathayana. Environ. Sci. 2016, 37, 3642–3649. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.; Shang, B.; Dai, L.; Uddling, J.; Tarvainen, L. Mesophyll conductance limitation of photosynthesis in poplar under elevated ozone. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshika, Y.; Fares, S.; Pellegrini, E.; Conte, A.; Paoletti, E. Water use strategy affects avoidance of ozone stress by stomatal closure in Mediterranean trees-A modelling analysis. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castagna, A.; Ranieri, A. Detoxification and repair process of ozone injury: From O3 uptake to gene expression adjustment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranieri, A.; Castagna, A.; Pacini, J.; Baldan, B.; Mensuali Sodi, A.; Soldatini, G.F. Early production and scavenging of hydrogen peroxide in the apoplast of sunflower plants exposed to ozone. J. Exp. Bot. 2003, 54, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.Q.; Feng, Y. Influence of ozone to the growth of cultivating vegetables in guangzhou. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2001, 20, 344–347. [Google Scholar]
- Fiscus, E.L.; Booker, F.L.; Burkey, K.O. Crop responses to ozone: Uptake, modes of action, carbon assimilation and partitioning. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 997–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Li, Q.X.; Huang, S.J.; Tang, G.F.; Lin, J.H. Physiological and foliar symptom response of Pinus massoniana, Eucalyptus urophylla and Aglaia odorata to ozone in southern China. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 15, 674–681. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.H.; Feng, Z.W.; Zhang, F.Z. Effects of ozone on membrane lipid peroxidation and antioxidant system of rice leaves. Environ. Sci. 2000, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.Q. The Impacts and Defence of O3 on Crop in Site. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.L.; Kobayashi, K.; Nouchi, I.; Masutomi, Y.; Feng, Z.Z. Quantifying determinants of ozone detoxification by apoplastic ascorbate in peach (Prunus persica) leaves using a model of ozone transport and reaction. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3147–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Z.; Cao, J.X.; Shang, H. Effects of elevated O3 level on photosynthesis, antioxidant capacity and biomass of Phoebe zhennan and Phoebe bournei seedlings in subtropical China. For. Res. 2018, 31, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.Z.; Uddling, J.; Tang, H.Y.; Zhu, J.G.; Kobayashi, K. Comparison of crop yield sensitivity to ozone between open-top chamber and free-air experiments. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.P. Growth stage division and growth and development characteristics of maize. Mod. Anim. Husb. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, S.; Mills, G.; Illidge, R.; Davies, W.J. How is ozone pollution reducing our food supply? J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandle, R.H. A cylindrical open-top chamber for the exposure of plants to air pollutants in the field. J. Environ. Qual. 1973, 15, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Okada, M. Effects of ozone on the light use of rice (Oryza sativa L.) plants. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1995, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, E. Ozone impacts on forests. CAB reviews: Perspectives in agriculture, veterinary science. Nutr. Nat. Resour. 2007, 2, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.F.; Wang, X.K.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Z.Z.; Zheng, Q.W.; Duan, X.N.; Ouyang, Z.Y.; Feng, Z.W. Response of photosynthesis, growth and yield of field-grown winter wheat to ozone exposure. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 32, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Feng, Z.; Xie, J.; Chen, Z. Response of gas exchange of rape to ozone concentration and exposure regimes. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Song, X.X.; Kong, J.J.; Han, Y.; Ruan, Y.N. Effects of Ozone Stress on Antioxidant Metabolism and Reproductive Growth of Soybean. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Sachdev, S.; Ansari, S.A.; Ansari, M.I.; Fujita, M.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Abiotic stress and reactive oxygen species: Generation, signaling, and defense mechanisms. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, I.J.; Rathore, D. Effects of ambient and elevated ozone on morphophysiology of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and its correlation with yield traits. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.L.; Shang, B.; Xu, Y.; Feng, Z.Z.; Calatayud, V. Effects of ozone on maize (Zea mays L.) photosynthetic physiology, biomass and yield components based on exposure- and flux-response relationships. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainsworth, E.A. Understanding and improving global crop response to ozone pollution. Plant J. 2017, 90, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.W.; Wang, X.K.; Feng, Z.Z.; Song, W.Z.; Feng, Z.W. Ozone effects on chlorophyll content and lipid peroxidation in the in situ leaves of winter wheat. Acta Bot. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2005, 25, 2240–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, K. Role of membrane glycerolipids in photosynthesis, thylakoid biogenesis and chloroplast development. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, K.; De Campos, M.K.F.; Domingues, D.S.; Pereira, L.F.P.; Vieira, L.G.E. The accumulation of endogenous proline induces changes in gene expression of several antioxidant enzymes in leaves of transgenic Swingle citrumelo. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 3269–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emberson, L.D.; Pleijel, H.; Ainsworth, E.A.; Van den Berg, M.; Ren, W.; Osborne, S.; Mills, G.; Pandey, D.; Dentener, F.; Büker, P.; et al. Ozone effects on crops and consideration in crop models. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 100, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuoli, R.; Monga, R.; Finco, A.; Gerosa, G. Biomass and physiological responses of Quercus robur (L.) young trees during 2 years of treatments with different levels of ozone and nitrogen wet deposition. Trees 2016, 30, 1995–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahisalu, T.; Puzõrjova, I.; Brosché, M.; Valk, E.; Lepiku, M.; Moldau, H.; Pechter, P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lindgren, O.; Salojärvi, J.; et al. Ozone-triggered rapid stomatal response involves the production of reactive oxygen species, and is controlled by SLAC1 and OST1. Plant J. 2010, 62, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.D.; Pfirrmann, T. The influence of CO2 and O3, singly and in combination, on gas exchange, growth and nutrient status of radish. New Phytol. 1992, 121, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshika, Y.; Katata, G.; Deushi, M.; Watanabe, M.; Koike, T.; Paoletti, E. Ozone-induced stomatal sluggishness changes carbon and water balance of temperate deciduous forests. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoletti, E.; Grulke, N.E. Ozone exposure and stomatal sluggishness in different plant physiognomic classes. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2664–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshika, Y.; Fares, S.; Savi, F.; Gruening, C.; Goded, I.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E. Stomatal conductance models for ozone risk assessment at canopy level in two Mediterranean evergreen forests. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 234, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| O3 treatments | CF | NF | NF40 | NF80 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (℃) | 26.33 | 28.06 | 28.86 | 29.27 |
| RH (%) | 84.01 | 83.89 | 82.17 | 80.42 |
| PAR (W/m2) | 457.81 | 461.92 | 461.92 | 453.06 |
| AOT40 (ppm h) | - | 0.5007 | 0.8445 | 1.2823 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Xie, S.; Lun, X.; He, Z.; Liu, X.; Lv, W.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. Exploring the Effects of Elevated Ozone Concentration on Physiological Processes in Summer Maize in North China Based on Exposure–Response Relationships. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060639
Wang M, Xie S, Lun X, He Z, Liu X, Lv W, Wang L, Wang T, Liu J. Exploring the Effects of Elevated Ozone Concentration on Physiological Processes in Summer Maize in North China Based on Exposure–Response Relationships. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(6):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060639
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mansen, Shuyang Xie, Xiaoxiu Lun, Zhouming He, Xin Liu, Wenjun Lv, Luxi Wang, Tian Wang, and Junfeng Liu. 2024. "Exploring the Effects of Elevated Ozone Concentration on Physiological Processes in Summer Maize in North China Based on Exposure–Response Relationships" Atmosphere 15, no. 6: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060639
APA StyleWang, M., Xie, S., Lun, X., He, Z., Liu, X., Lv, W., Wang, L., Wang, T., & Liu, J. (2024). Exploring the Effects of Elevated Ozone Concentration on Physiological Processes in Summer Maize in North China Based on Exposure–Response Relationships. Atmosphere, 15(6), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15060639






